6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone in the Urban Environment: Assessing Exposure Pathways and Human Health Risks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Occurrence of 6PPD and 6PPD-Q
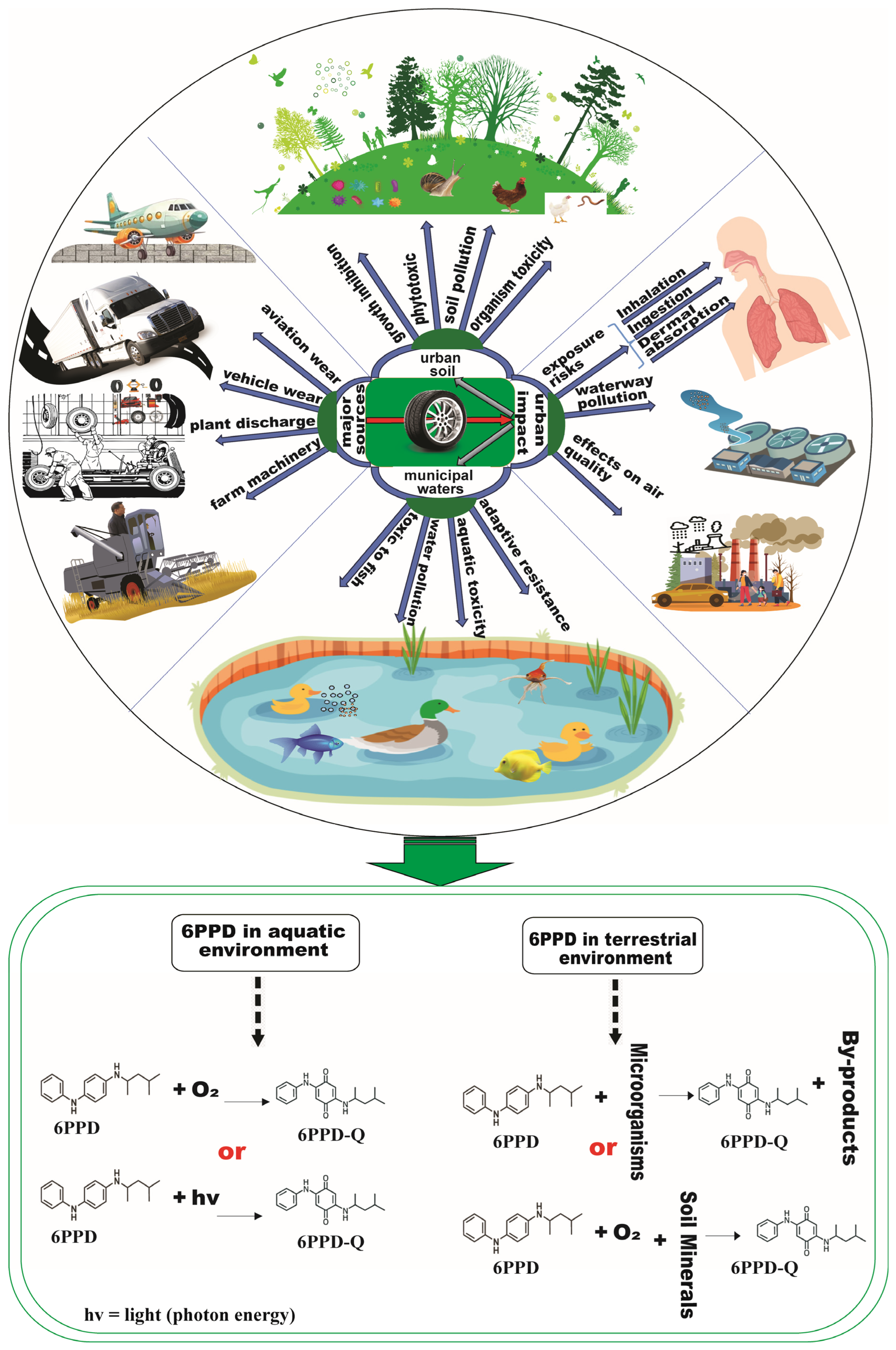
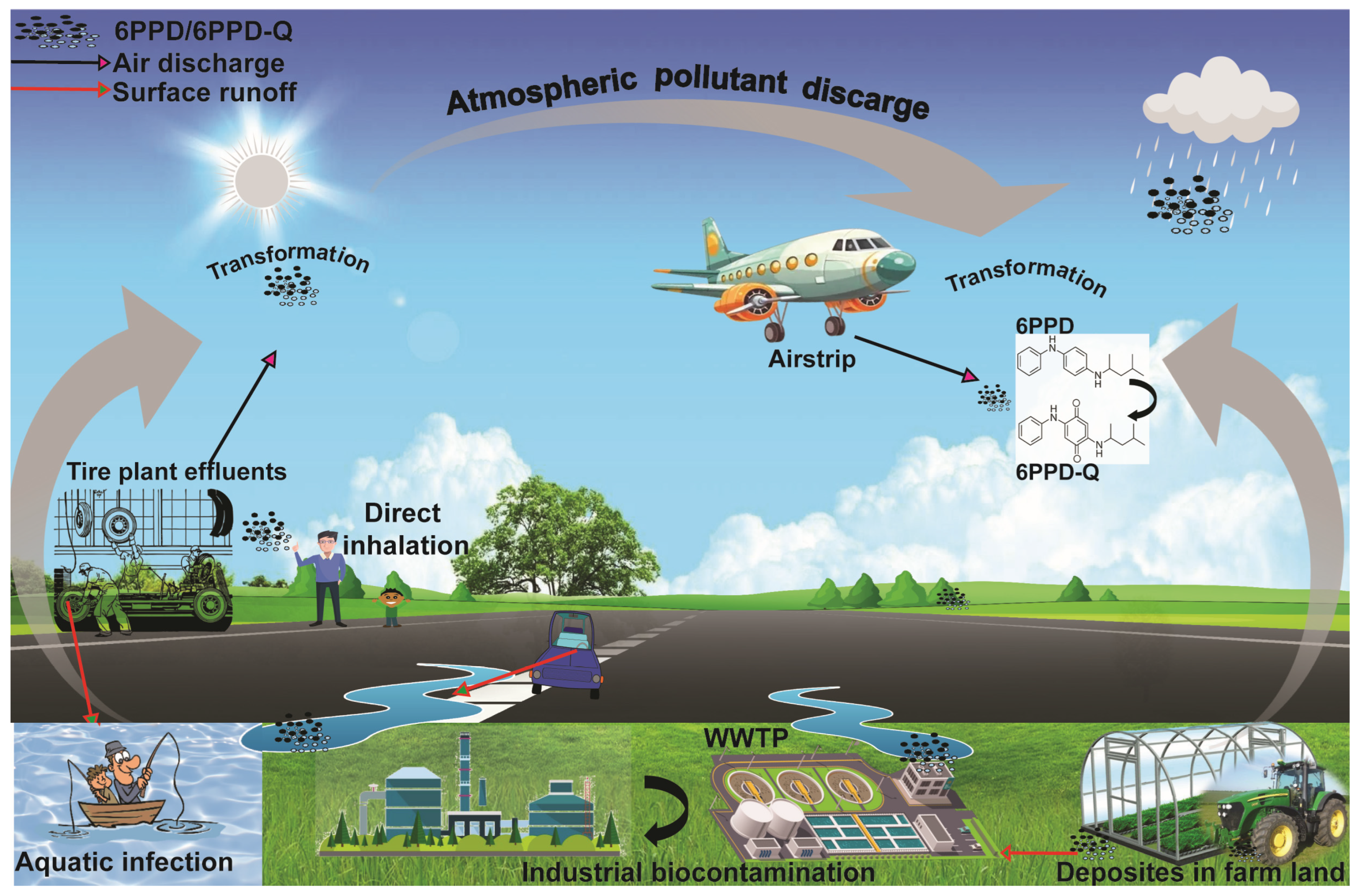
3.1. Sources of 6PPD in Urban Environments
3.2. Characteristics and Metabolism of 6PPD
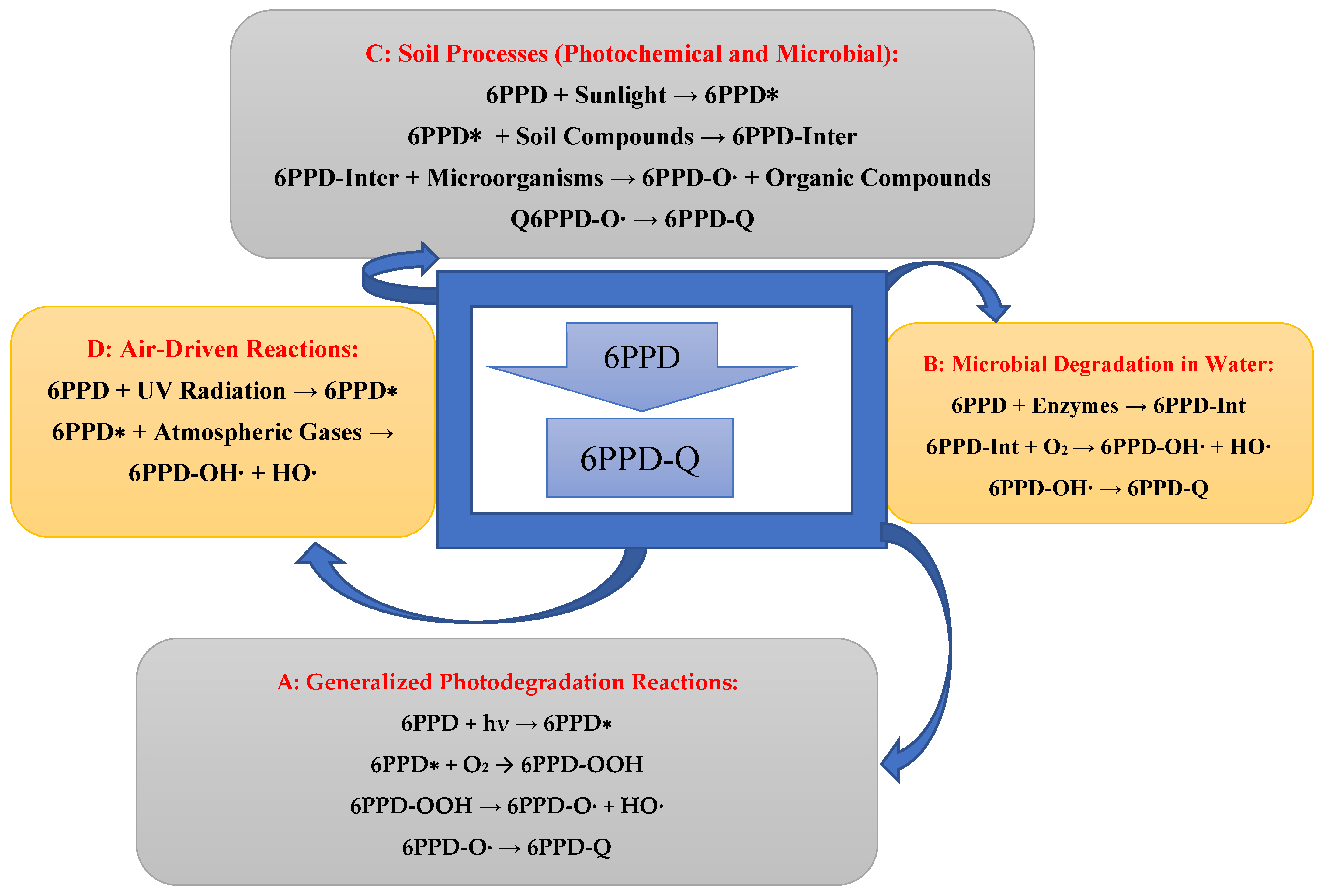
3.3. Formation of 6PPD-Q from 6PPD
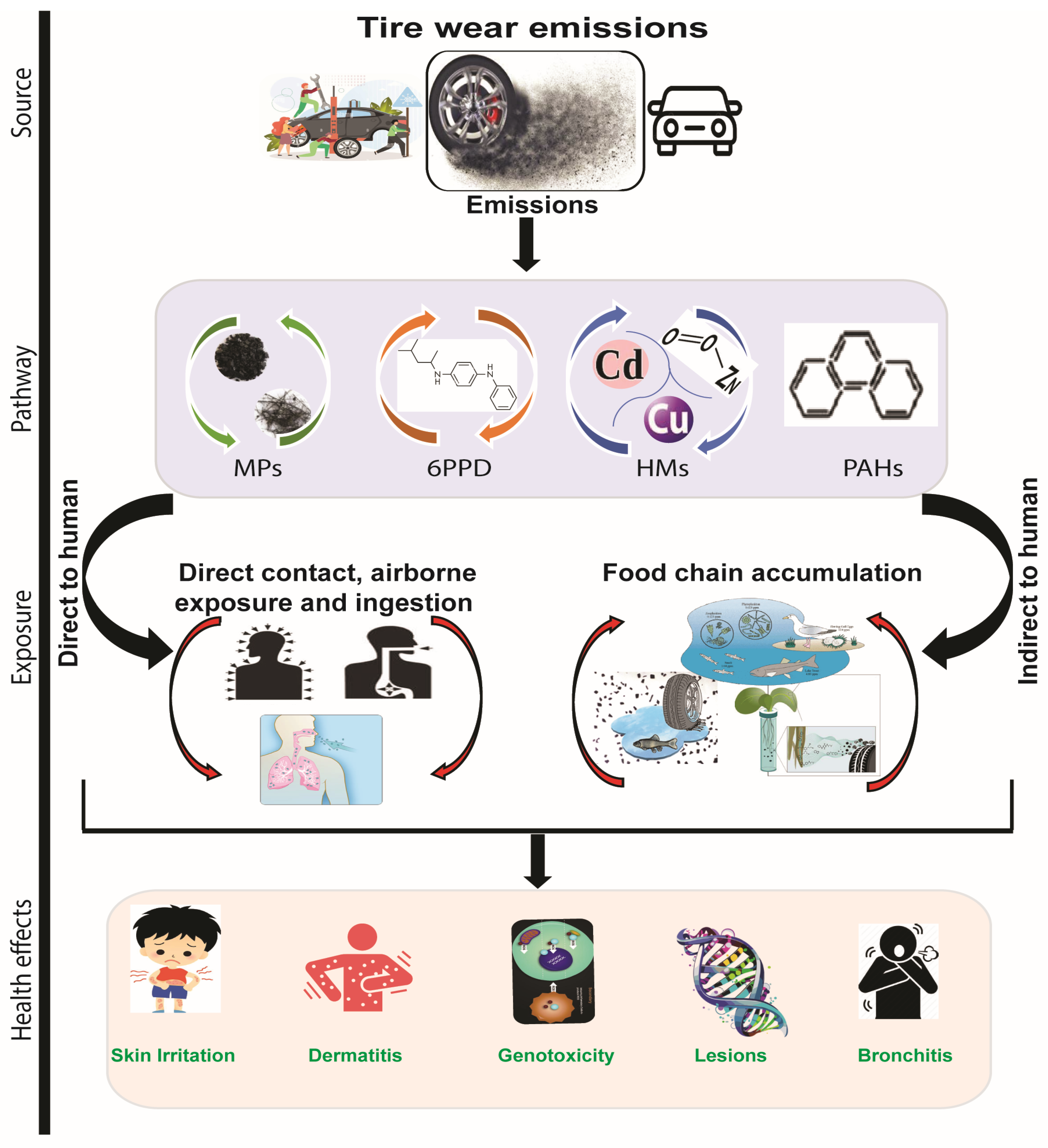
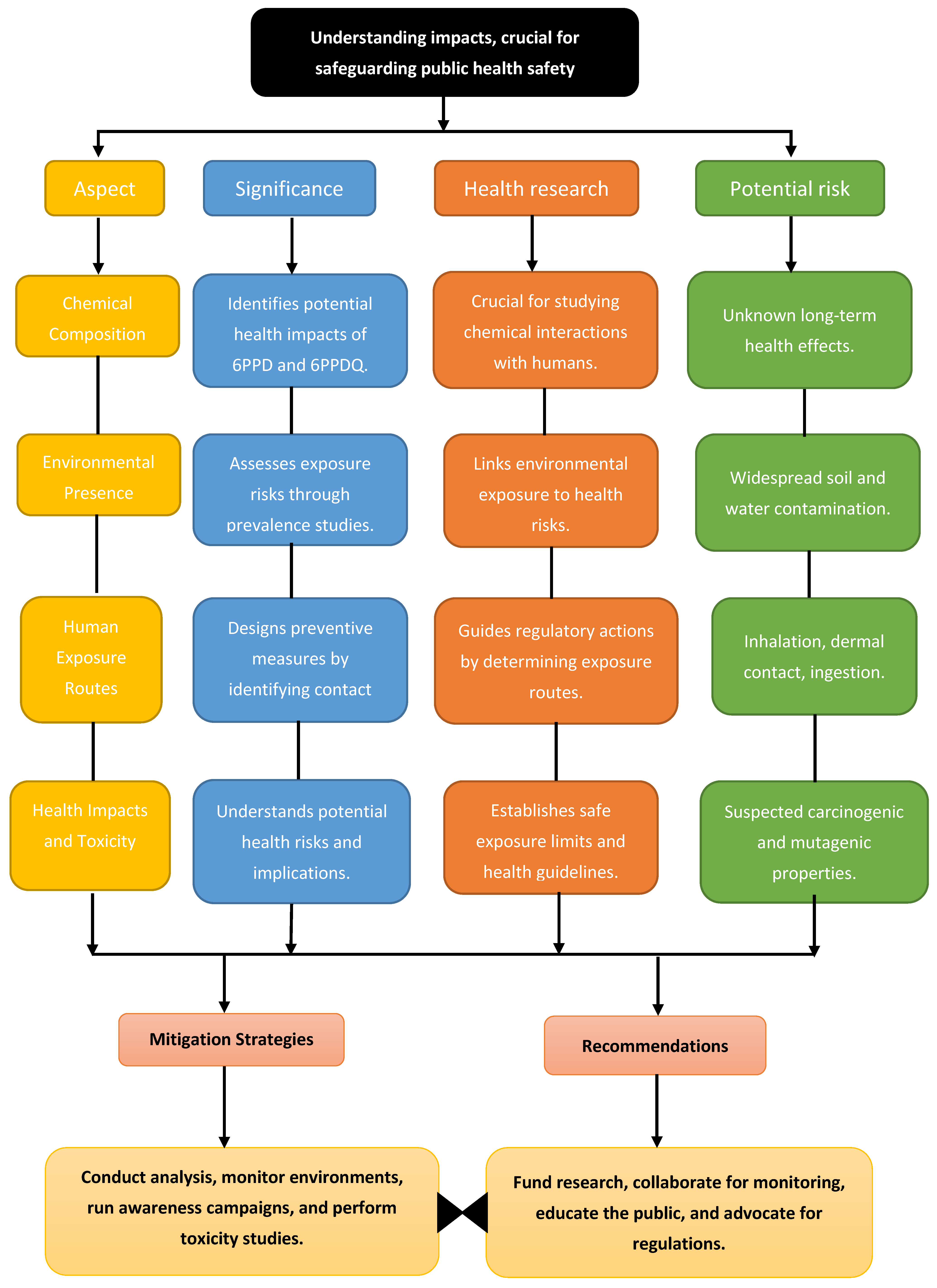
4. Human Exposure Pathways and Associated Health Risks
4.1. Potential Human Health Risk
Tire Wear Particles: A Cross-Domain Analysis of Ecological Impact
4.2. Routes of Exposure to Tire 6PPD-Derived Products
4.3. Occupational Exposure Consequences in Tire Manufacturing
4.4. Significance of Investigating Human Health Impacts
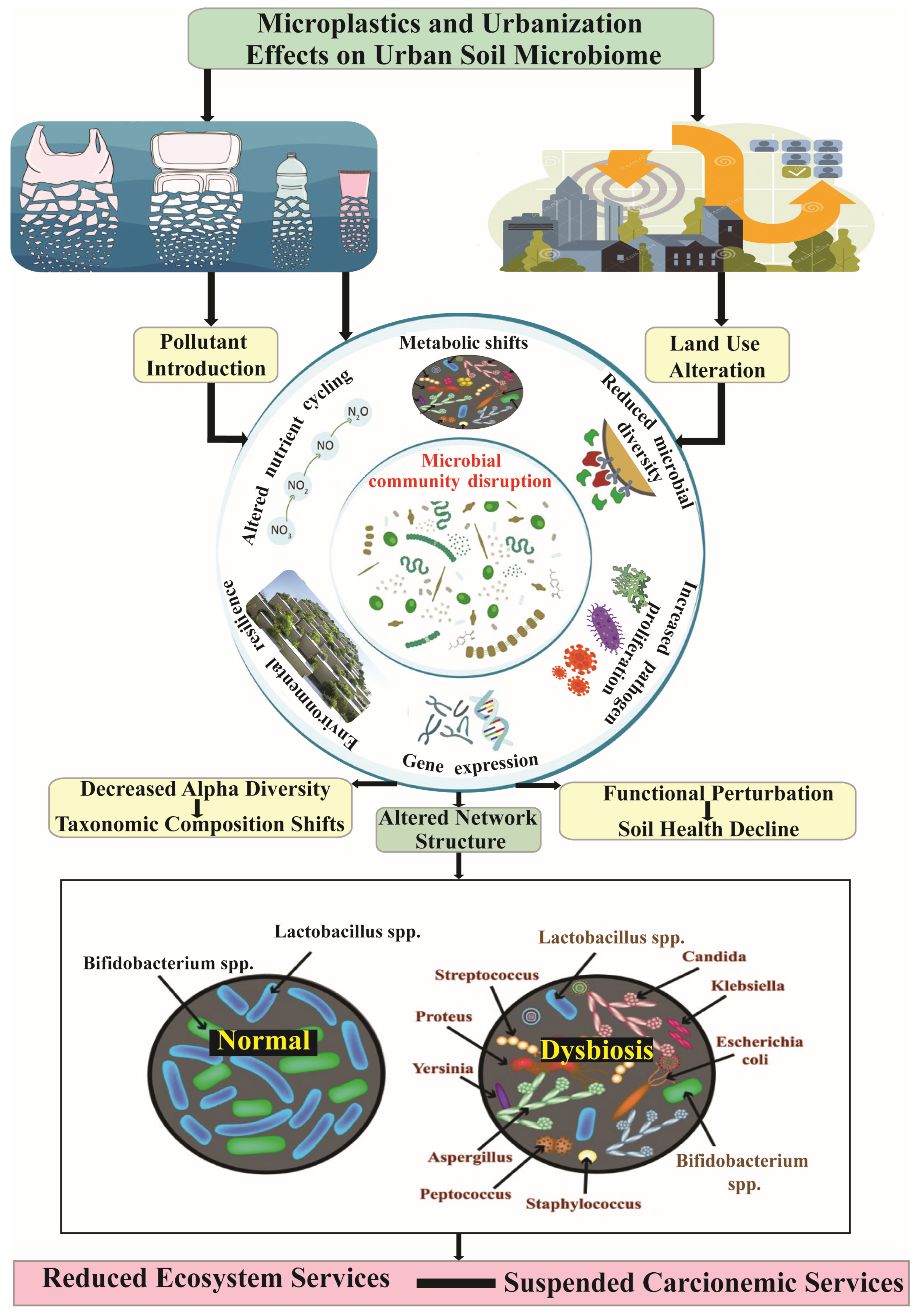
5. Role of Urban Soils and Tire Wear-Derived Pollutants in Ecosystem Services and Urban Environmental Resilience
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ihenetu, S.C.; Enyoh, C.E.; Wang, C.; Li, G. Sustainable urbanization and microplastic management: Implications for human health and the environment. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Kocher, B.; Altmann, K.; Braun, U. Determination of tire wear markers in soil samples and their distribution in roadside soil. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, R.; Subodh, K.M. Critical assessment of approach towards estimation of microplastics in environmental matrices. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2735–2749. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Urban Soils, Ecosystem Services, and the Application of Green Infrastructure Practices. 2025. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/water-research/urban-soils-ecosystem-services-and-application-green-infrastructure-practices (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Du, B.; Liang, B.; Li, Y.; Shen, M.; Liu, L.Y.; Zeng, L. First report on the occurrence of N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD) and 6PPD-quinone as pervasive pollutants in human urine from South China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, C.; Helm, P.; Metcalfe, C.D. Detection of selected tire wear compounds in urban receiving