Do Novices Struggle with AI Web Design? An Eye-Tracking Study of Full-Site Generation Tools
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Recruitment
2.2. Materials
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Outcome Measure
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Task Performance
3.2. User Barriers
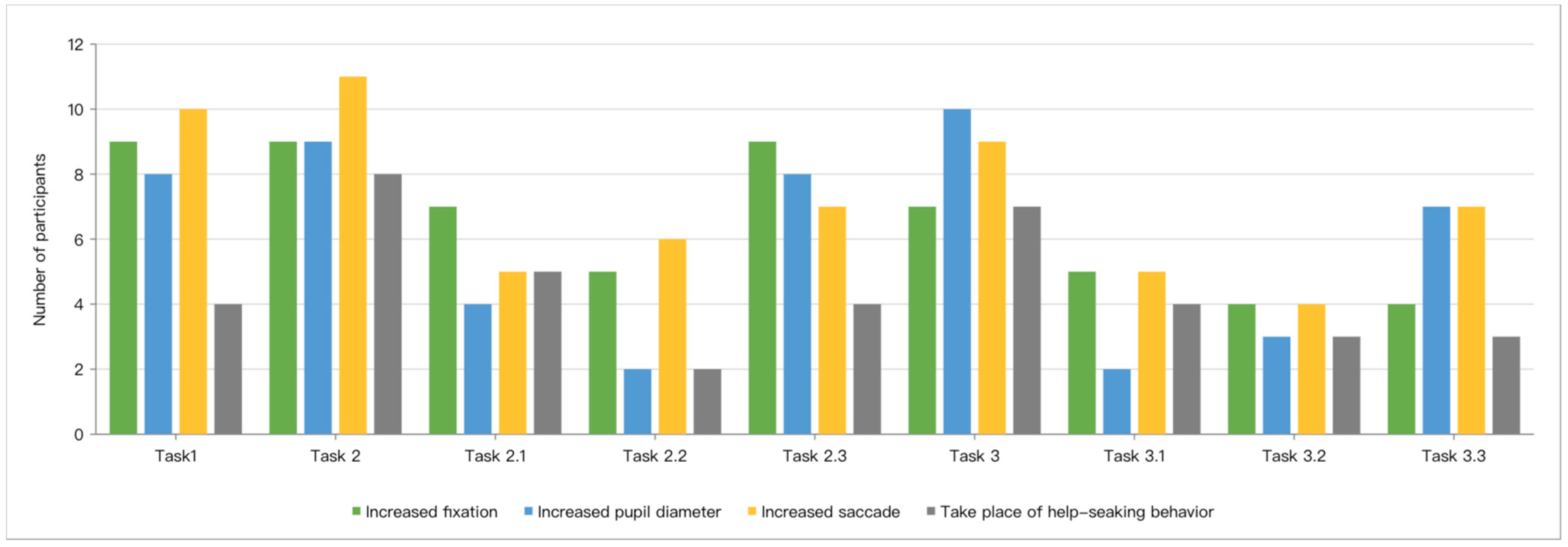
3.2.1. Eye-Tracking Metrics
3.2.2. Help-Seeking Behaviors
3.2.3. Qualitative Insights from Post-Task Interviews
- (1)
- Interface Confusion (nine participants)
- (2)
- AI Control Expectations (eight participants)
- (3)
- Workflow Interruptions (seven participants)
- (4)
- Design Specificity (six participants)
- (5)
- Human–AI Collaboration (5 participants)
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLean, D. Wix ADI Review 2025: Is It Really That Powerful? Available online: https://www.elegantthemes.com/blog/business/wix-adi-review (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- George, J. Using Bookmark’s AIDA to Build Your Website in 2 Minutes. Available online: https://www.sitepoint.com/using-bookmarks-aida-to-build-your-website-in-2-minutes/ (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Oswal, S.K.; Oswal, H.K. Examining the Accessibility of Generative AI Website Builder Tools for Blind and Low Vision Users: 21 Best Practices for Designers and Developers. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Professional Communication Conference (ProComm), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 14–17 July 2024; pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Calò, T.; De Russis, L. Advancing Code Generation from Visual Designs through Transformer-Based Architectures and Specialized Datasets. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2025, 9, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluarachchi, T.; Wickramasinghe, M. A Systematic Literature Review on Automatic Website Generation. J. Comput. Lang. 2023, 75, 101202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booyse, D.; Scheepers, C.B. Barriers to Adopting Automated Organisational Decision-Making through the Use of Artificial Intelligence. Manag. Res. Rev. 2024, 47, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.W.; Ji, Q. In the Eye of the Beholder: A Survey of Models for Eyes and Gaze. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 478–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardari, B.A.; Hussain, Z.; Arain, A.A.; Rizvi, W.H.; Vighio, M.S. QUEST E-Learning Portal: Applying Heuristic Evaluation, Usability Testing and Eye Tracking. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2021, 20, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagermann, J.; Pfeil, U.; Reiterer, H. Measuring Cognitive Load Using Eye Tracking Technology in Visual Computing. In Proceedings of the Sixth Workshop on Beyond Time and Errors on Novel Evaluation Methods for Visualization, Baltimore, MD, USA, 24 October 2016; pp. 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Novák, J.Š.; Masner, J.; Benda, P.; Šimek, P.; Merunka, V. Eye Tracking, Usability, and User Experience: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2024, 40, 4484–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Chen, M.; Park, H.