Abstract
The coronavirus pandemic has brought unprecedented challenges and has changed society; some of these changes seem temporary, and others seem permanent. The uncertainty of the duration of this pandemic has introduced changes without the knowledge of how permanent they are, and has raised awareness regarding a need for a shift to a new normal. This new normal will affect different aspects of our life routines and activities, such as travel behaviour, personal hygiene, socializing, and our working environment. In the wake of the global pandemic, which has been followed by lockdowns, curfews, social distancing, and working from home, the future of the office has turned into an open question, as COVID has changed our expectation of how, where, and when people can do their jobs. Big companies like Twitter and Facebook have announced that they are allowing employees to permanently work from home; however, some industry leaders are using the work-from-home experience to reimagine the role of the office in the future. What will the future office look like, and what can we expect of the workplace environment? In this paper, we propose a third solution, which is the merging of the current scenario of the classic office and working from home, which is entitled the ‘local co-working hub’. By studying the challenges and opportunities of each of the current approaches, the potential of the local co-working hub is highlighted.
1. Introduction and Statement of the Problem
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the pandemic as a global health emergency [1]. The COVID outbreak was not only a public health crisis; it also significantly affected the global economy through business closures, the loss of life, travel bans and trade disruption [2]. Notwithstanding the negative impact COVID-19 had on all aspects of our life, we have been surprised by our exceptional adaption, the possibility of remote working, and the power of digital technology and virtual communication. In just a few months, working from home has been suddenly normalised. According to new research conducted by Roy Morgan [3], over 4.3 million Australian workers (one third) have been working from home since the pandemic shutdowns. Millions of us used to spend about a third of our time in the office, but the COVID-19 forced–work-from-home time has shown us the possibility of flexible remote working and the power of choosing when, where and how we can productively do our jobs while experiencing a new work-life balance.
In addition to a reduction of operation costs, remote working has resolved the challenge of traveling to and from work. As can be seen in Figure 1, a substantial amount of workers’ time has been wasted in daily commuting.

Figure 1.
Average commuting time in big cities around the world.
According to statistics, New Yorkers have the longest commute times in the U.S. [4], at nearly 2 h, which is similar to those of Tokyo [5]. Seoulites spend 96 min on their daily commute [6]; in other big cities, such as London and Buenos Aires, the average commute time is from 74 to 76 min [7,8]. In two of the biggest mainland cities of Australia, Sydney and Melbourne, workers spend more than an hour travelling to and from work each day [9]. Although Tehran and Beijing have a better position in this list, their workers still spend an average of 52–55 min commuting to and from work [10,11].
Several studies have shown that long-duration commuting not only has negative impacts on worker’s efficiency and job satisfaction but also has serious negative impacts on both physical and mental health and wellbeing, as workers have less time for physical activities and social interaction. Moreover, increases to the degree of travel-related stress via exposure to traffic noise, congestion, and uncomfortable weather/temperature conditions are some of the other negative impacts of long commutes to and from work [12].
The COVID 19 pandemic has also resulted in the acceleration of the digital transformation, as according to Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella “We have seen two years’ worth of digital transformation in two months” [13]. This new flexible way of working provides an opportunity to spend more quality time with the family while using innovative ways to be a productive employee. On March 31, 2020, Microsoft Teams recorded 2.7 billion meeting minutes in one day [14].
Several cities around the globe have experienced lockdowns, curfews, economic and transport shutdowns, and different stages of restrictions to control the spread of the virus, which has been resulted in significant economic, physical, and mental health/wellbeing consequences. This major interruption has affected the environment through a major reduction in air pollution around the globe. According to the Carbon Brief 2020 analysis, the Coronavirus has resulted in the largest ever annual fall in CO2 emissions since the start of the 20th century [15]. Moreover, we observed the enhancement of the sense of localism, an injection of new life into the local civic center, and greater support for local businesses as a result of the commuting restriction. Additionally, it resulted in the growth of demands for and dependence on local businesses to achieve daily needs, as people spent more time in their local civic centers. Even buying a coffee from a local shop instead of a café in Central Business District (CBD) can change the game by improving the local economy, supporting local businesses, and providing an opportunity for people to get to know their local traders better, which enhances their sense of localism.
The positive environmental impacts of the COVID pandemic and the rise of a stronger sense of localism, which resulted in greater support of local businesses and a more flexible work–life regime, have already encouraged governments in several parts of the world to attempt to lock in some of the temporary changes caused by the pandemic in order to set a new normal. The new normal can help us to mitigate climate change challenges and other global issues through the reduction of traffic; the reallocation of road space to walking and cycling; the use of electric cars; a move towards smart, resilient, and sustainable cities; and support for local businesses.
