Abstract
Background: Commercial 3 Dimension (3D) scanners are relatively new to anthropometry. The purpose of this study was to explore ability of using a 3D imaging instrument to measure body volume with and without wearing a wetsuit. Three experiments were conducted to achieve this purpose: (1) to determine if the 3D imaging instrument could accurately measure volume of static objects; (2) to determine the resolution of accuracy of measuring volume of static objects; and (3) to compare whole-body volume of wearing a wetsuit using 3D imaging as well as another body volume measure (air displacement technique). Methods: Three experiments were performed: (1) measurement of volume of a mannequin head and a box using a 3D scanner, water displacement (for mannequin head), and dimension measurements (for box) techniques for determining volume, (2) volume measurements of 1, 2, and 3 layers of neoprene to assess the resolution capabilities of the 3D scanner, and (3) body volume with and without wearing a wetsuit using a 3D scanner and BodPod (air displacement instrument). Results: (1) Mannequin head volume using the 3D scanner was 1.46% greater than a water displacement technique; the box volume from scanning was significantly greater than volume calculated by measuring dimensions of a box. (2) The volume of a single layer of neoprene was 25.3% less with scanning than the criterion; the volume of two layers was 27.2% less than the criterion; the volume of three layers was not significantly different from the criterion. (3) Body volume was not influenced by the interaction of wetsuit and device; body volume was on average 5% greater with wetsuit than without regardless of instrument. Conclusions: We demonstrated that body volume as measured by a 3D scanner increased when a wetsuit was worn.
1. Introduction
3-Dimension (3D) imaging technology for quantifying segment shape and volume has been developed in a way that the technology is easy to use and has recently become affordable. The 3D technology and processing software continues to evolve and there is a growing number of 3D imaging options available. Research has been done to demonstrate the validity of some 3D imaging in quantifying volume of the body and/or segments [1,2].
An advantage of 3D imaging is that circumference and volume of body segments and/or the entire body can be made noninvasively. The application of 3D imaging has emerged in areas such as cycling aerodynamics [3], quantifying trunk segment mass relative to low back pain [4], and in the health sciences area through the measurement of body mass index (BMI) [5], for example.
A practical application of 3D imaging could be in the design of clothing in a way that the size and shape of the clothing is tailored specifically to an athlete. Some athletic garments are designed to be compressive. For example, it may be useful to custom make a triathlon wetsuit. In triathlons, it is very common for athletes to wear a wetsuit to provide thermoregulation as well as swim performance benefits [6,7]. However, there are limited data as to what size wetsuit an athlete should buy. Furthermore, wetsuit size recommendations are typically based upon height and weight of an athlete.
Anecdotally, the advice for selecting a wetsuit size is that the wetsuit should feel tight. However, there could be some negative aspects of having a wetsuit that is too tight [6,8,9]. For example, Agnelli and Mercer reported that shoulder muscle activity was greater while simulating swimming in a full sleeved wetsuit vs. no wetsuit [6]. Thus, wetsuits that fit improperly may increase resistance to movement and reduce performance. It has also been reported that resting blood pressure can increase if a wetsuit is too tight [8,9]. Therefore, it makes sense to have objective criteria for wetsuit fit. It may be possible to determine the amount of compression applied to the person by the wetsuit by measuring body volume while wearing the wetsuit vs. not wearing the wetsuit. However, presently it is not clear if the 3D imaging instrument has the resolution necessary to measure whole-body volume. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to explore ability of using a 3D imaging instrument to measure body volume with and without wearing a wetsuit. Three experiments were conducted to achieve this purpose: (1) to determine if the 3D imaging instrument could accurately measure volume of static objects; (2) to determine the resolution of accuracy of measuring volume of static objects; and (3) to compare whole-body volume of wearing a wetsuit using 3D imaging as well as another body volume measure (air displacement technique). The long-term goal of this work is to eventually be able to determine areas of high stress on the wetsuit material as well as where compression of the wetsuit may be too high.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Approach to the Problem
The overall goal of this experimental design was to determine if a commercial 3D scanner is an appropriate tool to detect body volume while wearing and not wearing a triathlon wetsuit. To understand the capabilities of the 3D scanner, three experiments were conducted.
The first experiment compared the volume measured of a mannequin head and of a box measured using the 3D scanner, water displacement (mannequin head), and measuring dimensions (box) techniques of determining volume. The second experiment assessed the resolution ability of the 3D scanner by measuring volume of different number of layers of wetsuit neoprene samples. The third experiment was done to compare the body volume of subjects while wearing a wetsuit and not wearing a wetsuit. A secondary purpose of this experiment was to compare the volume measurements between the 3D imaging scan and air displacement technique (BodPod).
2.2. Subjects
Experiment 1: No subjects were used for experiment one. Instead, a Styrofoam mannequin head and small rectangular box (12.0 × 7.0 × 7.0 cm; volume: 588 mL) were selected for scanning.
Experiment 2: No subjects were used for experiment two. Instead, three neoprene squares were cut from a wetsuit. The measured dimensions of the layers yielded volumes of 42.5 mL, 40.25 mL, and 41.5 mL.
Experiment 3: Ten subjects participated in experiment three (8 males, 2 females, age: 24 ± 6 years; mass: 68 ± 13 kg; height: 169 ± 8 cm; BMI: 23.6 ± 3.3 kg·m−2; Percent Body Fat (%BF): 13.6 ± 5.9%). Each subject was fitted to a wetsuit of appropriate size following manufacturer guidelines for height and weight. 5 subjects used a men’s medium sized wetsuit, 2 used a men’s small, 1 used a men’s large, 1 used a women’s small, and 1 used women’s medium. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (protocol #876958, approved 16 May 2016) of the host university and all subjects gave their informed consent prior to testing.
2.3. Instrumentation
A commercial 3D scanner (Structure Sensor, Occipital Inc., Boulder, CO, USA) was used in all experiments. The scanner was connected to a laptop via a USB cable. The scanner camera was attached to the laptop using a Velcro patch to ease mobility of the laptop/camera unit. 3D Scans were collected from specialized software (Skanect, Occipital, San Francisco, CA, USA) then exported and analyzed in an open-source application (MeshLab) for processing 3D triangular meshes. Within this application, geometric volumes were calculated and used for analysis.
For experiment 1, volume of objects was also determined using water displacement technique. A clear 5-gallon translucent bucket was filled with water for this purpose.
For experiment 3, an air displacement plethysmography (ADP) instrument (BodPod, Cosmed, Concord, CA, USA) was also used to measure body volume.
