A Dialogue-Act Taxonomy for a Virtual Coach Designed to Improve the Life of Elderly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
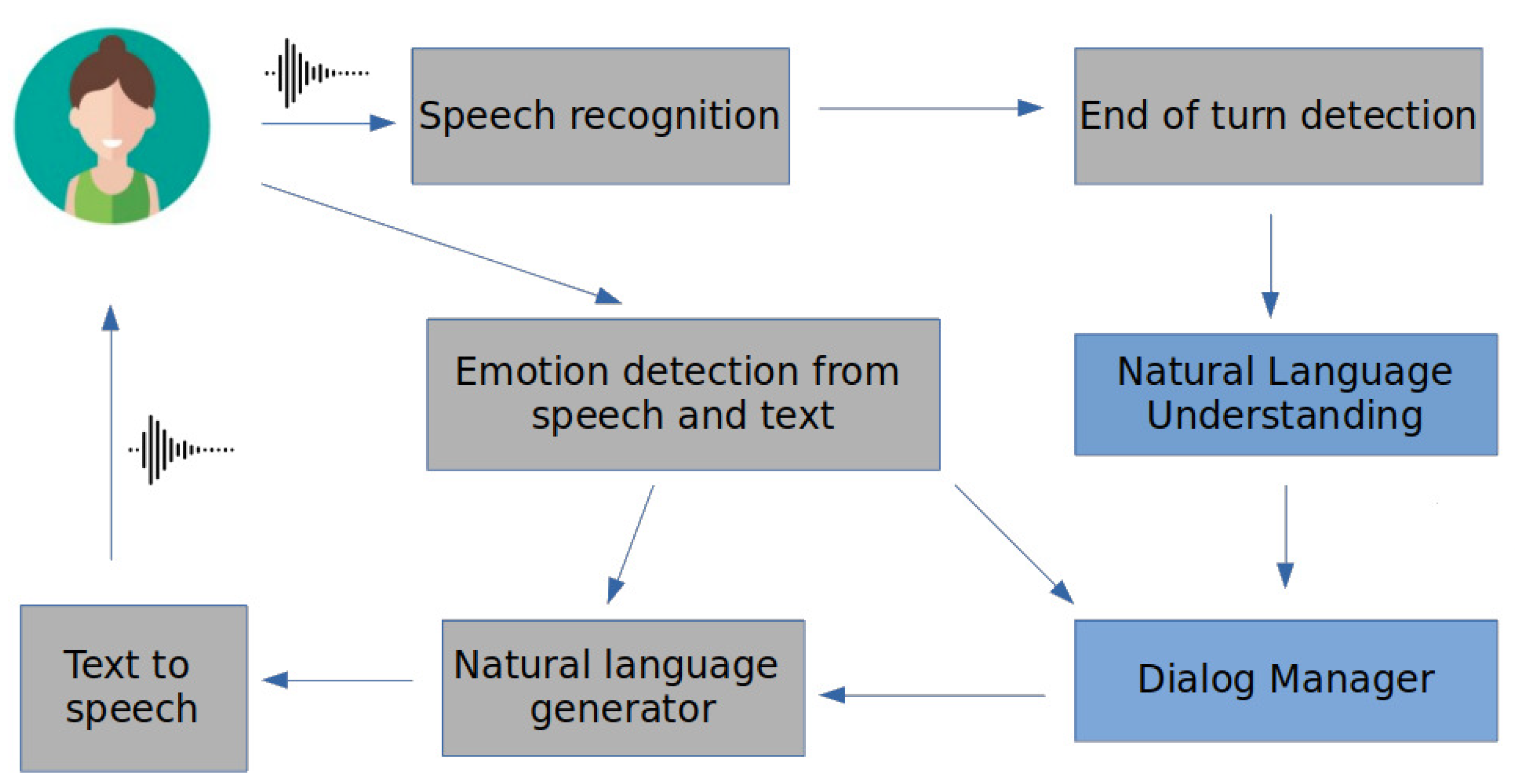
2. A Framework for Empathetic Conversations
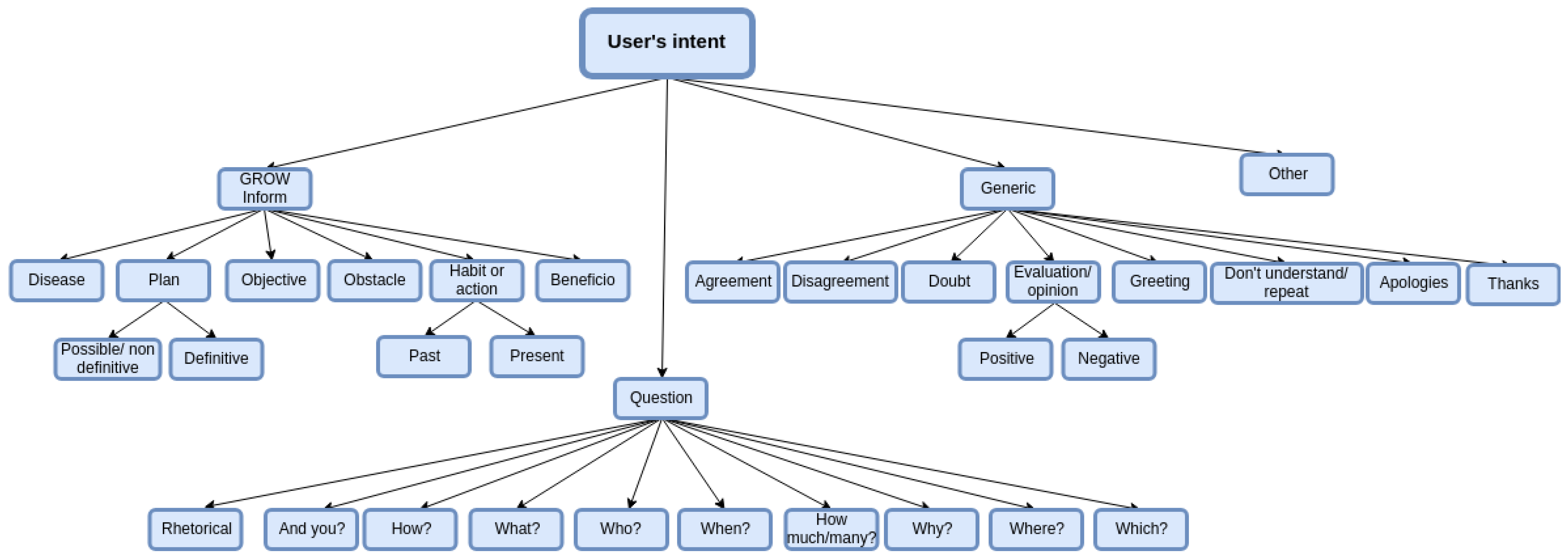
2.1. Dialogue Acts for an Empathetic Agent
2.2. GROW Model Implemented through the Dialogue Manager
2.3. Related Work
- Type of communication (i.e., synchronous vs. asynchronous).
