Abstract
The catchment area of River das Antas (Irati, Paraná, Brazil) is of high importance both for human consumption and irrigation. Within Irati, this river passes through a rural area and through the city of Irati, crossing both poor and rich neighbourhoods. We selected three study areas downstream (a rural area, poor community, and rich neighbourhood) in which we measured turbidity, the concentration of sediments and pH during rainy days. Our results showed downstream trends of increasing turbidity and concentrations of sediments with decreasing pH. The values of turbidity and of concentration of sediments were significantly different in the rural area, while the pH values were significantly different between the three study areas. These findings highlight the effect of agricultural activities in the generation of sediments and turbidity. The—presumably expected—effects of organic urban waste from the poor neighbourhood were also detected in the pH values. We conclude that efforts should be made to ensure that land planning and training/education programmes on sustainable farming practices are undertaken by the authorities to reduce water pollution and its effects on water bodies during rainfall events, since paving streets is not a feasible option in the short term due to the high costs associated with this measure.
1. Introduction
The municipality of Irati (Paraná, Brazil) is a relatively recent urban settlement (officially created in 1907 by European immigrants). The region in which the city of Irati is located was mainly occupied by disperse settlements of Europeans (Ukrainian, Polish and German) immigrants in the 19th century [1]. They established small farms well-adapted to low-fertility soils, mountainous terrain and Araucaria forest, which led to the formation of a particular agrosilvopastoral land system known as faxinal (of great importance in the south of Paraná). The difficulty to travel to important urban settlements in which inhabitants could buy tools and sell their products was one of the main reasons for the official birth of the city (Law no. 716 of the State of Paraná) [2]. Over the last century, the city has increased in size significantly, and its economy has diversified in multiple ways giving rise to the occurrence of poor and rich neighbourhoods as well as rural areas around the city. Nowadays, agriculture still represents the main economic activity around the waters of the River das Antas, whose springs are located within Irati’s territory [3].
At the beginning of the 20th century, Irati was involved in two important economic cycles linked to the production of two important primary products: yerba mate and timber. Some timber companies were established in the area and Irati became one of the most important centres of production and commercialization of timber in the whole of Brazil during the decades of 1940 and 1950 [4]. After the decline in prices of yerba mate and timber, the primary sector in the area moved to the production of potatoes, wheat and onions, making Irati a major producer of these crops. In the decade of 1970, the cultivation of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) arrived and it has since brought a significant economic input, nowadays being the most—or one of the most—important agricultural activities in many farms. In following decades, the profitability of these agricultural products was reduced, and many people that lived in rural areas until the 1970s eventually started to move to urban areas (Table 1).

Table 1.
Changes in Irati’s urban/rural population in decade time-steps (official census data).
According to Braga Moruzzi et al. [5], a significant part of the irregular settlements of the State of Paraná (mostly poor neighbourhoods) have been built in permanent, protected areas, as established/designated by federal laws. Often, agriculture and urban sprawl underpin the violation of laws for environmental protection in Parana. According to the federal Law no. 7803, the protection zone of a river is proportional to its width and it varies if the river passes, or does not pass, through an urban area [6]. For instance, a river of 10 m width can have a permanent protected zone of 30 m in width. In the case of urban rivers, such as the River das Antas that passes through Irati, this protected zone is set to 15 m, as an exception set for public reasons agreed by local, regional and federal authorities. Venancio et al. [7] found that almost 70% of the permanent protected area of the River das Antas has already been altered.
Irati is crossed by several rivers that belong to three major basins: Iguaçu, Ivaí and Tibagi. However, the River das Antas can be considered as the only urban river. Issues of water quality of these rivers have been directly or indirectly examined and studied by local researchers [8]. For instance, Venancio et al. [7] highlighted the impact of the removal of the riparian forest of the River das Antas due to urban sprawl as a driver that has led to the deterioration in water quality. Accordingly, Tomazzoni Lubenow et al. [9] conducted a detailed study on the water quality of the Nhapindazal River (20% of the urban area, three neighbourhoods) and they also concluded that recent changes in land use are the main causes of water pollution. The effects of changes in land use/cover on water quality represent a topic widely addressed by the scientific community, under many different climatic conditions [10]. For instance, Genxu et al. [11] found indications of eutrophication in arid areas of China induced by the conversion of grasslands into croplands. Wijesiri et al. [12] highlighted the importance of irrigated plantations and the lack of conservation in natural environments as two prominent causes of nutrients leaching to water courses.
