The Antimicrobial Resistance–Water–Corporate Interface: Exploring the Connections Between Antimicrobials, Water, and Pollution
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Water and Antimicrobial Resistance
1.2. Corporations and Antimicrobial Resistance
1.3. Agriculture and Antibiotics
1.4. Pollution and Antibiotic Resistance
1.5. Air Pollution and Antibiotic Resistance
1.6. Plastics, Water, and Antibiotic Resistance
1.7. Oil/Petroleum and Antibiotic Resistance
1.8. Mitigation: Where Do We Go from Here? What Can We Do?
1.9. Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Antibiotic-Resistant Organisms
1.10. Plastics
2. Conclusions
3. Future Directions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations; Review on Antimicrobial Resistance: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, J.H.; Powderly, W.G. The post-antibiotic era is here. Science 2021, 373, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.C.; Chia, J.H.; Kuo, A.J.; Su, L.H.; Wu, T.L. A 7-year surveillance for ESBL-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae at a university hospital in Taiwan: The increase of CTX-M-15 in the ICU. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, L.M.; Webb, A.K.; Limbago, B.; Dudeck, M.A.; Patel, J.; Kallen, A.J.; Edwards, J.R.; Sievert, D.M. Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens Associated with Healthcare-Associated Infections: Summary of Data Reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2011–2014. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, I.; Maugat, S.; Jarlier, V.; Astagneau, P. Ongoing increasing temporal and geographical trends of the incidence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae infections in France, 2009 to 2013. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 30014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013.
- Tansarli, G.S.; Karageorgopoulos, D.E.; Kapaskelis, A.; Falagas, M.E. Impact of antimicrobial multidrug resistance on inpatient care cost: An evaluation of the evidence. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathwani, D.; Raman, G.; Sulham, K.; Gavaghan, M.; Menon, V. Clinical and economic consequences of hospital-acquired resistant and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2014, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, J.P.; Kwon, J.H.; Olsen, M.A.; Babcock, H.M.; Kollef, M.H. Readmissions With Multidrug-Resistant Infection in Patients With Prior Multidrug Resistant Infection. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2018, 39, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, J.P.; Olsen, M.A.; Stwalley, D.; Kwon, J.H.; Babcock, H.M.; Kollef, M.H. Infectious Diseases Consultation Reduces 30-Day and 1-Year All-Cause Mortality for Multidrug-Resistant Organism Infections. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antimicrobial Resistance: Causes and How It Spreads. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/causes/index.html (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outpatient Antibiotic Prescriptions—United States, 2021; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021.
- Shively, N.R.; Buehrle, D.J.; Clancy, C.J.; Decker, B.K. Prevalence of Inappropriate Antibiotic Prescribing in Primary Care Clinics within a Veterans Affairs Health Care System. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00337-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.E.; Lund, B.C.; Heintz, B.H.; Alexander, B.; Egge, J.A.; Livorsi, D.J. Identifying Opportunities to Improve Guideline-Concordant Antibiotic Prescribing in Veterans with Acute Respiratory Infections or Cystitis. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2017, 38, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Hersh, A.L.; Shapiro, D.J.; Bartoces, M.; Enns, E.A.; File, T.M., Jr.; Finkelstein, J.A.; Gerber, J.S.; Hyun, D.Y.; Linder, J.A.; et al. Prevalence of Inappropriate Antibiotic Prescriptions Among US Ambulatory Care Visits, 2010–2011. JAMA 2016, 315, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsberg, K.J.; Patel, S.; Gibson, M.K.; Lauber, C.L.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N.; Dantas, G. Bacterial phylogeny structures soil resistomes across habitats. Nature 2014, 509, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, C.; Hong, J.; Deng, H.; Yu, D.J. Eutrophication and Related Antibiotic Resistance of Enterococci in the Minjiang River, China. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 80, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkman, A.; Do, T.T.; Walsh, F.; Virta, M.P.J. Antibiotic-Resistance Genes in Waste Water. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; McIlroy, S.E.; Archana, A.; Baker, D.M.; Panagiotou, G. A pollution gradient contributes to the taxonomic, functional, and resistome diversity of microbial communities in marine sediments. Microbiome 2019, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, C.W.; McCluskey, S.M.; Singh, B.K.; Campbell, C.D.; Hudson, G.; Graham, D.W. Antibiotic resistance gene abundances correlate with metal and geochemical conditions in archived Scottish soils. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiler, C.; Berendonk, T.U. Heavy metal driven co-selection of antibiotic resistance in soil and water bodies impacted by agriculture and aquaculture. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Andres, M.; Klümper, U.; Rojas-Jimenez, K.; Grossart, H.P. Microplastic pollution increases gene exchange in aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrenovic, J.; Ivankovic, T.; Durn, G.; Dekic, S.; Kazazic, S.; Kisic, I. Presence of carbapenem-resistant bacteria in soils affected by illegal waste dumps. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 29, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Pinnell, L.J.; Brambilla, D.; Elli, G.; Sabatino, R.; Sathicq, M.B.; Corno, G.; O’Donnell, C.; Turner, J.W. Bioplastic accumulates antibiotic and metal resistance genes in coastal marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Wu, W.; Grimes, D.J.; Saillant, E.A.; Griffitt, R.J. Community composition and antibiotic resistance of bacteria in bottlenose dolphins Tursiops truncatus—Potential impact of 2010 BP Oil Spill. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekadwad, B.N.; Shouche, Y.S.; Jangid, K. Oil spill pollution and diversity analyses of resistant bacteria isolated from soil across the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal coastlines. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diorio-Toth, L.; Wallace, M.A.; Farnsworth, C.W.; Wang, B.; Gul, D.; Kwon, J.H.; Andleeb, S.; Burnham, C.D.; Dantas, G. Intensive care unit sinks are persistently colonized with multidrug resistant bacteria and mobilizable, resistance-conferring plasmids. mSystems 2023, 8, e0020623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Reske, K.; O’Neil, C.A.; Cass, C.; Seiler, S.; Wallace, M.A.; Hink, T.; Liang, S.Y.; Fraser, V.J.; Burnham, C.D.; et al. Assessment of antibiotic-resistant organism transmission among rooms of hospitalized patients, healthcare personnel, and the hospital environment utilizing surrogate markers and selective bacterial cultures. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhum, K.V.; Newcomer, E.P.; Cass, C.; Wallace, M.A.; Johnson, C.; Fine, J.; Sax, S.; Barlet, M.H.; Burnham, C.D.; Dantas, G.; et al. Antibiotic-resistant organisms establish reservoirs in new hospital built environments and are related to patient blood infection isolates. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotay, S.; Chai, W.; Guilford, W.; Barry, K.; Mathers, A.J. Spread from the Sink to the Patient: In Situ Study Using Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)-Expressing Escherichia coli to Model Bacterial Dispersion from Hand-Washing Sink-Trap Reservoirs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e03327-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudermilk, E.M.; Kotay, S.M.; Barry, K.E.; Parikh, H.I.; Colosi, L.M.; Mathers, A.J. Tracking Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase gene as an indicator of antimicrobial resistance dissemination from a hospital to surface water via a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Parikh, H.; Vegesana, K.; Stoesser, N.; Barry, K.E.; Kotay, S.M.; Dudley, S.; Peto, T.E.A.; Crook, D.W.; Walker, A.S.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales (CPE) Positivity in the Hospital Wastewater Environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01715-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, A.J.; Vegesana, K.; German Mesner, I.; Barry, K.E.; Pannone, A.; Baumann, J.; Crook, D.W.; Stoesser, N.; Kotay, S.; Carroll, J.; et al. Intensive Care Unit Wastewater Interventions to Prevent Transmission of Multispecies Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing Organisms. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decraene, V.; Phan, H.T.T.; George, R.; Wyllie, D.H.; Akinremi, O.; Aiken, Z.; Cleary, P.; Dodgson, A.; Pankhurst, L.; Crook, D.W.; et al. A Large, Refractory Nosocomial Outbreak of Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli Demonstrates Carbapenemase Gene Outbreaks Involving Sink Sites Require Novel Approaches to Infection Control. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01689-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizny Gordon, A.E.; Mathers, A.J.; Cheong, E.Y.L.; Gottlieb, T.; Kotay, S.; Walker, A.S.; Peto, T.E.A.; Crook, D.W.; Stoesser, N. The Hospital Water Environment as a Reservoir for Carbapenem-Resistant Organisms Causing Hospital-Acquired Infections-A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, J.; Soderstrom, H.; Lindberg, R.H.; Phan, C.; Tysklind, M.; Larsson, D.G. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.G.; de Pedro, C.; Paxeus, N. Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidhofer, C.; Sib, E.; Neuenhoff, M.; Schwengers, O.; Dummin, T.; Buechler, C.; Klein, N.; Balks, J.; Axtmann, K.; Schwab, K.; et al. Hospital sanitary facilities on wards with high antibiotic exposure play an important role in maintaining a reservoir of resistant pathogens, even over many years. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2023, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Ye, J.; Yang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, L.; Munezero, S.; Lin, K.; Cui, C. Occurrence and removal of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and bacterial communities in hospital wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 57321–57333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babic, S.; Perisa, M.; Skoric, I. Photolytic degradation of norfloxacin, enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in various aqueous media. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, N.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Oturan, N.; Huguenot, D.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S.; Brillas, E.; Oturan, M.A. Kinetics of oxidative degradation/mineralization pathways of the antibiotic tetracycline by the novel heterogeneous electro-Fenton process with solid catalyst chalcopyrite. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 209, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, N.; Oturan, N.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Brillas, E.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S.; Oturan, M.A. Pyrite as a sustainable catalyst in electro-Fenton process for improving oxidation of sulfamethazine. Kinetics, mechanism and toxicity assessment. Water Res. 2016, 94, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werkneh, A.A.; Islam, M.A. Post-treatment disinfection technologies for sustainable removal of antibiotic residues and antimicrobial resistance bacteria from hospital wastewater. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yao, S.; Lin, K.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, C. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes and control of horizontal transfer risk by UV, chlorination and UV/chlorination treatments of drinking water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Ma, J.; Cai, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Qi, M.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, A.; et al. Response of chloramphenicol-reducing biocathode resistome to continuous electrical stimulation. Water Res. 2019, 148, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Ding, G.; Wang, K.; Zhuang, T.; Huang, X.; Wang, X. Synergistic effect of UV/chlorine in bacterial inactivation, resistance gene removal, and gene conjugative transfer blocking. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, L.; Luo, Y.; Yao, S.; Zhang, D.; Lin, K.; Cui, C. Occurrence and reduction of antibiotic resistance genes in conventional and advanced drinking water treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J. Pollution from Antibiotic Factories Highlighted as Public Health Risk. Financial Times, 24 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Limb, L. Rivers Polluted with Antibiotics Could Cause the ‘Next Pandemic’, Warn Scientists. EuroNews, 15 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lai, R.W.S.; Galban-Malagon, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Metian, M.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical pollution of the world’s rivers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113947119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukes, T.H.; Williams, W.L. Nutritional effects of antibiotics. Pharmacol. Rev. 1953, 5, 381–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Swine 2021 Part II: Reference of Management Practices on Large-Enterprise Swine Operations in the United States. In USDA-APHIS-VS-CEAN-NAHMS; USDA: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2023; Volume 799. [Google Scholar]