- Activity type and dialogue domain.
- Type of corpora (e.g., speech dialogues, videos, chat).
- Types of speech act classification schemes.
- Dimensions (unidimensional versus multidimensional annotation).
- Annotation tools and annotation procedure.
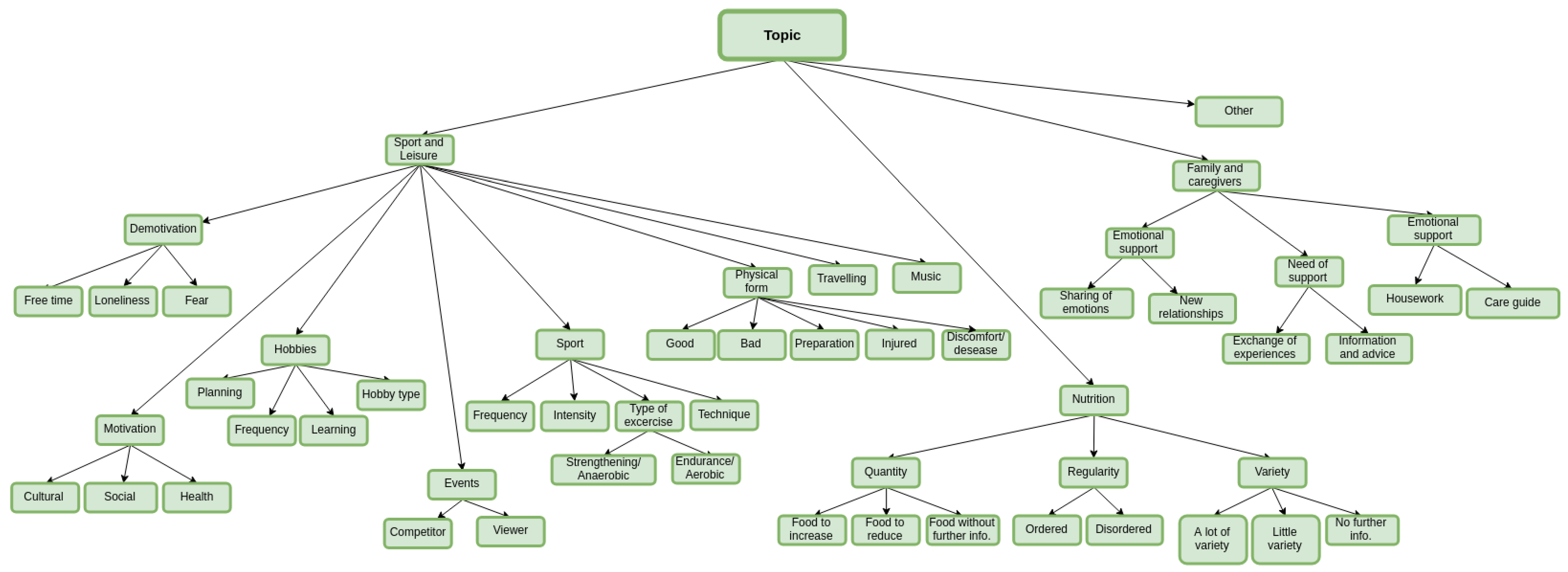
3. Characterization of the Proposed Dialogue Act Taxonomy
4. Using the Taxonomy to Get a Labelled Corpus
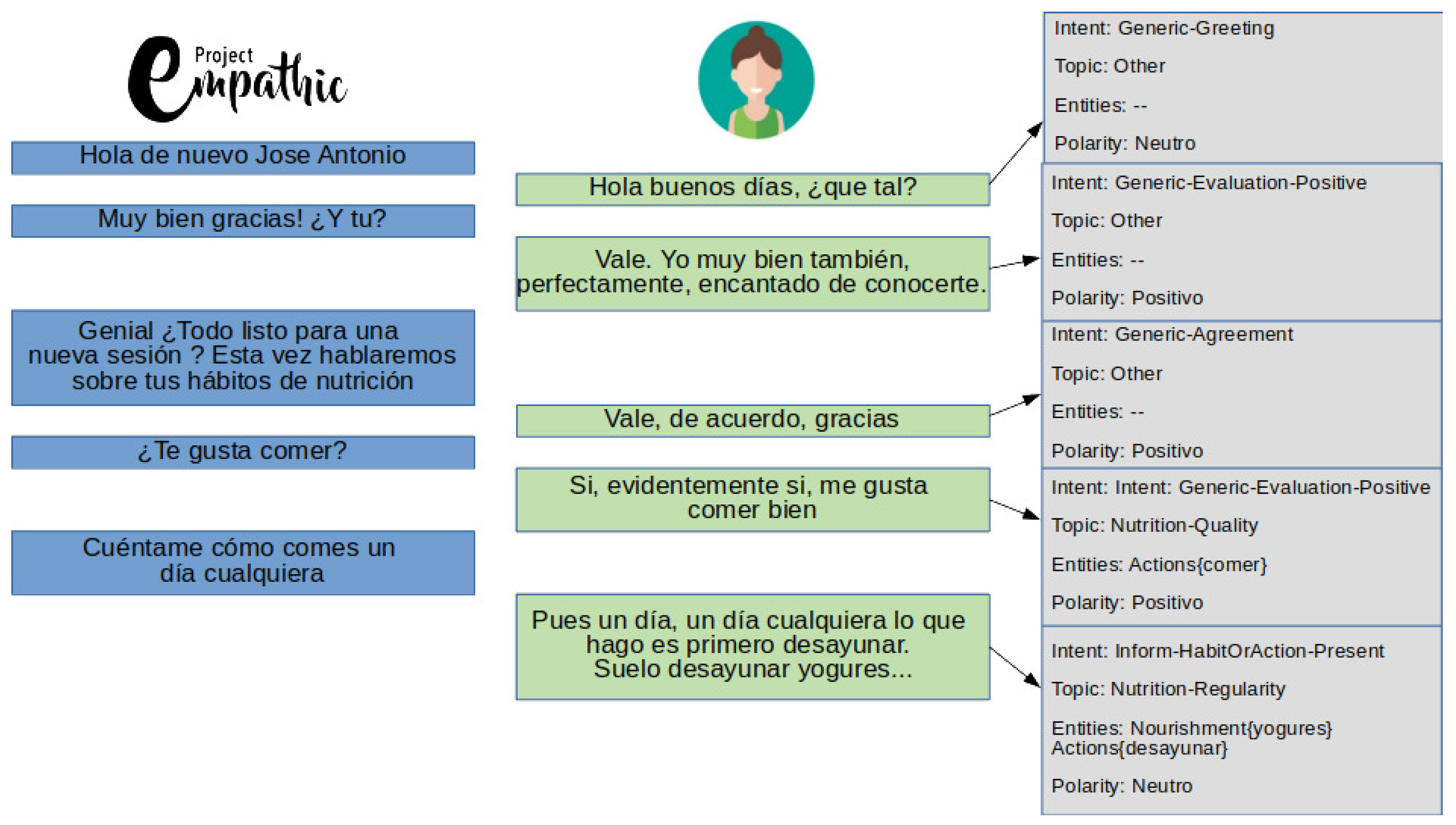
4.1. Annotation Procedure
4.2. Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding

Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A.
References
- Lampert, A.; Dale, R.; Paris, C. Classifying speech acts using verbal response modes. In Proceedings of the Australasian Language Technology Workshop 2006, Sydney, Australia, 30 November–1 December 2006; pp. 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Traum, D.R. 20 questions on dialogue act taxonomies. J. Semant. 2000, 17, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, H.; Alexandersson, J.; Choe, J.W.; Fang, A.C.; Hasida, K.; Petukhova, V.; Popescu-Belis, A.; Traum, D.R. ISO 24617-2: A semantically-based standard for dialogue annotation. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-2012), Istanbul, Turkey, 23–25 May 2012; pp. 430–437. [Google Scholar]
- Stolcke, A.; Ries, K.; Coccaro, N.; Shriberg, E.; Bates, R.; Jurafsky, D.; Taylor, P.; Martin, R.; Ess-Dykema, C.V.; Meteer, M. Dialogue act modeling for automatic tagging and recognition of conversational speech. Comput. Linguist. 2000, 26, 339–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, H. The DIT++ taxonomy for functional dialogue markup. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2009), Budapest, Hungary, 10–15 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Petukhova, V.; Bunt, H. The coding and annotation of multimodal dialogue acts. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-2012), Istanbul, Turkey, 23–25 May 2012; pp. 430–437. [Google Scholar]