Tudela Haberland et al. [13] provided a deep knowledge on the parameters of water quality, as well as on the effects of the urban stretch of the River das Antas, but the rural areas have been neglected. In this respect, and in the present work, we provide a full year’s worth of monitoring data for three basic parameters. Our main goal was to describe how the water quality of River das Antas changes spatially downstream, as it passes through a rural area of intensified agriculture and a poor neighbourhood. In addition, we assessed how water quality changes monthly during a representative year (not biased by droughts or exceptional rainfall events). Our hypothesis is that agriculture is the main driver increasing the turbidity of the river waters and that uncontrolled urbanisation seriously affects the water chemical quality (expressed by pH). Regarding temporal changes of these parameters within the year, we hypothesise that water parameters follow a stable to moderate pattern; based on the fact that Irati belongs to a climatic zone with a uniform temporal pattern in rainfall (monthly amounts are regularly distributed throughout the year).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study was carried out in the municipality of Irati (southern part of the State of Paraná, Brazil) (Figure 1). Its geographical location is 25°28′01″S, 50°39′03″W with an average elevation of 812 m and at a distance of 156 km east of Curitiba (the capital of the State of Paraná). Its size is 156 km2 and its estimated population is 60,000 inhabitants (2016), of which, more than 75% live in the urban area. Its climate is (mesothermic) humid subtropical (Cfb, Köppen classification) without a well-defined dry season [9]. The municipality is located in the so-called Second Plateau of Paraná or Ponta Grossa Plateau on basalt rocks, more specifically in the geomorphological unit known as Paraná basin (a large cratonic sedimentary basin) [14]. The dominant vegetation is mixed ombrophilous forests composed mostly by Araucaria angustifolia. The municipality of Irati is located on three major river basins (Iguaçu, Ivaí and Tibagi), but the River das Antas (tributary of the Tibagi River) is the only one that crosses the urban area (13 km length).
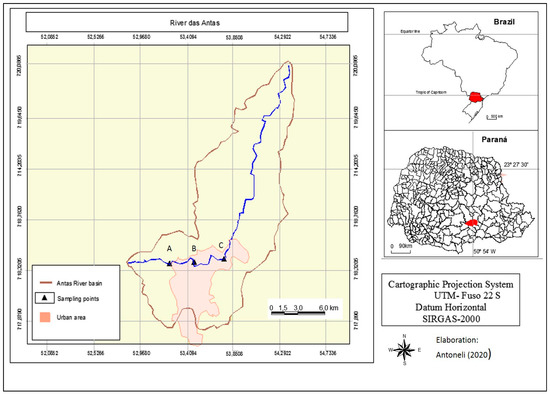
Figure 1.
Geographical location of the study area. A: rural area, B: poor community (effects of agriculture), C: rich neighbourhood (combined effects of agriculture and urban sprawl); water flows from point “A” (higher elevations) to point “C” (lower elevations).
2.2. Water Sampling and Analysis
Water samples were collected from 12 sampling points (4 sampling points × 3 areas, following the transversal section of the river) within three areas distributed downstream throughout the river in its passing through the municipality of Irati (see Figure 1) [15]. The first area (point A in Figure 1) was selected in the upper course, where 85% of land is agricultural fields (at the beginning of the urban area). The second one (point B in Figure 1) was placed in an area which receives water that drains from a poor neighborhood. Finally, the third sampling area (point C in Figure 1) was chosen in the final section of the urban area (the most developed). The time of collection was during the typical rainy days (1 day per month, rainfall >25 mm, previously foreseen by the meteorological services) in 2018. We only collected samples when the water level of the river exceeded the usual height/level to obtain a flow rate above 3 m3 s−1 (we installed metric tapes in each area) [16].
