High Efficacy of Triclabendazole/Ivermectin Combination Compared to Triclabendazole Monotherapy for Treating Human Fascioliasis in Upper Egypt: A Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment and Diagnosis
2.2. Treatment Regimens and Follow-Up
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Clinical, Laboratory, and Radiological Data of the Participants
3.3. Evaluation of Treatment Response
3.4. Factors Associated with Treatment Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCBZ | Triclabendazole |
| IVM | Ivermectin |
| NTDs | Neglected tropical diseases |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| HFL | Hepatic focal lesion |
References
- Fürst, T.; Duthaler, U.; Sripa, B.; Utzinger, J.; Keiser, J. Trematode infections: Liver and lung flukes. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 399–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PAHO. Operational Guidelines for the Elimination of Human Fascioliasis as a Public Health Problem in the Americas; World Health Organization. Pan American Health Organization: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789275128084 (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Mas-Coma, S. Human fascioliasis emergence risks in developed countries: From individual patients and small epidemics to climate and global change impacts. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 38, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Fascioliasis. Digenetic Trematodes. 2019, 71–103. [Google Scholar]
- Lotfy, W.; El-Morshedy, H.; Abou El-Hoda, M.; El-Tawila, M.; Omar, E.; Farag, H. Identification of the Egyptian species of Fasciola. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 103, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalafala, R.E. Prevalence and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciola species in upper Egypt based on ribosomal ITS-2 gene sequencing. Egyp. Vet. Med. Soc. Parasitol. J. 2020, 16, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, H.K.-A.; Hassan, W.A.; Elossily, N.A.; Ahmad, A.A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Abd-Elkader, A.S.; Abdelsalam, E.M.N.; Khojah, H.M. Evaluation of nitazoxanide treatment following triclabendazole failure in an outbreak of human fascioliasis in Upper Egypt. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.A.; Ramadan, H.K.-A.; Hassan, W.A.; Hakami, M.A.; Huseein, E.A.M.; Mohamed, S.A.-A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Elossily, N.A. New perspectives for fascioliasis in Upper Egypt’s new endemic region: Sociodemographic characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciola in humans, animals, and lymnaeid vectors. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0011000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periago, M.V.; Valero, M.A.; Artigas, P.; Agramunt, V.H.; Bargues, M.D.; Curtale, F.; Mas-Coma, S. Very high fascioliasis intensities in schoolchildren from Nile Delta Governorates, Egypt: The Old World highest burdens found in lowlands. J. Pathog. 2021, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaty, N.; Ibrahim, N.; Ramadan, H.K.-A.; Ahmad, A.A.; Saad-Hussein, A. Significance of climate change in the emergence of human fascioliasis in Upper Egypt. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2024, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Report of the WHO Informal Meeting on Use of Triclabendazole in Fascioliasis Control: WHO Headquarters, Geneva, Switzerland 17–18 October 2006; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, P.; Cabrera, M.; Jave, J.; Claxton, J.; Williams, D. Human fascioliasis: Prevalence and treatment in a rural area of Peru. Infect. Dis. Rev. 2000, 2, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Winkelhagen, A.J.; Mank, T.; de Vries, P.J.; Soetekouw, R. Apparent triclabendazole-resistant human Fasciola hepatica infection, the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabada, M.M.; Lopez, M.; Cruz, M.; Delgado, J.R.; Hill, V.; White, A.C., Jr. Treatment failure after multiple courses of triclabendazole among patients with fascioliasis in Cusco, Peru: A case series. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, J.M.; Elliott, T.P.; Beddoe, T.; Anderson, G.; Skuce, P.; Spithill, T.W. Current threat of triclabendazole resistance in Fasciola hepatica. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, A.; Omura, S. Ivermectin, ‘wonder drug’ from Japan: The human use perspective. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2011, 87, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, R.; Gillan, V.; Devaney, E. Ivermectin–old drug, new tricks? Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulik, M.; Antoszczak, M.; Huczyński, A.; Steverding, D. Antiparasitic activity of ivermectin: Four decades of research into a “wonder drug”. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 261, 115838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarez, M.; Schcolnik-Cabrera, A.; Dueñas-Gonzalez, A. The multitargeted drug ivermectin: From an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ico-Gómez, R.; González-Garduño, R.; Ortiz-Pérez, D.; Mosqueda-Gualito, J.J.; Flores-Santiago, E.d.J.; Sosa-Pérez, G.; Salazar-Tapia, A.A. Assessment of anthelmintic effectiveness to control Fasciola hepatica and paramphistome mixed infection in cattle in the humid tropics of Mexico. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, I.; Brennan, G.; Hanna, R.; Robinson, M.; Skuce, P. Drug resistance in liver flukes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 12, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartram, D.J.; Leathwick, D.M.; Taylor, M.A.; Geurden, T.; Maeder, S.J. The role of combination anthelmintic formulations in the sustainable control of sheep nematodes. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanusse, C.; Lifschitz, A.; Alvarez, L. Basic and clinical pharmacology contribution to extend anthelmintic molecules lifespan. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 212, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, T.G.; Sakanari, J.A.; Caffrey, C.R. Anthelmintic drug discovery: Into the future. J. Parasitol. 2015, 101, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Neto, I.; de Almeida, T.M.; Zugman, T.; Piovan, L.; Molento, M.B. Ovicidal activity of diaryl dichalcogenides and ivermectin on Fasciola hepatica: A novel candidate for a blending-based therapeutic strategy. Acta Trop. 2024, 258, 107363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, C.; Mahoney, R.; Fisara, P.; Strehlau, G.; Reichel, M. The efficacy of formulations of triclabendazole and ivermectin in combination against liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) and gastro-intestinal nematodes in cattle and sheep and sucking lice species in cattle. Aust. Vet. J. 2002, 80, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, R.; Cromie, L.; Taylor, S.; Couper, A. The effect of a parenteral ivermectin/closantel injection on the growth and reproductive development of early immature Fasciola hepatica in cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 142, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.M.; Wolstenholme, A.J. An ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel subunit from Dirofilaria immitis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, L.M. Ivermectin: Uses and impact 20 years on. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 19, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.; Dobson, R.; Barger, I. Worm control and anthelmintic resistance: Adventures with a model. Parasitol. Today 1995, 11, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottier, L.; Alvarez, L.; Fairweather, I.; Lanusse, C. Resistance-induced changes in triclabendazole transport in Fasciola hepatica: Ivermectin reversal effect. J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Failoc-Rojas, V.E.; Silva-Díaz, H.; Maguiña, J.L.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Díaz-Velez, C.; Apolaya-Segura, M.; Valladares-Garrido, M.J. Evidence-based indications for ivermectin in parasitic diseases: An integrated approach to context and challenges in Peru. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2023, 23, e00320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hien, T.T.; Truong, N.T.; Minh, N.H.; Dat, H.D.; Dung, N.T.; Hue, N.T.; Dung, T.K.; Tuan, P.Q.; Campbell, J.I.; Farrar, J.J.; et al. A randomized controlled pilot study of artesunate versus triclabendazole for human fascioliasis in central Vietnam. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravedo, M.A.; Cabada, M.M. Human fascioliasis: Current epidemiological status and strategies for diagnosis, treatment, and control. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2020, 11, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Bench Aids for the Diagnosis of Intestinal Parasites. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241515344 (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Sprague, D.J.; Park, S.-K.; Gramberg, S.; Bauer, L.; Rohr, C.M.; Chulkov, E.G.; Smith, E.; Scampavia, L.; Spicer, T.P.; Haeberlein, S.; et al. Target-based discovery of a broad-spectrum flukicide. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2024, 31, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.L.; Tanabe, M.B.; White, A.C., Jr.; Lopez, M.; Bascope, R.; Cabada, M.M. Triclabendazole treatment failure for Fasciola hepatica infection among preschool and school-age children, Cusco, Peru. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtale, F.; El-Wahab Hassanein, Y.A.; El Wakeel, A.; Mas-Coma, S.; Montresor, A. Distribution of human fascioliasis by age and gender among rural population in the Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2003, 49, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtale, F.; Mas-Coma, S.; Hassanein, Y.; Barduagni, P.; Pezzotti, P.; Savioli, L. Clinical signs and household characteristics associated with human fascioliasis among rural population in Egypt: A case-control study. Parassitologia 2003, 45, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Curtale, F.; Hassanein, Y.A.W.; Barduagni, P.; Yousef, M.M.; Wakeel, A.E.; Hallaj, Z.; Mas-Coma, S. Human fascioliasis infection: Gender differences within school-age children from endemic areas of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 101, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Fasciola, lymnaeids and human fascioliasis, with a global overview on disease transmission, epidemiology, evolutionary genetics, molecular epidemiology and control. Adv. Parasitol. 2009, 69, 41–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, N.; Abdel Khalek, E.M.; Makhlouf, N.A.; Abdel-Gawad, M.; Mekky, M.; Ramadan, H.K.-A.; Abu-Elfatth, A.; El-Latif, N.A.; Hassan, M.K.; Eldeeb, R.; et al. Clinical characteristics of human fascioliasis in Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, P.; Schmitt, E.K.; Chen, C.-W.; Samantray, S.; Venishetty, V.K.; Hughes, D. Triclabendazole in the treatment of human fascioliasis: A review. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 113, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, J.; Engels, D.; Büscher, G.; Utzinger, J. Triclabendazole for the treatment of fascioliasis and paragonimiasis. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2005, 14, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Velarde, F.; Flores-Ramos, M.; Cruz-Mendoza, I.; Vera-Montenegro, Y.; Hernández-Campos, A.; Leyva-Gómez, G.; Rojas-Campos, T.; Tovar-Escobar, D.; Castillo, R.; Arias-García, R.; et al. Fosfatriclaben: Effective dose determination and comparative efficacy assessment with closantel, triclabendazole+ ivermectin, triclabendazole+ albendazole in artificially infected cattle. Exp. Parasitol. 2024, 266, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashima, A.; Canales, M.; Maco, V.; Marcos, L.A. Observational study on the effectiveness and safety of multiple regimens of triclabendazole in human fascioliasis after failure to standard-of-care regimens. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Morshedy, H.; Farghaly, A.; Abou-Basha, S.S.L.; Barakat, R. human fascioliasis: A community-based study. East. Mediterr. Health J. 1999, 5, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaie, H.; Emami, H.; Yadegarinia, D.; Nava-Ocampo, A.A.; Massoud, J.; Azmoudeh, M.; Mas-Coma, S. Randomized trial of a single, double and triple dose of 10 mg/kg of a human formulation of triclabendazole in patients with fascioliasis. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004, 31, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.; Shehab, A.; Zaki, A.; Farag, H. Evaluation of two doses of triclabendazole in treatment of patients with combined schistosomiasis and fascioliasis. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2011, 17, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.; Dawson, K.; Fitzgibbon, C.; Martin, P. Efficacy of an injectable combination anthelmintic (nitroxynil+clorsulon+ivermectin) against early immature Fasciola hepatica compared to triclabendazole combination flukicides given orally or topically to cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 162, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifschitz, A.; Virkel, G.; Ballent, M.; Sallovitz, J.; Lanusse, C. Combined use of ivermectin and triclabendazole in sheep: In vitro and in vivo characterisation of their pharmacological interaction. Vet. J. 2009, 182, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Blavo, C.; Parmar, M.S. Ivermectin: A multifaceted drug with a potential beyond anti-parasitic therapy. Cureus 2024, 16, e56025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Ci, X.; An, N.; Ju, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Han, C.; Cui, J.; Deng, X. Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice. Inflamm. Res. 2008, 57, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diab, T.M.; Mansour, H.H.; Mahmoud, S.S. Fasciola gigantica: Parasitological and scanning electron microscopy study of the in vitro effects of ivermectin and/or artemether. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lespine, A.; Ménez, C.; Bourguinat, C.; Prichard, R.K. P-glycoproteins and other multidrug resistance transporters in the pharmacology of anthelmintics: Prospects for reversing transport-dependent anthelmintic resistance. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 2, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, S.; Da Costa, V.; Costa, M.; Festari, M.F.; Landeira, M.; Rodríguez-Zraquia, S.A.; Härtel, S.; Toledo, J.; Freire, T. Eosinophils control liver damage by modulating immune responses against Fasciola hepatica. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 579801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.W.; Zeb, A.; Mansoor, A.; Hayat, A.; Mas-Coma, S. Fasciola hepatica infection in children actively detected in a survey in rural areas of Mardan district, Khyber Pakhtunkhawa province, northern Pakistan. Parasitol. Int. 2019, 69, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Items | Total n = 136 (n, %) | TCBZ (n = 65) (n, %) | TCBZ + IVM (n = 71) (n, %) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender: | ||||
