Reference Tolerance Ellipses in Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis Across General, Pediatric, Pathological, and Athletic Populations: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preliminary Search
2.2. Review Questions
2.3. Protocol and Checklist
2.4. Inclusion Criteria
2.4.1. Participants
2.4.2. Concept
2.4.3. Context
2.4.4. Types of Evidence Sources
2.5. Search Strategy
2.6. Source of Screening and Selection of Evidence
2.7. Extraction of Results
2.8. Presentation of Results
3. Results
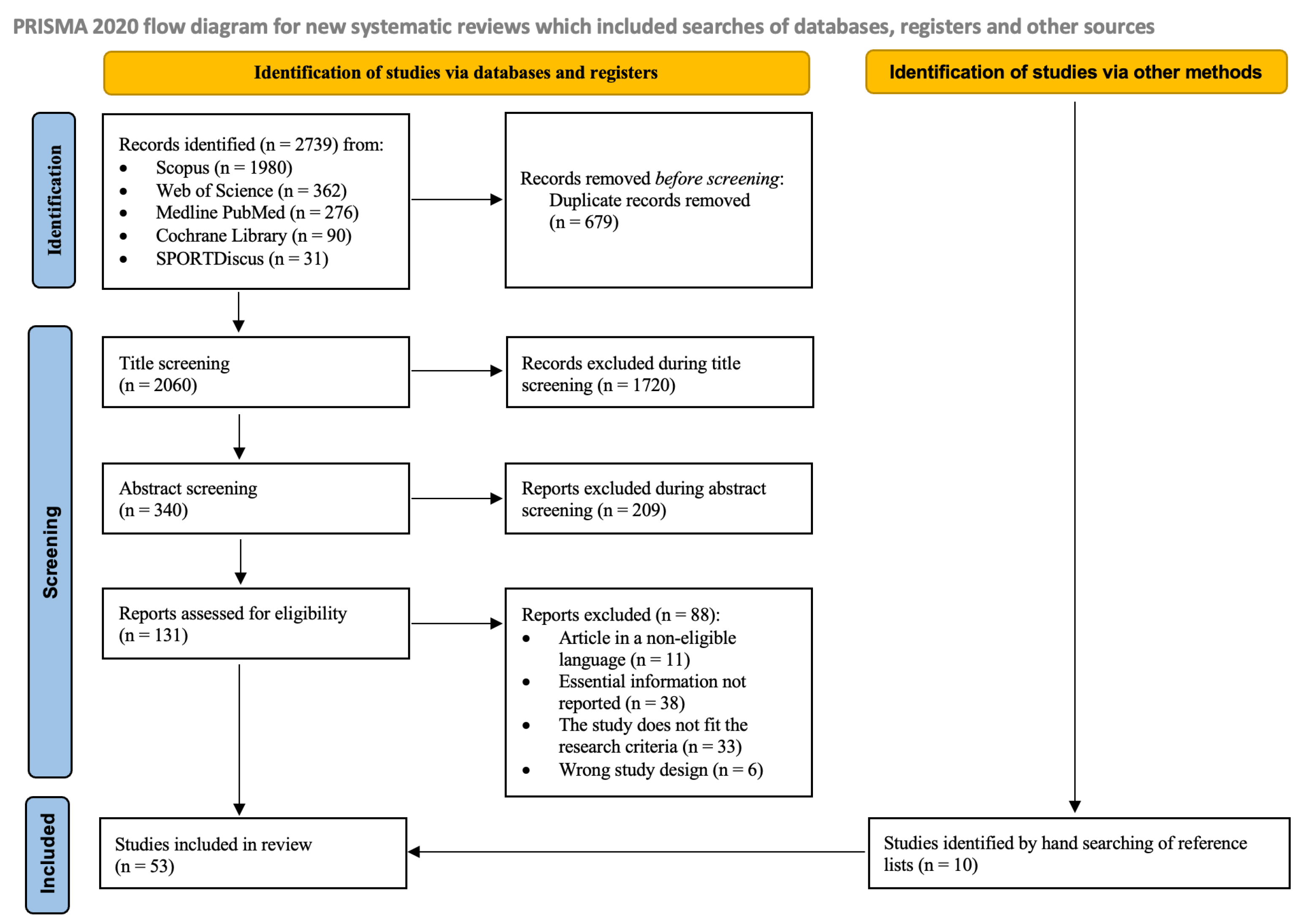
3.1. Search
3.2. Characteristics of Reports
3.3. Characteristics of the Population
3.3.1. General Population
3.3.2. Children and Adolescents
3.3.3. Pathological Population
3.3.4. Athletic Population
3.4. Sample Size of Reports
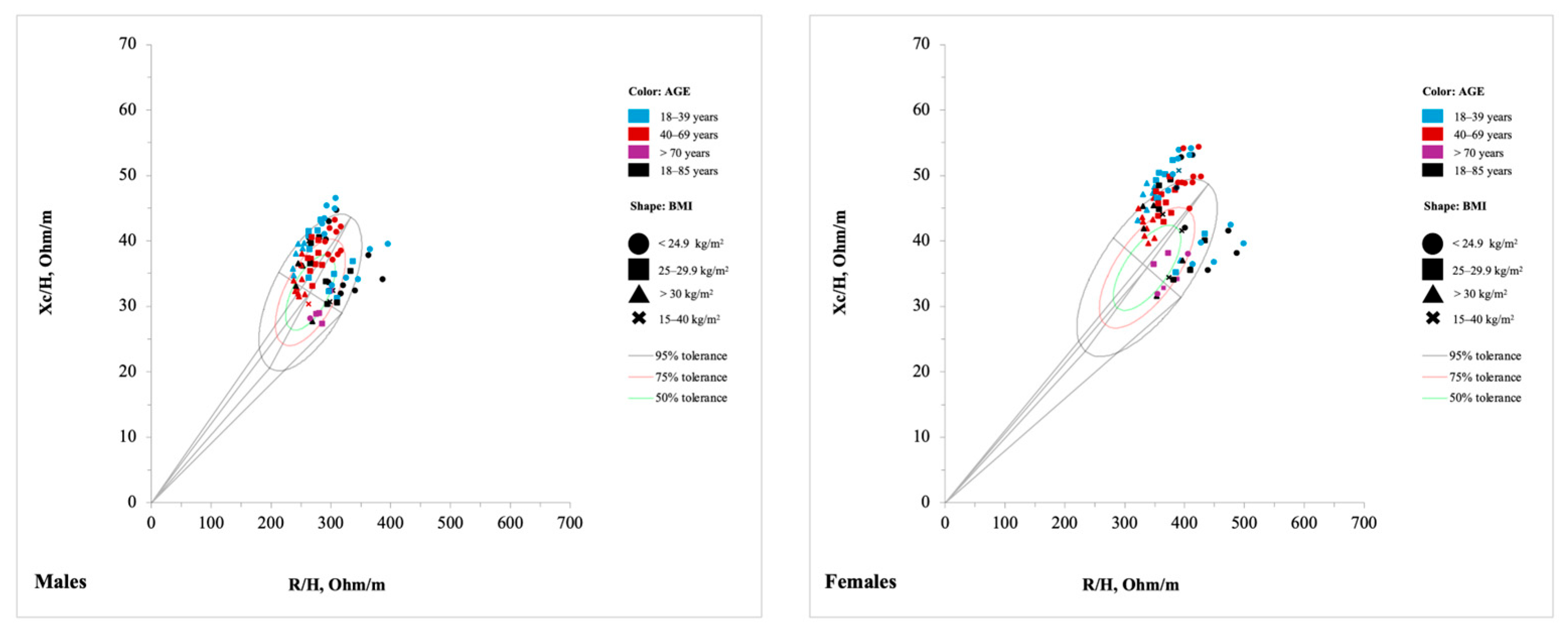
3.5. Tolerance Ellipse Method
3.6. Statistical Analysis
3.7. Analyzer
3.8. Body Side
3.9. Measurement Error
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of the Population and Sample Size
4.1.1. General Population
4.1.2. Children–Adolescent Population
4.1.3. Pathological Population
4.1.4. Athletic Population
4.2. Tolerance Ellipse Method
4.3. Statistical Analysis
4.4. Analyzer and Body Side
4.5. Measurement Error
4.6. Practical Implications
4.7. Strengths and Limits
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BIA | Bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| Z | Impedance |
| TBW | Total body water |
| R | Resistance |
| Xc | Reactance |
| PhA | Phase angle |
| FM | Fat mass |
| FFM | Fat-free mass |
| BIVA | Bioelectrical impedance vector analysis |
| ICW:ECW | Intracellular-to-extracellular water ratio |
| BCM | Body cellular mass |
| OSF | Open Science Framework |
| JBI | Joanna Briggs Institute |
| PRISMA-ScR | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews |
| MeSH | Medical Subject Headings |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| r | Linear correlation coefficient |
References
- Campa, F.; Gobbo, L.A.; Stagi, S.; Cyrino, L.T.; Toselli, S.; Marini, E.; Coratella, G. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis versus Reference Methods in the Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 122, 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Gómez, J.M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis—Part I: Review of Principles and Methods. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, E.C.; Meador, C.K.; Simpson, D.C. Correlation of Whole-Body Impedance with Total Body Water Volume. J. Appl. Physiol. 1969, 27, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Johnson, P.E.; Bolonchuk, W.W.; Lykken, G.I. Assessment of Fat-Free Mass Using Bioelectrical Impedance Measurements of the Human Body. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 41, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Kyle, U.G.; Kondrup, J. Assessment of Adult Malnutrition and Prognosis with Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: Phase Angle and Impedance Ratio. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterberger, S.; Aschauer, R.; Zöhrer, P.A.; Draxler, A.; Aschauer, M.; Kager, B.; Franzke, B.; Strasser, E.M.; Wagner, K.H.; Wessner, B. Association of Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle with Physical Performance and Nutrient Intake of Older Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodziej, M.; Kozieł, S.; Ignasiak, Z. The Use of the Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle to Assess the Risk of Sarcopenia in People Aged 50 and above in Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa Pereira, J.P.d.; Rebouças, A.d.S.; Prado, C.M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Cabral, P.C.; Diniz, A.d.S.; Trussardi Fayh, A.P.; Silva, F.M. Phase Angle as a Marker of Muscle