On the Usefulness of Employing ANSYS Motor-CAD Software in Designing Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The PMSM to Be Studied
2.1. Automotive Applications and the Electrical Machine Type Selection
2.2. The Design Specifications of the PMSM to Be Developed
- number of phases: 3;
- number of pole pairs: 3;
- DC bus voltage: 72 V;
- rated power: 4 kW;
- rated speed: 8000 r/min;
- rated torque: 4.77 N·m.
2.3. Pre-sizing the PMSM
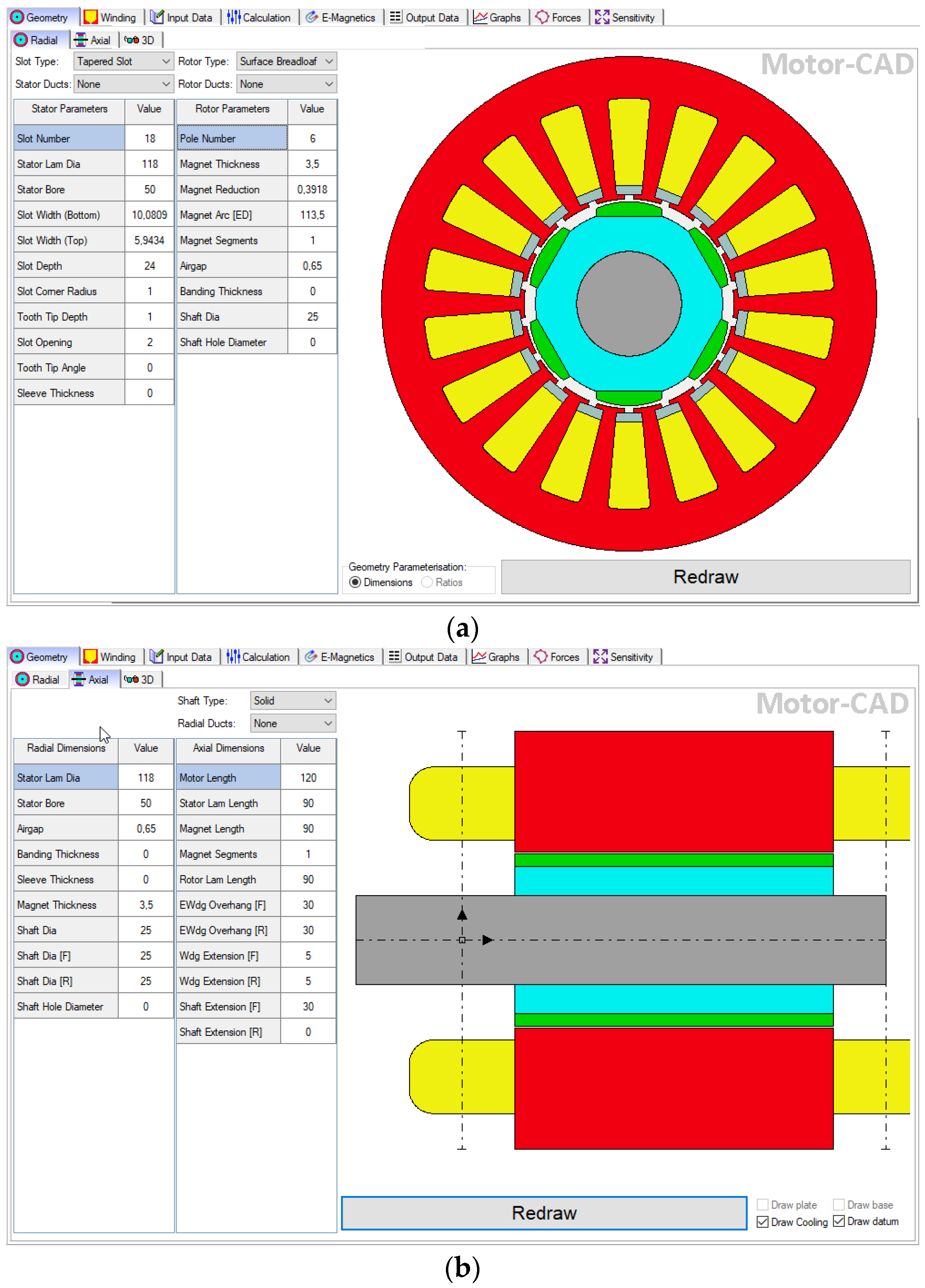
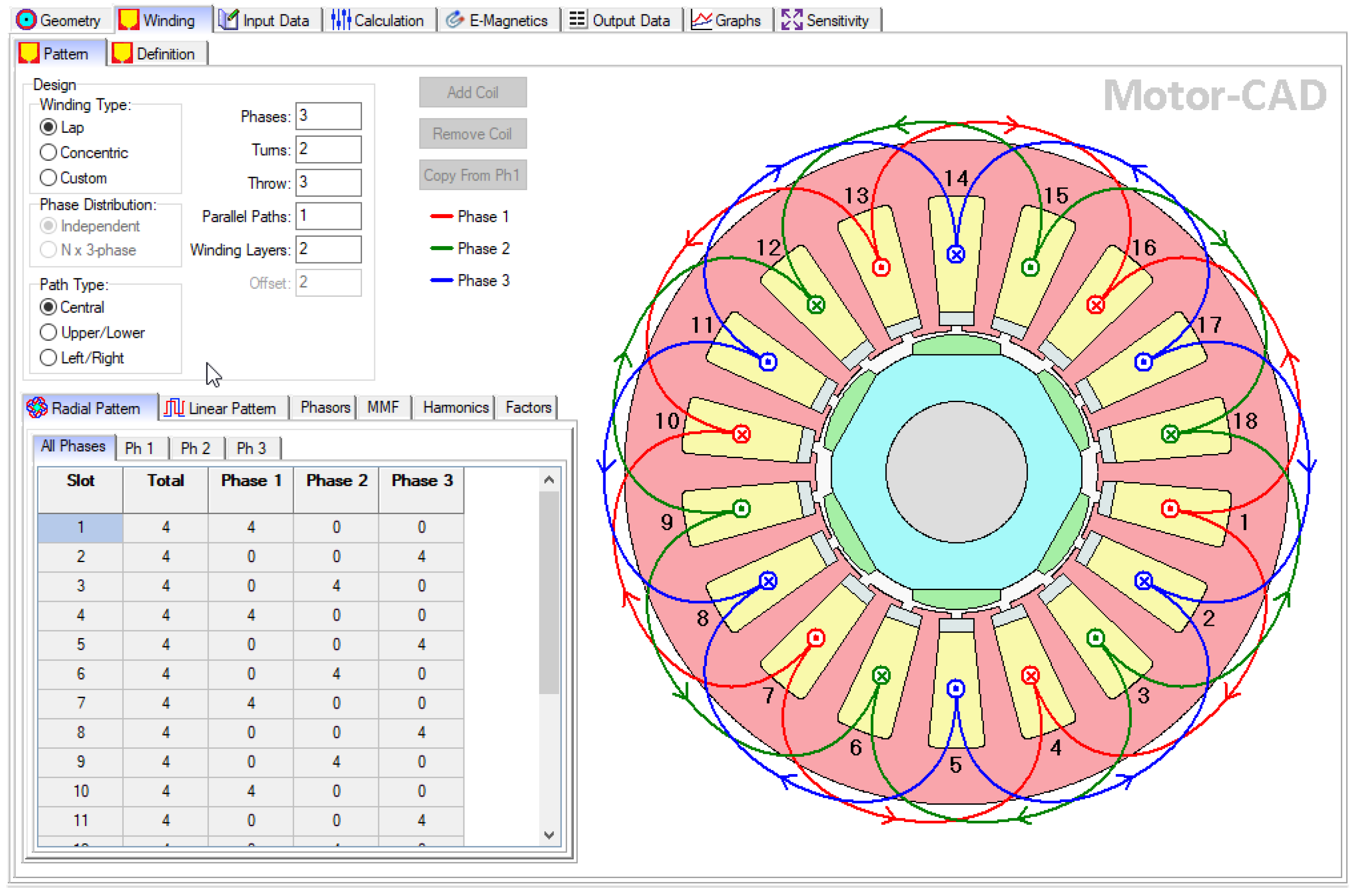