In each sampling point we filled up 5 (plastic) buckets of 20 litres totaling 60 samples per month and 720 samples in the whole year. Two aliquots of 0.5 litres were extracted onsite from each sample of 20 litres to calculate the concentration of sediments, turbidity and pH in the laboratory [17]. In the laboratory, after 1 h from sampling sub-samples were stirred prior to measuring [18]. The concentration of sediments (expressed in g L−1) was calculated by using the evaporation method [15]. The samples were placed in glass containers (previously weighed), well-identified and oven-dried at 105°C for 24 h. After this, the glass containers were weighed again. The final value was calculated as: (total dry weight − glass container weight)/2 [19]. The turbidity was determined by using three sub-samples of 10 mL (maximum capacity of the turbidimeter model HI93703) within glass containers of different sizes and the average of the three subsamples was calculated [20]. The pH was estimated by using a portable pHmeter [21].
2.3. Data Analysis
The dataset was composed by 720 cases/replicates (water samples collected monthly belonging to 3 areas × 4 sampling points per area × 5 samples collected in each point × 12 months) of 3 variables, i.e., turbidity, concentration of sediments, and pH. In addition, daily rainfall and flow rate at the time of sampling was also estimated in order to better understand the potential temporal patterns. Data were averaged both per month and per sampling area. The mean values between study areas were compared by means of the F test, and p (ANOVA) was used to determine whether there were any statistically significant differences between the means of the three connected study areas. In addition, a post-hoc Fisher LSD (Least Significant Difference) test (p < 0.05) was used to identify significant homogenous groups. The statistical procedure was made by using the software package Statistica version 6.0 [22]. The monthly minimum and maximum values of each parameter are discussed and their temporal patterns are explored.
3. Results
3.1. Turbidity
An increasing trend downstream of mean values of turbidity between the three sampling areas was clearly observed, although the two urban areas (poor and rich neighbourhoods) were significantly statistically homogenous (Figure 2). The lowest mean value was observed in the rural area (131.8 ± 31.2 NTU, Nephelometric Turbidity Units) and the highest ones were observed in the points where the river passes through the rich neighbourhood (189.3 ± 33.8 NTU). At the points where the river passes through the poor neighbourhood, the mean value of turbidity was 164.6 ± 33.7 NTU. Regarding data variability, the standard deviation of the three groups was about 30 NTU, corresponding mostly to the temporal variability of the parameter. The statistics of Kruskal–Wallis and F test, p (ANOVA) also showed significant differences between three sets of groups compared.
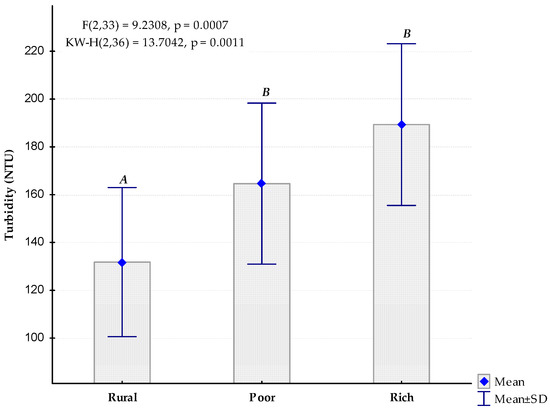
Figure 2.
Comparison of mean values of turbidity (all monthly values included per site) between the three study areas. The same letters indicate non-different homogenous groups according to the post-hoc LSD-Fisher test (p < 0.05).
3.2. Concentration of Sediments
The sediment concentration values had a behavior downstream similar to that of turbidity (Figure 3). Similarly, the two samples from the urban areas also showed statistical homogeneity between them and significant differences with the rural area. The mean values ranged from 8.7 g L−1 recorded in the rural area, to 12.3 g L−1 observed in the rich neighbourhood.
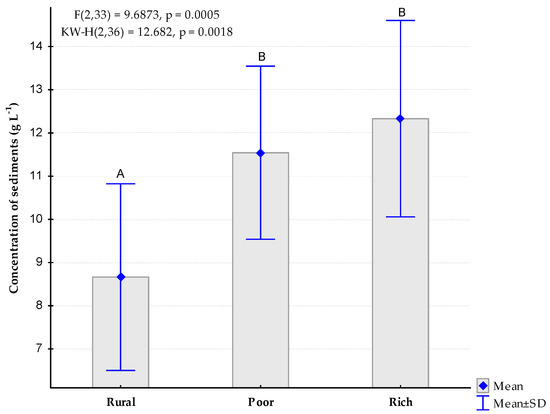
Figure 3.
