Karla: A Simple and Affordable 3-D Printed Body-Powered Prosthetic Hand with Versatile Gripping Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Inventions
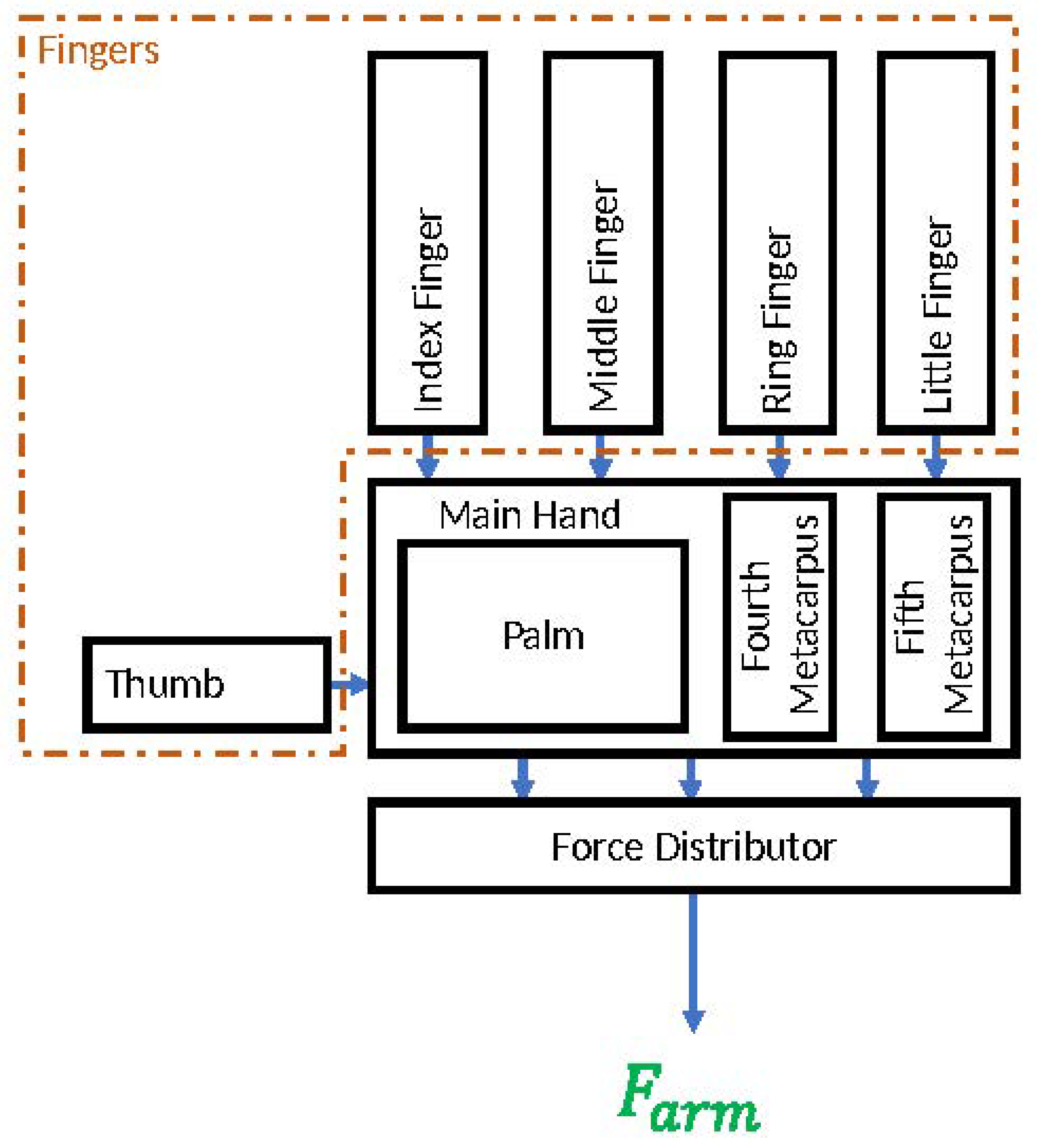
3. System Design
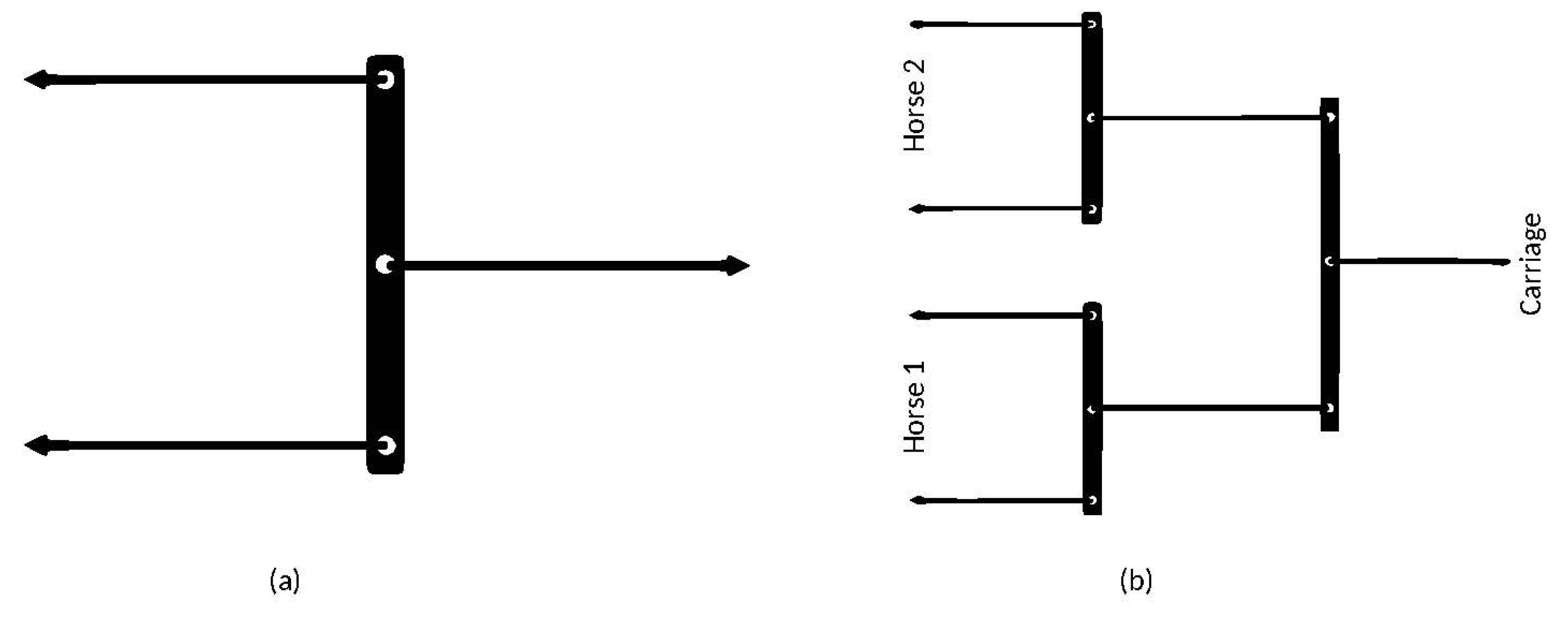
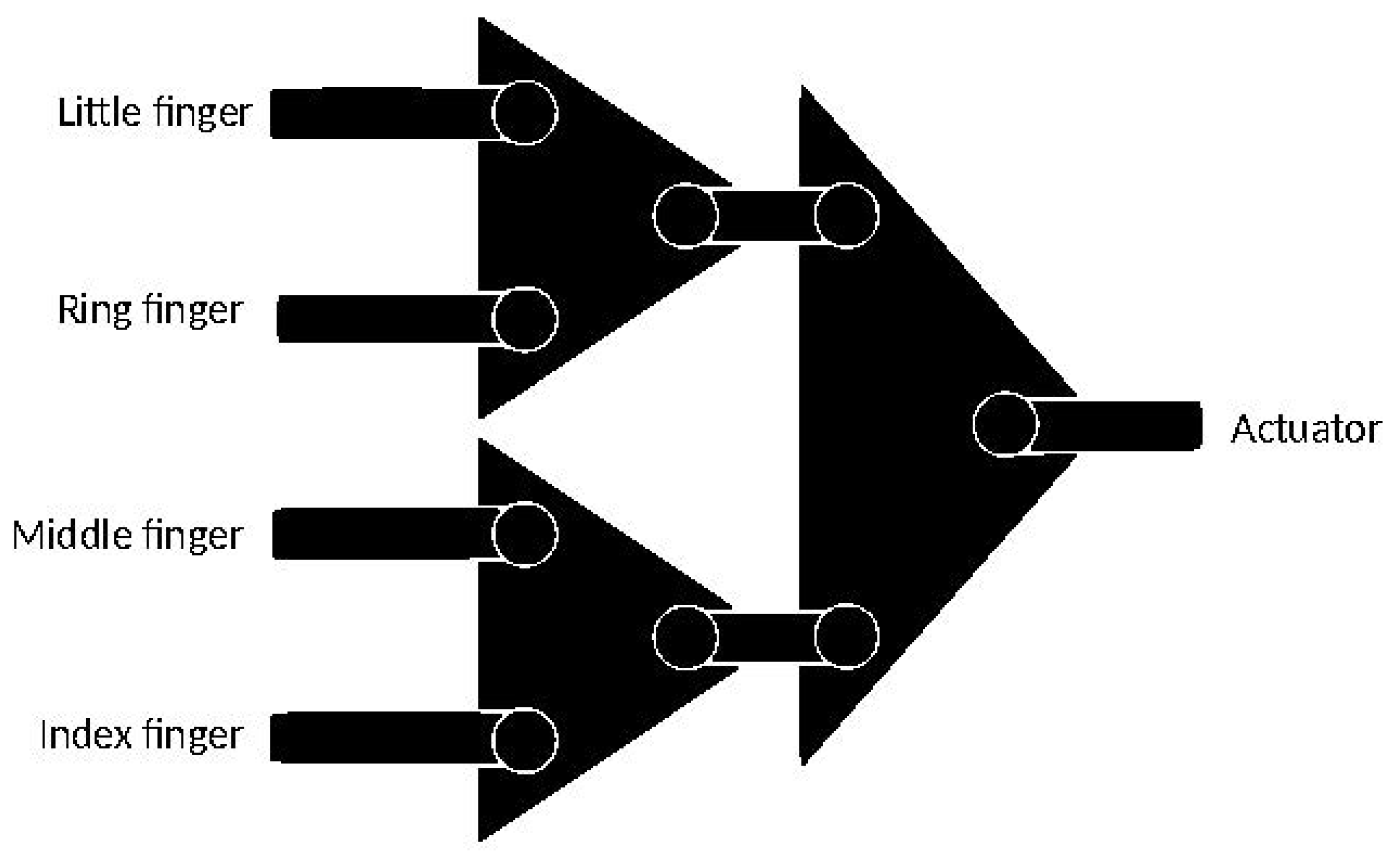
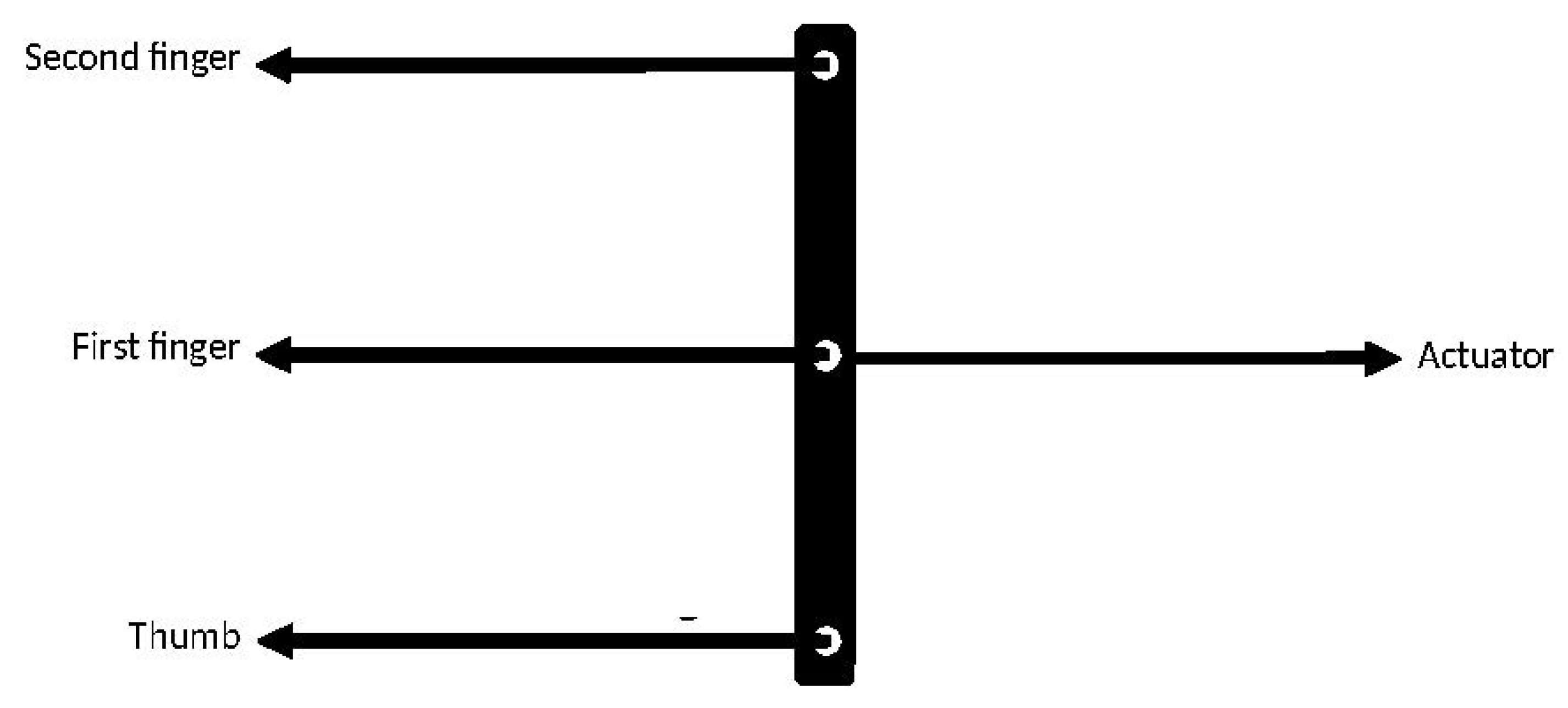
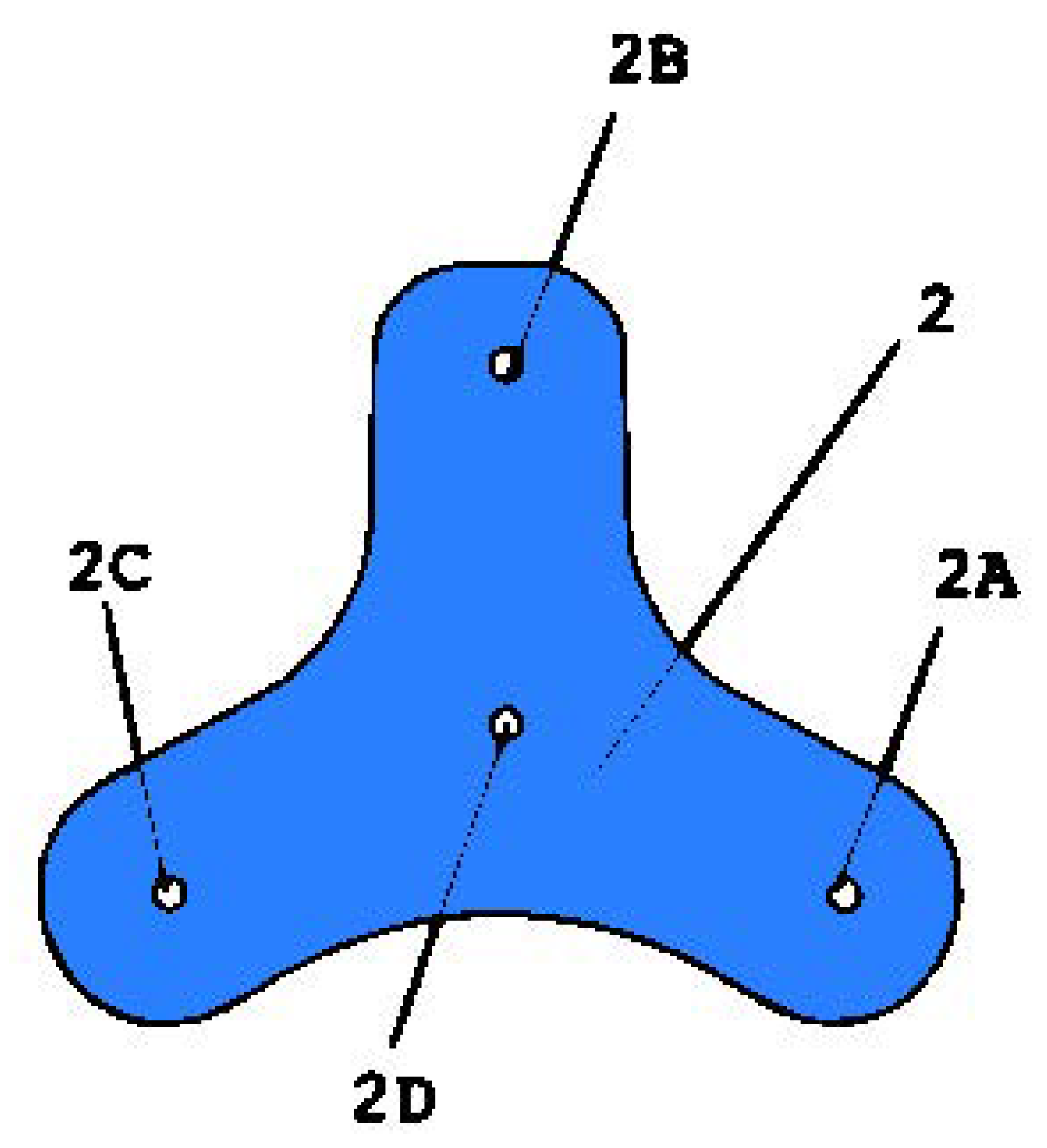
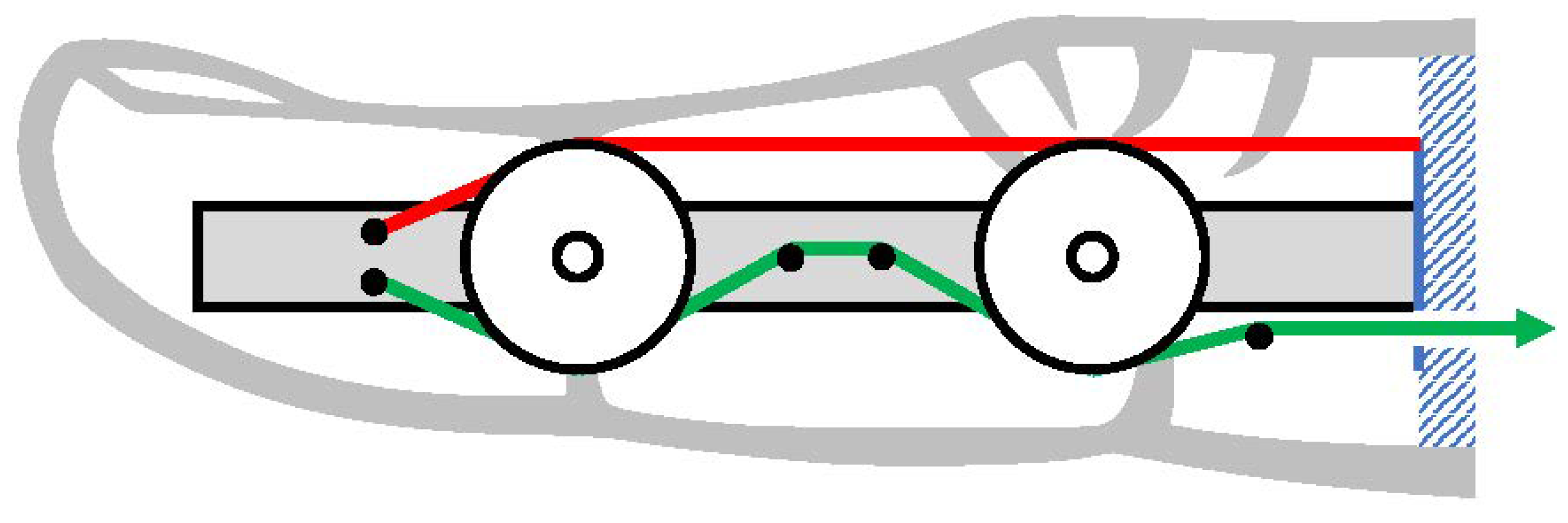
3.1. Force Distributor
3.1.1. Force Distributor Review
3.1.2. Force Distribution Design
- Distribute the force to all the fingers;
- Maximize the force distributed to the fingers.
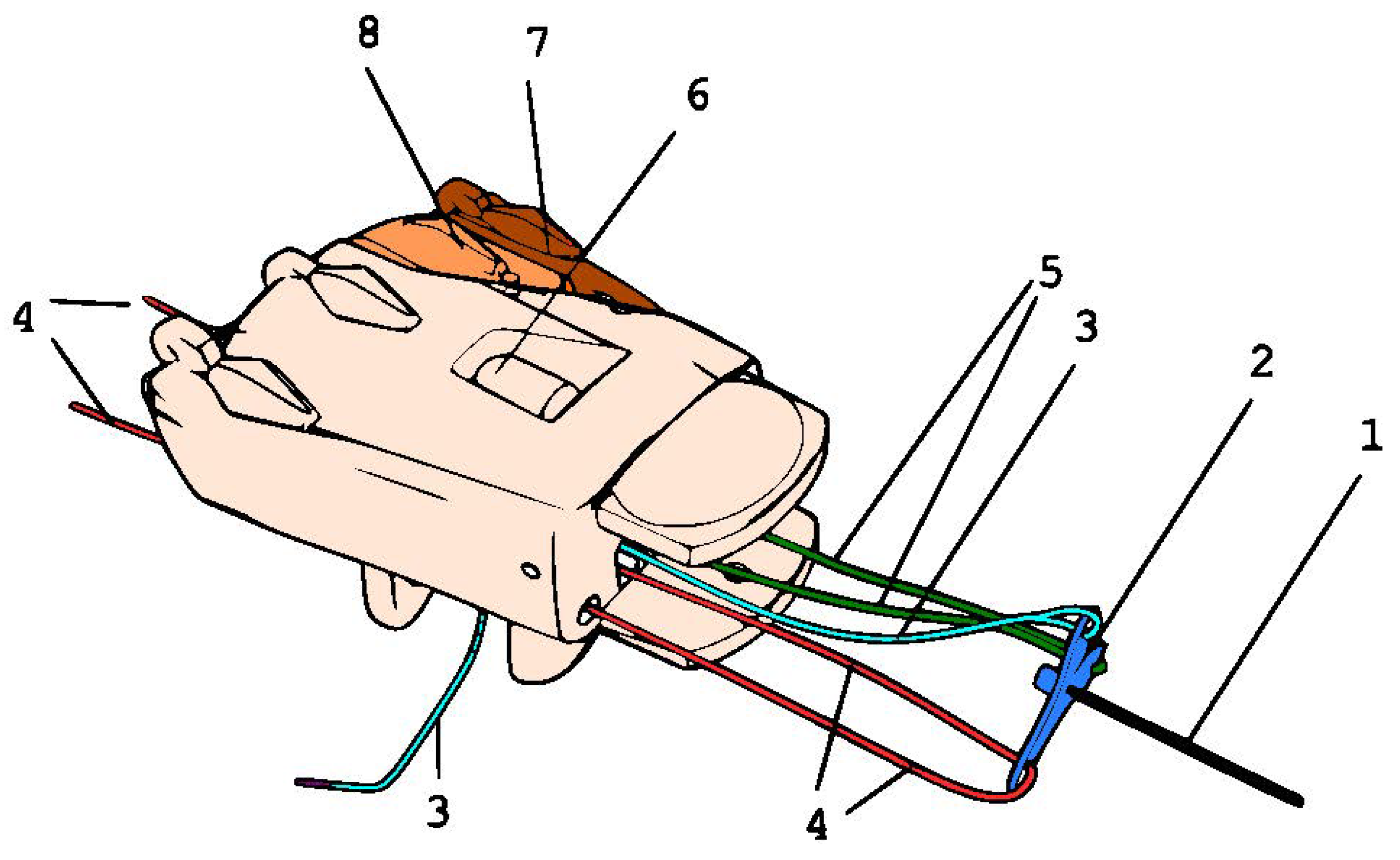
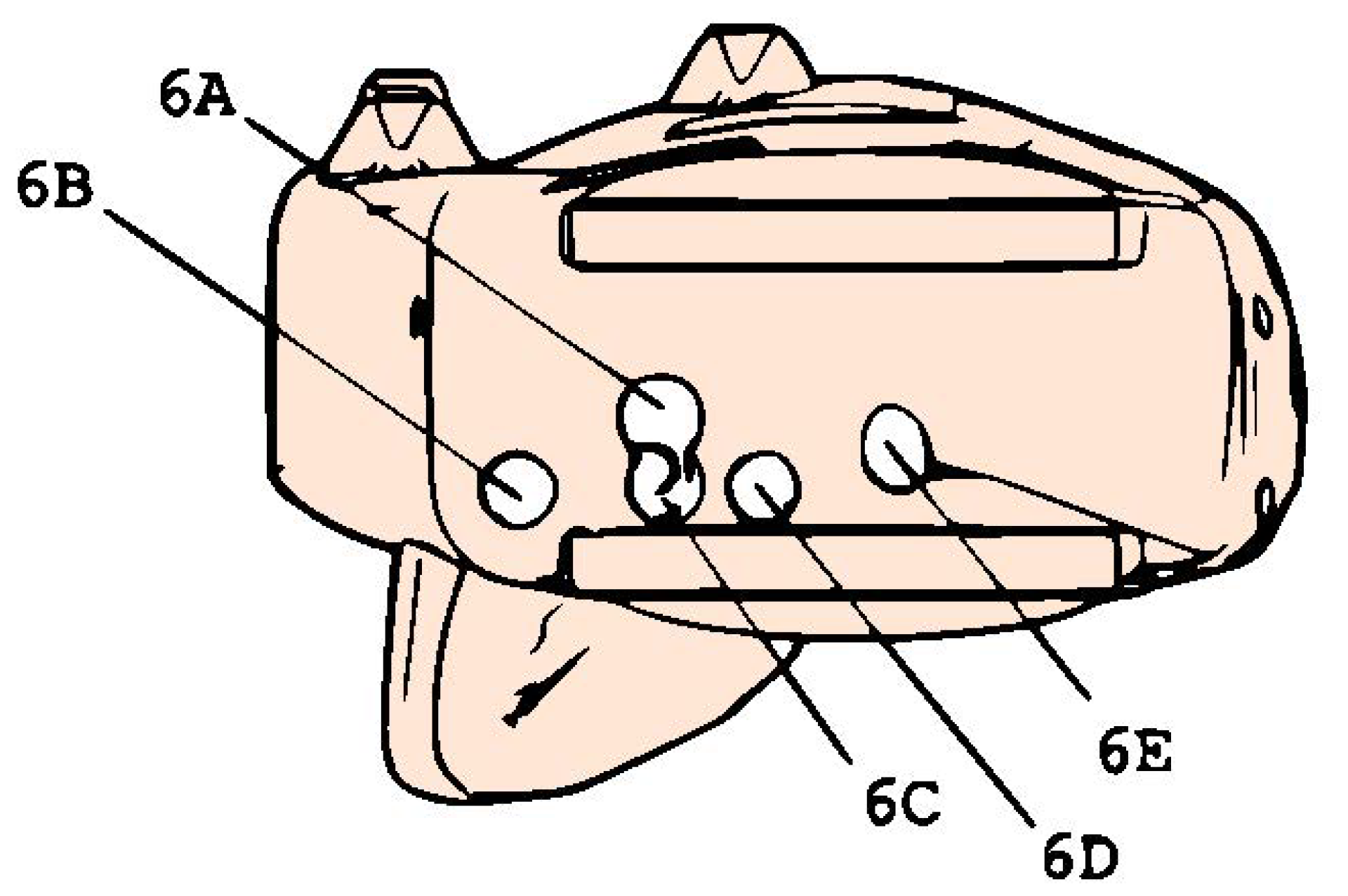
3.2. Main Hand
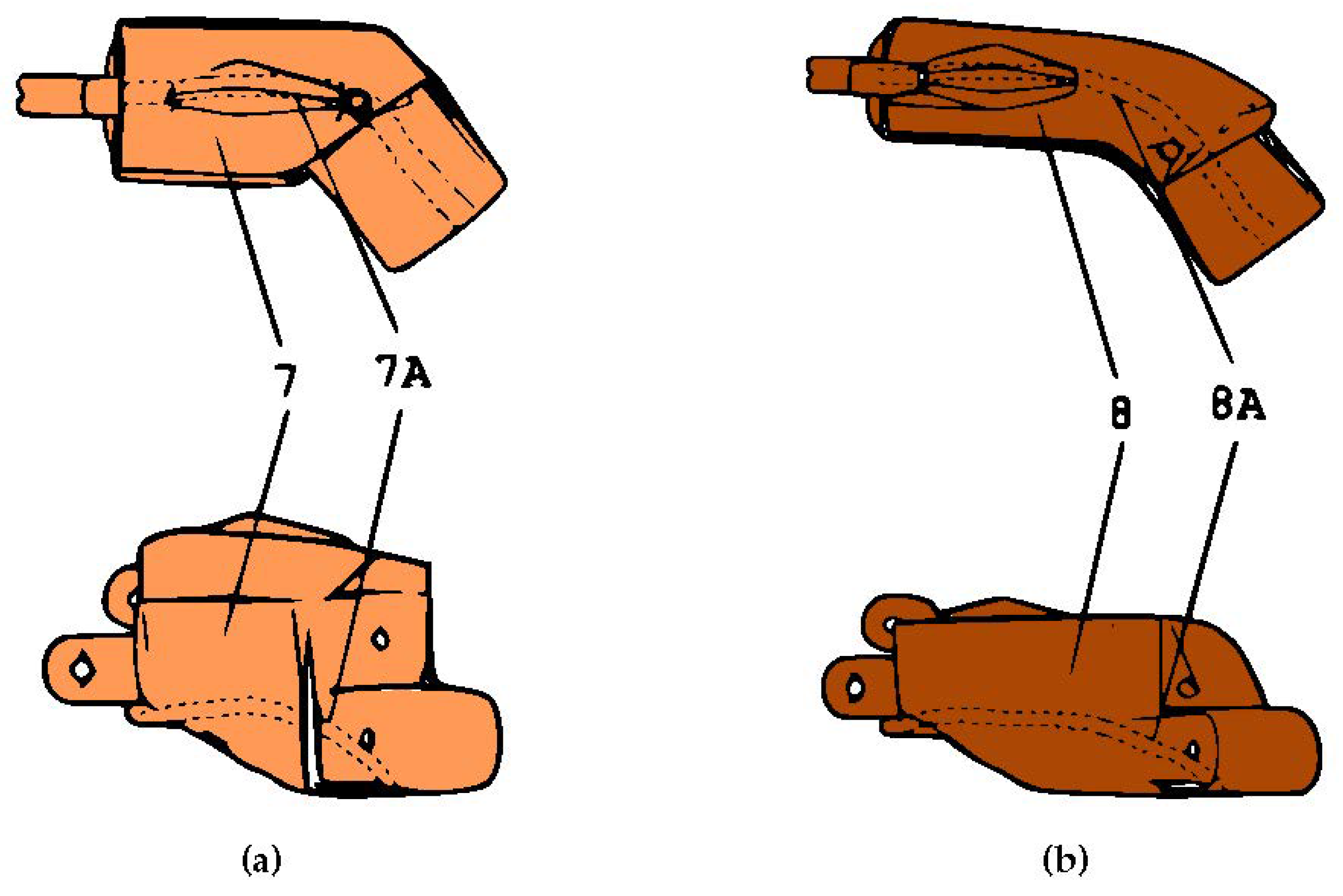
3.3. Fingers’ Mechanism
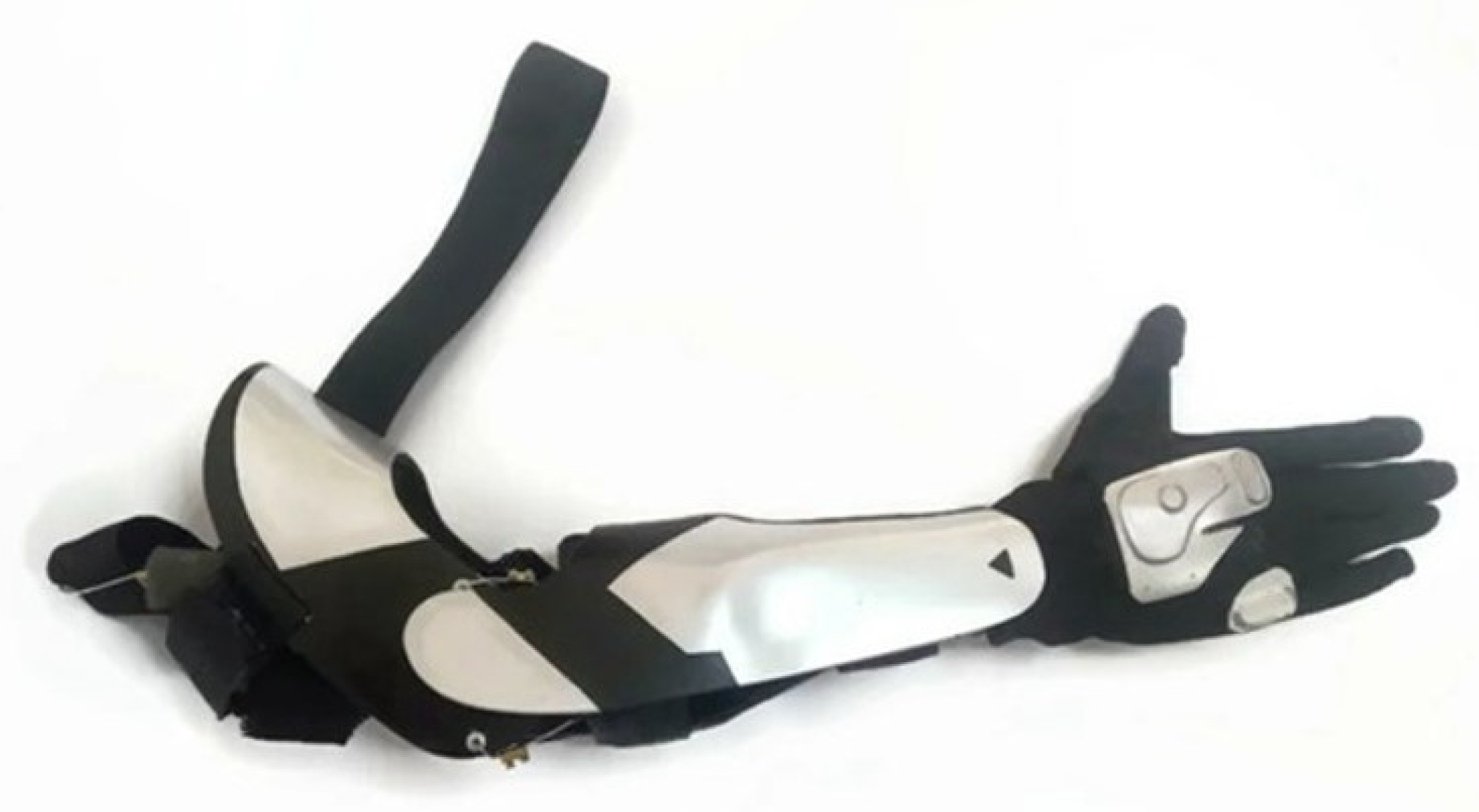
3.4. Prototype Production and Packaging
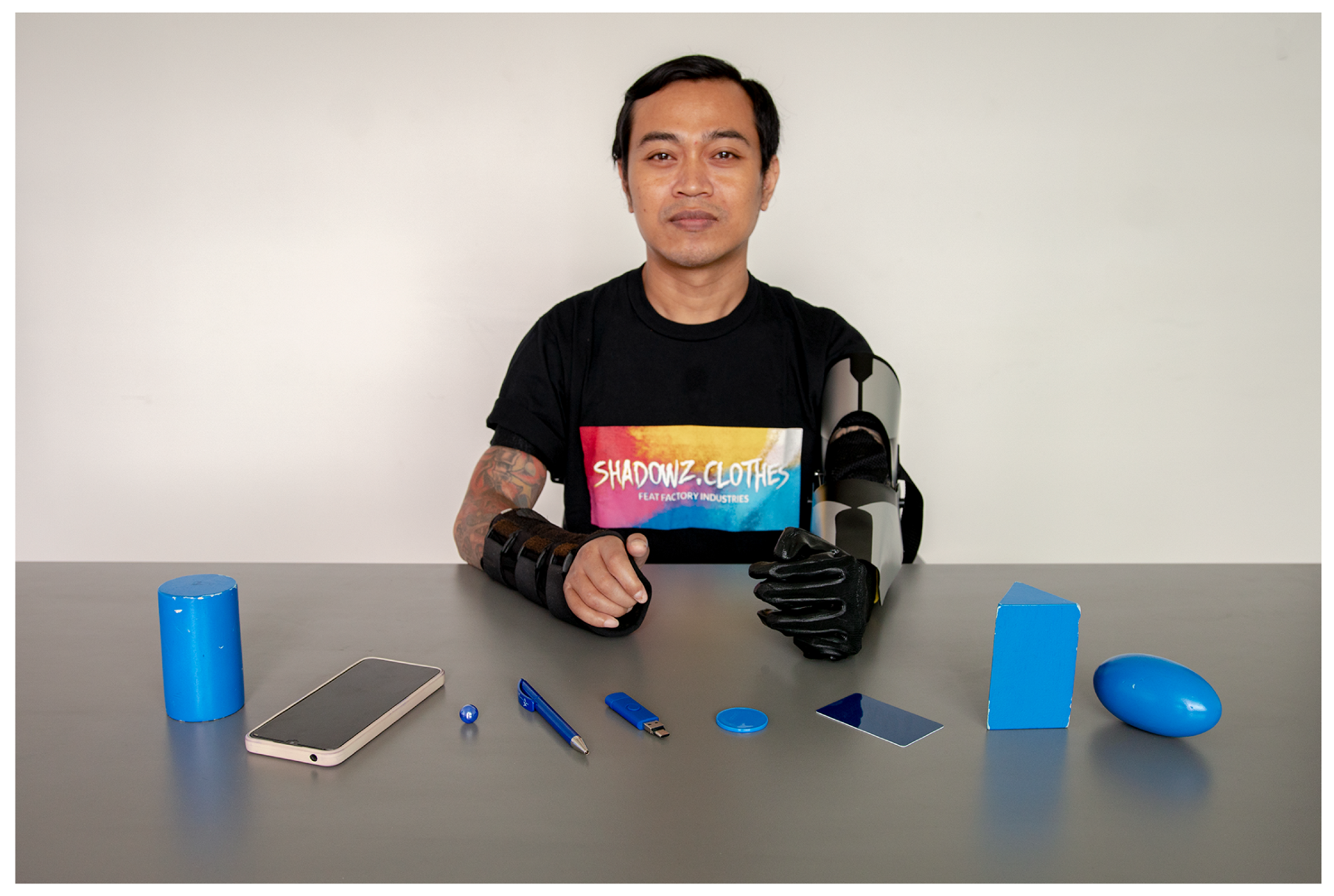
4. Results and Performance Evaluations
- It can help with daily necessities, such as sweeping the floor, putting the laundry on a drying rack; and also can help with playing sports confidently.
- It can be a starting point for a conversation in a public place, such as a train or bus, which helps in gaining more confidence.
5. Comparison to Other Works
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DIP | Distal-interphalangeal |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| FSR | Force-sensitive resistor |
| MP | Metacarpophalangeal |
| SHAP | Southampton Hand Assessment Procedure |
| VGT | Versatile Gripping Technology |
References