2.4. Procedures
Each 3D scan was conducted by recording a continuous scan while moving around an object of interest. For all experiments, a research team member scanned each object of interest by moving the laptop/scanner unit physically around the object, pausing eight times at different positions to move and tilt the scanner upwards and downwards. This was done to increase the capture detail of corners and crevices (e.g., axilla, groin, etc.) of the objects and subjects.
2.4.1. Experiment One
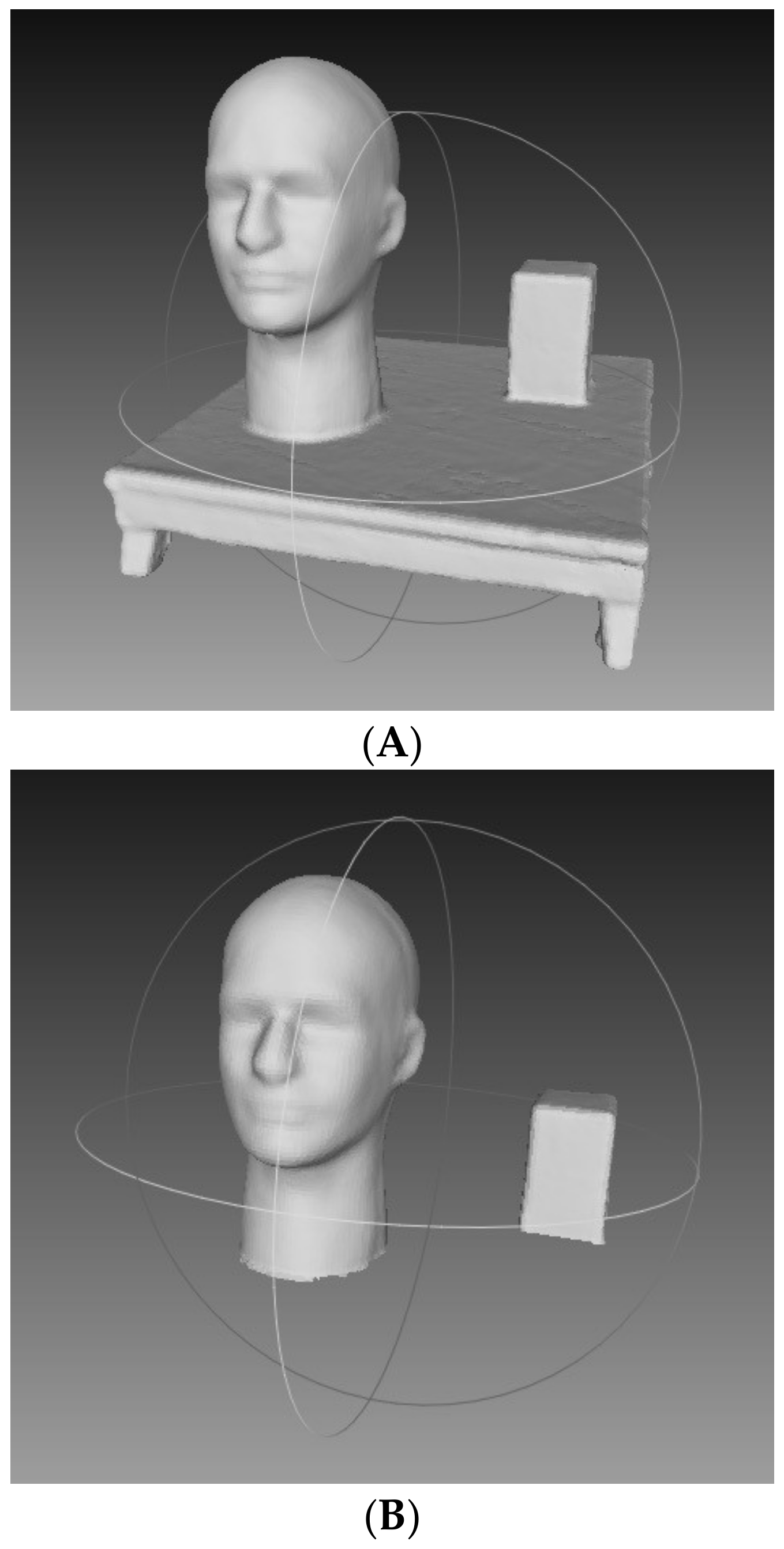
The mannequin head and box were placed on a platform for scanning (Figure 1). 25 scans were taken by the same researcher. Once scans were completed, holes in the 3D mesh were filled by selecting the watertight procedure in Skanect. Next, the object of interested needed to be dissected from the platform that was also present in the scanned image. The dissection was done in MeshLab (Figure 1). Once dissection was complete, volume was calculated for the mannequin head and box separately.
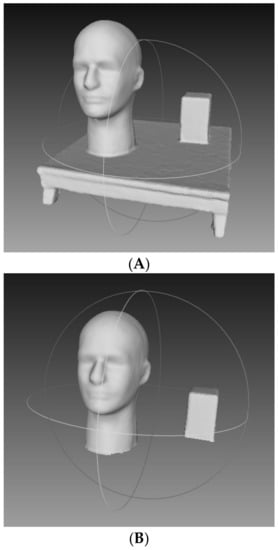
Figure 1.
Example 3D scan of mannequin head and box. (A) Raw image on platform. (B) Object dissected from table.
The dimensions of the box were recorded to the nearest mm and used to calculate its volume (12.0 × 7.0 × 7.0 cm; volume = 588 mL).
The water displacement technique was used to measure the volume of the mannequin head. A clear 5-gallon translucent bucket was filled with water and left to settle. A line was drawn on the outside of the bucket level with the water. The mannequin was fully submerged by hand, allowing no more than 1 cm of the fingers to be submerged. To minimize the influence of the fingers on volume, water level was set to just greater than the length of the head when submerged. Once the mannequin head was submerged and water settled, a line was marked at the new water level and the mannequin head was removed.
With the mannequin head removed from the water, the amount of water displaced was determined by adding water in 50 mL increments until water level reached the top line. The amount of added water was recorded and used as the measure of the volume of the mannequin head. Water was then removed until it was level with the original level and the process repeated. A total of 5 measures were taken. Volume of water displaced was 4250 mL (50 mL resolution) each time.
