An Overview of the Penguin Visual System
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Evolutionary Considerations
1.2. Requirements of an Amphibious Lifestyle
1.3. Behavioural Repertoire and Light Intensity
1.4. Aim of the Review
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
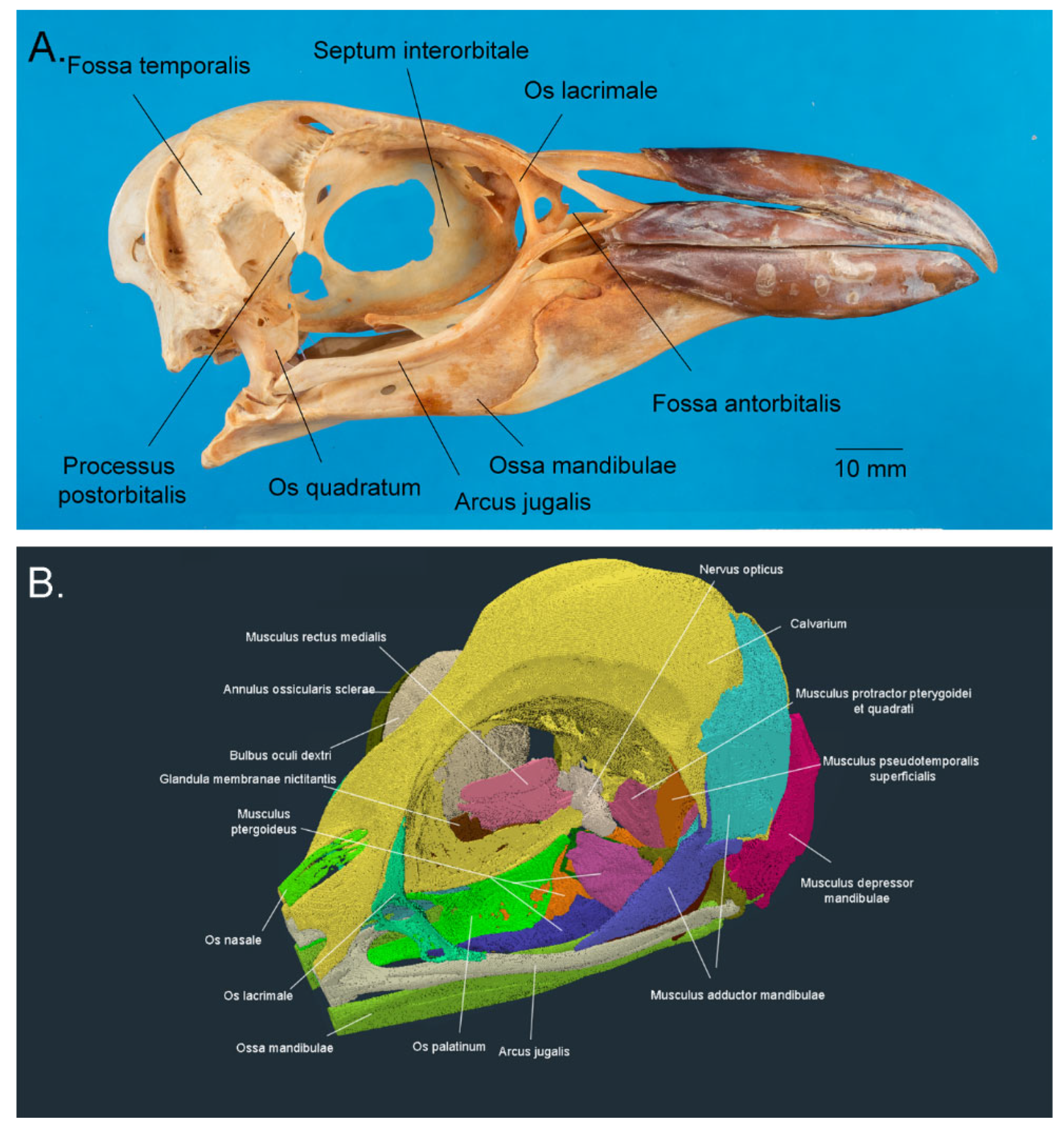
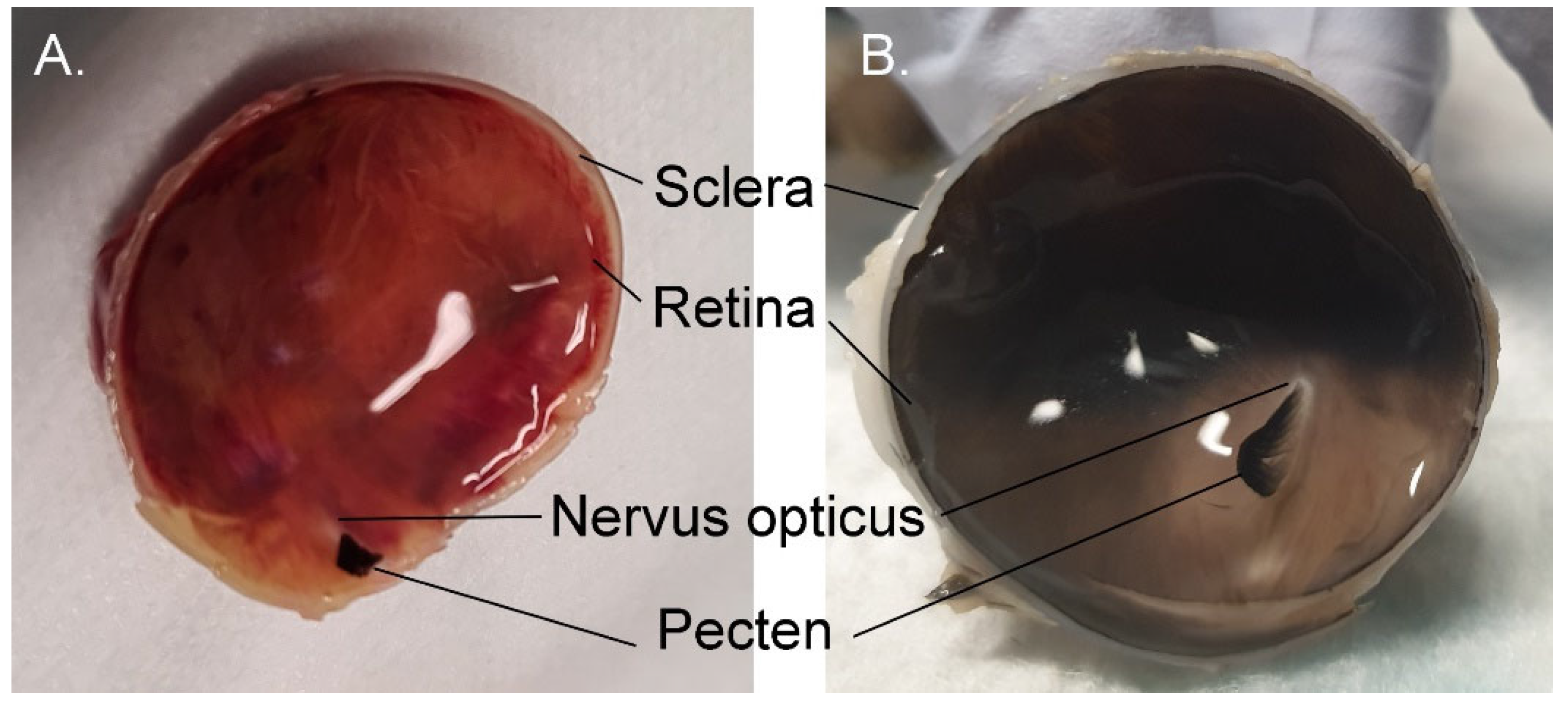
3.1. Ocular and Adnexal Anatomy
3.1.1. The Orbit (Orbita)
3.1.2. The Lids (Palpebrae)
3.1.3. The Globe (Bulbus oculi)
3.1.4. Optics of the Globe
3.1.5. Cornea
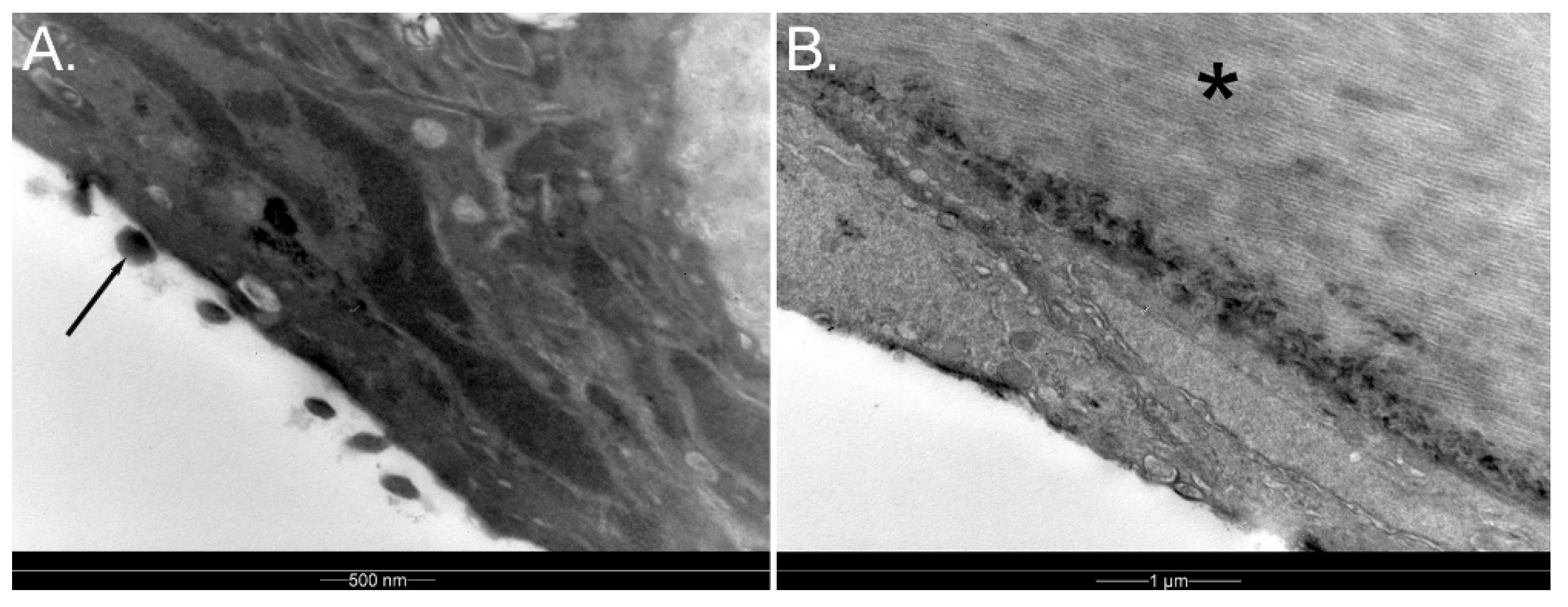
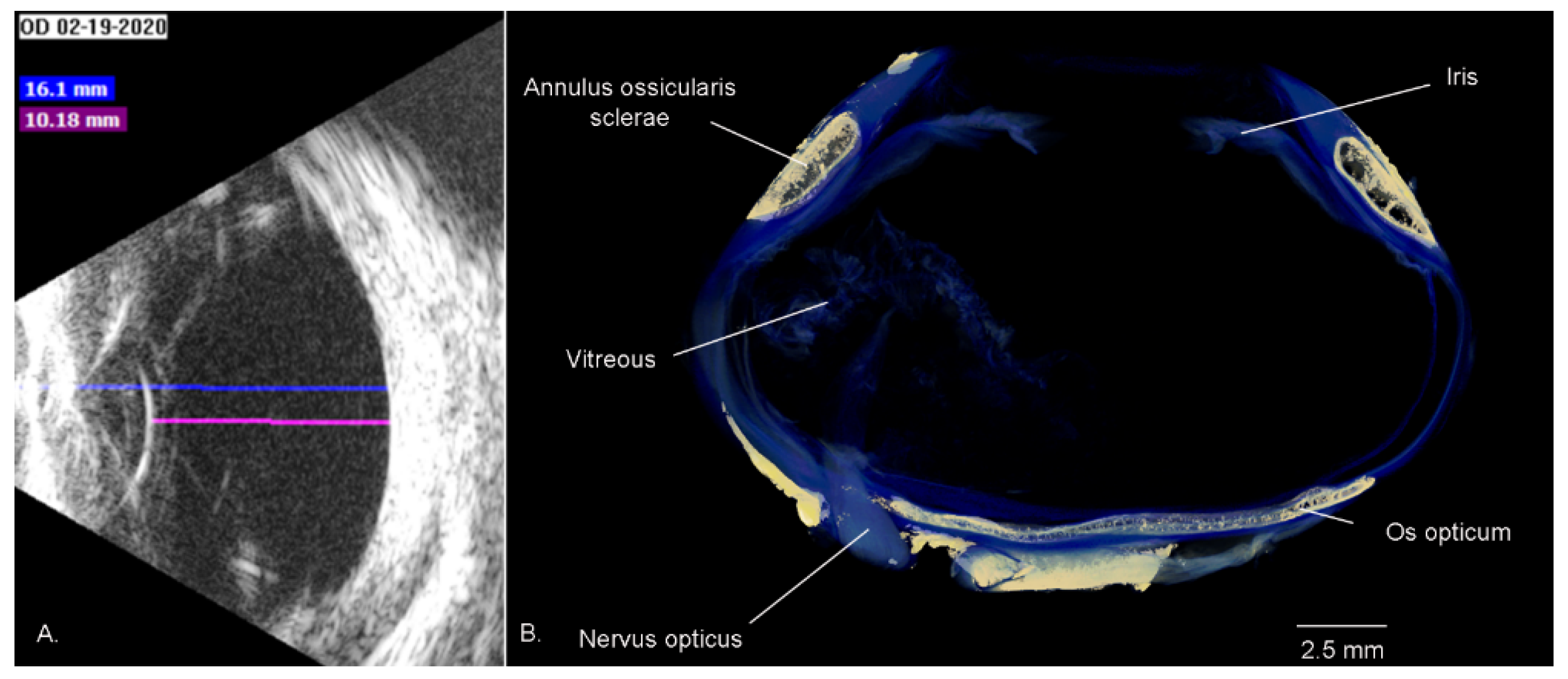
3.1.6. Sclera
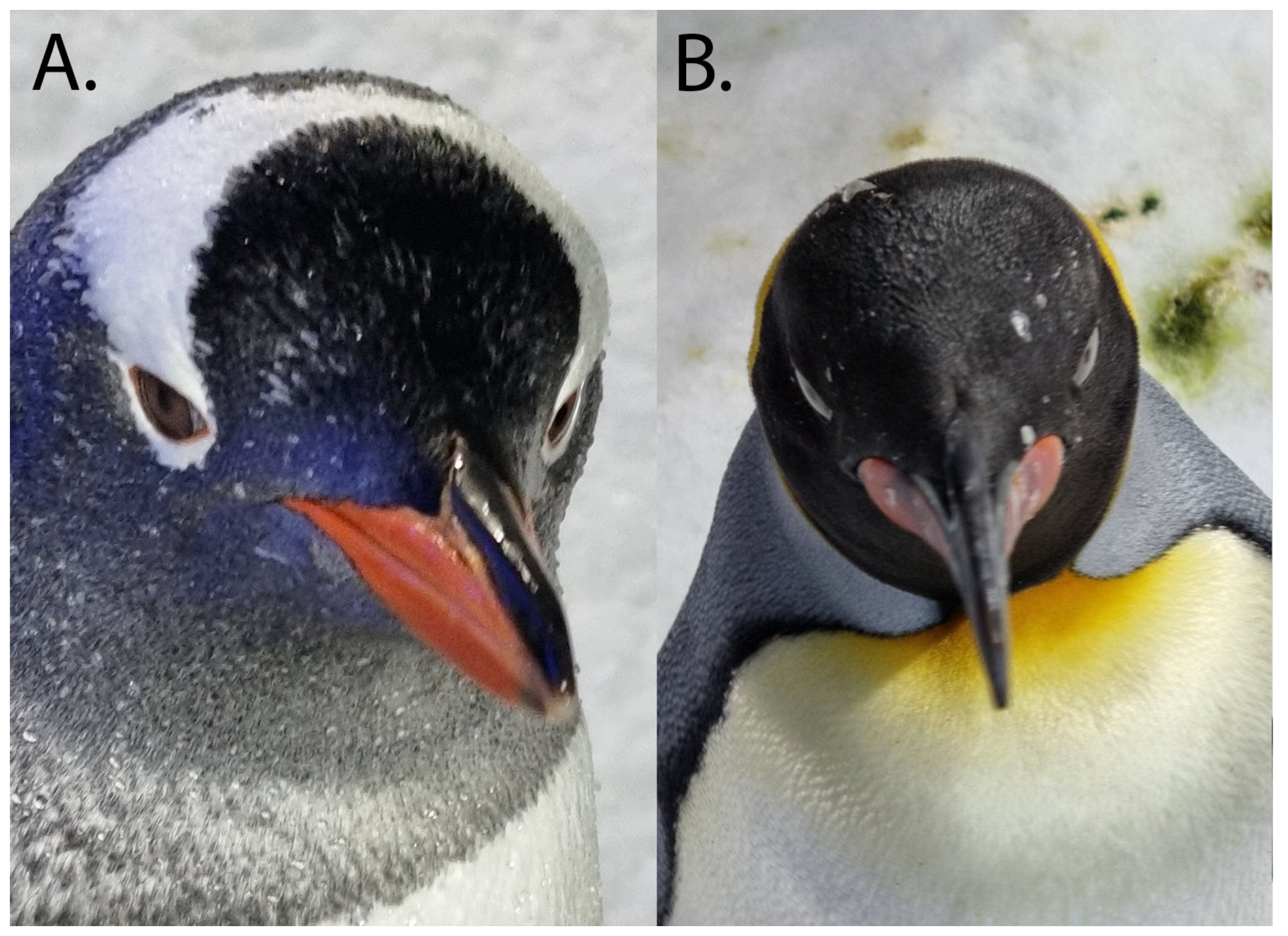
3.1.7. Iris and Pupil
3.1.8. Lens, Accommodation, and the Ciliary Body
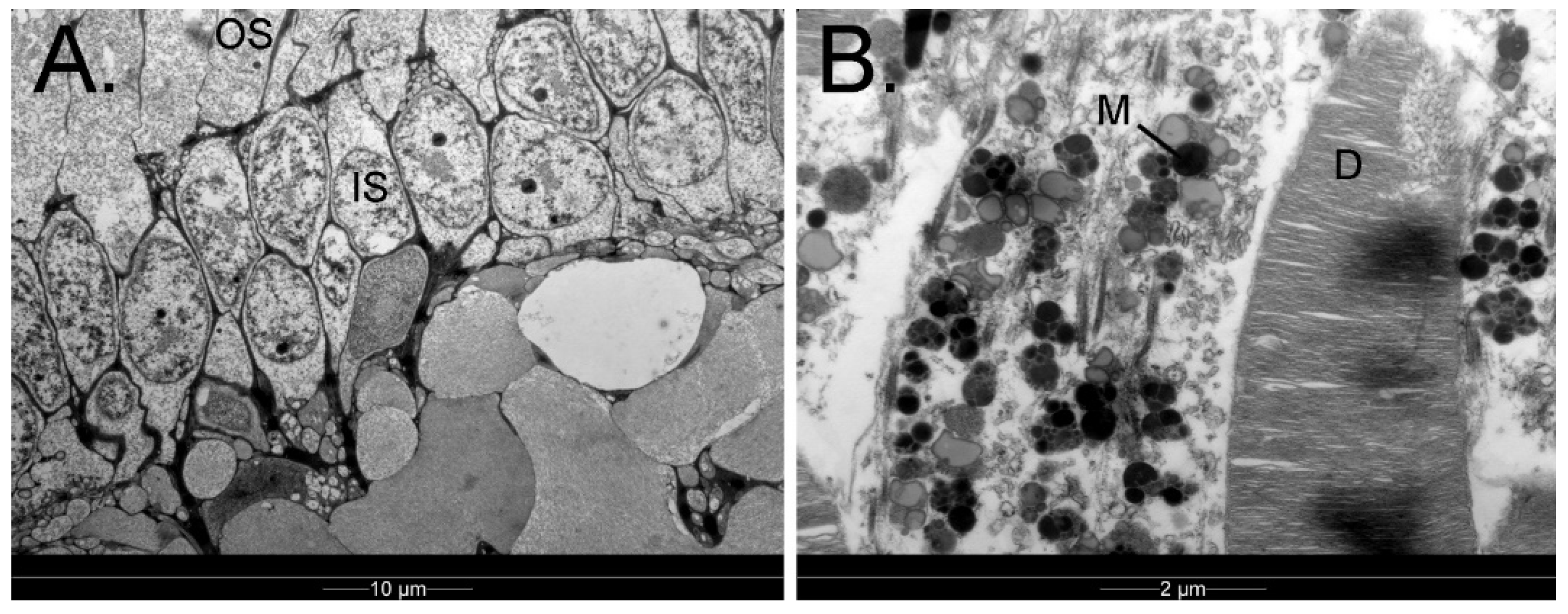
3.1.9. Retina
3.1.10. Choroid and Posterior Segment Nutrition
3.2. Physiology of the Penguin Eye
3.2.1. Intraocular Pressure
3.2.2. Tear Production
3.2.3. Visual Fields
3.2.4. Stereopsis
4. Discussion
4.1. Adaptions to Allow Amphibious Vision
4.2. Adaptations for Dim Light
4.3. Compression
4.4. Other Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cole, T.L.; Zhou, C.; Fang, M.; Pan, H.; Ksepka, D.T.; Fiddaman, S.R.; Emerling, C.A.; Thomas, D.B.; Bi, X.; Fang, Q.; et al. Genomic insights into the secondary aquatic transition of penguins. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.R. The Sensory Ecology of Bird; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 27, 49–55, 122, 125, 191–196, 259–296. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, S. The size of the olfactory bulb in 108 species of birds. Auk 1968, 85, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First Penguin in New Zealand to Undergo Cataract Surgery Makes Full Recovery. Available online: https://www.stuff.co.nz/national/health/129758464/first-penguin-in-new-zealand-to-undergo-cataract-surgery-makes-full-recovery (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Church, M.L.; Priehs, D.R.; Denis, H.; Croft, L.; DiRocco, S.; Davis, M. Technique, postoperative complications, and visual outcomes of phacoemulsification cataract surgery in 21 penguins (27 eyes): 2011–2015. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2018, 21, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, J.A.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Frugone, M.J.; Figueiró, H.V.; Pertierra, L.R.; Noll, D.; Bi, K.; Wang-Claypool, C.Y.; Lowther, A.; Parker, P.; et al. Genome-wide analyses reveal drivers of penguin diversification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22303–22310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, K.E.; Jones, C.M.; Ando, T.; Harrison, G.L.; Fordyce, R.E.; Arnason, U.; Penny, D. Early penguin fossils, plus mitochondrial genomes, calibrate avian evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatt, J.F.; Nettleship, D.N. Diving depths of four alcids. Auk 1985, 102, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratz, H.; Murphy, B. Effects of