2. Work from Home (WFH)
The unprecedented changes in our daily life routines, the acceleration of the digital transformation, and the adoption of remote working in response to this global pandemic has raised serious questions regarding commuting, the use and purpose of office spaces, the reassessment of space utilization, the volume of office demand, and the need for a more flexible working regime, which has forced companies across a variety of industries to reimagine what office work will look like in the future. In the wake of the Coronavirus pandemic, one of the largest tech firms, Google, has changed its work routine by announcing that its employees will work from home until at least summer 2021; similarly, Twitter has announced that its employees can work remotely forever if they wish, and Facebook expects that at least half of its employees will work from home for the next five to ten years [16].
It has been reported that, from March 2020, one in three Australians with a job worked from home, compared to one in eight before March [17]. In response to more staff working from home, and the growing demand for a more flexible working regime, a global engineering consultancy, AECOM, has broken its lease two years early and cut two floors from the space it occupies in central Sydney [18]. All of these actions due to the uncertainty regarding the future resulted in a rise of vacancy rates and available office space for subleasing, even in the best locations of big cities such as Sydney and Melbourne.
However, it is believed that working from home (WFH) will not replace the office in the future, but a complementary remote working and rotation-based working routine will benefit employers in different ways. Surveys around the world have revealed that a high percentage of employees are willing to adopt a more flexible working regime by spending just two to three days a week in the office and working remotely for the rest of the week, which makes the requirement for big office spaces to accommodate all employees on a daily basis inessential. This new work routine will result in lower operational costs and office expenses for employers, such as a reduction of rental costs, utilities, office supplies and insurance. According to Global Workplace Analytics’ estimation, “a typical employer can save about $11,000 per year for every person who works remotely half of the time” [19].
Freeing up spaces and the increase in space options in the market also provide an opportunity for employers to reduce their rental cost by finding more affordable and flexible lease options.
On the other hand, employees will benefit from this new remote working regime, as it will provide a more flexible and location-independent working style, with an opportunity to save commuting costs and time, and to achieve a better life–work balance.
Although the new work routine in the COVID-19 Global pandemic period provides a more flexible work regime which has several positive impacts, not only on employers and employees’ lifestyles but also on the environment, working from home can be quite a challenge (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Benefits and challenges of working from home for employers and employees.
Unlike the work environment, which has been designed to help employees to effectively engage in work, the home environment has not been set up for that purpose, which means adapting to new sets of distractions, technical issues, screen fatigue, less social interaction, a sense of isolation and loneliness, a loss of motivation, and lack of ergonomic and standard workplace facilities. Overcoming all of these demands in order to be able to engage effectively in work requires self-control.
In occupational health psychology, self-control is defined as the ability to suppress intrusive thoughts, behaviours, and emotions which are not relevant or helpful for achieving a goal [20]. As such, battling more with self-control consumes more mental energy, which has negative impacts on mental health and wellbeing [21]. Unlike the effect of leaving the office on the immediate detachment from work, managing the boundaries between work and non-work time—and the detachment from work and all work-related thoughts and activities—is not that simple, and many employees end up squeezing in work anytime they can, which increases the negative effect of self-control, which can threaten the worker’s wellbeing.
In addition, the lack of access to a dedicated workplace with ergonomic and standard facilities is another challenge of WFH, which has negative impacts on employee’s physical health and well-being.
Despite the positive impact of WFH on the elimination of commute time and its associated stress and challenges, research by Ettema et al. [22] on the analysis of travel behaviour based on a subjective well-being (SWB) framework (SWB is the degree to which an individual positively evaluates the overall quality of their life) has revealed the other side of the coin. According to the research outcome, participation in goal-directed activities, facilitated or hindered by travel, can contribute to SWB; although the travel-related stress reduces SWB, the positive affect associated with travel can enhance SWB [22]. According to this framework, the negative impact of no work travel should not be ignored, as it might result in the reduction of the sense of motivation and progress toward goals, and may lead to isolation in employees who are working from home.
Reviewing all of the benefits and challenges of WFH has raised the question of “how long we can continue to work from home?”
3. Local Co-Working Hub Design Principals
As some countries, such as Australia and New Zealand, became mostly COVID-free, with continuous days of zero cases and promising news of access to the vaccine in the next few months, workers have been encouraged to go back to the workplace. Although the work regime will not go back to its previous normal, there is a fear of more car-dependent travel after the pandemic, as people are afraid to use public transport, and even heavier traffic congestion and extended commute times are expected, which will not only affect employees’ wellbeing but also have a serious negative impact on the environment. We don’t want to go back to the past situation; as such, there is a need to set a new normal and a new life and working regime, and to take the most from this major interruption by COVID 19, as it offers us a chance to rethink our working-life routine in order to be able to respond better to other major issues such as global warming and climate change challenges. Considering the WFH challenges that have been discussed above, working from home might not be the best solution for all workers, which highlights the need for the creation of a third space that offers workers a standard workplace environment with the best facilities and technologies within walking distance of their home.
