Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex II: Neutron Scattering Instruments
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
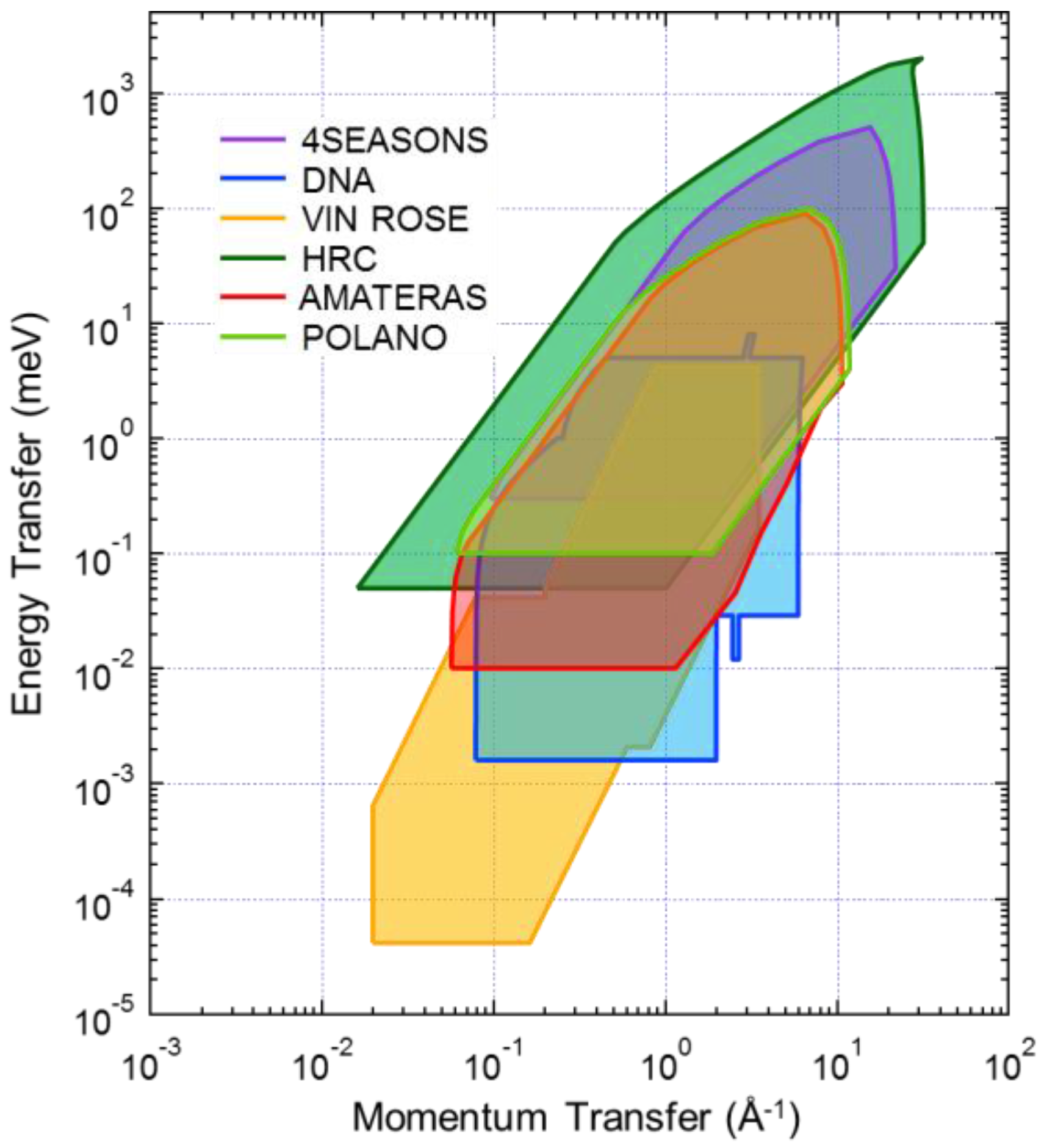
- Spectroscopy group (inelastic instruments)4SEASONS: 4D-Space Access Neutron Spectrometer [14]AMATERAS: Cold-Neutron Disk-Chopper Spectrometer [9]DNA: Biomolecular Dynamics Spectrometer [12]VIN ROSE: Village of Neutron Resonance Spin Echo Spectrometers [20].
- (ii)
- Crystal-structure group (diffractometers)SuperHRPD: Super High-Resolution Powder Diffractometer [21]SPICA: Special Environment Powder Diffractometer [22]iMATERIA: IBARAKI Materials Design Diffractometer (Versatile Neutron Diffractometer) [23]PLANET: High-Pressure Neutron Diffractometer [24]SENJU: Extreme Environment Single-crystal Neutron Diffractometer [29].
- (iii)
- Nano-structure group (small-angle neutron scattering instrument, reflectometers, and total scattering instruments)TAIKAN: Small- and Wide-angle Neutron Scattering Instrument [30]SHARAKU: Polarized Neutron Reflectometer [33]NOVA: High-Intensity Total Diffractometer.
- (iv)
- Pulsed neutron application group (other than neutron scattering instruments (beamlines for neutronics studies, fundamental physics, prompt gamma-ray analysis, versatile test port, and neutron imaging))ANNRI: Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument [34]NOP: Neutron Optics and Physic [35]NOBORU: NeutrOn Beam-line for Observation and Research Use [36]RADEN: Energy Resolved Neutron Imaging System [37].
2. Spectroscopy Group Instruments
2.1. 4D-Space Access Neutron Spectrometer, 4SEASONS
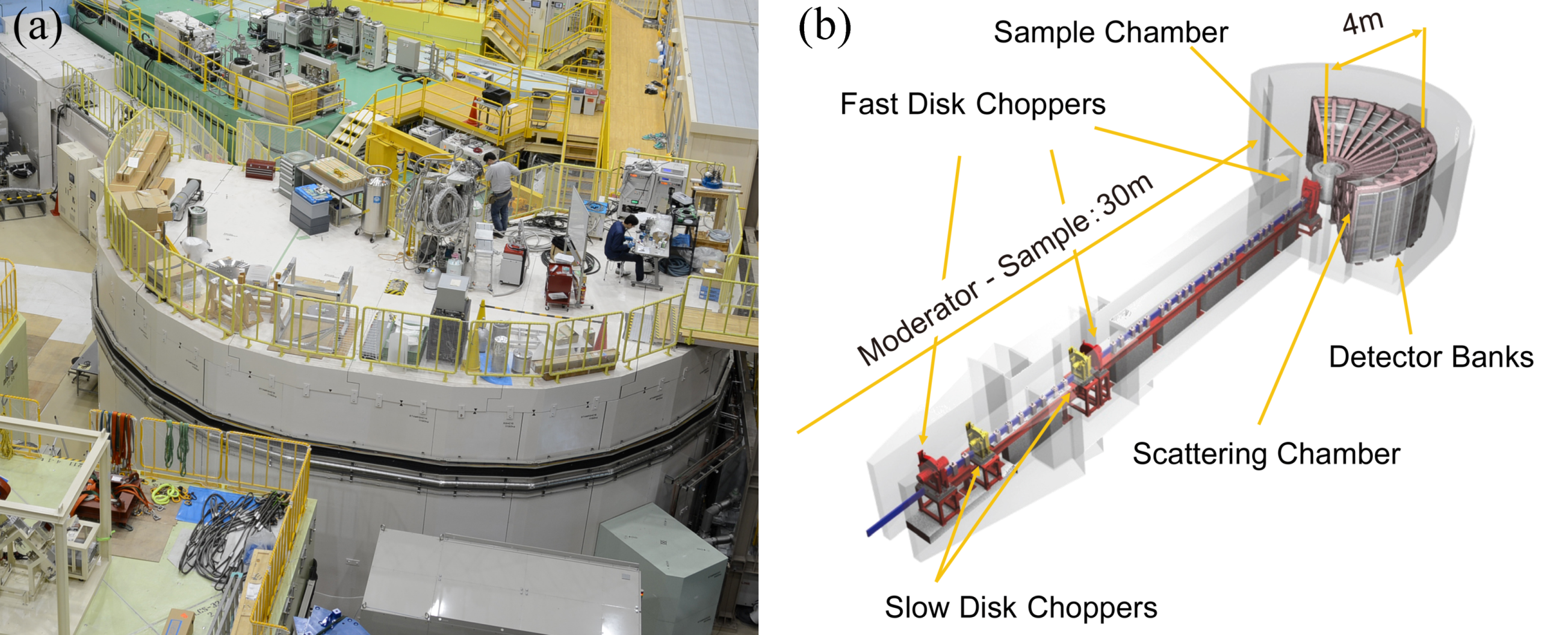
2.2. High Resolution Chopper Spectrometer, HRC