3. The ANSYS Motor-CAD Model of the PMSM
4. Simulation Results
- 8000 r/min;
- 50 A RMS currents;
- 72 V DC bus voltage.
- Drive: data concerning the back EMF, supply voltages and currents, d-q axes inductances and currents, machine constants, short circuit parameters, etc.;
- E-Magnetics: the main parameters of the analyzed electrical machines are provided here (see Figure 15), such as the electromagnetic power, torque, cogging torque, power factor, system efficiency, load angle, cogging period, base frequency, etc.;
- Phasor Diagram;
- Equivalent Circuit: shows all the parameters of the most complete equivalent circuit;
- Flux densities in different critical parts of the machine;
- Losses in all the parts of the machine;
- Winding: provides the parameters and current densities of all the conductors, phase resistance, slot filling factors, copper volume, etc.;
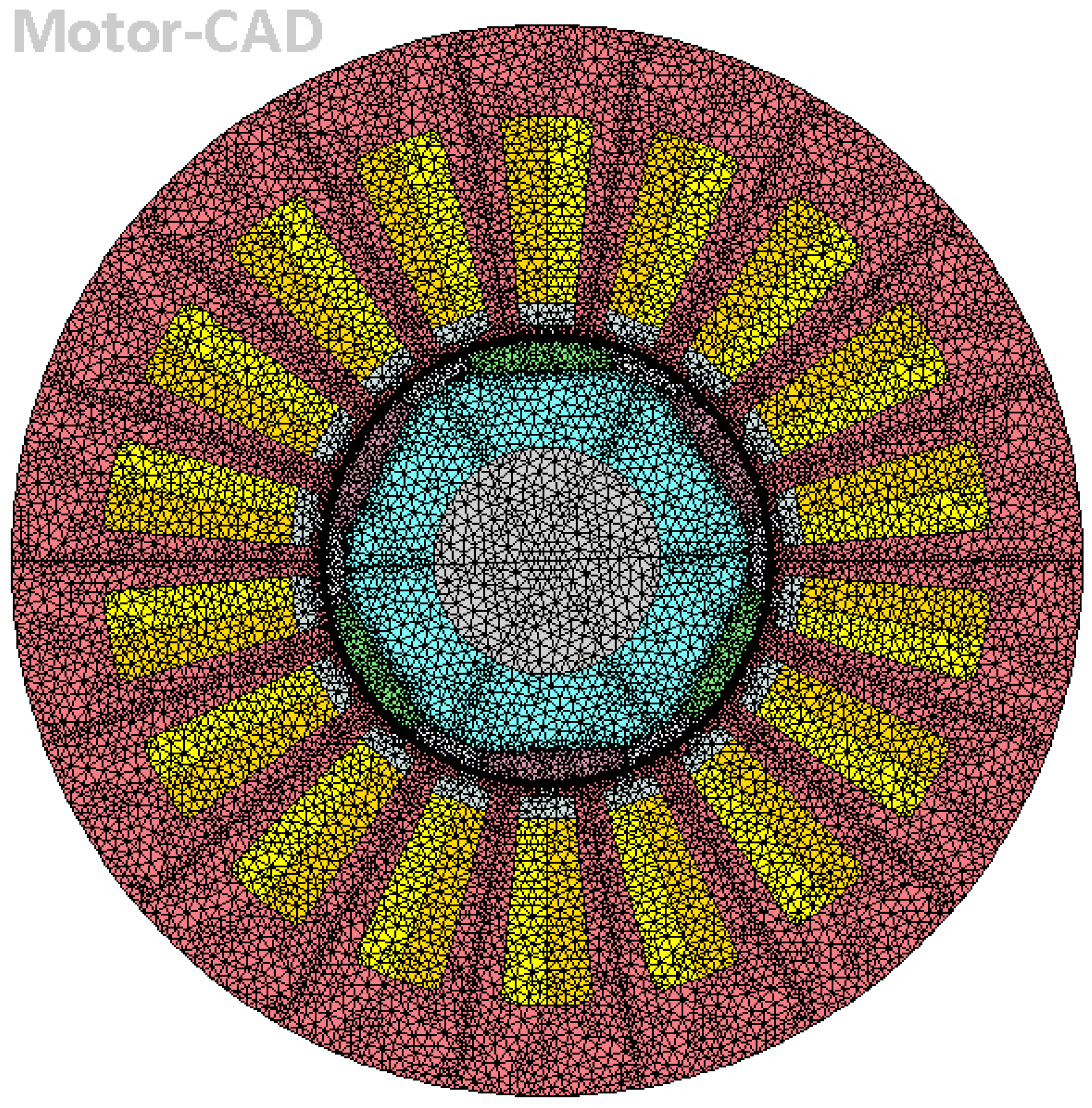
- Miscellaneous: data about the FEA mesh generated by the program;
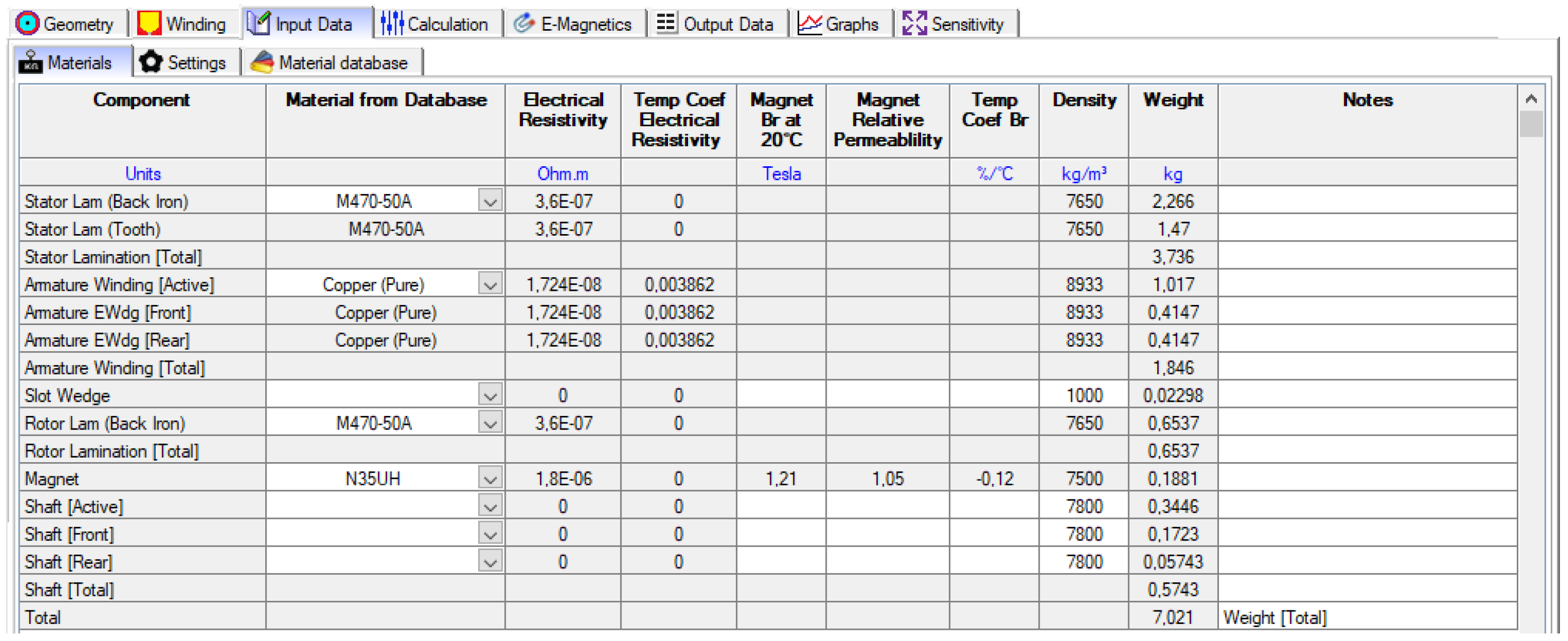
- Materials: the properties and masses of all the used materials.
