Abstract
Strongyloidiasis is a common intestinal infection that may persist in humans for decades without symptoms or can present as a potentially fatal, broadly disseminated infection in an immunocompromised host. This report describes a rare case of concomitant strongyloidiasis and E. coli meningitis that was successfully recognized and treated in a patient 20 years post-renal transplantation.
1. Introduction
Strongyloidiasis is a parasitic infection caused by Strongyloides stercoralis, which affects over 100 million people globally [1,2]. Risk factors for exposure include travel to endemic areas, including Southeast Asia, where countries have reported an average 30% seroprevalence of S. stercoralis. The rural highlands of Vietnam have the highest rate in the region of 42% [3]. Within the United States, the Southeast has been linked to strongyloidiasis from exposure to contaminated soil (e.g., walking barefoot, gardening without gloves) [4]. In addition, dogs and humans share certain S. stercoralis genotypes, and there are case reports supporting the hypothesis of transmission from dogs (reservoir) to humans [5,6]. However, the zoonotic potential between these two hosts is controversial and not well understood [7]. The estimated global prevalence of S. stercoralis in dogs is 6%, with prevalence in lower-income countries higher at 22% [5].
This parasite is seldom regarded as a primary contributor to meningitis in patients who have undergone renal transplantation. Additionally, organ system involvement and symptoms of strongyloidiasis can vary. A transplanted host on active immunosuppression may provide an easy migration path for the parasite from the skin and gastrointestinal tract to the lungs and meninges [8]. Symptoms can be indolent for years and can be non-specific, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, nausea, and gastrointestinal bleeding [9]. Pulmonary symptoms may include cough, wheezing, chest pain, and hemoptysis. Meningeal inflammation as a result of direct invasion of S. stercoralis can mimic aseptic or bacterial meningitis [10], and concomitant bacteremia and meningeal inflammation are seen in 50% of cases [11].
Here, we aim to highlight the importance of considering strongyloidiasis as a risk factor for Gram-negative meningitis. This report is in alignment with NEJM HIPAA policies, and consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case.
2. Case Presentation
Our patient was a 77-year-old (83.6 kg) Caucasian male with a history of hypertension and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) secondary to congenital atrophy (left) and traumatic kidney injury (right) from a motor vehicle accident, now status-post living-related kidney transplant (20 years prior). He was maintained on immunosuppressive therapy with tacrolimus, mycophenolate, and steroids, with a stable creatinine of 1.2 mg/dL. Additional history included a cochlear implant and history of a neurogenic bladder from lumbar disk disease, requiring self-catheterization and trimethoprim for urinary tract infection (UTI) prophylaxis.
The patient initially presented with a fever and delusions, and he quickly became encephalopathic and hypoxic, necessitating urgent intubation. His highest temperature was recorded at 103.9 °F, raising concerns for acute meningitis. A diagnostic lumbar puncture was performed, and results were suspicious for a suppurative central nervous system (CNS) infection, as the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) obtained was yellow and cloudy, with an opening pressure of 37 mm H2O. Initial bloodwork revealed a white blood cell (WBC) count of 17.5 × 109/L with 90% neutrophils, a blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level of 39 mg/dL, and a creatinine level of 1.5 mg/dL. Eosinophil count was 0 cells/mcL (0%) in the setting of chronic immunosuppressive therapy. Procalcitonin level was 54.6 ng/mL, and Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and influenza (A and B) polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing were negative. Dexamethasone, cefepime, ampicillin, vancomycin, and acyclovir were initiated empirically for broad coverage. Mycophenolate was discontinued on day 1, while tacrolimus was stopped on day 8.
Findings from the initial CSF in tube #3 are shown in Table 1 (first column). Blood, urine, and spinal fluid cultures all grew out pan-sensitive Escherichia coli on follow-up, concerning for an E. coli UTI and septicemia with meningeal seeding. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis with intravenous contrast showed the transplanted kidney in the right lower quadrant without hydronephrosis, and non-specific bladder wall thickening without other acute evidence of an ascending UTI. In addition, there was no clinical or radiological evidence of an epidural abscess or discitis.

Table 1.
Patient CSF findings by hospital day.
A transthoracic echocardiogram showed an ejection fraction of 65–70%, no significant valvular lesions, and no obvious vegetations. His high-dose steroid was discontinued after 2 days. Due to concerns for seeding of his cochlear implant, a repeat lumbar puncture was performed after 48 h of Gram-negative coverage to assess efficacy. His spinal fluid WBC count remained elevated at 2150, with 98% leukocytes, a glucose level of 21 mg/100 mL, and a CSF protein level of 347 mg/100 mL. CSF cultures were persistently positive for E. coli. Cefepime was changed to ceftriaxone based on blood culture susceptibilities on hospital day #4. The CSF continued to have similar characteristics and remained E. coli positive on a repeat lumbar puncture conducted 5 days after initiation of Gram-negative treatment, and levofloxacin was added the same day for dual Gram-negative coverage.