According to Carlos Moreno, who is a driving force behind Paris’s 15-minute city plan, “The 15-minute city represents the possibility of a decentralized city,” [23]. This model, which aims to provide access to most people’s needs within a short walk or bike ride from their home, has already been established in many cities around the world, and has been picked up by the C40 Mayors as part of their ‘Green and Just’ recovery plan [23,24].
As stated by Moreno, “because we now have the possibility to stay closer to home, people have rediscovered useful time—another pace for living” [23]. According to Moreno, “not all people have the possibility of having jobs within 15 min”; thus, it is time to follow a more inclusive approach by creating a third space, i.e., a local co-working hub within the 15–20 min distance, which offers a free and bookable co-working space in order to provide an opportunity for remote working. Although, in 2020–2021, the creation of such a local co-working space/hub becomes a demanding method to help cities work around COVID-19, it could be a great solution to offer a more local, healthy, and sustainable way of life for the future beyond the post pandemic period. Figure 3 shows the key principals of the creation of a 15–20 min neighborhood.
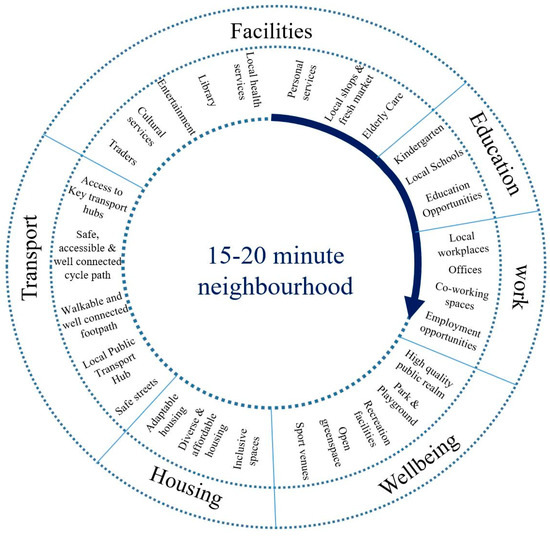
Figure 3.
Key principles of creating a 15–20 min neighbourhood.
These local co-working hubs can provide an opportunity for workers to work with like-minded people in a standard, smart and modern space within walking/cycling distance, away from any of the distractions that workers experienced at home.
More specifically, the local work hubs will help to reduce unnecessarily-long work commutes, create less environmental impact, and enhance worker’s physical and mental health and wellbeing. They will do this by the provision of better work–life balance through immediate detachment from work, more social interaction, and adequate facilities to perform their duties, enhance their motivation, and increase their sense of progressing to a destination in order to achieve the goal of the day. Everyone can book a space within the co-working hub based on their personal schedule in order to be able to work in a hub and use its facilities.
Creating a local co-working hub for workers within the 15–20 min neighborhood/city will also provide a great opportunity to support local high street businesses, strengthen the sense of community and localism, and fight inequality—especially in disadvantaged locations—by increasing the demand for shops, parks, and facilities on the local scale.
In order to be ready for any future pandemic and to set a new normal for the future beyond the post-pandemic period, the following design principles are required considerations for the design of the proposed local co-working hubs (Figure 4). Following these eight proposed principals will provide an opportunity to achieve an anti-infection, healthy and smart co-working space. The use of technology for thermal screening, air filtration and contactless design; the use of antibacterial and antiviral coatings for furniture and other materials; and the provision of access to open green space, hygiene stations, signage and breath barriers are the key principals that can provide a safe, healthy and high-tech co-working space.

Figure 4.
Proposed design principles for local co-working hubs.
Although finding the right location within the local high street and achieving design principals in existing buildings or designing a new building can be expensive, it is believed that—if the project is run by councils—it could provide more opportunities for access to the right location, the ability to repurpose available public places, and access to government funding to cover the cost.
It should not be forgotten that dedicating a place to or designing a local co-working hub within the 15–20 min neighborhood might be challenging. The access to open space, as well as Internet of Things (IOT) issues such as information/cyber security, are some of the other issues which might be in the way, and which need further investigation.
As the provision of such a co-working hub in the 15–20 min neighborhood requires enough population density, as well as good access to public transport and job opportunities in other regions, it might not be a suitable or achievable solution in small and isolated cities.
