Campylobacter Colonisation of Poultry Slaughtered at Nigerian Slaughterhouses: Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Risk of Zoonotic Transmission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Informed Consent
2.2. Study Area and Design
2.3. Sample Size Determination and Sample Collection
2.4. Isolation of Zoonotic Campylobacter Species
2.5. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiling
2.5.1. Antibiogram
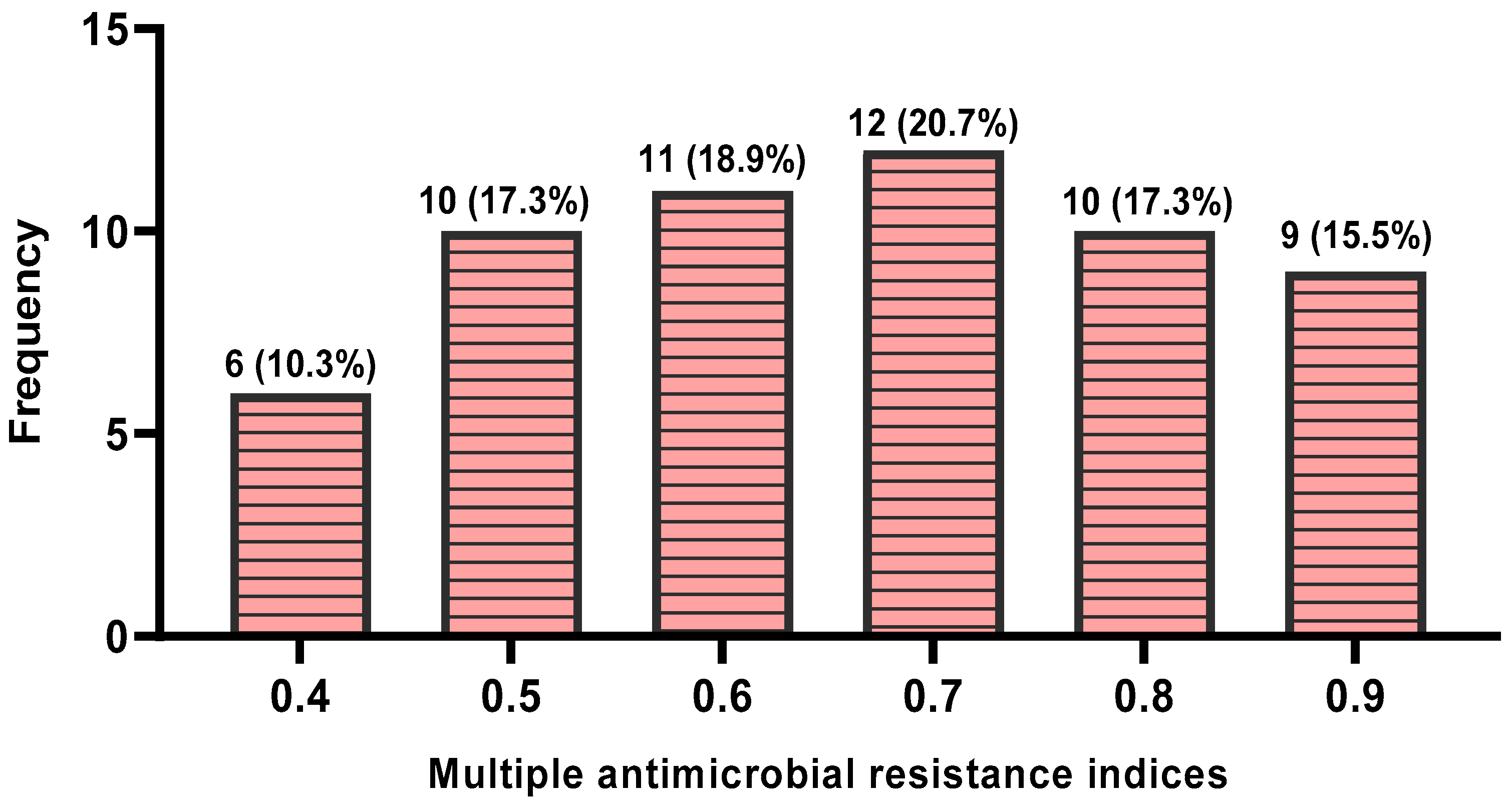
2.5.2. Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance Indices
2.6. Risk Practices
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Campylobacter Species
3.2. Results on Antimicrobial Resistance
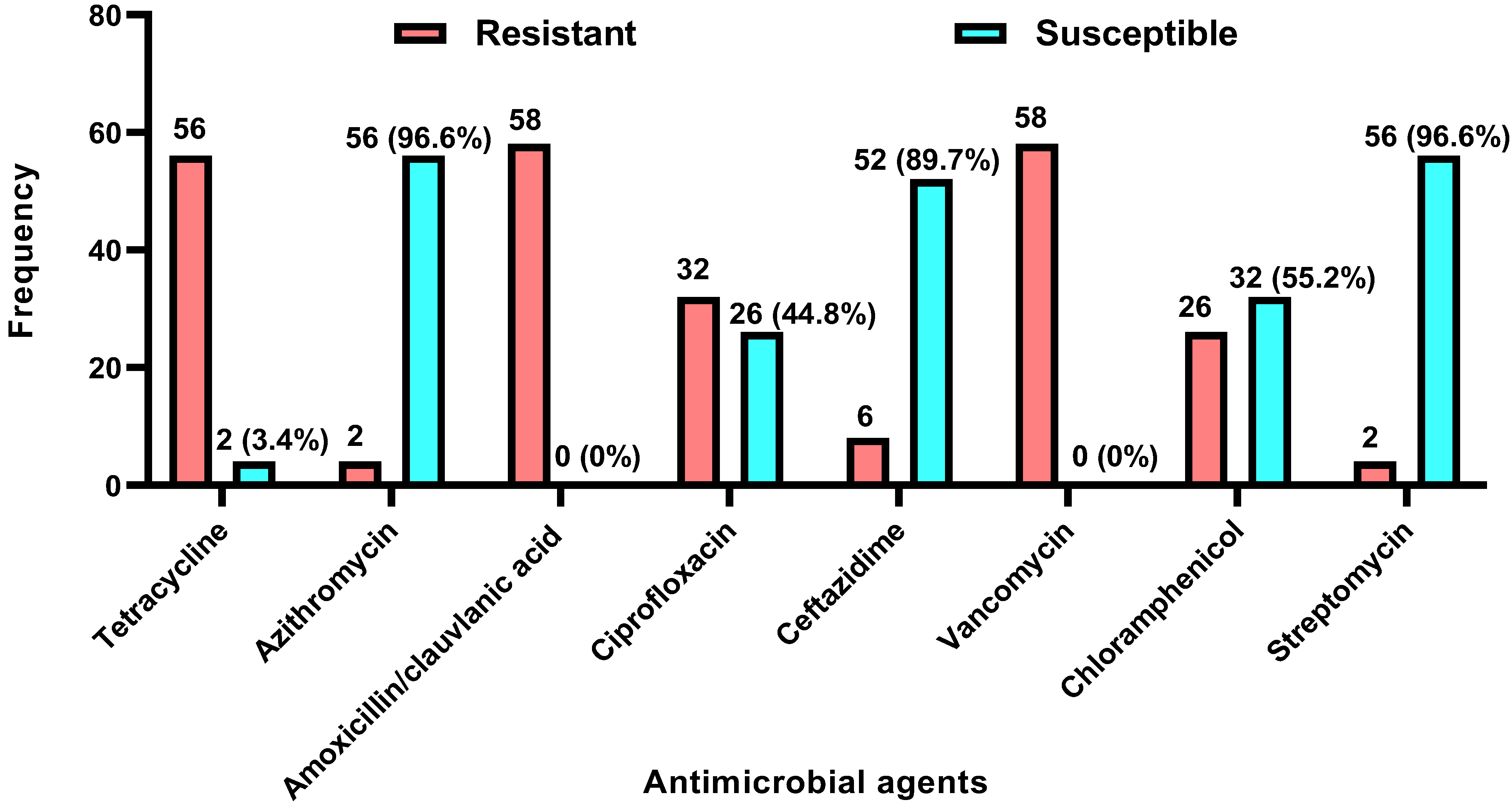
3.2.1. Antibiogram
3.2.2. Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance Indices and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns
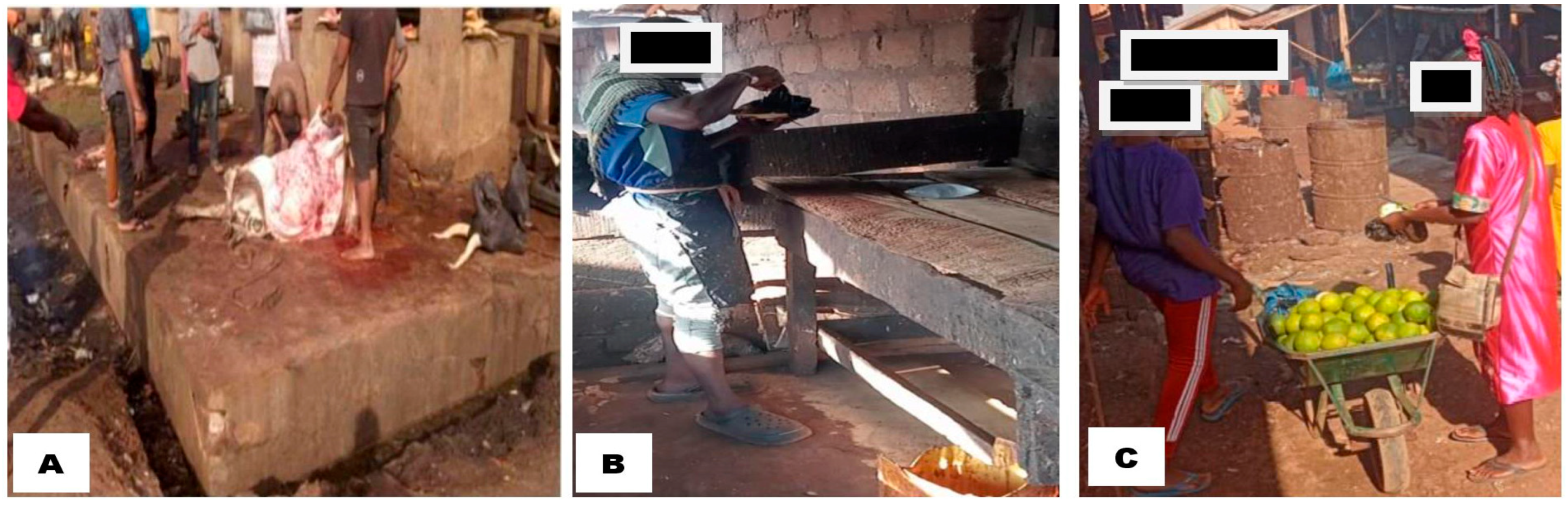
3.2.3. Practices that Heighten the Risk of Zoonotic Campylobacter Transmission
4. Discussion
4.1. Prevalence of Zoonotic Campylobacter Species
4.2. Antimicrobial Resistance
4.3. Zoonotic Campylobacter Transmission Risk Factors
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
6. Limitation of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global Epidemiology of Campylobacter Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwaran, A.; Okoh, A.I. Human campylobacteriosis: A public health concern of global importance. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarp, C.P.A.; Hänninen, M.L.; Rautelin, H.I.K. Campylobacteriosis: The role of poultry meat. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njoga, E.O.; Nwankwo, I.O.; Ugwunwarua, J.C. Epidemiology of thermotolerant Campylobacter infection in poultry in Nsukka agricultural zone, Nigeria. Int. J. One Health 2019, 5, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoga, E.O.; Nnaemeka, V.C.; Jaja, I.F.; Oguttu, J.W.; Nwanta, J.A.; Chah, K.F. Systematic review and meta-analysis of Campylobacter species infections in humans and food-producing animals in Nigeria, 2002–2023: The imperative of a One Health control approach. One Health 2025, 20, 101029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoga, E.O.; Nwanta, J.A.; Chah, K.F. Detection of multidrug-resistant Campylobacter species from food-producing animals and humans in Nigeria: Public health implications and one health control measures. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 103, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoga, E.O.; Ezenduka, E.V.; Nwanta, J.A. Surveillance of Campylobacter infections in indigenous poultry reared in Nsukka, Nigeria. Not. Sci. Biol. 2020, 12, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibo, F.E.; Njoga, E.O.; Azor, N.; Idika, K.I.; Nwanta, J.A. Epidemiology of infections with zoonotic pig parasites in Enugu State, Nigeria. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 20, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idika, K.I.; Njoga, U.J.; Ezeh, I.O.; Iheagwam, C.N.; Ezenduka, E.V.; Njoga, E.O.; Onah, D.N. Re-evaluation of Porcine Cysticercosis in Nsukka Area of Enugu State, Nigeria. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2017, 7, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Key Facts about Campylobacter. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/campylobacter (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240093461 (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Njoga, E.O.; Ilo, S.U.; Nwobi, O.C.; Onwumere-Idolor, O.S.; Ajibo, F.E.; Okoli, C.E.; Jaja, I.F.; Oguttu, J.W. Pre-slaughter, slaughter, and post-slaughter practices of slaughterhouse workers in Southeast Nigeria: Animal welfare, meat quality, food safety, and public health implications. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, D.; Pasmans, F.; Messens, W.; Martel, A.; Van Immerseel, F.; Rasschaert, G.; Heyndrickx, M.; Van Deun, K.; Haesebrouck, F. Poultry as a host for the zoonotic pathogen Campylobacter jejuni. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; Yang, T.; Salem, H.M.; Korma, S.A.; Ahmed, A.E.; Mosa, W.F.A.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Selim, S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; et al. Avian campylobacteriosis, prevalence, sources, hazards, antibiotic resistance, poultry meat contamination, and control measures: A comprehensive review. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, L.J.; Tanganyika, J. Livestock provide more than food in smallholder production systems of developing countries. Anim. Front. 2021, 11, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, P.C.; Njoga, E.O.; Njoga, U.J.; Aronu, C.J.; Atadiose, E.O.; Okoli, C.E.; Onwumere-Idolor, O.S.; Ajibo, F.E.; Azor, N.N.; Bernard, S.N.; et al. The indiscriminate slaughter of pregnant goats for meat in Enugu, Nigeria: Causes, prevalence, implications, and ways-out. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoga, U.J.; Njoga, E.O.; Nwobi, O.C.; Abonyi, F.O.; Edeh, H.O.; Ajibo, F.E.; Azor, N.; Bello, A.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Okpala, C.O.R.; et al. Slaughter Conditions and Slaughtering of Pregnant Cows in Southeast Nigeria: Implications to Meat Quality, Food Safety and Security. Foods 2021, 10, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankwo, I.O.; Faleke, O.O.; Salihu, M.D.; Musa, U.; Magaji, A.; Audu, B.; Ngulukun, S. Prevalence and molecular identification of Campylobacter species isolates from poultry and humans in Sokoto, Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Salihu, M.D.; Junaidu, A.U.; Magaji, A.A.; Abubakar, M.B.; Adamu, A.Y.; Yakubu, A.S. Prevalence of Campylobacter in poultry meat in Sokoto Northwestern Nigeria. J. Public Health Epidemiol. 2010, 1, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ngulukun, S.; Oboegbulem, S.; Klein, G. Multilocus sequence typing of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates from poultry, cattle and humans in Nigeria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahamanyi, N.; Mboera, L.E.G.; Matee, M.I.; Mutangana, D.; Komba, E.V.G. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Thermophilic Campylobacter Species in Humans and Animals in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 2092478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paintsil, E.K.; Masanta, W.O.; Dreyer, A.; Ushanov, L.; Smith, S.I.; Frickmann, H.; Zautner, A.E. Campylobacter in Africa—A Specific Viewpoint. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 13, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinbobola, J.S.; Dinga, J.N.; Omeje, J.N.; Akinbobola, R.I.A.; Oguntade, E.E.; Babalola, J.O.; Ifarajimi, O.R.; Tijani, K.A. Protective equipments use by veterinarians in Nigeria. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2023, 19, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekere, S.O.; Njoga, E.O.; Onunkwo, J.I.; Njoga, U.J. Serosurveillance of Brucella antibody in food animals and role of slaughterhouse workers in the spread of Brucella infection in Southeast Nigeria. Vet. World 2018, 11, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juzbašić, T.; Andrijašević, N.; Ferenčak, I.; Jurić, D.; Šoprek, S.; Poje Janeš, V.; Žmak, L.; Tambić Andrašević, A.; Gverić Grginić, A. Emergence of Multidrug-Resistant Campylobacter jejuni in a Common Variable Immunodeficiency Patient: Evolution of Resistance Under the Selective Antibiotic Pressure. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onwumere-Idolor, O.S.; Kperegbeyi, J.I.; Imonikebe, U.G.; Okoli, C.E.; Ajibo, F.E.; Njoga, E.O. Epidemiology of multidrug-resistant zoonotic E. coli from beef processing and retail points in Delta State, Nigeria: Public health implications. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 106, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoga, E.O.; Onunkwo, J.I.; Chinwe, C.E.; Ugwuoke, W.; Nwanta, J.A.; Chah, K.F. Assessment of antimicrobial drug administration and antimicrobial residues in food animals in Enugu State, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoga, E.O.; Ogugua, A.J.; Nwankwo, I.O.; Awoyomi, O.J.; Okoli, C.E.; Buba, D.M.; Oyeleye, F.A.; Ajibo, F.E.; Azor, N.; Ogunniran, T.M. Antimicrobial drug usage pattern in poultry farms in Nigeria: Implications for food safety, public health and poultry disease management. Vet. Ital. 2021, 57, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odey, T.O.J.; Tanimowo, W.O.; Afolabi, K.O.; Jahid, I.K.; Reuben, R.C. Antimicrobial use and resistance in food animal production: Food safety and associated concerns in Sub-Saharan Africa. Int. Microbiol. 2024, 27, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). 2021 AWaRe Classification. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/2021-aware-classification (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Muteeb, G.; Rehman, M.T.; Shahwan, M.; Aatif, M. Origin of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, and Their Impacts on Drug Development: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Antunes, W.; Mota, S.; Madureira-Carvalho, Á.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Dias da Silva, D. An Overview of the Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241509763 (accessed on 19 July 2025).