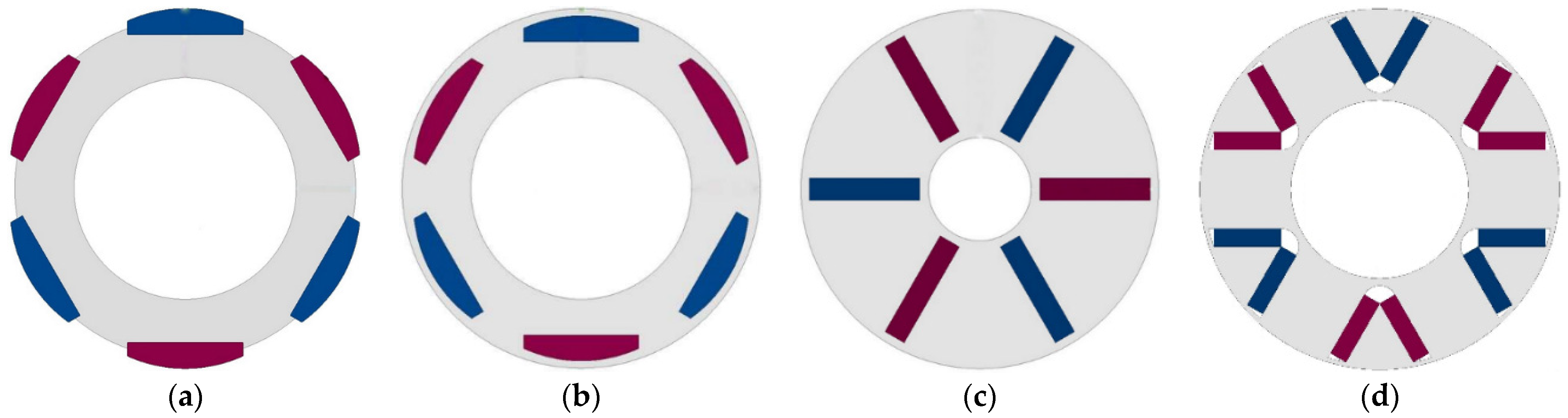
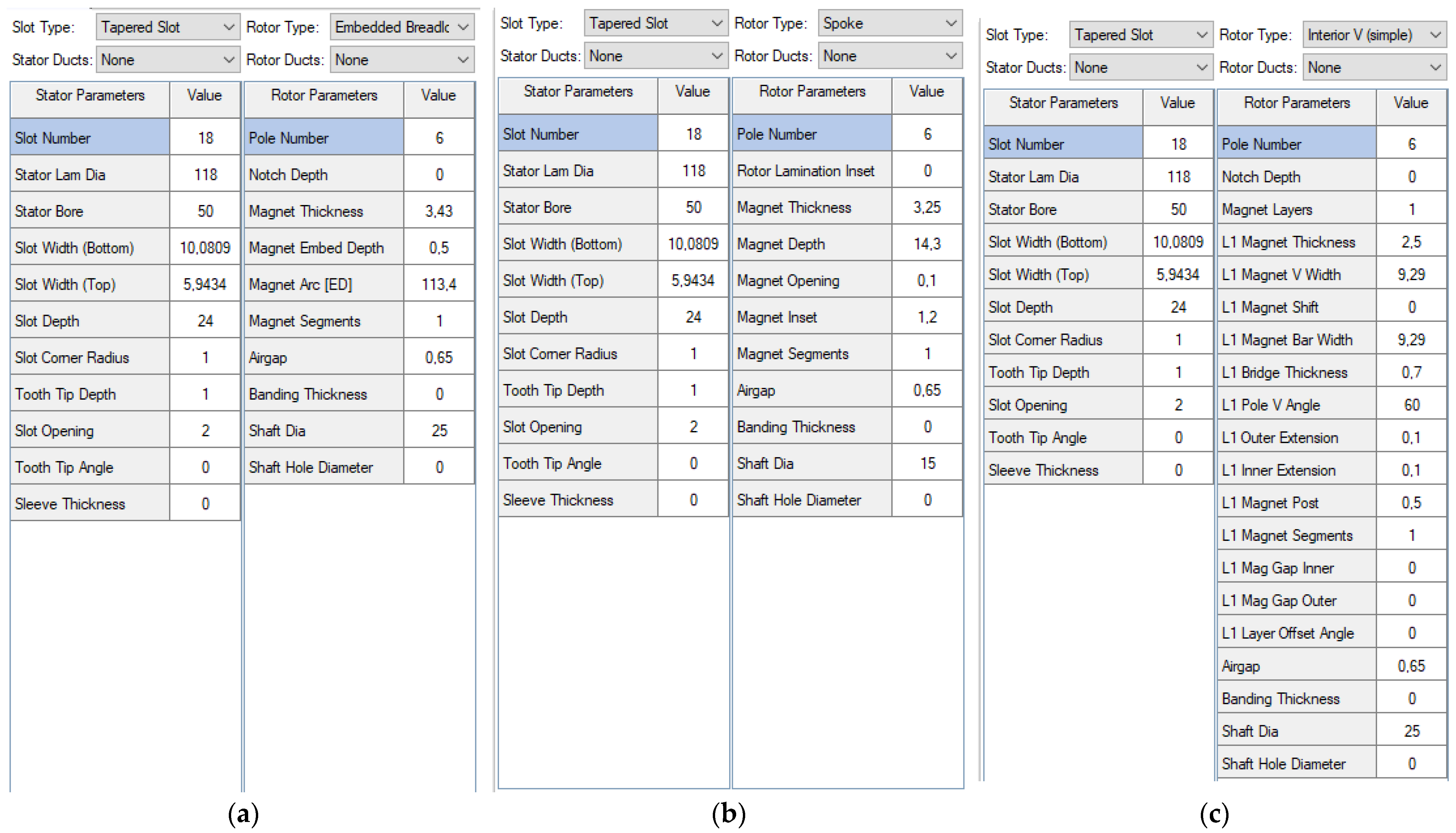
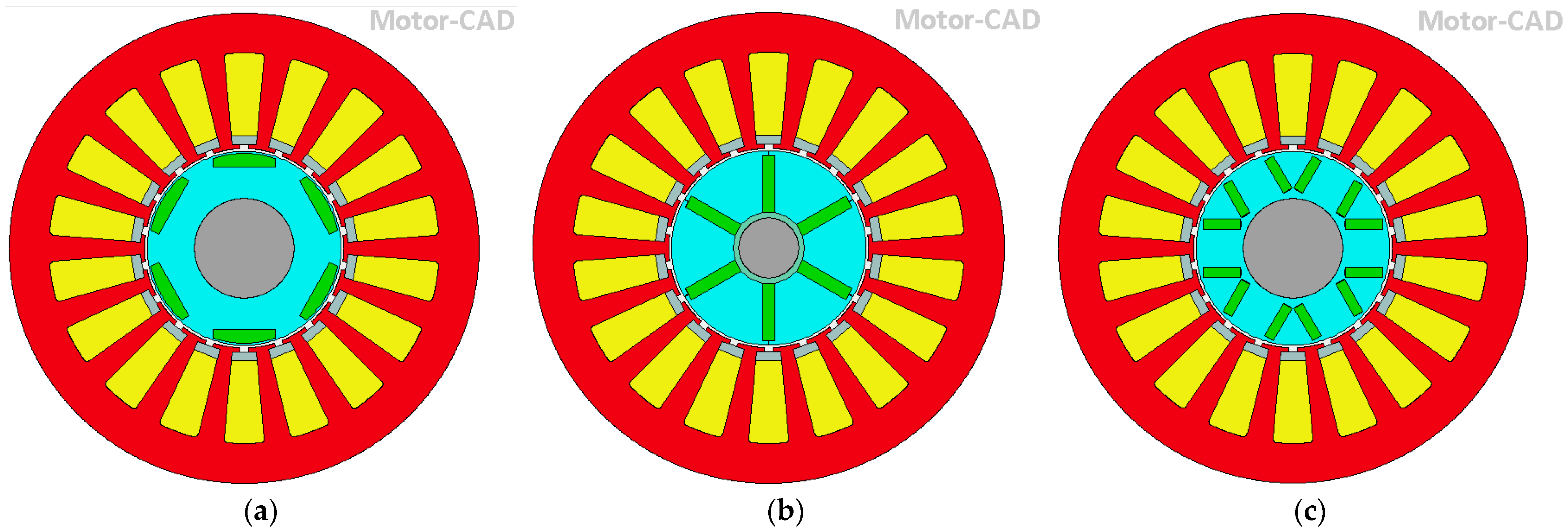
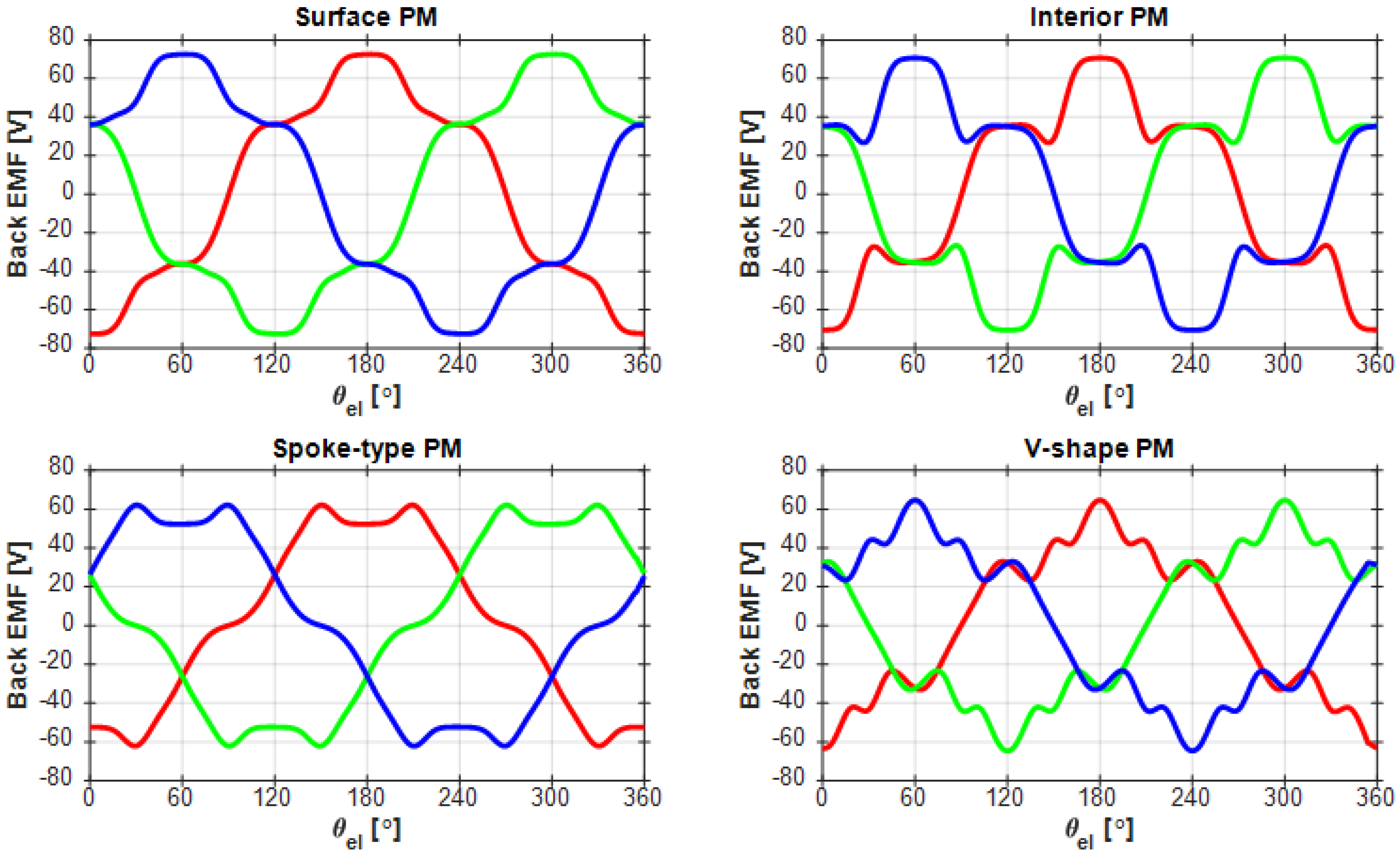
5. Comparison of Four PMSM Types
5.1. Building up the Models of the Alternative PMSMs in ANSYS Motor-CAD
5.2. The Comparison of the Obtained Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosu, M.; Zhou, P.; Lin, D.; Ionel, D.M.; Popescu, M.; Blaabjerg, F.; Rallabandi, V.; Staton, D. Multiphysics Simulation by Design for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, G.; Zhu, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, B. A review of design optimization methods for electrical machines. Energies 2017, 10, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Fu, W. Optimal design of permanent magnet arrangement in synchronous motors. Energies 2017, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepoi, R.D.; Jaşcău, F.F.; Szabó, L. Current trends in energy efficient electrical machines. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2017, 10, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, Z.; Bibri, S.E.; Sharpe, S.A. The Rising Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Russia–Ukraine War: Energy Transition, Climate Justice, Global Inequality, and Supply Chain Disruption. Resources 2022, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobba, S.; Carrara, S.; Huisman, J.; Mathieux, F.; Pavel, C. Critical Raw Materials for Strategic Technologies and Sectors in the EU. A Foresight Study; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hameyer, K.; Belmans, R. Numerical Modelling and Design of Electrical Machines and Devices; WIT Press: Ashurst Lodge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Salon, S.J. Finite Element Analysis of Electrical Machines; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- JMAG-Designer. User’s Manual Solver, 19th ed.; JSOL Corporation: Tokyo, Japan, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, S.-B.; Kim, C.-H.; Cha, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jung, S.-Y. A novel method for establishing an efficiency map of IPMSMs for EV propulsion based on the finite-element method and a neural network. Electronics 2021, 10, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecer, B.; Tosun, O.; Apaydin, H.; Serteller, N.F.O. Comparative Analysis of SRM, BLDC and Induction Motor Using ANSYS/Maxwell. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Computer, Communications and Mechatronics Engineering (ICECCME ‘2021), Mauritius, 7–8 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishwarya, M.; Brisilla, R. Design of Energy-Efficient Induction motor using ANSYS software. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvolik, V.; Prystupa, D.; Buticchi, G.; Peresada, S.; Galea, M.; Bozhko, S. Co-simulation analysis for performance prediction of synchronous reluctance drives. Electronics 2021, 10, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobzhanskyi, O.; Grebenikov, V.; Gouws, R.; Gamaliia, R.; Hossain, E. Comparative thermal and demagnetization analysis of the PM machines with neodymium and ferrite magnets. Energies 2022, 15, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, K.; Kurnyta-Mazurek, P.; Szolc, T.; Henzel, M. Radial magnetic bearings for rotor–shaft support in electric jet engine. Energies 2022, 15, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukočius, R.; Vilkauskas, A.; Marčiulionis, P.; Grigaliūnas, V.; Nakutis, Ž.; Deltuva, R. An analysis of axial magnetic coupling force and torque dependencies on its structure parameters using a 3D FEM. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Frosini, L.; Szabó, L. A new design procedure for rotor laminations of synchronous reluctance machines with fluid shaped barriers. Electronics 2022, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Reja, M.I.; Mirza, F.; Ahmed, H. Design of permanent magnet synchronous machines of direct-driven generator with Emetor and FLUX 2D. In Proceedings of the IEEE Business, Engineering & Industrial Applications Colloquium (BEIAC ‘2012), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 7–8 April 2012; pp. 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Someşan, L.; Pădurariu, E.; Viorel, I.A.; Szabó, L. Design of a permanent magnet flux-switching machine. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference ELEKTRO ‘2012, Žilina–Rajecké Teplice, Slovakia, 21–22 May 2012; pp. 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.A.D.; Carralero, N.D.; Vázquez, E.G. A 3-D Simulation of a Single-Sided Linear Induction Motor with Transverse and Longitudinal Magnetic Flux. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Agoro, S.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Husain, I. Heavy rare earth free high power density traction machine for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC ‘2021), Hartford, CT, USA, 17–20 May 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, L.T.; Fontes, F.A.C.C. Optimal control algorithms with adaptive time-mesh refinement for kite power systems. Energies 2018, 11, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S. Finite element mesh generation and adaptive meshing. Prog. Struct. Eng. Mater. 2002, 4, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okereke, M.; Keates, S. Finite Element Applications. A Practical Guide to the FEM Process; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. The finite element method. In Graded Finite Element Methods for Elliptic Problems in Nonsmooth Domains. Surveys and Tutorials in the Applied Mathematical Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 10, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mersha, T.K.; Du, C. Co-simulation and modeling of PMSM based on ANSYS software and Simulink for EVs. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipenko, M.; Biser, S.; Boll, M.; Corduan, M.; Noe, M.; Rostek, P. Comparative analysis and optimization of technical and weight parameters of turbo-electric propulsion systems. Aerospace 2020, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.; Silva, R.; Lowther, D.A. Application of surrogate models to the multiphysics sizing of permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 7401604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldea, I.; Tutelea, L.N. Electric Machines: Steady State, Transients, and Design with MATLAB®; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Motor-CAD Software. Available online: https://www.motor-design.com/motor-cad/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Staton, D.; Goss, J. Open Source Electric Motor Models for Commercial EV & Hybrid Traction Motors; Motor Design Ltd.: Ellesmere, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Hua, W.; Zhang, H. Thermal analysis of modular-spoke-type permanent-magnet machines based on thermal network and FEA method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 8104105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staton, D. Servo motor size reduction—Need for thermal CAD. In Proceedings of the Drives & Controls Conference (ExCeL‘2001), London, UK, 13–15 March 2001; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Staton, D.; Hawkins, D.; Popescu, M. Motor-CAD software for thermal analysis of electrical motors–Links to electromagnetic and drive simulation models. In Proceedings of the Coil Winding, Insulation & Electrical Manufacturing Exhibitions Conference (CWIEME ‘2010), Berlin, Germany, 5 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, D. Thermal performance analysis of motor based on Motor-CAD. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advances in Materials, Machinery, Electronics, AMME, 2019, Wuhan, China, 19–20 January 2019; AIP Conference Proceedings. Volume 2073, p. 5090703. [Google Scholar]
- Deaconu, D.I.; Ghiţă, C.; Chirilă, A.I.; Năvrăpescu, V.; Popescu, M. Thermal study of induction machine using Motor-CAD. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ISEEE ‘2010), Galați, Romania, 16–18 September 2010; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staton, D.; Boglietti, A.; Cavagnino, A. Solving the more difficult aspects of electric motor thermal analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC ‘03), Madison, WI, USA, 1–4 June 2003; pp. 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramerdorfer, G.; Tapia, J.A.; Pyrhönen, J.J.; Cavagnino, A. Modern electrical machine design optimization: Techniques, trends, and best practices. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7672–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boglietti, A.; Cavagnino, A.; Staton, D.; Shanel, M.; Mueller, M.; Mejuto, C. Evolution and modern approaches for thermal analysis of electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, N.; Villani, M.; Popescu, M. Optimisation of a high speed copper rotor induction motor for a traction application. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON ‘2019), Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; pp. 2720–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.A.; Guo, Y.; Dorrell, D.G. Predicting the behavior of induction machine using motor-CAD and MATLAB packages. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG ‘2018), Doha, Qatar, 10–12 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyshevski, S.E. Electromechanical Systems, Electric Machines, and Applied Mechatronics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Matković, K.; Splechtna, R.; Gračanin, D.; Todorović, G.; Goja, S.; Bedić, B.; Hauser, H. Getting insight into noise, vibration, and harshness simulation data. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference (WSC ‘2021), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, S. Automotive Air Conditioning and Climate Control Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J.; VanGelder, K. Automotive Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, VT, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; He, Y. Parameterization and performance of permanent magnet synchronous motor for vehicle based on Motor-CAD and OptiSLang. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Liu, Z.S. Optimization design and analysis of permanent magnet synchronous generator based on Motor-CAD. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2345, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.; Soulard, J. A permanent magnet synchronous motor for traction applications of electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC ‘2003), Madison, WI, USA, 1–4 June 2003; pp. 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Matsumura, N.; Takeda, K. Development of high efficiency scroll compressors, for air conditioners. In Proceedings of the 1988 International Compressor Engineering Conference, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 18–21 July 1988; p. 603. [Google Scholar]