Comparison of mean values of concentration of sediments (g L−1) between the three study areas. Same letters indicate non-different homogenous groups according to the post-hoc LSD-Fisher test (p < 0.05).
3.3. Water Acidity (pH)
A decreasing trend downstream of the mean values of pH between the three sampling areas was observed (Figure 4). Fisher’s LSD test indicated three different statistically homogenous groups. The mean values ranged from 5.4 in the rich neighbourhood to almost 6.4 in the rural area, with similar levels of data variability (standard deviation) equal to approximately 0.4. The highest difference in mean values was observed between the rural area and the poor neighbourhood (reduction in pH by 0.7).
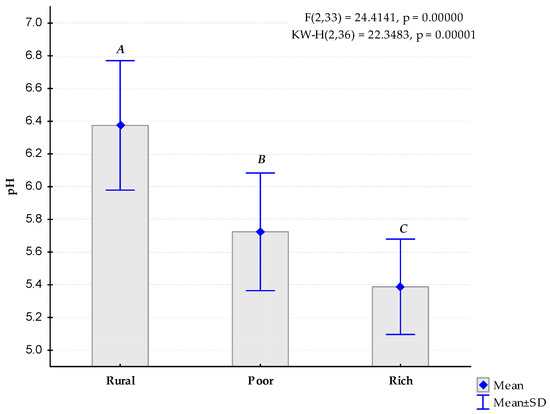
Figure 4.
Comparison of mean values of pH between the three study areas. Letters indicate statistically different homogenous groups according to the post-hoc LSD-Fisher test (p < 0.05).
3.4. Temporal Patterns by Month
The total monthly rainfall varied from 25.4 mm (April) to 52.0 mm (July), generating a flow rate between 3.2 m3 s−1 (April, December) and 3.7 m3 s−1 (May, July). Both variables were highly correlated (r = 0.904, p < 0.001). Regarding turbidity (Figure 5) and the concentration of sediments (Figure 6), the maximum values were recorded in March (cultivation of soya ends in February and of potato in March), and in September (cultivation of tobacco) matching with the lowest pH values (Figure 7). The concentration of sediments was reduced when the area received lower levels of rainfall (r < −0.650, p < 0.05).
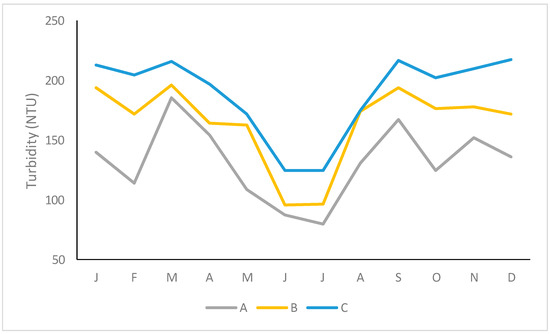
Figure 5.
Temporal variability of turbidity. A: rural area, B: poor community, C: rich neighbourhood.
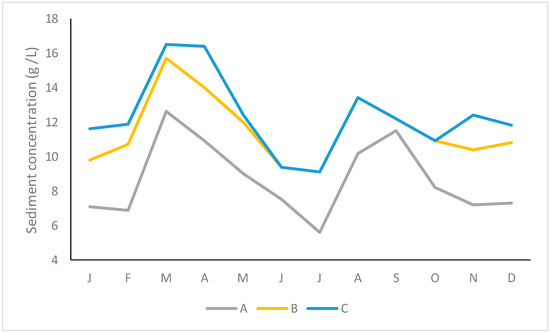
Figure 6.
Temporal variability of sediment concentration. A: rural area, B: poor community, C: rich neighbourhood.
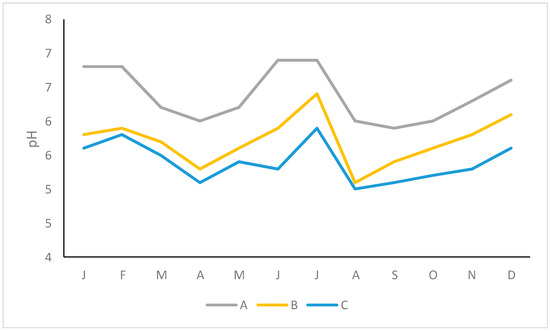
Figure 7.
