A Study on the Use of Eye Tracking to Adapt Gameplay and Procedural Content Generation in First-Person Shooter Games
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Zombie Runner
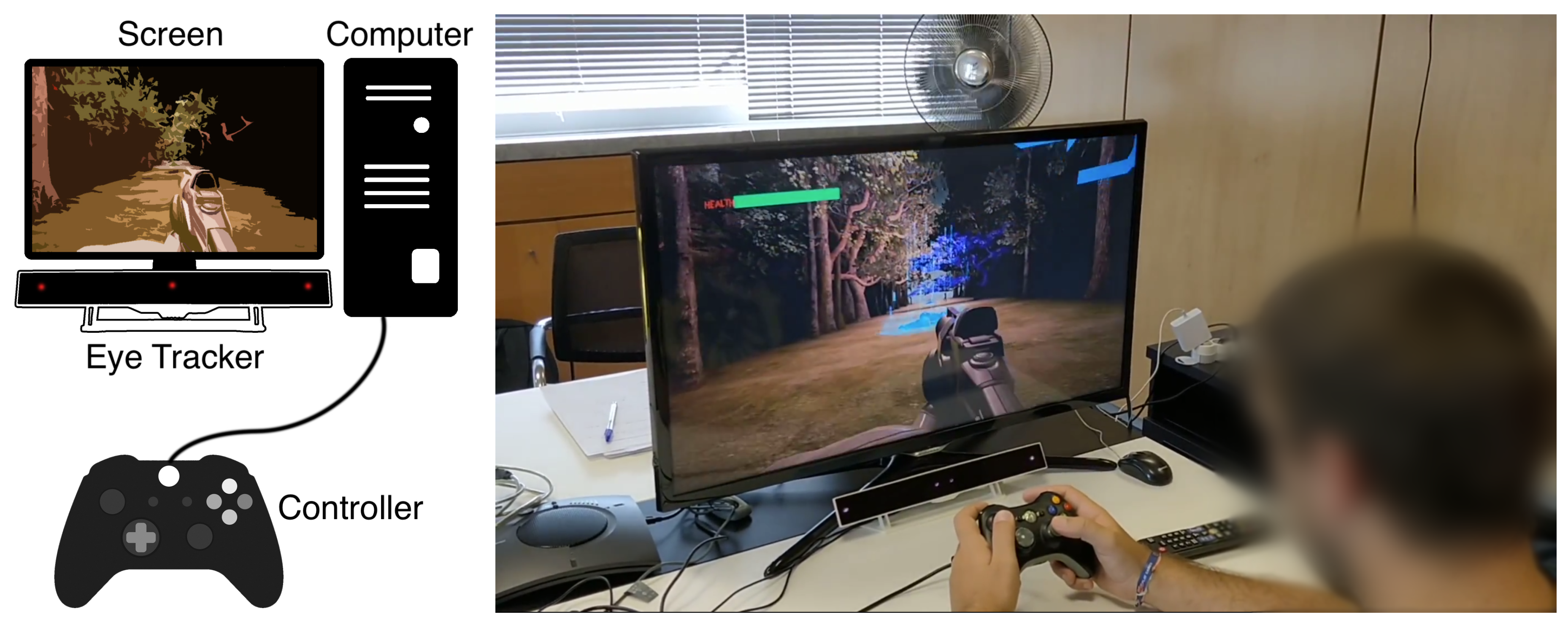
3.1. System Configuration
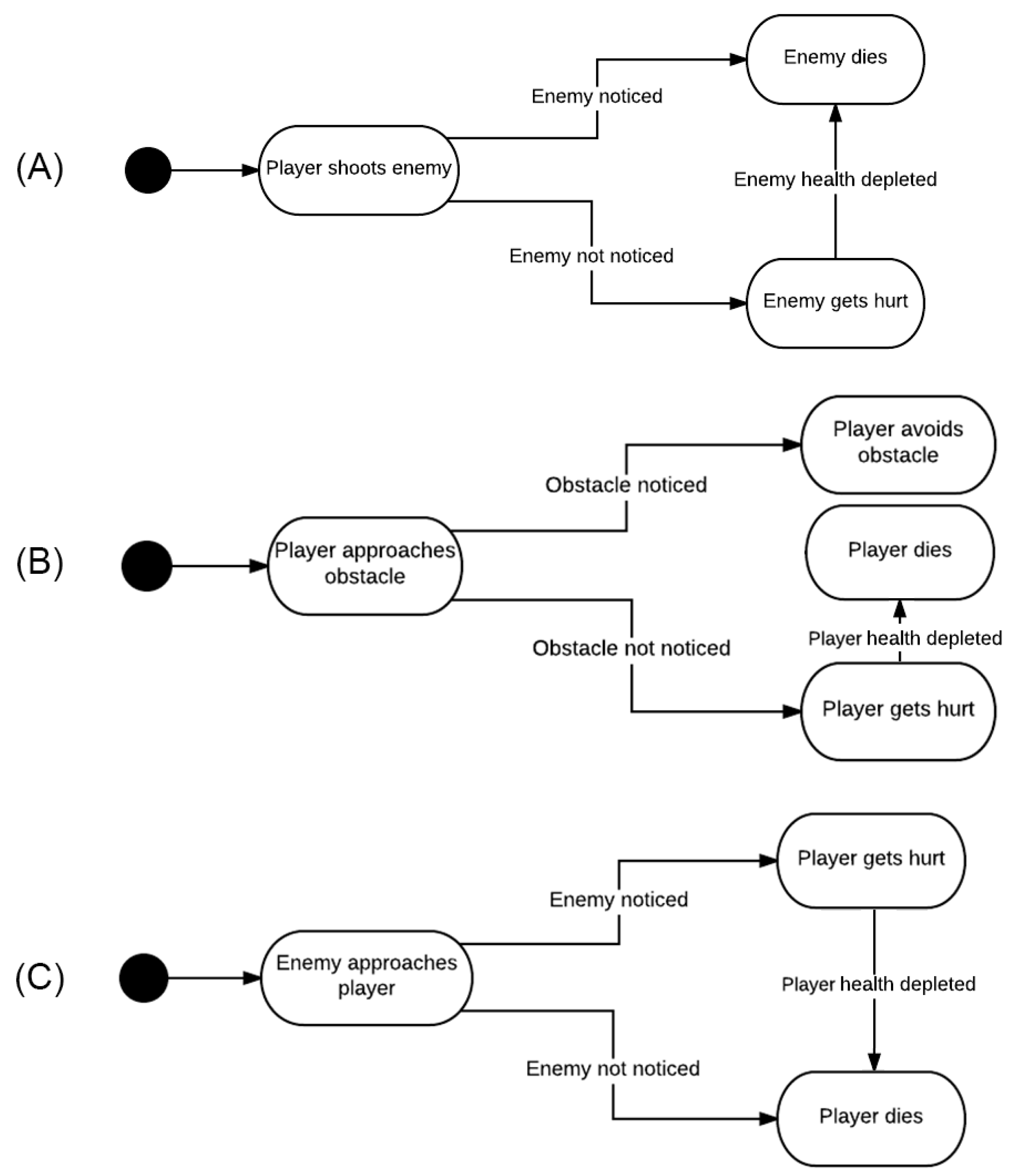
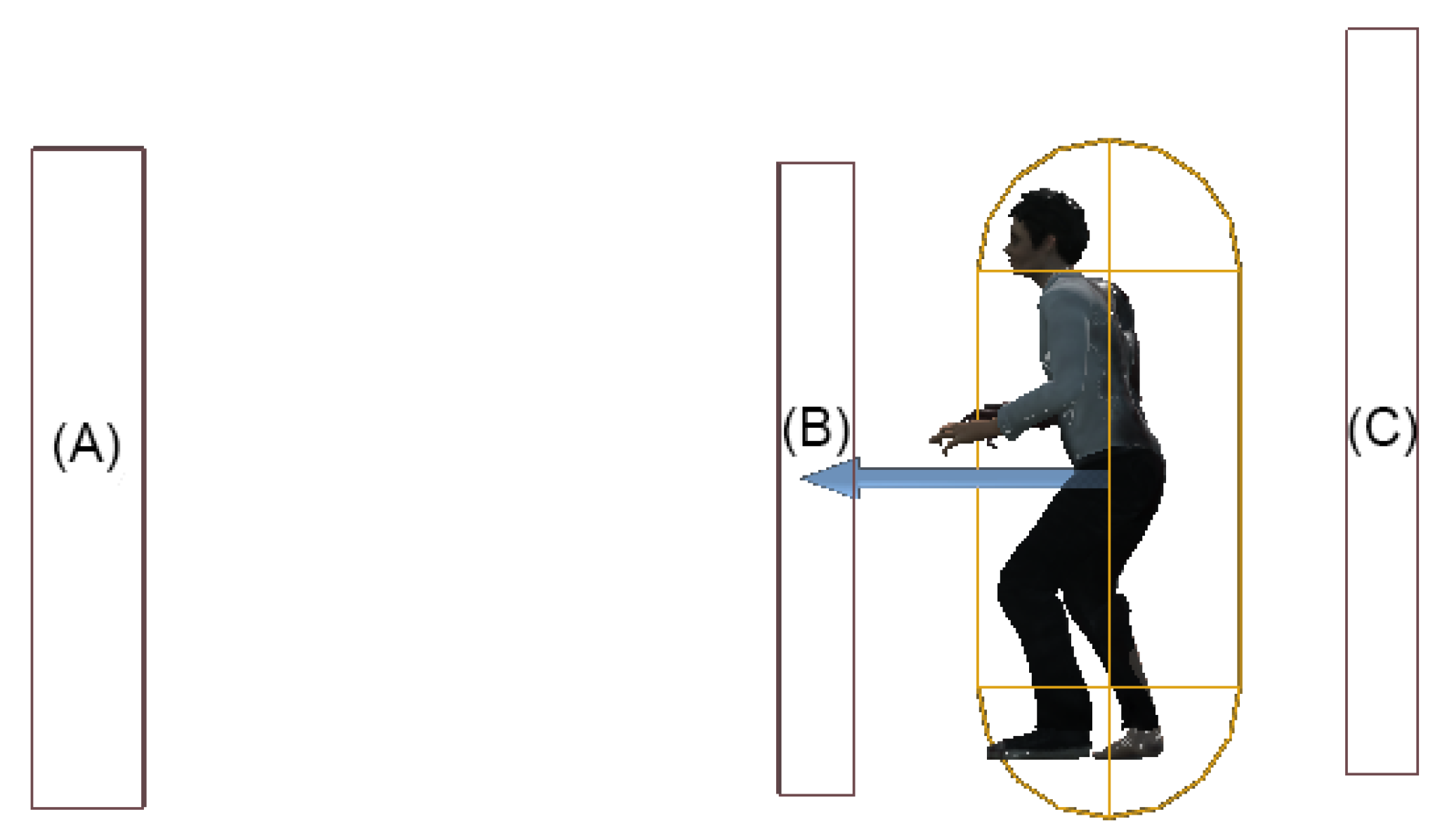
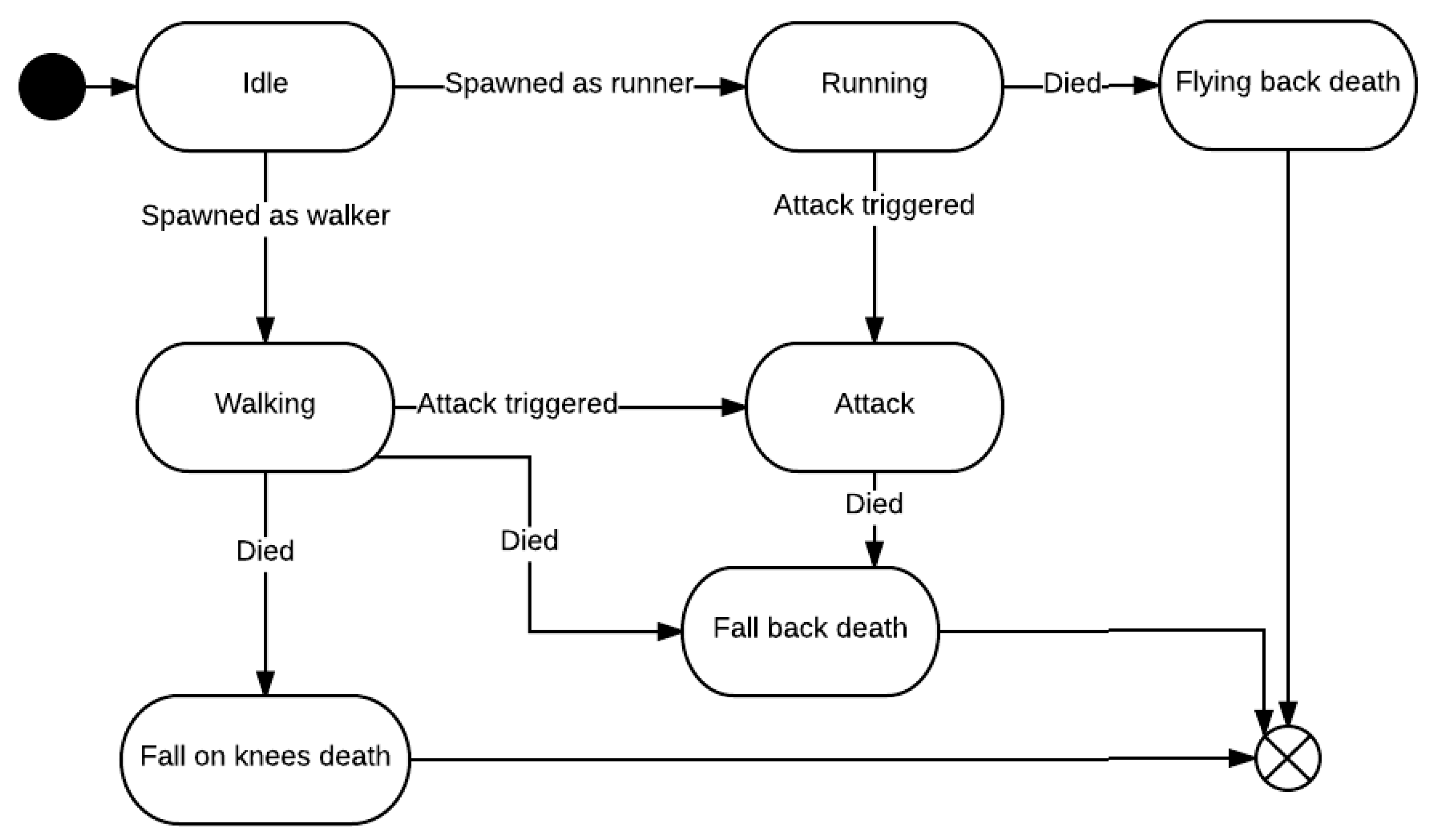
3.2. Game Rules and Mechanics
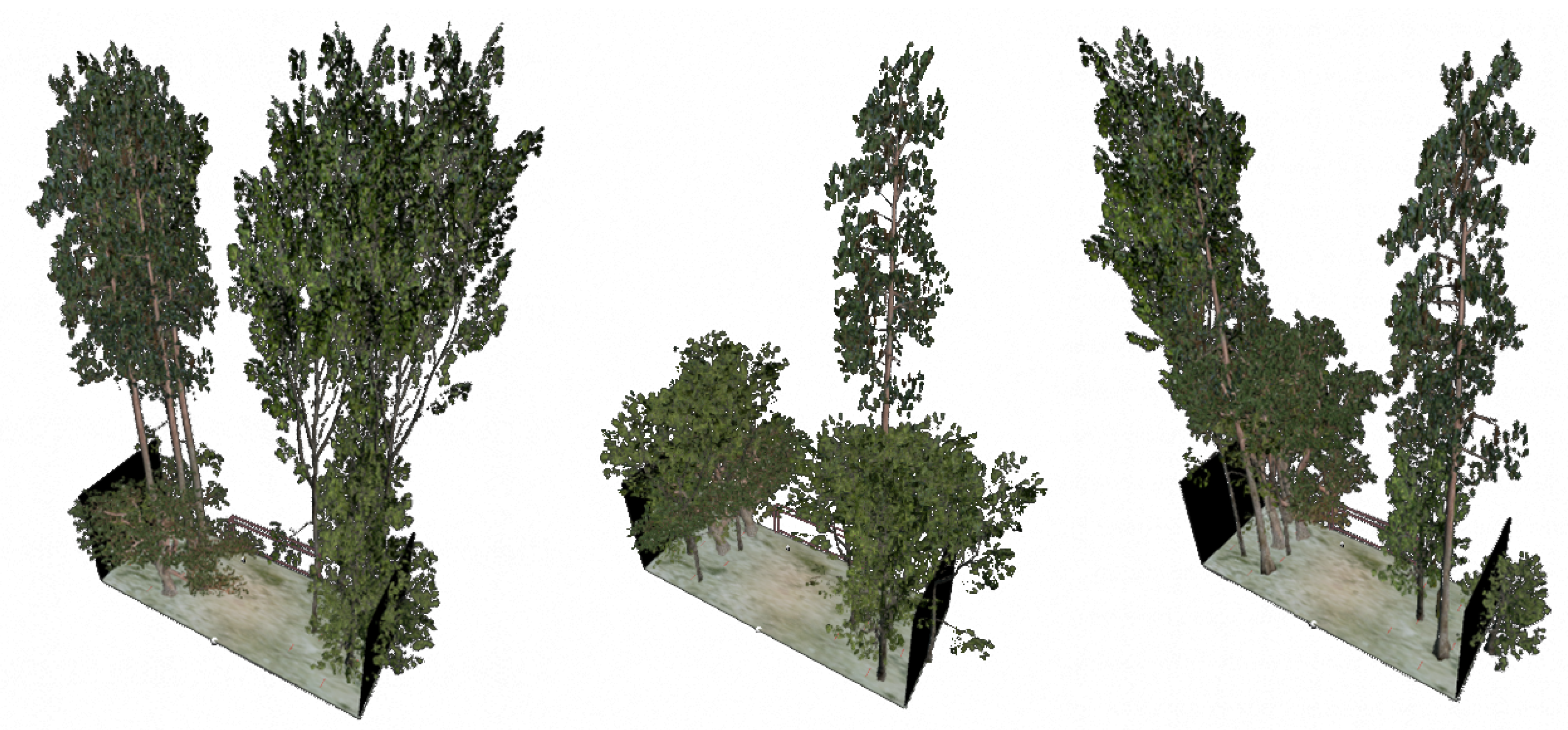
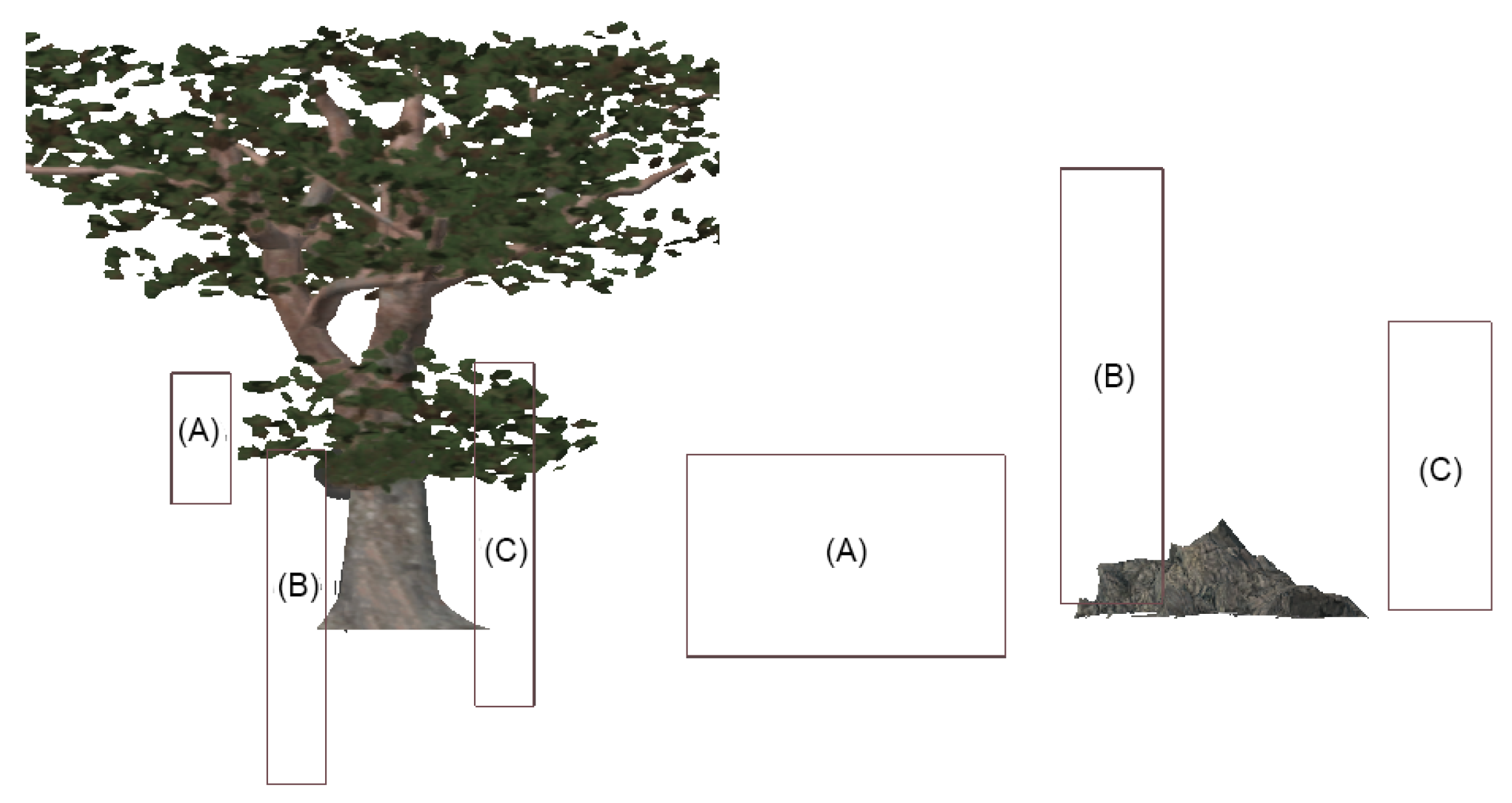
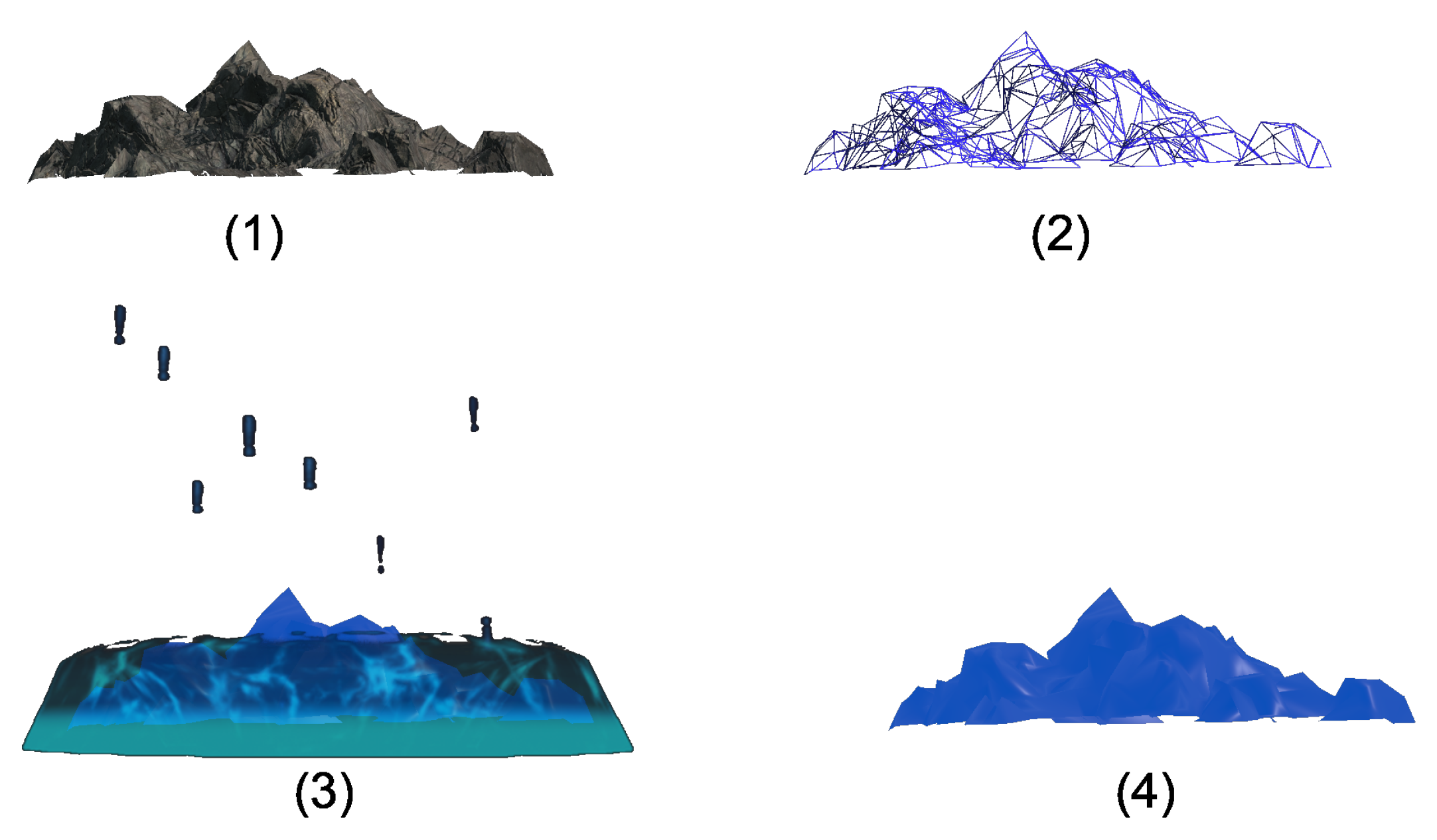
3.3. Game Implementation
4. Evaluation and Discussion
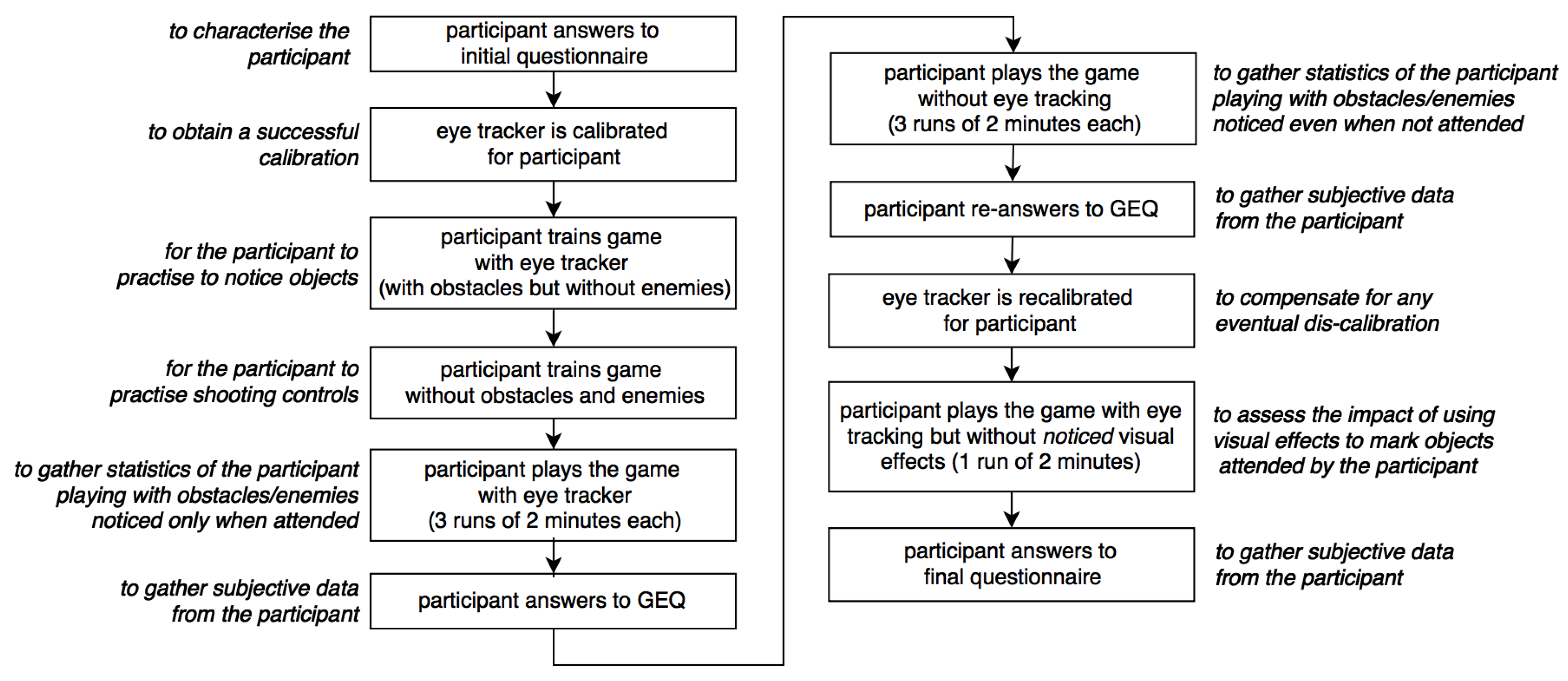
4.1. Evaluation Method
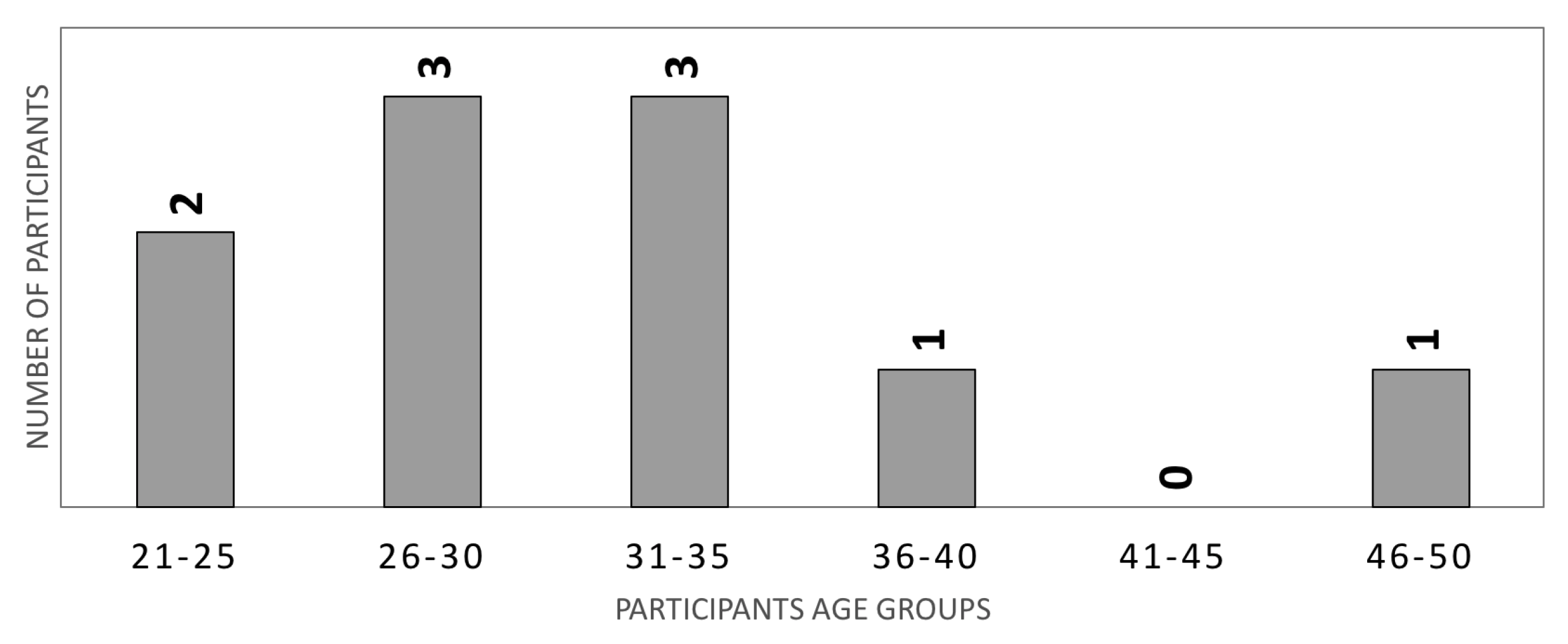
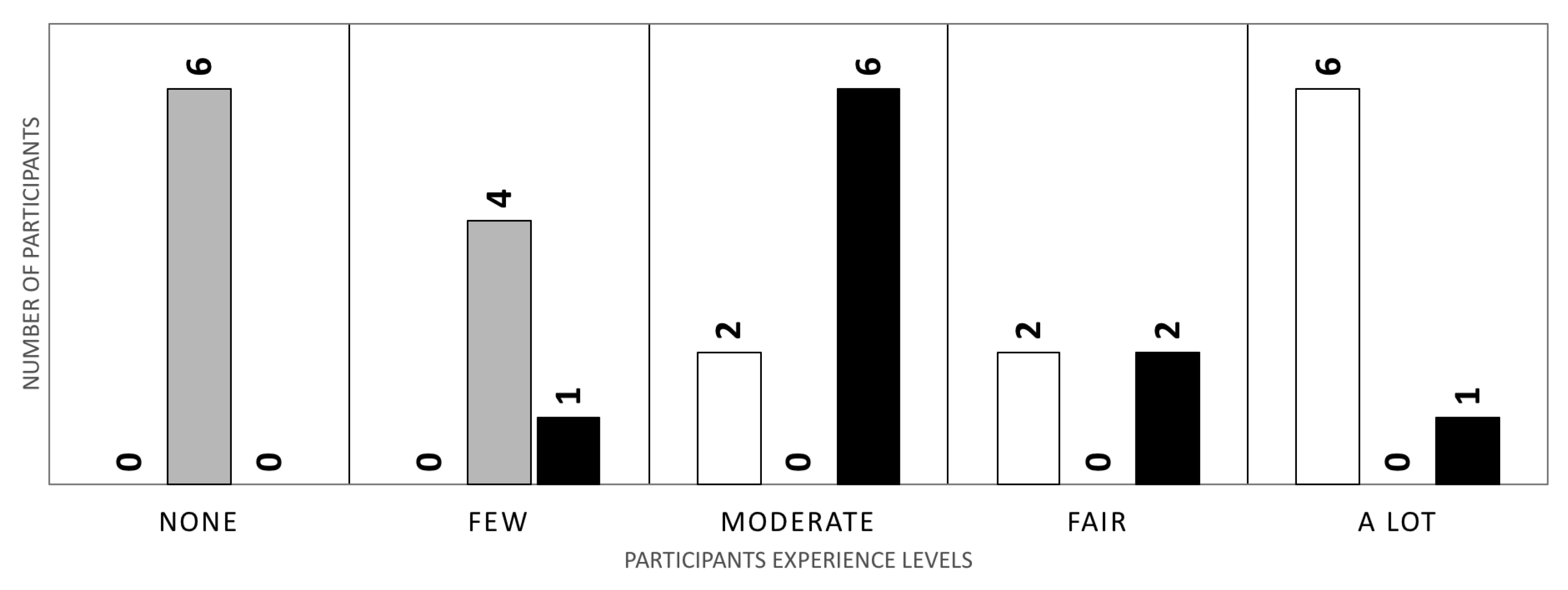
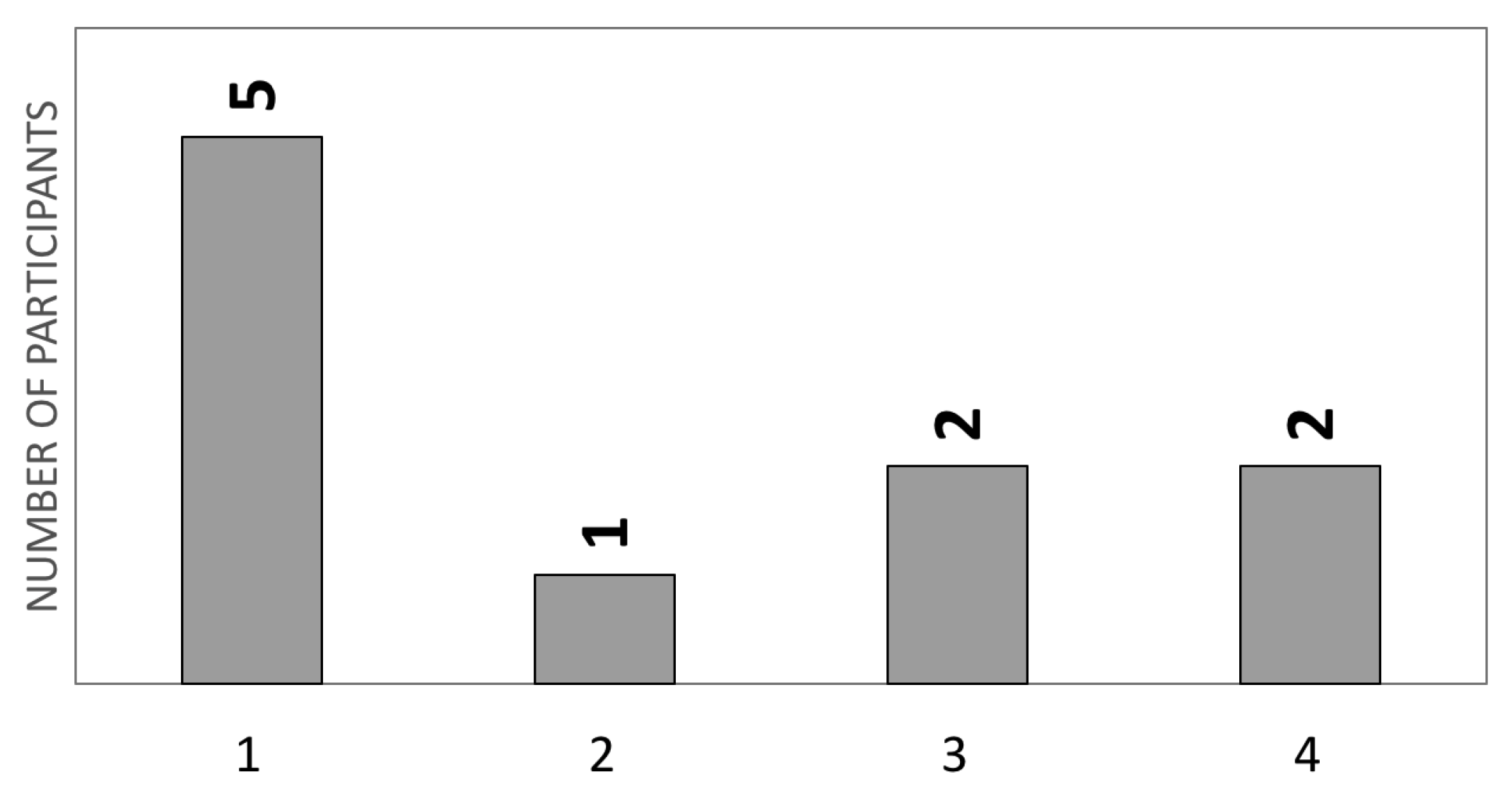
4.1.1. Test Sessions
4.2. Experimental Results
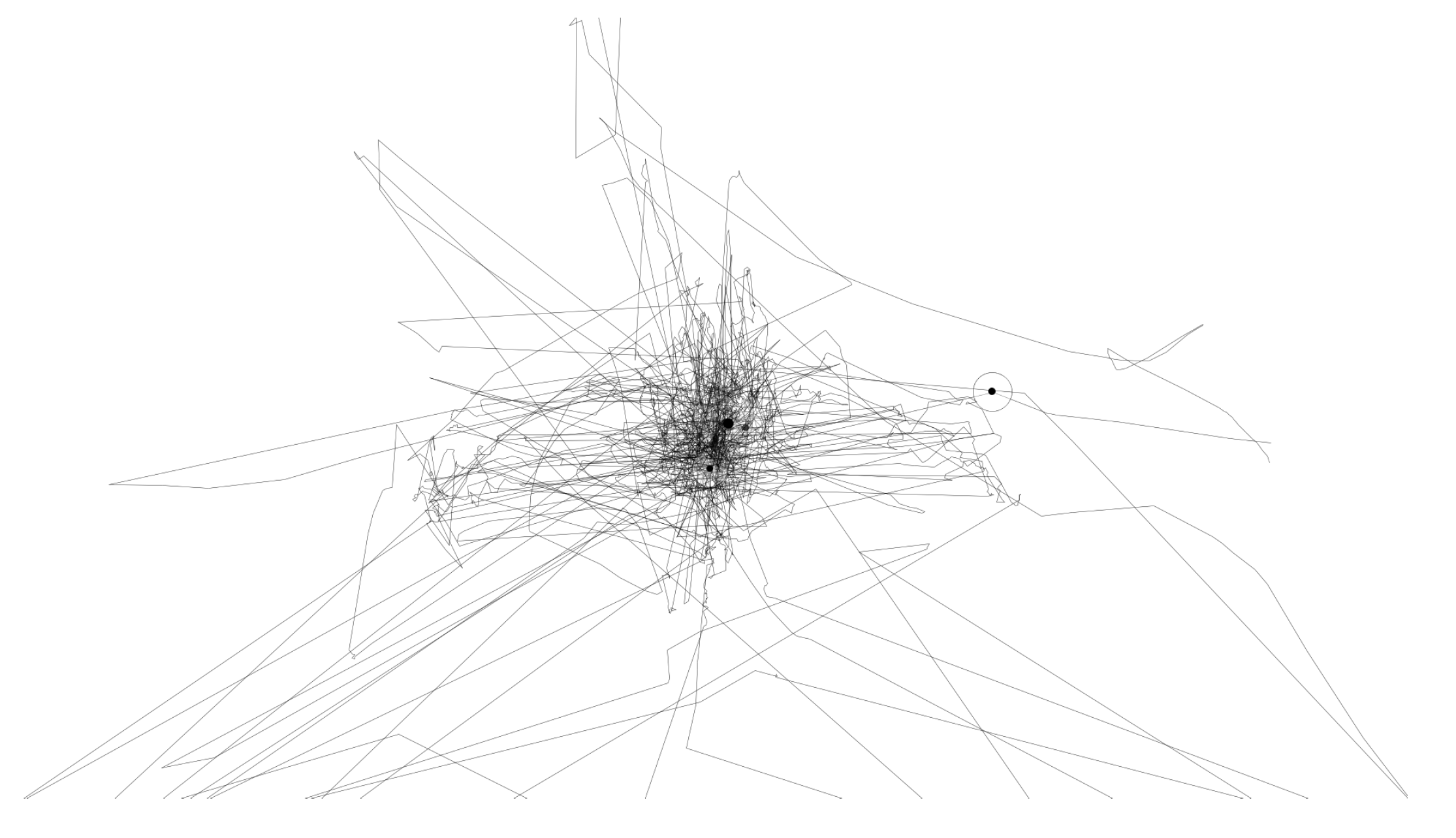
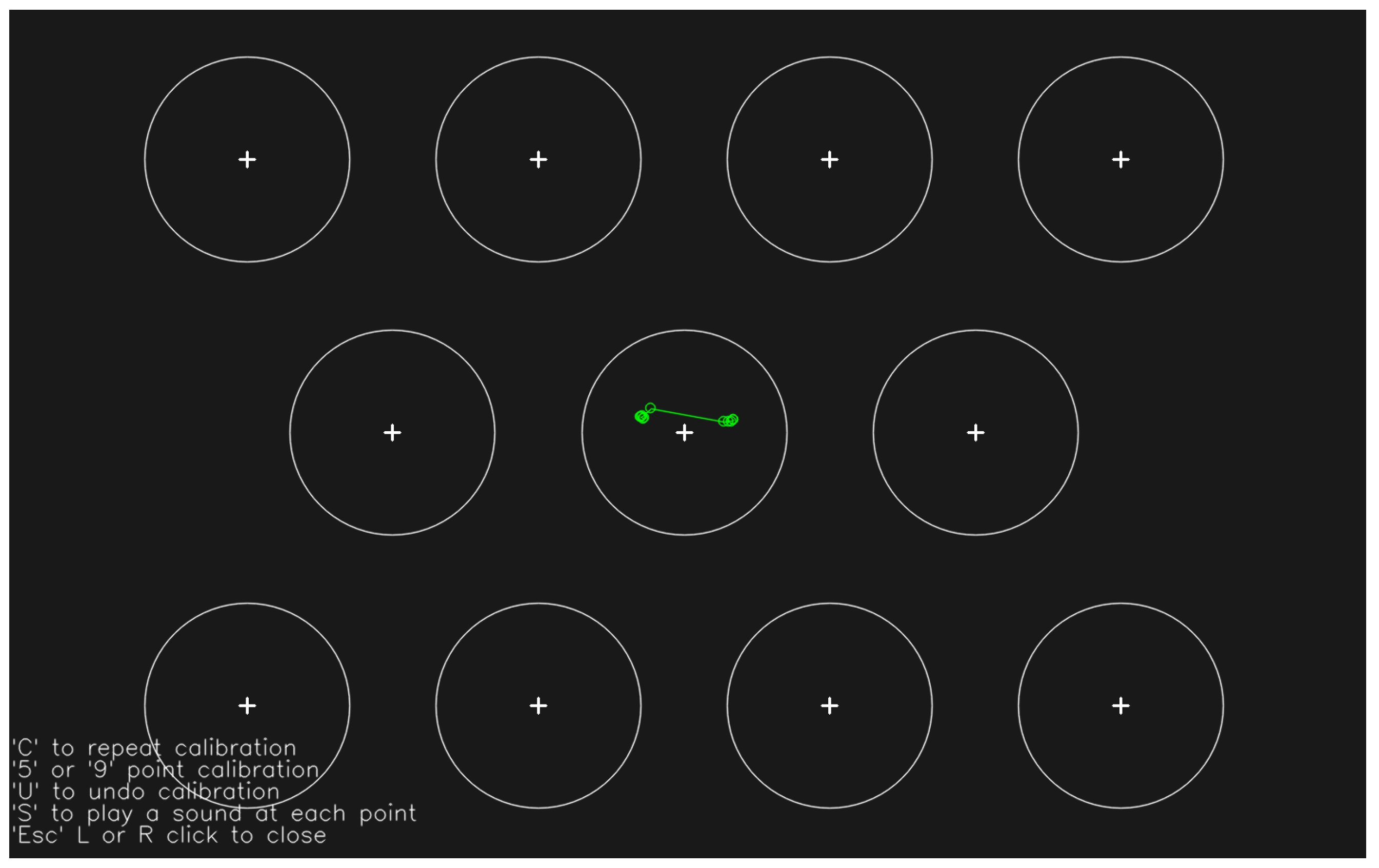
4.2.1. Eye Tracker Calibration Process
4.2.2. Play Sessions
4.2.3. Informal Questions
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Javal, L. Essai sur la physiologie de la lecture. Ann. d’Ocul. 1879, 82, 242–253. [Google Scholar]
- Holzman, P.S.; Proctor, L.R.; Hughes, D.W. Eye-Tracking Patterns in Schizophrenia. Science 1973, 181, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcmullen, D.P.; Hotson, G.; Katyal, K.D.; Wester, B.A.; Fifer, M.S.; Mcgee, T.G.; Harris, A.; Johannes, M.S.; Vogelstein, R.J.; Ravitz, A.D.; et al. Demonstration of a Semi-Autonomous Hybrid Brain-Machine Interface Using Human Intracranial EEG, Eye Tracking, and Computer Vision to Control a Robotic Upper Limb Prosthetic. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.; Marques, F.; Lourenço, A.; Mendonça, R.; Santana, P.; Barata, J. Gaze-Directed Telemetry in High Latency Wireless Communications: The Case of Robot Teleoperation. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON), Florence, Italy, 24–27 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Krugman, D.M.; Fox, R.J.; Fletcher, J.E.; Fischer, P.M.; Rojas, T.H. Do adolescents attend to warnings in cigarette advertising? An eye-tracking approach. J. Adv. Res. 1994, 34, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.D.; Graham, T.C.N. Use of Eye Movements for Video Game Control. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGCHI International Conference on Advances in Computer Entertainment Technology-ACE ’06, Hollywood, CA, USA, 14–16 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Leyba, J.; Malcolm, J. Eye tracking as an Aiming Device in a Computer Game. In Course work (CPSC 412/612 Eye Tracking Methodology and Applications by A. Duchowski); Clemson University: Clemson, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Isokoski, P.; Martin, B. Eye Tracker Input in First Person Shooter Games. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Communication by Gaze Interaction: Communication by Gaze Interaction-COGAIN 2006: Gazing into the Future, Turin, Italy, 4–5 September 2006; pp. 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Isokoski, P.; Joos, M.; Spakov, O.; Martin, B. Gaze controlled games. Univ. Access Inf. Soc. 2009, 8, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, M.; Pomarjanschi, L.; Barth, E. Gaze beats mouse: A case study. PsychNol. J. 2009, 7, 197–211. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, J.; Santana, P. Gaze-Oriented Gameplay in First-Person Shooter Games. In Proceedings of the 24th Portuguese Meeting on Computer Graphics and Interaction (EPCGI), Guimarães, Portugal, 12–13 October 2017; pp. 231–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lukander, K. Measuring Gaze Point on Handheld Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the 2004 Conference on Human Factors and Computing Systems-CHI ’04, Vienna, Austria, 24–29 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, K.; Mardiyanto, R. Eye-based HCI with Full Specification of Mouse and Keyboard Using Pupil Knowledge in the Gaze Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2011 Eighth International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–13 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, W.C. An essay upon single vision with two eyes together with experiments and observations on several other subjects in optics. T. Cadell: London, UK, 1792. [Google Scholar]