habitat and introduced mammalian predators on the breeding success of yellow-eyed penguins Megadyptes antipodes, South Island, New Zealand. Pac. Conserv. Biol. 1999, 5, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, J.T.; Seddon, P.J.; Davis, L. Breeding biology of yellow-eyed penguins (Megadyptes antipodes). In Penguin Biology; Stonehouse, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 1990; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, J.T.; Dawson, S.M. Bycatch of yellow-eyed penguins (Megadyptes antipodes) in gillnets in New Zealand waters 1979–1997. Biol. Conserv. 2000, 93, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, O. Subsea optics: An introduction. In Subsea Optics and Imaging; Watson, J., Zielinski, O., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J. Optical properties of the ocean. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1973, 36, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracher, A.U.; Tilzer, M.M. Underwater light field and phytoplankton absorbance in different surface water masses of the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean. Polar Biol. 2001, 24, 87–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Odate, T. Seasonal variability of phytoplankton biomass and composition in the major water masses of the Indian Ocean sector of the Southern Ocean. Polar Sci. 2014, 8, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gales, R.; Williams, C.; Ritz, D. Foraging behaviour of the little penguin, Eudyptula minor: Initial results and assessment of instrument effect. J. Zool. 1990, 220, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of variations in ocean color 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.R. Eye structure and foraging in king penguins Aptenodytes patagonicus. IBIS 1999, 141, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, T.W.; Johnsen, S.; Marshall, N.J.; Warrant, E.J. Visual Ecology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 232–261, 271, 281, 282. [Google Scholar]
- Wienecke, B.; Robertson, G. Comparison of foraging strategies of incubating king penguins Aptenodytes patagonicus from Macquarie and Heard islands. Polar Biol. 2006, 29, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienecke, B.; Robertson, G.; Kirkwood, R.; Lawton, K. Extreme dives by free-ranging emperor penguins. Polar Biol. 2007, 30, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, S.; Ruxton, G.D. Why did some ichthyosaurs have such large eyes? J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Millero, F.J. Modeling the density and isentropic compressibility of seawater. J. Solut. Chem. 2013, 42, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, G.L.; Dowling, J.E. Intracellular recordings from single rods and cones in the mudpuppy retina. Science 1973, 180, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamame, M.; Antezana, T. Vertical diel migration and feeding of Euphausia vallentini within southern Chilean fjords. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxall, J.P.; O’Connell, M.J. Diving patterns in relation to diet of gentoo and macaroni penguins at South Georgia. Condor 1988, 90, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosciano, N.G.; Putz, K.; Polito, M.J.; Rey, A.R. Foraging behaviour of Magellanic penguins during the early chick-rearing period at Isla de los Estados, Argentina. Ibis 2018, 160, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattern, T.; McPherson, M.D.; Ellenberg, U.; van Heezik, Y.; Seddon, P.J. High definition video loggers provide new insights into behaviour, physiology, and the oceanic habitat of a marine predator, the yellow-eyed penguin. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattern, T.; Ellenberg, U.; Houston, D.M.; Davis, L.S. Consistent foraging routes and benthic foraging behaviour in yellow-eyed penguins. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 343, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galapagos Penguin: Endangered Animals Spotlight. Available online: https://earth.org/endangered-species/galapagos-penguin-endangered-animals-spotlight/ (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Miller, A.K.; Trivelpiece, W.Z. Chinstrap penguins alter foraging and diving behavior in response to the size of their principle prey, Antarctic krill. Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacquié-Garcia, J.; Royer, F.; Dragon, A.-C.; Viviant, M.; Bailleul, F.; Guinet, C. Foraging in the darkness of the Southern Ocean: Influence of bioluminescence on a deep diving predator. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackleson, S.G. Light in shallow waters: A brief research review. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, P.W.; Vorobyev, M.; Cassidy, S.B.; Gokul, A.; Simkin, S.K.; Tran, H.; McGhee, C.N.; Zhang, J. Selected ocular dimensions of three penguin species. Vis. Res. 2022, 201, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, P.W.; Gerneke, D.A.; McGhee, C.N.J.; Zhang, J. Skeletal elements of the penguin eye and their functional and phylogenetic implications (Aves: Sphenisciformes: Spheniscidae). J. Morphol. 2021, 282, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, P.W.; Ober, W.C.; Gerneke, D.A.; Thomas, D.; Scadeng, M.; McGhee, C.N.J.; Zhang, J. Micro-CT guided illustration of the head anatomy of penguins (Aves: Sphenisciformes: Spheniscidae). J. Morphol. 2022, 282, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadden, P.W.; Gerneke, D.A.; Mcghee, C.N.J.; Zhang, J. Micro-computed tomography orbital anatomy of the little blue or fairy penguin, Eudyptula minor. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 48, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zusi, R. An interprepation of skull structure in the pengiuns. In The Biology of Penguins; Stonehouse, B., Ed.; Macmillan Press: London, UK, 1975; pp. 59–84. [Google Scholar]