- Aurich, J.; Baumgart, R. Comparison and evaluation of different A/C compressor concepts for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 24th International Compressor Engineering Conference, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 9–12 July 2018; p. 2608. [Google Scholar]
- Cardone, M.; Gargiulo, B. Numerical simulation and experimental validation of an oil free scroll compressor. Energies 2020, 13, 5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everything You Need to Know About Scroll Pumps. Available online: https://www.vacuumscienceworld.com/blog/everything-you-need-to-know-about-scroll-pumps (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Cosman, S.-I.; Văscan, I.; Bilațiu, C.-A.; Tintelecan, A.; Marțiș, C.S.; Zorlescu, B. Design and analysis of a heating, ventilation and air conditioning system for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM ‘2020), Sorrento, Italy, 24–26 June 2020; pp. 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodorean, D.; Popa, D.; Minciunescu, P.; Irimia, C.; Szabó, L. Study of a high-speed motorization for electric vehicle based on PMSM, IM and VRSM. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM ‘2014), Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 2577–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, C.S.; Manjrekar, M.; Essakiappan, S.; Sahu, P.; Shah, N. Landscaping and review of traction motors for electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo (ITEC ‘2021), Chicago, IL, USA, 21–25 June 2021; pp. 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Adamas Intelligence. Global PMSM Market Share Continues to Rise Despite Soaring Rare Earth Prices; Adamas Intelligence: Toronto, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Naphade, A. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) Market Report, History and Forecast Breakdown Data by Types and Application till 2028; Skyline Market Research LLP: Kalyani Nagar, India, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Văscan, I.; Szabó, L. Improvement trends in the development of permanent magnet synchronous machines for automotive applications. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Carpathian Control Conference (ICCC ‘2022), Sinaia, Romania, 29 May–1 June 2022; pp. 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrhonen, J.; Jokinen, T.; Hrabovcova, V. Design of Rotating Electrical Machines; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Candelo-Zuluaga, C.; Espinosa, A.G.; Riba, J.-R.; Blanch, P.T. PMSM design for achieving a target torque-speed-efficiency map. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 14448–14457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbelen, F.; Abdallh, A.; Vansompel, H.; Stockman, K.; Sergeant, P. Sizing methodology based on scaling laws for a permanent magnet electrical variable transmission. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechkemmer, S.K.; Izumi, R.; Zhang, W.; Sawodny, O. Estimation of permanent magnet synchronous machine performance for pre-design using a reluctance network. IFAC-Pap. 2018, 51, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Li, S.; Liao, X.; Wang, T.; He, X.; Zhang, J. Design and analysis of the high-speed permanent magnet motors: A review on the state of the art. Machines 2022, 10, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipo, T.A. Introduction to AC Machine Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, S.; Kou, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Modeling and simulation of a novel low-speed high-torque permanent magnet synchronous motor with asymmetric stator slots. Machines 2022, 10, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electrical Steel Sheets—JFE G-CORE, JFE N-CORE; JFE Steel Corporation: Tokyo, Japan, 2016.
