Novel Surgical Approach for Limbal Dermoid Excision: Utilizing Bowman’s Membrane Lenticule and Autologous Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation for Enhanced Epithelial Healing and Visual Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects Selection
2.3. Bowman Layer (Membrane) Harvesting
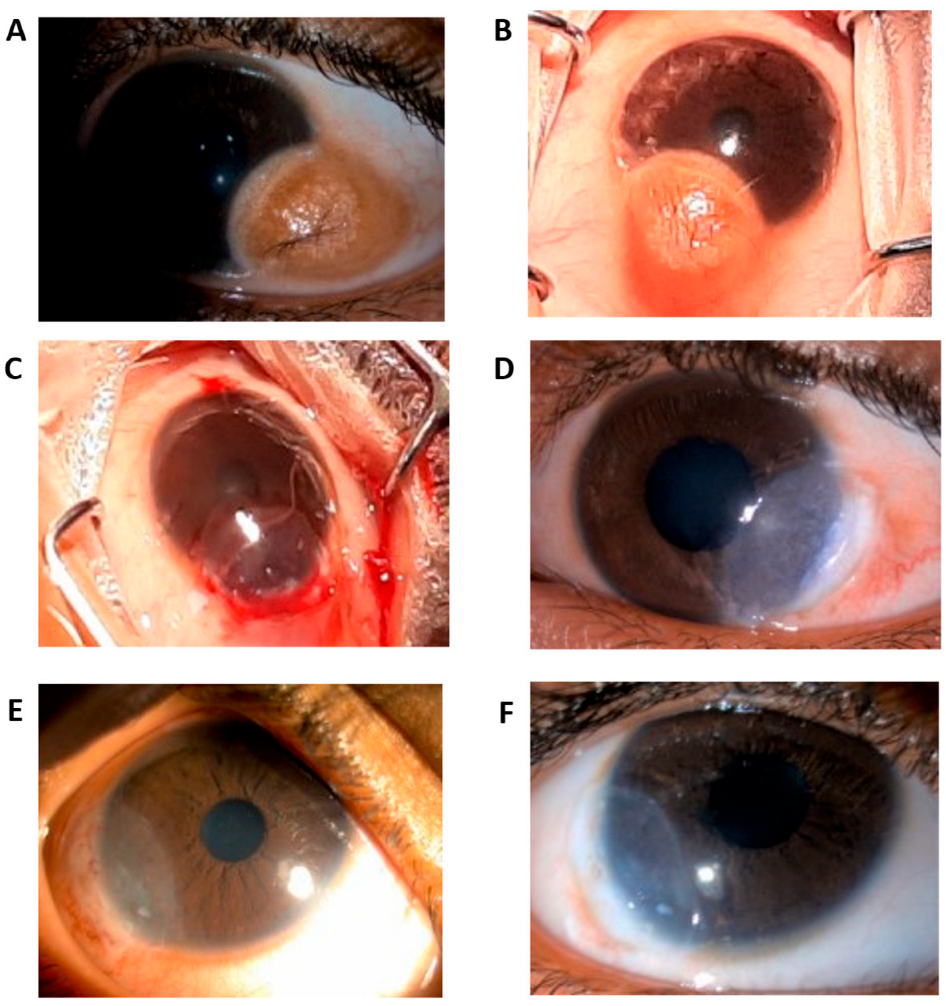
2.4. Surgical Technique
2.5. Postoperative Course
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Epithelial Healing
3.2. Visual Outcomes
3.3. Corneal Thickness and Structural Changes
3.4. Postoperative Observations and Complications
- Early Postoperative Changes: A small cystic space was detected between the corneal bed and the Bowman’s membrane graft on AS-OCT around postoperative day 2–3. This cyst persisted for about one to two weeks before resolving naturally without intervention.
- No Major Complications: Importantly, no cases of graft rejection, infection, or persistent inflammation were observed throughout the follow-up period.
- No Need for Additional Surgery: All subjects responded well to the procedure, and none required further surgical intervention during the study duration.