- Bunt, H.; Petukhova, V.; Malchanau, A.; Wijnhoven, K.; Fang, A. The DialogBank. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2016), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; Chair, N.C.C., Choukri, K., Declerck, T., Goggi, S., Grobelnik, M., Maegaard, B., Mariani, J., Mazo, H., Moreno, A., Odijk, J., et al., Eds.; European Language Resources Association (ELRA): Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- López Zorrilla, A.; Velasco Vázquez, M.D.; Irastorza, J.; Olaso Fernández, J.M.; Justo Blanco, R.; Torres Barañano, M.I. EMPATHIC: Empathic, Expressive, Advanced Virtual Coach to Improve Independent Healthy-Life-Years of the Elderly. Proces. Del Leng. Nat. 2018, 61, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, M.L.; Olaso, J.M.; Montenegro, C.; Santana, R.; Vazquez, A.; Justo, R.; Lozano, J.A.; Schloegl, S.; Chollet, G.; Dugan, N.; et al. The EMPATHIC Project: Mid-term Achievements. In Proceedings of the 12th Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference (PETRA-19), Rhodes, Greece, 5–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Willcox, D.C.; Scapagnini, G.; Willcox, B.J. Healthy aging diets other than the Mediterranean: A focus on the Okinawan diet. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, A. Behavioural coaching—The GROW model. In Excellence in Coaching: The Industry Guide, 2nd ed.; Jonathan, P., Ed.; Kogan Page: London, UK, 2006; pp. 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, M.I.; Olaso, J.M.; Glackin, N.; Justo, R.; Chollet, G. A Spoken Dialogue System for the EMPATHIC Virtual Coach. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Spoken Dialog System Technology (IWSDS), Singapore, 14–16 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bohus, D.; Rudnicky, A.I. The RavenClaw dialog management framework: Architecture and systems. Comput. Speech Lang. 2009, 23, 332–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.M. The impact of life coaching on goal attainment, metacognition and mental health. Soc. Behav. Personal. 