Breath Stacking: Acute Effects on Cough Peak Flow and Chest Wall Volumes of Healthy Subjects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Type
2.2. Procedures and Data Collection
2.3. Spirometry
2.4. Respiratory Muscle Strength
2.5. Assessment of Cough Peak Flow and Chest Wall Volumes
2.6. Breath Stacking
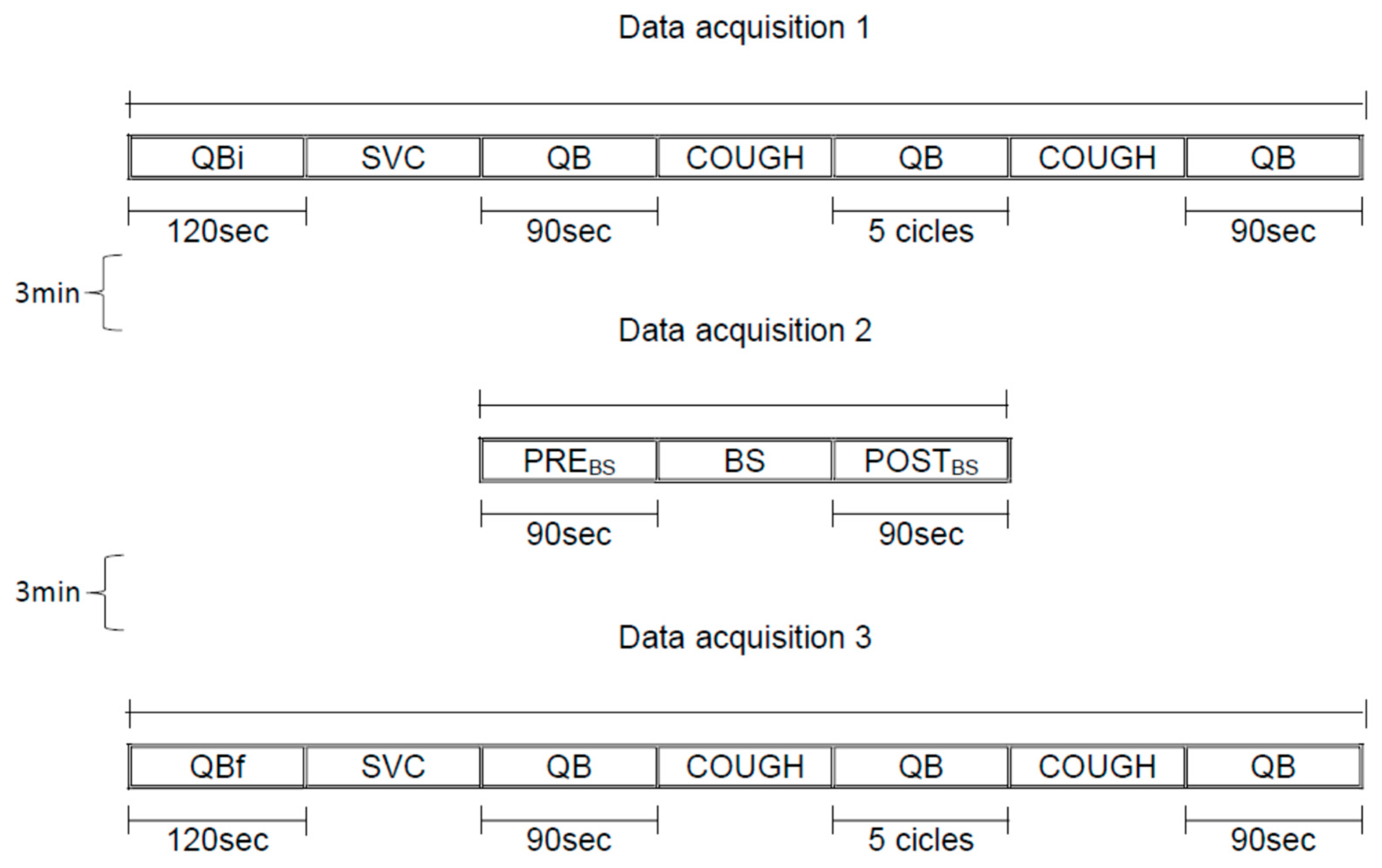
2.7. Study Design
- (a)
- Data acquisition 1: 120 s of quiet breathing initial (QBi), slow vital capacity maneuver (SVC), 90 s of quiet breathing (QB), spontaneous cough, 5 cycles of quiet breathing (QB), spontaneous cough, 90 s of quiet breathing (QB);
- (b)
- Data acquisition 2: 90 s of quiet breathing pre Breath Stacking maneuver (PREBS), Breath Stacking (BS), 90 s of quiet breathing post Breath Stacking maneuver (POSTBS);
- (c)
- Data acquisition 3: 120 s of quiet breathing initial (QBi), slow vital capacity maneuver (SVC), 90 s of quiet breathing (QB), spontaneous cough, 5 cycles of quiet breathing (QB), spontaneous cough, 90 s of quiet breathing (QB).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Breath Stacking on Cough Peak Flow
3.2. Effects of Breath Stacking on Total and Operational Chest Wall Volumes
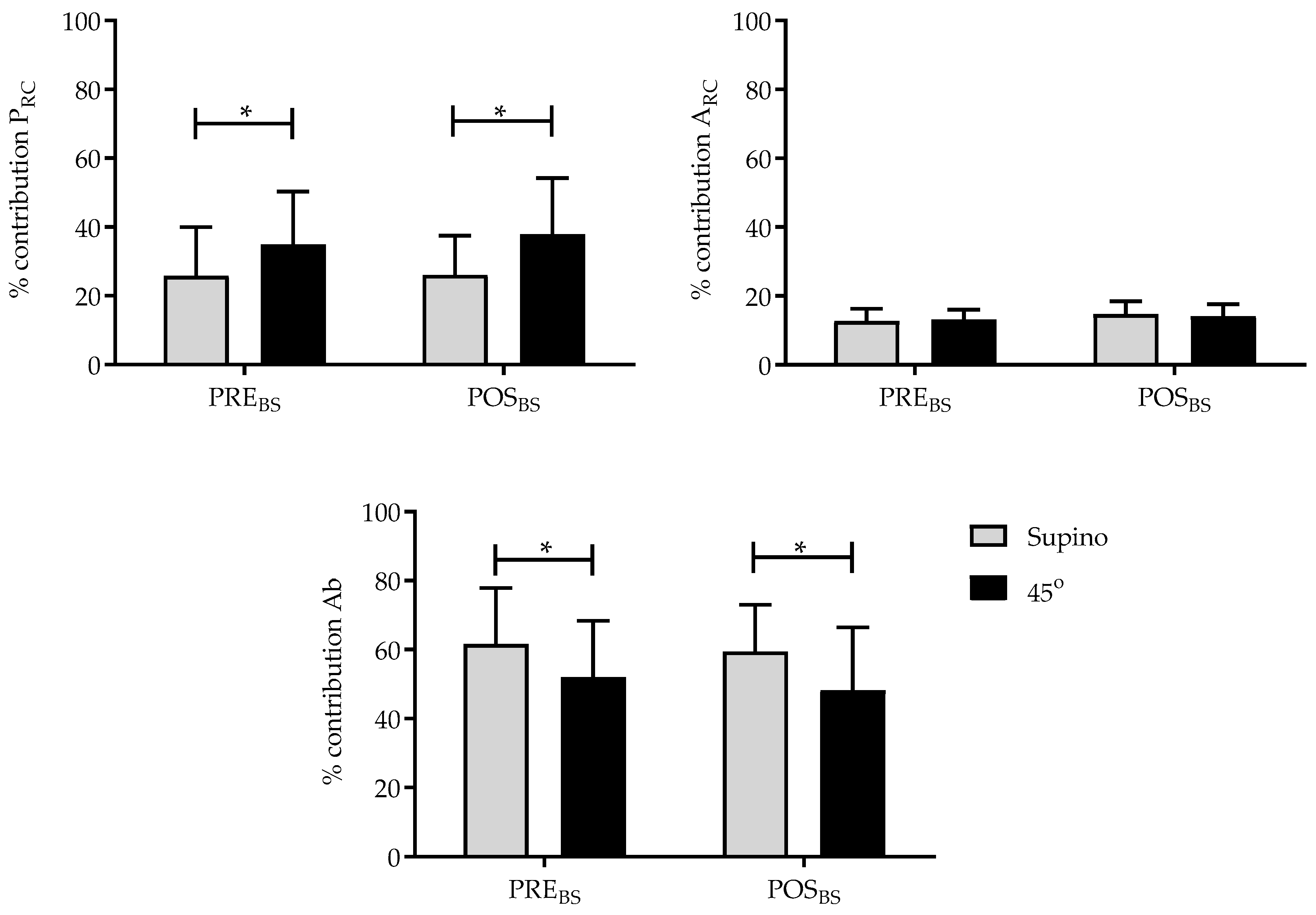
3.3. Effects of Breath Stacking on the Contribution of the Compartments to Tidal Volume
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BS | Breath Stacking |
| CPF | Cough Peak Flow |
| FVC | Forced Vital Capacity |
| FEV1 | Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 Second |
| MIP | Maximal Inspiratory Pressure |
| MEP | Maximal Expiratory Pressure |
| SNIP | Sniff Nasal Inspiratory Pressure |
| FRC | Functional Residual Capacity |
| OEP | Optoelectronic Plethysmography |
| VT(CW) | Tidal Volume of Chest Wall |
| ΔVT(CW)/Δt | Derived by the volume displaced by chest wall and time during the cough |
| QBi | Quiet Breathing initial |
| QB | Quiet Breathing |
| SVC | Slow Vital Capacity |
| PREBS | Pre–Breath Stacking |
| POSTBS | Post–Breath Stacking |
| BIM | Body Index Mass |
| VT(rcp) | Tidal Volume of Pulmonary Rib Cage |
| VT(rca) | Tidal Volume of Abdominal Rib Cage |
| VT(Ab) | Tidal Volume of Abdomen |
| PRC | Pulmonary Rib Cage |
| ARC | Abdominal Rib Cage |
| Ab | Abdomen |
| EIV | End-Inspiratory Volume |
| EEV | End-Expiratory Volume |
References
