Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex I: Pulsed Spallation Neutron Source
Abstract
:1. Introduction
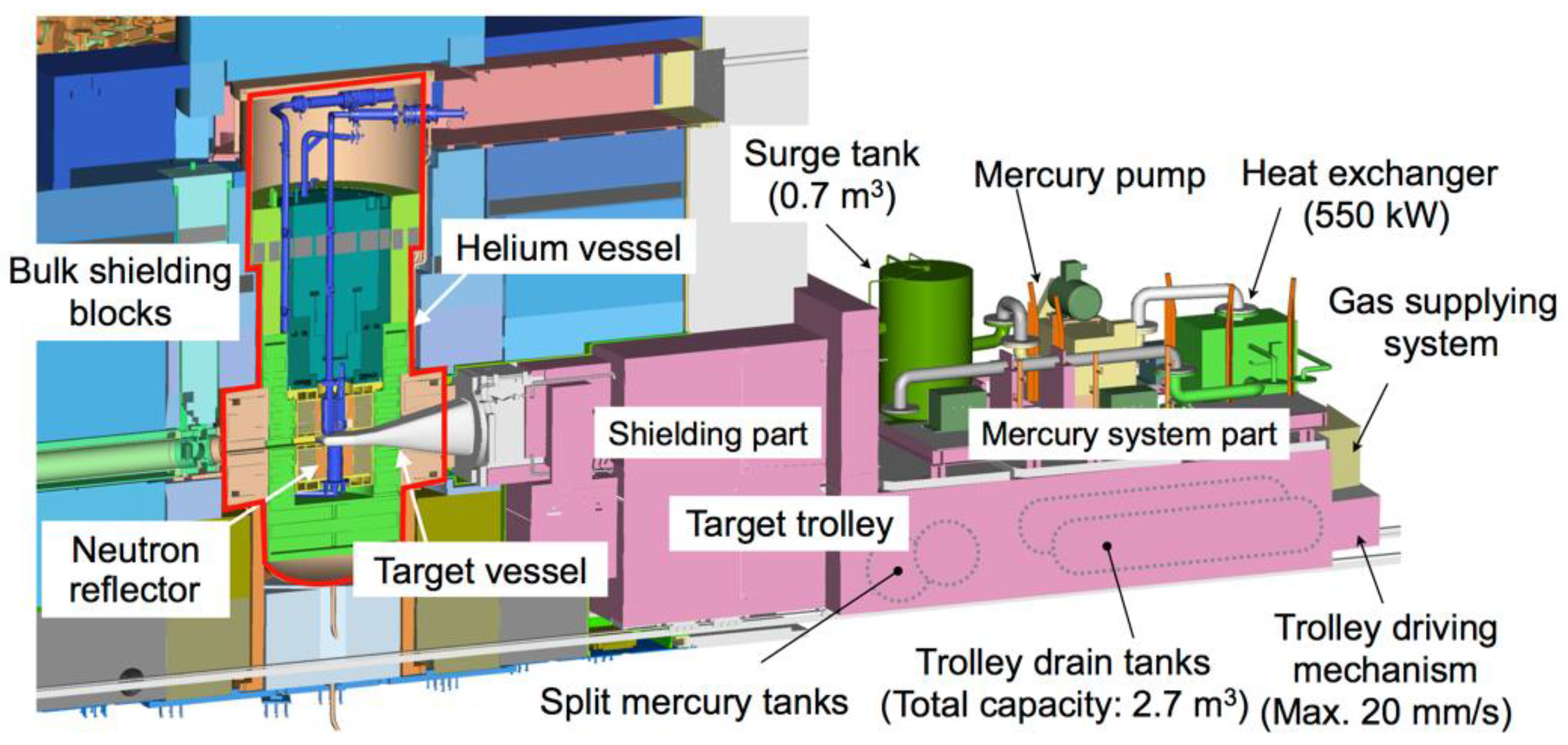
2. Mercury Target System
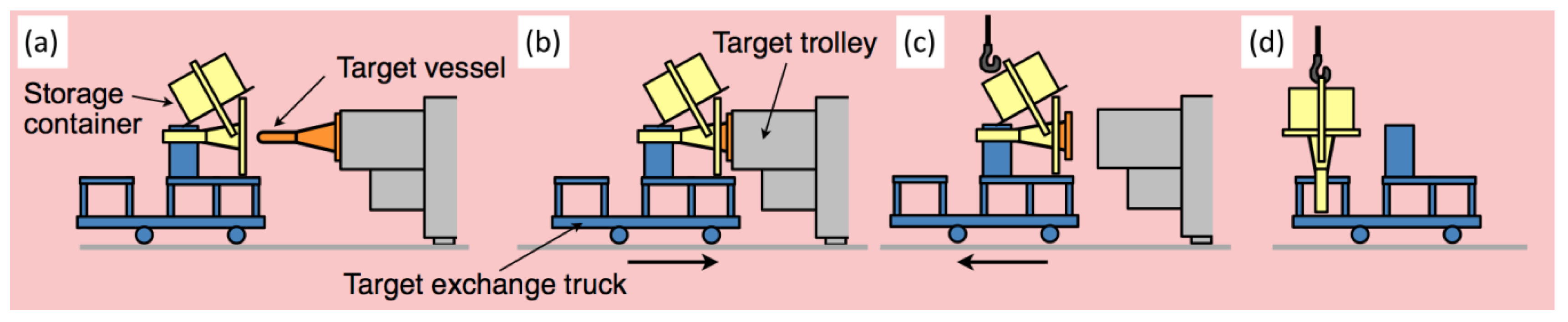
2.1. Target Trolley
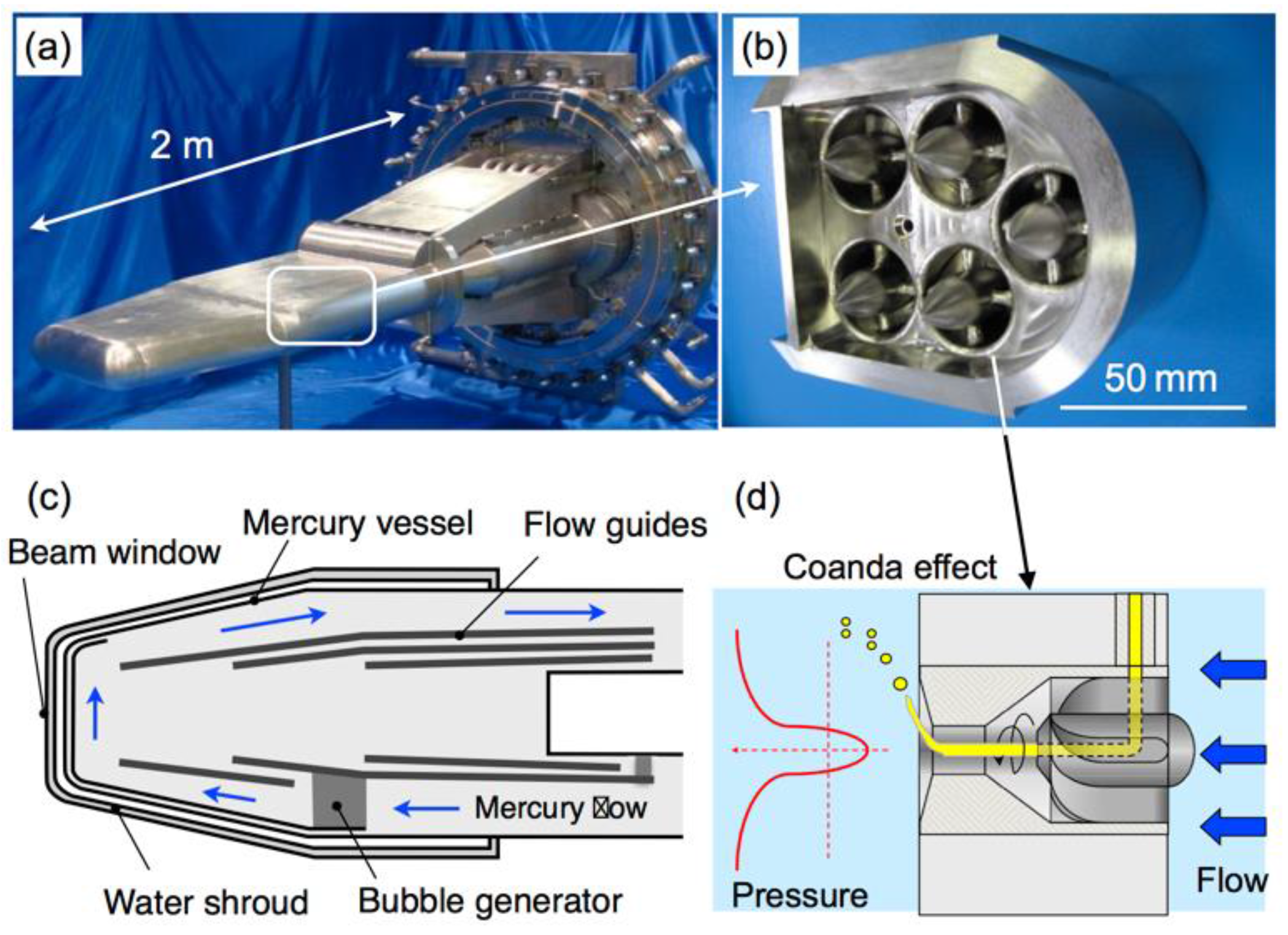
2.2. Mercury Target Vessel
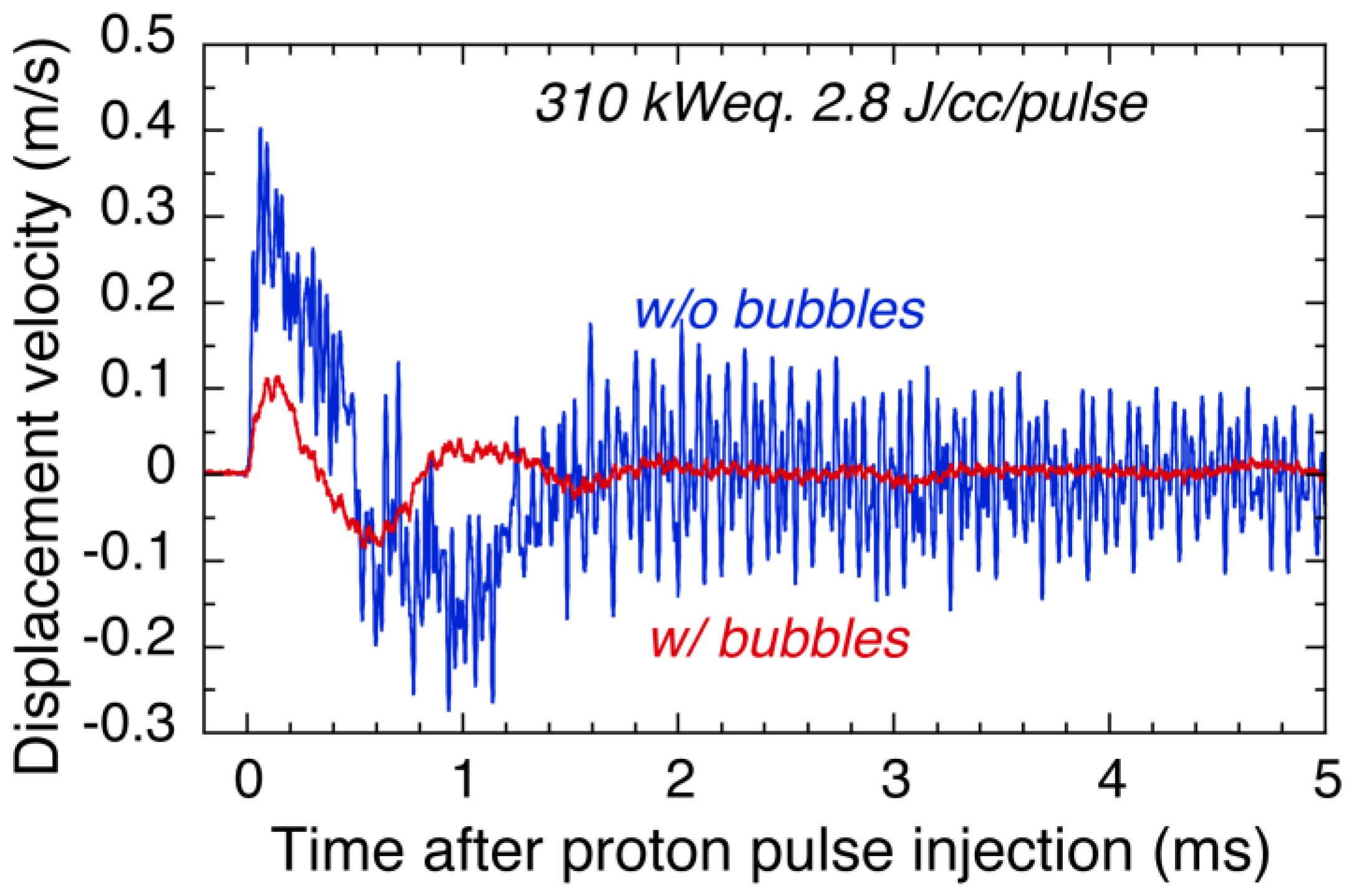
2.3. Microbubble Injection System
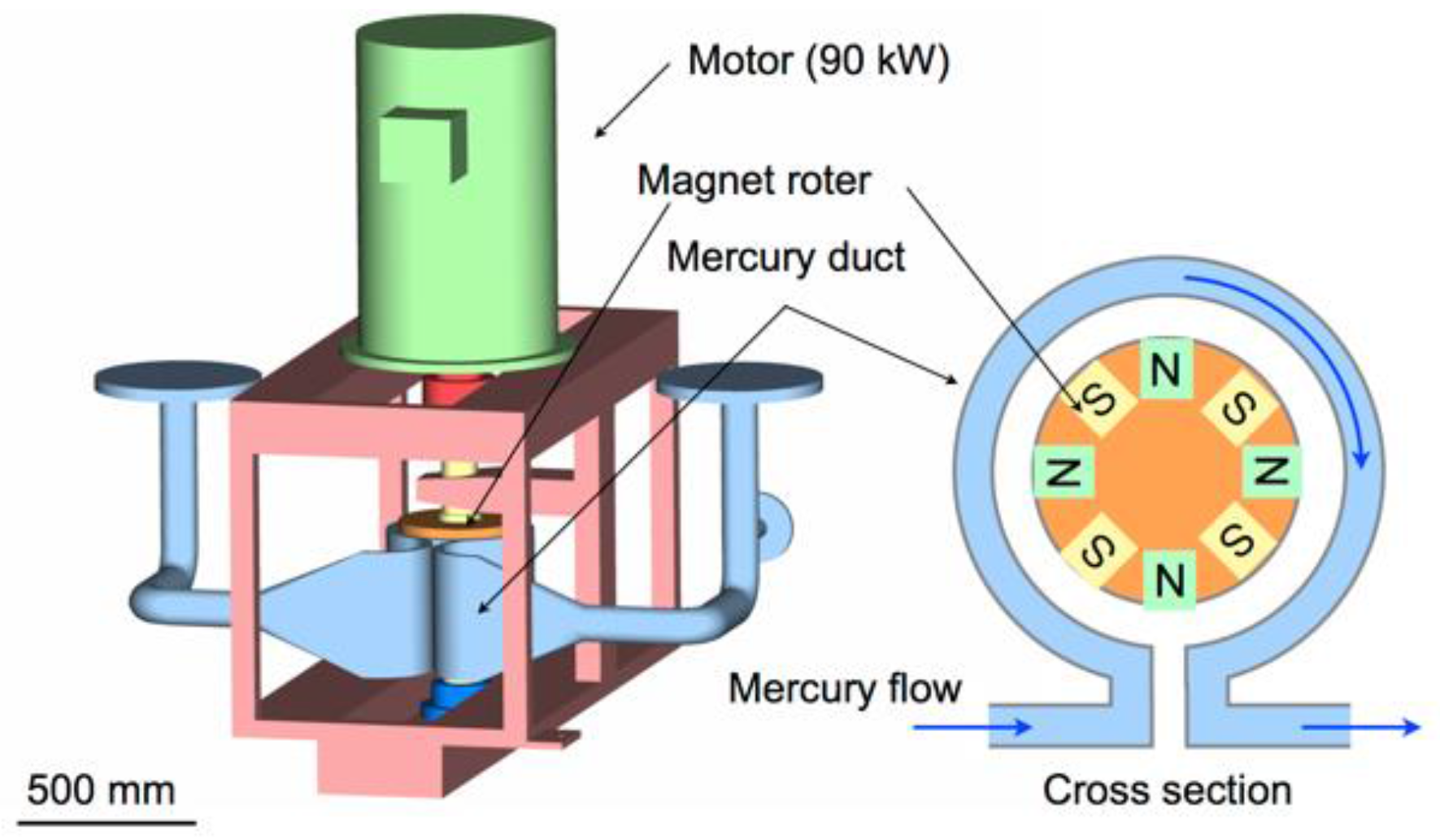
2.4. Mercury Circulation System
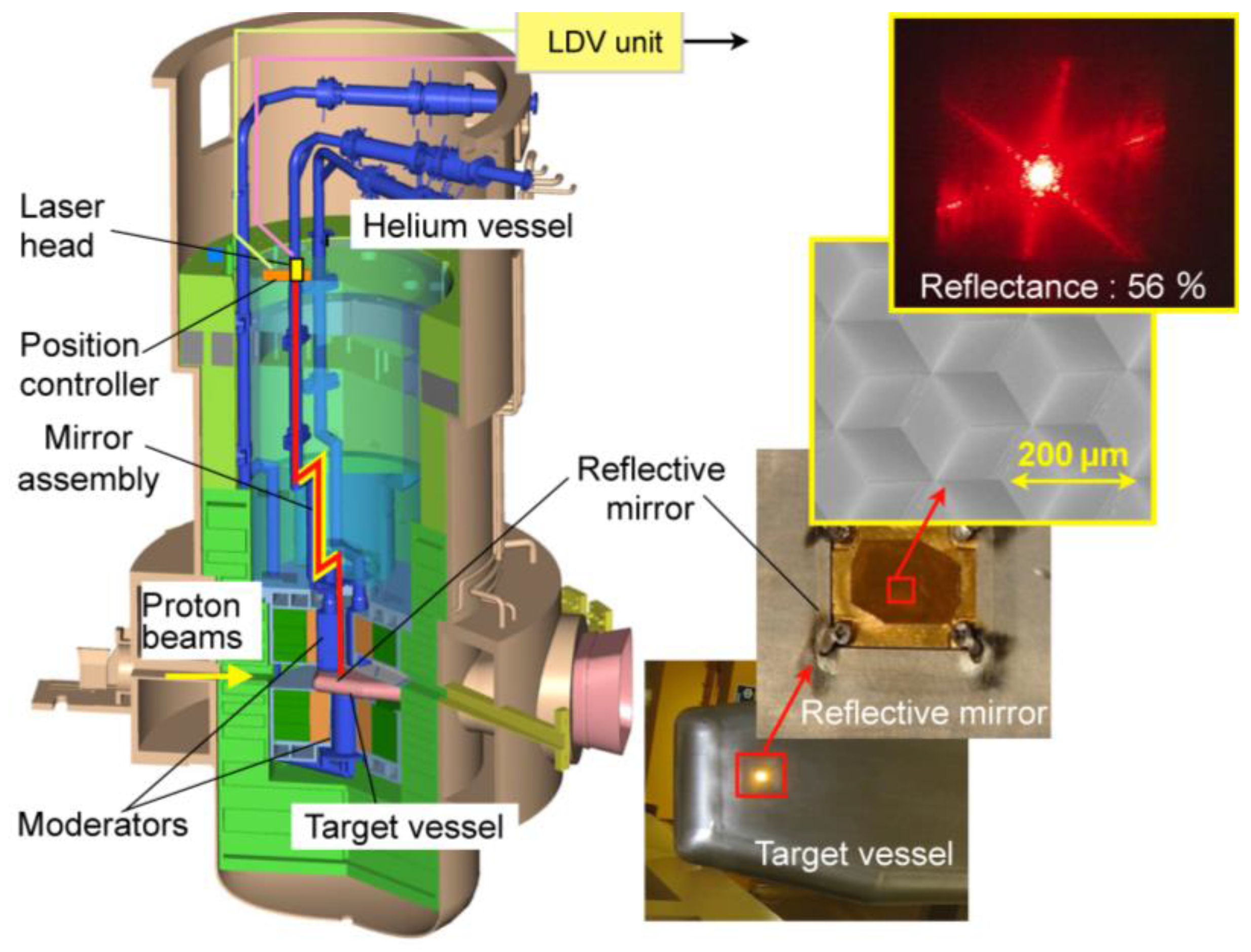
2.5. Target Diagnostic System
2.6. Target Vessel Replacement
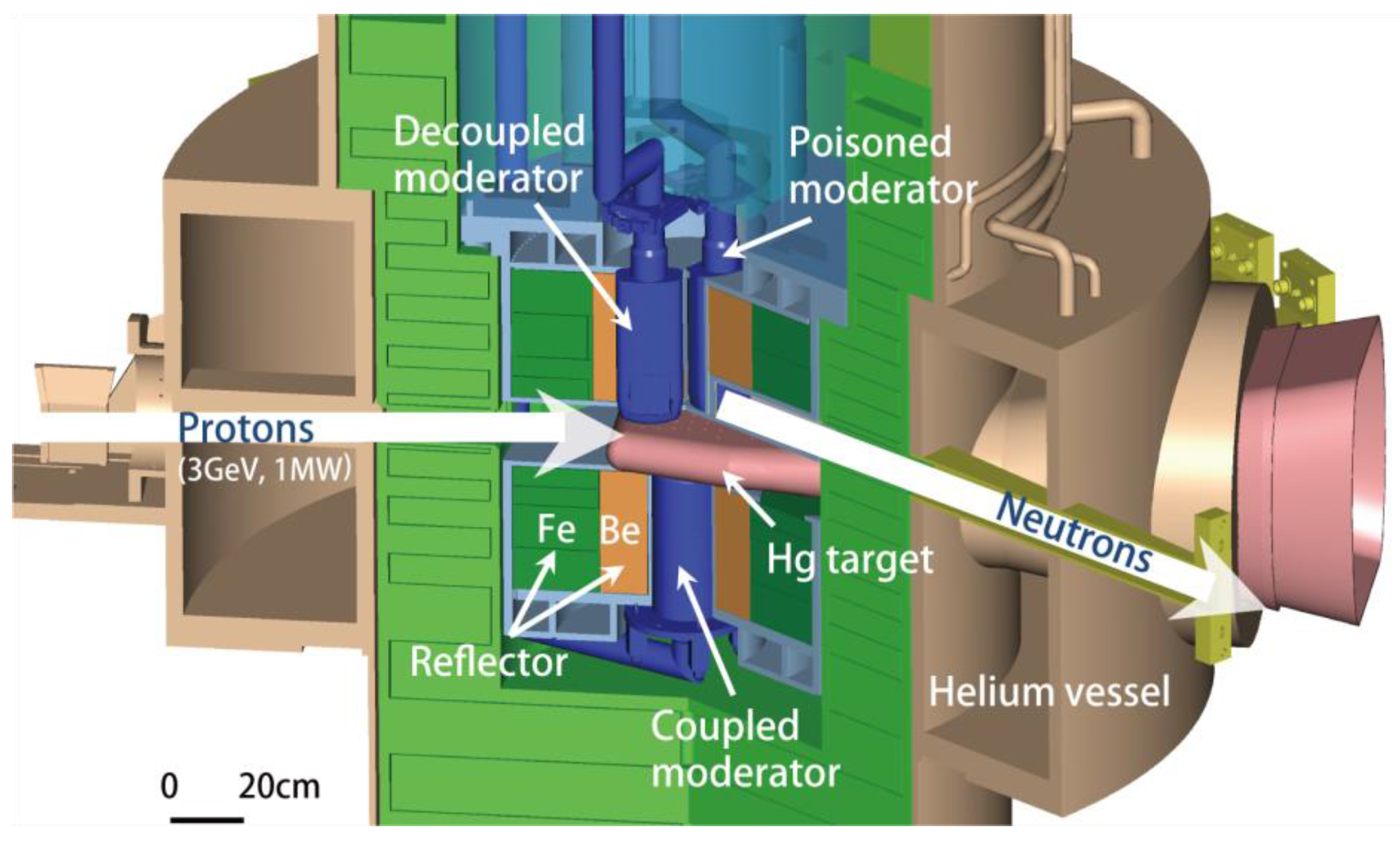
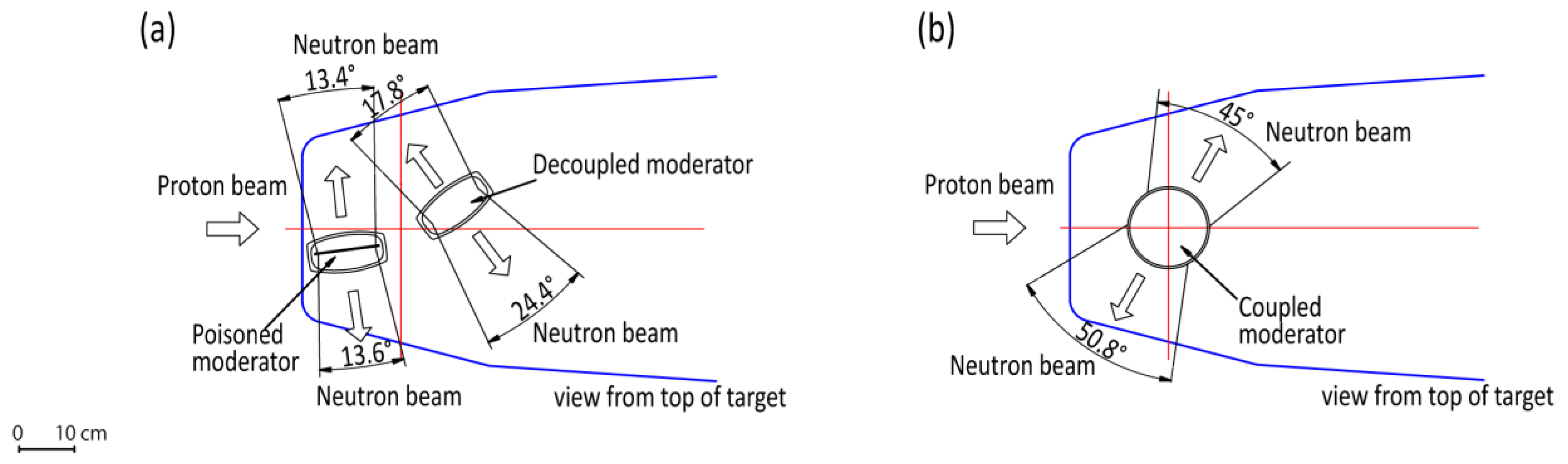
