The Most Frequently Cited Topics in Urban Planning Scholarship
Abstract
1. Introduction
Citation Analyses
2. Methodology
Support Vector Machine
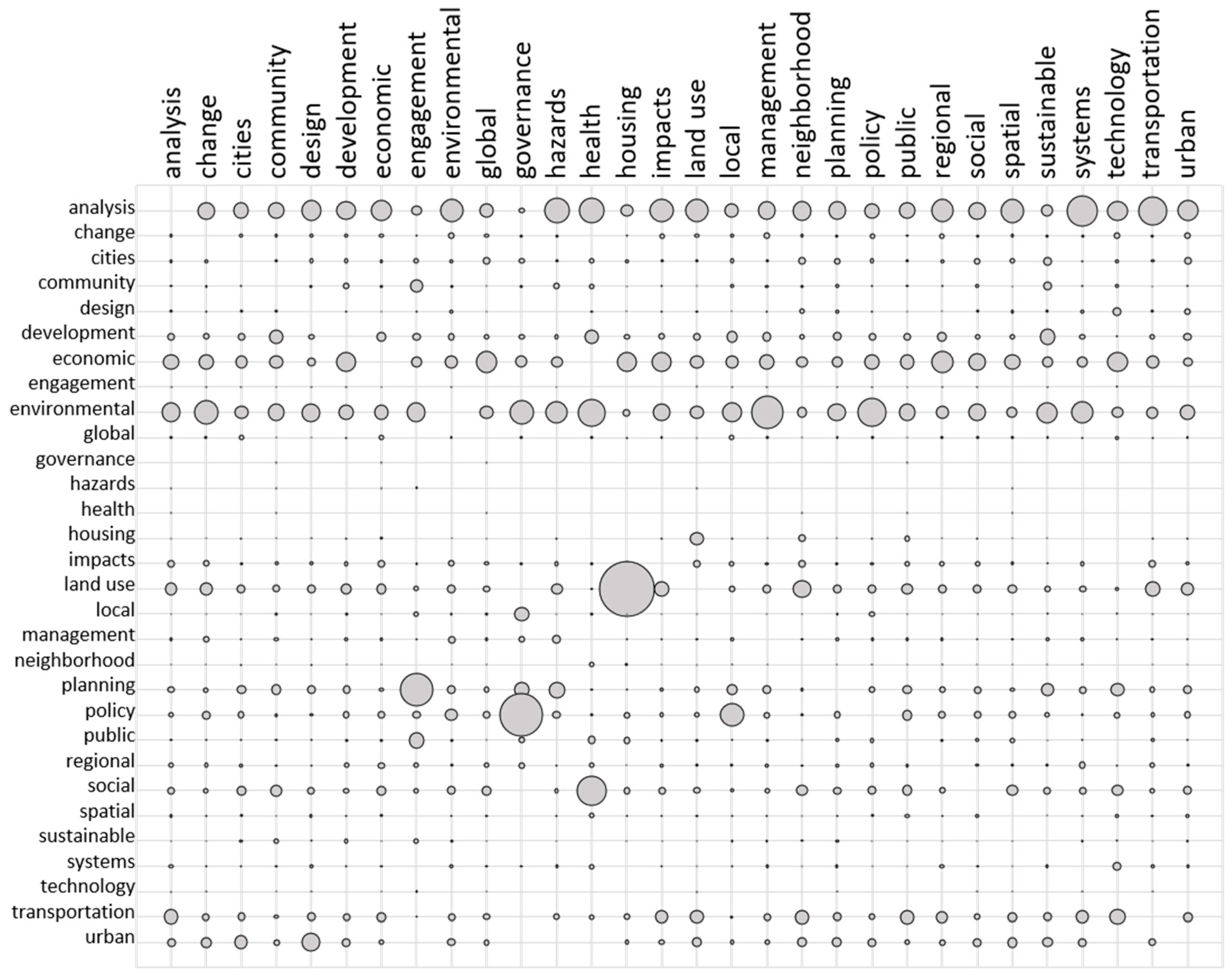
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, P.; Tewdwr-Jones, M. Urban and Regional Planning, 5th ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, D.J.; Stahmer, C.; Smith, M. Impacting Capabilities: A Conceptual Framework for the Social Value of Research. Front. Res. Metr. Anal. 2018, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shneiderman, B. The New ABCs of Research: Achieving Breakthrough Collaborations; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, E.R. How Theory Links Research and Practice: 70 Years’ Planning Theory: A Critical Review. In Planning Knowledge and Research; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 7–23. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, P. Striving for Impact Beyond the Academy? Planning Research in Australia. In Planning Knowledge and Research; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, C.G. Learning from Practice, Learning for Practice in Local Land Use Planning Research. In Planning Knowledge and Research; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wachs, M. The case for practitioner faculty. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 1994, 13, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spain, D. Creating and defending links between teaching, research, and public service. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 1992, 12, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiewel, W.; Carlson, V.; Friedman, S. Planning the new urban university: The role of planning departments. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 1996, 16, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumholz, N. From planning practice to academia. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 1986, 6, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, E. Citation analysis as a tool in journal evaluation. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 1972, 178, 471–479. [Google Scholar]
- Garfield, E.; Merton, R.K. Citation Indexing: Its Theory and Application in Science, Technology, and Humanities; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Moed, H.F. Citation Analysis in Research Evaluation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Tahamtan, I.; Bornmann, L. What Do Citation Counts Measure? An Updated Review of Studies on Citations in Scientific Documents Published between 2006 and 2018. Scientometrics 2019, 121, 1635–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, T.W. Academic Visibility and the Webometric Future. J. World Univ. Forum 2014, 6, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meho, L.I.; Yang, K. Impact of data sources on citation counts and rankings of LIS faculty: Web of Science versus Scopus and Google Scholar. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2007, 58, 2105–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Pitsouni, E.I.; Malietzis, G.A.; Pappas, G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, web of science, and Google scholar: Strengths and weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Burnham, J.F.; Lemley, T.; Britton, R.M. Citation Analysis: Comparison of Web of Science®, Scopus ™, SciFinder®, and Google Scholar. J. Electron. Resour. Med. Libr. 2010, 7, 196–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzing, A.W.; Van der Wal, R. Google Scholar: The democratization of citation analysis. Ethics Sci. Environ. Politics 2007, 8, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkalbasi, N.; Bauer, K.; Glover, J.; Wang, L. Three options for citation tracking: Google Scholar, Scopus and Web of Science. Biomed. Digit. Libr. 2006, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine-Clark, M.; Gil, E.L. A comparative citation analysis of Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar. J. Bus. Financ. Librariansh. 