2.4.2. Experiment Two
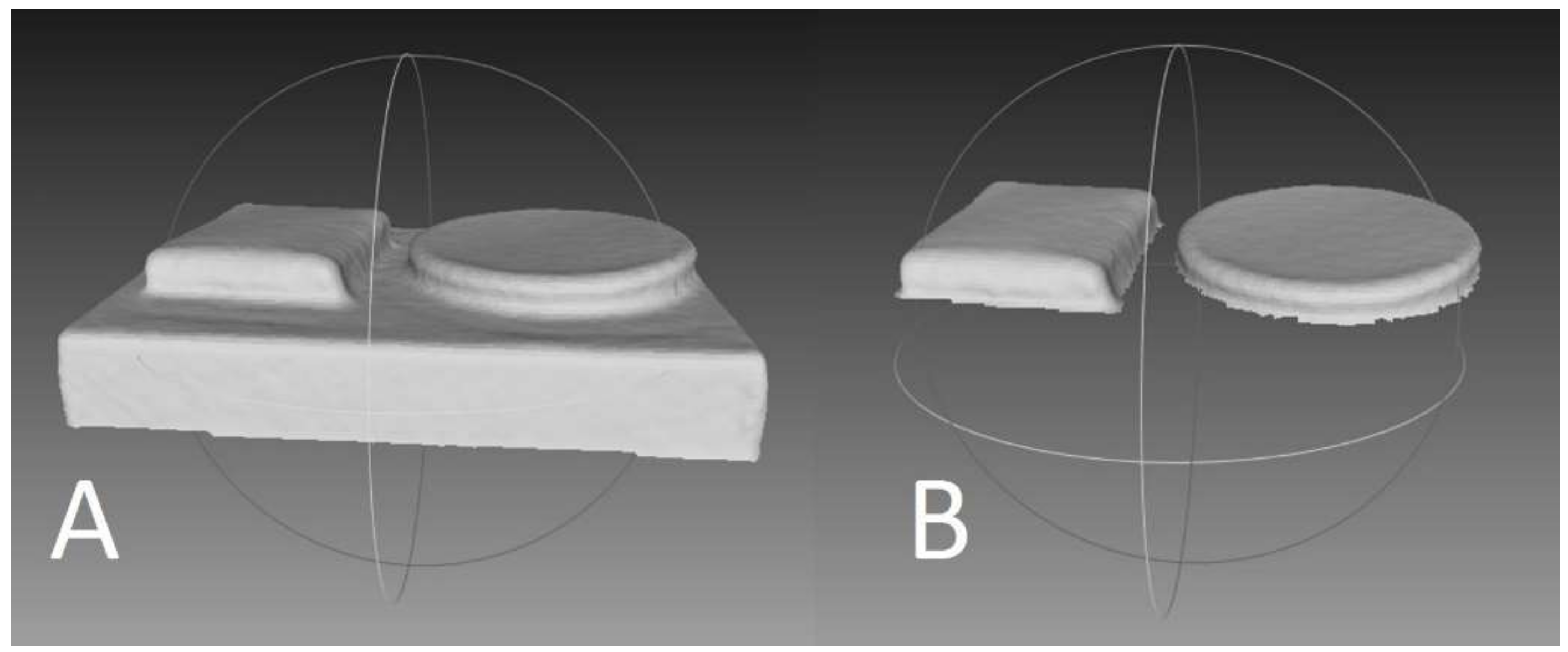
Three rectangular shapes were cut from a single wetsuit. The neoprene rectangles were placed on a platform (Figure 2). Ten scans were collected for each condition: one layer, two layers, and three layers. The same neoprene sheets were scanned by two separate research assistants. The same processing and dissection procedures used in experiment one were used in experiment two. The neoprene sheets were measured manually (width × height × depth) and used to calculate volume. The volume of each layer was 42.5 mL, 40.25 mL, and 41.5 mL (41.4 ± 1.1 mL).
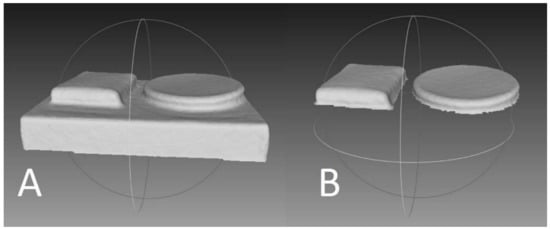
Figure 2.
Three layers of neoprene and a reference shape (not used in the experiment). (A) Raw image of object on platform. (B) Object of interest dissected from platform. Only the rectangular neoprene layers were of interest.
2.4.3. Experiment Three
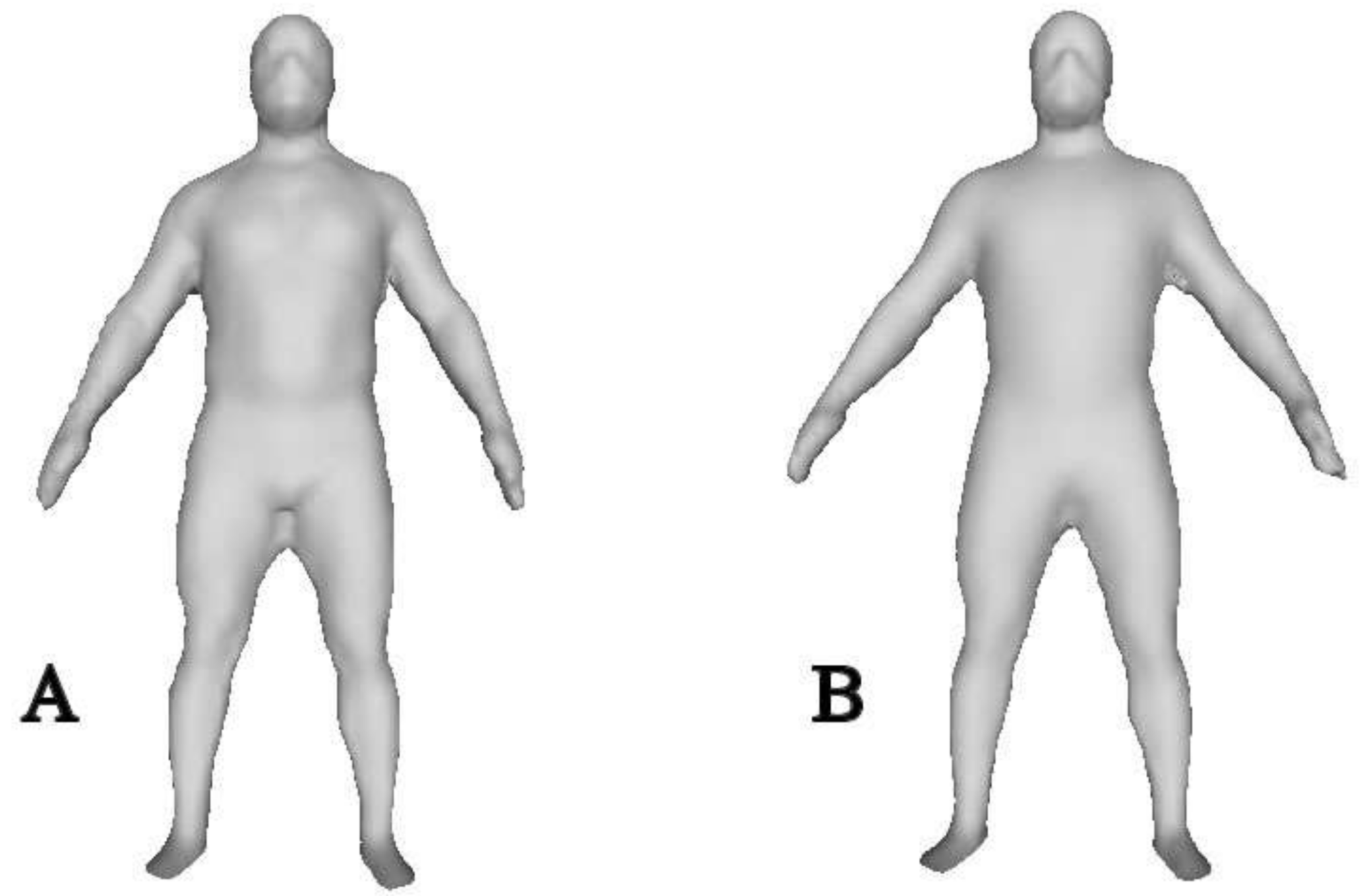
Subjects wore a head cap to reduce the effect hair may have on volume measurements. Subjects were each scanned with and without wearing a wetsuit. An example of the scans is illustrated in Figure 3. Non-wetsuit scans were done wearing compression shorts and sports bra for females. During the scan, subjects were asked to stay as still as possible to minimize the influence of movement on subsequent volume measurement. Furthermore, subjects were asked to hold their arms laterally to allow the scanner to see delineate the axial area. Each scan took approximately 30 s. Scans that resulted in obvious errors due to movement and/or limb placement or did not fully capture the entire body were discarded and repeated.
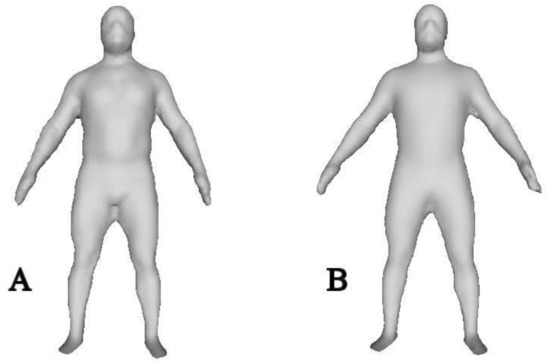
Figure 3.
Illustration of a single scan for a single subject (A) not wearing a wetsuit and (B) wearing a wetsuit.