2.3. Cold-Neutron Disk-Chopper Spectrometer, AMATERAS
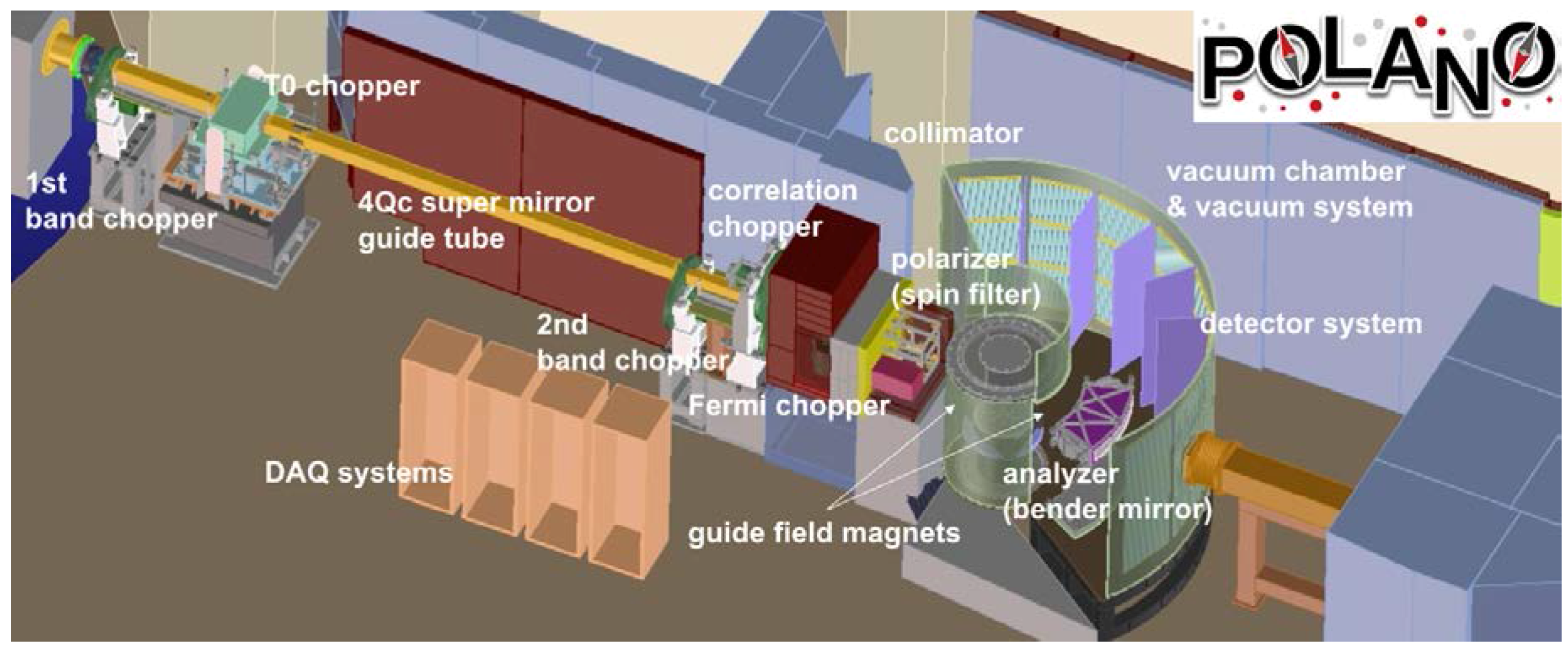
2.4. Polarized Neutron Spectrometer, POLANO
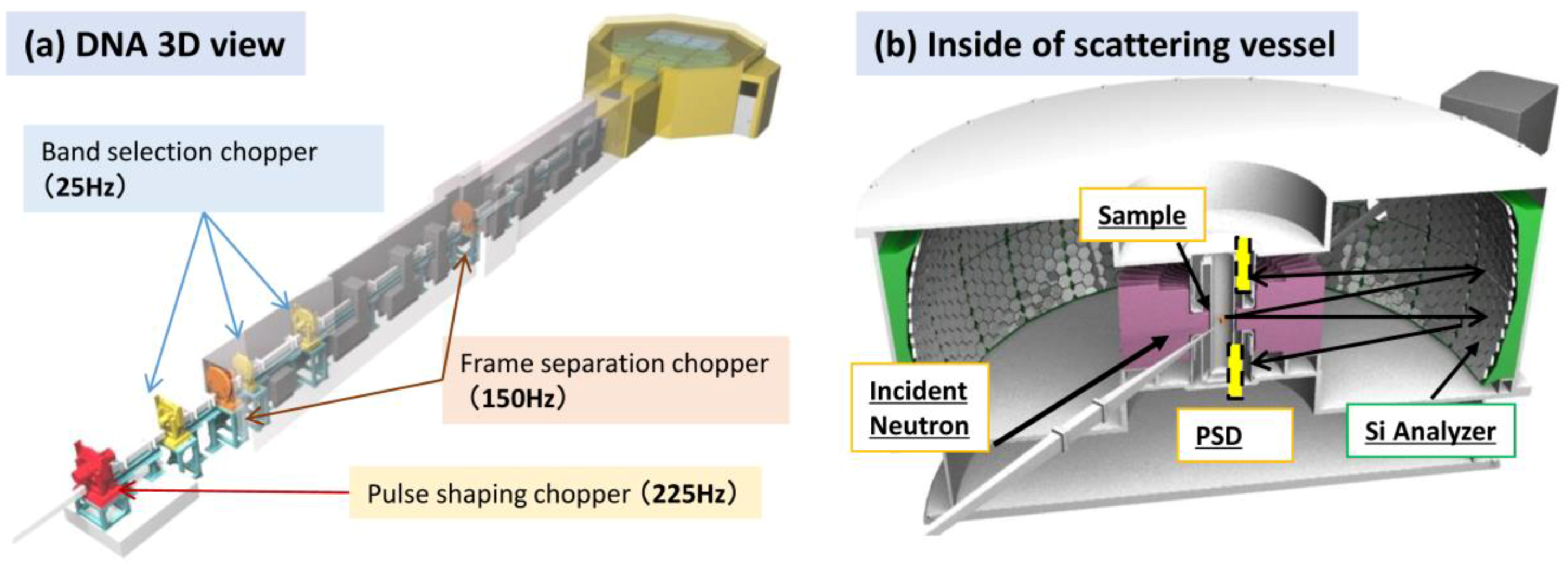
2.5. Biomolecular Dynamics Spectrometer, DNA
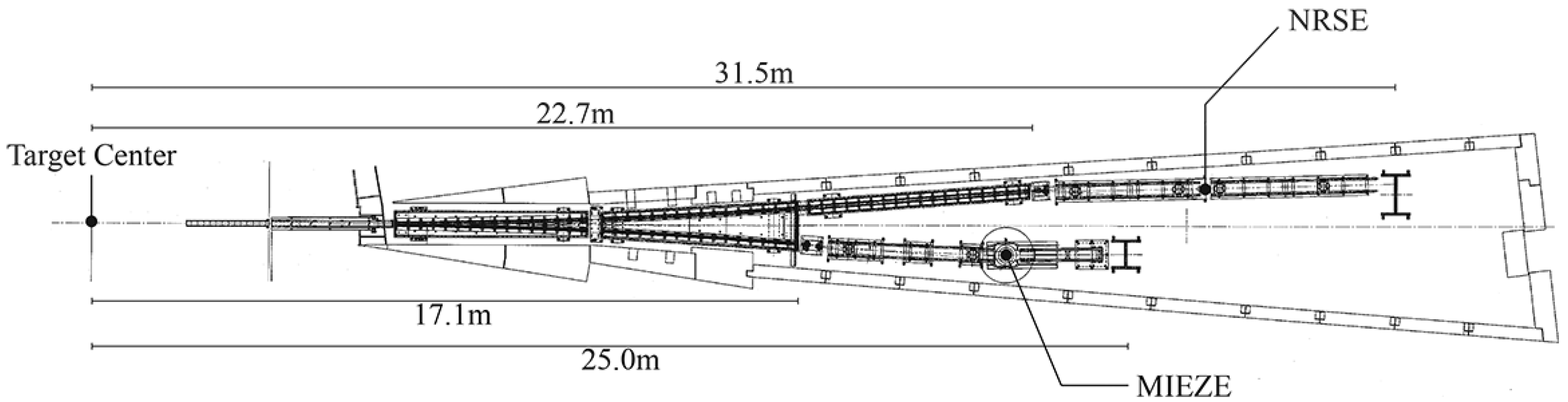
2.6. Village of Neutron Resonance Spin Echo Spectrometers, VIN ROSE
3. Crystal Structure Group Instruments
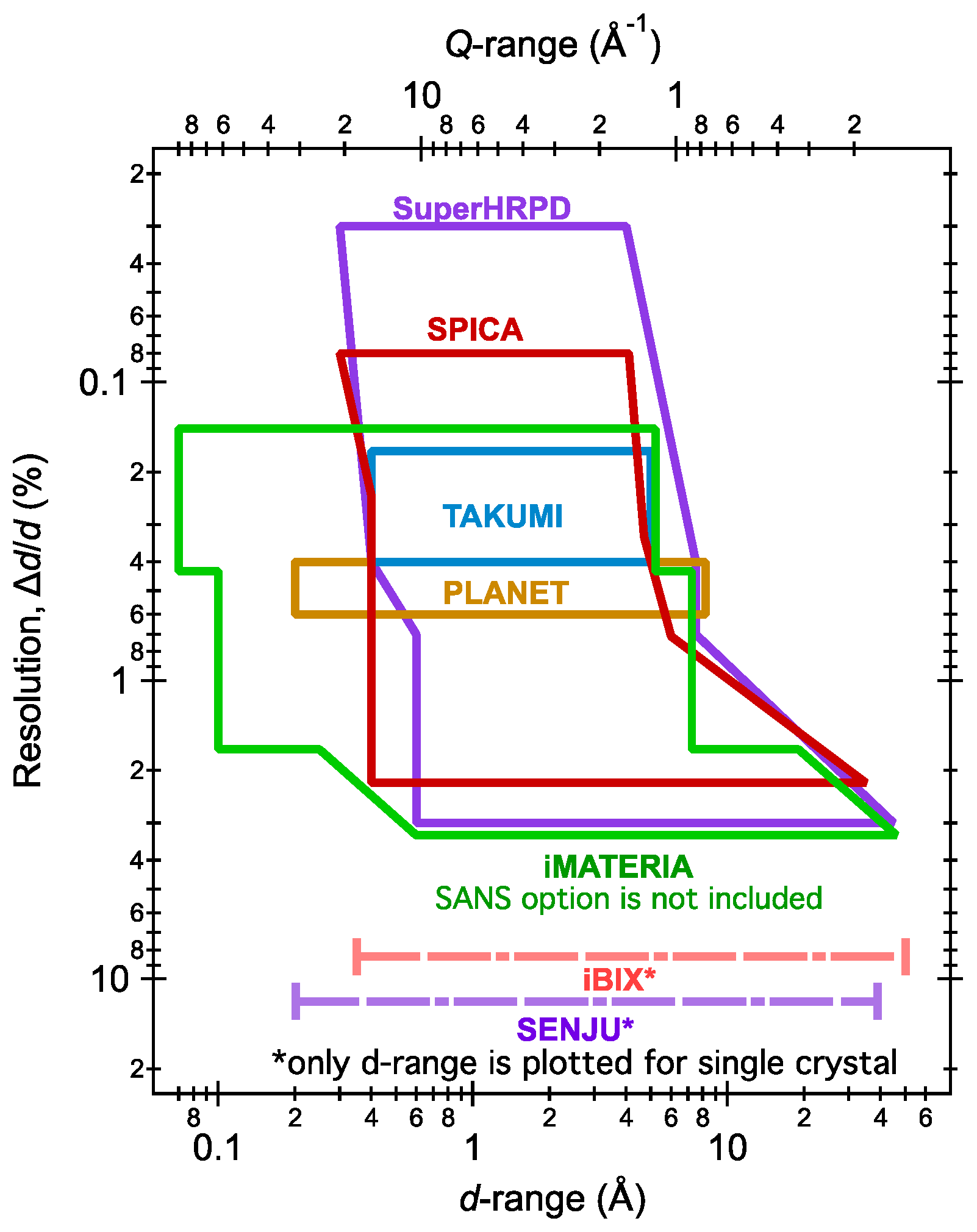
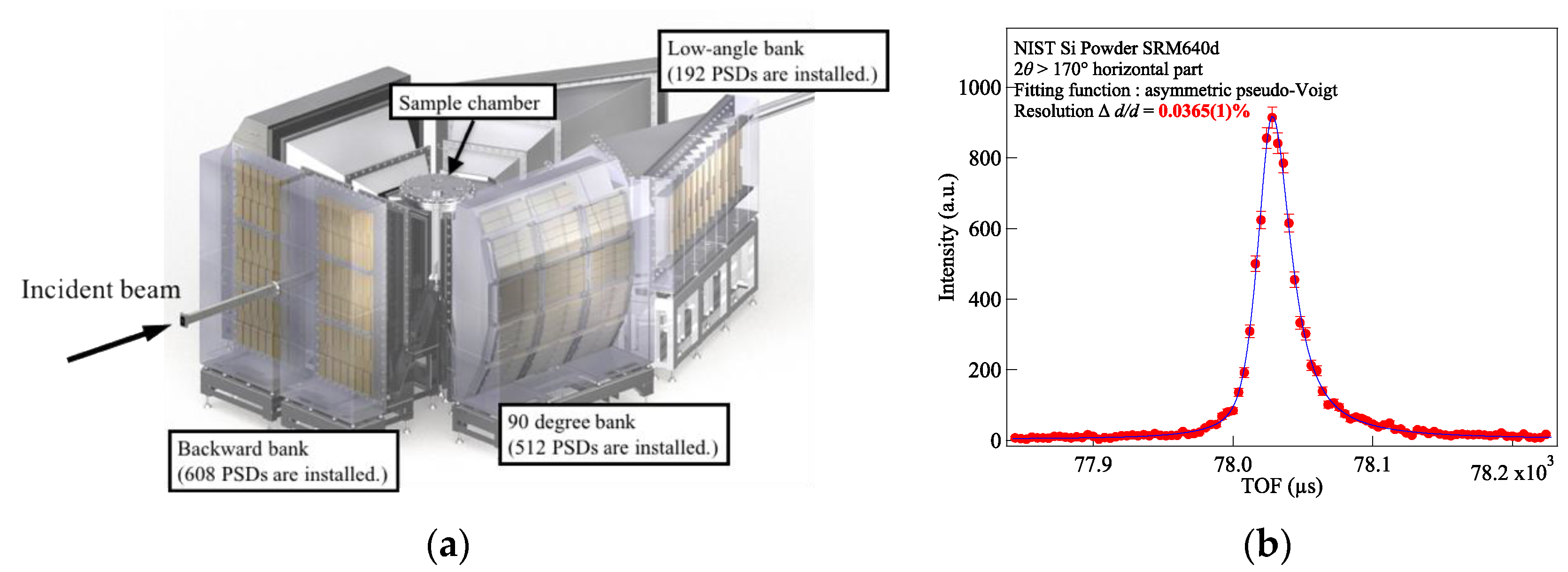
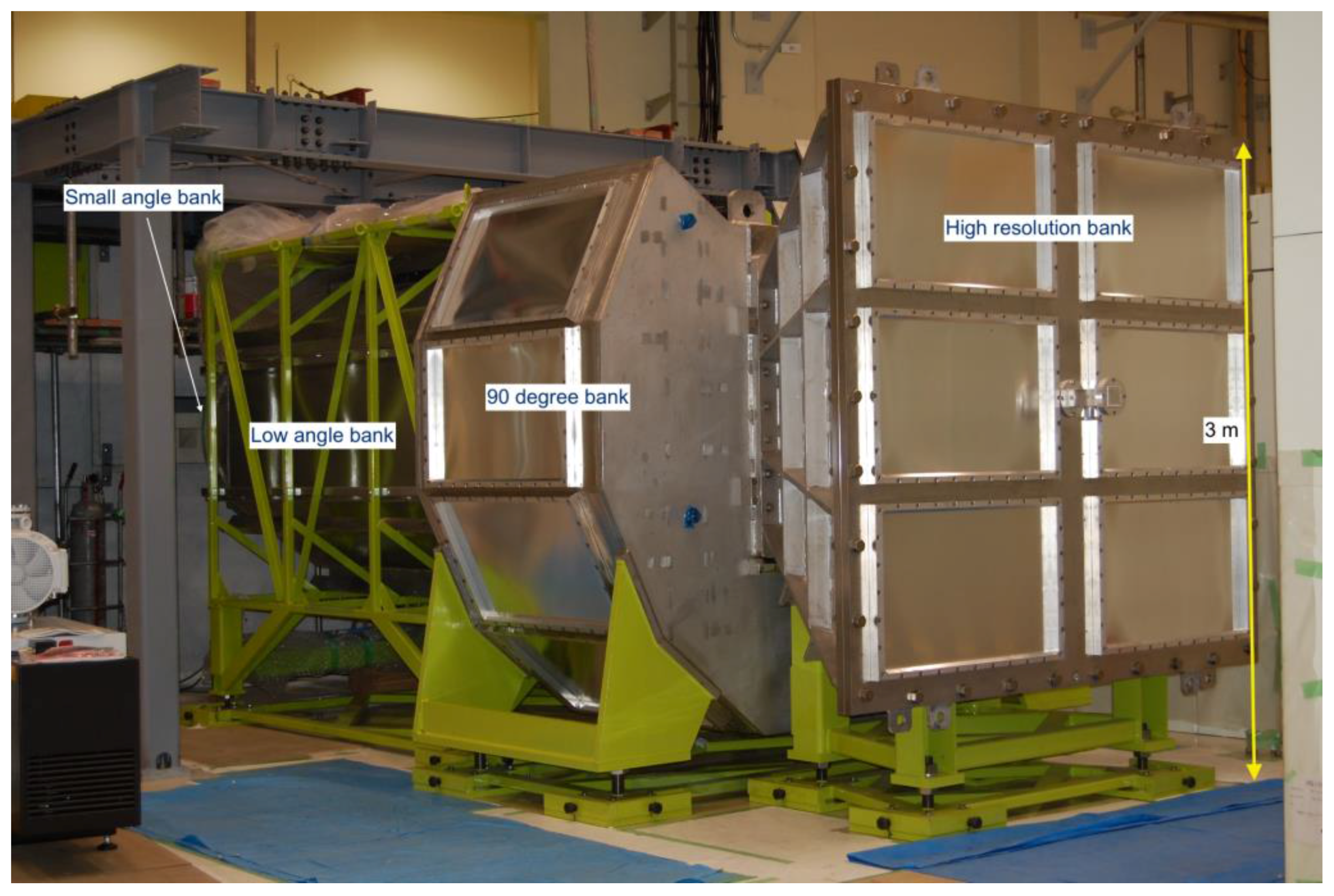
3.1. Super High-Resolution Powder Diffractometer, SuperHRPD
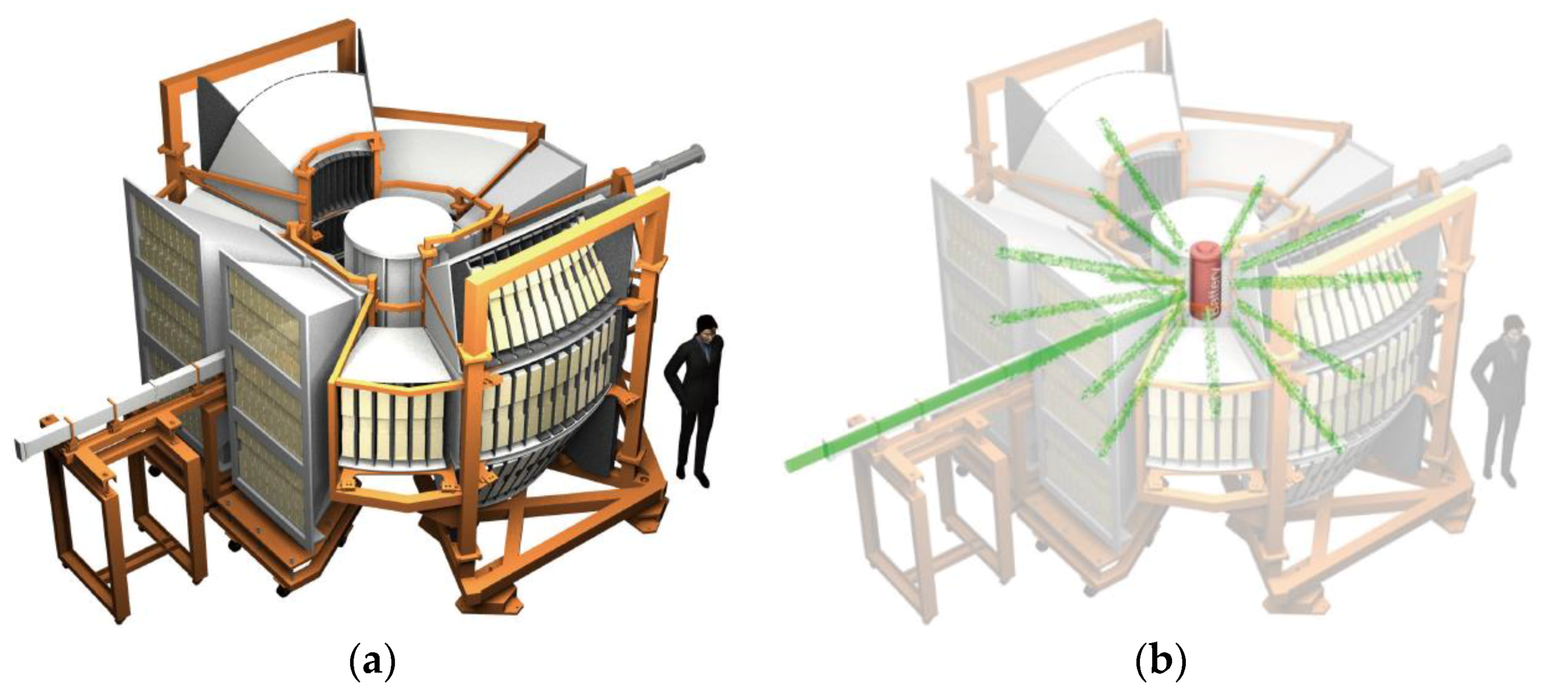
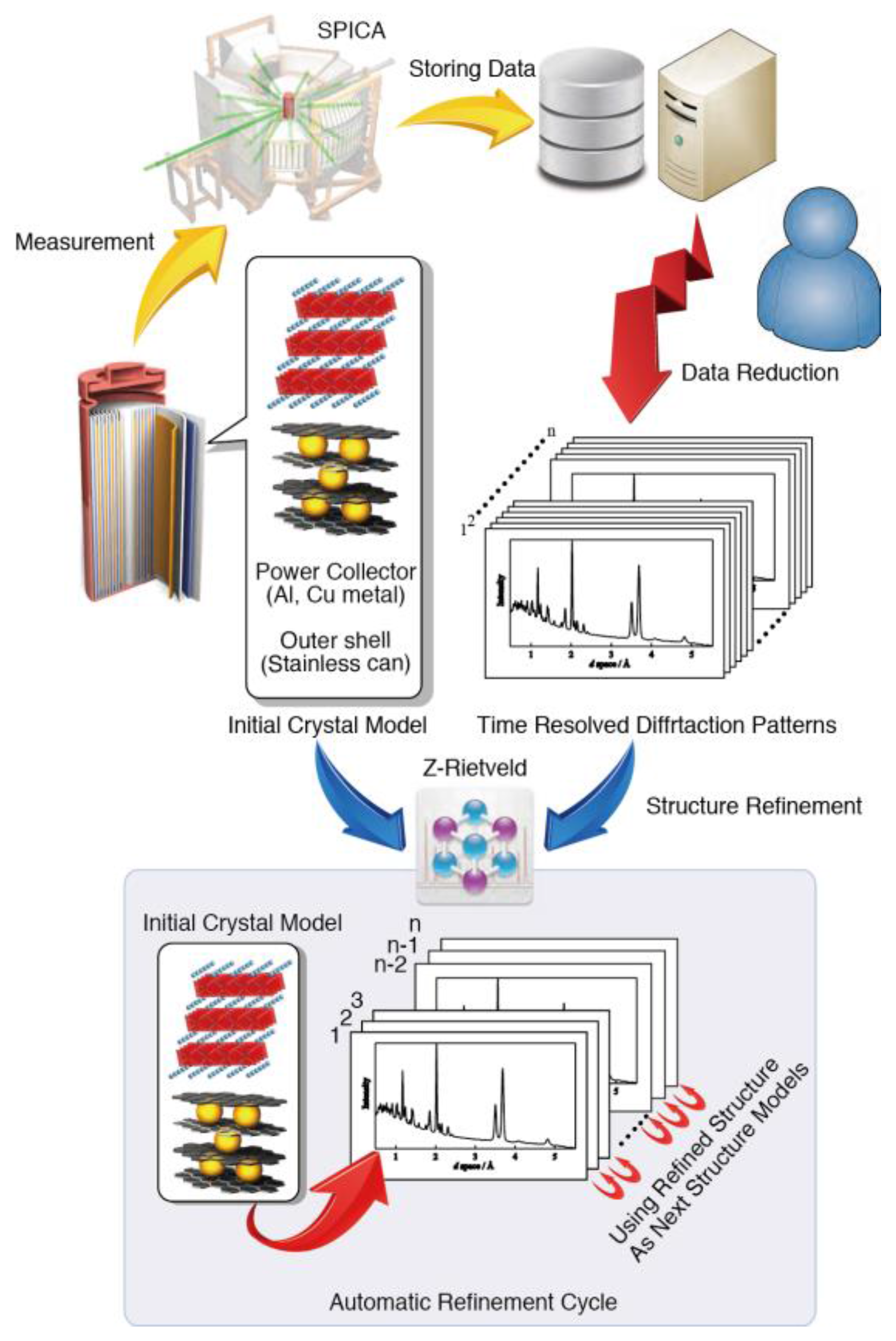
3.2. Special Environment Powder Diffractometer, SPICA
3.3. IBARAKI Materials Design Diffractometer (Versatile Neutron Diffractometer), iMATERIA
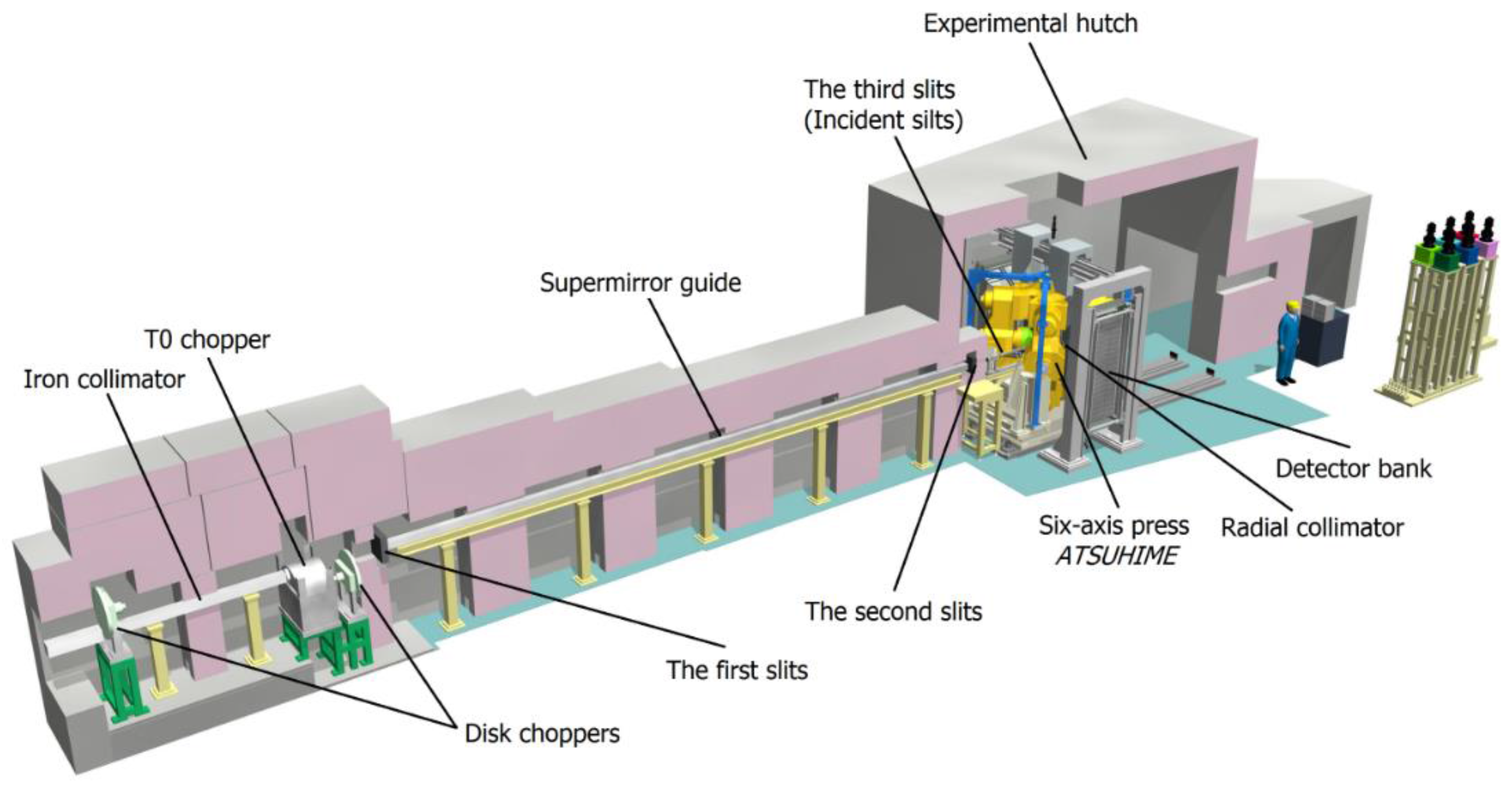
3.4. High-Pressure Neutron Diffractometer, PLANET
3.5. Engineering Materials Diffractometer, TAKUMI
3.6. IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer, iBIX
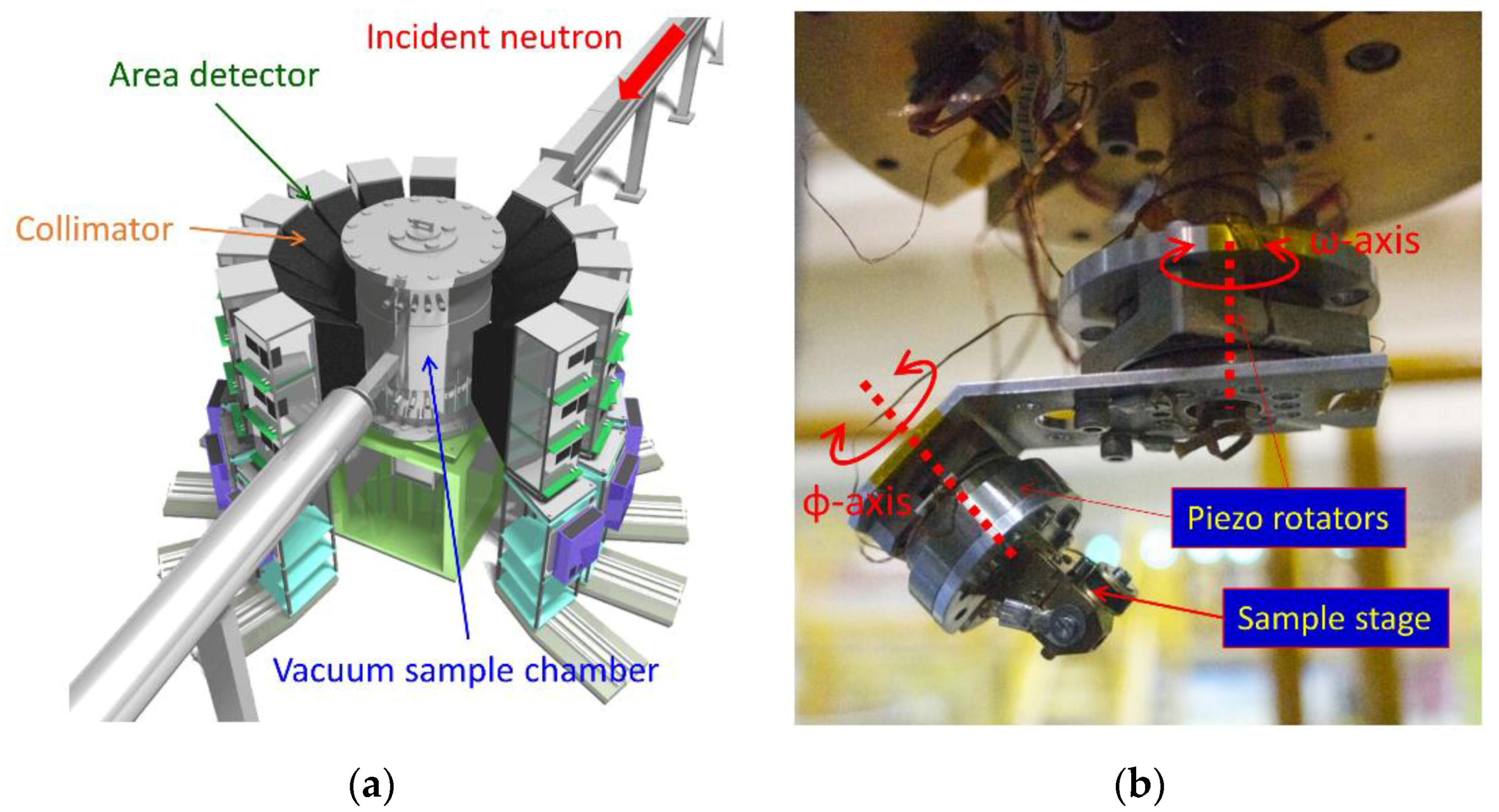
3.7. Extreme Environment Single-crystal Neutron Diffractometer, SENJU
4. Nano-Structure Group Instruments
4.1. Small- and Wide-angle Neutron Scattering Instrument, TAIKAN
4.2. Soft Interface Analyzer, SOFIA
4.3. Polarized Neutron Reflectometer, SHARAKU
4.4. High-Intensity Total Diffractometer, NOVA
5. Pulsed Neutron Application Group Instruments
5.1. Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument, ANNRI
5.1.1. Instrument Description
5.1.2. Applications
5.1.3. Specifications
5.1.4. Highlights
- A novel analytical technique that combines prompt gamma-ray analysis with the TOF technique (TOF-PGA) was developed [110].