waters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødland, E.S.; Lind, O.C.; Reid, M.J.; Heier, L.S.; Okoffo, E.D.; Rauert, C. Occurrence of tire and road wear particles in urban and peri-urban snowbanks, and their potential environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiwert, B.; Nihemaiti, M.; Troussier, M.; Weyrauch, S.; Reemtsma, T. Abiotic oxidative transformation of 6-PPD and 6-PPD quinone from tires and occurrence of their products in snow from urban roads and in municipal wastewater. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Cao, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, P.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qi, Z.; Li, R.; Dong, C.; Cai, Z. Beyond substituted p-phenylenediamine antioxidants: Prevalence of their quinone derivatives in PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10629–10637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Kazmi, S.S.U.; Li, G. Tracking the biogeochemical behavior of tire wear particles in the environment—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Occurrence and effects of tire wear particles in the environment: A critical review and an initial risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihenetu, S.C.; Xu, Q.; Khan, Z.H.; Kazmi, S.S.U.H.; Ding, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, G. Environmental fate of tire-rubber related pollutants 6PPD and 6PPD-Q: A review. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Gonzalez, M.; Rideout, C.A.; Zhao, H.N.; Hu, X.; Wetzel, J.; Mudrock, E.; James, C.A.; McIntyre, J.K.; Kolodziej, E.P. 6PPD-quinone: Revised toxicity assessment and quantification with a commercial standard. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, D. Exposure to 6PPD quinone at environmentally relevant concentrations inhibits both lifespan and healthspan in C. elegans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 19295–19303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, J.; Ann-Margret, S.; Kerstin, M.; Hel’en, G.; Karin, B.; Maria, P.; Rita, G.; Anna, M.; Maria, A.; Mats, G.; et al. Traffic-related microplastic particles, metals, and organic pollutants in an urban area under reconstruction. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145503. [Google Scholar]