Temporal variability of pH. A: rural area, B: poor community, C: rich neighbourhood.
4. Discussion
Our findings provide evidence for a noticeable contribution of agricultural activities in terms of water pollution, as indicated by a high concentration of sediments and a remarkable reduction in water pH, presumably catalysed by the untreated urban waste from the poor neighbourhoods. The most reasonable causes that lead to these negative effects on water quality include the intensification of agriculture and urban sprawl that have altered land use in areas adjacent to the river course (removal of around 70% of the former riparian forests) that are permanently protected areas according to the federal legislation (Law no. 7803 enacted on 18 July 1989), i.e., farmers are cropping and citizens are building their houses too close to the course of the river [7]. Therefore, efforts aimed at promoting sustainable farming practices via teaching/education programmes, mainly for farmers, could be a feasible option to combat this issue.
As a consequence of the agricultural activities, the pH values do not reach the required minimum value of 6.0, as set as the minimal threshold by the federal law of the CONAMA (Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente, National Environmental Council) no. 357/2005, i.e., this water is no longer drinkable after its passes through the adjacent rural area. The turbidity also exceeded the 100 NTU value, proposed as the maximum threshold by CONAMA, in the three study areas. Such detrimental effects are often observed in riparian zones where man-made activities take place [11]. Nevertheless, turbidity must be also assessed on a sunny day without rainfall effects in order to compare the real range of changes in values. In fact, Tomazzoni Lubenow et al. [9] consistently found turbidity values below 100 NTU in the Nhapindazal River because they collected samples on sunny days. On the one hand, the effects of turbidity associated with soil erosion can provoke undesired consequences downstream, such as reservoir silting, eutrophication, etc. On the other hand, Irati is located in a climatic area where rainfall events are quite regular, and so rainy days are common in this type of environment, a fact which provides further reasoning to conduct our methodology of collecting samples on rainy days.
Our results can be also compared to other similar studies conducted around the world. For instance, Gatica et al. [23] analysed the water quality of the Chocancharava River (Córdoba, Argentina) and they found average values of turbidity in the wet season of 130.6 NTU, although a great deal of data variability was observed (SD: 102.8). Al Bakri et al. [24] studied the effects of storm water runoff in the orange urban catchment (New South Wales, Australia), finding moderate to high levels of pollution, in spite of being situated at the headwater of its river system (minimally affected by agriculture). According to Sargoankar and Deshpande [25], all these values should be considered as slightly polluted. In fact, Shukla et al. [26] have not found values of turbidity so high even under post-monsoon conditions in India.
The effects of the river passing through a poor neighbourhood with more than 40% of streets being unpaved are depicted in the pH values. Agricultural residuals (manure, fertilizers, and pesticides) usually result in decreases in pH, but in urban areas these are accompanied with domestic waste. The “black waters” from animals (slurries) and from houses (untreated) can be a serious problem in terms of water pollution due to the proliferation of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli [27,28,29,30]. In fact, Tomazzoni Lubenow et al. [9] have already detected the presence of E. coli in the Nhapindazal River, particularly in the part where water is collected for human consumption in some neighbourhoods of Irati. These pessimistic findings are in accordance with the results reported by Tudela Haberland et al. [13] for the urban stretch of the River das Antas.
The historical conversion of the municipality of Irati from a predominant rural area of low agrochemical input to an urban one, and the progressive occurrence of neighbourhoods with poor infrastructure can be explained by economic causes. These include the reduction in labour force in farmlands due to mechanization, in addition to many owners of small farms being made bankrupt due to them not being able to adapt their farms to remain competitive. The low level of economic development has led to problems of unemployment and a lack of services. Many of these people “expulsed” from the rural areas, have progressively moved to neighbourhoods away from the central city complex, in which there is no efficient sewage system, paved streets, or regular and selective garbage collection service, among many other additional environmental threats caused by the lack of sustainable land planning.