- In the neutron-capture cross section measurements of minor actinides, analyses of 244Cm, 246Cm, 241Am, and 237Np have been completed. The results for 244Cm and 246Cm show that neutron-capture cross sections are deduced by using ANNRI, where a small amount (less than 1 mg) of a high radioactive sample can be used [111,112,113].
5.2. Neutron Optics and Fundamental Physics, NOP
5.2.1. Instrument Description
5.2.2. Applications
5.2.3. Specifications
5.2.4. Highlights
5.3. NeutrOn Beam-line for Observation and Research Use, NOBORU
5.3.1. Instrument Description
5.3.2. Applications
5.3.3. Specifications
5.3.4. Highlights
- Studies on the high-field magnetic structure of BiFeO3 [130], multiferroic materials, and magnetoelectric oxides were performed by combining neutron Laue diffraction with pulsed magnetic fields of up to 42 T.
5.4. Energy Resolved Neutron Imaging System, RADEN
5.4.1. Instrument Description
5.4.2. Applications
5.4.3. Specifications
5.4.4. Highlights
6. Outcomes from Neutron Instruments at MLF
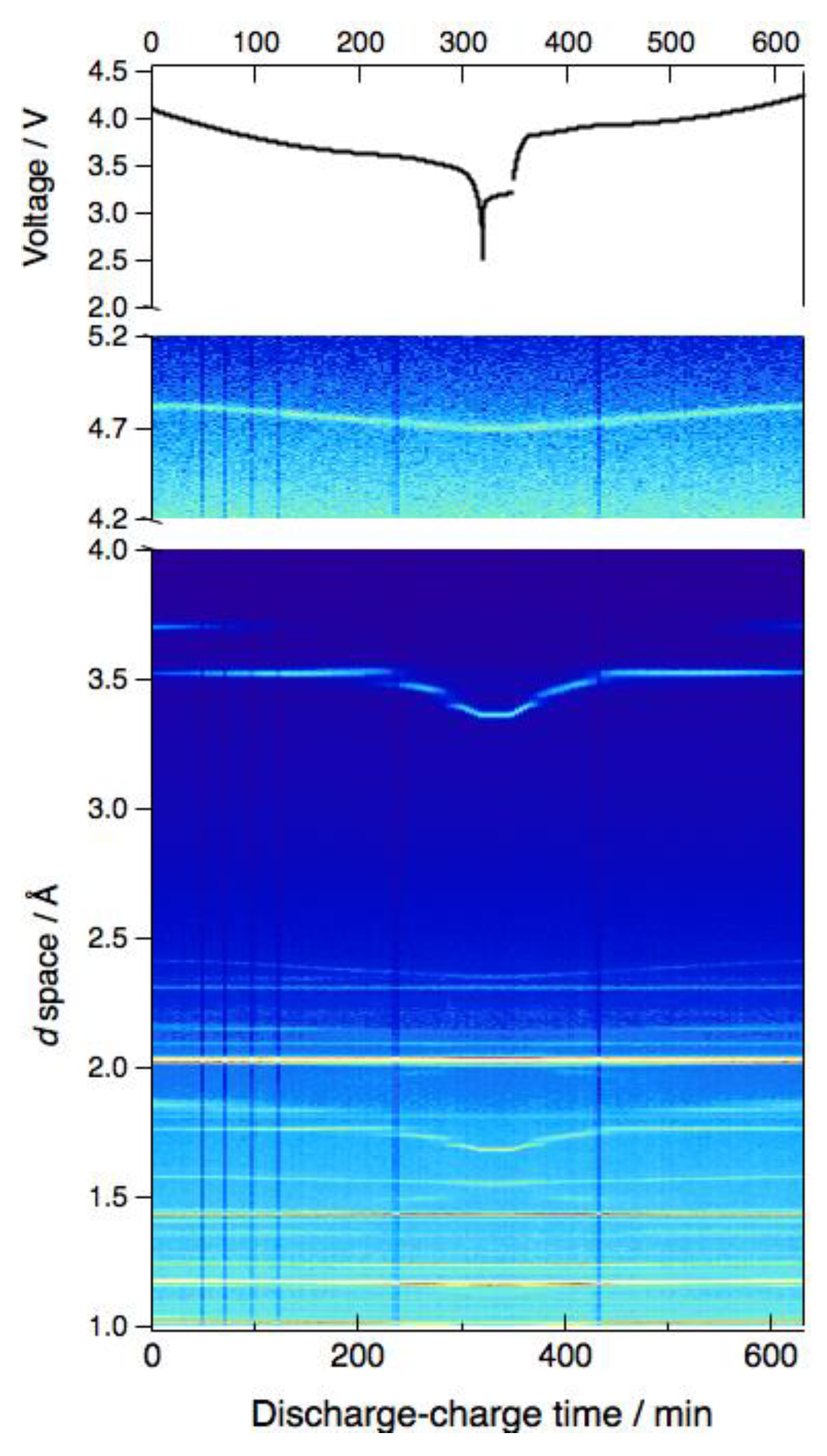
6.1. Structural Study of Sulfide Super-Ionic Conductor for High-Power All-solid-state Batteries at MLF
6.2. Neutron Diffraction Study of Phase Transformations in Steels—Effect of Partial Quenching on Phase Transformation in Nano-Bainite Steel
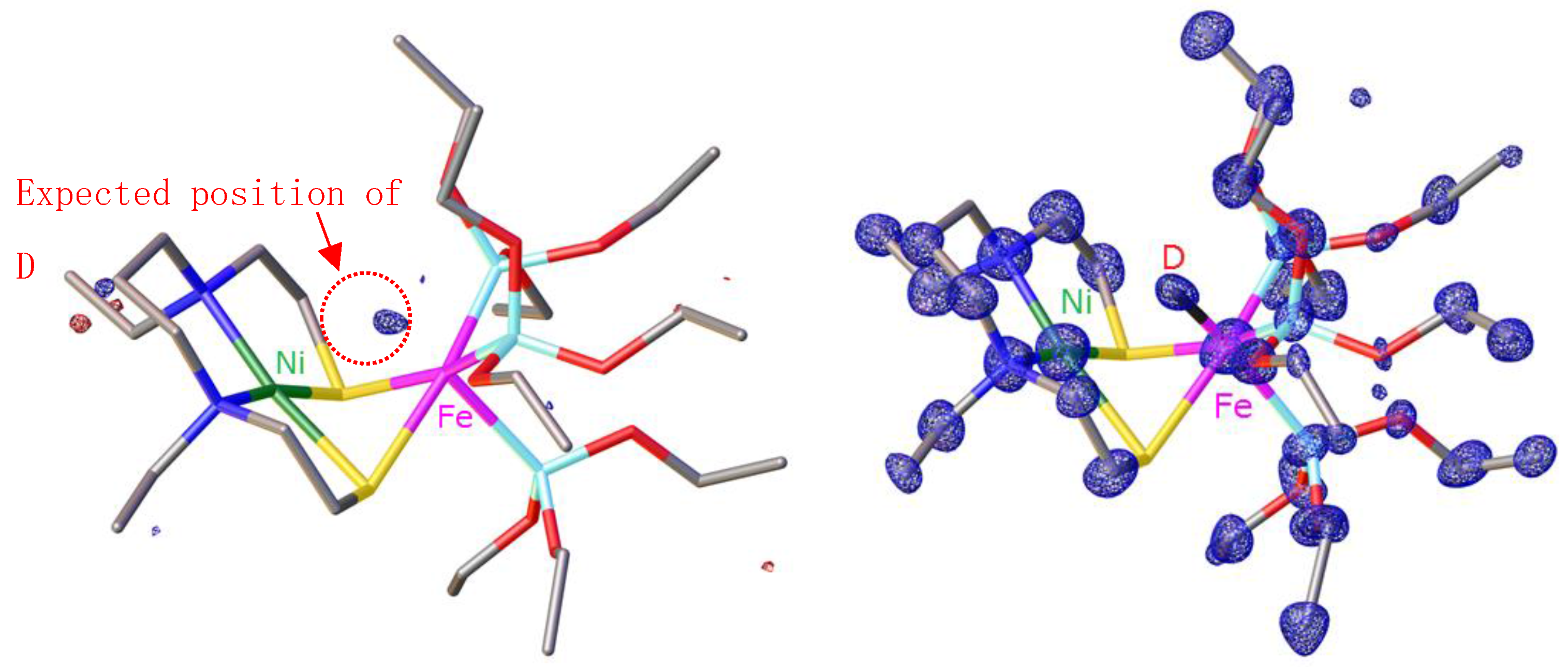
6.3 Neutron Structure Analysis of a [NiFe]hydrogenase-mimicking Complex at BL03 iBIX
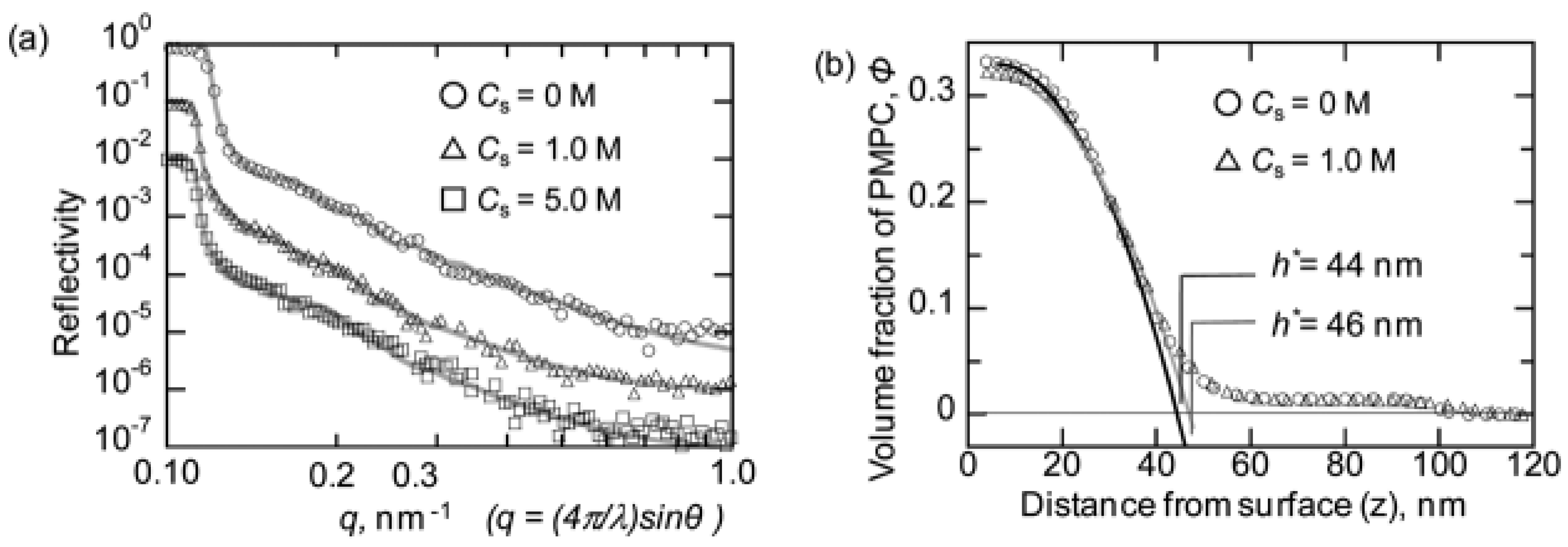
6.4. Characterization of Zwitterionic Polyelectrolyte Brush Swelled in Water by SOFIA Reflectometer
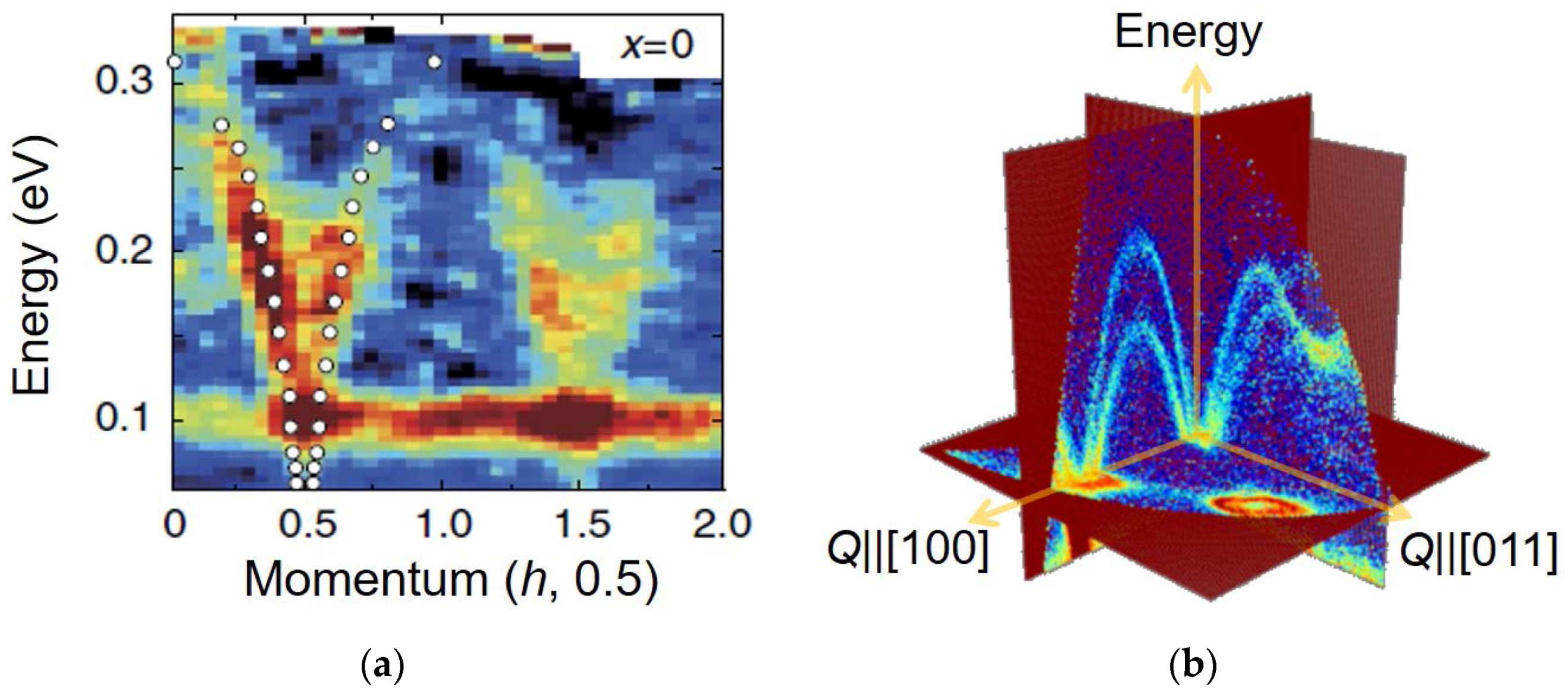
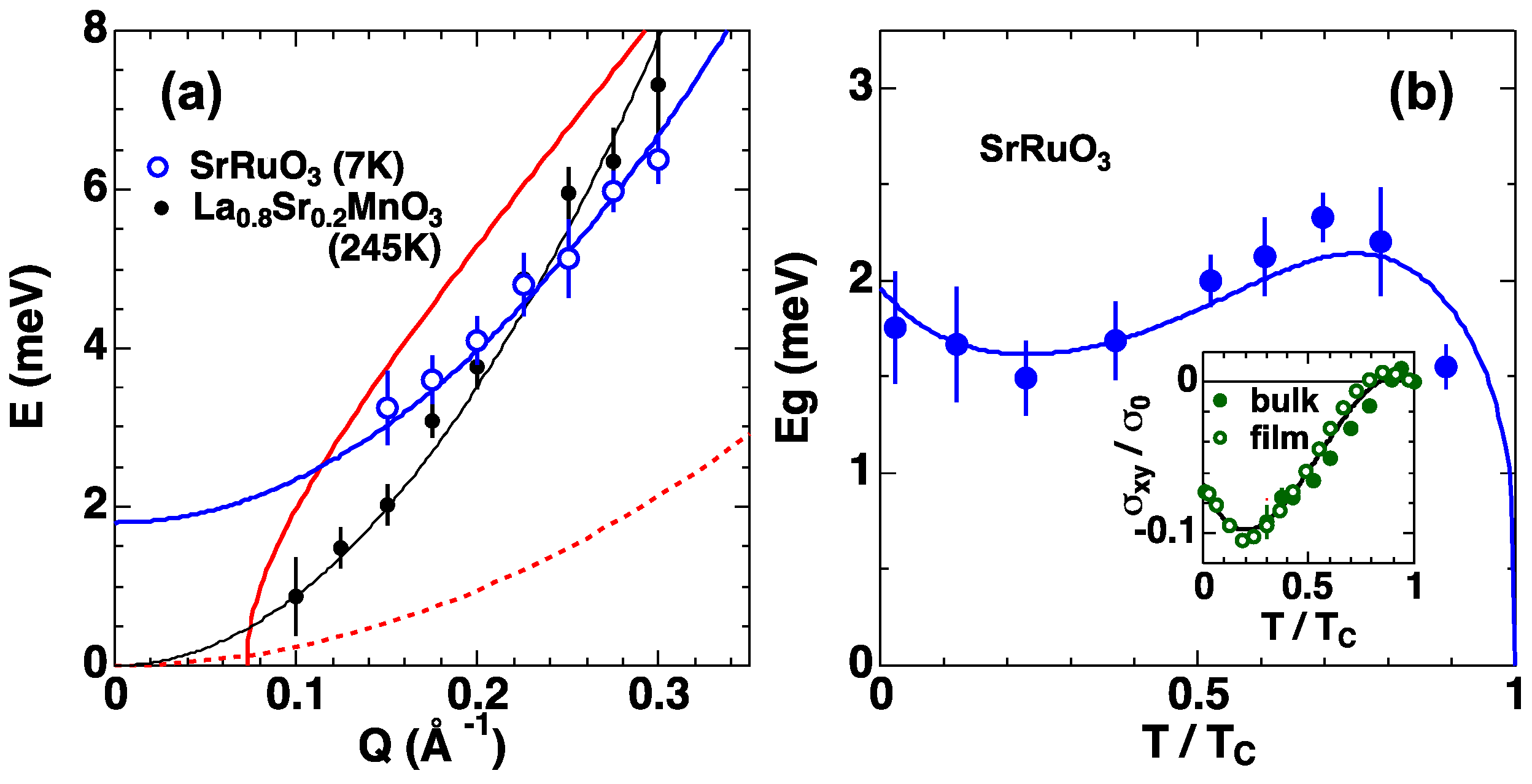
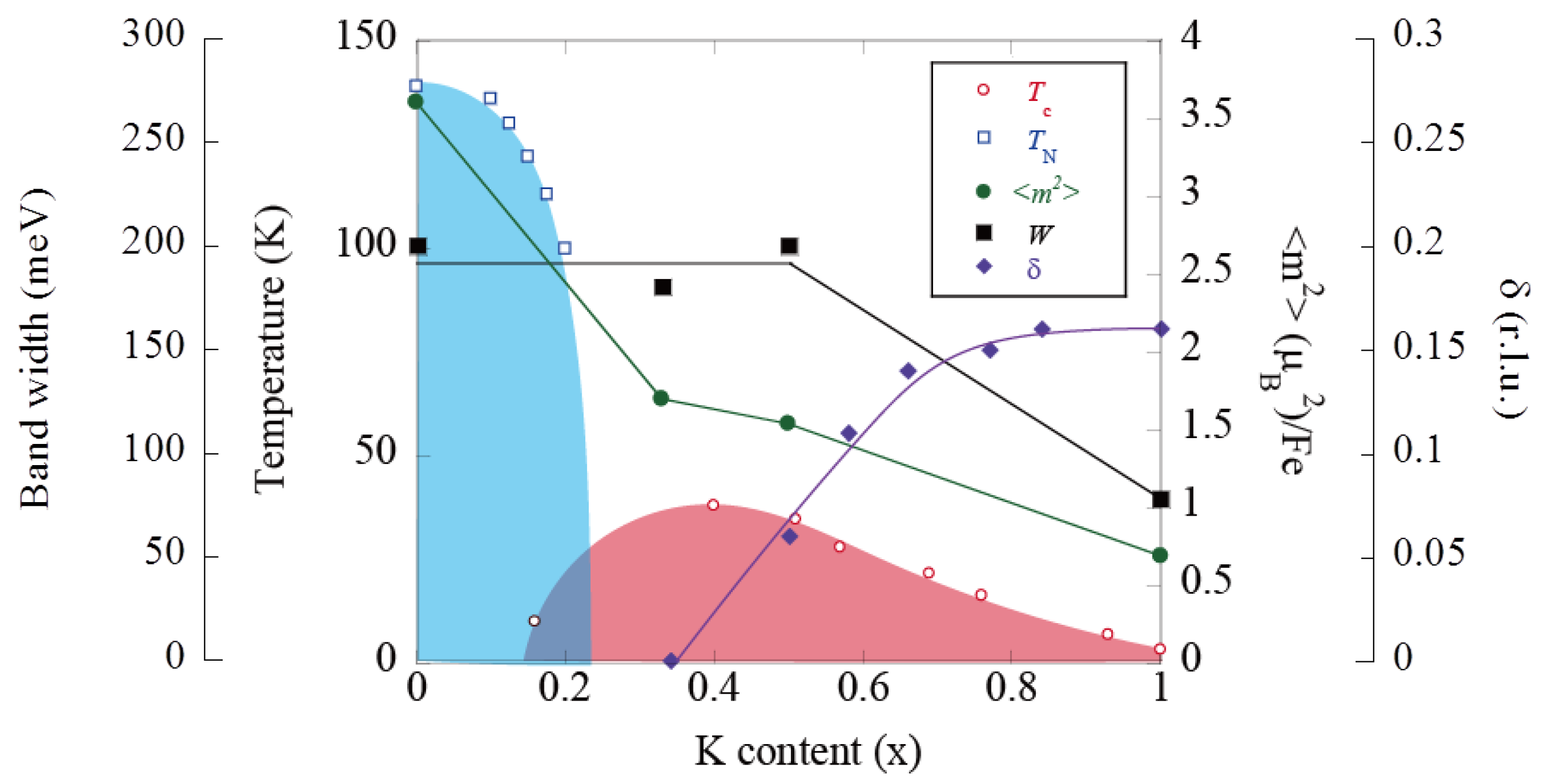
6.5. Study of Magnetism in Condensed Matters by Neutron Scattering at MLF—Magnetic Excitations in Hole-Overdoped Iron-Based Superconductors
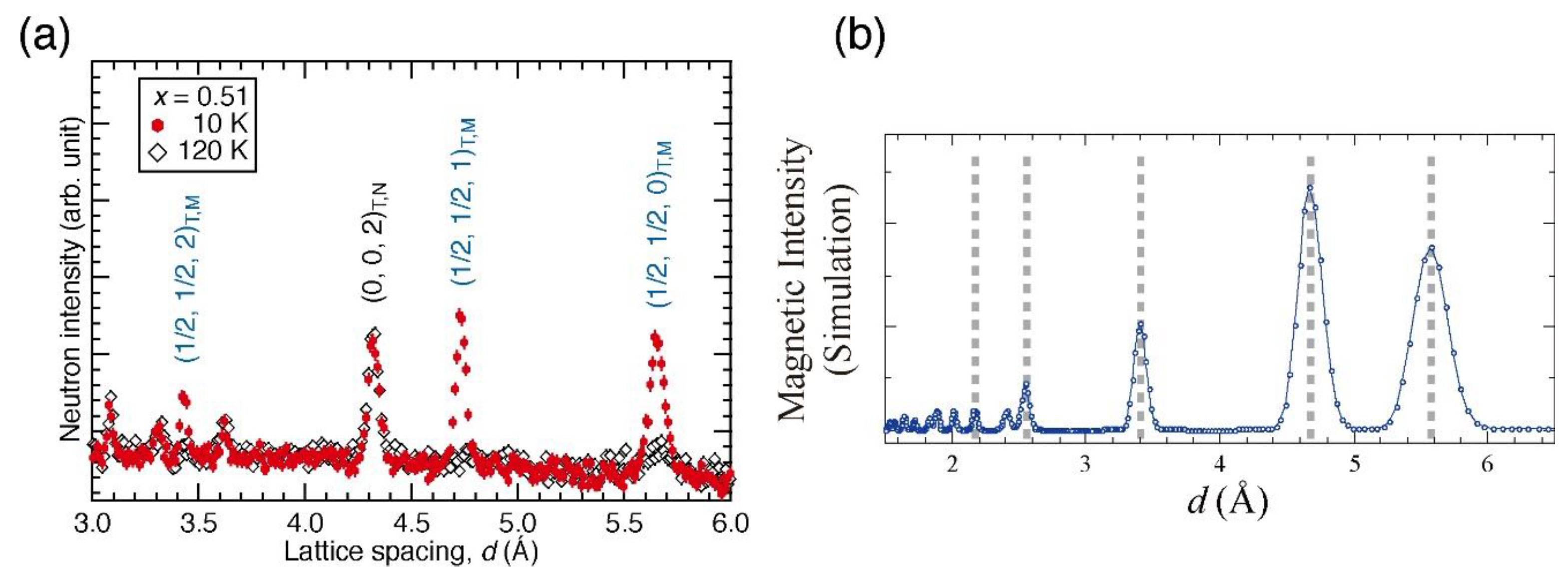
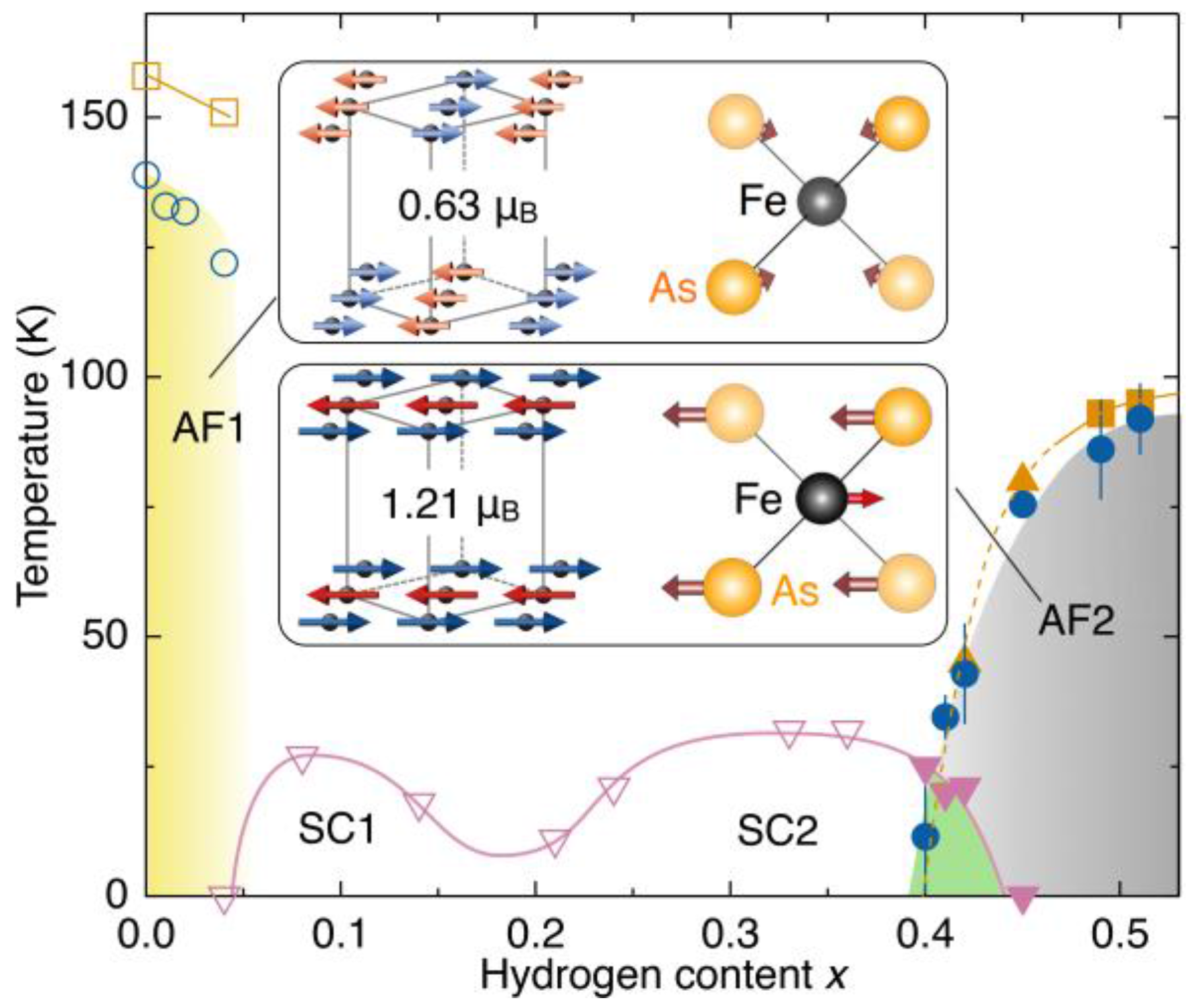
6.6. Multiple Quantum Beam Investigation of Iron Oxypnictide Superconductor LaFeAsO1−xHx
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otomo, T.; Nakajima, K.; Arai, M. (Eds.) Report of Neutron Instruments Working Group for the Joint Project of KEK and JAERI; KEK Report 2001-22: Tsukuba, Japan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, K.; Nakatani, T.; Torii, S.; Higemoto, W.; Otomo, T. (Eds.) Study on a Conceptual Design of a Data Acquisition and Instrument Control System for Experimental Suites at MLF of J-PARC; JAEA-Technology 2005-005: Tokai, Japan, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani, T.; Inamura, Y.; Moriyama, K.; Ito, T.; Muto, S.; Otomo, T. Event recording data acquisition system and experiment data management system for neutron experiments at MLF, J-PARC. JPS Conf. Proc. 2014, 1, 014010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Kajimoto, R.; Inamura, Y.; Mizuno, F.; Fujita, M.; Yokoo, T.; Arai, M. First demonstration of novel method for inelastic neutron scattering measurement utilizing multiple incident energies. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 78, 093002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Ito, T.; Inamura, Y.; Nakatani, T.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Iwahashi, T.; Aizawa, K. Neutron Diffraction Study of Piezoelectric Material under Cyclic Electric Field using Event Recording Technique. In Proceedings of the 21st Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-XXI), Ibaraki, Japan, 29 September–3 October 2014; Oku, T., Nakamura, M., Sakai, K., Teshigawara, M., Tatsumoto, H., Yonemura, M., Suzuki, J., Arai, M., Eds.; Japan Atomic Energy Agency: Ibaraki, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, T.; Hiroi, K.; Su, Y.; Kai, T.; Nakatani, T.; Oikawa, K.; Segawa, M.; Hayashida, H.; Parker, J.D.; Matsumoto, Y.; et al. Polarization analysis for magnetic field imaging at RADEN in J-PARC/MLF. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 862, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroi, K.; Shinohara, T.; Hayashida, H.; Parker, J.D.; Oikawa, K.; Harada, M.; Su, Y.; Kai, T. Magnetic field imaging of a model electric motor using polarized pulsed neutrons at J-PARC/MLF. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 862, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russina, M.; Mezei, F. First implementation of Repetition Rate Multiplication in neutron spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2009, 604, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Ohira-Kawamura, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Nakamura, M.; Kajimoto, R.; Inamura, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Aizawa, K.; Suzuya, K.; Shibata, K.; et al. AMATERAS: A Cold-Neutron Disk Chopper Spectrometer. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 80, SB028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, G.; Podlesnyak, A.A.; Niedziela, J.L.; Iverson, E.B.; Sokol, P.E. The new cold neutron chopper spectrometer at the Spallation Neutron Source: Design and performance. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 085108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, R.I.; Taylor, J.W.; Bennington, S.M. LET, a cold neutron multi-disk chopper spectrometer at ISIS. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2011, 637, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Takahashi, N.; Kawakita, Y.; Matsuura, M.; Yamada, T.; Tominaga, T.; Kambara, W.; Kobayashi, M.; Inamura, Y.; Nakatani, T.; et al. The performance of TOF near backscattering Spectrometer DNA in MLF, J-PARC. JPS Conf. Proc. 2015, 8, 036022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; Endoh, Y.; Yokoo, T.; Kawana, D.; Kaneko, Y.; Tokura, Y.; Fujita, M. Neutron Brillouin scattering with pulsed spallation neutron source – spin-wave excitations from ferromagnetic powder samples. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 82, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, R.; Nakamura, M.; Inamura, Y.; Mizuno, F.; Nakajima, K.; Ohira-Kawamura, S.; Yokoo, T.; Nakatani, T.; Maruyama, R.; Soyama, K.; et al. The Fermi chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at J-PARC. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 80, SB025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; Yokoo, T.; Satoh, S.; Yano, S.; Kawana, D.; Suzuki, J.; Sato, T.J. High Resolution Chopper Spectrometer (HRC) at J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2011, 631, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; Yokoo, T.; Kawana, D.; Yoshizawa, H.; Masuda, T.; Soda, M.; Sato, T.J.; Satoh, S.; Sakaguchi, M.; Muto, S. Progress in High Resolution Chopper Spectrometer, HRC. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 82, SA033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, T.; Ohoyama, K.; Itoh, S.; Suzuki, J.; Iwasa, K.; Sato, T.J.; Kira, H.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Ino, T.; Oku, T.; et al. Newly proposed inelastic neutron spectrometer POLANO. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 82, SA035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, T.; Ohoyama, K.; Itoh, S.; Suzuki, J.; Nanbu, M.; Kaneko, N.; Iwasa, K.; Sato, T.J.; Kimura, H.; Ohkawara, M. Construction of polarized inelastic neutron spectrometer in J-PARC. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 502, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, T.; Ohoyama, K.; Itoh, S.; Iwasa, K.; Kaneko, N.; Suzuki, J.; Ohkawara, M.; Aizawa, K.; Tasaki, S.; Ino, T.; et al. Polarized neutron spectrometer for inelastic experiments at J-PARC: Status of POLANO project. EPJ Web Conf. 2015, 83, 03018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, M.; Oda, T.; Yamada, N.L.; Endo, H.; Seto, H.; Kitaguch, M.; Harada, M.; Kawabata, Y. Supermirror neutron guide system for neutron resonance spin echo spectrometers at a pulsed neutron source. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, S.; Yonemura, M.; Surya Panca Putra, T.Y.; Zhang, J.; Miao, P.; Muroya, T.; Tomiyasu, R.; Morishima, T.; Satoh, S.; Sagehashi, H.; et al. Super High Resolution Powder Diffractometer at J-PARC. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2011, SB020, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemura, M.; Mori, K.; Kamiyama, T.; Fukunaga, T.; Torii, S.; Nagao, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; Onodera, Y.; Adipranoto, D.S.; Arai, H.; et al. Development of SPICA, New Dedicated Neutron Powder Diffractometer for Battery Studies. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 502, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, T.; Hoshikawa, A.; Yonemura, M.; Morishima, T.; Kamiyama, T.; Oishi, R.; Aizawa, K.; Sakuma, T.; Tomota, Y.; Arai, M.; et al. IBARAKI materials design diffractometer (iMATERIA) -Versatile neutron diffractometer at J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2009, 600, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Sano-Furukawa, A.; Arima, H.; Komatsu, K.; Yamada, A.; Inamura, Y.; Nakatani, T.; Seto, Y.; Nagai, T.; Utsumi, W.; et al. Design and performance of high-pressure PLANET beamline at pulsed neutron source at J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2015, 780, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjo, S.; Ito, T.; Aizawa, K.; Arima, H.; Abe, J.; Moriai, A.; Iwahashi, T.; Kamiyama, T. Current status of engineering materials diffractometer at J-PARC. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 681, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Nakatani, T.; Harjo, S.; Arima, H.; Abe, J.; Aizawa, K.; Moriai, A. Application software development for the engineering materials diffractometer, TAKUMI. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 652, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, I.; Kusaka, K.; Hosoya, T.; Niimura, N.; Ohhara, T.; Kurihara, K.; Yamada, T.; Ohnishi, Y.; Tomoyori, K.; Yokoyama, T. Neutron structure analysis using the IBARAKI biological crystal diffractometer iBIX at J-PARC. Acta Cryst. 2010, D66, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusaka, K.; Hosoya, T.; Yamada, T.; Tomoyori, K.; Ohhara, T.; Katagiri, M.; Kurihara, K.; Tanaka, I.; Niimura, N. Evaluation of performance for IBARAKI biological crystal diffractometer iBIX with new detectors. J. Synchrotron Rad. 2013, 20, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohhara, T.; Kiyanagi, R.; Oikawa, K.; Kaneko, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Tamura, I.; Nakao, A.; Hanashima, T.; Munakata, K.; Moyoshi, T.; et al. SENJU: A new time-of-flight single-crystal neutron diffractometer at J-PARC. J. Appl. Cryst. 