- Strungaru, S.A.; Jijie, R.; Nicoara, M.; Plavan, G.; Faggio, C. Micro-(nano) plastics in freshwater ecosystems: Abundance, toxicological impact, and quantification methodology. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossomme, E.; Hart-Cooper, W.M.; Orts, W.J.; McMahan, C.M.; Head-Gordon, M. Computational studies of rubber ozonation explain the effectiveness of 6PPD as an antidegradant and the mechanism of its quinone formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5216–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, R.; Zhou, S.; Xu, E.G.; Xing, B. Environmental occurrence, fate, impact, and potential solution of tire microplastics: Similarities and differences with tire wear particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bao, Z.; Wan, Z.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastic exposure disturbs hepatic glycolipid metabolism at the physiological, biochemical, and transcriptomic levels in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Shen, M.; Du, B. Widespread occurrence and transport of p-phenylenediamines and their quinones in sediments across urban rivers, estuaries, coasts, and deep-sea regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauschies, T.; Isanta-Navarro, J. The joint effects of salt and 6PPD contamination on a freshwater herbivore. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment: A review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate, and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, D.; Cai, Z. New evidence of rubber-derived quinones in water, air, and soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4142–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Huang, J.; Qi, Y.; Chen, D.; Huang, W. Distribution patterns of rubber tire-related chemicals with particle size in road and indoor parking lot dust. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, D.; Gao, R.; Ma, Y.; Pang, S.; et al. Exploration of emerging environmental pollutants 6PPD and 6PPDQ in honey and fish samples. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, M.; Montgomery, D.; Selinger, S.; Miller, J.G.P.; Stock, E.; Alcaraz, A.J.; Challis, J.K.; Weber, L.; Janz, D.; Hecker, M.; et al. Acute toxicity of the tire rubber-derived chemical 6PPD-quinone to four fishes of commercial, cultural, and ecological importance. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; Gonzalez, M.; Wetzel, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Prat, J.; Mudrock, E.; Hettinger, R.; et al. A ubiquitous tire rubber–derived chemical induces acute mortality in coho salmon. Science 2021, 371, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, D.; Duan, X.; Zhong, L. Exposure to N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD) affects the growth and development of zebrafish embryos/larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, S.; Gora, A.H.; Siriyappagouder, P.; Kiron, V.; Olsvik, P.A. Toxicological effects of 6PPD and 6PPD quinone in zebrafish larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, R.S.; Gillis, P.L.; Holman, E.A.M.; Schissler, D.; Ikert, H.; Toito, J.; Gilroy, E.; Campbell, S.; Bartlett, A.J.; Milani, D.; et al. Effect of substituted phenylamine antioxidants on three life stages of the freshwater mussel Lampsilis siliquoidea. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiki, K.; Asahina, K.; Kato, K.; Yamagishi, T.; Omagari, R.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Acute toxicity of a tire rubber-derived chemical, 6PPD quinone, to freshwater fish and amphibians. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, G. The spatio-temporal accumulation of 6PPD-Q in greenbelt soils and its effects on soil microbial communities. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 358, 124477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, C.; Han, D.; Ji, Z. Characterization and source identification of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in air in Xi’an: Based on a five-year study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, W.; Qi, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhu, L.; Dong, C.; Chen, J.; Cai, Z. Widespread N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine quinone in size-fractioned atmospheric particles and dust of different indoor environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)—A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 773, 145627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihenetu, S.C.; Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Li, G. Effects of biochar on tire wear particle-derived 6PPD, 6PPD-Q, and antimony levels and microbial community in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 491, 137951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.M.; Fiala, M.J.; Wade, T.L.; Park, D. Review of pollutants in urban road dust: Part II. Organic contaminants from vehicles and road management. Int. J. Urban. Sci. 2019, 23, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Tian, L.; Mo, Y.; Yi, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Aquatic environmental fates and risks of benzotriazoles, benzothiazoles, and p-phenylenediamines in a catchment providing water to a megacity of China. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; Gonzalez, M.; Wetzel, J.; Wu, C. Impact of 6PPD and 6PPD-Q on algal photosynthetic activity and growth in freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 310–320. [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen, C.; Metcalfe, C.D. The occurrence of tire wear compounds and their transformation products in municipal wastewater and drinking water treatment plants. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xiao, J.; Kiki, C.; Zhang, Y.; Manzi, H.P.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; Sun, Q. Unraveling the fate of 6PPD-Q in aquatic environment: Insights into formation, attenuation, and transformation under natural conditions. Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanie, C.; Anya, S.; Ruoting, P.; Michael, T.Z.; Wolfgang, W.; Thorsten, H.; Thilo, H. Uptake, metabolism, and accumulation of tire wear particle-derived compounds in lettuce. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 168–178. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, G.; Wang, F.; Ru, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J.; Xu, J.; et al. 6PPD-quinone exposure induces neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction to exacerbate Lewy neurites formation induced by α-synuclein preformed fibrils seeding. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangjian, Z.; Lacuo, Y.; Qingqing, K.; Jianglin, P.; Yanheng, P.; Junlang, Q.; Xin, Y. Sunlight-induced transformation of tire rubber antioxidant N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD) to 6PPD-quinone in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 798–803. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Men, Z.; Mao, H. Occurrence of benzothiazole and its derivatives in tire wear, road dust, and roadside soil. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, E.P. Chemical characteristics, leaching, and stability of the ubiquitous tire rubber-derived toxicant 6PPD-quinone. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2023, 25, 901–911. [Google Scholar]