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Y. Evaluating Non-AI Experts’ Interaction with AI: A Case Study In Library Context. In Proceedings of the CHI 2025: CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 26 April–1 May 2025; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Birhane, A.; Isaac, W.; Prabhakaran, V.; Diaz, M.; Elish, M.C.; Gabriel, I.; Mohamed, S. Power to the People? Opportunities and Challenges for Participatory AI. In Proceedings of the EAAMO ‘22: Equity and Access in Algorithms, Mechanisms, and Optimization 2022, Arlington, VA, USA, 6–9 October 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- WIX Logo. Wix.Com (WIX) Company Profile. Available online: https://www.financecharts.com/stocks/WIX/profile (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Salehi Fadardi, M.; Salehi Fadardi, J.; Mahjoob, M.; Doosti, H. Post-Saccadic Eye Movement Indices Under Cognitive Load: A Path Analysis to Determine Visual Performance. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2022, 17, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Greef, T.; Lafeber, H.; Oostendorp, H.; Lindenberg, J. Eye Movement as Indicators of Mental Workload to Trigger Adaptive Automation. Neuroergon. Oper. Neurosci. 2009, 5638, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Xie, T.; Zhang, W. Predicting Women’s Intentions to Screen for Breast Cancer Based on the Health Belief Model and the Theory of Planned Behavior. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2019, 45, 2440–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, R.R.; Keselman, H.J. Repeated Measures One-way ANOVA Based on a Modified One-step M-estimator. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2003, 56, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitsara, I. Artificial Intelligence and the Digital Divide: From an Innovation Perspective. In Platforms and Artificial Intelligence: The Next Generation of Competences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 245–265. [Google Scholar]
- Mahanama, B.; Jayawardana, Y.; Rengarajan, S.; Jayawardena, G.; Chukoskie, L.; Snider, J.; Jayarathna, S. Eye Movement and Pupil Measures: A Review. Front. Comput. Sci. 2022, 3, 733531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehmke, C.; Wilson, S. Identifying Web Usability Problems from Eyetracking Data. In BCS-HCI ‘07: Proceedings of the 21st British HCI Group Annual Conference on People and Computers: HCI … But Not as We Know It—Volume 1, University of Lancaster, Lancaster, UK, 3–7 September 2007; BCS Learning & Development Ltd.: Swindon, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Wel, P.; Van Steenbergen, H. Pupil Dilation as an Index of Effort in Cognitive Control Tasks: A Review. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2018, 25, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, D.; Chang, F.; Han, T. Rehab-Diary: Enhancing Recovery Identity with an Online Support Group for Middle Aged and Older Ovarian Cancer Patients. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2024, 8, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amershi, S.; Weld, D.; Vorvoreanu, M.; Fourney, A.; Nushi, B.; Collisson, P.; Suh, J.; Iqbal, S.; Bennett, P.N.; Inkpen, K.; et al. Guidelines for Human-AI Interaction. In Proceedings of the CHI ‘19: CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, 4–9 May 2019; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Namoun, A.; Alrehaili, A.; Nisa, Z.U.; Almoamari, H.; Tufail, A. Predicting the Usability of Mobile Applications Using AI Tools: The Rise of Large User Interface Models, Opportunities, and Challenges. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 238, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Huang, C.M. Understanding User Reliance on AI in Assisted Decision-Making. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2022, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Crespo, M.A. Human-Centered AI and the Future of Translation Technologies: What Professionals Think about Control and Autonomy in the AI Era. Information 2025, 16, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (mins) | Q&A | Length (mins) | Template Selection | Content Editing | Visual Elements Customization | General Task Completion | Length (mins) | New Buying Page | Name and Price Editing | Product Picture Editing | General Task Completion | |
| 1 | 4.13 | succeed | 13.37 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed | 4.15 | succeed | failed | failed | failed |
| 2 | 5.12 | succeed | 6.27 | succeed | failed | failed | failed | 17.54 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed |
| 3 | 4.05 | succeed | 11.52 | succeed | failed | failed | failed | 5.08 | succeed | succeed | failed | failed |
| 4 | 5.15 | succeed | 15.02 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed | 6.27 | succeed | failed | succeed | failed |
| 5 | 7.20 | succeed | 27.11 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed | 4.50 | succeed | failed | failed | failed |
| 6 | 4.13 | succeed | 22.48 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed | 4.43 | failed | failed | failed | failed |
| 7 | 3.09 | succeed | 14.32 | succeed | succeed | failed | failed | 7.15 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed |
| 8 | 2.06 | succeed | 18.50 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed | 9.05 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed |
| 9 | 3.38 | succeed | 10.28 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed | 5.40 | succeed | failed | failed | failed |
| 10 | 2.44 | succeed | 13.38 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed | 10.08 | succeed | succeed | failed | failed |
| 11 | 6.44 | succeed | 3.38 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed | 7.04 | succeed | succeed | succeed | succeed |
| 12 | 3.15 | succeed | 6.32 | succeed | failed | succeed | failed | 3.09 | failed | failed | failed | failed |
| Task No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Ave |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixation no. | |||||||||||||
| Task 1 | 66.10 (11.00) | 66.00 (9.90) | 72.30 (10.10) | 68.50 (8.70) | 70.10 (9.20) | 74.20 (11.30) | 58.60 (12.50) | 63.40 (10.50) | 69.70 (9.80) | 65.80 (10.20) | 71.50 (11.00) | 55.30 (13.20) | 67.40 (8.30) |
| Task 2 | 70.20 (8.90) | 68.40 (7.30) | 75.60 (9.40) | 71.30 (6.50) | 73.50 (8.10) | 77.80 (10.20) | 62.30 (11.10) | 66.70 (9.30) | 72.90 (8.50) | 69.10 (9.00) | 74.80 (10.10) | 59.10 (12.00) | 70.70 (7.50) |
| Task 3 | 68.50 (5.10) | 65.10 (6.20) | 71.20 (7.80) | 67.90 (5.40) | 70.40 (6.70) | 74.50 (8.90) | 59.80 (9.70) | 64.10 (7.60) | 70.30 (6.90) | 66.50 (7.20) | 72.10 (8.50) | 56.70 (10.40) | 68.10 (6.80) |
| Ave pupil size (mm) | |||||||||||||
| Task 1 | 3.76 (0.31) | 3.81 (0.29) | 2.85 (0.18) | 4.25 (0.42) | 4.51 (0.45) | 4.18 (0.40) | 3.63 (0.33) | 4.33 (0.43) | 3.12 (0.25) | 2.73 (0.21) | 2.66 (0.20) | 3.13 (0.26) | 3.57 (0.62) |