- Chicayban, L.M.; Hemétrio, A.C.; Azevedo, L.T.R. Comparison of the effects of voluntary and involuntary breath stacking techniques on respiratory mechanics and lung function patterns in tracheostomized patients: A randomized crossover clinical trial. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2020, 46, e20190295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorça, A.; Sarmet, M.; Rocha, E.M.S.S.; Marra, M.B.; Million, J.L.; Diniz, D.S.; Maldaner, V. A Pilot Study of the Breath Stacking Technique Associated with Respiratory Muscle Endurance Training in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Videofluoroscopic Findings in the Upper Airway. Adv. Respir. Med. 2021, 89, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, M.F.; Moreira, G.A.; Pradella-Hallinan, M.; Tufik, S. Air stacking and chest compression increase peak cough flow in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2009, 35, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macagnan, F.E.; Martha, B.A.; Lourenzon, I.M.; Pedroni, A.S.; Kessler, A. Alternative therapy for respiratory muscle training using breath stacking. Fisioter. Bras. 2022, 23, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, A.; de Andrade, A.F.; Lima, Í.N.; Aliverti, A.; de Freitas Fregonezi, G.A.; Resqueti, V.R. Air Stacking: A Detailed Look Into Physiological Acute Effects on Cough Peak Flow and Chest Wall Volumes of Healthy Subjects. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS Statement on respiratory muscle testing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 518–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.A.; Sato, T.; Rodrigues, S.C. New reference values for forced spirometry in white adults in Brazil. J. Bras. de Pneumol. 2007, 33, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neder, J.A.; Andreoni, S.; Lerario, M.C.; Nery, L.E. Reference values for lung function tests. II. Maximal respiratory pressures and voluntary ventilation. Braz. J. Med Biol. Res. 1999, 32, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliverti, A.; Dellacà, R.; Pelosi, P.; Chiumello, D.; Gatihnoni, L.; Pedoti, A. Compartmental analysis of breathing in the supine and prone positions by optoelectronic plethysmography. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 29, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaroni, C.; Carraro, E.; Vianello, A.; Miccinilli, S.; Morrone, M.; Levai, I.K.; Schena, E.; Saccomandi, P.; Sterzi, S.; Dickinson, J.W.; et al. Optoelectronic Plethysmography in Clinical Practice and Research: A Review. Respiration 2017, 93, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cala, S.J.; Kenyon, C.M.; Ferrigno, G.; Carnevali, P.; Aliverti, A.; Pedotti, A.; Macklem, P.T.; Rochester, D.F. Chest wall and lung volume estimation by optical reflectance motion analysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81, 2680–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanini, B.; Masolini, M.; Bianchi, R.; Binazzi, B.; Romagnoli, I.; Gigliotti, F.; Scano, G. Chest wall kinematics during voluntary cough in neuromuscular patients. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2008, 161, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanini, B.; Bianchi, R.; Binazzi, B.; Romagnoli, I.; Pala, F.; Gigliotti, F.; Scano, G. Chest wall kinematics during cough in healthy subjects. Acta Physiol. 2007, 190, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, D.D.L.; Righi, N.C.; Rubin Neto, L.J.; Bellé, J.M.; Pippi, C.M.; Ribas, C.Z.D.M.; Nichele, L.F.I.; Signori, L.U.; Silva, A.M.V.D. Effects of the breath stacking technique after upper abdominal surgery: A randomized clinical trial. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2022, 48, e20210280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Spinou, A. A Review on Cough Augmentation Techniques: Assisted Inspiration, Assisted Expiration and Their Combination. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69 (Suppl. 1), S93–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Romei, M.; Mauro, A.L.; D’Angelo, M.G.; Turconi, A.C.; Bresolin, N.; Pedotti, A.; Aliverti, A. Effects of gender and posture on thoraco-abdominal kinematics during quiet breathing in healthy adults. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010, 172, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.Y.; Wu, W.L.; Kuo, H.C.; Liu, S.F.; Chang, C.L.; Chang, H.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Liu, J.F. Effect of abdominal weight training with and without cough machine assistance on lung function in the patients with prolonged mechanical ventilation: A randomized trial. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mohamed Ahmad, I.; MElmenshawy, A.; Abdelrazek, S. Effect of breath stacking on respiratory efficiency, airway clearance and cough intensity in mechanically ventilated patients. Egypt. J. Health Care 2025, 16, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Yoo, W.G. Effects of air stacking on pulmonary function and peak cough flow in patients with cervical spinal cord injury. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 1951–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sarmento, A.; Resqueti, V.; Dourado-Júnior, M.; Saturnino, L.; Aliverti, A.; Fregonezi, G.; de Andrade, A.D. Effects of Air Stacking Maneuver on Cough Peak Flow and Chest Wall Compartmental Volumes of Subjects with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation 2017, 98, 2237–2246.