- Jang, C.H.; Yang, H.S.; Yang, H.E.; Lee, S.Y.; Kwon, J.W.; Yun, B.D.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.N.; Jeong, H.W. A survey on activities of daily living and occupations of upper extremity amputees. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 35, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, L.A.; Sevelda, F.; Fraberger, G.; Bluder, O.; Kickinger, W.; Holzer, G. Body image and self-esteem in lower-limb amputees. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaine, W.; Smart, C.; Bransby-Zachary, M. Upper limb traumatic amputees: Review of prosthetic use. J. Hand Surg. 1997, 22, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saradjian, A.; Thompson, A.R.; Datta, D. The experience of men using an upper limb prosthesis following amputation: Positive coping and minimizing feeling different. Disabil. Rehabil. 2008, 30, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddiss, E.A.; Chau, T.T. Upper limb prosthesis use and abandonment: A survey of the last 25 years. Prosthetics Orthot. Int. 2007, 31, 236–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maat, B.; Smit, G.; Plettenburg, D.; Breedveld, P. Passive prosthetic hands and tools: A literature review. Prosthetics Orthot. Int. 2018, 42, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellini, C. Upper limb active prosthetic systems—Overview. Wearable Robot. 2020, 365–376. [Google Scholar]
- Millstein, S.; Heger, H.; Hunter, G. Prosthetic use in adult upper limb amputees: A comparison of the body powered and electrically powered prostheses. Prosthetics Orthot. Int. 1986, 10, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, R.; Carrozza, B.; Lopez, J.; Ordonez, Y.; Sanchez, E.; Kim, D.; Lee, A.; Teh, K.S. Accessible Children’s Prosthetics Created Using 3D Printing Technologies 2018. Available online: https://canadacollege.edu/stemcenter/images/aspiresintern2017/ME-paper.