The patient remained intubated. Given his unresolved clinical picture, the patient’s wife was re-interviewed, at which point she revealed significant additional history. The patient had traveled to Vietnam 6 years prior, had been on several cruises in the past 6 years (West Caribbean, Mexico, Hawaii), and routinely traveled to Florida each summer. She also recounted that they had a 7-year-old pet dog that had vomited on the carpet prior to the patient’s illness, and he had cleaned the carpet after this event. Their dog was taken to the veterinarian and later passed away from unspecified multisystem organ failure. In light of this new information, the hospital pathologist was asked to review the CSF slides for Strongyloides. At this time, filariform larvae were noted on all slides (Figure 1). A heavy burden of inflammatory cells and bacteria was present despite 6 days of antibiotics.
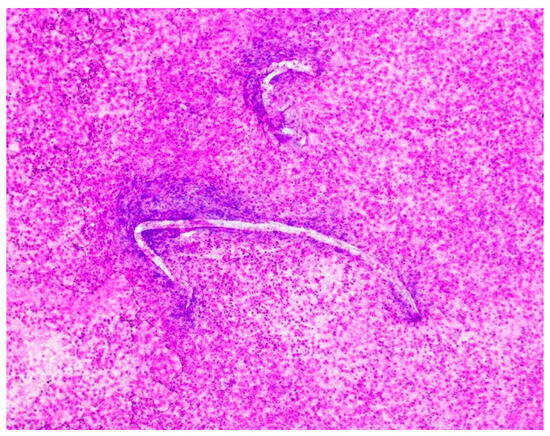
Figure 1.
Hospital day #1, Magnification 20×; Diff-Quik stain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shows filariform larvae of Strongyloides stercoralis observed by microscopy of the cerebrospinal fluid from the patient. In the background, there is a massive load of rod-shaped E. coli organisms and numerous acute inflammatory cells.
Serum Strongyloides antibody titer was positive on hospital day #6 at 0.5 IV (reference < 0.1 IV), and the patient was started on ivermectin 18 mg/day (200 mcg/kg body weight) via nasogastric tube. Additional Strongyloides testing was attempted from tracheal secretions, gastric contents, and duodenal biopsies, which all returned negative. The stool Strongyloidiasis PCR was not available at our facility or reference lab. Further CSF testing indicated that the CSF was negative for cytomegalovirus (CMV), Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Herpes simplex virus (HSV), and human T-cell lymphotropic virus types 1 and 2 (HTLV-1 and HTLV-2). CSF immunoglobulin panels were also normal.
Ivermectin, ceftriaxone, and levofloxacin were continued, with serial lumbar punctures conducted every 3–4 days. The patient stabilized and was extubated on hospital day #9. CSF cell counts decreased on serial studies, but persistent evidence of Strongyloides larvae and filamentous structures was noted. On hospital day #10, albendazole 400 mg twice a day was initiated for a 7-day course. In light of continued pleocytosis despite adequate therapy, a full workup for autoimmune conditions, Tropheryma whipplei, and BioFire film array was initiated, but all returned negative.
The patient received a total of 5 weeks of ivermectin, given his initial heavy load of Strongyloides and continued pleocytosis in addition to 6 weeks of coverage for E. coli meningitis. His immunosuppression was held for the entire duration, and renal function remained normal. He was resumed on tacrolimus 0.5 mg once a day before discharge, and was discharged home after a 48-day admission. Overall, he demonstrated no signs of neurotoxicity from prolonged ivermectin therapy. At the 6-week outpatient mark, his tacrolimus dosage was increased to 0.5 mg twice daily, and mycophenolate was permanently discontinued due to concerns about the potential recurrence of strongyloidiasis.
3. Discussion
Our renal transplant patient presented with late strongyloidiasis superimposed on E. coli bacteremia and meningitis, requiring prolonged therapy with Ivermectin in addition to routine therapies indicated for Gram-negative bacteremia. Subsequently, we learned that his non-specific symptoms (pulmonary infections and diarrheal episodes) were ongoing for more than 9 months prior to presentation. CNS involvement later during the described admission was what prompted further workup.
A manifestation of strongyloidiasis as Gram-negative meningitis is rare and the proposed mechanism is multi-faceted, involving disruption of the gastrointestinal mucosa by the parasite, followed by direct entry of bowel flora into the bloodstream and subsequently translocation of bowel flora with the infected larvae across the blood–brain barrier after repeated bacteremic episodes [12,13].