2003, 31, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theeboom, T.; Beersma, B.; van Vianen, A.E. Does coaching work? A meta-analysis on the effects of coaching on individual level outcomes in an organizational context. J. Posit. Psychol. 2014, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Woods, S.; Guillaume, Y. The effectiveness of workplace coaching: A meta-analysis of learning and performance outcomes from coaching. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 2015, 89, 249–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitemore, J. Coaching for Performance: Growing Human Potential and Purpose: The Principles and Practice of Coaching and Leadership; Nicholas Brealey Publishing: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Passmore, J. An integrated model of goal-focused coaching: An evidence-based framework for teaching and practice. Int. Coach. Psychol. Rev. 2012, 7, 146–165. [Google Scholar]
- Passmore, J. Motivational Interviewing—A model for coaching psychology practice. Coach. Psychol. 2011, 7, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sayas, S. Dialogues on Nutrition; Technical Report DP1, Empathic Project; Internal Documents: Tampere, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sayas, S. Dialogues on Physical Exercise; Technical Report DP2, Empathic Project; Internal Documents: Tampere, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sayas, S. Dialogues on Leisure and Free Time; Technical Report DP3, Empathic Project; Internal Documents: Tampere, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, J.L. How to do Things with Words; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.; Dinesh, N.; Lee, A.; Miltsakaki, E.; Robaldo, L.; Joshi, A.K.; Webber, B.L. The Penn Discourse TreeBank 2.0. In Proceedings of the 6th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marrakech, Morocco, 28–30 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu-Belis, A. Dialogue Acts: One or More Dimensions; ISSCO Work: Alexandra, New Zealand, 2005; p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Gao, D.; Ouyang, Y. Automatic twitter topic summarization with speech acts. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2013, 21, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, A.; Riloff, E. Classifying sentences as speech acts in message board posts. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Edinburgh, UK, 27–31 July 2011; pp. 748–758. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, A.H.; Bader, M.; Bard, E.G.; Boyle, E.; Doherty, G.; Garrod, S.; Isard, S.; Kowtko, J.; McAllister, J.; Miller, J.; et al. The HCRC map task corpus. Lang. Speech 1991, 34, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R.; Pow, N.; Serban, I.; Pineau, J. The ubuntu dialogue corpus: A large dataset for research in unstructured multi-turn dialogue systems. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.08909. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Dinan, E.; Urbanek, J.; Szlam, A.; Kiela, D.; Weston, J. Personalizing Dialogue Agents: I have a dog, do you have pets too? arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.07243. [Google Scholar]
- Serban, I.V.; Lowe, R.; Henderson, P.; Charlin, L.; Pineau, J. A survey of available corpora for building data-driven dialogue systems. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.05742. [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey, J.J.; Holliman, E.C.; McDaniel, J. SWITCHBOARD: Telephone speech corpus for research and development. In Proceedings of the ICASSP-92: 1992 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, San Francisco, CA, USA, 23–26 March 1992; Volume 1, pp. 517–520. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.; Core, M. Draft of DAMSL: Dialog Act Markup in Several Layers. Available online: http://www.cs.rochester.edu/research/cisd/resources/damsl/RevisedManual/ (accessed on 11 June 2019).