Body volume was also measured via ADP by having subjects sit in the BodPod. This measurement was performed in accordance with manufacture procedures, which included a system warm up, calibration, and measurement of subject weight. During body volume measurement, subjects were instructed to breathe lightly and not to move once the BodPod door was closed.
Condition order was conducted as follows: No wetsuit by 3D scanner, with wetsuit by 3D scanner, with wetsuit by ADP, and no wetsuit by ADP. This specific order was followed because the wetsuit is difficult to take on and off. Three trials were done for each condition for a total of 12 volume measurements.
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Experiment One
One-Sample t-tests were performed to determine the validity of the measured 3D scan volumes (mannequin, box) to the respective criterion measurement. The criterion measurement of the mannequin was 4250 mL using water displacement and the box was 588 mL. The t-score (t = 2.064) was based upon 24 degrees of freedom and an alpha level of 0.05 for a two-tailed test.
For descriptive purposes, error measurements were calculated as the difference in volume between the 3D scan from the 4250 mL volume attained from the water displacement test for the mannequin head. Likewise, the difference in volume of the box measured using the 3D scan and measured dimensions was calculated.
2.5.2. Experiment Two
Two analyses were conducted for Experiment Two: First, one-Sample t-tests were performed to determine the validity of the measured 3D scan volumes from one, two, and three layers of neoprene. The t-score (t = 2.262) was based upon 9 degrees of freedom and an alpha level of 0.05 for a two-tailed test. Second, a one-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare volume between layers. If the omnibus F-ratio was significant, post hoc tests were used to compare volume of 1 layer vs. 2 layers, and 2 layers vs. 3 layers.
For descriptive purposes, error measurements were calculated. The scanned volume from each trial was subtracted from the measured volumes for 1, 2, and 3 layers of neoprene.