3.5. Overall Implications & Novelty
4. Discussion
4.1. Bowman’s Membrane as an Alternative Graft Material
4.2. Postoperative Observations and Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pirouzian, A. Management of pediatric corneal limbal dermoids. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2013, 7, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, P.S.; Rajeswari, S.; Kavitha, K. Caruncular dermoid: A report of a rare case. TNOA J. Ophthalmic Sci. Research. 2018, 56, 263–265. [Google Scholar]
- Bajric, J.; Griepentrog, G.J.; Mohney, B.G. Pediatric Periocular Dermoid Cysts: Incidence, Clinical Characteristics, and Surgical Outcomes. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2019, 26, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Huang, H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Peng, L.; Yang, R.; Xu, J.; et al. New Grading System for Limbal Dermoid: A Retrospective Analysis of 261 Cases Over a 10-Year Period. Cornea 2018, 37, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shareef, S.; Ettefagh, L. Dermoid Cyst; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.; Rand, G.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Kwon, J.W. Novel limbal dermoid surgery for visual acuity and cosmesis improvement: A 7-year retrospective review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, M.Z.; Jhanji, V. Surgical management of limbal dermoids: 10-year review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, e517–e518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, D.S.; Verma, G.; Kumar, K.; Choudhary, P.; Kalal, B.S.; Chaudhary, A. Bowman’s membrane lenticule tuck-in: A new approach for the management of neurotrophic ulcers. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 37, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddi, M.; Romano, V.; Borgia, A.; Porcaro, F.; Cagini, C.; Messina, M. Combined Multilayered Amniotic Membrane Graft and Fibrin Glue as a Surgical Management of Limbal Dermoid Cyst. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucakhan Gunduz, O.O.; Gunduz, A.K.; Nalci Baytaroglu, H. Lamellar Keratoplasty Using Microkeratome-Assisted Anterior Lamellar Graft in the Management of Deep Limbal Dermoid: A Case Report. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 53, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wu, T.; Guo, X. Sutureless lamellar keratoplasty with lenticule from small incision lenticule extraction for treating limbal dermoid: A case report. Exp. Ther. Med. 2024, 27, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umfress, A.C.; Mawn, L.A.; Joos, K.M.; Donahue, S.P.; Schmitt, A.D.; Shieh, C. Surgical management of large bilateral epibulbar dermoids with autologous oral mucous membrane transplantation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case. Rep. 2020, 20, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Dubey, A.; Prakash, G.; Vajpayee, R.B. Bowman’s layer transplantation: Evidence to date. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 12, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, D.S.; Ghanolia, K.; Shaheen, J.; Choudhary, S.; Chaudhary, A.; Kalal, B.S. Intrastromal autologous buffy coat as an adjuvant therapy for fungal corneal ulcer: A case report of two cases. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 68, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jurkunas, U.; Johns, L.; Armant, M. Cultivated Autologous Limbal Epithelial Cell Transplantation: New Frontier in the Treatment of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 239, 244–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkunas, U.V.; Kaufman, A.R.; Yin, J.; Ayala, A.; Maguire, M.; Samarakoon, L.; Johns, L.K.; Parekh, M.; Li, S.; Gauthier, A.; et al. Cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell (CALEC) transplantation for limbal tem cell deficiency: A phase I/II clinical trial of the first xenobiotic-free, serum-free, antibiotic-free manufacturing protocol developed in the US. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 8.33 ± 6.47 |
| Sex | Male (10, 29.41%)/Female (24, 75.59%) |
| Epithelization Time (weeks) | 3.36 ± 0.74 |
| Ulcer Size (mm) | 4.1 × 4.0 ± 0.20 |
| Comorbidity | Goldenhar syndrome (1, 2.94%) |
| Parameter | Preoperative Value (Mean ± SD) | Postoperative Value (Mean ± SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA) | 0.136 ± 0.121 | 0.336 ± 0.214 | <0.001 |
| Corneal Thickness (µm) | 294 ± 49.68 | 484 ± 5.037 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choudhary, D.S.; Hada, M.; Ghanolia, K.; Shaheen, J.; Dhakad, A.; Kalal, B.S. Novel Surgical Approach for Limbal Dermoid Excision: Utilizing Bowman’s Membrane Lenticule and Autologous Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation for Enhanced Epithelial Healing and Visual Outcomes. Vision 2025, 9, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030056
Choudhary DS, Hada M, Ghanolia K, Shaheen J, Dhakad A, Kalal BS. Novel Surgical Approach for Limbal Dermoid Excision: Utilizing Bowman’s Membrane Lenticule and Autologous Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation for Enhanced Epithelial Healing and Visual Outcomes. Vision. 2025; 9(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoudhary, Dharamveer Singh, Maya Hada, Kavita Ghanolia, Jeba Shaheen, Ajay Dhakad, and Bhuvanesh Sukhlal Kalal. 2025. "Novel Surgical Approach for Limbal Dermoid Excision: Utilizing Bowman’s Membrane Lenticule and Autologous Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation for Enhanced Epithelial Healing and Visual Outcomes" Vision 9, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030056
APA StyleChoudhary, D. S., Hada, M., Ghanolia, K., Shaheen, J., Dhakad, A., & Kalal, B. S. (2025). Novel Surgical Approach for Limbal Dermoid Excision: Utilizing Bowman’s Membrane Lenticule and Autologous Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation for Enhanced Epithelial Healing and Visual Outcomes. Vision, 9(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030056