- Fohet, L.; Andanson, J.M.; Charbouillot, T.; Malosse, L.; Leremboure, M.; Delor-Jestin, F.; Verney, V. Time-concentration profiles of tire particle additives and transformation products under natural and artificial aging. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Shi, Y.; Huang, J.; Deng, C.; Tang, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, D. Occurrence of substituted p-phenylenediamine antioxidants in dusts. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, W.; Qi, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhu, L.; Dong, C.; Chen, J.; Cai, Z. p-Phenylenediamine antioxidants in PM2.5: The underestimated urban air pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6914–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Fang, C.; Di, S.; Yundong, Y.; Caihong, W.; Xinquan, W.; Yuanxiang, J. Oral exposure to tire rubber-derived contaminants 6PPD and 6PPD-quinone induces hepatotoxicity in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Guo, H.; Cheng, T.; Li, X. Particle size distributions of oxidative potential of lung-deposited particles: Assessing contributions from quinones and water-soluble metals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6592–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castan, S.; Henkel, C.; Hüffer, T.; Hofmann, T. Microplastics and nanoplastics barely enhance contaminant mobility in agricultural soils. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mordechay, E.; Mordehay, V.; Tarchitzky, J.; Chefetz, B. Pharmaceuticals in edible crops irrigated with reclaimed wastewater: Evidence from a large survey in Israel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Gan, J. Uptake and metabolism of phthalate esters by edible plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8471–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sheng, G.; Chiou, C.T.; Xu, O. Relation of organic contaminant equilibrium sorption and kinetic uptake in plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4864–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.H.; Liu, C.H.; Sallach, J.B.; Hammerschmidt, R.; Zhang, W.; Boyd, S.A.; Li, H. Mechanistic study on uptake and transport of pharmaceuticals in lettuce from water. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.-H.; Hu, L.