2.5.3. Experiment Three
The volume measures of the three trials from each of the four conditions (3D scan vs. ADP; Wetsuit vs. no wetsuit) were averaged for each subject by condition and used for analysis. A 2 (wetsuit, no wetsuit) × 2 (3D scan, ADP) ANOVA was used to compare body volume measurements (α = 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Experiment One
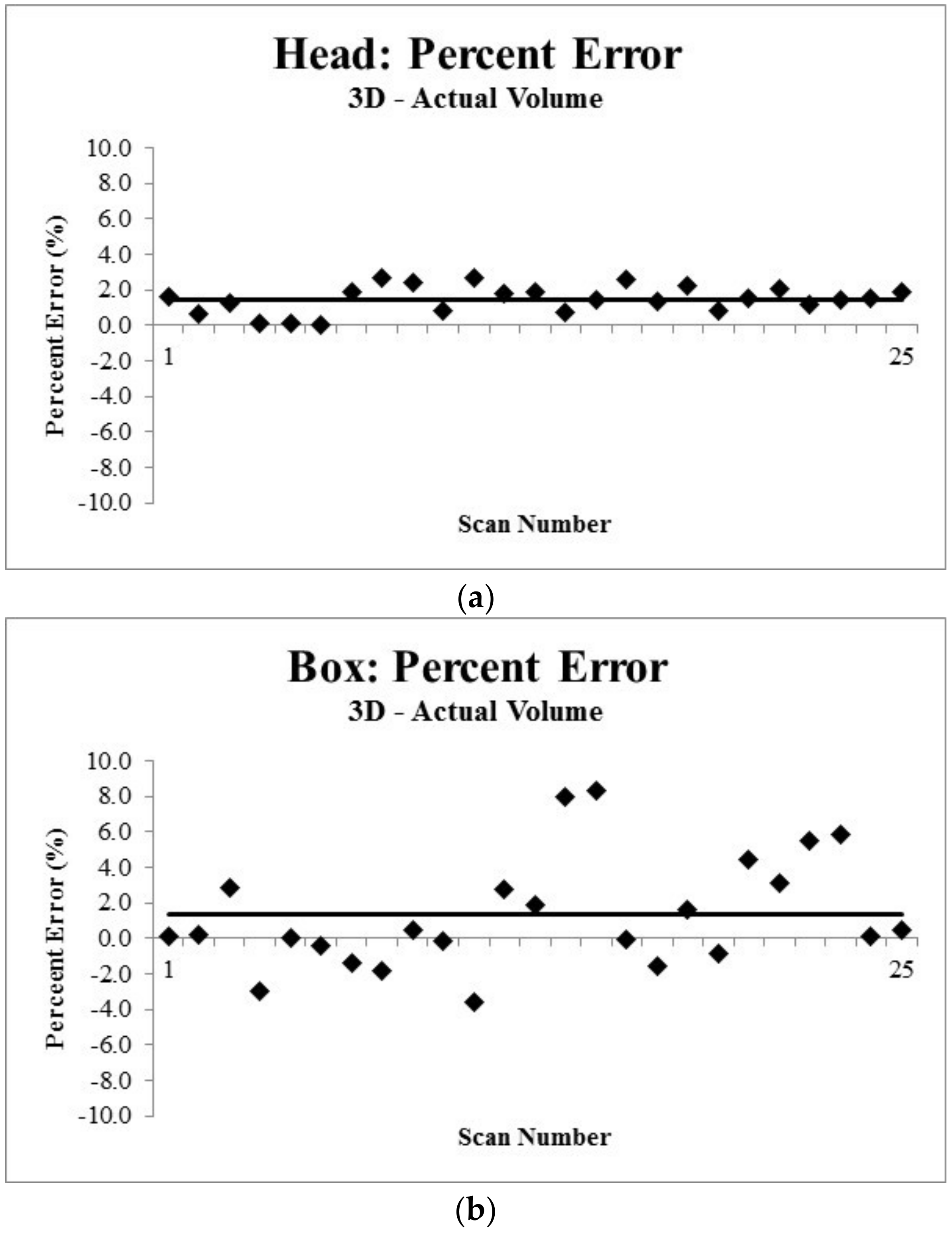
The mannequin volume measured by the 3D scanner was 1.46% greater than the water displacement measurement (4311.89 ± 32.92 mL vs. 4250 mL, t(24) = 9.3987, Figure 4, p < 0.0001). The box volume measured by the 3D scanner was significantly greater than the volume measured by ruler (595.63 ± 18.45 mL vs. 588 mL, t(24) = 2.0678, p = 0.0496). Figure 4a,b is an illustration of the error measurement (i.e., difference in volume between techniques for each measurement).
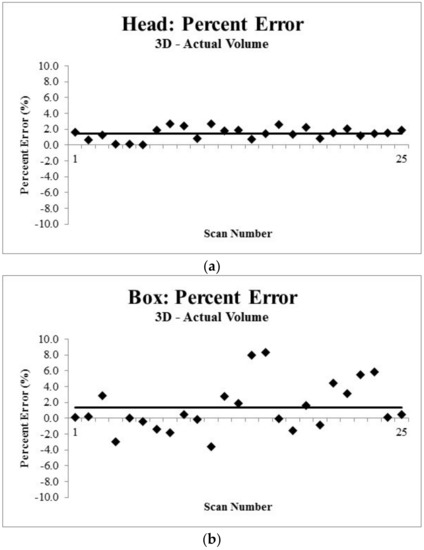
Figure 4.
Percent error between the volume measured using the 3D scan of the Mannequin Head (a) and of a box (b). Using a one sample t-test, the volume measured using the 3D scanner was different than the criterion measure (p < 0.05). Each symbol represents the percent error for a scan (presented in order completed) with the solid line representing the mean percent error.
3.2. Experiment Two
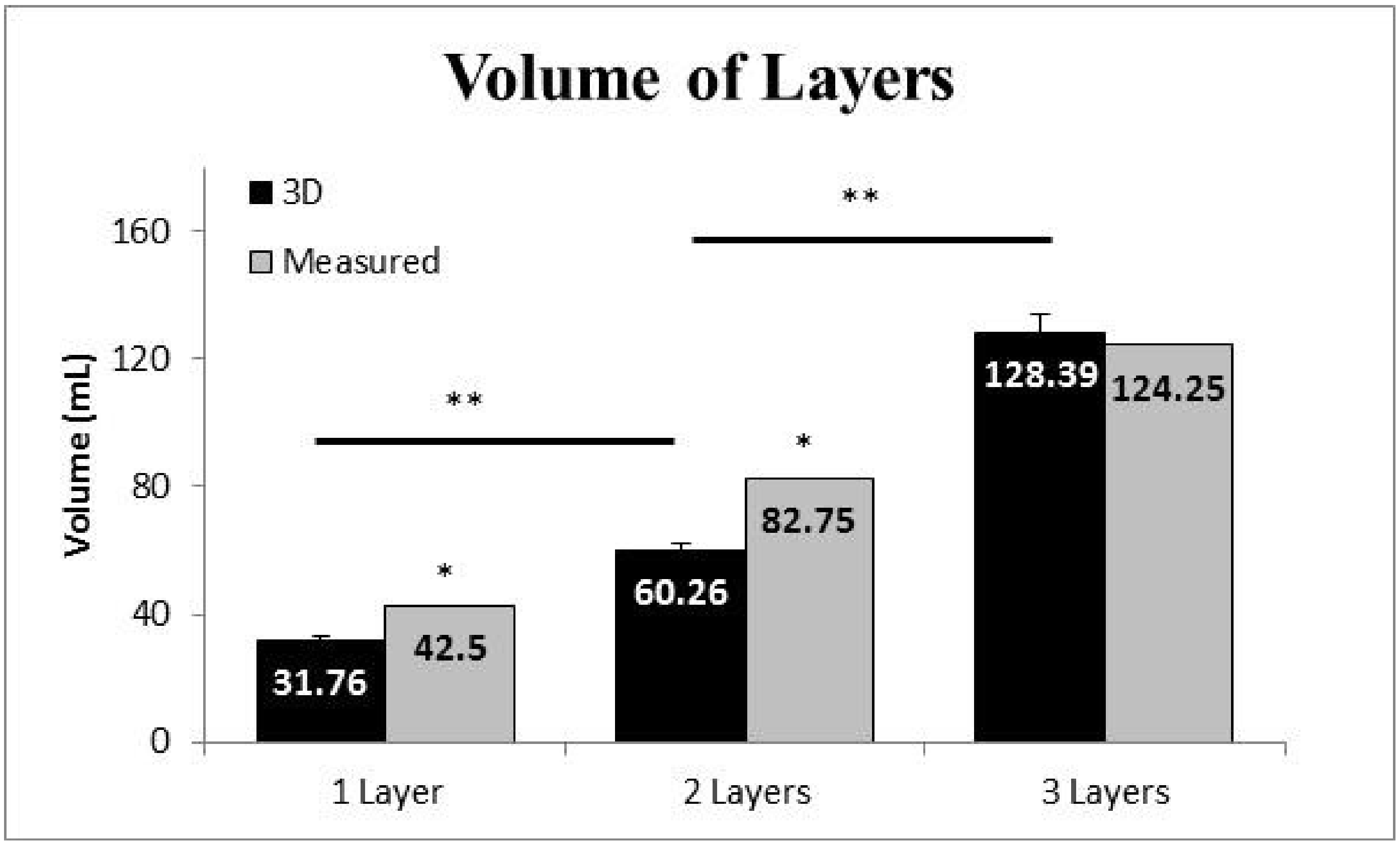
The single-layer volume measured by the 3D scanner was 25.3% less than the criterion measurement (31.76 ± 6.39 mL vs. 42.5 mL, t(9) = 15.717, p < 0.0001). The double-layer volume measured by the 3D scanner was 27.2% less than the criterion measurement (60.26 ± 10.11 mL vs. 82.75 mL, t(9) = 7.035, p < 0.0001). The triple-layer volume measured by the 3D scanner was not significantly different than the criterion measurement (128.39 ± 28.13 mL vs. 124.15 mL, t(9) = 0.477, p = 0.645).