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Ten Kate, J.; Smit, G.; Breedveld, P. 3D-printed upper limb prostheses: A review. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2017, 12, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkins, C.S.; McGarry, A.; Buis, A. Provision of prosthetic and orthotic services in low-income countries: A review of the literature. Prosthetics Orthot. Int. 2013, 37, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, S.L.; Lura, D.J.; Highsmith, M.J. Differences in myoelectric and body-powered upper-limb prostheses: Systematic literature review. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2015, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnik, L.; Meucci, M.R.; Lieberman-Klinger, S.; Fantini, C.; Kelty, D.L.; Disla, R.; Sasson, N. Advanced upper limb prosthetic devices: Implications for upper limb prosthetic rehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belter, J.; Dollar, A.; Leddy, M. Multi-Grasp Prosthetic Hand. US Patent 20170049583, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Trusaji, W.; Hammam, S. Alat Penggerak Jari Untuk Menghasilkan Genggaman Adaptif Dan Efisien Pada Lengan Prostetik (English: Design of Finger Mechanism to Produce An Adaptive and Efficient Grip in Prostethic Hand). Indonesian Patent P00202007576, 2020. pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrovich, L.M. Arm Prosthesis for Patients with the Degree of Amputation From Fingers to the Forearm, Prosthesis of the Wrist Joint, Which Includes The Hand Prosthesis, the Finger Rod Cable Locking Device of the Hand Prosthesis (3 Options), the Finger Position Combination Control Device of the Hand Prosthesis (2 Options). Russian Patent RU2664171C1, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Trusaji, W.; Irianto, D.; Satriawan, A.; Setianingsih, C.; Nurtriandari, E.; Geosasi, R.Z. Design Process of Whippletree-Like Mechanism for Versatile Gripping in Arm Prosthesis 2022. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202210.0011/v1 (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Groenewegen, M. Design of a Compliant, Multi-Phalanx Underactuated Prosthetic Finger. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dukij, A. Makerhand. Available online: https://www.makerhand.com/ (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Esposito, D.; Savino, S.; Andreozzi, E.; Cosenza, C.; Niola, V.; Bifulco, P. The “Federica” Hand. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusaji, W.; Hammam, S. Tangan prostetik bermekanisme penggerak adaptif untuk kelima jari serta memiliki metakarpus keempat dan kelima (English: Prosthetic hand with an adaptive grip mechanism with fourth and fifth metacarpal). Indonesian Patent P00202101141, 2021. pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Toro-Ossaba, A.; Tejada, J.C.; Rúa, S.; López-González, A. A Proposal of Bioinspired Soft Active Hand Prosthesis. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Wahit, M.A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Marhaban, M.H.; Wada, C.; Izhar, L.I. 3D Printed Robot Hand Structure Using Four-Bar Linkage Mechanism for Prosthetic Application. Sensors 2020, 20, 4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainul, I.; Deb, S.; Deb, A. A three finger tendon driven robotic hand design and its kinematics model. In CAD/CAM, Robotics and Factories of the Future; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Trusaji, W.; Hammam, S. Soket Untuk Lengan Prostetik Yang Dapat Disesuaikan Dengan Ukuran Dan Kontur Puntung Lengan Serta Mampu Memindahkan Kalor Dari Puntung Lengan Ke Udara (English: Size-and-Contour Adaptive Prosthetic Arm Socket Capable Of Releasing Heat to the Air). Indonesian Patent P00202205996, 2022. pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kyberd, P.J.; Murgia, A.; Gasson, M.; Tjerks, T.; Metcalf, C.; Chappell, P.H.; Warwick, K.; Lawson, S.E.; Barnhill, T. Case studies to demonstrate the range of applications of the Southampton Hand Assessment Procedure. Br. J. Occup. Ther. 2009, 72, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karla Bionics in Cybathlon Challenge 2022. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iE5XzEyAOmg&t=48s/ (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Permana, A. Karla Bionics in Cybathlon Challenge 2022. Available online: https://www.itb.ac.id/news/read/58685/home/karla-bionics-startup-wins-the-2022-international-cybathlon-challenge (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Arm V2. Available online: https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:1131463 (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Bionic Flexy Arm. Available online: https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:1768698 (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- NIOP Kwawu Remix. Available online: https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:3639854 (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Unlimbited Armv2.1. Available online: https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:1672381 (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Prótesis Personalizada Cinderella. Available online: https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:1768562 (accessed on 17 February 2023).









| Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Compliant mechanism [22] | - No moving part | - Prone to fatigue |
| - Materials are difficult to obtain | ||
| - Expensive to manufacture | ||
| 4-bar linkage [23] | - High reliability | - Consists of many small customized parts |
| - Hard to assembly | ||
| Pulley-line [24] | - Low-cost | - Ropes prone to frictions |
| - Materials available locally | - Ropes need regular maintenance | |
| - Similar to actual human fingers mechanism |
| Part | Designator | Quantity | Note | Materials |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balancer | Force distributor | 1 unit | Manually cut to Figure 8 shape | 2-mm aluminium sheet |
| Main Hand | Palm | 1 unit | 3-D printed | ABS, 20% infill, 2 mm layer, 65 gram |
| Fourth metacarpus | 1 unit | 3-D printed | ABS, 20% infill, 2 mm layer, 65 gram | |
| Fourth metacarpus | 1 unit | 3-D printed | ABS, 20% infill, 2 mm layer, 65 gram | |