- FAO. The FAO Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance 2021–2025; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonyi, F.O.; Njoga, E.O. Prevalence and determinants of gastrointestinal parasite infection in intensively managed pigs in Nsukka agricultural zone, Southeast, Nigeria. J. Parasit. Dis. 2020, 44, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, S.N.; Njoga, E.O.; Abonyi, F.O.; Nnadi, P.A.; Ozioko, I.K.; Ugwuoke, C.U. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal worm infections in pigs reared in Enugu State, Nigeria. J. Parasit. Dis. 2021, 45, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njoga, E.O.; Onunkwo, J.I.; Ekere, S.O.; Njoga, U.J.; Okoro, W.N. Seroepidemiology of equine brucellosis and role of horse carcass processors in spread of Brucella infection in Enugu State, Nigeria. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2018, 10, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raosoft® Sample Size Calculator. Available online: http://www.raosoft.com/samplesize.html (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Hagos, Y.; Gugsa, G.; Awol, N.; Ahmed, M.; Tsegaye, Y.; Abebe, N.; Bsrat, A. Isolation, Identification, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from Cattle, Goat, and Chicken Meats in Mekelle, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.J.; Patton, C.M.; Morris, G.K. Differentiation of Campylobacter species using phenotypic characterization. J. Lab. Med. 1988, 19, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Shakir, Z.M.; Alhatami, A.O.; Ismail Khudhair, Y.; Muhsen Abdulwahab, H. Antibiotic resistance profile and multiple antibiotic resistance index of Campylobacter species isolated from poultry. Arch. Razi Inst. 2021, 76, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rodloff, A.; Bauer, T.; Ewig, S.; Kujath, P.; Müller, E. Susceptible, intermediate, and resistant—The intensity of antibiotic action. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2008, 105, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnidge, J.; Paterson, D.L. Setting and revising antibacterial susceptibility breakpoints. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somphou, P.; Takano, T.; Nakamura, K. Cohabitation with farm animals in urban households with and without occupational farm work: Associations between participation in educational activities and good hygiene practices in at-risk households cohabiting with farm animals. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2008, 13, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onunkwo, J.I.; Njoga, E.O.; Njoga, U.J.; Ezeokafor, E.; Ekere, S.O. Brucella seropositivity in chicken and risk factors for Brucella infection at the animal-human interface in Anambra State, Nigeria. Int. J. One Health 2018, 4, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakeem, W.G.; Fathima, S.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R.K. Campylobacter jejuni in poultry: Pathogenesis and control strategies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, R.; Semedo-Lemsaddek, T.; Cunha, E.; Tavares, L.; Oliveira, M. Antimicrobial drug resistance in poultry production: Current status and innovative strategies for bacterial control. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternhag, A.; Törner, A.; Svensson, A.; Giesecke, J.; Ekdahl, K. Mortality following Campylobacter infection: A registry-based linkage study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esan, O.B.; Pearce, M.; van Hecke, O.; Roberts, N.; Collins, D.; Violato, M.; McCarthy, N.; Perera, R.; Fanshawe, T.R. Factors associated with sequelae of Campylobacter and non-typhoidal Salmonella infections: A systematic review. EBioMedicine 2017, 15, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoli, C.E.; Njoga, E.O.; Enem, S.I.; Godwin, E.E.; Nwanta, J.A.; Chah, K.F. Prevalence, toxigenic potential and antimicrobial susceptibility profile of Staphylococcus isolated from ready-to-eat meats. Vet. World 2018, 11, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, P.J.; Gao, Y.K.; Kotiw, M.; Eastwood, S.; Van, T.T.H.; Moore, R.J.; Muir, W.I. Descriptive epidemiology of spotty liver disease in Australian cage-free brown egg layer chicken flocks with a scratch area. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O.; Fitzgerald, C.; Stroika, S.; Zhao, S.; Sippy, R.J.; Kwan, P.; Plummer, P.J.; Han, J.; Yaeger, M.J.; Zhang, Q. Molecular evidence for zoonotic transmission of an emergent highly pathogenic Campylobacter jejuni clone in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O.; Burrough, E.R.; Pavlovic, N.; Frana, T.S.; Madson, D.M.; Zhang, Q. Campylobacter jejuni as a cause of canine abortions in the United States. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2014, 26, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, O.; Yaeger, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Campylobacter-associated diseases in animals. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 5, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akwuobu, C.A.; Oboegbulem, S.I.; Ofukwu, R.A. Characterization and antibiogram of local isolates of Campylobacter species from chicken in Nsukka Area, Southeast Nigeria. Am.-Eurasian J. Sustain. Agric. 2010, 4, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial resistance: A growing serious threat for global public health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenebe, T.; Zegeye, N.; Eguale, T. Prevalence of Campylobacter species in human, animal and food of animal origin and their antimicrobial susceptibility in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Backert, S.; Alter, T.; Bereswill, S. Human campylobacteriosis—A serious infectious threat in a One Health perspective. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 431, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benites, C.; Anampa, D.; Torres, D.; Avalos, I.; Rojas, M.; Conte, C.; Lázaro, C. Prevalence, tetracycline resistance and TetO gene identification in pathogenic Campylobacter strains isolated from chickens in retail markets of Lima, Peru. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karikari, A.; Saba, C.; Kpordze, S. Biotyping of multidrug-resistant Campylobacter jejuni from poultry and humans in Northern Region of Ghana. Open J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawes, J.R.; Vidal, A.; Clifton-Hadley, F.A.; Sayers, R.; Rodgers, J.; Snow, L.; Evans, S.J.; Powell, L.F. Investigation of prevalence and risk factors for Campylobacter in broiler flocks at slaughter: Results from a UK survey. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 1725–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, S.A.; Herman, V.; Tîrziu, E.; Morar, A.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Imre, M.; Pătrînjan, R.-T.; Imre, K. Public Health Risk of Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Slaughterhouse and Retail Poultry Meat: Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles. Pathogens 2025, 14, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayou, B.A.; Kassa, G.M.; Sori, T.; Mondin, A.; Tucciarone, C.M.; Cecchinato, M.; Pasotto, D. Molecular survey and identification of Campylobacter spp. in layer farms in central Ethiopia. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavinafchi, S.B.; Rahimi, E.; Shakerian, A. Campylobacter spp. isolated from poultry in Iran: Antibiotic resistance profiles, virulence genes, and molecular mechanisms. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 11, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwanibe, J.N.; Olawoye, I.B.; Happi, C.T.; Folarin, O.A. Genomic characterization of multidrug-resistant pathogenic enteric bacteria from healthy children in Osun State, Nigeria. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedman, H.D.; Vasco, K.A.; Zhang, L. A review of antimicrobial resistance in poultry farming within low-resource settings. Animals 2020, 10, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, R.K.; Basnet, H.B.; Dhakal, I.P.; Devkota, B. Antimicrobial resistance of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from broiler, layer, and breeder chickens. Vet. World 2024, 17, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, R.; Salari, S.; Najimi, M.; Rashki, A. Determination of frequency, multiple antibiotic resistance index and resistotype of Salmonella spp. in chicken meat collected from southeast of Iran. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunlade, A.O.; Ogunleye, A.O.; Jeminlehin, F.O.; Ajuwape, A.T.P. Occurrence of Campylobacter species in beef cattle and local chickens and their antibiotic profiling in Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portes, A.B.; Panzenhagen, P.; Pereira Dos Santos, A.M.; Junior, C.A.C. Antibiotic Resistance in Campylobacter: A Systematic Review of South American Isolates. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayukekbong, J.A.; Ntemgwa, M.; Atabe, A.N. The threat of antimicrobial resistance in developing countries: Causes and control strategies. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.; Abdi, S.M.; Ahad, A.A. Factors and challenges contributing to antimicrobial resistance in East African pastoral settings and importance of One Health approach. CABI One Health 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Cooper, B.S.; Coast, J.; Oppong, R.; Thuy, N.D.T.; Phodha, T.; Celhay, O.; Guerin, P.J.; Wertheim, H.; Lubell, Y. Enumerating the economic cost of antimicrobial resistance per antibiotic consumed to inform the evaluation of interventions affecting their use. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, A.; Countryman, A.; Laurence, T.; Gulliver, S.; Drake, T.; Edwards, S.; Kenny, C.; Lamberti, O.; Morton, A.; Shafira, A.; et al. Forecasting the Fallout from AMR: Economic Impacts of Antimicrobial Resistance in Humans—A Report from the EcoAMR Series; World Organisation for Animal Health and World Bank: Paris, France; Washington, DC, USA, 2024; p. 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, P.; Bjöersdorff, O.G.; Hansson, I.; Boqvist, S.; Erume, J. Prevalence and antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter spp. in broiler chicken carcasses and hygiene practices in informal urban markets in a low-income setting. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0318516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainyakou-Sanga, M.A.; Goualie, B.G.; Kipre, R.C.; Kra, D.K.; Karou, G.T. Risks associated with the discharge of poultry slaughterhouse waste in public landfill sites in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2025, 19, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, Y.; Haruna, M.; Murakami, M.; Asai, T.; Yamada, Y. Contamination pathways and persistence of Campylobacter in slaughterhouse environments: A risk to human health. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA BIOHAZ Panel (EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards); Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Fašmon Durjava, M.; Kouba, M.; López-Alonso, M.; Puente, S.L.; et al. Scientific opinion on the public health risks related to the consumption of raw and undercooked meat. EFSA J. 2020, 13, 3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, M.A.; Adebowale, O.O.; Fasanmi, O.G.; Fasina, F.O. One Health and the global challenge of zoonotic diseases: Emerging trends in antimicrobial resistance of zoonotic Campylobacter spp. in developing countries. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 667831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonyi, F.O.; Njoga, E.O.; Njoga, U.J.; Ozioko, I.E.; Aronu, C.J.; Bernard, S.N.; Ugwuoke, C.U. Gut balance booster as a viable alternative to antibiotic growth promoter in swine production: Evaluation of the effects on growth and health parameters. Not. Sci. Biol. 2022, 14, 11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Epidemiological Variables | Levels | Number Tested | Number Positive (Campylobacter Isolated) | Number Negative (Campylobacter Not Isolated) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poultry type | Broiler | 280 | 50 | 232 | 0.0031 * |
| Others † | 120 | 8 | 112 | ||
| Season | Rainy/wet | 220 | 46 | 174 | 0.0001 * |
| Dry/hot | 180 | 12 | 168 | ||
| Slaughterhouse location | Nsukka | 208 | 31 | 177 | 0.7784 |
| Enugu | 192 | 27 | 165 |
| Antimicrobial Agent | Campylobacter jejuni (n = 6) | Campylobacter coli (n = 52) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant (%) | Susceptible (%) | Resistant (%) | Susceptible (%) | ||