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.E.; Choi, W.A.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.W. Impact of Airstacking and Digital Pressure Feedback on Pulmonary Function in Restrictive Lung Disease: A Stratified Randomized Controlled Trial. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abdallah, S.J.; Smith, B.M.; Wilkinson-Maitland, C.; Li, P.Z.; Bourbeau, J.; Jensen, D. Effect of Abdominal Binding on Diaphragmatic Neuromuscular Efficiency, Exertional Breathlessness, and Exercise Endurance in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Porto, E.F.; Tavolaro, K.C.; Kümpel, C.; Oliveira, F.M.S.; Sousa, J.B.M.; Carvalho, G.R.; Castro, A.N. Comparative analysis between the alveolar recruitment maneuver and breath stacking technique in patients with acute lung injury. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2014, 26, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.K.; Bradburn, M.; Proctor, A.R.; Billings, C.G.; Bianchi, S.; McDermott, C.J.; Shaw, P.J. A preliminary randomized trial of the mechanical insufflator-exsufflator versus breath-stacking technique in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2015, 16, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Subject | Sex | Age (Years) | BMI (kg/m2) | FVC (L) | FVC (%pred) | FEV1/FCV | FEV1/FCV (%pred) | MIP (cmH2O) | MIP (%pred) | MEP (cmH2O) | MEP (%pred) | SNIP (cmH2O) | SNIP (%pred) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 23 | 25.72 | 4.91 | 92.98 | 0.83 | 85.67 | 128 | 93.49 | 142 | 96.81 | 88 | 75.12 |
| 2 | M | 21 | 22.22 | 4.68 | 80.36 | 0.84 | 84.66 | 132 | 95.30 | 138 | 93.06 | 89 | 75.43 |
| 3 | M | 27 | 24.97 | 4.81 | 84.44 | 0.86 | 85.23 | 130 | 97.23 | 130 | 90.63 | 95 | 82.27 |
| 4 | M | 27 | 25.84 | 5.60 | 111.73 | 0.85 | 85.23 | 132 | 98.72 | 130 | 90.63 | 87 | 75.35 |
| 5 | M | 20 | 24.58 | 4.78 | 88.80 | 0.85 | 86.09 | 140 | 100.50 | 140 | 93.89 | 102 | 86.14 |
| 6 | M | 21 | 21.56 | 4.65 | 90.84 | 0.83 | 86.94 | 142 | 102.52 | 153 | 103.17 | 96 | 81.36 |
| 7 | M | 24 | 23.89 | 3.89 | 97.86 | 0.84 | 84.61 | 95 | 96.30 | 102 | 101.03 | 89 | 99.30 |
| 8 | F | 23 | 23.81 | 3.46 | 81.25 | 0.84 | 83.93 | 110 | 110.96 | 110 | 108.29 | 90 | 100.17 |
| 9 | F | 27 | 23.93 | 3.58 | 84.70 | 0.83 | 83.15 | 98 | 100.85 | 115 | 116.00 | 95 | 106.78 |
| 10 | F | 25 | 20.43 | 4.34 | 98.70 | 0.82 | 83.05 | 100 | 101.88 | 120 | 119.58 | 87 | 97.31 |
| 11 | F | 22 | 22.95 | 3.68 | 93.77 | 0.83 | 85.20 | 95 | 95.36 | 90 | 88.07 | 96 | 106.59 |