2008, 14, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Aziz, B.; Shams, I.; Busse, J.W. Comparisons of citations in Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar for articles published in general medical journals. JAMA 2009, 302, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, R. Pointing users toward citation searching: Using Google Scholar and Web of Science. Portal Libr. Acad. 2007, 7, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschet, M. A comparison of bibliometric indicators for computer science scholars and journals on Web of Science and Google Scholar. Scientometrics 2010, 83, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.H. Google Scholar coverage of a multidisciplinary field. Inf. Process. Manag. 2007, 43, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.L.; Aguillo, I.F. Microsoft academic search and Google scholar citations: Comparative analysis of author profiles. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 65, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousha, K.; Thelwall, M. Sources of Google Scholar citations outside the Science Citation Index: A comparison between four science disciplines. Scientometrics 2007, 74, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantz, J. Google Scholar and 100% Availability of Information. Inf. Technol. Libr. 2013, 25, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzing, A.W. A longitudinal study of Google Scholar coverage between 2012 and 2013. Scientometrics 2013, 98, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Stergiou, K.I. Equivalence of results from two citation analyses: Thomson ISI’s Citation Index and Google’s Scholar service. Ethics Sci. Environ. Politics 2005, 2005, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiftel, B.; Rukmana, D.; Alam, B. Faculty quality in US planning schools: An NRC-style study. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2004, 24, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, T.W. Faculty Performance Evaluation Using Citation Analysis: An Update. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2017, 37, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojani, D.; Olvera-Garcia, J.; Sipe, N.; Byrne, J. Research productivity of Australian planning academics: A bibliometric analysis. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.R.; Park, K.; Tian, G.; Kim, K.; Ewing, R. Why Do Some Articles in Planning Journals Get Cited More than Others? J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornmann, L.; Schier, H.; Marx, W.; Daniel, H.D. What factors determine citation counts of publications in chemistry besides their quality? J. Informetr. 2012, 6, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornmann, L.; Wohlrabe, K. Normalisation of citation impact in economics. Scientometrics 2019, 120, 841–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, G.S.; Mimno, D.; McCallum, A. Bibliometric impact measures leveraging topic analysis. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM/IEEE-CS Joint Conference on Digital Libraries ACM, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 11–15 June 2006; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.E.; Jiang, X.; Kim, J.; Ohno-Machado, L. Trends in biomedical informatics: Most cited topics from recent years. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2011, 18, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halverson, L.R.; Graham, C.R.; Spring, K.J.; Drysdale, J.S.; Henrie, C.R. A thematic analysis of the most highly cited scholarship in the first decade of blended learning research. Internet High. Educ. 2014, 20, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, E.; Knipps, A. What’s in a Title? J. Wildl. Manag. 2014, 78, 761–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, C.E.; Lima, J.P.D.S.N.; Paiva, B.S.R. Articles with short titles describing the results are cited more often. Clinics 2012, 67, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.A.; Thacker, S.B.; Siegel, P.Z. What’s in a title? A descriptive study of article titles in peer reviewed medical journals. Science 2001, 24, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Liao, Z.; Chen, X. Fixed-income securities: Bibliometric review with network analysis. Scientometrics 2018, 116, 1615–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Y.; Ellis, T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Inf. Sci. Int. J. Emerg. Transdiscipl. 2006, 9, 181–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.R.; Nikzad, M. Article title type and its relation with the number of downloads and citations. Scientometrics 2011, 88, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subotic, S.; Mukherjee, B. Short and amusing: The relationship between title characteristics, downloads, and citations in psychology articles. J. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, T.S.; Sebire, N.J. The impact of article titles on citation hits: An analysis of general and specialist medical journals. JRSM Short Rep. 2010, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, E. Dealing with data: Using NVivo in the qualitative data analysis process. Forum Qual. Soc. Res. 2002, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, T.W.; Afzalan, N. Mapping the Knowledge Domain of Urban Planning. In Planning Knowledge and Research; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Yoshida, T.; Tang, X. Text classification based on multi-word with support vector machine. Knowl. Based Syst. 2008, 21, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertsalov, K.; McCreary, M. Document classification with support vector machines. ACM Comput. Surv. CSUR 2009, 42, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Joachims, T. Text categorization with support vector machines: Learning with many relevant features. In European Conference on Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer Science Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
| Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Analysis | Governance | Policy |
| Change | Hazards | Public |
| Cities | Health | Regional |
| Community | Housing | Social |
| Design | Impacts | Spatial |
| Development | Land Use | Sustainable |
| Economic | Local | Systems |
| Engagement | Management | Technology |
| Environmental | Neighborhood | Transportation |
| Global | Planning | Urban |
| Labels | ||
|---|---|---|
| Analysis | Growth | Planning |
| Change | Health | Policy |
| City | History | Public |
| Community | Housing | Regional |
| Design | International | Social |
| Development | Land-use | Studies |
| Economic | Management | Sustainable |
| Environmental | Methods | Theory |
| Finance | Neighborhood | Transportation |
| GIS | Participation | Urban |
| Rank | Topic | Number | Total Cites | Mean Cites | Mean Cites/Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Development Economic Global Regional | 3 | 4874 | 1624.7 | 76.8 |
| 2 | Change Management Transportation | 5 | 5539 | 1107.8 | 75.5 |
| 3 | Policy Spatial Urban | 4 | 3779 | 944.8 | 67.6 |
| 4 | Environmental Social Systems | 4 | 2571 | 642.8 | 58.6 |