Comparing the volume measurements of the 3D scanner among layers it was determined that the volume measured of one layer was different between the volume measured by two layers (mean difference: 28.50 mL; p < 0.05) as well as between two and three layers (mean difference: 68.13 mL; p < 0.05) (Figure 5).
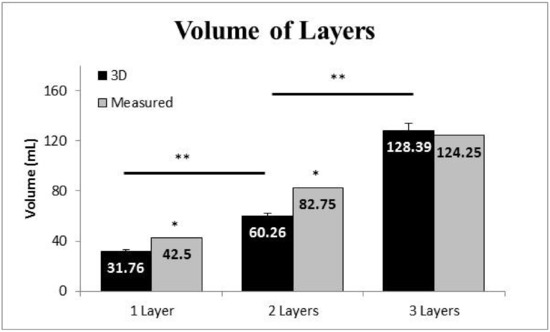
Figure 5.
Mean and standard error of the mean for volume measures of 1 layer, 2 layers, and 3 layers of neoprene. Note: * indicates the volume measured by the 3D scan was different than the measured (criterion) volume (p < 0.05); ** indicates that the volume measured by the 3D scan was different between consecutive layers (p < 0.05).
3.3. Experiment Three
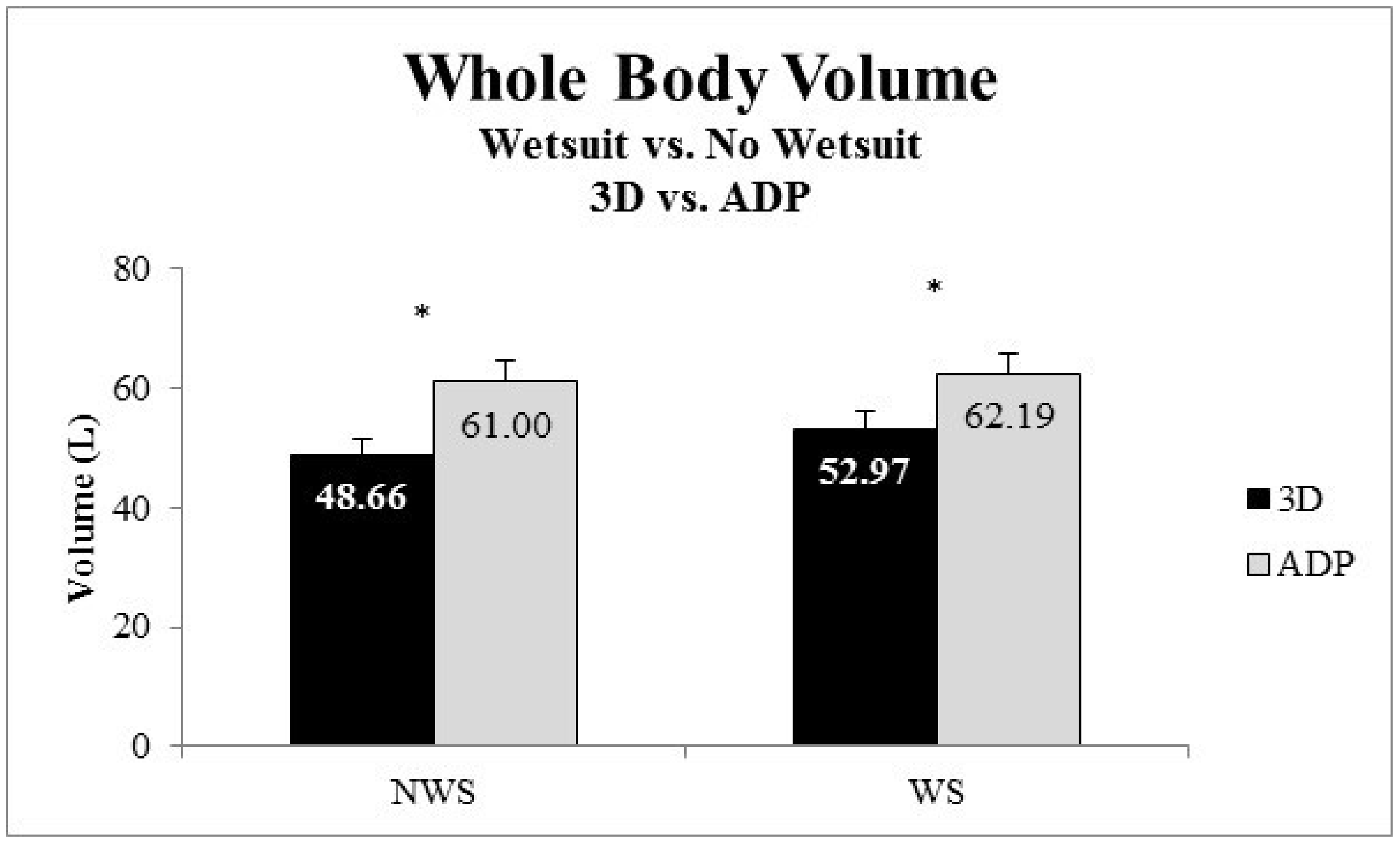
Body volume was not influenced by the interaction of wetsuit and device (p > 0.05). Body volume was on average 5.02% greater with the wetsuit than without the wetsuit regardless of instrument used (Figure 6). Specifically, as measured by the 3D scanner body volume was greater with wetsuit (52.97 ± 10.36 L) then without (48.66 ± 8.86 L) (p < 0.05). Likewise, body volume was greater with the wetsuit than without the wetsuit using ADP (wetsuit: 62.19 ± 11.79 L vs. no wetsuit: 61.00 ± 11.84 L, p < 0.05). Body volume was different between instruments (p < 0.05), with body volume being on average 17% less using 3D scan vs. ADP (Figure 6).