- Baumel, J.J.; Nuttall Ornithological Club (USA); World Association of Veterinary Anatomists (USA); International Committee on Avian Nomenclature. Handbook of Avian Anatomy: Nomina Anatomica Avium; Nuttall Ornithological Club: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ghetie, V. Atlas de Anatomie a Pasarilor Domestice = Anatomical Atlas of Domestic Birds; Editura Avademiei Republicii Socialiste Romania: Bucharest, Romania, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, I.R. Evolution’s Witness: How Eyes Evolved; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 126, 178, 185, 186–187, 197, 199–201. [Google Scholar]
- Sivak, J.G.; Glover, R.F. Anatomy of the avian membrana nictitans. Can. J. Zool. 1986, 64, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potier, S.; Mikkus, M.; Kelber, A. Visual adaptations of diurnal and nocturnal raptors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 106, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suburo, A.M.; Scolaro, J.A. The eye of the magellanic penguin (Spheniscus magellanicus): Structure of the anterior segment. Am. J. Anat. 1990, 189, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmrich, W. Der skleralring der vögel. Z. Naturforsch. 1931, 65, 513–586. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, E.L.; Miller, R.C. The sclerotic ring in North American birds. AUK 1938, 55, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.R.; Young, S. The eye of the Humboldt penguin, Spheniscus humboldti: Visual fields and schematic optics. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1984, 223, 197–222. [Google Scholar]
- Bliss, C.D.; Aquino, S.; Woodhouse, S. Ocular findings and reference values for selected ophthalmic diagnostic tests in the macaroni penguin (Eudyptes chrysolophus) and southern rockhopper penguin (Eudyptes chrysocome). Vet. Ophthalmol. 2015, 18, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montague, T. A maximum dive recorder for little penguins. Emu-Austral Ornithol. 1985, 85, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivak, J. The role of a flat cornea in the amphibious behaviour of the blackfoot penguin (Spheniscus demersus). Can. J. Zool. 1976, 54, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundlach, R.H.; Chard, R.D.; Skahen, J.R. The mechanism of accommodation in pigeons. J. Comp. Psychol. 1945, 38, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafarnik, C.; Fritsche, J.; Reese, S. In vivo confocal microscopy in the normal corneas of cats, dogs and birds. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2007, 10, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivak, J.; Millodot, M. Optical performance of the penguin eye in air and water. J. Comp. Physiol. 1977, 119, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, H.C.; Sivak, J.G. Penguin vision in air and water. Vis. Res. 1984, 24, 1905–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivak, J.; Howland, H.C.; McGill-Harelstad, P. Vision of the Humboldt penguin (Spheniscus humboldti) in air and water. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Boil. Sci. 1987, 229, 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, S.E.; Hendrix, D.V.H.; Jones, M.P.; Ward, D.A.; Baine, K.H.; Franklin, S.R. Biometry, keratometry, and calculation of intraocular lens power for the bald eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus). Vet. Ophthalmol. 2015, 18, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, P.W.; Pas, A.E.; Cassidy, S.B.; Ober, W.C. The eye of the takahe, Porphyrio hochstetteri. N. Z. J. Zool. 2020, 48, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigatto, J.A.T.; Laus, J.L.; Santos, J.M.; Cerva, C.; Cunha, L.S.; Ruoppolo, V.; Barros, P.S.M. Corneal endothelium of the Magellanic penguin (Spheniscus magellanicus) by scanning electron microscopy. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2005, 36, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.C.; Mitchell, A.; Waas, J.R.; Paterson, A.M. An unexpected pattern of molecular divergence within the blue penguin (Eudyptula minor) complex. Notornis 2002, 49, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Grosser, S.; Scofield, R.P.; Waters, J.M. Multivariate skeletal analyses support a taxonomic distinction between New Zealand and Australian Eudyptula penguins (Sphenisciformes: Spheniscidae). Emu-Austral Ornithol. 2017, 117, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.P.; Collin, H.B. Functional morphology of the cornea of the little penguin Eudyptula minor (Aves). J. Anat. 2021, 239, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weddell, J.E.; Alvarado, J.A.; Hogan, M.J. Histology of the Human Eye: An Atlas and Textbook; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1971; pp. 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, O.; Schoenemann, B. Why are bones in vertebrate eyes? Morphology, development and function of scleral ossicles in vertebrate eyes—A comparative study. J. Anat. Physiol. Stud. 2019, 3, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, F.; Vieira, L.G.; Santos, A.L.Q.; De Simone, S.B.S.; Hirano, L.Q.L.; Silva, J.M.M.; Romão, M.F. Anatomy of the scleral ossicles in Brazilian birds. J. Morphol. Sci. 2017, 26, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Franz-Odendaal, T.A.; Vickaryous, M.K. Skeletal elements in the vertebrate eye and adnexa: Morphological and developmental perspectives. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2006, 235, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahecha, G.B.; de Oliveira, C.A. An additional bone in the sclera of the eyes of owls and the common potoo (Nictibius griseus) and its role in the contraction of the nictitating membrane. Cells Tissues Organs 1998, 163, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, C.M.; Rodarte-Almeida, A.C.d.V.; Santana, M.I.S.; Galera, P.D. Avian ophthalmic peculiarities. Ciência Rural 2018, 48, e20170904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemeier, O.W. The os opticus of birds. J. Morphol. 