| Finger knuckles | Distal phalanx | 5 units | 3-D printed | ABS, 20% infill, 2 mm layer, 40 gram |
| Middle phalanx | 5 units | 3-D printed | ABS, 20% infill, 2 mm layer, 40 gram | |
| Proximal phalanx | 5 units | 3-D printed | ABS, 20% infill, 2 mm layer, 40 gram | |
| Ropes | Non-elastic rope | 8 units | For inner channels (3 units) and finger tendons (5 units) | High-grade fishing line |
| Elastic rope | 5 units | For finger tendons | ABS, 20% infill, 2 mm layer, 40 gram | |
| Main rope | 1 unit | For main pulling rope | Bowden cable or bicycle brake cable. | |
| Rivets | Rivets | 18 units | As fastener between parts | mm rivets |
| Glove | Glove | 1 unit | To increase the friction for a better grip | Elastic, leather, and high-grip glove. We use a mountain-biking glove. |
| Designs | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Arm V2 [29] | Whippletree mechanism can be assembled inside the palm. | Thumb not included in the whippletree mechanism, thus it moves independently from the other four fingers. |
| Bionic Flexy Arm [30] | Aesthetically pleasing | Whippletree mechanism does not available, making it hard for users to grip various shaped objects. |
| NIOP Kwawu Remix [31] | Whippletree mechanism can be assembled inside the palm, capable of inward and outward rolling. | The thumb is not included in the whippletree mechanism, making it moves independently from the fingers. |
| Unlimbited Arm v2.1 [32] | Aesthetically pleasing, especially for children. | No whippletree mechanism, hence not capable of flexible gripping. |