Wang et al. [31] analysed the effects of a rapid urbanization on surface water quality in rural, semi-urban and urban areas of the Chinese city of Shanghai from 1982 to 2005. They found levels of pollution (assessed by their integrated pollution index) to be much lower in the rural areas than in the semi-urban and urban areas. In fact, only the rural areas maintained levels below the standard value suggested by the Chinese standard protocols. In line with this, Mouri et al. [32] also found high levels of phosphorous in an urban catchment in Shikoku (Japan) as a consequence of agricultural activities. Even, in countries such as the United Kingdom, where rainy days are usual, McGrane et al. [33] found values of turbidity above 1000 NTU as a consequence of winter storms in a rural–urban catchment.
The expansion of soybean (Glycine max) cultivation in the whole Brazil in the last 50 years has been interpreted by many authors as posing a serious threat to both the sustainability of traditional agriculture and to the preservation of protected areas [34], and Paraná is not an exception [35]. However, some agroecological practices have also been proposed [36]. In Irati agricultural areas, soybean is planted annually in October, after several months during which soils are covered with oat (Avena strigosa), usually used for grazing and as protection against soil erosion. Soybean is harvested in February or March, depending on the year [37], and potatoes (as alternative crop) in March [38]. The cultivation of tobacco also demands land with uncovered soil. It is cultivated in September, after the coldest months, in attempt to benefit from the natural hot and regular rainfall (it does not need irrigation in this part of the world) [39], although the highest soil erosion rates have been detected in summer during the harvesting period [40].
Another aspect not contemplated by this research, but that should be considered both by stakeholders and scientists, is the reduction in biodiversity as a progressive consequence of the declines in the riparian forest [41,42]. Therefore, it would be convenient to carry out initiatives that make the population aware of this problem and its consequences. Nevertheless, some experiences have already been gained from efforts to restore degraded areas, with a certain level of success [43,44]. One of the most well-known initiatives has been the Riparian Forest Programme (Programa Mata Ciliar in Portuguese) applied in the whole country at the beginning of the 21st century. Araújo [45] studied the effects of this programme specifically in the whole State of Paraná. Officially, an area of more than 60,000 ha was restored by direct seeding (33,775 ha), fencing (5053 ha) and abandonment of agricultural activities (25,696 ha). Other authors have also studied the application of this programme at a municipal scale [46].
5. Conclusions—Policy Implications
The water quality of the River das Antas in the municipality of Irati, Paraná, Brazil, has been progressively declining as a consequence of—mainly—the agricultural activities in its upper course, particularly during the months of February, March and September, when the oat grass cover is removed for the cultivation of soybean, potato and tobacco. The effects of poor land planning are also evident in the low values of river water pH at the point where the water exits the urban area. The water of the River das Antas is currently not drinkable according to the CONAMA standards, while there are additional environmental problems that affect the integrity of the system. Furthermore, the laws on the conservation of riparian forests are not being respected in many circumstances. We encourage the municipality of Irati to increase its efforts to effectively restore and conserve the riparian forest in accordance with the federal and local laws, in order to improve the water quality and meet the adequate standards. Public investment to improve the living conditions of the poor neighbourhoods, such as the construction of paved streets, selective garbage collection services and improvements in the sewage system is also needed. In addition, training/education programmes focused on sustainable farming practices that promote riparian forest conservation could be very helpful in combating these issues. We hope this work can be of use to the municipality of Irati and land planners within the region. In case some related policies are implemented, a pre/post assessment of the effects of the adopted measures is considered to be essential.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.A. and J.A.B.; methodology, V.A.; software, L.B.; validation, M.V., J.L.