2016, 49, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, S.; Suzuki, J.; Shinohara, T.; Oku, T.; Tominaga, T.; Ohishi, K.; Iwase, H.; Nakatani, T.; Inamura, Y.; Ito, T.; et al. The Design and Q resolution of the Small and Wide Angle Neutron Scattering Instrument (TAIKAN) in J-PARC. JPS Conf. Proc. 2015, 8, 036020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.L.; Torikai, N.; Mitamura, K.; Sagehashi, H.; Sato, S.; Seto, H.; Sugita, T.; Goko, S.; Furusaka, M.; Oda, T.; et al. Design and Performance of Horizontal Type Neutron Reflectometer SOFIA at J-PARC/MLF. Euro. Phys. J. Plus 2011, 126, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitamura, K.; Yamada, N.L.; Sagehashi, H.; Torikai, N.; Arita, H.; Terada, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Sato, S.; Seto, H.; Gokou, S.; et al. Novel Neutron Reflectometer SOFIA at J-PARC/MLF for In-Situ Soft-Interface Characterization. Polymer J. 2013, 45, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Yamazaki, D.; Soyama, K.; Maruyama, R.; Hayashida, H.; Asaoka, H.; Yamazaki, T.; Kubota, M.; Aizawa, K.; Arai, M.; et al. Current Status of a New Polarized Neutron Reflectometer at the Intense Pulsed Neutron Source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of J-PARC. Chin. J. Phys. 2012, 50, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, A.; Harada, H.; Nakamura, S.; Iwamoto, O.; Toh, Y.; Koizumi, M.; Kitatani, F.; Furutaka, K.; Igashira, M.; Katabuchi, T.; et al. Current activities and future plans for nuclear data measurements at J-PARC. Eur. Phys. J. A 2015, 51, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, K.; Ino, T.; Sakai, K.; Shinohara, T.; Hirota, K.; Ikeda, K.; Sato, H.; Otake, Y.; Ohmori, H.; Muto, S.; et al. Design of neutron beamline for fundamental physics at J-PARC BL05. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2009, 600, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, K.; Maekawa, F.; Harada, M.; Kai, T.; Meigo, S.; Kasugai, Y.; Ooi, M.; Sakai, K.; Teshigawara, M.; Hasegawa, S.; et al. Design and application of NOBORU—NeutrOn Beam line for Observation and Research Use at J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2008, 589, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, T.; Kai, T.; Oikawa, K.; Segawa, M.; Harada, M.; Nakatani, T.; Ooi, M.; Aizawa, K.; Sato, H.; Kamiyama, T.; et al. Final design of the Energy-Resolved Neutron Imaging System “RADEN” at J-PARC. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 746, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, H.; Itoh, S.; Yokoo, T.; Endo, H.; Nakajima, K.; Shibata, K.; Kajimoto, R.; Ohira-Kawamura, S.; Nakamura, M.; Kawakita, Y.; et al. Inelastic and quasi-elastic neutron scattering spectrometers in J-PARC. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 3651–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajimoto, R.; Nakajima, K.; Nakamura, M.; Soyama, K.; Yokoo, T.; Oikawa, K.; Arai, M. Study of the neutron guide design of the 4SEASONS spectrometer at J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2009, 600, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Kawakita, Y.; Kambara, W.; Aoyama, K.; Kajimoto, R.; Nakajima, K.; Ohira-Kawamura, S.; Ikeuchi, K.; Kikuchi, T.; Inamura, Y.; et al. Oscillating radial collimators for the chopper spectrometers at MLF in J-PARC. JPS Conf. Proc. 2015, 8, 036011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, K.; Ikeuchi, K.; Ishikado, M.; Suzuki, J.; Kajimoto, R.; Nakamura, M.; Inamura, Y.; Arai, M. Energy- and Q-resolution investigations of a chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at J-PARC. JPS Conf. Proc. 2014, 1, 014016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, F. The raison d’être of long pulse spallation sources. J. Neutron Res. 1997, 6, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, F.; Russina, M.; Schorr, S. The multiwavelength cold neutron time-of-flight spectrometer project IN500 at LANSCE. Physica B 2000, 276–278, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iimura, S.; Matsuishi, S.; Miyakawa, M.; Taniguchi, T.; Suzuki, K.; Usui, H.; Kuroki, K.; Kajimoto, R.; Nakamura, M.; Inamura, Y.; et al. Switching of intra-orbital spin excitations in electron-doped iron pnictide superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 060501(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Fujita, M.; Sasaki, T.; Minola, M.; Dellea, G.; Mazzoli, C.; Kummer, K.; Ghiringhelli, G.; Braicovich, L.; Tohyama, T.; et al. High-energy spin and charge excitations in electron-doped copper oxide superconductors. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Pan, B.; Zhang, X.; Ikeuchi, K.; Iida, K.; Christianson, A.D.; Walker, H.C.; Adroja, D.T.; Abdel-Hafiez, M.; et al. Magnetic ground state of FeSe. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ewings, R.A.; Ikeuchi, K.; Nakamura, M.; Roessli, B.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, G.; et al. Spin excitations in optimally P-doped BaFe2(As0.7P0.3)2 superconductor. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 094504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horigane, K.; Kihou, K.; Fujita, K.; Kajimoto, R.; Ikeuchi, K.; Ji, S.; Akimitsu, J.; Lee, C.H. Spin excitations in hole-overdoped iron-based superconductors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, M.; Kawamura, S.; Fujita, M.; Kajimoto, R.; Yamada, K. Development of spin-wave-like dispersive excitations below the pseudogap temperature in the high-temperature superconductor La2−xSrxCuO4. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 024504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; Yokoo, T.; Masuda, T.; Yoshizawa, H.; Soda, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Kawana, D.; Sato, T.J.; Nambu, Y.; Kuwahara, K.; et al. Science from the initial operation of HRC. JPS Conf. Proc. 2015, 8, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, J.F.; Blackman, J.A. Calculation of neutron cross sections for interband transitions in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 1982, 26, 4410–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passell, L.; Dietrich, O.W.; Als-Nielsen, J. Neutron scattering from the Heisenberg ferromagnets EuO and EuS. I. The exchange interactions. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 14, 4897–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Yamada, K.; Taijma, K.; Fukamachi, K. Spin dynamics in the amorphous invar alloy of Fe86B14. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1981, 50, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A. Neutron Brillouin scattering with chopper spectrometers. Physica B 1989, 156–157, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisa, D.; Aisa, S.; Babucci, E.; Barocchi, F.; Cunsolo, A.; De Francesco, A.; Formisano, F.; Gahl, T.; Guarini, E.; Laloni, A.; et al. BRISP: A new thermal-neutron spectrometer for small-angle studies of disordered matter. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 5130–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Nagaosa, N.; Takahashi, K.S.; Asamitsu, A.; Mathieu, R.; Ogasawara, T.; Yamada, H.; Kawasaki, M.; Tokura, Y.; Terakura, K. The Anomalous Hall effect and magnetic monopoles in momentum space. Science 2003, 302, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, S.; Endoh, Y.; Yokoo, T.; Ibuka, S.; Park, J.-G.; Kaneko, Y.; Takahashi, K.S.; Tokura, Y.; Nagaosa, N. Weyl fermions and spin dynamics of metallic ferromagnet SrRuO3. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, K.; Nakamura, M.; Kajimoto, R.; Osakabe, T.; Kakurai, K.; Matsuda, M.; Metoki, N.; Wakimoto, S.; Sato, T.J.; Itoh, S.; et al. Cold-neutron disk-chopper spectrometer at J-PARC. J. Neutron Res. 2007, 15, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Nakajima, K.; Kajimoto, R.; Arai, M. Utilization of multiple incident energies on Cold-Neutron Disk-Chopper Spectrometer at J-PARC. J. Neutron Res. 2007, 15, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, F. Multiplexing chopper systems for pulsed neutron sources: Practical basics. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 82, SA025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, R.; Nakamura, M.; Osakabe, T.; Sato, T.J.; Nakajima, K.; Arai, M. Study of converging neutron guides for the Cold Neutron Double-Chopper Spectrometer at J-PARC. Physica B 2006, 385–386, 1236–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, R.; Nakajima, K.; Nakamura, M.; Osakabe, T.; Sato, T.J.; Arai, M. Curved neutron guide of the cold neutron disk-chopper spectrometer at J-PARC. J. Neutron Res. 2008, 16, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Ohira-Kawamura, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Kajimoto, R.; Takahashi, N.; Nakamura, M.; Soyama, K.; Osakabe, T. Beam-transport optimization for cold-neutron spectrometer. EPJ Web Conf. 2015, 83, 03011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Nakajima, K.; Ohira-Kawamura, S.; Inamura, Y.; Yamamuro, O.; Kofu, M.; Kawakita, Y.; Suzuya, K.; Nakamura, M.; Arai, M. Mode-distribution analysis of quasielastic neutron scattering and application to liquid water. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 062314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neutron Spin Echo, Lecture Notes in Physics Volume 128; Mezei, F., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Gähler, R.; Golub, R. Neutron resonance spin echo, bootstrap method for increasing the effective magnetic field. J. Phys. France 1988, 49, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Monkenbusch, M.; Arbe, A.; Colmenero, J. Neutron spin echo in polymer systems. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2005, 174, 1–221. [Google Scholar]
- Nambu, Y.; Gardner, J.S.; MacLaughlin, D.E.; Stock, C.; Endo, H.; Jonas, S.; Sato, T.J.; Nakatsuji, S.; Broholm, C. Spin Fluctuations from Hertz to Terahertz on a Triangular Lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 127202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, C.; Lelievre-Berna, E.; Falus, P.; Bentley, P.M.; Moskvin, E.; Grigoriev, S.; Fouquet, P.; Farago, B. Chiral Paramagnetic Skyrmion-like Phase in MnSi. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 197202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindervater, J.; Martin, N.; Haeussler, W.; Krautloher, M.; Fuchs, C.; Muehlbauer, S.; Lim, J.A.; Blackburn, E.; Boeni, P.; Peiderer, C. Neutron spin echo spectroscopy under 17 T magnetic field at RESEDA. EPJ Web Conf. 2015, 83, 03008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T. Study on Time-of-Flight Neutron Resonance Neutron Spin Echo Technique at J-PARC MLF BL06. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, 23 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oda, T.; Hino, M.; Kitaguchi, M.; Geltenbort, P.; Kawabata, Y. Pulsed neutron time-dependent intensity modulation for quasi-elastic neutron scattering spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 105124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, H.; Noguchi, Y.; Miyayama, M.; Suzuki, M.; Watanabe, A.; Sasabe, S.; Ozaki, T.; Mori, S.; Torii, S.; Kamiyama, T. Structural and piezoelectric properties of high-density (Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3-BiFeO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.; Kang, M.; Jang, K.