| Task 2 | 3.92 (0.28) | 3.97 (0.26) | 3.01 (0.15) | 4.41 (0.39) | 4.67 (0.42) | 4.34 (0.37) | 3.79 (0.30) | 4.49 (0.40) | 3.28 (0.22) | 2.89 (0.18) | 2.82 (0.17) | 3.29 (0.23) | 3.73 (0.60) |
| Task 3 | 4.15 (0.35) | 4.20 (0.33) | 3.22 (0.21) | 4.63 (0.45) | 4.89 (0.48) | 4.56 (0.43) | 4.01 (0.36) | 4.71 (0.46) | 3.50 (0.28) | 3.11 (0.24) | 3.04 (0.23) | 3.51 (0.29) | 3.95 (0.65) |
| Saccade no. | |||||||||||||
| Task 1 | 32.00 (5.10) | 49.00 (7.80) | 55.00 (8.90) | 17.00 (3.20) | 46.00 (7.40) | 40.00 (6.40) | 0.00 (0.00) | 46.00 (7.40) | 47.00 (7.60) | 55.00 (8.90) | 44.00 (7.10) | 22.00 (4.30) | 37.80 (15.20) |
| Task 2 | 35.20 (4.70) | 52.30 (7.20) | 58.10 (8.30) | 20.10 (2.80) | 49.10 (6.80) | 43.10 (5.80) | 3.10 (1.20) | 49.10 (6.80) | 50.10 (7.00) | 58.10 (8.30) | 47.10 (6.50) | 25.10 (3.90) | 40.90 (14.50) |
| Task 3 | 33.10 (4.10) | 49.80 (6.50) | 55.60 (7.60) | 18.00 (2.40) | 46.60 (6.10) | 40.60 (5.10) | 1.50 (0.70) | 46.60 (6.10) | 47.60 (6.30) | 55.60 (7.60) | 44.60 (5.80) | 23.00 (3.40) | 38.40 (13.80) |
| Metric | F | df | p | η2 | Significant Contrasts (Bonferroni Adjusted) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixation Count | 16.83 | 2, 22 | <0.001 | 0.605 | Task 2 > Task 1 (p = 0.002), Task 2 > Task 3 (p = 0.001) |
| Pupil Diameter | 12.74 | 1.3, 14.3 | <0.001 | 0.537 | Task 3 > Task 1 (p < 0.001), Task 3 > Task 2 (p = 0.003) |
| Saccade Count | 9.61 | 2, 22 | <0.001 | 0.466 | Task 2 > Task 1 (p = 0.004), Task 2 > Task 3 (p = 0.009) |
| Participant No. | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 | Help-Seeking Behavior No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Answering Questions | Template Choosing | Content Editing | Design Element Editing | Add a Mock Buying Page | Add Product Name and Price | Add Product Picture | ||
| 1 | 5 | 5 | ||||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| 7 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | |||
| 8 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | ||||
| 9 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||||
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| 11 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |||||
| 12 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Percentage | 15.63% | 18.75% | 6.25% | 18.75% | 25.00% | 9.37% | 6.25% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, C.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z. Do Novices Struggle with AI Web Design? An Eye-Tracking Study of Full-Site Generation Tools. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9090085
Chu C, Zhao J, Dong Z. Do Novices Struggle with AI Web Design? An Eye-Tracking Study of Full-Site Generation Tools. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction. 2025; 9(9):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9090085
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Chen, Jianan Zhao, and Zhanxun Dong. 2025. "Do Novices Struggle with AI Web Design? An Eye-Tracking Study of Full-Site Generation Tools" Multimodal Technologies and Interaction 9, no. 9: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9090085
APA StyleChu, C., Zhao, J., & Dong, Z. (2025). Do Novices Struggle with AI Web Design? An Eye-Tracking Study of Full-Site Generation Tools. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 9(9), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9090085