| Prótesis personalizada Cinderella [33] | Aesthetically pleasing, feminine design. | No whippletree for versatile gripping. |
| Karla (Ours) | All the fingers are included in the whippletree mechanism, making it capable of grasping various shapes. | The whippletree mechanism has a 3-D shape and movement, therefore it needs more room and space in the forearm, near the wrist. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Satriawan, A.; Trusaji, W.; Irianto, D.; Anshori, I.; Setianingsih, C.; Nurtriandari, E.; Goesasi, R.Z. Karla: A Simple and Affordable 3-D Printed Body-Powered Prosthetic Hand with Versatile Gripping Technology. Designs 2023, 7, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs7020037
Satriawan A, Trusaji W, Irianto D, Anshori I, Setianingsih C, Nurtriandari E, Goesasi RZ. Karla: A Simple and Affordable 3-D Printed Body-Powered Prosthetic Hand with Versatile Gripping Technology. Designs. 2023; 7(2):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs7020037
Chicago/Turabian StyleSatriawan, Ardianto, Wildan Trusaji, Dradjad Irianto, Isa Anshori, Casi Setianingsih, Erza Nurtriandari, and Rachmat Zulkarnain Goesasi. 2023. "Karla: A Simple and Affordable 3-D Printed Body-Powered Prosthetic Hand with Versatile Gripping Technology" Designs 7, no. 2: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs7020037
APA StyleSatriawan, A., Trusaji, W., Irianto, D., Anshori, I., Setianingsih, C., Nurtriandari, E., & Goesasi, R. Z. (2023). Karla: A Simple and Affordable 3-D Printed Body-Powered Prosthetic Hand with Versatile Gripping Technology. Designs, 7(2), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs7020037