- N35UH Sintered Neodymium-Iron-Boron Magnets; Arnold Magnetic Technologies Corp.: Rochester, NY, USA, 2014.
- Majumdar, N.; Banerjee, S. MATLAB Graphics and Data Visualization Cookbook; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.; Nilssen, R.; Nysveen, A. Harmonic analysis and comparison of the back EMFs of four permanent magnet machine with different winding arrangements. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS ‘2008), Wuhan, China, 17–20 October 2008; pp. 3043–3048. [Google Scholar]

















| Item | Rated Value | Resulted from Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| DC bus voltage | 72 V | 72 V (imposed) |
| Rated power | 4 kW | 4.0596 kW |
| Rated speed | 8000 r/min | 8000 r/min (imposed) |
| Rated average torque | 4.77 N·m | 4.82 N·m |
| Mass [kg] | Permanent Magnet Topology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Interior | Spoke-Type | V-Shape | |
| Stator core | 3.736 | 3.736 | 3.736 | 3.736 |
| Rotor core | 0.6537 | 0.7301 | 0.9116 | 0.7274 |
| Permanent magnets | 0.1881 | 0.1881 | 0.1882 | 0.1881 |
| Windings | 1.846 | 1.846 | 1.846 | 1.846 |
| Shaft | 0.5743 | 0.5743 | 0.5743 | 0.5743 |
| Total mass | 6.9981 | 7.0745 | 7.2561 | 7.0718 |
| Characteristics | Permanent Magnet Topology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Interior | Spoke-Type | V-Shape | |
| Output power [W] | 4067 | 3516.6 | 3520.9 | 3129.4 |
| Mean torque [N·m] | 4.851 | 4.192 | 4.193 | 3.731 |
| Torque ripple [%] | 43.87 | 83.5 | 56.16 | 97.78 |
| Cogging torque peak-to-peak [N·m] | 1.58 | 2.56 | 1.28 | 4.16 |
| Efficiency [%] | 95.354 | 92.912 | 94.081 | 92.289 |
| Power factor [–] | 0.975 | 0.851 | 0.89 | 0.853 |
| Power density [W/kg] | 581.15 | 497.08 | 485.23 | 442.52 |
| Torque density [N·m/kg] | 0.69 | 0.59 | 0.58 | 0.52 |
| Torque Features | Permanent Magnet Topology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Interior | Spoke-Type | V-Shape | |
| Tmin [N·m] | 3.55 | 1.97 | 2.76 | 1.77 |
| Tmax [N·m] | 5.68 | 5.47 | 5.12 | 5.41 |
| Tmean [N·m] | 4.85 | 4.19 | 4.19 | 3.73 |
| Tripple [%] | 43.87 | 83.5 | 56.16 | 97.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coteț, F.-A.; Văscan, I.; Szabó, L. On the Usefulness of Employing ANSYS Motor-CAD Software in Designing Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. Designs 2023, 7, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs7010007
Coteț F-A, Văscan I, Szabó L. On the Usefulness of Employing ANSYS Motor-CAD Software in Designing Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. Designs. 2023; 7(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs7010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoteț, Florina-Ambrozia, Iulia Văscan, and Loránd Szabó. 2023. "On the Usefulness of Employing ANSYS Motor-CAD Software in Designing Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines" Designs 7, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs7010007
APA StyleCoteț, F.-A., Văscan, I., & Szabó, L. (2023). On the Usefulness of Employing ANSYS Motor-CAD Software in Designing Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. Designs, 7(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs7010007