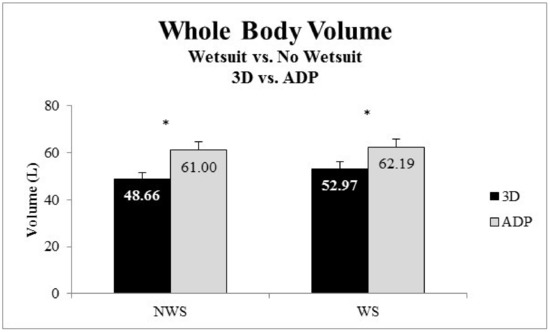
Figure 6.
Mean and standard error of the mean of whole-body volume measured by the 3D scan and air displacement plethysmography (ADP) while not wearing a wetsuit (NWS) and wearing a wetsuit (WS). Note: * Volume was greater while wearing a wetsuit regardless of instrument (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
There were clear statistical differences between the volume measured by the 3D scanner and criterion measures. However, the volume measurements using the 3D scanner were remarkably reasonable given the ease of recording 3D scans. For example, the 3D scanner yielded volume measures of static objects were within 2% of the criterion measure of volume. Specifically, the volume measured of mannequin head was 1.46 ± 0.77% different to the volume measured using a water displacement technique. Likewise, the volume measured using the 3D scanner of a box was 1.30 ± 3.14% of the volume calculated by measuring the dimensions of the box. Interestingly, the greatest error in measurement of volume was 8.28% greater volume using the 3D vs. measured dimensions technique. This is partly explained by the procedures that we used to scan the layers. We placed the layers flat on a surface and scanned—which means that the bottom surface area was not scanned. In any case, it seems that the 3D scanner was better suited to measuring volume of an object without sharp edges (i.e., the mannequin head).
We also were able to determine that the volume measured by the 3D scanner could discern the difference in volume of one, two, and three layers of neoprene (each with a thickness of about 41.4 ± 1.1 mL). This information was important for confirming that the 3D scanner could be used to detect a possible change in whole-body volume of a person wearing a wetsuit.
We were also able to determine that whole-body volume measured using the 3D scanner was greater while wearing a wetsuit vs. no wetsuit. Although this would seem obvious since the wetsuit itself adds volume to the body, the wetsuit also provides compression to the person. Prior to this research, it was not known if whole-body volume would be influenced by wearing the wetsuit due to compression. Interestingly, the volume measured by ADP was 17% less using the 3D scanner vs. ADP.
Our whole-body volume measures are similar to other studies [2,5,10] given the size subjects in our study. For example, Daniell et al. [5] reported whole-body volume of “thin” subjects (BMI: 23.9 ± 4.6 kg·m−2) of 52.7 ± 4.9 L (women) and 62.4 ± 5.4 L (men). In our study, whole-body volume (all subjects, both techniques) was 56.2 ± 11.8 L. Subjects in our study had a BMI of 23.6 ± 3.26 kg·m−2.
Buffa et al. [11] reported that a 3D scan technique yielded volume data of an upper arm that were reliable and valid. In that study, volume error measures of an arm were between 1.4% and 2.6% —which is similar to the error observations we made. In our study, scans were made by having the researcher freely move the scanner around the object of interest. Buffa et al. [11] constructed a device that controlled the movement of the scanner about the object. It seems that the error we observed was reasonable especially given the lack of control of movement of the scanner. Interestingly, Buffa et al. [11] also reported a greater error in measuring volume of inanimate objects of known dimensions.
Ng et al. [2] also observed a smaller whole-body volume measured using a 3D scan technique vs. ADP. Specifically, Ng et al. [2] reported a mean difference of 4.15 L between 3D scan and ADP but a high correlation of whole-body volume measured by the two techniques (R2 = 0.99). In the present study, the mean difference in whole-body volume was 12.3 L between instruments. The correlation of volume measurements between instruments was calculated (Pearson Product-Moment Correlation Coefficient) and a strong correlation between measurement techniques (R2 = 0.68) was observed. The difference in observations between our study and Ng et al. [2] may be related to the type of subjects tested and/or the 3D scan techniques. The subjects tested by Ng et al. [2] had a higher BMI (27.5 ± 6.5 kg·m−2) than subjects in our study. It may be that accuracy of whole-body scan is related to body size. Regarding measurement techniques, Ng et al. [2] had subjects stand and grasp handles and the 3D scanner moved around the subject in a fixed frame. In our study, subjects held their arms out to the side and a researcher moved the scanner (by hand) around the subject. From the example images of a single subject presented in Figure 3, it is clear that the accuracy of the 3D scan to capture areas under the arms or between legs is compromised. Given this, a main source of error when measuring whole-body volume from the 3D scanner is the posture the subject is asked to hold while the scan is conducted. For example, we asked subjects to stand with their arms out from their sides. That allowed for a level of detail that separated the arms from the trunk. The downside of this position was that it was hard for the subject to stand entirely still during the scan—which took about 30 s to complete. Any movement of the subject during the scan would erroneously influence the measured volume. It seems that any movement may have resulted in underestimating the whole-body volume since 3D scan volume was less than volume determined using ADP.