- Dodge, R.; Cline, T.S. The angle velocity of eye movements. Psychol. Rev. 1901, 8, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh, J. Human Eye tracking and Related Issues: A Review. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. (IJSRP) 2012, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Shell, J.S.; Vertegaal, R.; Cheng, D.; Skaburskis, A.W.; Sohn, C.; Stewart, A.J.; Aoudeh, O.; Dickie, C. ECSGlasses and EyePliances. In Proceedings of the Eye Tracking Research and Applications Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications-ETRA’2004, San Antonio, TX, USA, 22–24 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.D.; Vertegaal, R.; Sohn, C. ViewPointer. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology-UIST ’05, Seattle, WA, USA, 23–27 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Perreira da Silva, M.; Courboulay, V.; Prigent, A. Gameplay Experience based on a Gaze Tracking System. In Proceedings of the Communication by Gaze Interaction IST FP6 European Project (COGAIN), Leicester, UK, 3–4 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, N.; Togelius, J.; Nelson, M. Procedural Content Generation in Games: A Textbook and an Overview of Current Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, C.; Yannakakis, G.N.; Colton, S. Guest Editorial: Special Issue on Computational Aesthetics in Games. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 2012, 4, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannakakis, G.N. Game AI Revisited. In Proceedings of the 9th Conference on Computing Frontiers, Cagliari, Italy, 15–17 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gow, J.; Baumgarten, R.; Cairns, P.; Colton, S.; Miller, P. Unsupervised Modeling of Player Style With LDA. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 2012, 4, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannakakis, G.N.; Togelius, J. Experience-Driven Procedural Content Generation. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 2, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, H.; Takeshita, N.; Yoshimura, J. A Metric for Entertainment of Boardgames: Its Implication for Evolution of Chess Variants. In Entertainment Computing; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Spronck, P.; Sprinkhuizen-Kuyper, I.; Postma, E. Difficulty Scaling of Game AI. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Intelligent Games and Simulation (GAME-ON 2004), Ghent, Belgium, 25–27 November 2004; pp. 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, G.; Ramalho, G.; Santana, H.; Corruble, V. Automatic Computer Game Balancing. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems-AAMAS ’05, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 25–29 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yannakakis, G.N.; Hallam, J. Towards Optimizing Entertainment In Computer Games. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2007, 21, 933–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.K.; Yannakakis, G.N.; Hallam, J. Real-Time Challenge Balance in an RTS Game Using rtNEAT. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Symposium On Computational Intelligence and Games, Perth, Australia, 15–18 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lankveld, G.V.; Spronck, P.; Herik, H.J.V.D.; Rauterberg, M. Incongruity-Based Adaptive Game Balancing. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science Advances in Computer Games; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 208–220. [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson, N.; Pasquier, P. Towards a Generic Framework for Automated Video Game Level Creation. In Applications of Evolutionary Computation Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Gazepoint Control. Available online: http://www.gazept.com (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Zugal, S.; Pinggera, J. Low–Cost Eye–Trackers: Useful for Information Systems Research? In International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- IJsselsteijn, W.A.; de Kort, Y.A.W.; Poels, K. The Game Experience Questionnaire; Technical Report; Technische Universiteit Eindhoven: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Drachen, A.; Nacke, L.E.; Yannakakis, G.; Pedersen, A.L. Correlation between Heart Rate, Electrodermal Activity and Player Experience in First-Person Shooter Games. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Video Games-Sandbox ’10, New York, NY, USA, 26–30 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gerling, K.M.; Klauser, M.; Niesenhaus, J. Measuring the Impact of Game Controllers on Player Experience in FPS Games. In Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference on Envisioning Future Media Environments-MindTrek ’11, Tampere, Finland, 28–30 September 2011. [Google Scholar]



| Play Session | Ratio [%] of Killed Enemies | Ratio [%] of Noticed Elements | Number of Deaths |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | |||
| 2nd | |||
| 3rd |
| GEQ Average Score | ||
|---|---|---|
| Component | With ET | Without ET |
| Competence | ||
| Immersion | ||
| Flow | ||
| Tension | ||
| Challenge | ||
| Negative affect | ||
| Positive affect | ||
| GEQ Average Score | ||
|---|---|---|
| Component | With ET | Without ET |
| Positive experience | ||
| Negative experience | ||
| Tiredness | ||
| Returning to reality | ||
| Complaint | Nr. of Participants |
|---|---|
| Impact of noticed-related visual effects to feeling of immersion/realism | 7 |
| Need for being as static as possible for proper eye tracking operation | 3 |
| Failures in mis-registering enemies/obstacles as noticed | 2 |
| Time required for obstacles/enemies to be considered as noticed | 1 |
| Problems in tracking the eyes of people wearing glasses | 1 |
| Game lacks progression | 1 |
| Response | Nr. of Participants |
|---|---|
| No | 2 |
| Maybe, when eye tracking becomes more reliable | 3 |
| Yes | 5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antunes, J.; Santana, P. A Study on the Use of Eye Tracking to Adapt Gameplay and Procedural Content Generation in First-Person Shooter Games. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2018, 2, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti2020023
Antunes J, Santana P. A Study on the Use of Eye Tracking to Adapt Gameplay and Procedural Content Generation in First-Person Shooter Games. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction. 2018; 2(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti2020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntunes, João, and Pedro Santana. 2018. "A Study on the Use of Eye Tracking to Adapt Gameplay and Procedural Content Generation in First-Person Shooter Games" Multimodal Technologies and Interaction 2, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti2020023
APA StyleAntunes, J., & Santana, P. (2018). A Study on the Use of Eye Tracking to Adapt Gameplay and Procedural Content Generation in First-Person Shooter Games. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 2(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti2020023