| 12 | F | 22 | 23.65 | 3.98 | 99.19 | 0.83 | 84.92 | 102 | 102.38 | 98 | 95.90 | 88 | 97.71 |
| 13 | F | 24 | 19.56 | 4.10 | 105.49 | 0.81 | 84.89 | 97 | 98.33 | 96 | 95.08 | 97 | 108.23 |
| 14 | F | 27 | 23.23 | 4.23 | 105.58 | 0.82 | 83.85 | 115 | 118.34 | 100 | 100.87 | 92 | 103.41 |
| Mean ± SD | 23.79 ± 2.48 | 23.31 ± 1.84 | 4.26± 0.60 | 97.92 ± 7.42 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 83.43 ± 1.34 | 115.4 ± 17.87 | 100.87 ± 6.64 | 118.86 ± 20.16 | 99.51 ± 9.49 | 92.21 ± 4.62 | 92.52 ± 12.65 |
| Subjects | Male (7) | Female (7) | p § |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 23.29 ± 2.87 | 24.29 ± 2.13 | 0.47 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.11 ± 1.66 | 22.51 ± 1.76 | 0.10 |
| %FVCpred | 91.00 ± 12.06 | 95.53 ± 9.55 | 0.45 |
| %FEV1/FVCpred | 99.44 ± 1.75 | 98.74 ± 1.55 | 0.44 |
| %MIPpred | 97.73 ± 3.1 | 104.00 ± 7.93 | 0.07 |
| %MEPpred | 95.61 ± 4.94 | 103.40 ± 11.63 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maciel, A.C.d.M.G.; Resqueti, V.R.; Fonseca, J.D.M.d.; Lima, I.N.D.F.; Otto-Yáñez, M.; Florêncio, R.B.; Aliverti, A.; Fregonezi, G.A.d.F.; Andrade, A.d.F.D.d. Breath Stacking: Acute Effects on Cough Peak Flow and Chest Wall Volumes of Healthy Subjects. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040421
Maciel ACdMG, Resqueti VR, Fonseca JDMd, Lima INDF, Otto-Yáñez M, Florêncio RB, Aliverti A, Fregonezi GAdF, Andrade AdFDd. Breath Stacking: Acute Effects on Cough Peak Flow and Chest Wall Volumes of Healthy Subjects. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(4):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040421
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaciel, Ana Cristina de Medeiros Garcia, Vanessa Regiane Resqueti, Jéssica Danielle Medeiros da Fonseca, Illia Nadinne Dantas Florentino Lima, Matías Otto-Yáñez, Rêncio Bento Florêncio, Andrea Aliverti, Guilherme Augusto de Freitas Fregonezi, and Arméle de Fátima Dornelas de Andrade. 2025. "Breath Stacking: Acute Effects on Cough Peak Flow and Chest Wall Volumes of Healthy Subjects" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 4: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040421
APA StyleMaciel, A. C. d. M. G., Resqueti, V. R., Fonseca, J. D. M. d., Lima, I. N. D. F., Otto-Yáñez, M., Florêncio, R. B., Aliverti, A., Fregonezi, G. A. d. F., & Andrade, A. d. F. D. d. (2025). Breath Stacking: Acute Effects on Cough Peak Flow and Chest Wall Volumes of Healthy Subjects. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(4), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040421