-X.; He, L.-Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhao, J.-L.; Ying, G.-G. Occurrence and risks of 23 tire additives and their transformation products in an urban water system. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, L.; Palmqvist, A.; Kampmann, K.; Khan, F.R. Ecotoxicology of micronized tire rubber: Past, present and future considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 706, 135694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zeb, A.; Fu, X.; Shi, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Sun, W.; et al. Environmental occurrence, fate, human exposure, and human health risks of p-phenylenediamines and their quinones. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Li, J.; Wan, X.; Ge, Y.; Liang, G.; Zhou, Y. P-phenylenediamine antioxidants and their quinone derivatives: A review of their environmental occurrence, accessibility, potential toxicity, and human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Schloter, M.; Roccotiello, E.; Weisser, W.W.; Schulz, S. Improving ecosystem services of urban soils—How to manage the microbiome of Technosols? Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1460099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lyu, H.; Guo, Y.; Man, Q.; Niu, H.; Li, J.; Jing, X.; Ren, G.; Ma, X. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polybrominated diphenyl ethers inside university campus: Indoor dust-bound pollution characteristics and health risks to university students. Build. Environ. 2022, 221, 109312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Lv, M.; Zhu, D.; Leifheit, E.F.; Chen, Q.-L.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Chen, L.-X.; Rillig, M.C.; Zhu, Y.-G. Tire wear particles: An emerging threat to soil health. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Property/Impact | Description | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | 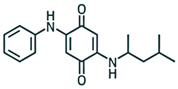 6PPD-Q (298.39) | 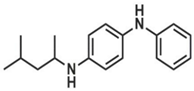 6PPD(268.40) | [27,43] |
| Chemical Formula | 6PPD: C18H24N2; 6PPD-Q: C18H20N2O2 | [27] | |
| Impact on Mice | Oral exposure to 6PPD and 6PPD-Q causes hepatotoxicity in mice, affecting hepatic metabolism and immune response | [44] | |
| Effect on Rubber Properties | Adding 0.5 wt % 6PPD to rubber improves thermal stability, lowers glass transition temperature, increases ionic conductivity | [27] | |