His risk factors included travel to endemic areas, an immunosuppressed status, and a possible exposure via his pet dog. As disseminated strongyloidiasis carries a mortality rate of almost 80%, early diagnosis and treatment were imperative to maximize chances of recovery. There is currently no gold standard test for making this diagnosis.
This case highlights a need to formalize screening and testing for re-infection in transplant patients. Organ procurement organizations are not currently required to test donors for Strongyloides [14], although transplant organizations have made an effort since 2010 to extend practical recommendations for potential recipient screening [15,16]. These algorithms, in addition to recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), and American Society of Transplantation (AST) include suggestions for targeted donor and recipient screening based on travel to or residence in an endemic area, demographic risk factors, animal exposures, or evidence of peripheral eosinophilia (present in approximately 20% of Strongyloides-seropositive patients [17]). Screening should be conducted with serological testing by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or with stool examination. ELISA testing has 84–95% sensitivity and 82–100% specificity [18,19]. Of significant note, post-transplant monitoring guidelines for Strongyloides currently do not exist. We suggest post-transplant screening of recipients with a detailed questionnaire, including travel, exposures, and recreational activities, in order to prevent future hyperinfection. Testing should also be quickly performed when suspicion is high for Strongyloides. Among the available tests (stool exams, molecular diagnostics, and serological tests), the droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) assay to detect S. stercoralis larvae may provide the best sensitivity and specificity for detection in stool samples [20], although this testing is not widely available. Use of corticosteroid therapy in this patient population may mask blunt high peripheral eosinophil counts, and as such, this particular marker should be used with caution in marker for screening.
The choice of drug therapy in our patient was carefully selected, given the circumstances of the late presentation. In general, treatment options for strongyloidiasis include albendazole, thiabendazole, and ivermectin [21]. Overall, ivermectin is well tolerated, with minimal side effects and an association with greater eradication of parasite larvae when compared to albendazole. Because of continued evidence of parasites in the CNS, we chose to use it in combination with albendazole. There is limited data on the duration of treatment for CNS strongyloidiasis and treatment of hyperinfection in immunocompromised patients. The CDC recommends ivermectin 200 ug/kg per day orally, until stool and/or sputum exams are negative for 2 weeks, along with suspension of immunosuppressive therapy. A combination of ivermectin and albendazole 10 mg/kg/day has been utilized in case reports and is reasonable given the severity of illness, despite the lack of high-quality data comparing this approach to ivermectin monotherapy [22,23]. Maintenance after initial therapy has been described with 2 doses of ivermectin at 200 mg/kg every 2 weeks for 6 weeks in immunocompromised patients to ensure microscopic clearance of larvae from infected sites [24], prevent recurrence of hyperinfection, and achieve adequate future prophylaxis [25]. Given the severity of illness in these patients and in the setting of suboptimal gastrointestinal absorption, administration of subcutaneous ivermectin can also be considered.
Duration of therapy was guided by our patient’s prolonged pleocytosis attributed to Strongyloides presence in the CSF. We opted for a longer course of Ivermectin (total duration of 5 weeks; until CSF clearance + an additional 14 days), in order to assure elimination of the larvae and prevent recurrence, as a development cycle takes 2 weeks [26]. Ivermectin was tolerated well in our patient without toxicity or side effects. Although CSF cultures returned negative for bacteria on hospital day #24, filariform organisms were present on slides until day #35. Of note, the patient received an initial short course of high-dose corticosteroids for meningitis and respiratory failure, and it remains unclear whether this short steroid burst played a role in promoting the transition of S. stercolaris larvae from the rhabdiform stage to the filariform stage, thus delaying the clearance of infection.
4. Conclusions
We demonstrate here a case of late disseminated strongyloidiasis post-transplant, with an initial presentation of E. coli urosepsis and acute meningitis. Disseminated strongyloidiasis is fatal in immunocompromised hosts, but initiation of dual drug therapy allowed our particular patient to have a great outcome.