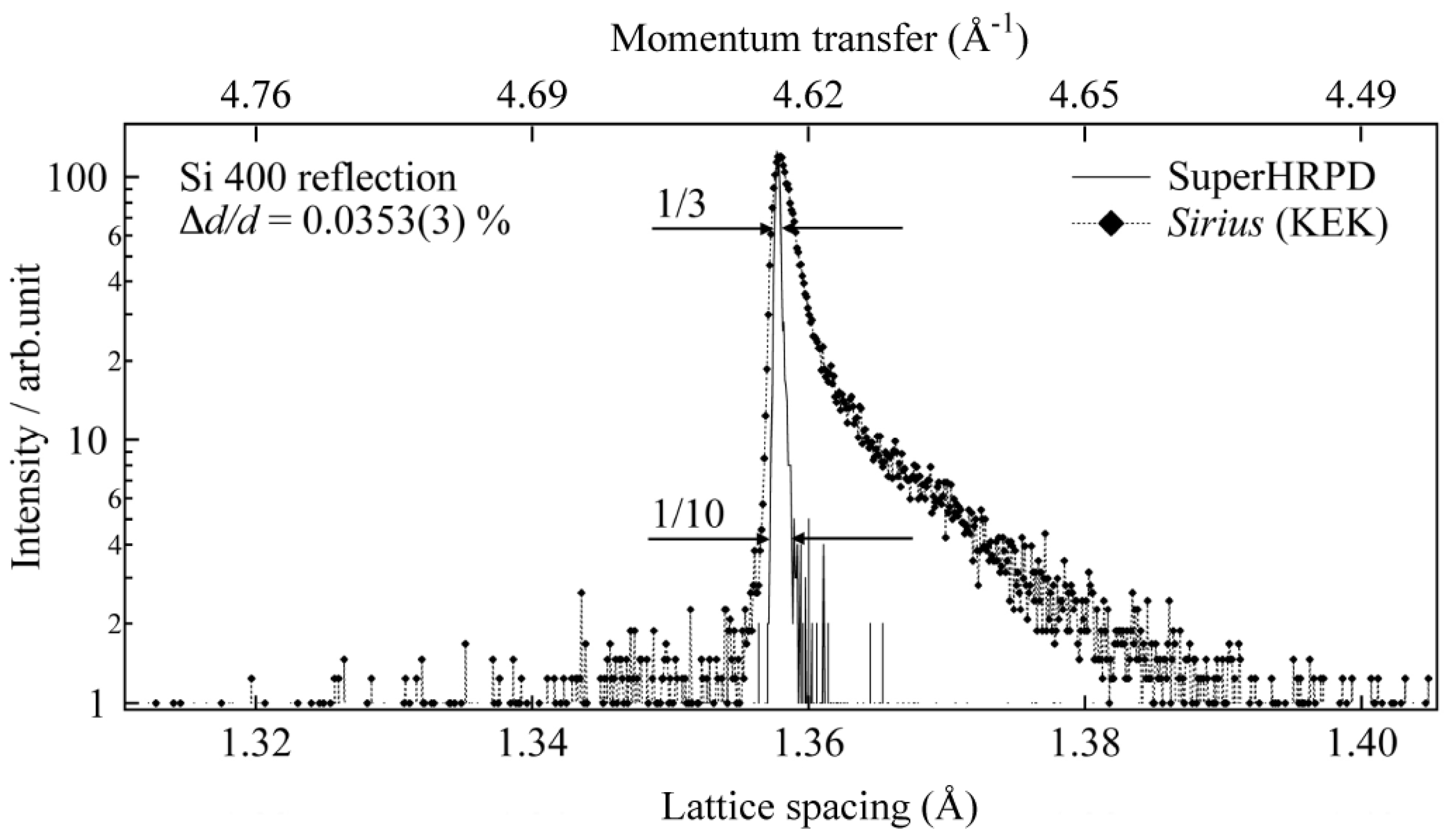
3. Moderator and Reflector Development
- high decoupling energy of 1 eV was achieved by adopting a Ag-In-Cd decoupler, providing short tail in the pulsed neutron beam emitted from the decoupled and poisoned moderators,
- cut-off energy was extended up to 0.4 eV by adopting a cadmium poison sheet, resulting in sharper pulse width for the poisoned moderator.
4. Cryogenic Hydrogen System
4.1. Design Requirements
- (1)
- Average temperature at the moderators is kept less than 20 K at 1.5 MPa in order to achieve constant density.
- (2)
- Temperature difference between the inlet and the outlet of moderators is kept less than 3 K to prevent hydrogen density fluctuation.
- (3)
- Para-hydrogen concentration of the moderators is kept more than 99% for the neutronic performance that helps to slow down to cold neutrons.
- (4)
- In order to reduce hazard potentials, it is necessary to minimize the inventory of hydrogen in the system.
- (5)
- Blanket structure with inert gases needs to prevent the hydrogen leakage to the outside from the system and to prevent air from entering the system.
- (6)
- Hydrogen vent line is required to release hydrogen safely when the refrigerator operation stops and any off-normal event takes place.
