CPAP Use and Retinal Disease Risk in Obstructive Apnea: A Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Outcome Definition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Pathways by Disease
4.2. Which Patients to Flag/Clinical Workflow
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OSA | Obstructive Sleep Apnea |
| CPAP | Continuous Positive Airway Pressure |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CSC | Central Serous Chorioretinopathy |
| AMD | Age-Related Macular Degeneration |
| RVO | Retinal Vein Occlusion |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| RR | Risk Ratio |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| HIPAA | Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act |
| STROBE | Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| UMLS | Unified Medical Language System |
| ICD-10-CM | International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification |
| SNOMED | Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine |
| CPT | Current Procedural Terminology |
References
- Wang, W.; He, M.; Huang, W. Changes of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, B.; Tong, J.Y.; Schulz, A.M.; Graham, S.L.; Farah, C.S.; Fraser, C.L. The impact of continuous positive airway pressure treatment on retinal vascular changes in obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021, 17, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimy, E.; Koo, E.B.; Wai, K.M.; Ludwig, C.A.; Kossler, A.L.; Mruthyunjaya, P. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Diabetic Retinopathy Progression and Systemic Complications. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2025, 270, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uslu, H.; Kanra, A.Y.; Cetintas, G.; Tatar, M.G. Effect of Therapy on Choroidal Thickness in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2018, 49, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshaikhsalama, A.M.; Alsoudi, A.F.; Wai, K.M.; Koo, E.; Mruthyunjaya, P.; Rahimy, E. Association between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Age-related Macular Degeneration Development and Progression. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2025, 9, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Wu, Z.; Lu, J.; Wan, W.; Gao, J.; Su, H.; Zhu, W. Obstructive Sleep Apnea is Related with the Risk of Retinal Vein Occlusion. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2021, 13, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Yeung, L.; Kuan, J.C.; Sun, M.H.; Sun, C.C. Relationship between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Central Serous Chorioretinopathy: A Health Insurance Database Study. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2022, 29, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.W.; Lin, H.C.; Friedman, M.; Chang, H.W.; Salapatas, A.M.; Lin, M.C.; Chen, Y.C. Effects of CPAP for patients with OSA on visual sensitivity and retinal thickness. Sleep Med. 2020, 67, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, H.; Kapoor, K.G. Retinal vascular manifestations of obstructive sleep apnea. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 31, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Panagiotakos, D. Real-world data: A brief review of the methods, applications, challenges and opportunities. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2022, 22, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, A.; Villalaín-Rodes, I.; Jaureguizar, A.; Zamarrón, E.; Martínez-Cerón, E.; Casitas, R.; Galera, R.; Cubillos-Zapata, C.; García, J.; Asencio, M.; et al. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Effect on Progression of Retinal Disease in Patients with Sleep Apnea and Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2024, 21, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrilin, M.A.; Porter, K.; Samouilov, A.; Khayat, R.N. Pathways of Microcirculatory Endothelial Dysfunction in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Comprehensive Ex Vivo Evaluation in Human Tissue. Am. J. Hypertens. 2022, 35, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, C.D.; Stockley, J.A.; Madathil, S.; Huq, S.S.A.; Cooper, B.G.; Ali, A.; Wharton, S.; Stradling, J.R.; Heitmar, R. Effect of obstructive sleep apnoea on retinal microvascular function: A randomised controlled trial. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2022, 260, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristescu, T.R.; Mihălțan, F.D. Ocular pathology associated with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 64, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero-Garcés, G.; Ascaso, F.J.; Casas, P.; Adiego, M.I.; Baptista, P.; O’Connor-Reina, C.; Vicente, E.; Plaza, G. Assessment of the Effectiveness of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Treatment Using Optical Coherence Tomography to Evaluate Retinal Findings. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.D.; Prudon, B.; Hughes, J.; Gupta, R.; Mohammed, S.B.; Gerry, S.; Stradling, J.R.; for the ROSA trial investigators. Continuous positive airway pressure effect on visual acuity in patients with type 2 diabetes and obstructive sleep apnoea: A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1801177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongchan, P.; Banhiran, W.; Chirapapaisan, N.; Kasemsuk, N. The effect of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on intraocular pressure in patients with OSA: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2025, 21, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Deokar, K.; Dutta, S.; Sinha, B.P.; Katoch, C.D.S. Impact of positive airway pressure therapy on intraocular pressure in obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2025, 35, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, L.X.; He, K.; Li, X.Q. Correlation between obstructive sleep apnea and central retinal vein occlusion. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 1634–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Terán, T.D.; Boira, I.; Cerveró, A.; Casado, A.; Lopez-de-Eguileta, A.; Fonseca, S.; Muñoz, P.; Nebot, C.; Nicolini, A.; Banfi, P.; et al. Benefit of continuous positive airway pressure on optic nerve damage in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2025, 29, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutome, T.; Kuze, M. Effects of continuous positive air pressure on intraocular pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea during the split-night study: An open-label randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2023, 102, e33566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
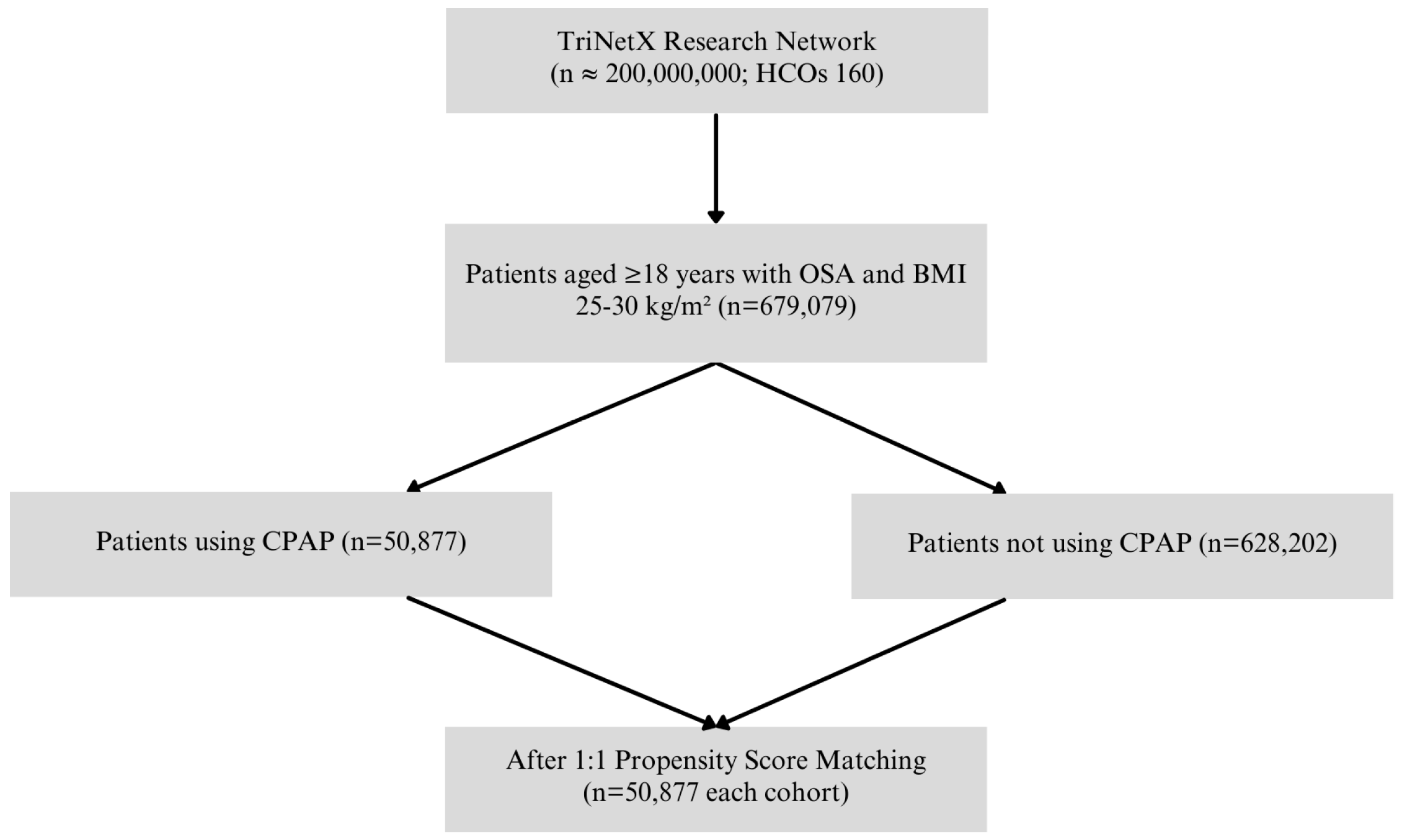
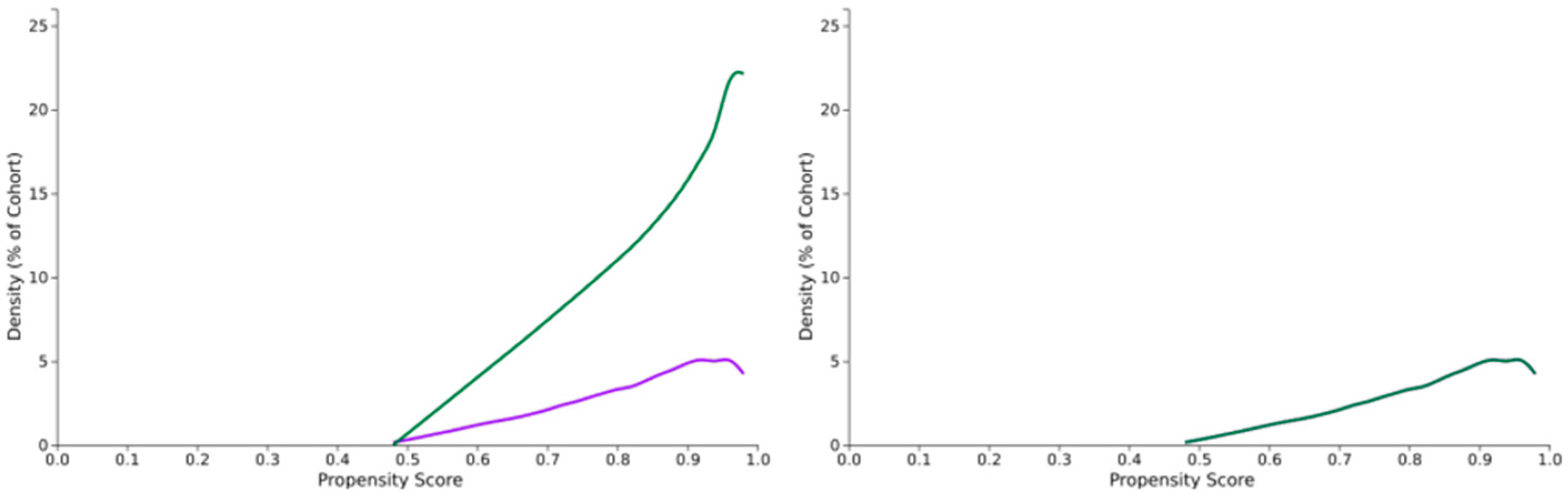

| Variable | CPAP+ 4 (n = 50,877) | CPAP− (n = 50,877) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Follow-up, mean ± SD 1 (days) | 966.9 ± 1031.4 | 1106.5 ± 1111.0 | |
| Follow-up, median (IQR 2) (days) | 597 (1373) | 744 (1434) | |
| Age at Index (years), mean ± SD | 66.8 ± 13.8 | 66.9 ± 13.6 | 0.089 |
| Male, n (%) | 33,593 (66.0%) | 33,606 (66.1%) | 0.852 |