| Toxicity in Aquatic Life | 6PPD-Q is highly toxic to coho salmon and other fish species, causing acute mortality | [27] | |
| Environmental Occurrence | 6PPD and 6PPD-Q are commonly found in urban watersheds | [6,20] | |
| Photodegradation Pathway | 6PPD undergoes photodegradation to form 6PPD-Q when exposed to sunlight in water | [45] | |
| Bioaccumulation Potential | 6PPD-Q has been shown to bioaccumulate in aquatic organisms, leading to long-term exposure risks | [20] | |
| Persistence in Soil | 6PPD and 6PPD-Q persist in roadside soils, with slow degradation due to low microbial activity | [46] | |
| Oxidative Stress Induction | 6PPD-Q exposure induces oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in aquatic organisms | [39] | |
| Impact on Algae | 6PPD and 6PPD-Q reduce algal photosynthetic efficiency and impair growth | [40] | |
| Effects on Amphibians | Exposure to 6PPD-Q disrupts reproductive hormones and impairs development in amphibians | [31] | |
| Transformation in Air | 6PPD can form secondary pollutants like quinones when exposed to atmospheric oxidants | [34] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ihenetu, S.C.; Xu, Q.; Fang, L.; Azeem, M.; Li, G.; Enyoh, C.E. 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone in the Urban Environment: Assessing Exposure Pathways and Human Health Risks. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9060228
Ihenetu SC, Xu Q, Fang L, Azeem M, Li G, Enyoh CE. 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone in the Urban Environment: Assessing Exposure Pathways and Human Health Risks. Urban Science. 2025; 9(6):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9060228
Chicago/Turabian StyleIhenetu, Stanley Chukwuemeka, Qiao Xu, Li Fang, Muhamed Azeem, Gang Li, and Christian Ebere Enyoh. 2025. "6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone in the Urban Environment: Assessing Exposure Pathways and Human Health Risks" Urban Science 9, no. 6: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9060228
APA StyleIhenetu, S. C., Xu, Q., Fang, L., Azeem, M., Li, G., & Enyoh, C. E. (2025). 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone in the Urban Environment: Assessing Exposure Pathways and Human Health Risks. Urban Science, 9(6), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9060228