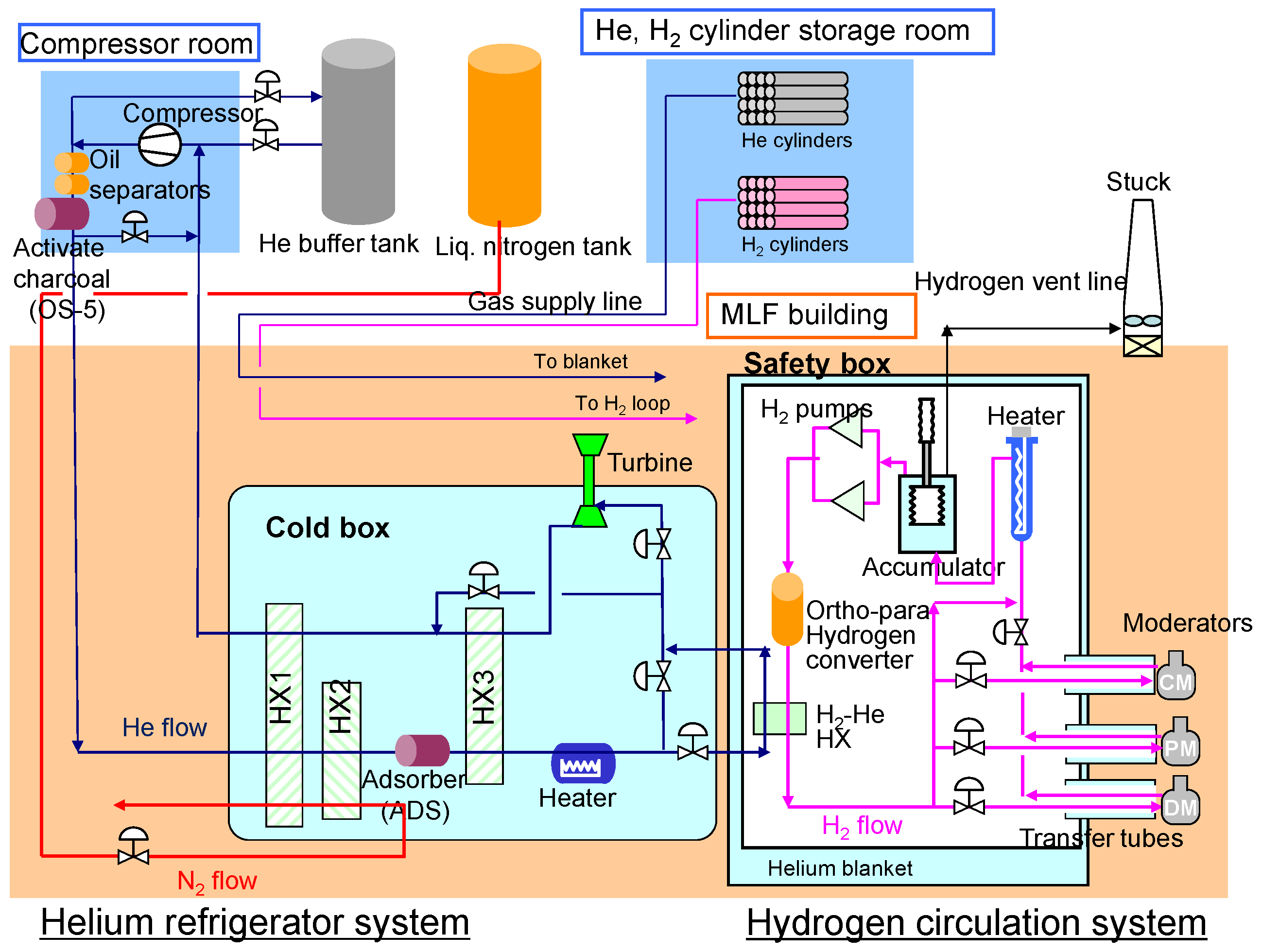
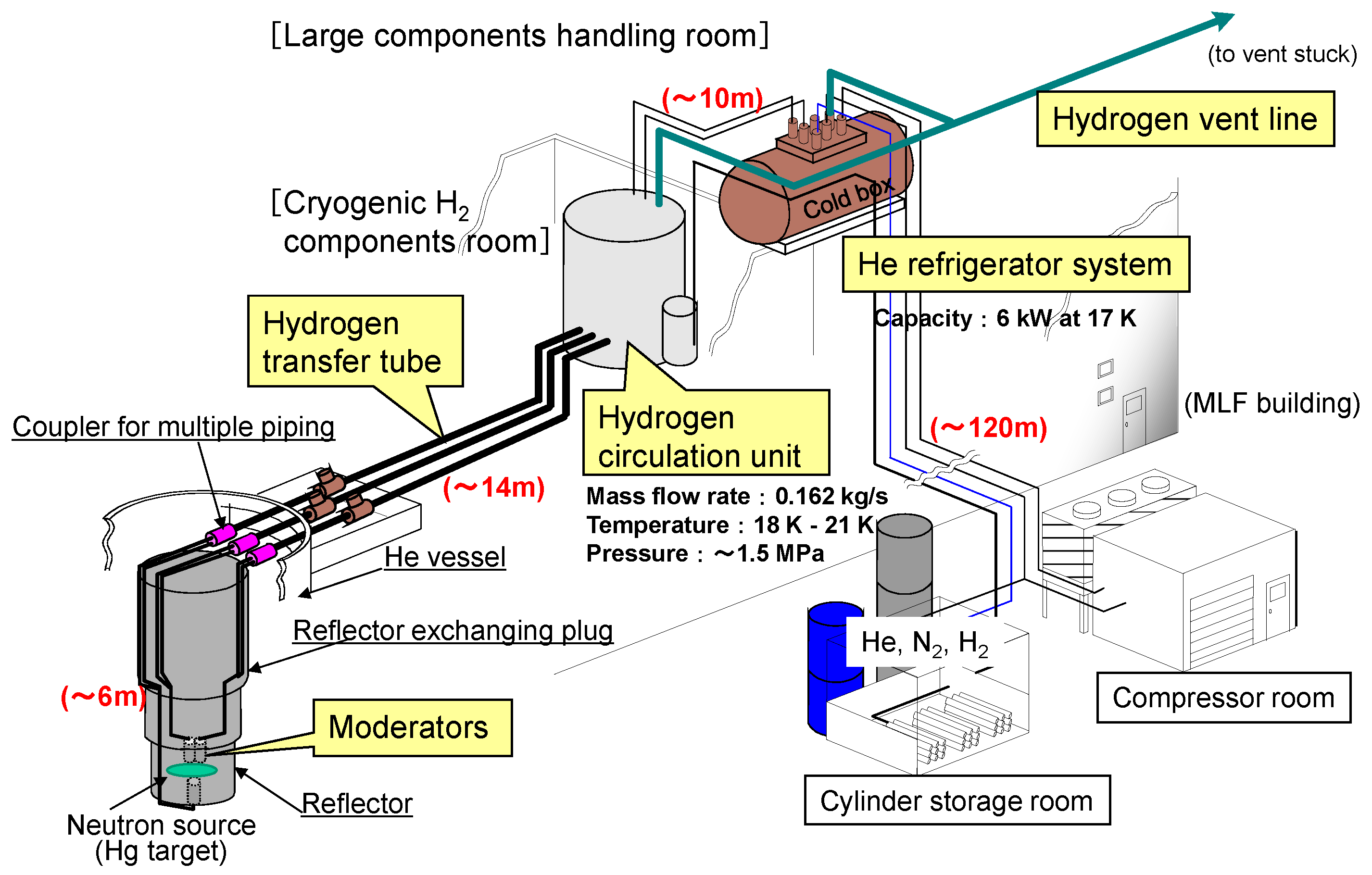
4.2. Design of the Cryogenic Hydrogen System
4.2.1. System Configuration and Specification of the Main Components
4.2.2. Helium Refrigerator System
4.2.3. Hydrogen Circulation System
4.2.4. Hydrogen Vent System
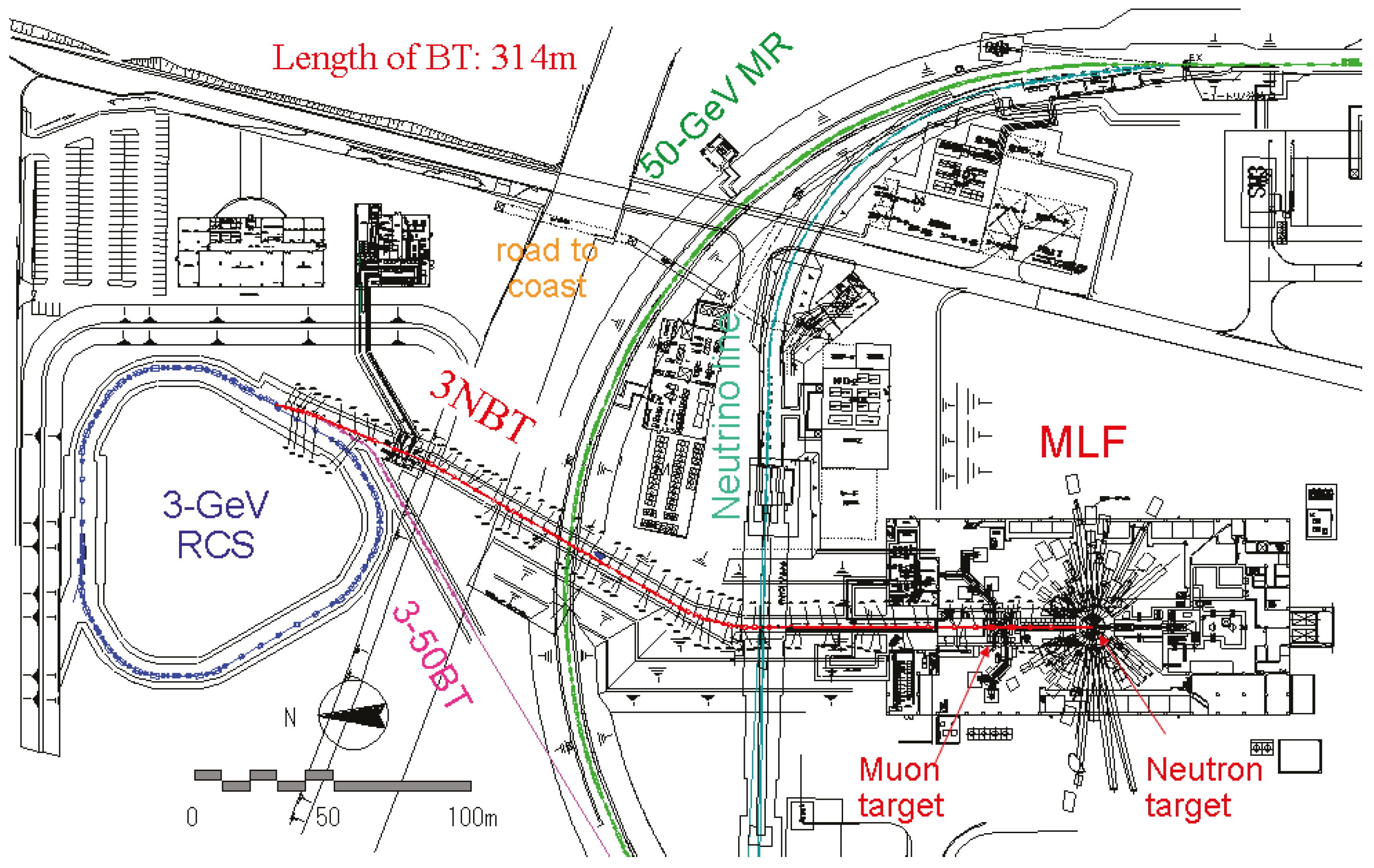
5. Proton Beam Transport
5.1. Overview of the Proton Beam Transport
5.2. Instruments for Beam Transport to Target
5.2.1. Magnets for Beam Transport
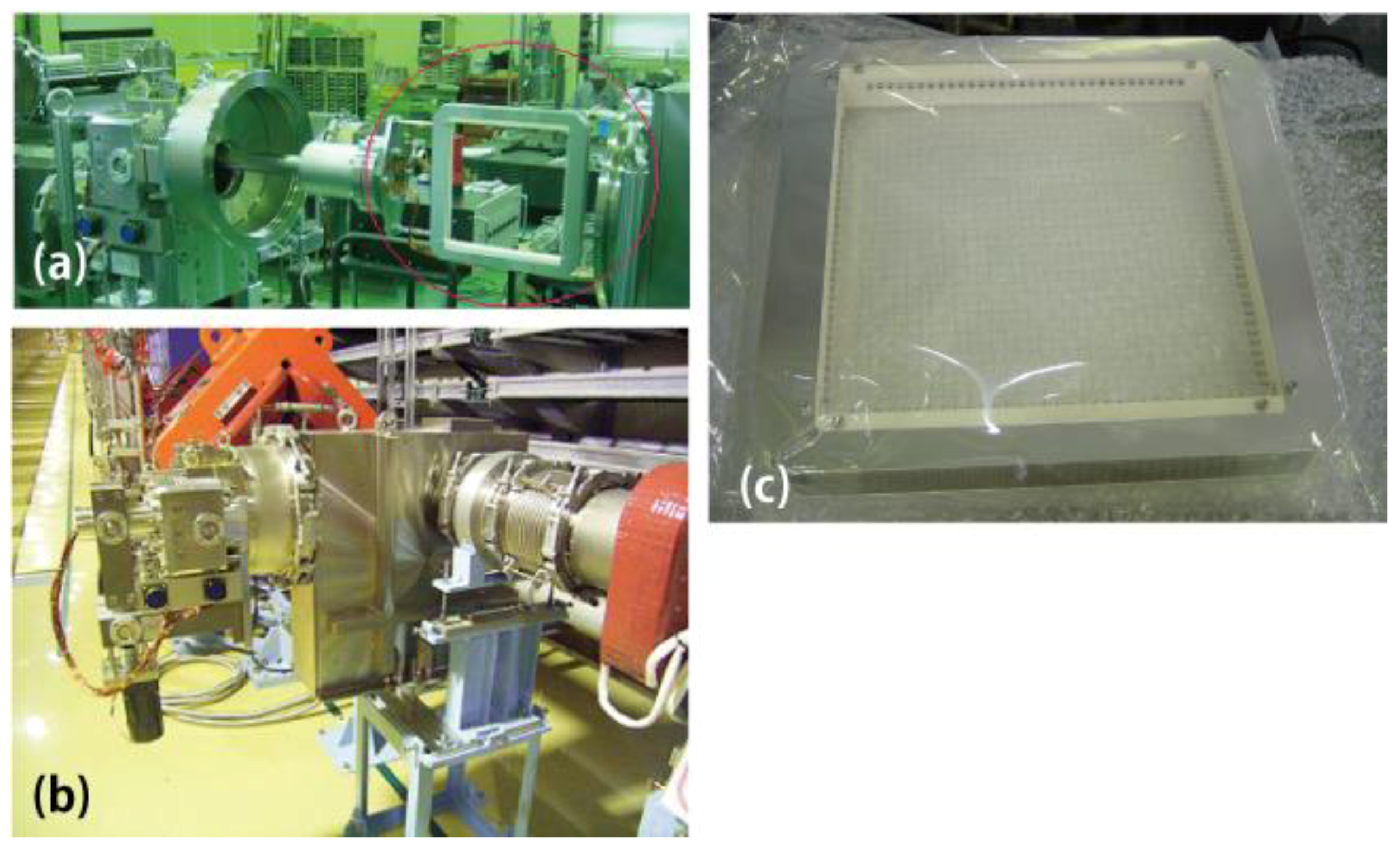
5.2.2. Proton Beam Monitor
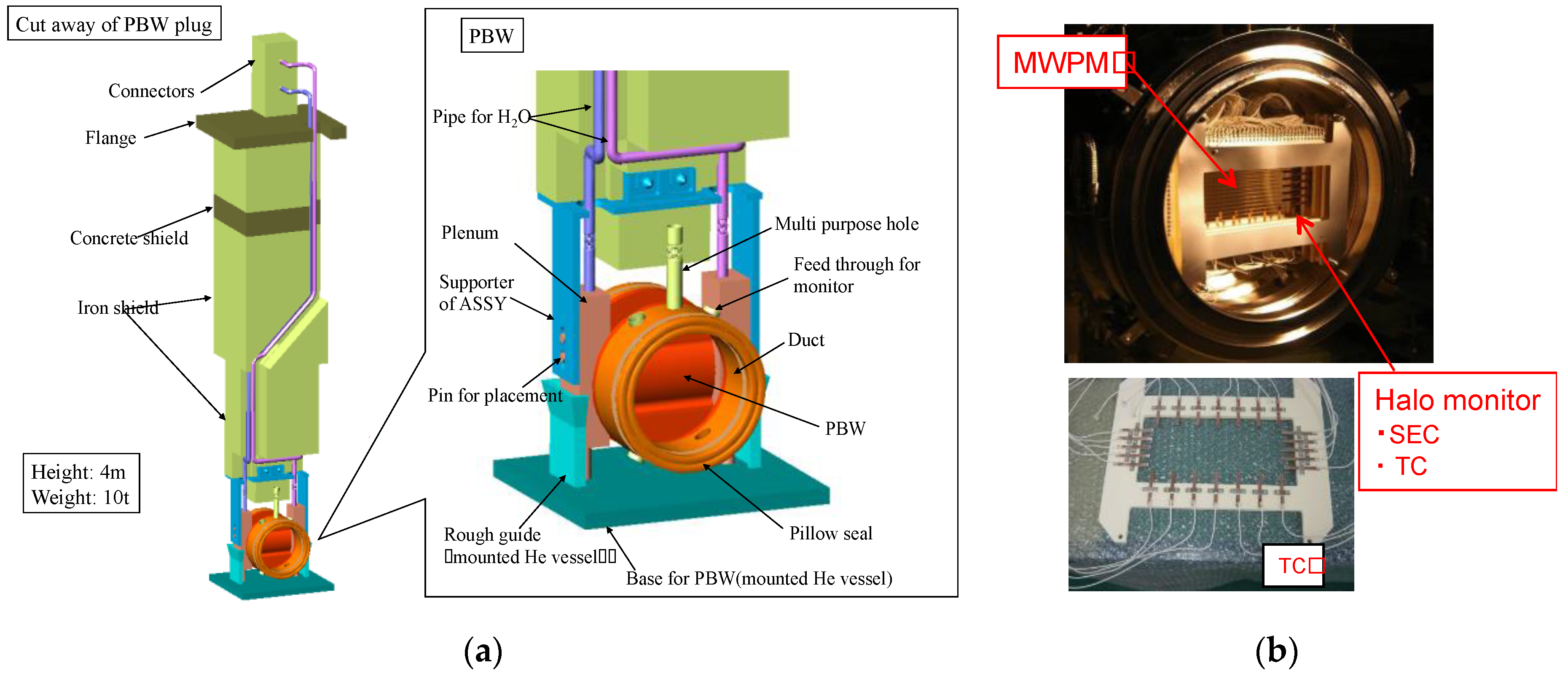
5.2.3. Proton Beam Window
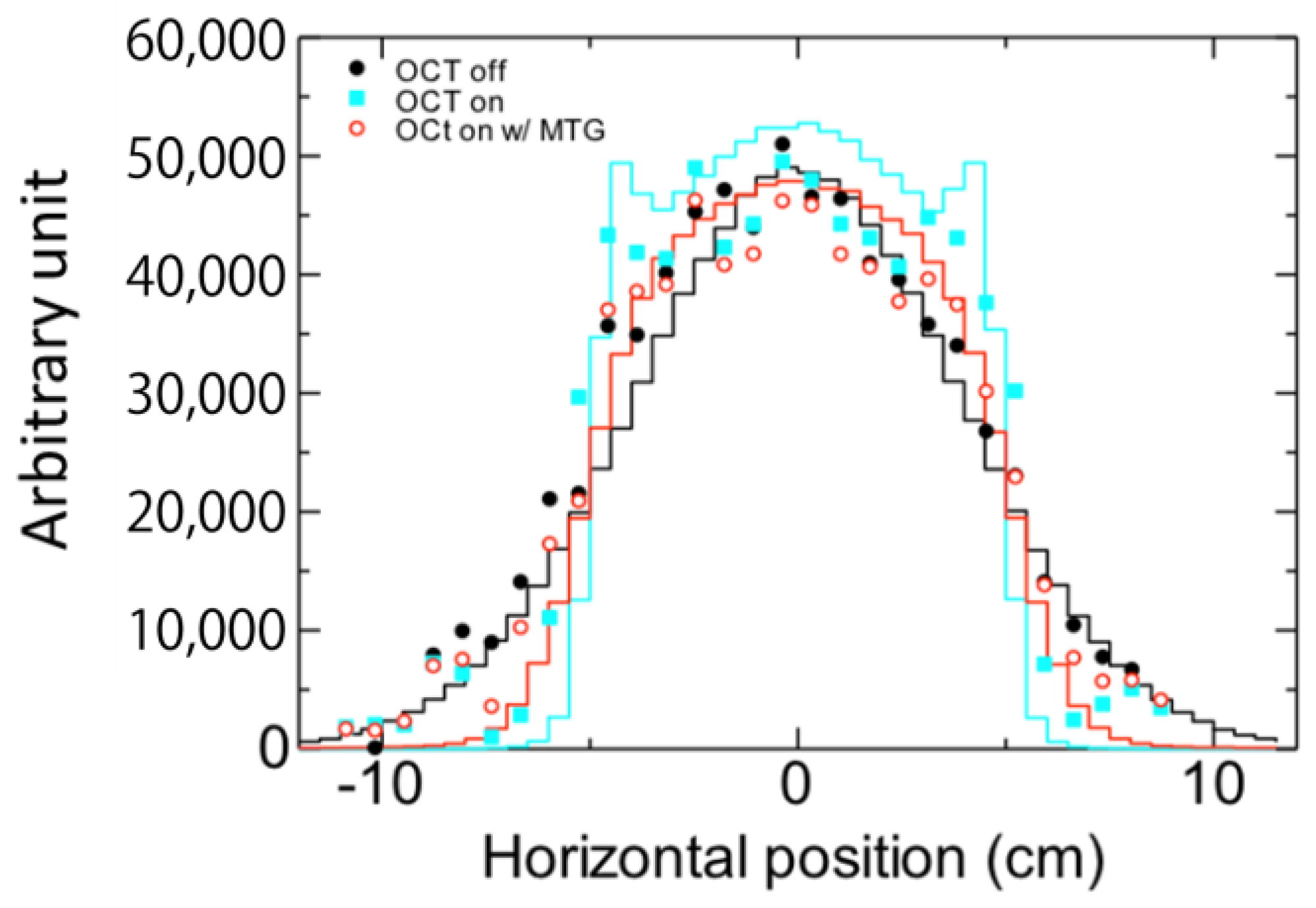
5.3. Non-Linear Beam Optics for Mitigation of Cavitation Erosion at the Target Vessel
6. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakamoto, S. Technical design report of spallation neutron source facility in J-PARC. In Neutron Source Section; JAEA-Technology 2011-035; Japan Atomic Energy Agency: Tokai, Japan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, S.; Meigo, S.; Fujimori, H.; Harada, M.; Konno, C.; Kasugai, Y.; Kai, T.; Miyake, Y.; Ikeda, Y. Advanced design of high-intensity beam transport line in J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2006, 562, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meigo, S.; Noda, F.; Ishikura, S.; Futakawa, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Ikeda, Y. Evaluation of the 3-GeV proton beam profile at the spallation target of the JSNS. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2006, 562, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meigo, S.; Ooi, M.; Kai, T.; Ono, T.; Ikezaki, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Fujimori, H.; Sakamoto, S. Beam commissioning for neutron and muon facility at J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2009, 600, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y. Accelerator