-P. and R.G.-M.; formal analysis, M.P.-F.; investigation, V.A.; resources, L.B.; data curation, J.A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.P.-F.; writing—review and editing, M.V. and Y.K.; visualization, J.A.B.; supervision, R.G.-M.; project administration, V.A.; funding acquisition, V.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study did not involve humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this article are not available on Internet. Nevertheless, they can be consulted upon request to the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thanks to the Research Project IB16052 cofounded by the Regional Government of Extremadura and the European Fund of Rural Development for its methodological support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rudek, C.M. A Cultura Ucraniana e Polonesa em Irati; Gráfica Darte: Irati, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Orreda, J.M. História de Irati; Edipar: Route Jarzé, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha de Freitas, A. Identificação de áreas potencializadoras de inundações e enxurradas: Uma proposta metodológica aplicada na Bacia Arroio dos Pereiras, Irati PR. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Estadual de Ponta Grossa, Ponta Grossa, Brazil, 2018; p. 150. [Google Scholar]
- Prefeitura de Irati. Plano Diretor Municipal de Irati; Prefeitura de Irati: Irati, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Braga Moruzzi, R.; Braga, R.; Lupinaccida Cunha, C.M. Proposta de roteiro para coleta de dados visando diagnóstico da drenagem urbana em planos diretores municipais. Ambiência 2009, 5, 523–536. [Google Scholar]
- Governo Federal do Brasil. Lei n° 7.803, de 18 de Julho de 1989. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/l7803.htm (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Venancio, D.L.; Costa de Oliveira Filho, P.; Disperati, A.A. Uso do geoprocessamento em estudo ambiental na bacia hidrográfica do rio das Antas, Irati (Paraná). Ambiência 2010, 6, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro de Andrade, A.; Felchak, I.M. A poluição urbana e o impacto na qualidade da água do Rio das Antas-Irati/PR. Geoambiente Line 2009, 12, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tomazzoni Lubenow, A.; Costa de Oliveira Filho, P.C.; Magno de Sousa Vidal, C.; Soares Cavallini, G.; Caldeira Canterle, Y. Impacto do uso e ocupação da terra na qualidade da água da bacia hidrográfica do rio Nhapindazal, Irati (PR). Ambiência 2012, 8, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; López-Vicente, M.; Kumar, V.; Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Valkó, O.; Rojas, C.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Salvati, L.; Bakr, N.; Vaudour, E.; et al. Soil Science challenges in a new era: A transdisciplinary overview of relevant topics. Air Soil Water Res. 2020, 13, 1178622120977491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genxu, W.; Haiyan, M.; Ju, Q.; Juan, C. Impact of land use changes on soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus and water pollution in an arid region of northwest China. Soil Use Manag. 2004, 20, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesiri, B.; Deilami, K.; Goonetilleke, A. Evaluating the relationship between temporal changes in land use and resulting water quality. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudela Haberland, N.; Berger Silva, F.C.; Costa Oliveira Filho, P.; Magno de Sousa Vidal, C.; Soares Cavallin, G. Análise da influência antrópica na qualidade da água do trecho urbano do Rio das Antas na cidade de Irati, Paraná. Rev. Tecnológica 2012, 21, 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Milani, E.J.; Zalán, P.V. An outline of the geology and petroleum systems of the Paleozoic interior basins of South America. Int. Union Geol. Sci. 1999, 22, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, N.O. Hidrossedimentologia Prática; CPRM: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Palhares, J.C.P.; Ramos, C.; Klein, J.B.; de Lima, J.; Muller, S.; Cestonaro, T. Medição da Vazão em Rios Pelo Método do Flutuador; EMBRAPA Suínos e Aves-Comunicado Técnico (INFOTECA-E): Concórdia, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lawler, D.M. Spectrophotometry: Turbidimetry and nephelometry. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 343–351. [Google Scholar]
- Rainwater, F.H.; Thatcher, L.L. Methods for Collection and Analysis of Water Samples; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1960.