| Females | 77 (56.6) | 33 (44) | 44 (62) | 0.188 |
| Males | 59 (43.4) | 32 (27) | 27 (38) | |
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 33.6 ± 17.3 | 31.6 ± 18.2 | 35.5 ± 16.4 | 0.195 |
| Residence: | ||||
| Rural | 100 (73.5) | 46 (54) | 54 (76.1) | 0.485 |
| Urban | 36 (26.5) | 19 (17) | 17 (23.9) | |
| Chronic fascioliasis | 17 (12.5) | 9 (13.8) | 8 (11.3) | 0.650 |
| Fasciola antibody levels (mean) | 890.6 ± 390.3 | 960 ± 396 | 827 ± 376.7 | 0.047 * |
| Items | Before TCBZ (n = 65) (n, %) | After TCBZ (n = 65) (n, %) | p-Value | Before TCBZ + IVM (n = 71) (n, %) | After TCBZ + IVM (n = 71) (n, %) | p-Value |
| Fever | 44 (67.7) | 5 (7.7) | 0.000 * | 32 (45.1) | 0 | <0.001 * |
| Abdominal pain | 63 (96.9) | 8 (12.3) | 0.000 * | 71 (100) | 3 (4.2) | <0.001 * |
| Ascites | 7 (10.8) | 0 | 0.016 * | 4 (5.6) | 0 | 0.125 |
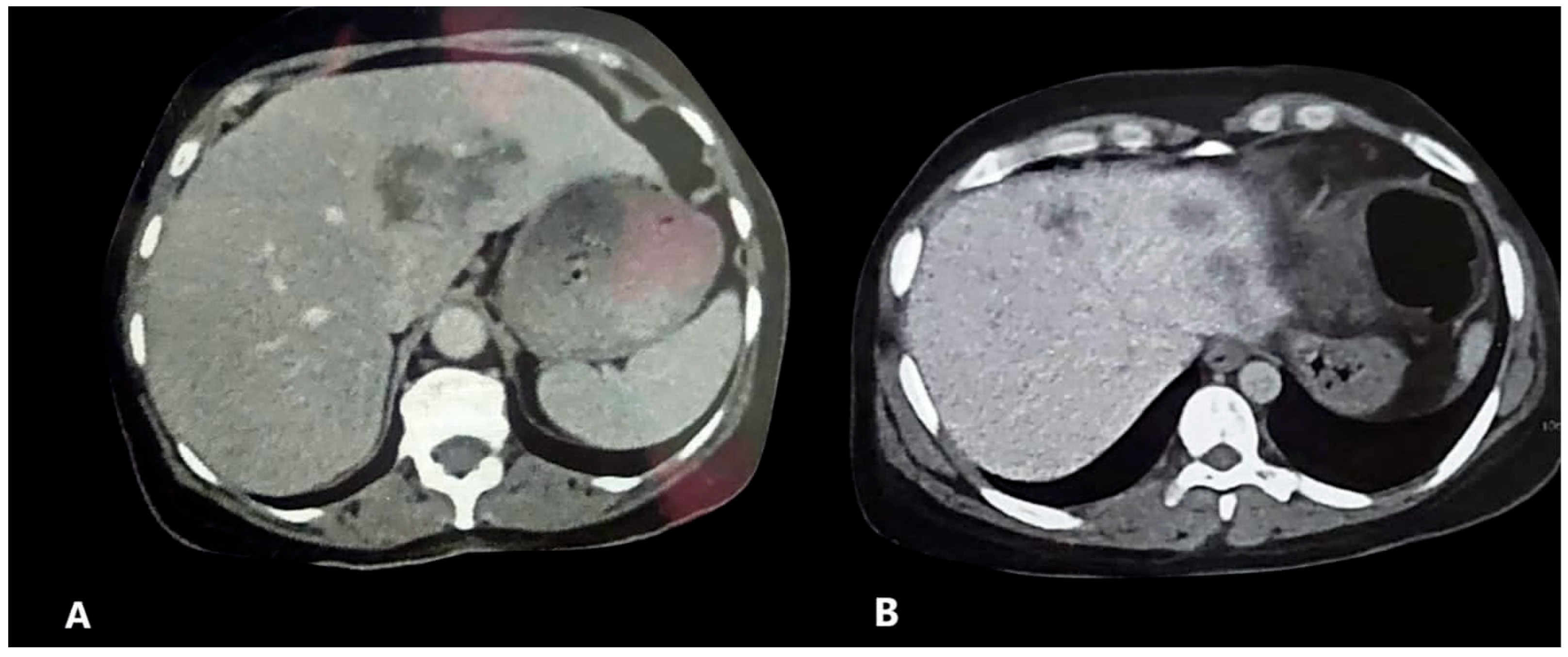
| HFL | 25 (38.5) | 8 (12.3) | 0.000 * | 41 (57.7) | 6 (8.5) | <0.001 * |
| Presence of ova in stool | 6 (9.2) | 1 (1.5) | 0.063 | 4 (5.6) | 1 (1.4) | 0.250 |
| ALT (IU/L) (median) | 35 (28) | 30 (12) | 0.000 * | 31 (20) | 25 (12) | <0.001 * |
| AST (IU/L) (median) | 32 (28.5) | 26 (12) | 0.000 * | 28 (19) | 22 (11) | <0.001 * |
| WBCs cells/μL (median) | 10,500 (8830) | 8600 (3355) | 0.000 * | 10,500 (6140) | 7430 (3020) | <0.001 * |
| Eosinophilic count (median) cells/μL | 3576 (5717) | 970 (1854.5) | 0.000 * | 3250 (6500) | 400 (400) | <0.001 * |
| Eosinophilic percent (median) | 36 (29) | 13 (17.8) | 0.000 * | 30 (37.5) | 6 (6) | <0.001 * |
| Items | TCBZ (n = 65) (n, %) | TCBZ + IVM (n = 71) (n, %) | p-Value |
| Clinical response | 56 (86.2) | 68 (95.8) | 0.048 * |
| Eosinophilic response | 21 (32.3) | 50 (70.4) | <0.001 * |
| Radiological response | 18 (27.7) | 35 (49.3) | 0.036 * |
| Complete response | 17 (26.2) | 40 (53.3) | <0.001 * |
| Variables | p-Value | OR | CI Upper Level | CI Lower Level |
| Age | 0.234 | 0.985 | 0.961 | 1.010 |
| Gender | 0.841 | 0.915 | 0.382 | 2.189 |
| Residence | 0.899 | 0.938 | 0.351 | 2.509 |
| Duration of symptoms | 0.297 | 0.992 | 0.976 | 1.007 |
| HFL at baseline | 0.330 | 0.648 | 0.271 | 1.552 |
| High eosinophil counts at baseline | 0.009 * | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Treatment type | 0.168 | 1.860 | 0.770 | 4.494 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, W.A.; Ramadan, H.K.-A.; Gaber, M.; Alkhalil, S.S.; Ahmad, A.A. High Efficacy of Triclabendazole/Ivermectin Combination Compared to Triclabendazole Monotherapy for Treating Human Fascioliasis in Upper Egypt: A Prospective Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080221
Hassan WA, Ramadan HK-A, Gaber M, Alkhalil SS, Ahmad AA. High Efficacy of Triclabendazole/Ivermectin Combination Compared to Triclabendazole Monotherapy for Treating Human Fascioliasis in Upper Egypt: A Prospective Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(8):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080221
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Waleed Attia, Haidi Karam-Allah Ramadan, Mona Gaber, Samia S. Alkhalil, and Alzahraa Abdelraouf Ahmad. 2025. "High Efficacy of Triclabendazole/Ivermectin Combination Compared to Triclabendazole Monotherapy for Treating Human Fascioliasis in Upper Egypt: A Prospective Study" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 8: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080221
APA StyleHassan, W. A., Ramadan, H. K.-A., Gaber, M., Alkhalil, S. S., & Ahmad, A. A. (2025). High Efficacy of Triclabendazole/Ivermectin Combination Compared to Triclabendazole Monotherapy for Treating Human Fascioliasis in Upper Egypt: A Prospective Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(8), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080221