Quality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, R.; Tanabe, N.; Oshima, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Maetani, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Sato, A.; Sato, S.; Ikeguchi, R.; Matsuda, S.; et al. Phase Angle Measured by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Associations with Physical Inactivity and Frailty. Respir. Med. 2024, 233, 107778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, Y.; Kusakabe, T.; Arai, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nakao, K.; Ikeue, K.; Ishihara, Y.; Tagami, T.; Yasoda, A.; Ishii, K.; et al. Phase Angle from Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Is a Useful Indicator of Muscle Quality. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.C. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for Body Composition Assessment: Reflections on Accuracy, Clinical Utility, and Standardisation. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 73, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coratella, G.; Campa, F.; Matias, C.N.; Toselli, S.; Koury, J.C.; Andreoli, A.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Generalized Bioelectric Impedance-Based Equations Underestimate Body Fluids in Athletes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupertuis, Y.M.; Jimaja, W.; Beardsley Levoy, C.; Genton, L. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Instruments: How Do They Differ, What Do We Need for Clinical Assessment? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2025, 28, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Losurdo, G.; Iannone, A.; Leandro, G.; Di Leo, A.; Trerotoli, P. Assessment of Body Composition: Intrinsic Methodological Limitations and Statistical Pitfalls. Nutrition 2022, 102, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manole, L.M.; Ghiga, G.; Iftinchi, O.; Boca, L.O.; Donos, M.A.; Țarcă, E.; Ionuț, N.; Revenco, N.; Margasoiu, I.; Trandafir, L.M. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Versus Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry for Obesity Assessment in Pediatric Populations: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looney, D.P.; Schafer, E.A.; Chapman, C.L.; Pryor, R.R.; Potter, A.W.; Roberts, B.M.; Friedl, K.E. Reliability, Biological Variability, and Accuracy of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for Measuring Body Composition Components. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1491931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, F.; Coratella, G.; Cerullo, G.; Noriega, Z.; Francisco, R.; Charrier, D.; Irurtia, A.; Lukaski, H.; Silva, A.M.; Paoli, A. High-Standard Predictive Equations for Estimating Body Composition Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: A Systematic Review. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, S.; Charrier, D.; Izzicupo, P.; Esparza-Ros, F.; Vaquero-Cristóbal, R.; Petri, C.; Mecherques-Carini, M.; Baglietto, N.; Holway, F.; Tinsley, G.; et al. Anthropometric-Based Predictive Equations Developed with Multi-Component Models for Estimating Body Composition in Athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2024, 125, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Amaya, H.; Rojano-Ortega, D.; Molina-López, A.; Berral-Aguilar, A.J.; Portolan, A.; Berral-de la Rosa, F.J. Development and Validation of New Bioimpedance Equations to Estimate Skeletal Muscle Mass Percentage in a White, Healthy Population. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2025, 68, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, G.L.; Aguiar, A.J.; Cruz, B.; Chandler, A.J.; Brush, C.J.; Brown, A.F. Agreement Between Six Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Devices and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry: Original Research. J. Exerc. Nutr. 2025, 8, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli, A.; Rossi, B.; Pillon, L.; Bucciante, G. A New Method for Monitoring Body Fluid Variation by Bioimpedance Analysis: The RXc Graph. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertow, G.M.; Lowrie, E.G.; Wilmore, D.W.; Gonzalez, J.; Lew, N.L.; Ling, J.; Leboff, M.S.; Gottlieb, M.N.; Huang, W.; Zebrowski, B.; et al. Nutritional Assessment with Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1995, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, E.; Campa, F.; Buffa, R.; Stagi, S.; Matias, C.N.; Toselli, S.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Phase Angle and Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis in the Evaluation of Body Composition in Athletes. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaski, H.C. Evolution of Bioimpedance: A Circuitous Journey from Estimation of Physiological Function to Assessment of Body Composition and a Return to Clinical Research. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, R.; Saragat, B.; Cabras, S.; Rinaldi, A.C.; Marini, E. Accuracy of Specific BIVA for the Assessment of Body Composition in the United States Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palo, T.; Messina, G.; Edefonti, A.; Perfumo, F.; Pisanello, L.; Peruzzi, L.; Di Iorio, B.; Mignozzi, M.; Vienna, A.; Conti, G.; et al. Normal Values of the Bioelectrical Impedance Vector in Childhood and Puberty. Nutrition 2000, 16, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragat, B.; Buffa, R.; Mereu, E.; De Rui, M.; Coin, A.; Sergi, G.; Marini, E. Specific Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Reference Values for Assessing Body Composition in the Italian Elderly. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 50, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, F.; Matias, C.; Gatterer, H.; Toselli, S.; Koury, J.C.; Andreoli, A.; Melchiorri, G.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Classic Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Reference Values for Assessing Body Composition in Male and Female Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogonez, P.; Rabinovich, R.; Nescolardel, L.; Roca, J.; Roselll, I.; Riu, P.; Piccoli, A. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis in COPD Patients. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Parker, D.; Soares, C.B. Guidance for Conducting Systematic Scoping Reviews. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Godfrey, C.M.; Mcinerney, P.; Munn, Z. Chapter 11: Scoping Reviews. In JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI): Adelaide, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, C.R.T.; Izadi, S.; Fowler, S.; Green, P.; Suls, J.; Colditz, G.A. The Value of a Second Reviewer for Study Selection in Systematic Reviews. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarczyk, L.M.; Heyward, V.H.; Hicks, V.L.; Baumgartner, R.N. Predictive Accuracy of Bioelectrical Impedance in Estimating Body Composition of Native American Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 59, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, A.; Nigrelli, S.; Caberlotto, A.; Bottazzo, S.; Rossi, B.; Pillon, L.; Maggiore, Q. Bivariate Normal Values of the Bioelectrical Impedance Vector in Adult and Elderly Populations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubenoff, R.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Harris, T.B.; Dallal, G.E.; Hannan, M.T.; Economos, C.D.; Stauber, P.M.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Kiel, D.P. Application of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis to Elderly Populations. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 1997, 52A, M129–M136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, A.; Pillon, L.; Dumler, F. Impedance Vector Distribution by Sex, Race, Body Mass Index, and Age in the United States: Standard Reference Intervals as Bivariate Z Scores. Nutrition 2002, 18, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, A. Identification of Operational Clues to Dry Weight Prescription in Hemodialysis Using Bioimpedance Vector Analysis. The Italian Hemodialysis-Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (HD-BIA) Study Group. Kidney Int. 1998, 53, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, A.; Brunani, A.; Savia, G.; Pillon, L.; Favaro, E.; Berselli, M.E.; Cavagnini, F. Discriminating between Body Fat and Fluid Changes in the Obese Adult Using Bioimpedance Vector Analysis. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1998, 22, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, F.W.; Mastronuzzi, T.; Pietrini, L.; Panarese, A.; Panella, C.; Francavilla, A. The RXc Graph in Evaluating and Monitoring Fluid Balance in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 1999, 873, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toso, S.; Piccoli, A.; Gusella, M.; Menon, D.; Bononi, A.; Crepaldi, G.; Ferrazzi, E. Altered Tissue Electric Properties in Lung Cancer Patients as Detected by Bioelectric Impedance Vector Analysis. Nutrition 2000, 16, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, A.; Fanos, V.; Peruzzi, L.; Schena, S.; Pizzini, C.; Borgione, S.; Bertino, E.; Chiaffoni, G.; Coppo, R.; Tatò, L. Reference Values of the Bioelectrical Impedance Vector in Neonates in the First Week after Birth. Nutrition 2002, 18, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Grasso, G.; Cresi, F.; Oggero, R.; Silvestro, L. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Distribution in the First Year of Life. Nutrition 2003, 19, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Danielzik, S.; Dörhöfer, R.P.; Piccoli, A.; Müller, M.J. Patterns of Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Distribution by Body Mass Index and Age: Implications for Body-Composition Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, B.; Pietrobelli, A.; Trio, R.; Laccetti, R.; Falconi, C.; Perrino, N.R.; Principato, S.; Pecoraro, P. Body Mass Index and Bioelectrical Vector Distribution in 8-Year-Old Children. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margutti, A.V.B.; Monteiro, J.P.; Camelo, J.S. Reference Distribution of the Bioelectrical Impedance Vector in Healthy Term Newborns. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Abée, C.; Poorts-Borger, P.H.; Gorter, E.H.G.M.; Piccoli, A.; Stolk, R.P.; Sauer, P.J.J. The Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Migration in Healthy Infants. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, R.F.; de Azevedo, Z.M.A.; Fonseca, V.M.; Peixoto, M.V.M.; dos Anjos, L.A.; Gaspar-Elsas, M.I.C.; Moore, D.C.B.C.; Ramos, E.G. Distribution of Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Values in Multi-Ethnic Infants and Pre-School Children. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nescolarde, L.; Núñez, A.; Bogónez-Franco, P.; Lara, A.; Vaillant, G.; Morales, R.; Rosell-Ferrer, J. Reference Values of the Bioimpedance Vector Components in a Caribbean Population. ESPEN J. 2013, 8, e141–e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nescolarde, L.; Piccoli, A.; Román, A.; Núñez, A.; Morales, R.; Tamayo, J.; Doñate, T.; Rosell, J. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis in Haemodialysis Patients: Relation between Oedema and Mortality. Physiol. Meas. 2004, 25, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Hall, C.B.; Siders, W.A. Assessment of Change in Hydration in Women during Pregnancy and Postpartum with Bioelectrical Impedance Vectors. Nutrition 2007, 23, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siváková, D.; Vondrová, D.; Valkovič, P.; Cvíčelová, M.; Danková, Z.; Luptáková, L. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) in Slovak Population: Application in a Clinical Sample. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2013, 8, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, A. Bioelectric Impedance Vector Distribution in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients with Different Hydration Status. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheli, M.L.; Pagani, L.; Marella, M.; Gulisano, M.; Piccoli, A.; Angelini, F.; Burtscher, M.; Gatterer, H. Bioimpedance and Impedance Vector Patterns as Predictors of League Level in Male Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castizo-Olier, J.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Roy, A.; Chaverri, D.; Iglesias, X.; Pérez-Chirinos, C.; Rodríguez, F.; Irurtia, A. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) and Body Mass Changes in an Ultra-Endurance Triathlon Event. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2018, 17, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Campa, F.; Toselli, S. Bioimpedance Vector Analysis of Elite, Subelite, and Low-Level Male Volleyball Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 1250–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, A.; Vicini, M.; Pollastri, L.; Lombardi, E.; Magni, E.; Andreazzoli, A.; Orsini, M.; Bonifazi, M.; Lukaski, H.; Gatterer, H. Bioimpedance Patterns and Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) of Road Cyclists. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 2608–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koury, J.C.; de Oliveira-Junior, A.V.; Portugal, M.R.C.; de Oliveira, K.d.J.F.; Donangelo, C.M. Bioimpedance Parameters in Adolescent Athletes in Relation to Bone Maturity and Biochemical Zinc Indices. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 46, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toselli, S.; Marini, E.; Latessa, P.M.; Benedetti, L.; Campa, F. Maturity Related Differences in Body Composition Assessed by Classic and Specific Bioimpedance Vector Analysis among Male Elite Youth Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nescolarde, L.; Roca, E.; Bogónez-Franco, P.; Hernández-Hermoso, J.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Ara, J. Relationship Between Bioimpedance Vector Displacement and Renal Function After a Marathon in Non-Elite Runners. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, T.; Mascherini, G.; Genovesi, F.; Pasta, G.; Iaia, F.M.; Trecroci, A.; Ventimiglia, M.; Alberti, G.; Campa, F. Bioimpedance Vector References Need to Be Period-Specific for Assessing Body Composition and Cellular Health in Elite Soccer Players: A Brief Report. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Credico, A.; Gaggi, G.; Vamvakis, A.; Serafini, S.; Ghinassi, B.; Di Baldassarre, A.; Izzicupo, P. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis of Young Elite Team Handball Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzicupo, P.; Petri, C.; Serafini, S.; Galanti, G.; Mascherini, G. Morphological Characteristics of Elite International Soccer Referees: Somatotype and Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, C.; Micheli, M.L.; Izzicupo, P.; Timperanza, N.; Lastrucci, T.; Vanni, D.; Gulisano, M.; Mascherini, G. Bioimpedance Patterns and Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) of Body Builders. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, M.E.; Mereu, E.; Buffa, R.; Gualdi-Russo, E.; Zaccagni, L.; Cossu, S.; Rebato, E.; Marini, E. New Specific Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Reference Values for Assessing Body Composition in the Italian-Spanish Young Adult Population. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2015, 27, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.; Moritoyo, T.; Kaufer-Horwitz, M.; Peine, S.; Norman, K.; Maisch, M.J.; Matsumoto, A.; Masui, Y.; Velázquez-González, A.; Domínguez-García, J.; et al. Ethnic Differences in Fat and Muscle Mass and Their Implication for Interpretation of Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Song, S.; Rhee, H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Choe, J.C.; Ahn, J.; Park, J.S.; Shin, M.J.; Jeon, Y.K.; et al. Normal Reference Plots for the Bioelectrical Impedance Vector in Healthy Korean Adults. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 34, e198, Erratum in J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 34, e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini-Venturini, A.C.; Abdalla, P.P.; Fassini, P.G.; dos Santos, A.P.; Tasinafo Junior, M.F.; Alves, T.C.; Gomide, E.B.G.; de Pontes, T.L.; Pfrimer, K.; Ferriolli, E.; et al. Association between Classic and Specific Bioimpedance Vector Analysis and Sarcopenia in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, F.; Coratella, G.; Cerullo, G.; Stagi, S.; Paoli, S.; Marini, S.; Grigoletto, A.; Moroni, A.; Petri, C.; Andreoli, A.; et al. New Bioelectrical Impedance Vector References and Phase Angle Centile Curves in 4,367 Adults: The Need for an Urgent Update after 30 Years. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.L.; Tang, S.; Eom, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Chae, J.H.; Kim, C.H. Distribution of Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis and Phase Angle in Korean Elderly and Sarcopenia. Sensors 2023, 23, 7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias-Genovez, M.G.; Oliveira, C.C.; Camelo, J.S.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Monteiro, J.P. Bioelectrical Impedance of Vectorial Analysis and Phase Angle in Adolescents. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffano, R.B.D.; Hillesheim, E.; Margutti, A.V.B.; Camelo Junior, J.S.; Ferraz, I.S.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Monteiro, J.P. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis in Healthy Term Infants in the First Three Months of Life in Brazil. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-del-Río, M.P.; Camina-Martín, M.A.; Marugán-de-Miguelsanz, J.M.; de-Mateo-Silleras, B. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Reference Values for Assessing Body Composition in a Spanish Child and Adolescent Population. Am. J. Human Biol. 2017, 29, e22978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-del-Río, M.P.; Escribano-García, C.; Camina-Martín, M.A.; Caserío-Carbonero, S.; Cancho-Candela, R.; de-Mateo-Silleras, B. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Values in a Spanish Healthy Newborn Population for Nutritional Assessment. Am. J. Human Biol. 2019, 31, e23244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, T.L.M.; Peixoto, M.V.M.; de Azevedo, Z.M.A.; Fonseca, V.M.; Ramos, E.G. Association of Electrical Bioimpedance Vectors with the Nutritional Classification of Vulnerable Multiethnic Children. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnour, M.; Berkachy, R.; Nasreddine, L.; Fares, E.J. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) for Assessment of Hydration Status: A Comparison between Endurance and Strength University Athletes. Sensors 2024, 24, 6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrián-Ponce, Á.; Serafini, S.; Petri, C.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Izzicupo, P.; Mascherini, G. Somatotype and Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis of Italian CrossFit® Practitioners. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Ramos, R.; Escuder-Vieco, D.; Rico Cruz, C.; Diego-Poncela, C.D.; Vázquez-Román, S.; Germán-Díaz, M.; García-Lara, N.R.; Pallás-Alonso, C. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis in Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants to Assess Nutritional Status: Breakthroughs and Insights. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.K.; Lim, J.Y. The Implications of Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis in Older Adults with Hip Fractures. Maturitas 2025, 194, 108209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Annunziata, G.; Barrea, L.; Sampieri, A.; Ceolin, C.; De Rui, M.; Sguaizer, F.; Petri, C.; Spataro, F.; Mascherini, G.; et al. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis in Older Adults: Reference Standards from a Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1640407, Erratum in Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1673638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Micheli, M.L.; Pompignoli, M.; Cannataro, R.; Gulisano, M.; Toselli, S.; Greco, G.; Coratella, G. The Influence of Menstrual Cycle on Bioimpedance Vector Patterns, Performance, and Flexibility in Elite Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2022, 17, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez, J.; Mascarell, B.; Stubbe, H.; Ventura, S.; Bonanad, C.; Bodi, V.; Nunez, E.; Min-Ana, G.; Facila, L.; Bayes-Genis, A.; et al. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 17, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter-Jones, A.D.G.; Sherar, L.B. Paediatric Exercise Physiology. In Paediatric Exercise Physiology; Armstrong, N., Spurway, N., MacLaren, D., Sharp, N.C.C., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 2007; pp. 1–26. ISBN 978-0-443-10260-8. [Google Scholar]
- Serafini, S.; Di Credico, A.; Gaggi, G.; Pippi, R.; Mascherini, G.; Izzicupo, P. The Anthropometric Profile and Body Composition of Youth Soccer Goalkeepers after the COVID-19 Pandemic, According to the Maturity Offset. Sport. Sci. Health 2023, 19, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, R.; Floris, G.; Marini, E. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector in Pre- and Postmenarcheal Females. Nutrition 2002, 18, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse/2025-01/mms/en (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Sbrignadello, S.; Göbl, C.; Tura, A. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for the Assessment of Body Composition in Sarcopenia and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, H.; Teng, W.; Wang, X.; Ji, D. Application of Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis to Evaluate Volume Status of Hemodialysis Patients with Hypertension. Chin. J. Nephrol. 2020, 36, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A.G.; Janz, B.A.; Slavin, S.A.; Borud, L.J. The Use of Bioimpedance Analysis to Evaluate Lymphedema. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2007, 58, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Song, Y.; Artioli, G.G.; Gee, T.I.; French, D.N.; Zheng, H.; Lyu, M.; Li, Y. The Practice of Weight Loss in Combat Sports Athletes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Castizo-Olier, J.; Rodríguez-Zamora, L.; Iglesias, X.; Rodríguez, F.A.; Chaverri, D.; Brotons, D.; Irurtia, A. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) for Measuring the Hydration Status in Young Elite Synchronized Swimmers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, S.; Di Blasio, A.; Prestanti, I.; Di Credico, A.; Fusco, A.; Cilli, J.; Mascherini, G.; D’Anastasio, R.; Izzicupo, P. Hydration in Young Water Polo Players: A Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) Approach. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, R. Business or Cause? Gendered Institutional Logics in Women’s Professional Soccer. J. Sport. Soc. Issues 2016, 40, 237–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachino, C.; Valenti, M.; Bonadonna, A.; Bollani, L. Women’s Football: Don’t Judge Me, Support Me! Evidence from Young Generations. Soccer Soc. 2024, 25, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascherini, G.; Serafini, S.; Bianchi, E.; Izzicupo, P.; Levi Micheli, M. Physical Performance and Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis of Female Track and Field Athletes According to the Follicular Phase of the Menstrual Cycle. Sport. Sci. Health 2025, 21, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascherini, G.; Levi Micheli, M.; Serafini, S.; Politi, C.; Bianchi, E.; Cebrián-Ponce, Á.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Izzicupo, P. Raw Bioelectrical Data and Physical Performance in Track and Field Athletes: Are There Differences between the Sexes in the Relationship? Heliyon 2024, 10, e35754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, J.E.; Pollock, M.L.; Colvin, A.B.; Van Loan, M.; Lohman, T.G. Comparison of Different Bioelectrical Impedance Analyzers in the Prediction of Body Composition. Am. J. Human Biol. 1989, 1, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, A.; Pastori, G. BIVA Software 2002; Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences, University of Padova: Padova, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Graybeal, A.J.; Tinsley, G.M.; Brandner, C.F.; Aultman, R. Raw Bioelectrical Impedance Measurements Are Not Different between White and Black Adults When Matched for Sex, Age, BMI, and Other Physical Characteristics. Nutr. Res. 2023, 112, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.P.; Cataldi, D.; Liu, Y.E.; Kelly, N.N.; Quon, B.K.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Shepherd, J.A. Variations in Bioelectrical Impedance Devices Impact Raw Measures Comparisons and Subsequent Prediction of Body Composition Using Recommended Estimation Equations. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 63, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serafini, S.; Mascherini, G.; Vaquero-Cristóbal, R.; Esparza-Ros, F.; Campa, F.; Izzicupo, P. Reference Tolerance Ellipses in Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis Across General, Pediatric, Pathological, and Athletic Populations: A Scoping Review. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040415
Serafini S, Mascherini G, Vaquero-Cristóbal R, Esparza-Ros F, Campa F, Izzicupo P. Reference Tolerance Ellipses in Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis Across General, Pediatric, Pathological, and Athletic Populations: A Scoping Review. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(4):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040415
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerafini, Sofia, Gabriele Mascherini, Raquel Vaquero-Cristóbal, Francisco Esparza-Ros, Francesco Campa, and Pascal Izzicupo. 2025. "Reference Tolerance Ellipses in Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis Across General, Pediatric, Pathological, and Athletic Populations: A Scoping Review" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 4: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040415
APA StyleSerafini, S., Mascherini, G., Vaquero-Cristóbal, R., Esparza-Ros, F., Campa, F., & Izzicupo, P. (2025). Reference Tolerance Ellipses in Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis Across General, Pediatric, Pathological, and Athletic Populations: A Scoping Review. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(4), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040415