| Hypertensive diseases, n (%) | 41,936 (82.4%) | 42,040 (82.6%) | 0.443 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 24,360 (47.9%) | 24,240 (47.6%) | 0.821 |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) | 18,185 (35.7%) | 18,008 (35.4%) | 0.211 |
| BMI 3 (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 29.3 ± 3.6 | 29.3 ± 3.2 | 0.284 |
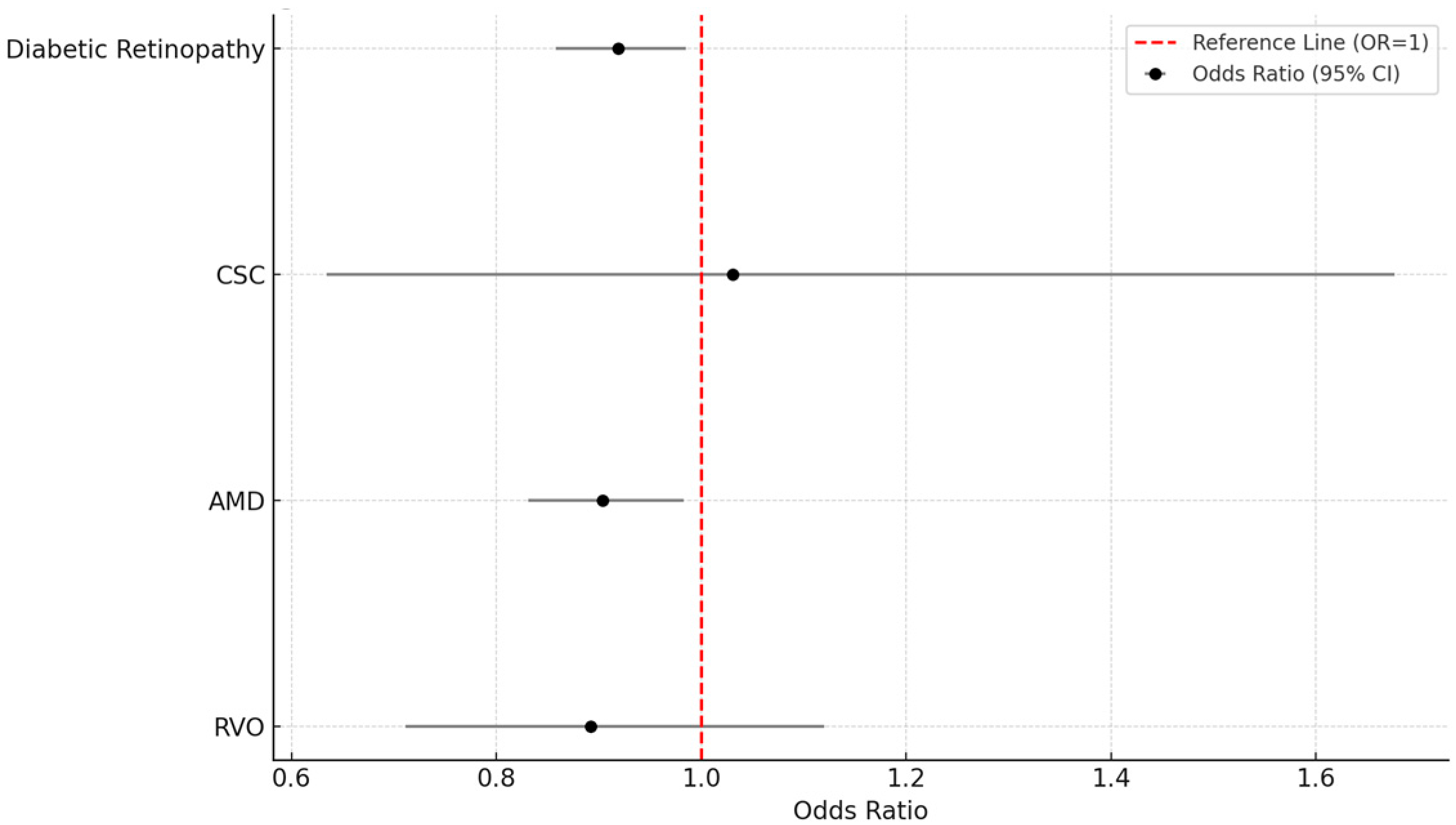
| Outcome | CPAP+ 4 (n, %) | CPAP− (n, %) | RD 5 (%) | RR 6 (95% CI 7) | OR 8 (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetic Retinopathy | 1611 (3.2%) | 1748 (3.4%) | −0.3 | 0.922 (0.862–0.985) | 0.919 (0.858–0.985) | 0.016 |
| CSC 1 | 33 (0.1%) | 32 (0.1%) | 0.0 | 1.031 (0.634–1.677) | 1.031 (0.634–1.677) | 0.901 |
| AMD 2 | 1057 (2.1%) | 1167 (2.3%) | −0.2 | 0.906 (0.834–0.983) | 0.904 (0.831–0.983) | 0.018 |
| RVO 3 | 141 (0.3%) | 158 (0.3%) | −0.0 | 0.892 (0.711–1.120) | 0.892 (0.711–1.120) | 0.325 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, D.C.; Magalhães, P.L.M.; Alfatih, M.; Miranda, B.G.; Abu Serhan, H.; Jacometti, R.; Ferreira, B.F.d.A.; Sant’Ana, L.; Santos, D.H.; Monteiro, M.L.R.; et al. CPAP Use and Retinal Disease Risk in Obstructive Apnea: A Cohort Study. Vision 2025, 9, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030065
Amaral DC, Magalhães PLM, Alfatih M, Miranda BG, Abu Serhan H, Jacometti R, Ferreira BFdA, Sant’Ana L, Santos DH, Monteiro MLR, et al. CPAP Use and Retinal Disease Risk in Obstructive Apnea: A Cohort Study. Vision. 2025; 9(3):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030065
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, Dillan Cunha, Pedro Lucas Machado Magalhães, Muhammad Alfatih, Bruna Gabriel Miranda, Hashem Abu Serhan, Raíza Jacometti, Bruno Fortaleza de Aquino Ferreira, Letícia Sant’Ana, Diogo Haddad Santos, Mário Luiz Ribeiro Monteiro, and et al. 2025. "CPAP Use and Retinal Disease Risk in Obstructive Apnea: A Cohort Study" Vision 9, no. 3: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030065
APA StyleAmaral, D. C., Magalhães, P. L. M., Alfatih, M., Miranda, B. G., Abu Serhan, H., Jacometti, R., Ferreira, B. F. d. A., Sant’Ana, L., Santos, D. H., Monteiro, M. L. R., & Louzada, R. N. (2025). CPAP Use and Retinal Disease Risk in Obstructive Apnea: A Cohort Study. Vision, 9(3), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030065