1950, 86, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, C. Iris colour of Humboldt penguins Spheniscus humboldti. Mar. Ornithol. 1999, 27, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Sivak, J.; Vrablic, O. The anatomy of the eye of the Adélie penguin with special reference to optical structure and intraocular musculature. Can. J. Zool. 1979, 57, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, G.L. The Vertebrate Eye and Its Adaptive Radiation; Hafner: New York, NY, USA, 1942; pp. 226, 295, 439. [Google Scholar]
- Sivak, J.; Hildebrand, T.; Lebert, C. Magnitude and rate of accommodation in diving and nondiving birds. Vis. Res. 1985, 25, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzir, G.; Howland, H.C. Corneal power and underwater accommodation in great cormorants (Phalacrocorax carbo sinensis). J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, A.; Howland, H.C. A history of studies of visual accommodation in birds. Q. Rev. Biol. 1996, 71, 475–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Johnson, C.A. Temporal properties of vision. In Adler’s Physiology of the Eye E-Book, 11th ed.; Levin, L.A., Ed.; Saunders/Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK, 2011; pp. 698–712. [Google Scholar]
- Suburo, A.M.; Marcantoni, M.; Scolaro, J.A. The structure of the eye in Spheniscus magellanicus: Dimensions of the cornea and lens in different age groups. Colonial Waterbirds 1988, 11, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiessen, L. Ueber die Beziehungen, welche zwischen dem Brechungsindex des Kerncentrums der Krystalllinse und den Dimensionen des Auges bestehen. Arch. Für Die Gesamte Physiol. Des Menschen Und Der Tiere 1882, 27, 510–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Pope, J.M.; Verkicharla, P.K.; Suheimat, M.; Atchison, D.A. Change in human lens dimensions, lens refractive index distribution and ciliary body ring diameter with accommodation. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suburo, A.M.; Scolaro, J.T. Environmental adaptations in the retina of the Magellanic penguin: Photoreceptors and outer plexiform layer. Waterbirds 1999, 22, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.A. The fundus oculi of birds: Especially as viewed by the ophthalmoscope. In A Study in the Comparative Anatomy and Physiology; Lakeside Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1917; pp. 75, 112–115, 132–133. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, N.S.; Hunt, D.M. Avian visual pigments: Characteristics, spectral tuning, and evolution. Am. Nat. 2007, 169, S7–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.; Johnson, W.E.; O’Brien, S.J.; Gomes, C.; Heesy, C.P.; Antunes, A. Adaptive genomic evolution of opsins reveals that early mammals flourished in nocturnal environments. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowmaker, J.; Martin, G. Visual pigments and oil droplets in the penguin, Spheniscus humboldti. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1985, 156, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Kong, L.; Hu, H.; Pan, H.; Xu, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, Q.; Jin, L.; et al. Two Antarctic penguin genomes reveal insights into their evolutionary history and molecular changes related to the Antarctic environment. Gigascience 2014, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Osorio, D. Vision in birds. In The Senses: A Comprehensive Reference; Masland, D., Albright, R.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, T.H.; Collins, J.S.; Licht, S. The cone oil droplets of avian retinas. Vis. Res. 1984, 24, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowmaker, J. Colour vision in birds and the role of oil droplets. Trends Neurosci. 1980, 3, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, J.T.; Normann, R.A.; Barber, P.W. Light intensification by cone oil droplets: Electromagnetic considerations. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1983, 73, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govardovskiĭ, V.I.; Golovanevskiĭ, E.I.; Zueva, L.V.; Vasil′Eva, I.L. Role of cellular organoids in photoreceptor optics (studies on microwave models). Zhurnal Evoliutsionnoi Biokhimii I Fiziol. 1981, 17, 492–497. [Google Scholar]
- Enoch, J.M. Response of a model retinal receptor as a function of wavelength. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1960, 50, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.S.; Vorobyev, M. Modelling oil droplet absorption spectra and spectral sensitivities of bird cone photoreceptors. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2005, 191, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toomey, M.B.; Corbo, J.C. Evolution, development and function of vertebrate cone oil droplets. Front. Neural. Circuits 2017, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondo, M.; Ando, H. Comparative histophysiological study of oil droplets in the avian retina. Jpn. J. Ornithol. 1995, 44, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suburo, A.M.; Herrero, M.V.; Scolaro, J.A. Regionalization of the ganglion cell layer in the retina of the Magellanic penguin. Colon. Waterbirds 1991, 14, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, J.P.; Nolan, P.M.; Collin, S.P.; Hart, N.S. Retinal ganglion cell topography and spatial resolving power in penguins. Brain, Behav. Evol. 2012, 80, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacho, M.; Ströckens, F.; Xiao, Q.; Güntürkün, O. Functional organization of telencephalic visual association fields in pigeons. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 303, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadden, P.W.; Vorobyev, M.; Turuwhenua, J.; Buckley, K.; Zhang, J.; McGhee, C.N.J. How well does that penguin see? In Proceedings of the 11th Australasian Ornithological Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 9 February 2022.