-H.; Lee, C.; Streltsov, S.; Mazurenko, V.; Valentyuk, M.; Medvedeva, J.; Kamiyama, T.; et al. Doping dependence of spin-lattice coupling and two-dimensional ordering in multiferroic hexagonal Y1−xLuxMnO3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1). Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 054428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaya, N.; Homma, K.; Yamakawa, Y.; Hirayama, M.; Kanno, R.; Yonemura, M.; Kamiyama, T.; Kato, Y.; Hama, S.; Kawamoto, K.; et al. A lithium superionic conductor. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, S.; Doi, Y.; Torii, S.; Zhang, J.; Surya Panca Putra, T.Y.; Miao, P.; Kamiyama, T.; Esaka, T. Structural and electrical properties of Pb-substituted La2Mo2O9 oxide ion conductors. Solid State Ionics 2013, 238, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Zhang, J.R.; Torii, S.; Choi, S.; Cho, D.-Y.; Kamiyama, T.; Yu, J.; McEwen, K.A.; Park, J.-G. Large in-plane deformation of RuO6 octahedron and ferromagnetism of bulk SrRuO3. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 465601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasim, I.; Blanchard, P.E.R.; Kennedy, B.J.; Kamiyama, T.; Miao, P.; Torii, S. Structural and electronic properties of Sr1−xCaxTi0.5Mn0.5O3. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 213, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, C.I.; Joo, H.W.; Chae, K.W.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Torii, S.; Kamiyama, T. Monoclinic ferroelectric NaNbO3 at room temperature: Crystal structure solved by using super high resolution neutron powder diffraction. Mater. Lett. 2015, 156, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubkin, A.F.; Proskurina, E.P.; Kousaka, Y.; Sherokalova, E.M.; Selezneva, N.V.; Miao, P.; Lee, S.; Zhang, J.; Ishikawa, Y.; Torii, S.; et al. Crystal and magnetic structures of Cr1/3NbSe2 from neutron diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 013903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, S.; Miao, P.; Lee, S.; Yonemura, M.; Kamiyama, T. MLF Annual Report 2014; Tokai, Japan, 2014; pp. 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kino, K.; Mori, K.; Miyayama, M.; Yonemura, M.; Torii, S.; Kawai, M.; Fukunaga, T.; Kamiyama, T. Design of Air Scattering Chamber for the Powder Diffractometer SPICA. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 80 (Suppl. B), SB001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, R.; Yonemura, M.; Nishimaki, Y.; Torii, S.; Hoshikawa, A.; Ishigaki, T.; Morishima, T.; Mori, K.; Kamiyama, T. Rietveld analysis software for J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2009, 600, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taminato, S.; Yonemura, M.; Shiotani, S.; Kamiyama, T.; Torii, S.; Nagao, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; Mori, K.; Fukunaga, T.; Onodera, Y.; et al. Real-time observations of lithium battery reactions—Operando neutron diffraction analysis during practical operation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshikawa, A.; Ishigaki, T.; Yonemura, M.; Iwase, K.; Oguro, H.; Sulistyanintyas, D.; Kamiyama, T.; Hayashi, M. Automatic sample changer for IBARAKI materials design diffractometer (iMATERIA). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 251, 012083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano-Furukawa, A.; Hattori, T.; Arima, H.; Yamada, A.; Tabata, S.; Kondo, M.; Nakamura, A.; Kagi, H.; Yagi, T. Six-axis multi-anvil press for high-pressure, high-temperature neutron diffraction experiments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 113905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, A.; Saitoh, H.; Sugimoto, H.; Hattori, T.; Sano-Furukawa, A.; Endo, N.; Katayama, Y.; Iizuka, R.; Sato, T.; Mastuo, M.; et al. Site occupancy of interstitial deuterium atoms in face-centred cubic iron. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, K.; Moriyama, M.; Koizumi, T.; Nakayama, K.; Kagi, H.; Abe, J.; Harjo, S. Development of a new P-T controlling system for neutron-scattering experiments. High Pressure Res. 2013, 33, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, K.; Noritake, F.; Machida, S.; Sano-Furukawa, A.; Hattori, T.; Yamane, R.; Kagi, H. Partially ordered state of ice XV. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, S.; Komatsu, K.; Pietrucci, F.; Kagi, H.; Ludl, A.-A.; Machida, S.; Hattori, T.; Sano-Furukawa, A.; Bove, L.E. Ice VII from aqueous salt solutions: From a glass to a crystal with broken H-bonds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmi, T.; Harjo, S.; Nunoya, Y.; Kajitani, H.; Koizumi, N.; Aizawa, K.; Machiya, S.; Osamura, K. Neutron diffraction measurement of internal strain in the first Japanese ITER CS conductor sample. Supercon. Sci. Tech. 2013, 26, 084002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Kusunoki, K.; Hatanaka, Y.; Mukai, T.; Tasai, A.; Kanematsu, M.; Kabayama, K.; Harjo, S. Measuring strain and stress distributions along rebar embedded in concrete using time-of-flight neutron diffraction. Meas. Sci. Tech. 2014, 25, 025602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoo, K.; Tomota, Y.; Harjo, S.; Okitsu, Y. Tensile behavior of a TRIP-aided ultra-fine grained steel studied by neutron diffraction. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Zhai, Z.; Nie, Z.H.; Harjo, S.; Cong, D.Y.; Wang, M.G.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.D. An in situ neutron diffraction study of anomalous superelasticity in a strain glass Ni43Fe18Ga27Co12 alloy. J. Appl. Cryst. 2015, 48, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Oguro, H.; Awaji, S.; Watanabe, K.; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, K.; Machiya, S.; Suzuki, H.; Osamura, K. Prebending effect on three-dimensional strain in CuNb/(Nb,Ti)3Sn wires under a tensile load. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercon. 2012, 22, 6000204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Harjo, S.; Nakamoto, T. Neutron diffraction study on very high elastic strain of 6% in an Fe3Pt under compressive stress. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 231908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.M.; Gong, W.; Tomota, Y.; Harjo, S.; Li, J.; Chi, B.; Pu, J. Study of tempering behavior of lath martensite using in situ neutron diffraction. Mater. Charact. 2015, 107, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Tomota, Y.; Harjo, S.; Su, Y.H.; Aizawa, K. Effect of prior martensite on bainite transformation in nanobainite steel. Acta Mater. 2015, 85, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungár, T.; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Tomota, Y.; Ribárik, G.; Shi, Z. Composite behavior of lath martensite steels induced by plastic strain, a new paradigm for the elastic-plastic response of martensitic steels. Metal. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohhara, T.; Kusaka, K.; Hosoya, T.; Kurihara, K.; Tomoyori, K.; Niimura, N.; Tanaka, I.; Suzuki, J.; Nakatani, T.; Otomo, T.; et al. Development of data processing software for a new TOF single crystal neutron diffractometer at J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2009, 600, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, N.; Yamada, T.; Hosoya, T.; Ohhara, T.; Tanaka, I.; Kusaka, K. Application of profile fitting method to neutron time-of-flight protein single crystal diffraction data collected at the iBIX. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, N.L.; Mitamura, K.; Sagehashi, H.; Torikai, N.; Sato, S.; Seto, H.; Furusaka, M.; Oda, T.; Hino, M.; Fujiwara, T.; et al. Development of Sample Environments for the SOFIA Reflectometer for Seconds-Order Time-Slicing Measurements. JPS Conf. Proc. 2015, 8, 036003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemura, M.; Hirayama, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kanno, R.; Torikai, N.; Yamada, N.L. Development of Spectroelectrochemical Cells for in situ Neutron Reflectometry. IOP Conf. Ser. 2014, 502, 012054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, A.; Honda, M.; Hattori, T.; Sano-Furukawa, A.; Watanuki, T.; Katayama, Y.; Aoki, K.; Komatsu, K.; Arima, H.; Ohshita, H.; et al. Formation of NaCl-type monodeuteride LaD by the disproportionation reaction of LaD2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 205501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, S.; Iijima, Y.; Sato, T.; Saitoh, H.; Ikeda, K.; Otomo, T.; Miwa, K.; Ikeshoji, T.; Orimo, S.-I. Formation of novel transition metal hydride complexes with ninefold hydrogen coordination. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Kasai, T.; Iwase, K.; Fujisaki, F.; Onodera, Y.; Fukunaga, T. Structural origin of massive improvement in Li-ion conductivity on transition from (Li2S)5(GeS2)(P2S5) glass to Li10GeP2S12 crystal. Solid State Ionics 2017, 301, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Watanabe, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Matsugami, M.; Tsuzuki, S.; Seki, S.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Atkin, R.; Ueno, K.; Dokko, K.; et al. Li(+) Local Structure in Li-Tetraglyme Solvate Ionic Liquid Revealed by Neutron Total Scattering Experiments with the (6/7)Li Isotopic Substitution Technique. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 2832–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraishi, M.; Iimura, S.; Kojima, K.M.; Yamaura, J.; Hiraka, H.; Ikeda, K.; Miao, P.; Ishikawa, Y.; Torii, S.; Miyazaki, M.; et al. Bipartite magnetic parent phases in the iron oxypnictide superconductor. Nat. Phys. 2014, 10, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kin, T.; Furutaka, K.; Goko, S.; Harada, H.; Kimura, A.; Kitatani, F.; Nakamura, S.; Ohta, M.; Oshima, M.; Toh, Y.; et al. The “4π Ge Spectrometer” for Measurements of Neutron Capture Cross Sections by the TOF Method at the J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2011, 59, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, Y.; Ebihara, M.; Kimura, A.; Nakamura, S.; Harada, H.; Hara, K.Y.; Koizumi, M.; Kitatani, F.; Furutaka, K. Synergistic Effect of Combining Two Nondestructive Analytical Methods for Multielemental Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12030–12036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, A.; Fujii, T.; Fukutani, S.; Furutaka, K.; Goko, S.; Hara, K.Y.; Harada, H.; Hirose, K.; Hori, J.; Igashira, M.; et al. Neutron-capture cross-sections of 244Cm and246Cm measured with an array of large germanium detectors in the ANNRI at J-PARC/MLF. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, H.; Ohta, M.; Kimura, A.; Furutaka, K.; Hirose, K.; Hara, K.Y.; Kin, T.; Kitatani, F.; Koizumi, M.