Group JAERI/KEK Joint Project Team, Accelerator Technical Design Report for High-Intensity Proton Accelerator Facility Project, J-PARC; KEK-Report 2002-13; JAERI-Tech 2003-044; Japan Atomic Energy Agency: Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori, C.; Ezura, E.; Hashimoto, Y.; Mori, Y.; Schnase, A.; Takagi, A.; Uesugi, T.; Yoshii, M.; Tamura, F.; Yamamoto, M. High field gradient cavity for JAERI-KEK joint project. In Proceedings of the 8th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC 2002), Paris, France, 3–7 June 2002; Laclare, J.-L., Ed.; The European Physical Society Interdivisional Group on Accelerators (EPS-IGA) and CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; pp. 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, M.; Maekawa, F. 3-Dimensional Shielding Design for a Spallation Neutron Source Facility in the High Intensity Proton Accelerator Project; JAERI-Tech 2003-010; Japan Atomic Energy Agency: Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan, 2003. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Wakui, T.; Meigo, S.; Seki, M.; Ito, M.; Suzuki, T.; Ikezaki, K.; Maekawa, F.; Futakawa, M.; et al. Maintenance of Used Components in Spallation Neutron Source, Moderator Reflector and Proton Beam Window; JAEA-Technology 2012-024; Japan Atomic Energy Agency: Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haines, J.R.; McManamy, T.J.; Gabriel, T.A.; Battle, R.E.; Chipley, K.K.; Crabtree, J.A.; Jacobs, L.L.; Lousteau, D.C.; Rennich, M.J.; Riemer, B.W. Spallation neutron source target station design, development and commissioning. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2014, 764, 94–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home page of European Spallation Source. Available online: https://europeanspallationsource.se/european-spallation-source (accessed on 25 July 2017).