4. Conclusions
In order to achieve a balance between the challenges and opportunities of working from home and the classical office, a third solution—entitled the local co-working hub—has been proposed. Based on this approach, the local work hubs will help to reduce commuting times and environmental impact, and to enhance both worker’s mental health and wellbeing via the provision of a better work–life balance through immediate detachment from work, and more social interaction. They will also provide adequate facilities for workers to perform their duties, enhance their motivation, and increase their sense of progressing toward a destination in order to achieve the goal of the day. It is believed that, based on the COVID-19 pandemic experiences, there is a need to adopt a working scenario based on the availability and type of the work in order to benefit from the opportunities of WFH and the classical office through a merging solution called a ‘co-working hub’.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and idea generation, B.M. and K.S.; methodology, B.M.; formal analysis, B.M.; visualization and data curation, B.M.; resources, B.M.; writing—original draft preparation, B.M. and K.S.; writing—review and editing, B.M. and K.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in references that cited in a paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report 100; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pak, A.; Adegboye, O.A.; Adekunle, A.I.; Rahman, K.M.; McBryde, E.S.; Eisen, D.P. Economic Consequences of the COVID-19 Outbreak: The Need for Epidemic Preparedness. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy Morgan. Nearly a Third of Australian Workers Have Been ‘#WFH’. Available online: http://www.roymorgan.com/findings/8451-roy-morgan-working-from-home-june-2020-202006290638 (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Perlman, M.J.; Brown, S.R. New Yorkers have longest commute times in the U.S.: Report. New York Daily News, 13 August 2013. Available online: https://www.nydailynews.com/new-york/new-yorkers-havelongest-commute-times-article-1.1426047 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Chie, S.; Yoko, W.; Masayuki, H. No More Decline in Sleeping Time, More Time Now Spent on Neccessary Activities—From the 2015 NHK Japanese Time Use Survey; NHK Broadcasting Culture Research Institute, Japan Broadcasting Corporation: Japan. 2016. Available online: https://www.nhk.or.jp/bunken/english/reports/pdf/report_16071301.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Bae, H.-j. Seoulites Spend 96 Minutes on Daily Commute: Data. The Korea Herald, 16 May 2018. Available online: http://www.koreaherald.com/ (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Alex, C. The Unforgiving Hour: What Our Longer Commutes Are Really Costing Us. Prospect, 17 September 2019. Available online: https://www.prospectmagazine.co.uk/politics/commute-times-london-uk-work (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Imogen, R.-T. City of Buenos Aires Residents Spend 13 days Commuting Every Year. Available online: https://www.thebubble.com/city-of-buenos-aires-residents-spend-13-days-commuting-every-year (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Liang, M.; Runing, Y. Australian City Workers’ Average Commute Has Blown Out to 66 Minutes a Day. How Does Yours Compare? Available online: https://theconversation.com/australian-city-workers-average-commute-has-blown-out-to-66-minutes-a-day-how-does-yours-compare-120598 (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Mahya, K. Tehran’s Traffic among Global Worst. Iran Economy in Brief (IEB), 30 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alex, G. Think Your Commute Is Bad? Some Beijing Workers Spend Six Hours a Day Getting to Work; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Ye, R. Australian city workers’ average commute has blown out to 66 minutes a day. How does yours compare? The Conversation, 30 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Spataro, J. 2 Years of Digital Transformation in 2 Months. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/blog/2020/04/30/2-years-digital-transformation-2-months/ (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Spataro, J. Remote Work Trend Report: Meetings. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/blog/2020/04/09/remote-work-trend-report-meetings/?wt.mc_id=AID2409697_QSG_SCL_424041&ocid=AID2409697_QSG_SCL_424041%2020 (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Evans, S. Analysis: Coronavirus Set to Cause Largest Ever Annual Fall in CO2 Emissions; Carbon Brief-Clear on Climate: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, K. Google employees will work from home until at least summer 2021. The Guardian, 27 July 2020. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2020/jul/27/google-employees-work-from-home-coronavirus-pandemic (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Household Impacts of COVID-19 Survey; Australian Bureau of Statistics: Belconnen, Australia, 2020. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/people-and-communities/household-impacts-covid-19-survey/latest-release (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Bleby, M. AECOM cuts Sydney office footprint as staff work from home. Financial Review, 19 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Global Workplace Analytics. Work-At-Home/Telecommuting/Mobile Work/Remote Work Statistics. 2020. Available online: https://globalworkplaceanalytics.com/telecommuting-statistics (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Klaus-Helmut, S.; Stefan, D. Self-Control Demands-From Basic Research to Job-Related Applications. J. Pers. Psychol. 2015, 14, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wladislaw, R. Working from home? Why detachment is crucial for mental health. The Conversation, 9 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ettema, D.; Gärling, T.; Olsson, L.E.; Friman, M. Out-of-home activities, daily travel, and subjective well-being. Transp. Res. Part A 2010, 44, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, L. The 15-Minute City Is Having a Moment. Available online: https://www.treehugger.com/the-15-minute-city-is-having-a-moment-5071739 (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group, Inc. How to Build Back Better with a 15-Minute City; C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group, Inc.: London, UK, 2020; Available online: https://www.c40knowledgehub.org/s/article/How-to-build-back-better-with-a-15-minute-city?language=en_US (accessed on 27 January 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).