- Bunt, H. The DIT++ taxonomy for functional dialogue markup. In Proceedings of the AAMAS 2009 Workshop, Towards a Standard Markup Language for Embodied Dialogue Acts, Budapest, Hungary, 10–15 May 2009; pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Pareti, S.; Lando, T. Dialog Intent Structure: A Hierarchical Schema of Linked Dialog Acts. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-2018), Miyazaki, Japan, 12 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Keizer, S.; Bunt, H.; Petukhova, V. Multidimensional dialogue management. In Interactive Multi-Modal Question-Answering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 57–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bunt, H.; Petukhova, V.; Traum, D.; Alexandersson, J. Dialogue Act Annotation with the ISO 24617-2 Standard. In Multimodal Interaction with W3C Standards: Toward Natural User Interfaces to Everything; Dahl, D.A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 109–135. [Google Scholar]
- Tur, G.; DeMori, R. Spoken Language Understanding: Systems for Extracting Semantic Information from Speech; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, S.; Deng, L.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Acero, A. An Integrative and Discriminative Technique for Spoken Utterance Classification. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2008, 16, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, L.; Hakkani-Tür, D. Exploiting the Semantic Web for unsupervised spoken language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Miami, FL, USA, 2–5 December 2012; pp. 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Acero, A. Discriminative models for spoken language understanding. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH 2006—ICSLP, Ninth International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 17–21 September 2006; ISCA: Woodbridge, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hakkani-Tür, D.; Tür, G.; Çelikyilmaz, A.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y. Multi-Domain Joint Semantic Frame Parsing Using Bi-Directional RNN-LSTM. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2016, 17th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2016; Morgan, N., Ed.; ISCA: Woodbridge, ON, Canada, 2016; pp. 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukotic, V.; Pintea, S.; Raymond, C.; Gravier, G.; van Gemert, J.C. One-Step Time-Dependent Future Video Frame Prediction with a Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Neural Network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.04125. [Google Scholar]
- Tur, G.; Celikyilmaz, A.; He, X.; Hakkani-Tür, D.; Deng, L. Deep Learning in Conversational Language Understanding. In Deep Learning in Natural Language Processing; Deng, L., Liu, Y., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.M. Is it time to REGROW the GROW model? Issues related to teaching coaching session structures. Coach. Psychol. 2011, 7, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro, C.; Santana, R.; Lozano, J.A. Data generation approaches for topic classification in multilingual spoken dialog systems. In Proceedings of the 12th Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference (PETRA-19), Rhodes, Greece, 5–7 June 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
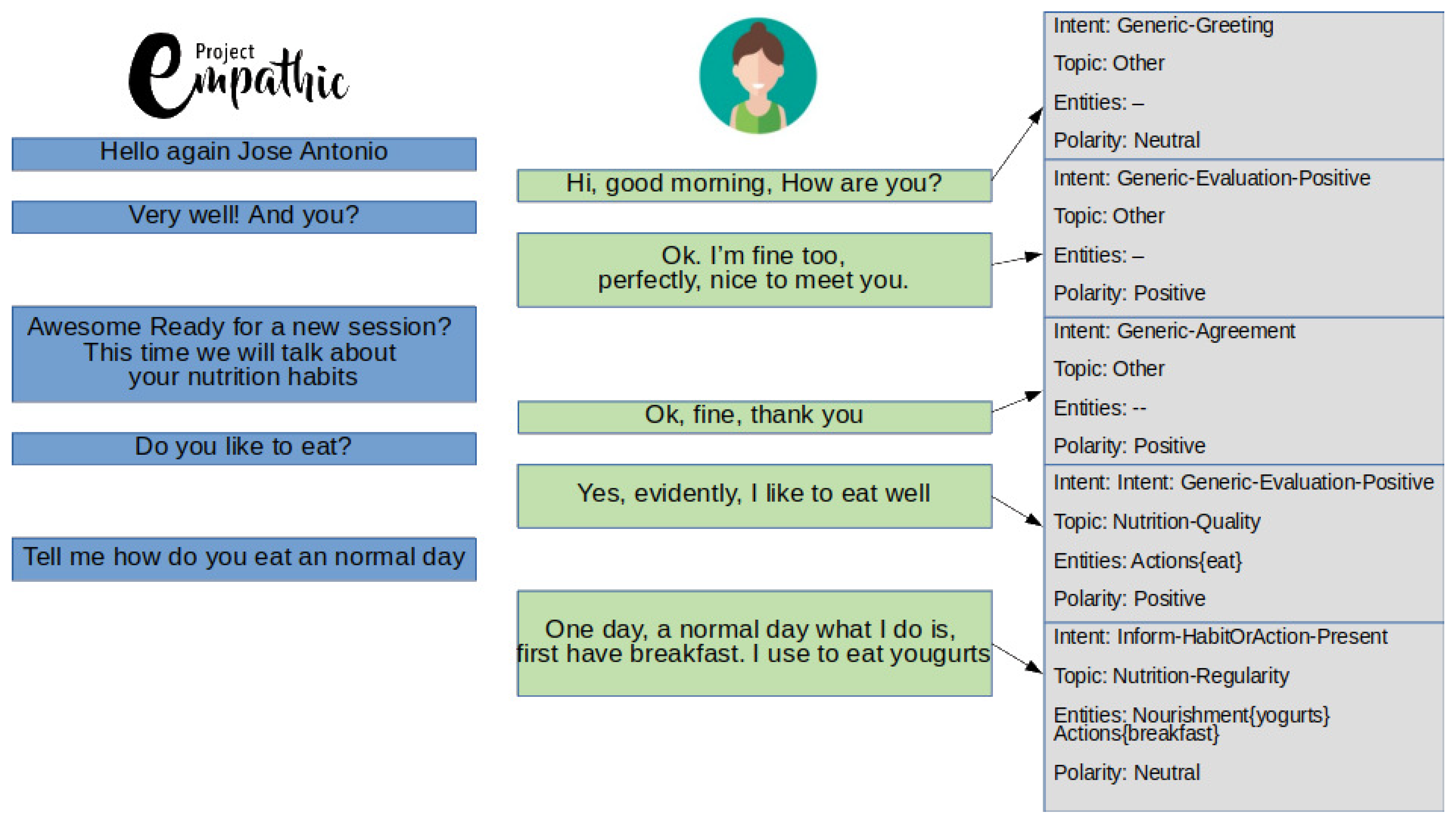
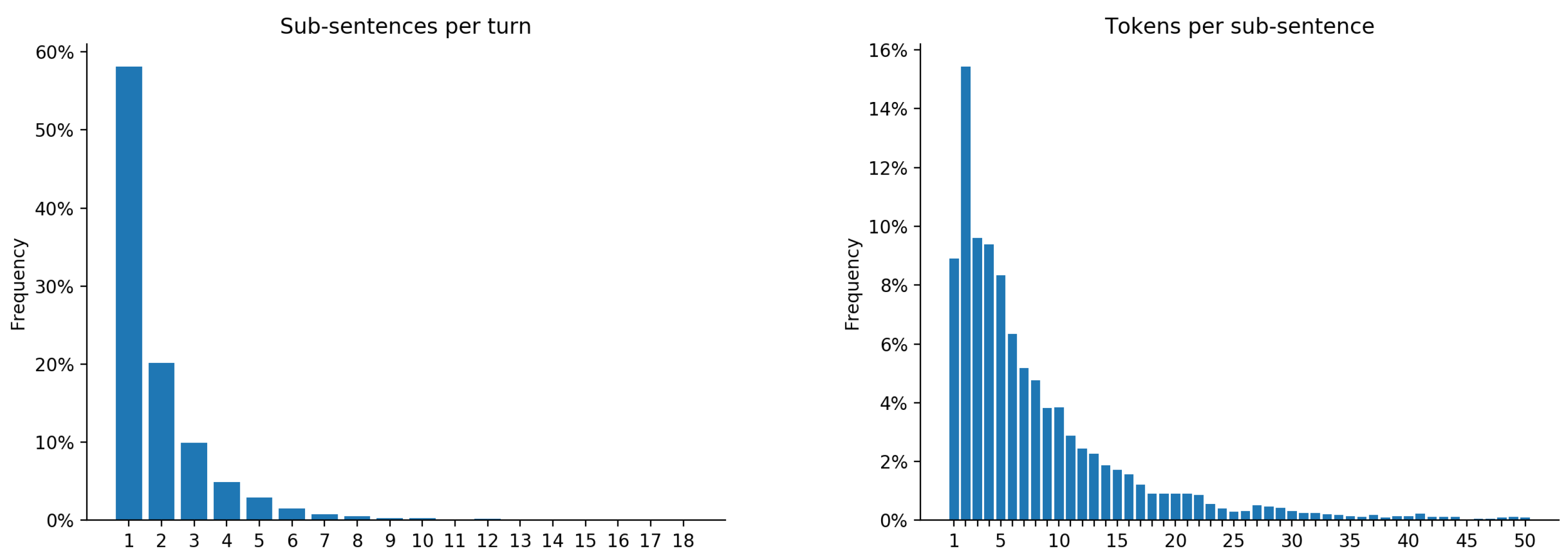
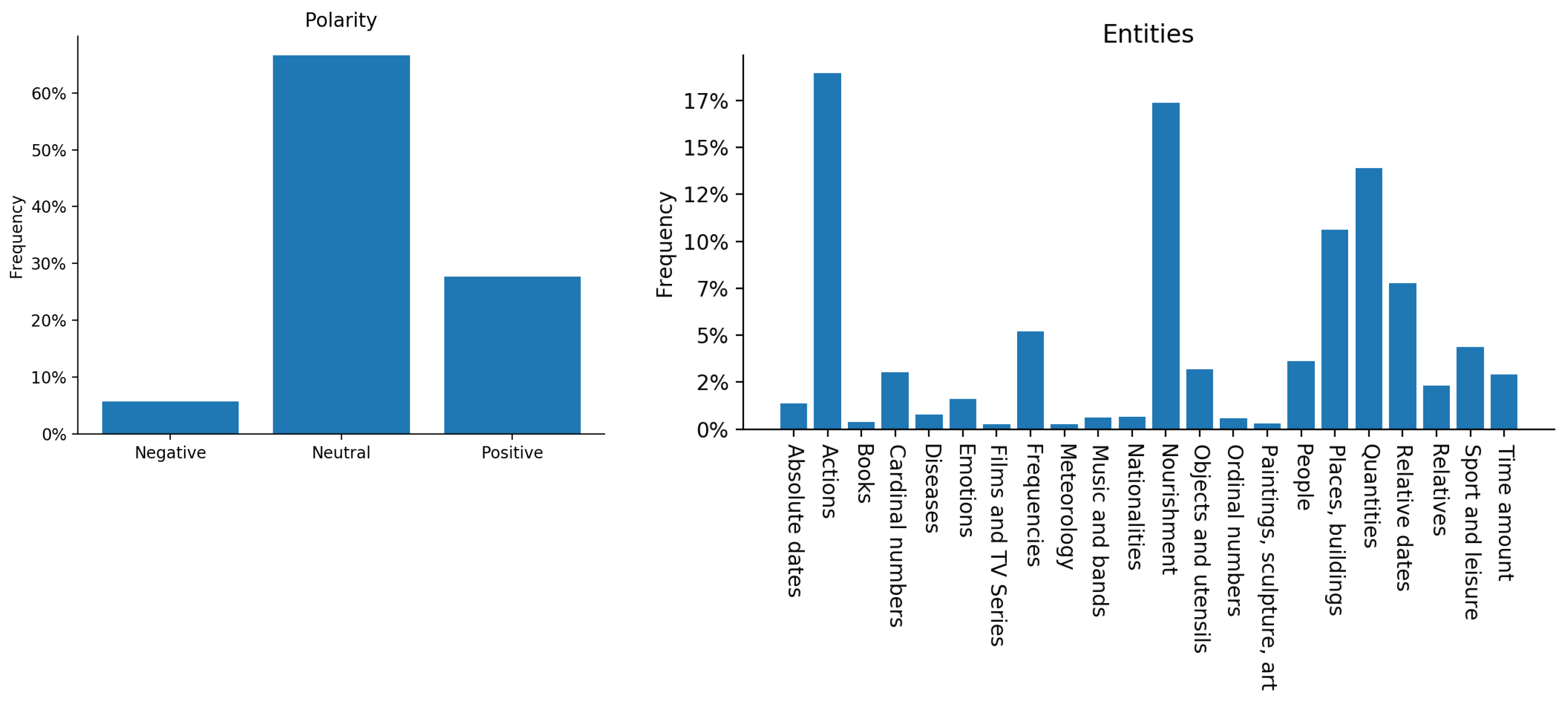
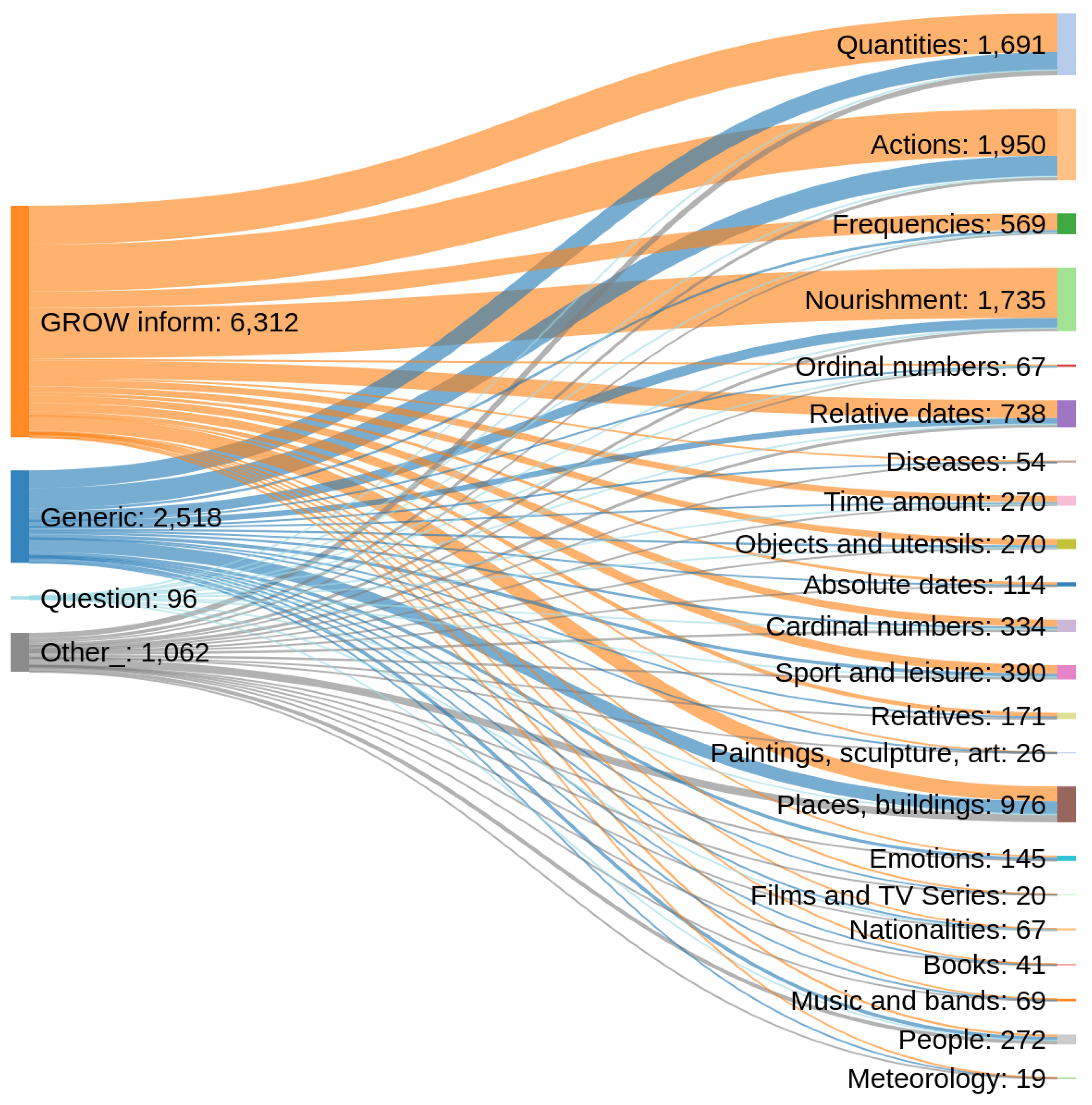
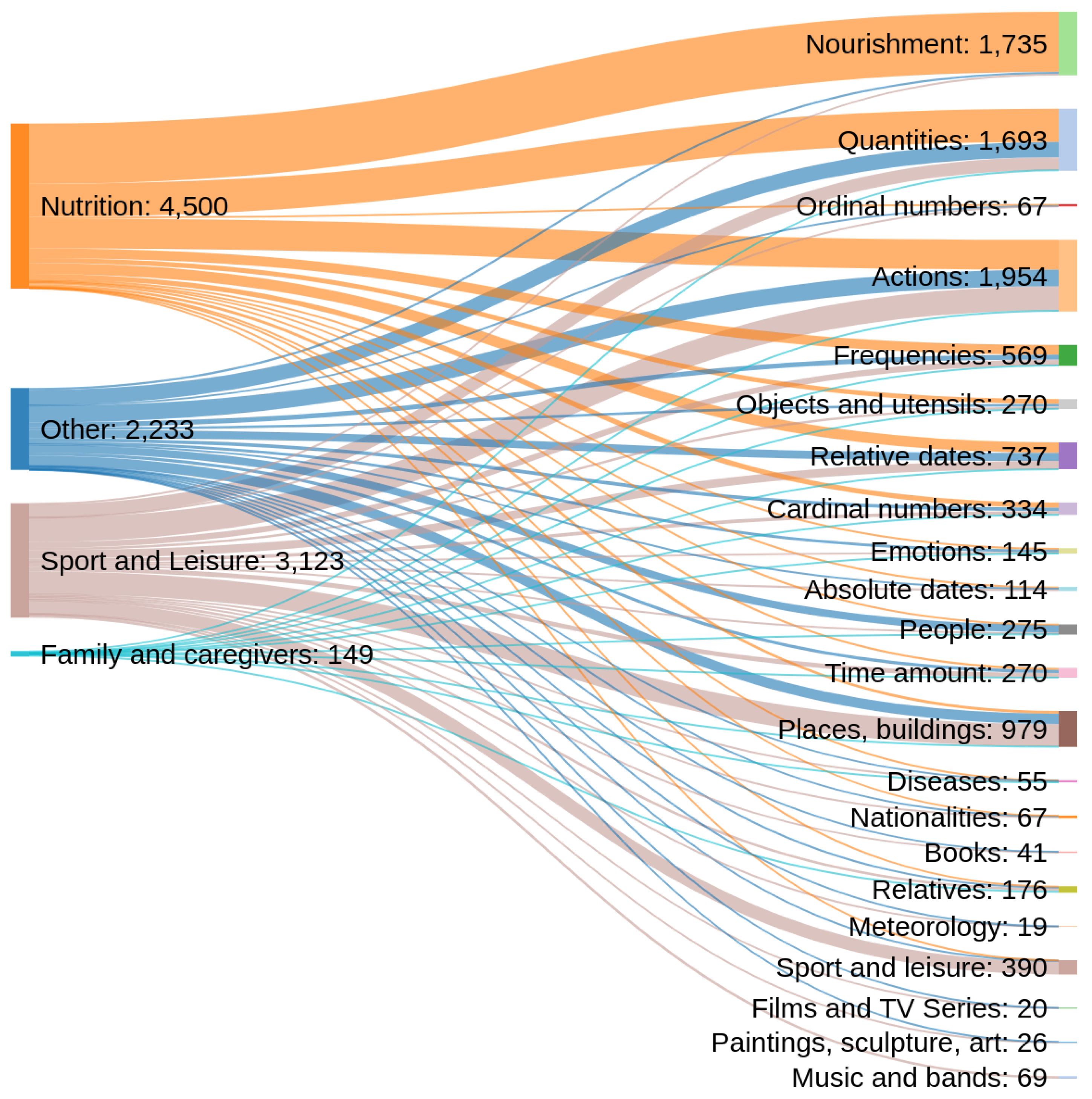
| Persons | Relatives | Objects/Utensils |
| Actions | Nourishment | Sport and leisure |
| Books | Cardinal numbers | Music/Bands |
| Quantities | Ordinal numbers | Films/TV Series |
| Frequencies | Time amount | Paintings/Sculpture/Art |
| Diseases | Absolute dates | Places, buildings and organizations |
| Emotions | Relative dates | Nationalities |
| Meteorology |
| Characteristics | Number |
|---|---|
| Number of users | 72 |
| Number of dialogues | 142 |
| Number of turns | 4522 |
| Number of running words | 72,350 |
| Vocabulary size | 5543 |
| Number of topic labels | 55 |
| Number of intent labels | 34 |