| 5 | Analysis Urban Environmental Social Systems | 3 | 1189 | 396.3 | 36.2 |
| 6 | Cities Urban Environment | 9 | 1526 | 169.6 | 29.7 |
| 7 | Environmental Planning Policy Analysis | 6 | 1250 | 208.3 | 29.0 |
| 8 | Impact Analysis Urban Systems | 3 | 1064 | 354.7 | 28.7 |
| 9 | Sustainable Community Policy | 3 | 891 | 297.0 | 23.5 |
| 10 | Urban Social Change | 4 | 828 | 207.0 | 22.4 |
| 11 | Urban Environmental Systems | 4 | 580 | 145.0 | 22.1 |
| 12 | Land Use Transportation Impacts | 11 | 3414 | 310.4 | 20.6 |
| 13 | Social Sustainability | 3 | 408 | 136.0 | 19.5 |
| 14 | Global Regional Economics | 9 | 1969 | 218.8 | 19.5 |
| 15 | Urban Environmental Land Use Impacts | 3 | 589 | 196.3 | 19.3 |
| 16 | Cities Environmental Change | 4 | 659 | 164.8 | 18.4 |
| 17 | Sustainable Development Planning Analysis | 3 | 927 | 309.0 | 18.3 |
| 18 | Design Impacts Analysis | 3 | 755 | 251.7 | 17.4 |
| 19 | Housing Land Use Environmental Planning | 12 | 964 | 80.3 | 17.0 |
| 20 | Social Design | 11 | 762 | 69.3 | 16.7 |
| Topic | Number | Total Cites | Mean Cites | Mean Cites/Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | 795 | 51,382 | 64.6 | 5.3 |
| Urban | 1897 | 96,802 | 51.0 | 5.1 |
| Spatial | 688 | 34,816 | 50.6 | 5.0 |
| Regional | 972 | 59,964 | 61.7 | 4.7 |
| Cities | 1179 | 51,755 | 43.9 | 4.6 |
| Governance | 20 | 894 | 44.7 | 4.5 |
| Neighborhood | 280 | 11,969 | 42.8 | 4.3 |
| Systems | 697 | 28,893 | 41.5 | 4.3 |
| Environmental | 3739 | 161,408 | 43.2 | 4.1 |
| Social | 1935 | 77,942 | 40.3 | 4.0 |
| Sustainable | 474 | 17,932 | 37.8 | 4.0 |
| Change | 951 | 40,893 | 43.0 | 3.9 |
| Transportation | 2609 | 100,091 | 38.4 | 3.9 |
| Health | 20 | 498 | 24.9 | 3.6 |
| Land Use | 2465 | 91,732 | 37.2 | 3.5 |
| Analysis | 4787 | 171,487 | 35.8 | 3.5 |
| Policy | 1442 | 56,212 | 39.0 | 3.5 |
| Impacts | 1293 | 42,989 | 33.3 | 3.5 |
| Management | 823 | 35,366 | 43.0 | 3.4 |
| Planning | 1756 | 61,550 | 35.1 | 3.3 |
| Housing | 532 | 18,097 | 34.0 | 3.3 |
| Economic | 3650 | 145,779 | 39.9 | 3.3 |
| Design | 803 | 28,213 | 35.1 | 3.3 |
| Development | 1699 | 68,765 | 40.5 | 3.3 |
| Local | 402 | 14,618 | 36.4 | 3.1 |
| Public | 696 | 21,452 | 30.8 | 3.0 |
| Community | 757 | 26,347 | 34.8 | 2.9 |
| Hazards | 42 | 1776 | 42.3 | 2.9 |
| Engagement | 20 | 553 | 27.7 | 2.3 |
| Technology | 28 | 387 | 13.8 | 1.7 |
| Theme | Publication | Cites | Cites/Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Development Economic Global Regional | Storper, M. (1997). The regional world: Territorial development in a global economy. Guilford Press. | 4728 | 225.1 |
| Change Management | Feldman, M. S., & Pentland, B. T. (2003). Reconceptualizing organizational routines as a source of flexibility and change. Administrative science quarterly, 48(1), 94–118. | 2988 | 199.2 |
| Policy Spatial Urban | Brenner, N. (2004). New State Spaces: Urban Governance and the Rescaling of Statehood. Oxford University Press. | 3674 | 262.4 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez, T.W. The Most Frequently Cited Topics in Urban Planning Scholarship. Urban Sci. 2020, 4, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci4010004
Sanchez TW. The Most Frequently Cited Topics in Urban Planning Scholarship. Urban Science. 2020; 4(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci4010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez, Thomas W. 2020. "The Most Frequently Cited Topics in Urban Planning Scholarship" Urban Science 4, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci4010004
APA StyleSanchez, T. W. (2020). The Most Frequently Cited Topics in Urban Planning Scholarship. Urban Science, 4(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci4010004