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Capture Cross-section Measurement of 241Am(n,γ) at J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI. Nucl. Data Sheets 2014, 119, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, K.; Furutaka, K.; Hara, K.Y.; Harada, H.; Kimura, A.; Kin, T.; Kitatani, F.; Koizumi, M.; Nakamura, S.; Oshima, M.; et al. Cross-section measurement of 237Np (n, γ) from 10 meV to 1 keV at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Hirose, K.; Nakamura, S.; Harada, H.; Hara, K.Y.; Hori, J.; Igashira, M.; Kamiyama, T.; Katabuchi, T.; Kino, K.; et al. Measurements of Neutron Capture Cross Sections of 112Sn and 118Sn with J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI. Nucl. Data Sheets 2014, 119, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Kimura, A.; Kitatani, F.; Ohta, M.; Furutaka, K.; Goko, S.; Hara, K.Y.; Harada, H.; Hirose, K.; Kin, T.; et al. Cross Section Measurements of the Radioactive 107Pd and STable 105,108Pd Nuclei at J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI. Nucl. Data Sheets 2014, 119, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katabuchi, T.; Matsuhashi, T.; Terada, K.; Igashira, M.; Mizumoto, M.; Hirose, K.; Kimura, A.; Iwamoto, N.; Hara, K.Y.; Harada, H.; et al. Misassigned neutron resonances of 142Nd and stellar neutron capture cross sections. Phys. Rev. C 2015, 91, 037603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, K. Neutron network news. Hamon 2015, 25, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Imajo, S.; Mishima, K.; Kitaguchi, M.; Iwashia, Y.; Yamada, N.L.; Hino, M.; Oda, T.; Ino, T.; Shimizu, H.M.; Yamashita, S.; et al. Pulsed UCN Production using a Doppler Shifter at J-PARC. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2016, 2016, 013C02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, F.; Harada, M.; Oikawa, K.; Teshigawara, M.; Kai, T.; Meigo, S.; Ooi, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Takada, H.; Futakawa, M.; et al. First neutron production utilizing J-PARC pulsed spallation neutron source JSNS and neutronic performance demonstrated. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2010, 620, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Kambara, W.; Krist, T.; Shinohara, T.; Ikeuchi, K.; Arai, M.; Kajimoto, R.; Nakajima, K.; Tanaka, H.; Suzuki, J.; et al. Feasibility demonstration of a new Fermi chopper with supermirror-coated slit package. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2014, 737, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Kawasaki, T.; Hosoya, T.; Toh, K.; Oikawa, K.; Sakasai, K.; Ebine, M.; Birumachi, A.; Soyama, K.; Katagiri, M. A large-area two-dimensional scintillator detector with a wavelength-shifting fibre readout for a time-of-flight single-crystal neutron diffractometer. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2012, 686, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Nakamura, T.; Toh, K.; Hosoya, T.; Oikawa, K.; Ohhara, T.; Kiyanagi, R.; Ebine, M.; Birumachi, A.; Sakasai, K.; et al. Detector system of the SENJU single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffractometer at J-PARC/MLF. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2014, 735, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Toh, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Honda, K.; Suzuki, H.; Ebine, M.; Birumachi, A.; Sakasai, K.; Soyama, K.; Katagiri, M. A scintillator-based detector with sub-100-um spatial resolution comprising a fibre-optic taper with wavelength-shifting fibre readout for time-of-flight neutron imaging. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2014, 737, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.D.; Hattori, K.; Fujioka, H.; Harada, M.; Iwaki, S.; Kabuki, S.; Kishimoto, Y.; Kubo, H.; Kurosawa, S.; Miuchi, K.; et al. Neutron imaging detector based on the micro-pixel chamber. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2013, 697, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, M.; Kai, T.; SaKai, T.; Ooi, M.; Kureta, M. Development of a high-speed camera system for neutron imaging at a pulsed neutron source. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2013, 697, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.D.; Harada, M.; Hattori, K.; Iwaki, S.; Kabuki, S.; Kishimoto, Y.; Kubo, H.; Kurosawa, S.; Matsuoka, Y.; Miuchi, K.; et al. Spatial resolution of a μPIC-based neutron imaging detector. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2013, 726, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, M.; Ooi, M.; Kai, T.; Shinohara, T.; Kureta, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Imaki, T. Development of a pulsed neutron three-dimensional imaging system using a highly sensitive image-intensifier at J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2015, 769, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasemi, H.; Harada, M.; Kai, T.; Shinohara, T.; Ooi, M.; Sato, H.; Kino, K.; Segawa, M.; Kamiyama, T.; Kiyanagi, Y. Evaluation of nuclide density by neutron resonance transmission at the NOBORU instrument in J-PARC/MLF. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2015, 773, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremsin, A.S.; Shinohara, T.; Kai, T.; Ooi, M.; Kamiyama, T.; Kiyanagi, Y.; Shiota, Y.; McPhate, J.B.; Vallerga, J.V.; Siegmund, O.H.W.; et al. Neutron resonance transmission spectroscopy with high spatial and energy resolution at the J-PARC pulsed neutron source. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2014, 746, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohoyama, K.; Lee, S.; Yoshii, S.; Narumi, Y.; Morioka, T.; Nojiri, H.; Jeon, G.S.; Cheong, S.W.; Park, J.G. High Field Neutron Diffraction Studies on Metamagnetic Transition of Multiferroic BiFeO3. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 80, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, M.G.; Strobl, M.; Lauridsen, E.M.; Frandsen, H.L.; Tremsin, A.S.; Shinohara, T.; Kuhn, L.T. Phase Transition Mapping by Means of Neutron Imaging in SOFC Anode Supports during Reduction under Applied Stress. ECS Trans. 2015, 68, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremsin, A.S.; Ganguly, S.; Meco, S.M.; Pardal, G.R.; Shinohara, T.; Feller, W.B. Investigation of dissimilar metal welds by energy-resolved neutron imaging. J. Appl. Cryst. 2016, 49, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremsin, A.S.; Gao, Y.; Dial, L.C.; Grazzi, F.; Shinohara, T. Investigation of microstructure in additive manufactured Inconel 625 by spatially resolved neutron transmission spectroscopy. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2016, 17, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Sato, T.; Shiota, Y.; Kamiyama, T.; Tremsin, A.S.; Ohnuma, M.; Kiyanagi, Y. Relation between Vickers Hardness and Bragg-Edge Broadening in Quenched Steel Rods Observed by Pulsed Neutron Transmission Imaging. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.H.; Oikawa, K.; Harjo, S.; Shinohara, T.; Kai, T.; Harada, M.; Hiroi, K.; Zhang, S.Y.; Parker, J.D.; Sato, H.; et al. Time-of-flight neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging of microstructures in bent steel plates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 675, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremsin, A.S.; Rakovan, J.; Shinohara, T.; Kockelmann, W.; Losko, A.S.; Vogel, S.C. Non-Destructive Study of Bulk Crystallinity and Elemental Composition of Natural Gold Single Crystal Samples by Energy-Resolved Neutron Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyajima, S.; Shishido, H.; Narukami, Y.; Yoshioka, N.; Fujimaki, A.; Hidaka, M.; Oikawa, K.; Harada, M.; Oku, T.; Arai, M.; et al. Neutron flux spectrum revealed by Nb-based current-biased kinetic inductance detector with a 10B conversion layer. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2017, 842, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, H.; Miyajima, S.; Narukami, Y.; Oikawa, K.; Harada, M.; Oku, T.; Arai, M.; Hidaka, M.; Fujimaki, A.; Ishida, T. Neutron detection using a current biased kinetic inductance detector. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 23601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, T.; Hiroi, K.; Su, Y.; Shinohara, T.; Parker, J.D.; Matsumoto, Y.; Hayashida, H.; Segawa, M.; Nakatani, T.; Oikawa, K.; et al. Reliability estimation of neutron resonance thermometry using tantalum and tungsten. Phys. Procedia 2017, 88, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghilaridjani, M.; Kato, K.; Shinohara, T.; Yashiro, W.; Momose, A.; Kato, H. High aspect ratio grating by isochronal imprinting of less viscous workable Gd-based metallic glass for neutron phase imaging. Intermetallics 2016, 78, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, Y.; Shinohara, T.; Parker, J.D.; Yashiro, W.; Momose, A.; Kato, K.; Kato, H.; Sadeghilaridjani, M.; Otake, Y.; Kiyanagi, Y. Development of Multi-colored Neutron Talbot-Lau Interferometer with Absorption Grating Fabricated by Imprinting Method of Metallic Glass. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 86, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, R.; Hata, T.; Kawamoto, Y.; Irie, M. Synthesis of a new lithium ionic conductor, thio-LISICON–lithium germanium sulfide system. Solid State Ionics 2000, 130, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, R.; Murayama, M. Lithium Ionic Conductor Thio-LISICON: The Li2S-GeS2-P2S5 System. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A742–A746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, M.; Kanno, R.; Kawamuto, Y.; Kamiyama, T. Structure of the thio-LISICON, Li4GeS4. Solid State Ionics 2002, 154–155, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.Y.-P. Crystal Structure and Ionic Conductivity of Li14Zn(GeO4)4 and Other New Li+ Superionic Conductors. Mater. Res. Bull. 1978, 13, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Hori, S.; Saito, T.; Suzuki, K.; Hirayama, M.; Mitsui, A.; Yonemura, M.; Iba, H.; Kanno, R. High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogo, S.; Kabe, R.; Uehara, K.; Kure, B.; Nishimura, T.; Menon, S.C.; Harada, R.; Fukuzumi, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Ohhara, T.; et al. A Dinuclear Ni(μ-H)Ru Complex Derived from H2. Science 2007, 316, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogo, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Kishima, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Nakai, H.; Kusaka, K.; Ohhara, T. A Functional [NiFe]Hyd rogenaze Mimic That Catalyzes Electron and Hydride Transfer from H2. Science 2013, 339, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Terayama, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Terada, M.; Murakami, D.; Ishihara, K.; Takahara, A. Wettability and Antifouling Behavior on the Surfaces of Superhydrophilic Polymer Brushes. Langmuir 2012, 28, 7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, A.J.; Edmondson, S.; Dupin, D.; Armes, S.P.; Zhang, Z.; Leggett, G.J.; Thompson, R.L.; Lewis, A.L. Biocompatible polymer brushes grown from model quartz fibres: Synthesis, characterisation and in situ determination of frictional coefficient. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Terayama, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Takahara, A. Chain dimensions and surface characterization of superhydrophilic polymer brushes with zwitterion side groups. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umegaki, I.; Tanaka, H.; Kurita, N.; Ono, T.; Laver, M.; Niedermayer, C.; Rüegg, C.; Ohira-Kawamura, S.; Nakajima, K.; Kakurai, K. Spinon, soliton, and breather in the spin-1/2 antiferromagnetic chain compound KCuGaF6. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 174412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanh, N.D.; Abe, N.; Sagayama, H.; Nakao, A.; Hanashima, T.; Kiyanagi, R.; Tokunaga, Y.; Arima, T. Magnetoelectric coupling in the honeycomb antiferromagnet Co4Nb2O9. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 075117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, M.; Goremychkin, E.A.; Adroja, D.T.; Danilkin, S.; Deng, G.; Yamani, Z.; Dai, P. Electron doping evolution of the magnetic excitations in BaFe2−xNixAs2. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 144516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Lu, X.; Tan, G.; Luo, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Goremychkin, E.A.; Perring, T.G.; et al. Doping dependence of spin excitations and its correlations with high-temperature superconductivity in iron pnictides. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Kihou, K.; Kawano-Furukawa, H.; Saito, T.; Iyo, A.; Eisaki, H.; Fukazawa, H.; Kohori, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Usui, H.; et al. Incommensurate spin fluctuations in hole-overdoped superconductor KFe2As2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 067003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knolle, J.; Eremin, I.; Chubukov, A.V.; Moessner, R. Theory of itinerant magnetic excitations in the spin-density-wave phase of iron-based superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 140506(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneshita, E.; Tohyama, T. Spin and charge dynamics ruled by antiferromagnetic order in iron pnictide superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 094441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, M.; Christensen, M.H.; Gastiasoro, M.N.; Andersen, B.M. Spin excitations in the nematic phase and the metallic stripe spin-density wave phase of iron pnictides. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 064424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, Y.; Böni, P. Magnetic excitations in metallic ferro- and antiferromagnets. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 75, 111002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, S.M.; Doubble, R.; Aeppli, G.; Perring, T.G.; Fawcett, E. Strongly enhanced magnetic excitations near the quantum critical point of Cr1−xVx and why strong exchange enhancement need not imply heavy Fermion behavior. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyoshi, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ohashi, M.; Cowley, E.R.; Shirane, G. Magnetic excitations in the itinerant antiferromagnets Mn3Si and Fe-doped Mn3Si. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 36, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, G.L. Introduction to the Theory of Thermal Neutron Scattering; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]





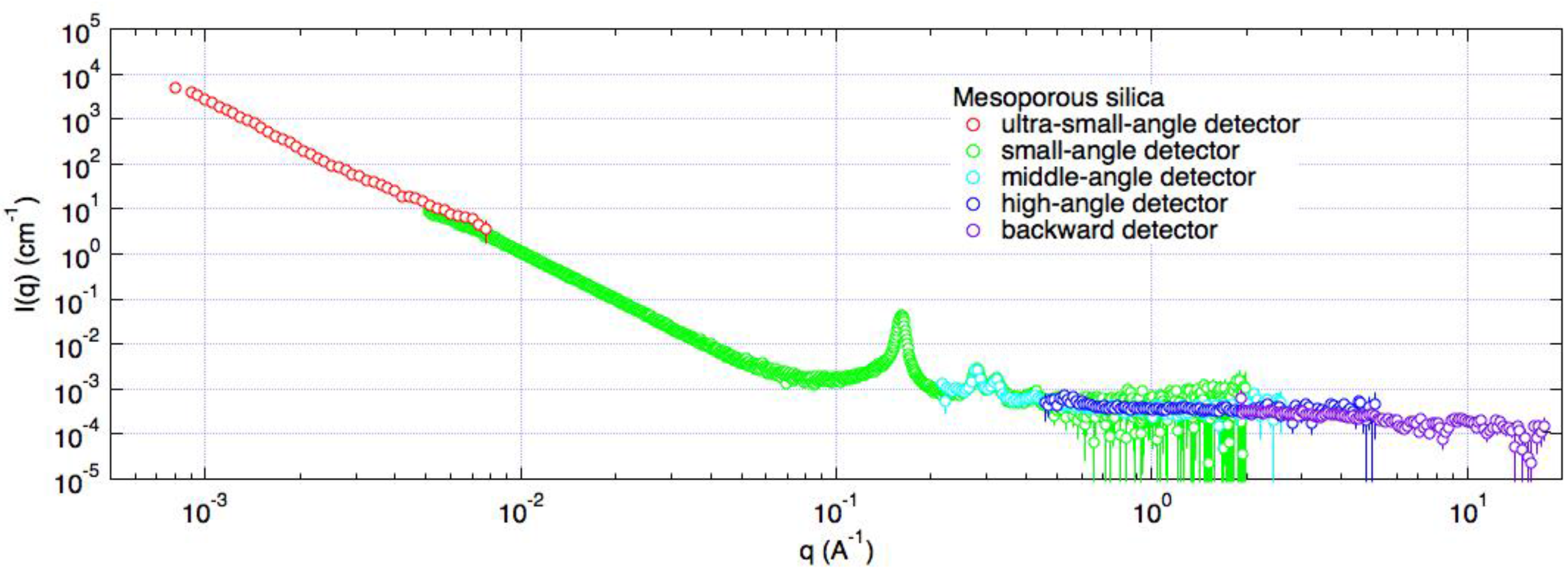


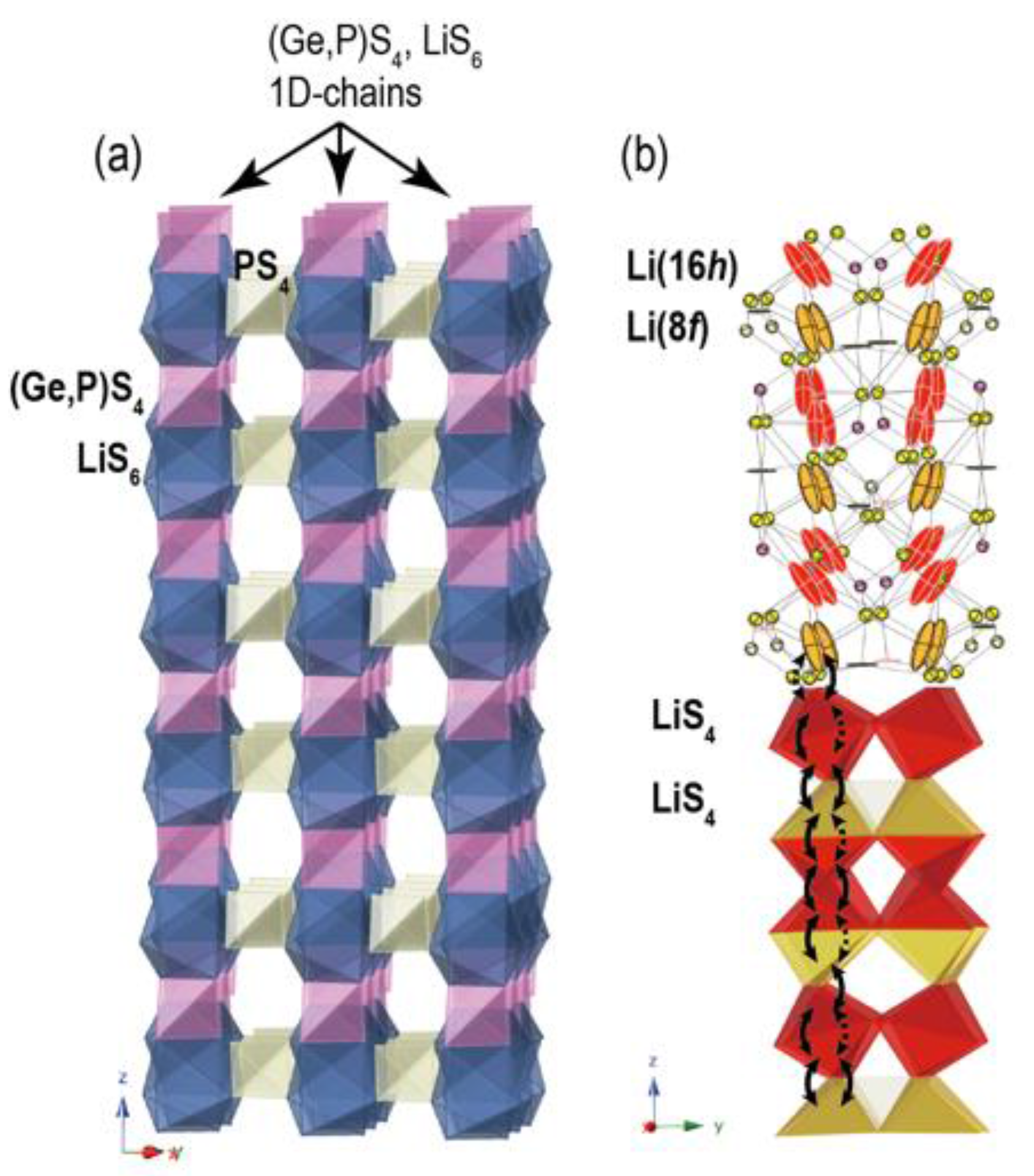
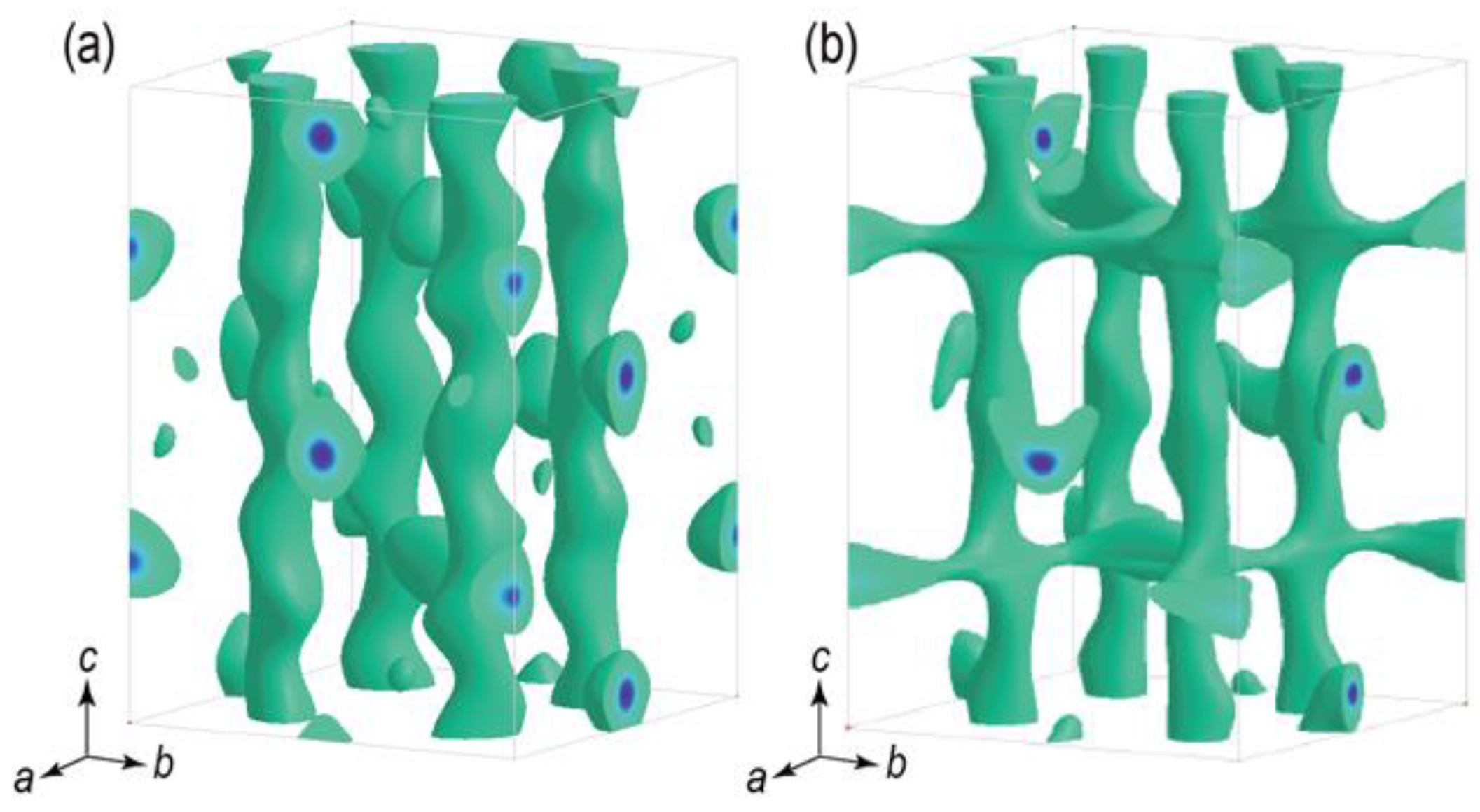

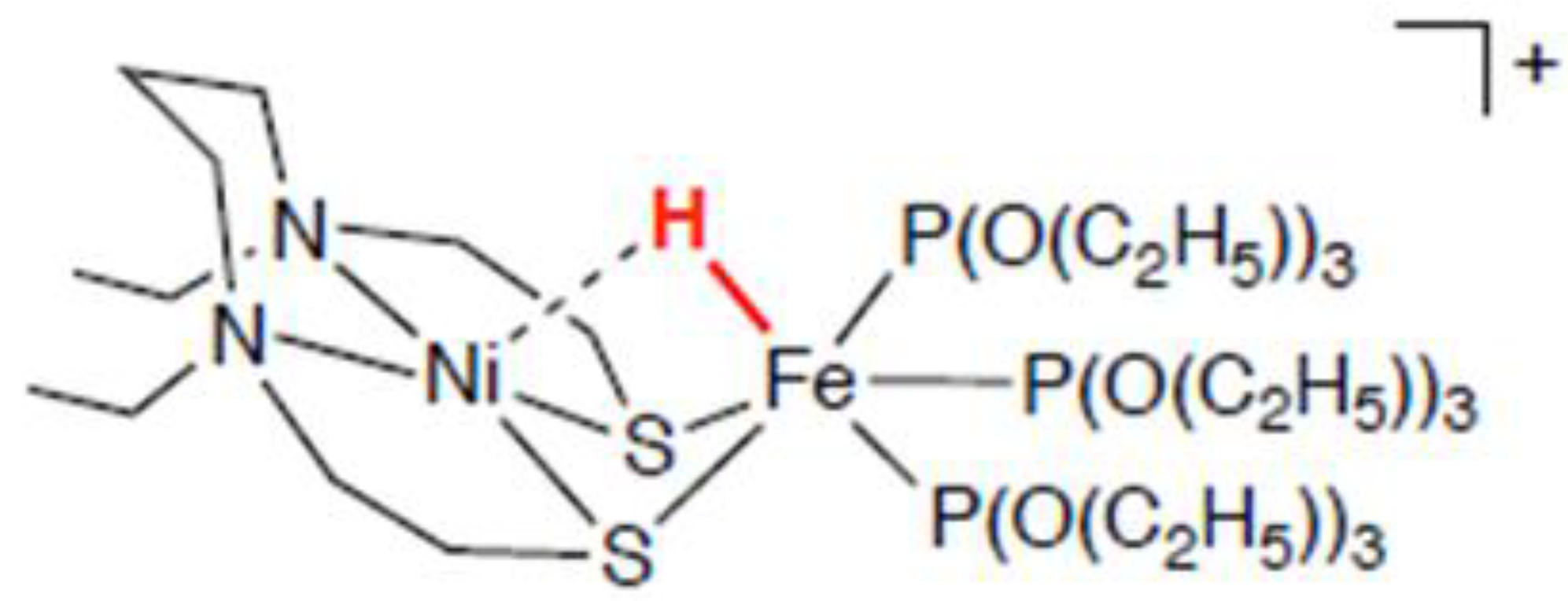


| Beam Line | Moderator | Short Name | Formal Name | Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL01 | Coupled H2 | 4SEASONS | 4D-Space Access Neutron Spectrometer | Operation (2008~) | [14] |
| BL02 | DNA | Biomolecular Dynamics Spectrometer | Operation (2011~) | [12] | |
| BL03 | iBIX | IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer | Operation (2008~) | [27,28] | |
| BL04 | ANNRI | Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction Measurement Instrument | Operation (2008~) | [34] | |
| BL05 | NOP | Neutron Optics and Fundamental Physics | Operation (2008~) | [35] | |
| BL06 | VIN ROSE | Village of Neutron Resonance Spin Echo Spectrometers | Operation (2017~) | [20] | |
| BL07 | Decoupled Poisoned H2 (thin) | Vacant | |||
| BL08 | SuperHRPD | Super High-Resolution Powder Diffractometer | Operation (2008~) | [21] | |
| BL09 | SPICA | Special Environment Powder Diffractometer | Operation (2011~) | [22] | |
| BL10 | Decoupled H2 | NOBORU | NeutrOn Beam-line for Observation and Research Use | Operation (2008~) | [36] |
| BL11 | PLANET | High-Pressure Neutron Diffractometer | Operation (2013~) | [24] | |
| BL12 | HRC | High Resolution Chopper Spectrometer | Operation (2008~) | [15,16] | |
| BL13 | Coupled H2 | Vacant | |||
| BL14 | AMATERAS | Cold-Neutron Disk-Chopper Spectrometer | Operation (2009~) | [9] | |
| BL15 | TAIKAN | Small- and Wide-angle Neutron Scattering Instrument | Operation (2011~) | [30] | |
| BL16 | SOFIA | Soft Interface Analyzer | Operation (2008~) | [31,32] | |
| BL17 | SHARAKU | Polarized Neutron Reflectometer | Operation (2011~) | [33] | |
| BL18 | Decoupled Poisoned H2 (thick) | SENJU | Extreme Environment Single-crystal Neutron Diffractometer | Operation (2011~) | [29] |
| BL19 | TAKUMI | Engineering Materials Diffractometer | Operation (2008~) | [25,26] | |
| BL20 | iMATERIA | IBARAKI Materials Design Diffractometer (Versatile Neutron Diffractometer) | Operation (2008~) | [23] | |
| BL21 | Decoupled H2 | NOVA | High-Intensity Total Diffractometer | Operation (2008~) | |
| BL22 | RADEN | Energy Resolved Neutron Imaging System | Operation (2015~) | [37] | |
| BL23 | POLANO | Polarized Neutron Spectrometer | Commissioning | [17,18,19] | |
| Beamline | BL01 |
| Moderator | Coupled hydrogen moderator |
| Flight path length | Lmoderator-sample = 18 m Lsample-detector = 2.5 m |
| Incident energy | 5–300 meV |
| Energy resolution | ΔE/Ei ≥ 5% FWHM at the elastic line |
| Detectors | 3He 1D- position-sensitive detectors (PSD) (16.4 atm partial pressure) 19 mm diameter, 2500 mm long, 352 (266*) tubes Angular coverage: −35° – +130° (−35° – +91° *) horizontal −25° – +27° vertical (* current values) |
| Fermi chopper | Lmoderator-chopper = 16.3 m Long slit package: 2 mm × 100 mm slots, revolution rate ≤ 350 Hz Short slit package: 0.4 mm × 20 mm slots, revolution rate ≤ 600 Hz |
| Slow disk choppers | Radius = 350 mm Revolution rate = 12.5 Hz or 25 Hz No. 1: Lmoderator-chopper = 9 m, opening angle = 77° No. 2: Lmoderator-chopper = 12 m, opening angle = 103° |
| T0 chopper | Lmoderator-chopper = 8.5 m Revolution rate = 25 Hz |
| Beam transport | m = 3.2–4 supermirror |
| Beam size at the sample position | maximum 45 mm × 45 mm, optimum 20 mm × 20 mm, adjustable by motorized slits |
| Beamline | BL12 |
| Moderator | Decoupled hydrogen moderator |
| Flight path length | Lmoderator-sample = 15 m Lsample-detector = 4 m, 5.2 m |
| Incident energy | 5–2000 meV |
| Energy resolution | ΔE/Ei = 3–10% (conventional), ΔE/Ei ≥ 2% (neutron Brillouin scattering (NBS)) |
| Q resolution (designed) | ΔQ/ki ≥ 1% |
| Detector coverage (scattering angle) | Horizontal: −31° – +124° (designed) −31° – +62° (current) Vertical: −20° – +20° |
| Detector system | 3He 1D-PSD [19.05 mm (diameter), 28,000 mm (length)] (256 tubes are currently installed) for 4 m position 3He 1D-PSD [12.7 mm (diameter), 8000 mm (length)] (68 tubes are currently installed) for 5.2 m position |
| T0 chopper | Revolution rate : 25, 50, 100 Hz Lmoderator-chopper = 9 m |
| Fermi chopper | Revolution rate: 100–600 Hz Lmoderator-chopper = 14 m |
| Beam transport | m = 3, 3.65 and 4 supermirror |
| Beam size at sample position | Maximum dimension: 50 mm width × 50 mm height |
| Beamline | BL14 |
| Moderator | Coupled hydrogen moderator |
| Flight path length | Lmoderator-sample = 30 m Lsample-detector = 4 m |
| Incident energy (designed) | 1–80 meV |
| Energy resolution | ΔE/Ei ≥ 1% @ Ei = 20 meV |
| Q resolution (designed) | 2% > ΔQ/ki > 0.2% |
| Detector coverage (scattering angle) | Horizontal: −40° – +140° (final state) +5° – +110° (current state) Vertical: −16° – +23° |
| Detector system | 3He 1D-PSD [φ = 25.4 mm, L = 2910 mm (effective length)] 448 tubes after full installation (266 tubes are currently installed) |
| Fast disk choppers | Radius 350 mm Revolution rate ≤ 350 Hz No. 1 (Pulse shaper) Lmoderator-chopper 7.1 m No. 2 (Monochromator) Lmoderator-chopper 28.4 m No. 3 (RRM frame overlap) Lmoderator-chopper 14.2 m |
| Slow disk choppers | Radius 350 mm Revolution Rate 12.5 Hz or 25 Hz Opening angle 0°–175° (variable) No. 1 Lmoderator-chopper 9 m No. 2 Lmoderator-chopper 13.7 m |
| Beam transport | m = 3 and 3.8 supermirror |
| Beam size at the sample position | Optimal dimensions for beam are 20 mm width × 10 mm height The maximum dimensions are 30 mm width × 50 mm height |
| Beamline | BL23 |
| Moderator | Decoupled hydrogen moderator |
| Flight path length | Lmoderator-sample = 17.5 m Lsample-detector = 2.0 m Lmonochromating chopper-sample = 1.85 m |
| Incident energy | (unpolarized) 1–500 meV (polarized) 1–100 meV (designed) |
| Energy resolution | ΔE/Ei ≥ 4% @ elastic |
| Q resolution (designed) | 1 to 2% = ΔQ/ki |
| Detector coverage (scattering angle) | Horizontal: −20° to +120° Vertical: −8° to +8° |
| Detector system | 3He 1D-PSD [φ = 19 mm, L = 600 mm (effective length)] |
| Beam transport | m = 4.0 supermirror |
| Beam size at the sample position | Optimal dimensions for beam are 20 mm width × 20 mm height The maximum dimensions are 50 mm width × 50 mm height |
| Beamline | BL02 |
| Moderator | Coupled Hydrogen Moderator |
| Lmoderator-sample | 42 m |
| Lsample-analyzer | ~ 2.3 m |
| Lanalyzer-detector | ~ 2.0 m |
| Pulse sharpening chopper (PS-chopper) | At ~7.5 m from the moderator Max speed: 300 Hz (designed value) (Present maximum speed: 225 Hz) 4 slits on one disk |
| Crystal analyzer | Crystal and reflection index Si(111) Si(311) in test Bragg angle of analyzers ~87.5° |
| Energy resolution | ~2.4 μeV: Si-111 with 10mm Slit @225Hz of PS-chopper ~3.5 μeV: Si-111 with 30mm Slit @225Hz of PS-chopper ~14 μeV: Si-111 without PS-chopper ~12 μeV: Si-311 with 10mm Slit @225Hz of PS-chopper |
| Momentum range | 0.08 < Q < 1.86 Å−1: Si-111 1.0 < Q < 3.80 Å−1: Si-311 (in plan) |
| Scan energy range | Si-111 −40 < E/μeV < 100 : Single pulse scan around Ef −400 < E/μeV < 600 : Multi pulse scan around Ef −500 < E/μeV < 1500: without PS-chopper in second frame Si(311) −150 < E/μeV < 300: Single pulse scan around Ef (the specifications by the end of March 2017) |
| Beamline | BL06 |
| Moderator | Coupled hydrogen moderator |
| Measured neutron flux and peak wavelength of guide exit | MIEZE: 2.7 × 108 n/cm2/s/MW, 4.8 Å NRSE: 6.9 × 108 n/cm2/s/MW, 5.5 Å |
| Band disk choppers | Radius 200 mm Revolution Rate 25 or 12.5 (or 8.33) Hz Opening angle 126° (MIEZE) Opening angle 162° (NRSE) Moderator-chopper 12.1 m |
| Ellipsoid focusing mirror (NRSE) | Semi-major axis: 1.25 m Semi-minor axis: 65.4 mm Sample size(NRSE) < 5 mm × 5 mm |
| Wavelength, Q range, Fourier time | MIEZE 3 < λ < 13 Å, 0.2 < Q < 3.5 Å−1, 1 ps < t < 2 ns *1 NRSE 5 < λ < 20 Å, 0.02 < Q < 0.65 Å−1, 0.1 ns < t < 0.1 μs *2 |