Another source of error in our study was that we used a specific order when testing the wetsuits. Another approach would be to randomize order of putting the wetsuit on and take only a single trial for each time the wetsuit is put on. Along with this, we did not test the consistency of body volume between researchers conducting the scans. A future study could be conducted to determine whether scans are influenced by the process a specific researcher would use. For example, users may vary in how long the scan, the path followed when scanning, as well as how far the scanner is from the object. This study provides only partial insight into the potential of using a 3D scanner to measure whole-body volume.
The volume measured from the 3D scanner is also influenced by the data processing steps. The 3D scanner’s accompanied software performs a reconstruction prior to “fill holes” with a watertight strategy and medium smoothing. Unlike experiments 1 and 2, experiment 3 scans did not require any dissections (i.e., head and feet are included in the scan). The processed scan was exported to MeshLab, where a built-in function calculates geometric volume of the scan.
We also recognize that the criterion measures include a source of error. For example, when measuring volume using the water displacement technique, the level of accuracy of water displacement was influenced by visual inspection of water level and using 50 mL increments to determine volume. Likewise, it was necessary to hold the objects underwater and the tips of the fingers had to be submerged. Likewise, we measured the dimensions of the box using a ruler visually with the accuracy of mm. Finally, volume measured by ADP is also influenced by several factors including such as clothing, breathing rate, residual lung volume [12]. It is known that body composition determined from ADP, dual energy X-ray (DEXA), and hydrostatic weighing can yield different values due to unique sources of error from each technique [12].
Taking these factors into consideration, it is remarkable that the 3D scanner yields volume measures that are even remotely close to other techniques to measuring volume. Furthermore, the 3D scanner was successful at determining whole-body volume was different while wearing a wetsuit. This is important since a longer-term goal of this work is to develop an algorithm to yield a custom-made wetsuit. Presently, wetsuit fit is largely-based upon athlete height and weight. It may be possible to determine how to use a 3D scan to custom cut a triathlon wetsuit for an athlete. However, there is still a need for further advances in the development of this instrument to yield highly accurate data.
Interestingly, whole-body volume was greater while wearing a wetsuit vs. not wearing the wetsuit. Although this may seem obvious since a layer of neoprene is added to the body, the wetsuit is designed in a way that provides compression to the person. We were interested as to whether the level of compression would cause a reduction of volume or keep whole-body volume the same despite adding a layer of neoprene to the body. Based upon the analysis of the data collected for this study, it is concluded that the wetsuit does not provide compression to the level that whole-body volume would be influenced. This study is limited, of course, in that we tested only one model of wetsuit and one size of wetsuit. Future research is needed to determine if there are areas of high-stress placed on the body while wearing the wetsuit. For example, the trunk region may be more susceptible to areas of high stress if the person wearing the wetsuit has a high level of trunk adiposity. Given the range of body sizes that use wetsuits, it makes sense to continue to explore the importance of creating custom made wetsuits that fit the specific body size of an athlete.
5. Conclusions
Whole-body volume was measured using 3D scanning and ADP. It was determined that that the whole-body volume measured using the 3D scan was greater while wearing a triathlon wetsuit vs. not wearing a wetsuit.
We also determined that the volume measured of static objects using the 3D scan were statistically different to criterion measures but there was less than 2% error in measurement. We also determined that the 3D scan could be used to measure volume differences of different layers of neoprene (thickness 42.5 mm). However, the measurement error was greatest for the smallest volume (i.e., 1 layer) measured. Finally, the 3D scanner was able to detect differences in whole-body volume when subjects wore a triathlon wetsuit vs. not wearing the wetsuit.
Acknowledgments
Partial funding provided by Nevada INBRE which is funded by grants from the National Center for Research Resources (5P20RR016464-11) and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (8 P20 GM103440-11) from the National Institutes of Health (NIH/NIDDK grant R25DK078382).
Author Contributions
Leland Barker and John A. Mercer conceived and designed the experiments. Diego Mendoza performed the experiments in experiment three. Leland Barker performed all experimental procedures and analyzed data. Leland Barker and John A. Mercer wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
References
- Daanen, H.A.M.; Ter Haar, F.B. 3D whole body scanners revisited. Displays 2013, 34, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, B.K.; Hinton, B.J.; Fan, B.; Kanaya, A.M.; Shepherd, J.A. Clinical anthropometrics and body composition from 3D whole-body surface scans. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doval, P.N. Aerodynamic Analysis and Drag Coefficient Evaluation of Time-Trial Bicycle Riders. MSc Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI, USA, December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pryce, R.; Kriellaars, D. Body segment inertial parameters and low back load in individuals with central adiposity. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 3080–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniell, N.; Olds, T.; Tomkinson, G. Volumetric differences in body shape among adults with differing body mass index values: An analysis using three-dimensional body scans. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2014, 26, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnelli, C.; Mercer, J.A. Muscle Activity during Dryland Swimming while Wearing a Triathlon Wetsuit. Int. J. Kinesiol. Sports Sci. 2018, 6, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomikawa, M.; Shimoyama, Y.; Nomura, T. Factors related to the advantageous effects of wearing a wetsuit during swimming at different submaximal velocity in triathletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2008, 11, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, A.; Dufek, J.; Navalta, J.; Lough, N.; Mercer, J. A first look into the influence of triathlon wetsuit on resting blood pressure and heart rate variability. Biol. Sport 2017, 34, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soucy, M.; Ciulei, M.; Mercer, J. Does Wearing a Triathlon Wetsuit Influence Resting Blood Pressure for Females? Gazzeta Med. Ital. 2016, 175, 523–527. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Niu, J.; Ran, L.; Liu, T. Estimation of Human Body Volume (BV) from Anthropometric Measurements Based on Three-Dimensional (3D) Scan Technique. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2017, 41, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffa, R.; Mereu, E.; Lussu, P.; Succa, V.; Pisanu, T.; Buffa, F.; Marini, E. A new, effective and low-cost three-dimensional approach for the estimation of upper-limb volume. Sensors 2015, 15, 12342–12357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, D.A.; Goran, M.I.; McCrory, M.A. Body-composition assessment via air-displacement plethysmography in adults and children: A review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 75, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).