For early diagnosis, we suggest screening with history including travel, recreational activities, and high steroid use, and early labs looking for eosinophilia. The protocols for screening in this patient population need to be adjusted.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B. and A.N.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B., C.M., D.M., T.G. and A.N.; writing—review and editing, A.B., C.M. and A.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
No external funding was received.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent for publication was obtained from the patient involved in this case report.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Kiran Belani (copy-editing) and Octavius A. Smith (literature search) for their contributions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Genta, R.M. Global prevalence of strongyloidiasis: Critical review with epidemiologic insights into the prevention of disseminated disease. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1989, 11, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthiyakannon, S.; Boddu, A.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Chen, X. Strongyloidiasis--an insight into its global prevalence and management. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, N.T.N.; Thai, P.Q.; Trang, N.N.M.; Jäger, J.; Fox, A.; Horby, P.; Phuong, H.V.M.; Anh, D.D.; Mai, L.T.Q.; Doorn, H.R.V.; et al. trongyloides stercoralis seroprevalence in Vietnam. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 3214–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites-Strongyloides. Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/strongyloides/about/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/strongyloides#cdc_disease_basics_risk-risk-factors (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Eslahi, A.V.; Hashemipour, S.; Olfatifar, M.; Houshmand, E.; Hajialilo, E.; Mahmoudi, R.; Badri, M.; Ketzis, J.K. Global prevalence and epidemiology of Strongyloides stercoralis in dogs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, J.L.N.; Lane, M.; Talundzic, E.; Richins, T.; Robertson, G.; Formenti, F.; Pritt, B.; Verocai, G.; de Souza, J.N.; Soares, N.M.; et al. A global genotyping survey of Strongyloides stercoralis and Strongyloides fuelleborni using deep amplicon sequencing. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaleta, T.F.; Zhou, S.; Bemm, F.M.; Schär, F.; Khieu, V.; Muth, S.; Odermatt, P.; Lok, J.B.; Streit, A. Strongyloides stercoralis in dogs and humans-Dogs as a possible source for zoonotic strongyloidiasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutcher, J.P.; Marcus, S.L.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Wittner, M.; Fuks, J.Z.; Wiernik, P.H. Disseminated strongyloidiasis with central nervous system involvement diagnosed antemortem in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and Burkitts lymphoma. Cancer 1990, 66, 2417–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, P.B.; Nutman, T.B. Strongyloides stercoralis in the Immunocompromised Population. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanath, S.; Baker, R.A.; Mansheim, B.J. Strongyloides infection and meningitis in an immunocompromised host. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1982, 31, 857–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.; Nellore, A. Management of Strongyloides in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 32, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, K.; Orenstein, R. Bacterial complications of strongyloidiasis: Streptococcus bovis meningitis. South. Med. J. 1999, 92, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorman, M.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection presenting as acute respiratory failure and Gram-negative sepsis in a patient with astrocytoma. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, e288–e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, C.K.R.; Bhaimia, E.; Schueta, A.N.; Razonable, R.R. A comprehensive review of Strongyloides stercoralis infection after solid organ and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 36, e14795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, W.T.; Pierrotti, L.C.; Abdala, E.; Morris, M.I.; Azevedo, L.S.; López-Vélez, R.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; Petersen, E.; Camargo, L.F.A.; et al. Recommendations for Management of Endemic Diseases and Travel Medicine in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients and Donors: Latin America. Transplantation 2018, 102, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.A.; Lu, K. Screening of donor and recipient in solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13 (Suppl. S4), 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutfy, M.P.; Wilson, M.; Keystone, J.S.; Kain, K.C. Serology and eosinophil count in the diagnosis and management of strongyloidiasis in a non-endemic area. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 66, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinis, M.; Boucher, H.W. Screening of donor and candidate prior to solid organ transplantation-Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Hoz Morris, M. Intestinal parasites including Cryptosporidium, Cyclospora, Giardia, and Microsporidia, Entamoeba histolytica, Strongyloides, Schistosomiasis, and Echinococcus: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iamrod, K.; Chaidee, A.; Rucksaken, R.; Kopolrat, K.Y.; Worasith, C.; Wongphutorn, P.; Intuyod, K.; Pinlaor, S.; Sithithaworn, J.; Sithithaworn, P.; et al. Development and Efficacy of Droplet Digital PCR for Detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in Stool. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 106, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez-Camacho, C.; Gotuzzo, E.; Echevarria, J.; White Jr, A.C.; Terashima, A.; Samalvides, F.; Pérez-Molina, J.A.; Plana, M.N. Ivermectin versus albendazole or thiabendazole for Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD007745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, R.; Nutman, T.B. Screening, prevention, and treatment for hyperinfection syndrome and disseminated infections caused by Strongyloides stercoralis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornsuriyasak, P.; Niticharoenpong, K.; Sakapibunnan, A. Disseminated strongyloidiasis successfully treated with extended duration ivermectin combined with albendazole: A case report of intractable strongyloidiasis. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2004, 35, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, A.A.; Hartmeyer, G.N.; Stensvold, C.R.; Martin-Iguacel, R. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome with cerebral involvement. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e247032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdha, B.R. Human strongyloidiasis: Often brushed under the carpet. Trop. Gastroenterol. 2009, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.A.; Churhc, L.W.P.; Salgado, C.D. Strongyloides hyperinfection: A treatment dilemma. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 336, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).