- World Organisation for Animal Health. Annual Report on Antimicrobial Agents Intended for Use in Animals; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2024; Volume 8, pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kivits, T.; Broers, H.P.; Beeltje, H.; van Vliet, M.; Griffioen, J. Presence and fate of veterinary antibiotics in age-dated groundwater in areas with intensive livestock farming. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Hou, Q.; Song, J.; Liu, R.; Qian, Y.; Huang, G. Groundwater antibiotics contamination in an alluvial-pluvial fan, North China Plain: Occurrence, sources, and risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley-Reicher, B.; Dutzik, T.; Rumpler, J.; Casale, M. Wasting Our Waterways: Toxic Pollution and the Unfulfilled Promise of the Clean Water Act; Environment America Research & Policy Center: Denver, CO, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Coates-Marnane, J.; Olley, J.; Burton, J.; Grinham, A. The impact of a high magnitude flood on metal pollution in a shallow subtropical estuarine embayment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shuai, X.; Lin, Z.; Yu, X.; Ba, X.; Holmes, M.A.; Xiao, Y.; Gu, B.; Chen, H. Association between particulate matter (PM)(2.5) air pollution and clinical antibiotic resistance: A global analysis. Lancet Planet. Health 2023, 7, e649–e659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.J.; Shuai, X.Y.; Zhu, L.; Xu, L.; Meng, L.X.; Sun, Y.J.; Chen, H. Spread of antibiotic resistance genes and microbiota in airborne particulate matter, dust, and human airways in the urban hospital. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, B.A.; Roy, S.; Tahsin, N.; Baidya, K.; Das, K.C.; Islam, M.S.; Ahsan, N.; Salam, A. Antibiotic resistance of bioaerosols in particulate matter from indoor environments of the hospitals in Dhaka Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhou, J.; Lan, Z.; Tan, R.; Chen, T.; Shi, D.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Jin, M.; et al. Carbonaceous particulate matter promotes the horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2024, 26, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B. The Top 14 Most Polluting Companies; The Eco Experts: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, N.; Amann, M.; Ayeb-Karlsson, S.; Belesova, K.; Bouley, T.; Boykoff, M.; Byass, P.; Cai, W.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Chambers, J.; et al. The Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: From 25 years of inaction to a global transformation for public health. Lancet 2018, 391, 581–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, J.P. Climate change and antibiotic resistance: A deadly combination. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, 2049936121991374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuvo, B.; Scarpaci, M.; Bracaloni, S.; Esposito, E.; Costa, A.L.; Ioppolo, M.; Casini, B. Microplastics and Antibiotic Resistance: The Magnitude of the Problem and the Emerging Role of Hospital Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Liu, S.; Liao, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J. Wastewater plastisphere enhances antibiotic resistant elements, bacterial pathogens, and toxicological impacts in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, N.; Muhvich, J.; Ching, C.; Gomez, B.; Horvath, E.; Nahum, Y.; Zaman, M.H. Effects of microplastic concentration, composition, and size on Escherichia coli biofilm-associated antimicrobial resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, e0228224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.E.; Lin, Z.; Gan, D.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Walsh, T.R. Microplastics mediates the spread of antimicrobial resistance plasmids via modulating conjugal gene expression. Environ. Int. 2025, 195, 109261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Liu, Y.J.; Fu, Y.M.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhang, T.L.; Cui, H.L.; Qiao, M.; Rillig, M.C.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zhu, D. Microplastic diversity increases the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in soil. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Song, W.; Ye, C.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Plastics in the marine environment are reservoirs for antibiotic and metal resistance genes. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Luo, Y. Effects of microplastics on distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in recirculating aquaculture system. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flach, C.F.; Pal, C.; Svensson, C.J.; Kristiansson, E.; Ostman, M.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Tysklind, M.; Larsson, D.G.J. Does antifouling paint select for antibiotic resistance? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, N.; Jiang, S.; Jin, H. Microplastics in polystyrene-made food containers from China: Abundance, shape, size, and human intake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 40084–40093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, D.N.; Clark, L.; Li, M. Microplastics as hubs enriching antibiotic-resistant bacteria and pathogens in municipal activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2021, 2, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.C.; Aggarwal, N.; Turner, R.J. Exploration of the presence and abundance of multidrug resistance efflux genes in oil and gas environments. Microbiology 2022, 168, 001248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christgen, B.; Yang, Y.; Ahammad, S.Z.; Li, B.; Rodriquez, D.C.; Zhang, T.; Graham, D.W. Metagenomics Shows That Low-Energy Anaerobic–Aerobic Treatment Reactors Reduce Antibiotic Resistance Gene Levels from Domestic Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Geng, J.; Ren, H.; Ding, L.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Y. Variation of antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater treatment plant with A(2)O-MBR system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 3715–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Nie, X.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Liao, W.; Liang, X. Occurrence and elimination of antibiotic resistance genes in a long-term operation integrated surface flow constructed wetland. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ying, G.G.; Wei, X.D.; Liu, Y.S.; Liu, S.S.; Hu, L.X.; He, L.Y.; Chen, Z.F.; Chen, F.R.; Yang, Y.Q. Removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from domestic sewage by constructed wetlands: Effect of flow configuration and plant species. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sheng, G.P.; Lu, Y.Z.; Zeng, R.J.; Yu, H.Q. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes from wastewater treatment plant effluent by coagulation. Water Res. 2017, 111, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; He, Y.; Zhu, J.; Long, D.; Tan, Q.; Xu, W.; Pu, S. Removal of microorganisms and antibiotic resistance genes from swine wastewater: A comparison between polyaluminum chloride (PAC), polyaluminum sulfate (LST), and aluminum hydroxide iron (LT). J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2022, 57, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yuan, C.; Ruan, C.; Zheng, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, G.; Chen, G. Coagulation promotes the spread of antibiotic resistance genes in secondary effluents. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 355, 124245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xu, G.; Yu, H.; Xing, J. Dynamic membrane for micro-particle removal in wastewater treatment: Performance and influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbort, A.F.; Schuhen, K. A concept for the removal of microplastics from the marine environment with innovative host-guest relationships. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 11061–11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaf, D.W.; Punzi, V.L.; Rolle, J.T.; Kleinberg, K.A. Removal of micron-sized microplastic particles from simulated drinking water via alum coagulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 386, 123807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
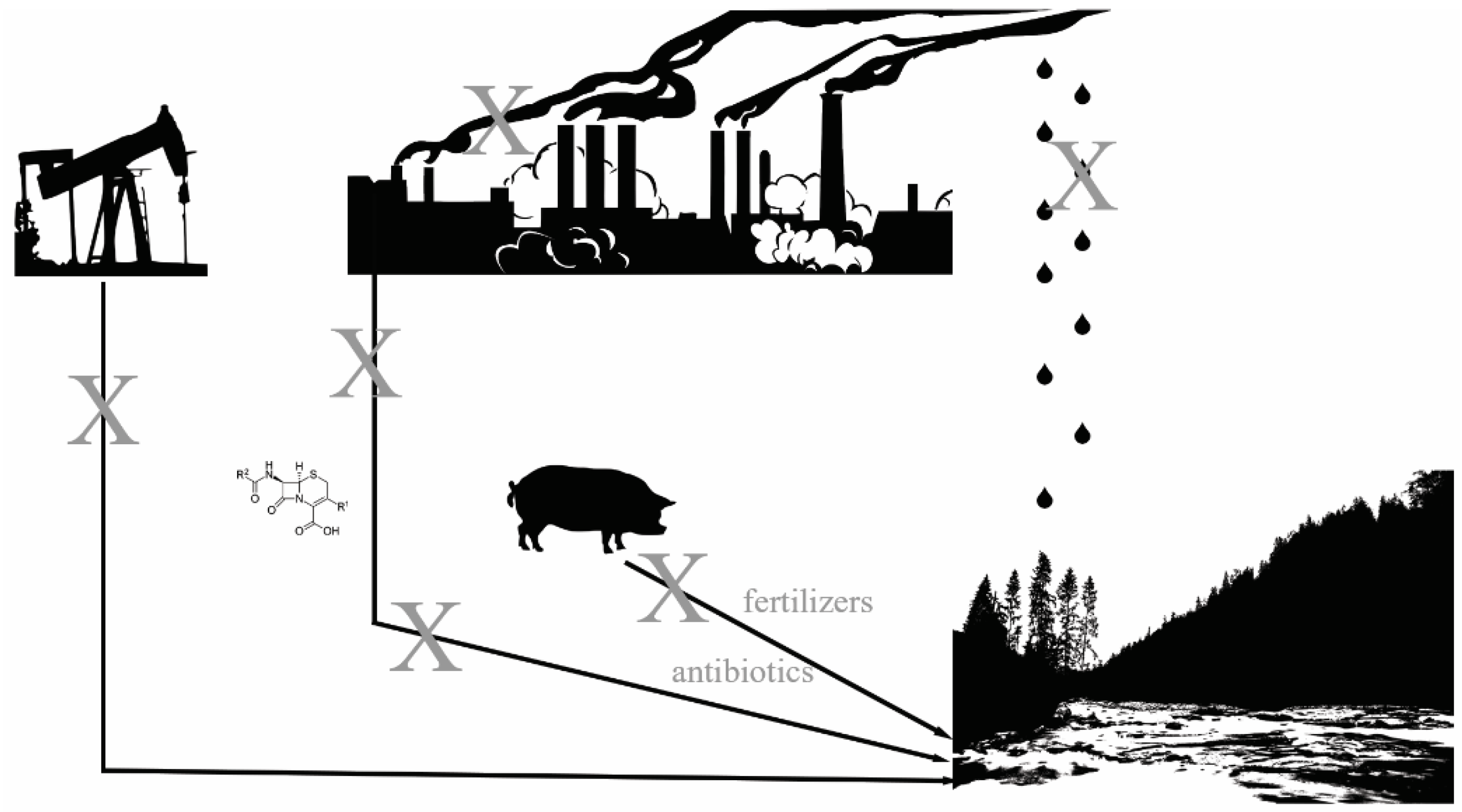
| Nidus of Antibiotic Resistance | Direct or Indirect Antibiotic Resistance? | Corporate Contributors | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic use (humans) | Direct | Healthcare | [12] |
| Antibiotic use (agricultural) | Direct | Agriculture | [17,18,52,53,54] |
| Pharmaceutical waste and residues | Direct and indirect | Pharma | [37,38,49,51] |
| Heavy metals | Indirect | Chemical and oil companies | [21,22,55] |
| Air pollution | Indirect | Oil and gas companies | [56,57,58,59,60] |
| Plastics | Indirect | Oil, gas, plastic companies | [23,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70] |
| Oil spills | Indirect | Oil companies | [26,27,71] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burnham, J.P. The Antimicrobial Resistance–Water–Corporate Interface: Exploring the Connections Between Antimicrobials, Water, and Pollution. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10040105
Burnham JP. The Antimicrobial Resistance–Water–Corporate Interface: Exploring the Connections Between Antimicrobials, Water, and Pollution. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(4):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10040105
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurnham, Jason P. 2025. "The Antimicrobial Resistance–Water–Corporate Interface: Exploring the Connections Between Antimicrobials, Water, and Pollution" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 4: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10040105
APA StyleBurnham, J. P. (2025). The Antimicrobial Resistance–Water–Corporate Interface: Exploring the Connections Between Antimicrobials, Water, and Pollution. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(4), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10040105