- Kaminaga, M.; Terada, A.; Haga, K.; Kinoshita, H.; Ishikura, S.; Hino, R. Study of Integrated Structure of Mercury Target Container with Safety Hull; JAERI-Tech 2000-076; Japan Atomic Energy Agency: Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Futakawa, M.; Kogawa, H.; Hino, R. Measurement of dynamics response of liquid metal subjected to uniaxial strain wave. J. Phys. IV Fr. 2000, 10, Pr9-237–Pr9-242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futakawa, M.; Naoe, T.; Kogawa, H.; Tsai, C.C.; Ikeda, Y. Pitting damage formation up to over 10 million cycles off-line test by MIMTM. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2003, 40, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoe, T.; Futakawa, M. Pressure wave-induced cavitation erosion in narrow channel of stagnant mercury. Trans. JSME 2014, 80, fe0025-1-12. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, K.; Takagi, S.; Matsumoto, Y. Propagation of pressure waves, caused by a thermal shock, in liquid metals containing gas bubbles. J. Fluid Sci. Technol. 2008, 3, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futakawa, M.; Kogawa, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Naoe, T.; Ida, M.; Haga, K.; Wakui, T.; Tanaka, N.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ikeda, Y. Mitigation technologies for damage induced by pressure waves in high-power mercury spallation neutron sources (II) bubbling effect to reduce pressure wave. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2008, 45, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogawa, H.; Naoe, T.; Kyotoh, H.; Haga, K.; Kinoshita, H.; Futakawa, M. Development of microbubble generator for suppression of pressure waves in mercury target of spallation source. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Haga, K.; Kaminaga, M.; Hino, R. Experiments on mercury circulation system for spallation neutron target. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2004, 41, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogawa, H.; Haga, K.; Wakui, T.; Futakawa, M. Development on mercury pump for JSNS. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2009, 600, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futakawa, M.; Kogawa, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Riemer, B.; Wendel, M.; Haines, J.; Bauer, G.; Naoe, T.; Okita, K.; et al. Cavitation damage prediction for spallation target vessels by assessment of acoustic vibration. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 377, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshigawara, M.; Wakui, T.; Naoe, T.; Kogawa, H.; Maekawa, F.; Futakawa, M.; Kikuchi, K. Development of JSNS target vessel diagnosis system using laser Doppler method. J. Nucl. Mater. 2010, 398, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogawa, H.; Naoe, T.; Futakawa, M.; Haga, K.; Wakui, T.; Harada, M.; Takada, H. Mitigation technologies for damage induced by pressure waves in high-power mercury spallation neutron source (IV)—Measurement on pressure wave response and microbubble effect on mitigation in JSNS mercury target. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, T.; Kasugai, Y.; Ooi, M.; Kogawa, H.; Haga, K.; Kinoshita, H.; Seki, M.; Harada, M. Experiences on radioactivity handling for mercury target system in MLF/J-PARC. Prog. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshigawara, M.; Watanabe, N.; Takada, H.; Nakashima, H.; Nagao, T.; Oyama, Y.; Kosako, K. Neutronic Studies of Bare Targets for JAERI 5 MW Pulsed Spallation Neutron Source; JAERI-Research 99-010; Japan Atomic Energy Agency: Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara, M.; Harada, M.; Watanabe, N.; Kai, T.; Sakata, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Ooi, M. Proton energy dependence of slow neutron intensity. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources ICANS-XV, Tsukuba, Japan, 6–9 November 2000; Suzuki, J., Itoh, S., Eds.; Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute: Ibaraki, Japan, 2001; pp. 835–847. [Google Scholar]
- Broome, T.A.; Hogston, J.R.; Holding, M.; Howells, W.S. The isis methane moderator. In Proceedings of the Twelfth meeting of International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, UK, 24–28 May 1993; Steigenberger, U., Broome, T., Rees, G., Soper, A., Eds.; Rutherford Appleton Laboratory: Oxfordshire, UK, 1994; pp. T156–T163. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, T.L.; Carpenter, J.M.; Miller, M.E. The development of solid methane neutron moderators at the intense pulsed neutron source facility of Argonne National Laboratory. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Cold Moderators for Pulsed Neutron Sources, Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, IL, USA, 29 September–2 October 1997; Carpenter, J.M., Iverson, E.B., Eds.; 1997; pp. 299–304. Available online: http://www.osti.gov/scitech/biblio/12385/ (accessed on 25 July 2017).
- Ishikawa, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Watanabe, N.; Kondo, K.; Inoue, K.; Kiyanagi, Y.; Iwasa, H.; Tsuchihashi, K. Grooved cold moderator at KENS. In Proceedings of the Seventh Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources ICANS-VII, Chalk River, Ontario, ON, Canada, 13–16 September 1983; Schriber, O.S., Ed.; Chalk River Nuclear Laboratories: Ontario, ON, Canada, 1984; pp. 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- MacFarlane, R.E. New Thermal Neutron Scattering Files for ENDF/B-VI Release 2; LA-12639-MS; Los Alamos National Laboratory Report: Los Alamos, NM, USA, March 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyanagi, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Iwasa, H. Premoderator studies for a coupled liquid-hydrogen moderator in pulsed spallation neutron sources. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 1994, 343, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, T.; Teshigawara, M.; Watanabe, N.; Harada, M.; Sakara, H.; Ikeda, Y. Optimization of coupled hydrogen moderator for a short pulse spallation neutron source. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2002, 39, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Teshigawara, M.; Kai, T.; Sakata, H.; Watanabe, N.; Ikeda, Y. Neutronic optimization of premoderator and reflector for decoupled hydrogen moderator in 1 MW spallation neutron source. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2002, 39, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Harada, M.; Kai, T.; Teshigawara, M.; Ikeda, Y. Optimization of coupled and decoupled moderators for a short pulse spallation source. J. Neutron Res. 2013, 11, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Teshigawara, M.; Watanabe, N.; Kai, T.; Ikeda, Y. Optimization of poisoned and unpoisoned decoupled moderators in JSNS. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS XVI), Düsseldorf-Neuss, Germany, 12–15 May 2003; Mank, G., Conrad, H., Eds.; Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH: Jülich, Germany, 2003; pp. 697–706. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, T.; Harada, M.; Teshigawara, M.; Watanabe, N.; Ikeda, Y. Coupled hydrogen moderator optimization with ortho/para hydrogen ratio. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2004, 523, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, T.; Harada, M.; Teshigawara, M.; Watanabe, N.; Kiyanagi, Y.; Ikeda, Y. Neutronic performance of rectangular and cylindrical coupled hydrogen moderators in wide-angle beam extraction of low-energy neutrons. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2005, 550, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, T.; Harada, M.; Teshigawara, M.; Watanabe, N.; Ikeda, Y. Neutronic study on coupled hydrogen moderator for J-PARC spallation neutron source. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS XVI), Düsseldorf-Neuss, Germany, 12–15 May 2003; Mank, G., Conrad, H., Eds.; Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH: Jülich, Germany, 2003; pp. 657–666. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, M.; Watanabe, N.; Teshigawara, M.; Kai, T.; Ikeda, Y. Neutronic studies on decoupled hydrogen moderator for a short-pulse spallation source. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2005, 539, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Watanabe, N.; Teshigawara, M.; Kai, T.; Kato, T.; Ikeda, Y. Neutronics of a poisoned para-hydrogen moderator for a pulsed spallation neutron source. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2007, 574, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, F.; Harada, M.; Oikawa, K.; Teshigawara, M.; Kai, T.; Meigo, S.; Ooi, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Takada, H.; Futakawa, M.; et al. First neutron production utilizing J-PARC pulsed spallation neutron source JSNS and neutronic performance demonstrated. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2010, 620, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batkov, K.; Takibayev, A.; Zanini, L.; Mezei, F. Unperturbed moderator brightness in pulsed neutron sources. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2013, 729, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, F.; Zanini, L.; Takibayev, A.; Batkov, K.; Klinkby, E.; Pitcher, E.; Schronfeldt, T. Low dimensional neutron moderators for enhanced source brightness. J. Neutron Res. 2014, 17, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallmeier, F.X.; Lu, W.; Riemer, B.W.; Zhao, J.K.; Herwig, K.W. Conceptual moderator studies for the spallation neutron source short-pulse second target station. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 063304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iverson, E.B.; Carpenter, J.M. Kinetics of irradiated liquid hydrogen. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Advanced Cold Moderators (ACoM-6), Jülich, Germany, 11–13 September 2002; Conrad, H., Ed.; Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH: Jülich, Germany, 2002; pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Iverson, E.B.; Carpenter, J.M. Kinetics of irradiated liquid hydrogen. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS XVI), Düsseldorf-Neuss, Germany, 12–15 May 2003; Mank, G., Conrad, H., Eds.; Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH: Jülich, Germany, 2003; pp. 707–718. [Google Scholar]
- Ooi, M.; Ogawa, H.; Kamiyama, T.; Kiyanagi, Y. Experimental studies of the effect of the ortho/para ratio on the neutronic performance of a liquid hydrogen moderator for a pulsed neutron source. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2011, 659, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, M.; Ino, T.; Muhrer, G.; Pitcher, E.J.; Russell, G.J.; Ferguson, P.D.; Iverson, E.B.; Freeman, D.; Kiyanagi, Y. Measurements of the change of neutronic performance of a hydrogen moderator at Manuel Lujan Neutron Scattering Center due to conversion from orth- to para-hydrogen state. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2006, 566, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshigawara, M.; Harada, M.; Tatsumoto, H.; Aso, T.; Ohtsu, K.; Takada, H.; Futakawa, M.; Ikeda, Y. Experimental verification of equilibrium para-hydrogen levels in hydrogen moderations irradiated by spallation neutrons at J-PARC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2016, 368, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshigawara, M.; Harada, M.; Saito, S.; Oikawa, K.; Maekawa, F.; Futakawa, M.; Kikuchi, K.; Kato, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Naoe, T.; et al. Development of aluminum (Al5083)-clad ternary Ag-In-Cd alloy for JSNS decoupled moderator. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 356, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Saito, S.; Teshigawara, M.; Kawai, M.; Kukuchi, K.; Watanabe, N.; Ikeda, Y. Silver-indium-cadmium decoupler and liner. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS XVI), Düsseldorf-Neuss, Germany, 12–15 May 2003; Mank, G., Conrad, H., Eds.; Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH: Jülich, Germany, 2003; pp. 677–687. [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara, M.; Harada, M.; Saito, S.; Kikkuchi, K.; Kogawa, H.; Kawai, M.; Kurishita, H.; Konashi, K. Cladding technique for development of Ag-In-Cd decoupler. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 343, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Teshigawara, M.; Harada, M.; Saito, S.; Maekawa, F.; Futakawa, M.; Ishigaki, T. A challenge for a high-resolution Ag-In-Cd decoupler in intensified short-pulsed neutron source. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 652, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Teshigawara, M.; Maekawa, F.; Futakawa, M. Study on low activation material for MW-Class spallation neutron sources. J. Nucl. Mater. 2010, 398, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, M.; Teshigawara, M.; Wakui, T.; Nishi, T.; Harada, M.; Maekawa, F.; Futakawa, M. Development status of low activation ternary Au-In-Cd alloy decoupler for a MW class spallation neutron source: 1st Production of Au-In-Cd alloy. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 431, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, M.; Teshigawara, M.; Kai, T.; Harada, M.; Maekawa, F.; Futakawa, M.; Hashimoto, E.; Segawa, M.; Kureta, M.; Tremsin, A.; et al. Neutron resonance imaging of a Au-In-Cd alloy for the JSNS. Phys. Procedia 2013, 43, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, M.; Teshigawara, M.; Harada, M.; Naoe, T.; Maekawa, F.; Kasugai, Y. Development of Au-In-Cd decoupler by a hot isostatic pressing (HIP) technique for short pulsed spallation neutron source. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 450, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, T.; Oikawa, K. Powder diffractometer at J-PARC. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS XVI), Dusseldorf-Neuss, Germany, 12–15 May 2003; Mank, G., Conrad, H., Eds.; Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH: Jülich, Germany, 2003; pp. 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Aso, T.; Tatsumoto, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Ushijima, I.; Ohtsu, K.; Kato, T.; Ikeda, Y. Design result of the cryogenic hydrogen circulation system for 1 MW pulse spallation neutron source (JSNS) in J-PARC. AIP Conf. Proc. 2006, 823, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, T.; Tatsumoto, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Ohtsu, K.; Uehara, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Sakurayama, H.; Maekawa, F.; Futakawa, M.; Ushijima, I. Commissioning of the cryogenic hydrogen system in J-PARC: Preliminary operation by helium gas. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Second International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2008, Seoul, Korea, 21–25 July 2008; Korea Institute of Applied Superconductivity and Cryogenics: Seoul, Korea, 2009; pp. 741–746. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumoto, H.; Aso, T.; Kato, T.; Ohtsu, K.; Hasegawa, S.; Maekawa, F.; Futakawa, M. Commissioning of the cryogenic hydrogen system in J-PARC: First cool-down operation with helium. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Second International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2008, Seoul, Korea, 21–25 July 2008; Korea Institute of Applied Superconductivity and Cryogenics: Seoul, Korea, 2009; pp. 717–722. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Kawamura, N.; Strasser, P.; Makimura, S.; Koda, A.; Fujimori, H.; Nakahara, K.; Kadono, R.; Kato, M.; et al. Birth of an intense pulsed muon source, J-PARC MUSE. Physica B 2009, 404, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higemoto, W.; Kadono, R.; Kawamura, N.; Koda, A.; Kojima, K. M.; Makimura, S.; Matoba, S.; Miyake, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Strasser, P. Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex IV: The Muon Facility. Quantum Beam Sci. 2017, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, H.; Kawamura, N.; Meigo, S.; Strasser, P.; Nakahara, K.; Miyake, Y. Radiation resistant magnets for the J-PARC muon facility. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2009, 600, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meigo, S.; Ooi, M.; Ikezaki, K.; Akutsu, A.; Sakamoto, S.; Futakawa, M. Development of profile monitor system for high intense spallation neutron source. In Proceedings of the 1st International Beam Instrumentation Conference, IBIC 2012, Tsukuba, Japan, 1–4 October 2012; Mitsuhashi, T., Shirakawa, A., Eds.; JACow: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 227–231. Available online: http://epaper.kek.jp/IBIC2012/papers/mopb68.pdf/ (accessed on 25 July 2017).