- Claessen, M.E.C. Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solo; EMBRAPA Solos: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna Instruments. Instruction Manual HI 93703 Portable Microprocessor Turbidity Meter; Sarmeola di Rubano: Padova, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Fundação Nacional de Saúde. Manual Prático de Análise de Água; FUNASA: Brasília, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Statsoft. Statistica 6.0. Statistic for Windows; Statsoft: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gatica, E.A.; Almeida, C.A.; Mallea, M.A.; Del Corigliano, M.C.; González, P. Water quality assessment, by statistical analysis, on rural and urban areas of Chocancharava River (Río Cuarto), Córdoba, Argentina. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 7257–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlBakri, D.; Rahman, S.; Bowling, L. Sources and management of urban stormwater pollution in rural catchments, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2008, 356, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargaonkar, A.; Deshpande, V. Development of an overall index of pollution for surface water based on a general classification scheme in Indian context. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2003, 89, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Gedam, S.; Khire, M.V. Implications of demographic changes and land transformations on surface water quality of rural and urban subbasins of Upper Bhima River basin, Maharashtra, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 129–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.; Humphrey, C.; O’Driscoll, M. Transport of indicator microorganisms from an on site waste water system to adjacent stream. Univers. J. Environ. Res. Technol. 2013, 3, 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- Brandes, M. Characteristics of effluents from gray and black water septic tanks. J. Water Pollut. Control. Fed. 1978, 2547–2559. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, S.; Paterson, E.; Withers, P.J.; Stutter, M. Septic tank discharges as multi-pollutant hotspots in catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinten, A.; Lewis, D.; Fenlon, D.; Leach, K.; Howard, R.; Svoboda, I.; Ogden, I. Fate of Escherichia coli and Escherichia coli O157 in soils and drainage water following cattle slurry application at 3 sites in southern Scotland. Soil Use Manag. 2002, 18, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Da, L.; Song, K.; Li, B.-L. Temporal variations of surface water quality in urban, suburban and rural areas during rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouri, G.; Takizawa, S.; Oki, T. Spatial and temporal variation in nutrient parameters in streamwater in a rural-urban catchment, Shikoku, Japan: Effects of land cover and human impact. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1837–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrane, S.J.; Hutchins, M.G.; Miller, J.D.; Bussi, G.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Loewenthal, M. During a winter of storms in a small UK catchment, hydrology and water quality responses follow a clear rural-urban gradient. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Soybean cultivation as a threat to the environment in Brazil. Environ. Conserv. 2001, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmello, V.; Santanna Neto, J.L. Rainfall variability and soybean yield in Paraná State, Southern Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Res. 2016, 2, 86–97. [Google Scholar]
- Franchini, J.C.; Balbinot Junior, A.A.; Sichieri, F.R.; Debiasi, H.; Conte, O. Yield of soybean, pasture and wood in integrated crop-livestock-forest system in Northwestern Paraná state, Brazil. Rev. Ciência Agronômica 2014, 45, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Antoneli, V.; Mosele, A.C.; Bednarz, J.A.; Pulido-Fernández, M.; Lozano-Parra, J.; Keesstra, S.D.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Effects of applying liquid swine manure on soil quality and yield production in tropical soybean crops (Paraná, Brazil). Sustainability 2019, 11, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira Sutilde Oliveira Roesler, P.; Damasceno Gomes, S.; Moro, E.; Barbosa Kummer, A.C.; Pascoli Cereda, M. Yield and quality of roots of sweet potato cultivars in the western region of Paraná. Acta Sci. Agron. 2008, 30, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Thomaz, E.; Antoneli, V. Long-term soil quality decline due to the conventional tobacco tillage in Southern Brazil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoneli, V.; Lenatorvicz, H.H.; Bednarz, J.A.; Pulido-Fernández, M.; Brevik, E.C.; Cerdà, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Rainfall and land management effects on erosion and soil properties in traditional Brazilian tobacco plantations. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.B.; Souza, M.C.D. Arboreous vegetation of an alluvial riparian forest and their soil relations: Porto Rico Island, Paraná River, Brazil. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2002, 45, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Filho, L.V.d.; Nanni, M.R.; Campos, J.B. Floristic and phytosociological description of a riparian forest and the relationship with the edaphic environment in Caiuá Ecological Station-Paraná-Brazil. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2006, 49, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, J.; Sanquetta, C.R.; Ugaya, C. Identificação de áreas prioritárias para recuperação da mata ciliar na UHE Salto Caxias. Espaço Energia 2005, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Quinteiro, T.; Lopes, J.; Martins, I.C.F. Diversidade de Carabidae (Coleoptera) amostra dos em áreas de reflorestamento de mata ciliar e fragmento florestal, no Estado do Paraná. Entomo Brasilis 2012, 5, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, J.A. O Programa Mata Ciliar no Estado do Paraná; Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná: Pato Branco, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Peres, M.C.A.P.; Ralisch, R.; Ripol, C.V. Avaliação do programa estadual “MataCiliar” no município de Pitangueiras, Paraná. Semin. Ciências Agrárias 2009, 30, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).