- Mercado, J.A.; Wirtu, G.; Beaufrère, H.; Lydick, D. Intraocular pressure in captive black-footed penguins (Spheniscus demersus) measured by rebound tonometry. J. Avian Med. Surg. 2010, 24, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, J.D.; Adkesson, M.J.; Allender, M.C.; Jankowski, G.; Langan, J.; Cardeña, M.; Cárdenas-Alayza, S. Determination of tear production and intraocular pressure with rebound tonometry in wild Humboldt penguins (Spheniscus humboldti). J. Avian Med. Surg. 2016, 31, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke-Elder, S. The Eye in Evolution: System of Ophthalmology; H. Kimpton: London, UK, 1958; Volume 1, p. 685. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.R. Visual fields and their functions in birds. J. Ornithol. 2007, 148, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.R. What is binocular vision for? A birds’ eye view. J. Vis. 2009, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakan, J.M.; Wylie, D.R. Two optic flow pathways from the pretectal nucleus lentiformis mesencephali to the cerebellum in pigeons (Columba livia). J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 499, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, O.C.; Wallman, J. Accessory optic system and pretectum of birds: Comparisons with those of other vertebrates (part 1 of 2). Brain, Behav. Evol. 1985, 26, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, Y.L.; Shashar, N.; Kröger, R.H. Adaptation in the optical properties of the crystalline lens in the eyes of the Lessepsian migrant Siganus rivulatus. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 2724–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iwaniuk, A.N.; Heesy, C.P.; Hall, M.I.; Wylie, D.R.W. Relative Wulst volume is correlated with orbit orientation and binocular visual field in birds. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2008, 194, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Uniocular Field | Posterior Blind Area | Binocular Field | Binocular Vertical Field | Cyclopean Field | Method | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humboldt, air | 155 | 78 | 28 | 125 | 282 | Histology, optical ray tracing | 47 |
| Humboldt, water | 123 | 114 | 0 | 77 | 246 | Histology, optical ray tracing | 47 |
| King, air | 183 | 14 | 29 | Fundus reflex | 18 | ||
| King, water | 127 | 70 | −36 1 | 254 (but missing 36 frontally | Fundus reflex | 18 | |
| Southern Rockhopper, air | 144 | 14 | Fundus reflex | 54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hadden, P.W.; Zhang, J. An Overview of the Penguin Visual System. Vision 2023, 7, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010006
Hadden PW, Zhang J. An Overview of the Penguin Visual System. Vision. 2023; 7(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleHadden, Peter W., and Jie Zhang. 2023. "An Overview of the Penguin Visual System" Vision 7, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010006
APA StyleHadden, P. W., & Zhang, J. (2023). An Overview of the Penguin Visual System. Vision, 7(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010006