| Tetracycline (30 µg) | 6 (100) | 0 (0) | 50 (96.2) | 2 (3.8) | 0.0999 |
| Azithromycin (15 µg) | 0 (0) | 6 (100) | 2 (3.8) | 50 (96.2) | 0.0999 |
| Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid (30 µg) | 6 (100) | 0 (0) | 52 (100) | 0 (0) | 0.0999 |
| Ciprofloxacin (5 µg) | 6 (100) | 0 (0) | 26 (50) | 26 (50) | 0.0281 * |
| Ceftazidime (30 µg) | 0 (0) | 6 (100) | 6 (11.5) | 46 (88.5) | 0.0999 |
| Vancomycin (30 µg) | 6 (100) | 0 (0) | 52 (100) | 0 (0) | 0.0999 |
| Chloramphenicol (30 µg) | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 24 (46.2) | 28 (53.8) | 0.6814 |
| Streptomycin (10 µg) | 0 (0) | 6 (100) | 2 (3.8) | 50 (96.2) | 0.0999 |
| S/n | Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern Exhibited | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | AMC-CIP | 2 (3.4) |
| 2. | AZM-STR | 2 (3.4) |
| 3. | TET-CIP | 5 (8.6) |
| 4. | TET-CLR | 5 (8.6) |
| 5. | AMC-CIP-VAN | 6 (10.3) |
| 6. | CIP-CRL-VAN | 8 (13.8) |
| 7. | AMC-TET-VAN | 10 (17.2) |
| 8. | CAZ-CRL-CIP | 6 (10.3) |
| 9. | AMC-CIP-TET-VAN | 6 (10.3) |
| 10. | AMC-CRL-CIP-TET-VAN | 6 (10.3) |
| 11. | AMC-CRL-CIP-TET-STR-VAN | 2 (3.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Njoga, E.O.; Mshelbwala, P.P.; Ogugua, A.J.; Enemuo-Edo, E.C.; Onwumere-Idolor, O.S.; Ogunniran, T.M.; Bernard, S.N.; Ugwunwarua, J.C.; Anidobe, E.C.; Okoli, C.E.; et al. Campylobacter Colonisation of Poultry Slaughtered at Nigerian Slaughterhouses: Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Risk of Zoonotic Transmission. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090265
Njoga EO, Mshelbwala PP, Ogugua AJ, Enemuo-Edo EC, Onwumere-Idolor OS, Ogunniran TM, Bernard SN, Ugwunwarua JC, Anidobe EC, Okoli CE, et al. Campylobacter Colonisation of Poultry Slaughtered at Nigerian Slaughterhouses: Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Risk of Zoonotic Transmission. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(9):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090265
Chicago/Turabian StyleNjoga, Emmanuel O., Philip P. Mshelbwala, Akwoba J. Ogugua, Excel C. Enemuo-Edo, Onyinye S. Onwumere-Idolor, Temitope M. Ogunniran, Sunday N. Bernard, Joel C. Ugwunwarua, Ebube C. Anidobe, Chinwe E. Okoli, and et al. 2025. "Campylobacter Colonisation of Poultry Slaughtered at Nigerian Slaughterhouses: Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Risk of Zoonotic Transmission" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 9: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090265
APA StyleNjoga, E. O., Mshelbwala, P. P., Ogugua, A. J., Enemuo-Edo, E. C., Onwumere-Idolor, O. S., Ogunniran, T. M., Bernard, S. N., Ugwunwarua, J. C., Anidobe, E. C., Okoli, C. E., Godwin, E., Enem, S. I., & Oguttu, J. W. (2025). Campylobacter Colonisation of Poultry Slaughtered at Nigerian Slaughterhouses: Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Risk of Zoonotic Transmission. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(9), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090265