- Sakai, K.; Kai, T.; Ooi, M.; Watanabe, A.; Nakatani, T.; Higemoto, W.; Meigo, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Takada, H.; Futakawa, M. Operation status of interlock system of Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC. Prog. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home Page of Experimental Physics and Industrial Control System (EPICS). Available online: http://www.aps.anl.gov/epics/ (accessed on 5 July 2017).
- Ooi, M.; Kai, T.; Meigo, S.; Kinoshita, H.; Sakai, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Kaminaga, M.; Katoh, T.; Katoh, T. Development of beam monitor DAQ system for 3NBT at J-PARC. In Proceedings of the 10th ICALEPCS International Conference on Accelerator and Large Experiment Physical Control System, Geneva, Switzerland, 10–14 October 2005; PO1.024. pp. 1–6. Available online: http://accelconf.web.cern.ch/accelconf/ica05/proceedings/pdf/P1_024.pdf/ (accessed on 25 July 2017).
- Home Page of Strategic Accelerator Design (SAD). Available online: http://acc-physics.kek.jp/SAD/ (accessed on 25 July 2017).
- Meigo, S.; Ooi, M.; Harada, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Akutsu, A. Radiation damage and lifetime estimation of the proton beam window at the Japan Spallation Neutron Source. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 450, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Hamaguchi, D. Mechanical properties and microstructure of AlMg3 irradiated in SINQ Target-3. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 343, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Naito, F.; Kubota, C.; Meigo, S.; Fujimori, H.; Ogiwara, N.; Kamiya, J.; Kinsho, M.; Kabeya, Z.; Kubo, T.; et al. Material and surface processing in J-PARC vacuum system. Vacuum 2012, 86, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, D.A.; Riemer, B.W.; Ferguson, P.D.; Carroll, A.J.; Dayton, M.J. Initial observations of cavitation-induced erosion of liquid metal spallation target vessels at the Spallation Neutron Source. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 431, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoe, T.; Xiong, Z.; Futakawa, M. Gigacycle fatigue behavior of austenitic stainless steels used for mercury target vessels. J. Nucl. Mater. 2016, 468, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meigo, S.; Ooi, M.; Ikezaki, K.; Akutsu, A. Beam flattening system based on non-linear optics for high power spallation neutron target at J-PARC. In Proceedings of the 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference, (IPAC2014), Dresden, Germany, 15–20 June 2014; Petit-Jean-Genaz, C., Arduini, G., Michel, P., Schaa, V.R.W., Eds.; JACow: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 896–898. Available online: http://accelconf.web.cern.ch/AccelConf/IPAC2014/papers/mopri116.pdf/ (accessed on 25 July 2017).

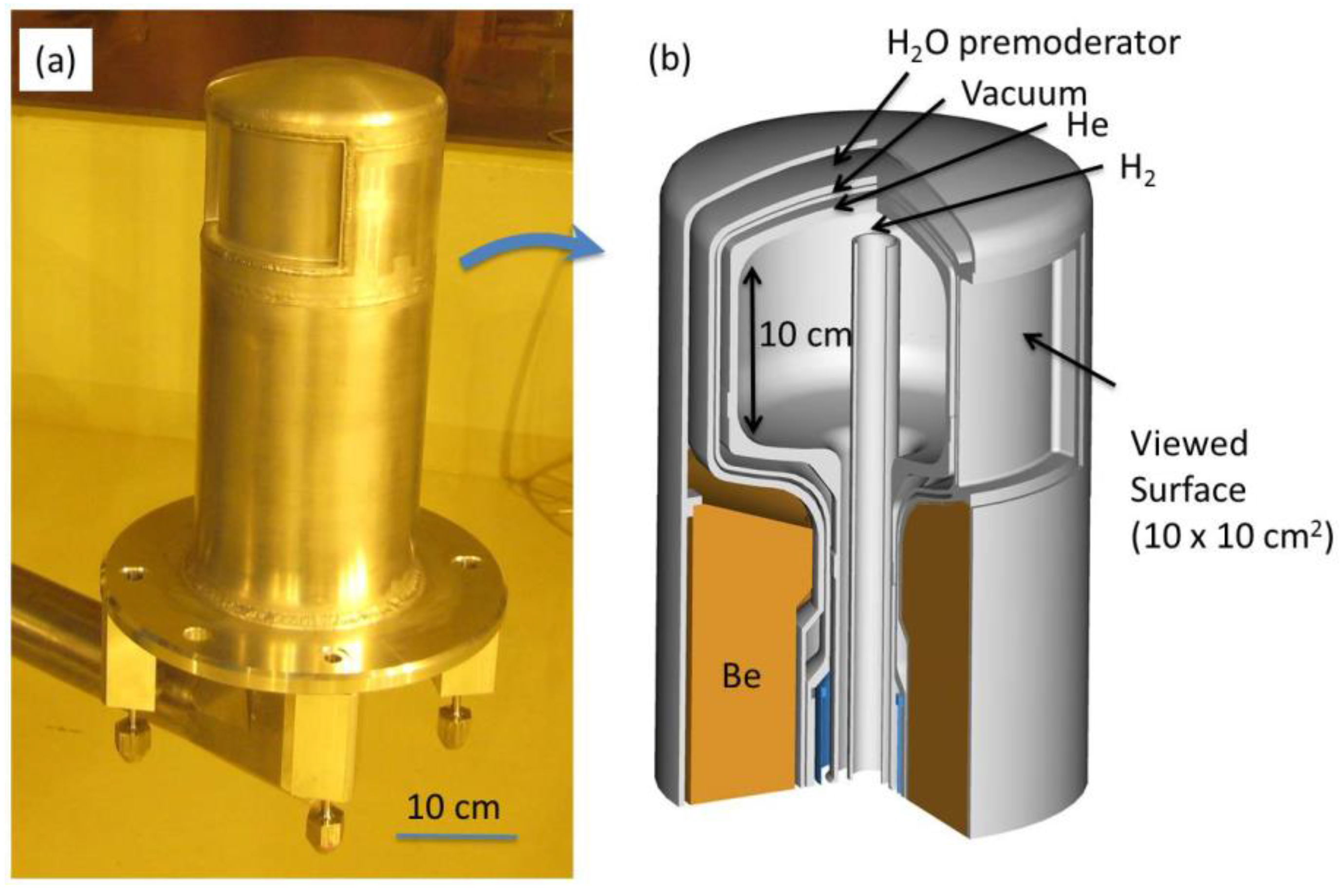
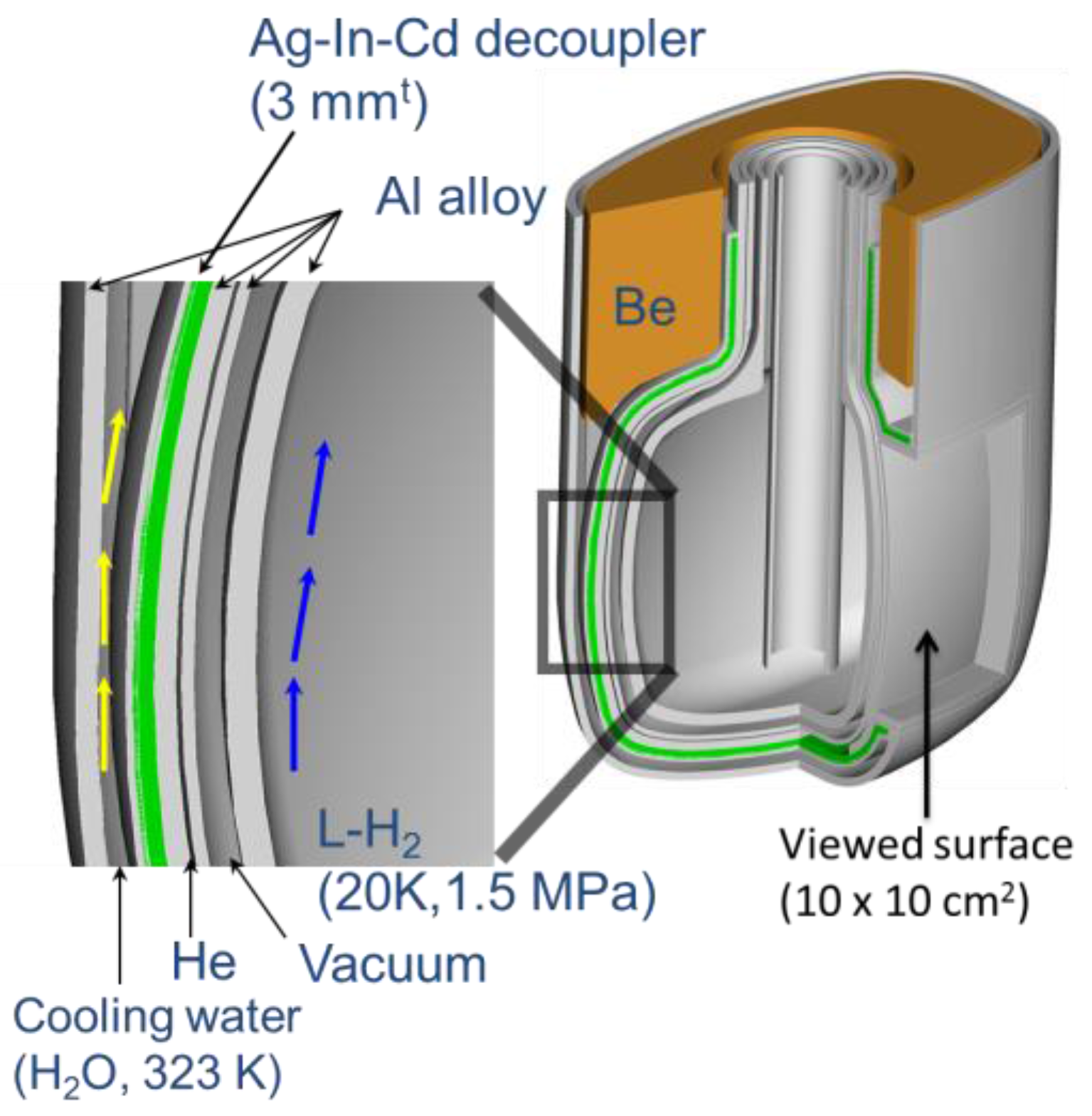
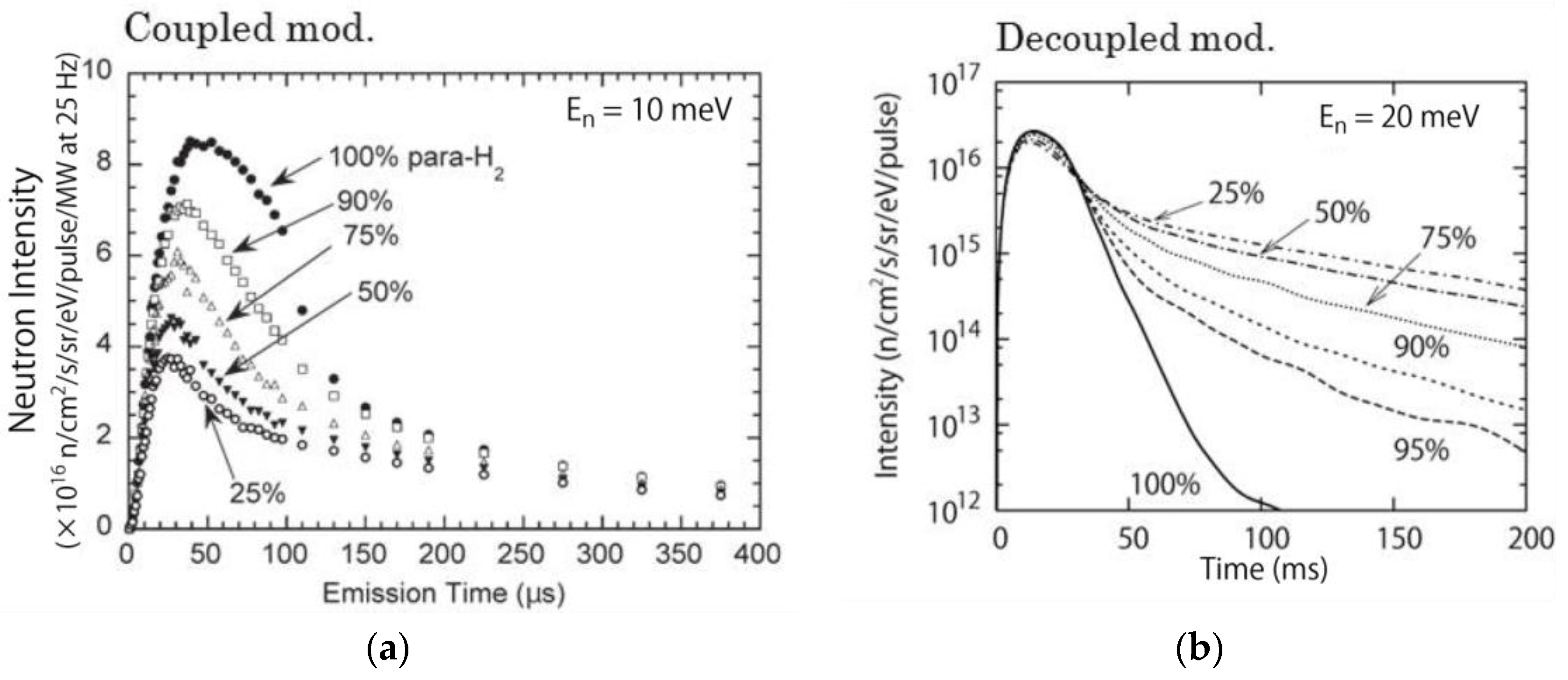
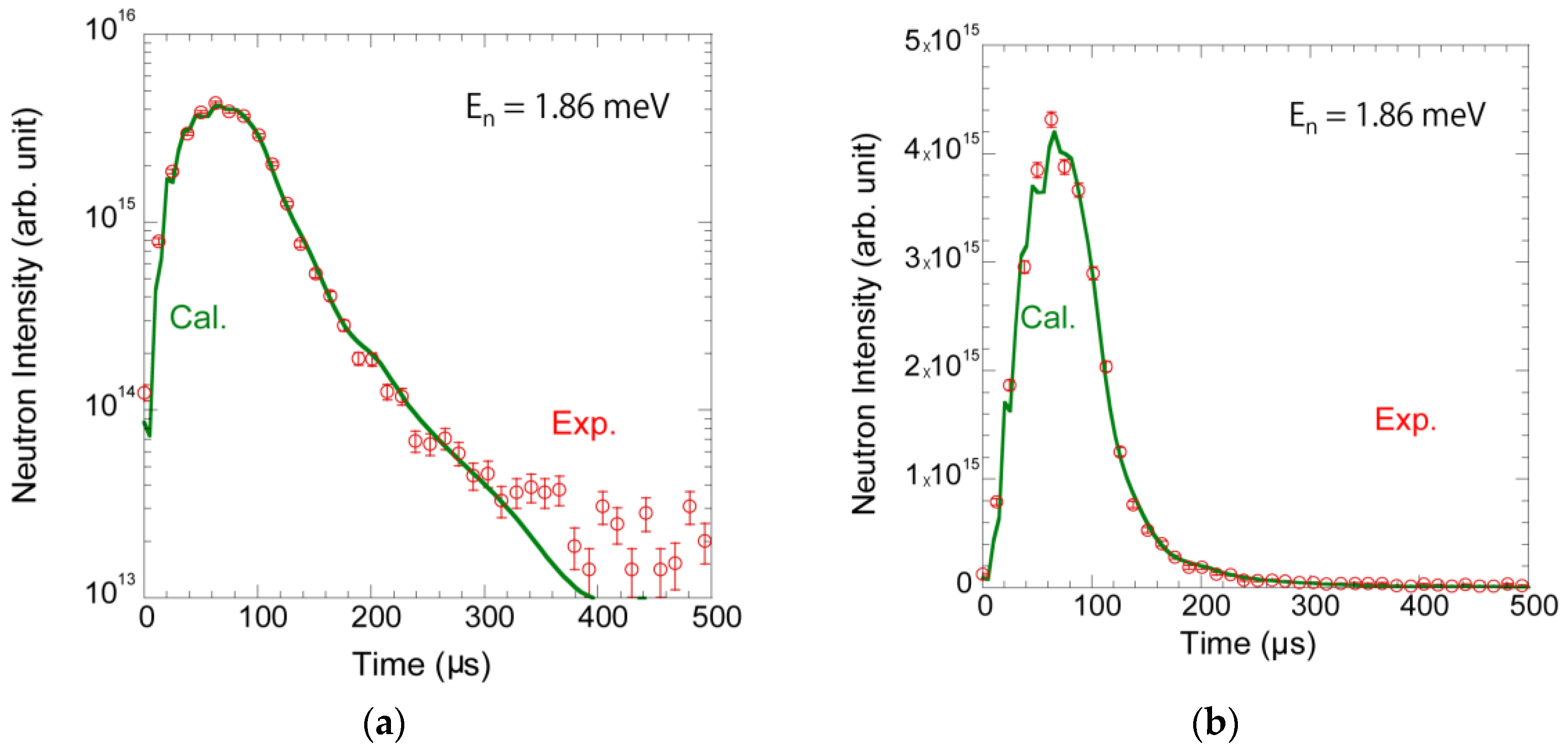
| Name of Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mercury Pipe | Inner Diameter: 143.2 mm |
| Wall thickness: 11 mm | |
| Surge tank | Capacity: 0.7 m3 |
| Mercury pump | Type: Permanent magnetic type |
| Rated flow rate: 41 m3/h | |
| Discharge pressure: 0.5 MPa | |
| Heat exchanger | Type: Double wall (All welded) |
| Heat removal capacity: 600 kW (max.) | |
| Flow Meter | Type: Venturi |
| Measurement range: 0~60 m3/h |
| Moderator | Coupled | Decoupled | Poisoned |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beam extraction | Two-sided | Two-sided | Two-sided |
| Angular coverage | 50.8°/45° | 24.4°/17.8° | 13.4°/13.6° |
| Main moderatow | H2, 20 K, 15 atm | H2, 20 K, 15 atm | H2, 20 K, 15 atm |
| Shape | Cylindrical | Canteen | Canteen |