| Number of running entities | 11,113 |
| Frequent Topic Labels | Frequency |
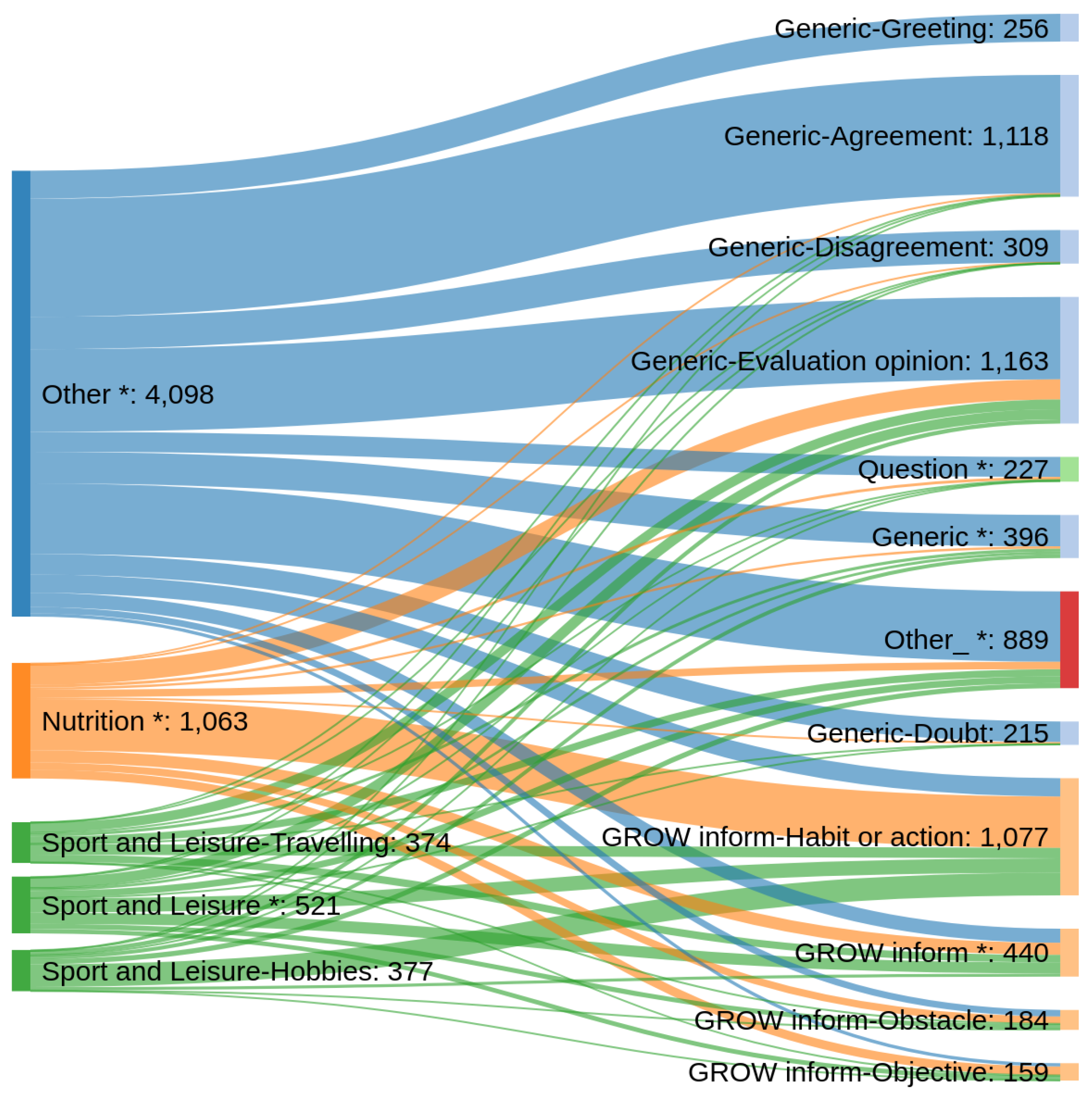
|---|---|
| nutrition | 16.5% |
| sport and leisure - hobbies | 5.9% |
| sport and leisure - travelling | 5.8% |
| sport and leisure - * | 8.1% |
| Other | 63.7% |
| Frequent Intent Labels | Frequency |
|---|---|
| generic - agreement | 17.4% |
| generic - disagreement | 4.8% |
| generic - evaluation/opinion | 18.1% |
| generic - doubt | 3.3% |
| generic - greeting | 4.0% |
| generic - * | 6.2% |
| GROW inform - habit or action | 16.7% |
| GROW inform - objective | 2.5% |
| GROW inform - obstacle | 2.9% |
| GROW inform - * | 6.8% |
| question | 3.5% |
| other | 13.8% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montenegro, C.; López Zorrilla, A.; Mikel Olaso, J.; Santana, R.; Justo, R.; Lozano, J.A.; Torres, M.I. A Dialogue-Act Taxonomy for a Virtual Coach Designed to Improve the Life of Elderly. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2019, 3, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3030052
Montenegro C, López Zorrilla A, Mikel Olaso J, Santana R, Justo R, Lozano JA, Torres MI. A Dialogue-Act Taxonomy for a Virtual Coach Designed to Improve the Life of Elderly. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction. 2019; 3(3):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontenegro, César, Asier López Zorrilla, Javier Mikel Olaso, Roberto Santana, Raquel Justo, Jose A. Lozano, and María Inés Torres. 2019. "A Dialogue-Act Taxonomy for a Virtual Coach Designed to Improve the Life of Elderly" Multimodal Technologies and Interaction 3, no. 3: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3030052
APA StyleMontenegro, C., López Zorrilla, A., Mikel Olaso, J., Santana, R., Justo, R., Lozano, J. A., & Torres, M. I. (2019). A Dialogue-Act Taxonomy for a Virtual Coach Designed to Improve the Life of Elderly. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 3(3), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3030052