| Moderator | Poisoned Decoupled Hydrogen Moderator |
| Primary flight path Lmoderator-sample | 94.2 m |
| Curved guide | 31.245 m (m = 3, r = 5 km) |
| Straight guide | 51.4 m (m = 3) |
| Position for disk choppers | 7.1 m (single), 12.75 m (double) |
| Backward bank | |
| 2θ | 150° ≤ 2θ ≤ 175° |
| Lsample-detector | 2.0–2.3 m |
| d-range | 0.3–4.0 Å |
| Resolution ∆d/d | 0.03–0.1% |
| 90° scattering bank | |
| 2θ | 60° ≤ 2θ ≤ 125° |
| Lsample-detector | 2.0–2.3 m |
| d-range | 0.4–7.5 Å |
| Resolution ∆d/d | 0.4–0.7% |
| Low angle scattering bank | |
| 2θ | 10° ≤ 2θ ≤ 40° |
| Lsample-detector | 2.0–4.5 m |
| d-range | 0.6–45 Å |
| Resolution ∆d/d | 0.7–3.0% |
| Ancillary equipment and sample environment | Auto sample changer (RT, 10 samples) |
| 4 K-type closed cycle refrigerator (4–300 K) | |
| Top-loading refrigerator (10–300 K) | |
| High temperature furnace (950 °C) | |
| Moderator | Poisoned-Decoupled Hydrogen Moderator |
| Primary flight path Lmoderator-sample | 52.0 m |
| Supermirror guide | 39.4 m (m = 3–6, r = 5 km) |
| Position for disk choppers | 7.25, 12.8, 18 m (Single) |
| Backward bank | |
| 2θ | 149° ≤ 2θ ≤ 172° |
| Lsample-detector | 2.0–2.3 m |
| d-range | 0.3–4.1 Å * |
| Resolution ∆d/d | 0.08–0.15% |
| High scattering bank | |
| 2θ | 116° ≤ 2θ ≤ 139° |
| Lsample-detector | 2.0 m |
| d-range | 0.4–4.7 Å * |
| Resolution ∆d/d | 0.24–0.33% |
| 90° scattering bank | |
| 2θ | 66° ≤ 2θ ≤ 110° |
| Lsample-detector | 2.0 m |
| d-range | 0.4–6.0 Å * |
| Resolution ∆d/d | 0.37–0.71% |
| Low angle scattering bank | |
| 2θ | 14° ≤ 2θ ≤ 58° |
| Lsample-detector | 2.0 m |
| d-range | 0.6–35 Å * |
| Resolution ∆d/d | 0.8–2.2% |
| Ancillary equipment and sample environment | Auto sample changer (RT, 40 samples) |
| Top-loading refrigerator (10–300 K) | |
| Top-loading cryo-furnace (20–800 K) | |
| High | 2θ | 150° ≤ 2θ ≤ 175° |
| Resolution | Lsample-detector | 2.0–2.3 m |
| Bank | d-range | 0.09 ≤ d (Å) ≤ 5.0 |
| Special | 2θ | 80° ≤ 2θ ≤ 100° |
| Environment | Lsample-detector | 1.5 m |
| Bank | d-range | 0.127 ≤ d (Å) ≤ 7.2 |
| Low | 2θ | 10° ≤ 2θ ≤ 40° |
| Angle | L2 | 1.2–4.5 m |
| Bank | d-range | 0.37 ≤ d(Å) ≤ 58 |
| Small | 2θ | 0.7° ≤ 2θ ≤ 5° |
| Angle | Lsample-detector | 4.5 m |
| Bank | Q-range | 0.007≤ q(Å−1) ≤ 0.6 |
| Characteristics | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Moderator | 20 K Para-hydrogen (decoupled) |
| Source-to-sample distance | 25 m |
| Sample-to-detector distance | 1.5–1.85 m (depending on the scattering angle) |
| Detector coverage | 90° ± 11.3° (horizontal), 0° ± 34.6° (vertical) |
| Wavelength | 0.3–6.0 Å |
| Resolution | ∆d/d = 0.4–0.6% |
| d-spacing range | 0.2–4.2 Å (in the single frame mode) 0.2–8.4 Å (in the double frame mode) |
| Q-value range | 1.5–30 Å−1 (in the single frame mode) 0.8–30 Å−1 (in the double frame mode) |
| Neutron flux at sample position in 10 mmφ | 5.291 × 107 neutrons cm−2 s−1 (@1 MW) |
| Pressure and temperature range | 0–16 GPa, RT–2000 K (ATSUHIME) 0–20 GPa, RT (PE-press) 0–10 GPa, 77–473 K (Mito system) |
| Moderator | Poisoned decoupled hydrogen moderator |
| d-range |
|
| S/N ratio | ~ 10−3 |
| Peak resolution | Tunable ; Low (~ 0.4 %) Medium (~ 0.3 %, most cases) High (~ 0.2 %) |
| Radial collimators | 1 mm, 2mm, 5 mm (a pair of each) |
| Data acquisition |
|
| Ancillary equipment and sample environment |
|
| Moderator | Coupled |
| Wavelength of incident neutron | 0.7–4.0 Å (1st frame) 4.0–8.0 Å (2nd frame) |
| Neutron intensity (@1MW) | 0.7 × 106 n/s/mm2 |
| Lmoderator-sample | 40 m |
| Lsample-detector | 500 mm |
| Solid angle of detectors | 19.5% for 4π |
| Detector covered region | 15.5–168.5° |
| Detector size | 133 mm × 133 mm |
| Detectors pixel size | 0.52 mm × 0.52 mm |
| No. of detectors | 30 |
| Moderator | Poisoned decoupled |
| Wavelength of incident neutron | 0.4–4.4 Å (1st frame) 4.6–8.8 Å (2nd frame) |
| Neutron intensity (@1 MW) | 1.3 × 106 n/s/mm2 |
| Lmoderator-sample | 34.8 m |
| Lsample-detector | 800 mm |
| Solid angle of detectors | 30.2% for 4π |
| Detector covered region | 13.0–167.0° |
| Detector size | 256 mm × 256 mm |
| Detectors pixel size | 4.0 mm × 4.0 mm |
| Number of detectors | 37 |
| Beamline | BL15 |
| Moderator | Coupled hydrogen moderator |
| Wavelength range | 0.5–8 Å (unpolarized neutron) 2–8 Å (polarized neutron) |
| Q range | 5×10−4–20 Å−1 (unpolarized neutron) 5×10−4–5 Å−1 (polarized neutron) |
| Q resolution | ΔQ/Q = 0.3 @ Q = 10−2 Å−1, 4.5 × 10−2 @ Q = 10−1 Å−1, 1.6 × 10−2 @ Q = 1 Å−1, 3 × 10−3 @ Q = 10 Å−1 |
| Detector system | 3He 1D-PSD [φ = 8 mm, L = 300, 500, 600, 800, 1000 mm (effective length)] 2272 tubes after full installation (1512 tubes are currently installed), ZnS/6LiF scintillation 2D-ultra-small-angle detector [Spatial resolution: 0.5 mm] |
| Beam monitor | N2 monitor [Efficiency: 10−5 @ 1 Å, 64 mm × 64 mm × 12 mm (effective volume)] |
| Beam transport | 3Qc Ni/Ti supermirror guide tube |
| Polarizer | 4.5Qc Fe/Si supermirror 4-channel V-cavity |
| Focusing device | Quadrupole magnet [dB/dr = 2.25 × 102 T/m], 1st sextupole magnet [dB/dr2 = 5.22 × 104 T/m2], 2nd sextupole magnet [dB/dr2 = 2.43 × 104 T/m2], Resonance spin flippers |
| Sample stage | Diameter: 700 mm, Weight limit: 750 kgf, Beam level above the stage: 350 mm |
| Sample Interface | Sample Size (Beam Size) | Q Range | Exposure Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| air/Si | 50.8 mm Ø (30 mm × 40 mm) | <2 nm−1 | ¾ h |
| air/protonated polymer/Si | 50.8 mm Ø (30 mm × 40 mm) | <2 nm−1 | 1 h |
| air/deuterated polymer/Si | 50.8 mm Ø (30 mm × 40 mm) | <4 nm−1 | ½ h |
| air/D2O | 25 mL (40 mm × 40 mm) | <2 nm−1 | ¼ h |
| air/no reflection water | 25 mL (40 mm × 40 mm) | <1 nm−1 | 3 h |
| Si/D2O | 76.2 mm Ø (30 mm × 50 mm) | <2 nm−1 | 1 h |
| Si/protonated polymer/D2O | 76.2 mm Ø (30 mm × 50 mm) | <2 nm−1 | 1 h |
| Si/deuterated polymer/H2O | 76.2 mm Ø (30 mm × 50 mm) | <2 nm−1 | 1 h |
| Wavelength | 0.2–0.88 nm (single frame) 0.2–1.7 nm (double frame) |
| Incident angle | <6° |
| Q range | <6 nm−1 (depend on reflectivity of a sample) |
| Wavelength | 0.24–0.88 nm (polarized neutron) 0.11–0.88 nm (unpolarized neutron) |
| Scattering angle | 0–18° |
| Maximum Q | 8.19 nm−1 (polarized neutron) 17.9 nm−1 (unpolarized neutron) |
| Beamline | BL21 | ||
| Moderator | Decoupled hydrogen moderator | ||
| Q range and resolution | Detector bank | ∆Q/Q [%] | Q-range [Å−1] (d-range[Å]) |
| Small-angle | 4–50 | 0.03–8 (0.8–209) | |
| 20° | 1.7–3.9 | 0.2–26 (0.2–31) | |
| 45° | 0.9–1.5 | 0.4–50 (0.1–16) | |
| 90° | 0.5–0.7 | 1–82 (0.08–6.3) | |
| High-angle | 0.3–0.35 | 1.4–100 (0.06–4.5) | |
| Detector system | 3He 1D-PSD [φ = 1/2 inch, L = 800 mm (effective length)] | ||
| Beam monitor | Gas Electron Multiplier (B converter, 0.1% efficiency) | ||
| Beam Size | Typical size: 6 mm width × 20 mm height Beam size can be changed from 5 mm×5 mm to 20 mm×20 mm | ||
| Apparatus | Purpose | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Sample changer | Automatic sample exchange | Samples per load: 10 or 40 |
| Temperature controlled sample changer | Automatic sample exchange and temp. control | Samples per load: 18 Temperature : 20–700 K |
| Top load cryostat | Low temperature | Temperature : 5–700 K |
| Vanadium furnace | High temperature | Temperature : RT–1373 K |
| Hydrogen pressure-composition-temperature measurement | H2 ab/desorption | Temperature : 50–473 K Gas pressure : ≤10 MPa H2/D2 |
| Moderator | Coupled Supercritical H2 |
| Incident neutron energy | En > 0.0015 eV |
| Spectrometer | Ge Spectrometer (Flight path length: 21.5 m) NaI Spectrometer (Flight path length: 27.9 m) |
| Neutron intensity (@sample position @1MW) | @21.5m sample position 4.3 × 107 n/cm2/s 1.5 meV < En < 25 meV 9.3 × 105 n/cm2/s 0.9 eV < En < 1.1 eV 1.0 × 106 n/cm2/s 0.9 keV < En < 1.1 keV |
| Sample size and/or volume | Using the most downstream collimator, neutron beams with diameters of 22, 15, 7 and 6 mm are provided to suit samples of different sizes. |
| Moderator | Coupled Supercritical H2 | ||
| Branch | Unpolarized | Polarized | Low-Divergence |
| Cross section (Y mm × X mm) | 50 × 40 | 120 × 60 | 80 × 40 |
| Beam flux (n/cm2/s@1 MW) | (3.8 ± 0.3) × 108 | (4.0 ± 0.3) × 107 | (5.4 ± 0.5) × 104 |
| Beam Divergence (Y mrad×X mrad) | m = 2 equivalent | 23 × 9.4 | 0.23 × 0.23 *1 |
| Luminance (n/cm2/str/s@1MW) | — | (1.8 ± 0.1) × 1011 | (1.0 ± 0.1) × 1012 |
| Polarization | — | 94–96% | — |
| Moderator | Decoupled Supercritical H2 |
| Incident neutron wavelength | λ < 10.5 Å |
| Resolution (Δλ/λ) | 0.35% (minimum) |
| Neutron intensity (@14.0 m sample position @1MW) | 4.8 × 107 n/s/cm2 (<0.4 eV), 1.2 × 107 n/s/cm2 (>1 MeV), 1.2 × 106 n/s/cm2 (>10 MeV) |
| Beam collimation ratio (L/D) | 140, 190, 600 and 1875 |
| Filters | none/Cd 2 mm/acryl 6 mm none/Ta 50 µm, In 50 µm, Cu 2 mm/borosilicate glass 1 mm none/Pb 50 mm/Bi 25 mm none/Bi 50 mm/Pb 25 mm |
| Moderator | Decoupled Supercritical H2 |
| Incident neutron wavelength | λ < 8.8 Å (L = 18m, 25 Hz) λ < 6.8 Å (L = 23m, 25 Hz) |
| Resolution (Δλ/λ) | 0.20% (minimum) |
| Neutron intensity (@sample position @1MW) | 9.8 × 107 n/s/cm2 (L/D = 180) 5.8 × 107 n/s/cm2 (L/D = 230) |
| Beam size | Maximum 300 mm × 300 mm @23 m sample position |
| Detectors | Cooled CCD (2k × 2k pixels) + ZnS(Li) scintillator, nGEM, μ-NID, Li-glass pixellerated scintillator with multi-anode PMT |
| Sample environment | Large (load capacity 1 ton), Medium (load capacity 650 kg), Small sample stage (load capacity 10 kg), Polarization analysis system |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakajima, K.; Kawakita, Y.; Itoh, S.; Abe, J.; Aizawa, K.; Aoki, H.; Endo, H.; Fujita, M.; Funakoshi, K.; Gong, W.; et al. Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex II: Neutron Scattering Instruments. Quantum Beam Sci. 2017, 1, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs1030009
Nakajima K, Kawakita Y, Itoh S, Abe J, Aizawa K, Aoki H, Endo H, Fujita M, Funakoshi K, Gong W, et al. Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex II: Neutron Scattering Instruments. Quantum Beam Science. 2017; 1(3):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs1030009
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakajima, Kenji, Yukinobu Kawakita, Shinichi Itoh, Jun Abe, Kazuya Aizawa, Hiroyuki Aoki, Hitoshi Endo, Masaki Fujita, Kenichi Funakoshi, Wu Gong, and et al. 2017. "Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex II: Neutron Scattering Instruments" Quantum Beam Science 1, no. 3: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs1030009
APA StyleNakajima, K., Kawakita, Y., Itoh, S., Abe, J., Aizawa, K., Aoki, H., Endo, H., Fujita, M., Funakoshi, K., Gong, W., Harada, M., Harjo, S., Hattori, T., Hino, M., Honda, T., Hoshikawa, A., Ikeda, K., Ino, T., Ishigaki, T., ... Yoshizawa, H. (2017). Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex II: Neutron Scattering Instruments. Quantum Beam Science, 1(3), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs1030009