| Size | φ14 cm × 10H cm | 13W × 12H × 6.2t cm3 | 13W × 12H × 6.2t cm3 |
| Premoderator | H2O (1 cmt) | Non | Non |
| Decoupler | - | Ag-In-Cd | Ag-In-Cd |
| Decoupling energy | 1 eV | 1 eV | |
| Poison | - | - | Cd (1.3 mmt) |
| Viewed surface | 10 × 10 cm2 | 10 × 10 cm2 | 10 × 10 cm2 |
| Coupled Moderator | Decoupled Moderator | Poisoned Moderator | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume (L) | 1.54 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 3.84 |
| Nuclear heating in hydrogen (W) | 946 | 467 | 442 | 1855 |
| Nuclear heating in vessel (W) | 793 | 519 | 584 | 1896 |
| Total heating in the moderator (W) | 1739 | 986 | 1026 | 3751 |
| Helium Refrigerator System | |
| Cold box | Type: Helium Brayton cycle Refrigeration capacity: 6000 W at 17 K Supply pressure: 1.6 MPa Liquid nitrogen consumption: 103 L/h |
| Helium compressor | Type: Oil injection screw compressor Suction/Discharge pressure: 0.31/1.7 MPa Mass flow rate: 0.285 kg/s Motor ratings: 690 kW |
| Hydrogen Circulation System | |
| Hydrogen circulation pump | Type: Centrifugal pump Inlet temperature: 19 K (available for 300 to 17 K) Inlet pressure: 1.5 MPa (available for 0.5 to 1.8 MPa) Mass flow rate: 0.162 kg/s Pressure head: 0.12 MPa (at 0.162 kg/s) Revolution: 30,000 rpm to 60,000 rpm |
| Ortho-Para hydrogen convertor | Catalyze: Iron hydroxide (Fe(OH)3) Outlet Ortho-Para concentration: 99.0% Catalyst filling volume: 35 liter |
| Pressure control system Accumulator Heater | Type: Bellows structure (Inner welding bellows, Outer molding bellows) Size: φ310/350 mm (Inner bellows), φ59/80 mm (Outer bellows) Design pressure: 2.1 MPa Variable volume: 3.5 L Type: Sheath heater with baffle plate Power: Max. 7 kW |
| Heat exchnger | Type: Aluminum plate fin Size: W200 × H120 × L700 mm Temperature: H2 22 (in)/18 (out) K, He 17 (in)/20 (out) K |
| Magnet Type | Dipole for Bending | Quadrupole | Dipole for Sterling | Octupole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insulator | Polyimide | Polyimide | MIC | Polyimide | MIC | Polyimide |
| Installed numbers | 9 | 51 | 3 | 45 | 2 | 2 |
| Aperture (mm) | 160 | 220~300 | 260 | 200~300 | 260 | 300 |
| Field or gradient | 1.1~1.5 T | 6~8 T/m | 8 T/m | 0.06 T | 0.08 T | 800 T/m3 |
| Field uniformity and region (mm) | 5 × 10−4 100 | 3 × 10−3 102~140 | 3 × 10−4 123 | 2 × 10−2 100 | 2 × 10−2 100 | |
| Total weigh (t) | 14~20 | 5~38 * | 38 * | 0.5~56 * | 56 * | 6 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takada, H.; Haga, K.; Teshigawara, M.; Aso, T.; Meigo, S.-I.; Kogawa, H.; Naoe, T.; Wakui, T.; Ooi, M.; Harada, M.; et al. Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex I: Pulsed Spallation Neutron Source. Quantum Beam Sci. 2017, 1, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs1020008
Takada H, Haga K, Teshigawara M, Aso T, Meigo S-I, Kogawa H, Naoe T, Wakui T, Ooi M, Harada M, et al. Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex I: Pulsed Spallation Neutron Source. Quantum Beam Science. 2017; 1(2):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs1020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakada, Hiroshi, Katsuhiro Haga, Makoto Teshigawara, Tomokazu Aso, Shin-Ichiro Meigo, Hiroyuki Kogawa, Takashi Naoe, Takashi Wakui, Motoki Ooi, Masahide Harada, and et al. 2017. "Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex I: Pulsed Spallation Neutron Source" Quantum Beam Science 1, no. 2: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs1020008
APA StyleTakada, H., Haga, K., Teshigawara, M., Aso, T., Meigo, S.-I., Kogawa, H., Naoe, T., Wakui, T., Ooi, M., Harada, M., & Futakawa, M. (2017). Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex I: Pulsed Spallation Neutron Source. Quantum Beam Science, 1(2), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs1020008





