Associations Between Visual Accommodation and Cervical Muscle Activity and Symptomatology: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Literature Review
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Risk of Bias and Quality of Evidence Assessments
3. Results
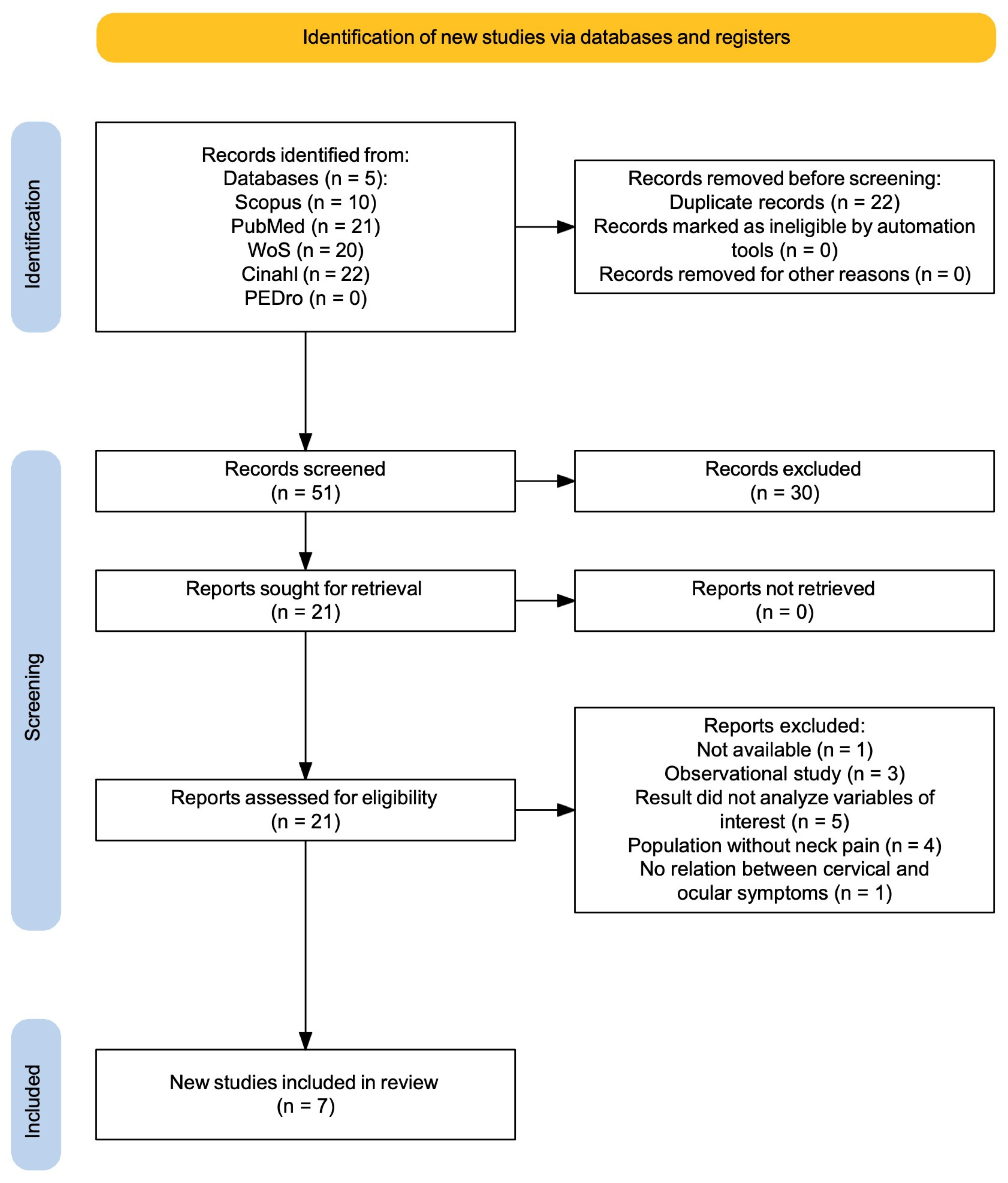
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Studies Included in the Review
3.3. Assessment of Methodological Quality and Main Biases Identified
3.4. Main Findings in Systematic Review
3.4.1. Effects of Visual Work on the Accommodation Response
3.4.2. Effects of Visual Work on Cervical Muscle Tone
3.4.3. Effects of Visual Work on Heart Rate
3.4.4. Effects of Visual Work on the Perception of Fatigue and Pain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Espí López, G.V.; Sentandreu Mañó, T.; Colorado Lluch, M.I.; Dueñas Moscardó, L. Efectos de Un Programa de Ejercicios Oculocervicales En Adultos En La Movilidad Cervical. Fisioterapia 2011, 33, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-González, M.C.; Pérez-Cabezas, V.; López-Izquierdo, I.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, E.; Ruiz-Molinero, C.; Rebollo-Salas, M.; Jiménez-Rejano, J.J. Is It Possible to Relate Accommodative Visual Dysfunctions to Neck Pain? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1421, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-González, M.C.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, E.; Sánchez-González, J.M.; Rebollo-Salas, M.; Ruiz-Molinero, C.; Jiménez-Rejano, J.J.; Pérez-Cabezas, V. Visual System Disorders and Musculoskeletal Neck Complaints: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1457, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodin, C.; Forsman, M.; Richter, H. Eye- and Neck/Shoulder-Discomfort during Visually Demanding Experimental near Work. Work 2012, 41 (Suppl. S1), 3388–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domkin, D.; Forsman, M.; Richter, H.O. Ciliary Muscle Contraction Force and Trapezius Muscle Activity during Manual Tracking of a Moving Visual Target. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2016, 28, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enix, D.E.; Scali, F.; Pontell, M.E. The Cervical Myodural Bridge, a Review of Literature and Clinical Implications. J. Can. Chiropr. Assoc. 2014, 58, 184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Antes, G.; Atkins, D.; Barbour, V.; Barrowman, N.; Berlin, J.A.; Clark, J.; et al. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions|Cochrane Training. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Mather, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.D.; Moseley, A.M.; Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro Scale for Rating Quality of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lie, I.; Watten, R. [Visually Induced Muscle Stress]. Tidsskr. Nor. Laegeforening 1985, 105, 1714–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Zetterberg, C.; Richter, H.O.; Forsman, M. Temporal Co-Variation between Eye Lens Accommodation and Trapezius Muscle Activity during a Dynamic near-Far Visual Task. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, C.; Forsman, M.; Richter, H.O. Effects of Visually Demanding near Work on Trapezius Muscle Activity. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsman, M.; Lodin, C.; Richter, H. Co-Variation in Time between near-Far Accommodation of the Lens and Trapezius Muscle Activity. Work 2012, 41, 3393–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, H.O.; Bänziger, T.; Abdi, S.; Forsman, M. Stabilization of Gaze: A Relationship between Ciliary Muscle Contraction and Trapezius Muscle Activity. Vis. Res. 2010, 50, 2559–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, H.O.; Bänziger, T.; Forsman, M. Eye-Lens Accommodation Load and Static Trapezius Muscle Activity. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, H.O.; Zetterberg, C.; Forsman, M. Trapezius Muscle Activity Increases during near Work Activity Regardless of Accommodation/Vergence Demand Level. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, C.; Forsman, M.; Richter, H.O. Neck/Shoulder Discomfort Due to Visually Demanding Experimental near Work Is Influenced by Previous Neck Pain, Task Duration, Astigmatism, Internal Eye Discomfort and Accommodation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamunér, A.R.; Moreno, M.A.; Camargo, T.M.; Graetz, J.P.; Rebelo, A.C.; Tamburús, N.Y.; Da Silva, E. Evaluación Del Esfuerzo Percibido Subjetivo En El Umbral Anaeróbico Con La Escala de Borg CR-10. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2010, 2010, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Giffard, P.; Daly, L.; Treleaven, J. Influence of Neck Torsion on near Point Convergence in Subjects with Idiopathic Neck Pain. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 32, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheron, E.; Zandi, A.; Wang, D.; Kapoula, Z. A 1-Diopter Vertical Prism Induces a Decrease of Head Rotation: A Pilot Investigation. Front Neurol. 2016, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Domkin, D.; Forsman, M.; Richter, H.O. Effect of Ciliary-Muscle Contraction Force on Trapezius Muscle Activity during Computer Mouse Work. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, H.O.; Camilla, L.; Forsman, M. Temporal Aspects of Increases in Eye-Neck Activation Levels during Visually Deficient near Work. Work 2012, 41, 3379–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, P.D. Ocular Manifestations of Whiplash Injuries. Ann. Ophthalmol. 1972, 4, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.P.; Orton, H.P.; West, J.; Strachan, I.M.; Hockey, M.S.; Ferguson, D.G. Whiplash and Its Effect on the Visual System. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1992, 230, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ischebeck, B.K.; De Vries, J.; Van Der Geest, J.N.; Janssen, M.; Van Wingerden, J.P.; Kleinrensink, G.J.; Frens, M.A. Eye Movements in Patients with Whiplash Associated Disorders: A Systematic Review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiebel-Kalish, H.; Amitai, A.; Mimouni, M.; Bach, M.; Saban, T.; Cahn, M.; Gantz, L. The Discrepancy between Subjective and Objective Measures of Convergence Insufficiency in Whiplash-Associated Disorder versus Control Participants. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ischebeck, B.K.; de Vries, J.; Janssen, M.; van Wingerden, J.P.; Kleinrensink, G.J.; van der Geest, J.N.; Frens, M.A. Eye Stabilization Reflexes in Traumatic and Non-Traumatic Chronic Neck Pain Patients. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 29, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.H.; Dai, S.Z.; Peng, H.Y.; Wang, L.Y. Binocular Vision and Abnormal Head Posture in Children When Watching Television. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 9, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nucci, P.; Kushner, B.J.; Serafino, M.; Orzalesi, N. A Multi-Disciplinary Study of the Ocular, Orthopedic, and Neurologic Causes of Abnormal Head Postures in Children. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 140, e1–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, H.O. Neck Pain Brought into Focus. Work 2014, 47, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed Medline | ((cervical pain) OR (cervicalgia) OR (neckache) OR (neck pain) OR (neck muscles) OR (trapezius muscle activity)) AND ((ocular accommodation) OR (lens accommodation)) |
| Cinahl | AB (cervical pain or neck pain or cervicalgia or neckache or neck muscles or trapezius muscle activity) AND AB (ocular accommodation or lens accommodation) |
| Web Of Science | TOPIC (cervical pain or neck pain or cervicalgia or neckache or neck muscles or trapezius muscle activity) TOPIC (ocular accommodation or lens accommodation) |
| PEDro | Cervical pain and Ocular accommodation |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY “cervical pain” OR “cervicalgia” OR “neckache” OR “neck pain” OR “neck muscles” OR “trapezius muscle activity” AND “ocular accommodation” OR “lens accommodation” |
| Study | N (F/M) | D | Experimental Group | Control Group | Outcomes/Measured | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Intervention | Sample | Intervention | ||||||
| Ne (Age) | Tt | Ses | Ne (Age) | Tt | Ses | ||||
| Richter et al., 2010 (Sweden) [14] FN: Yes | 28 (18/10) | Ne: chronic neck pain and/or professional oculomotor problems (asthenopia) Nc: healthy symptom | 13 (32 ± 7) | Four near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses of 5 min | 15 (27 ± 8) | Four near-to-far vision tasks | 1 ses of 5 min | Accommodative/vergence response (refractor) Heart rate variability (electrocardiography; electromyography) Trapezius muscle activity (electromyography) |
| Richter et al., 2011 (Sweden) [15] FN: Yes | 28 (18/10) | Ne: chronic neck pain and/or professional oculomotor problems (asthenopia) Nc: healthy symptom | 13 (32 ± 7) | Two near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses of 5 min | 15 (27 ± 8) | Two near-to-far vision tasks | 1 ses of 5 min | Accommodative/vergence response (refractor) Heart rate variability (electrocardiography; electromyography) Trapezius muscle activity (electromyography) |
| Forsman et al., 2012 (Sweden) [13] FN: No | 28 (18/10) | Ne: chronic neck pain and/or professional oculomotor problems (asthenopia) Nc: healthy symptom | 13 (32 ± 7) | Near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses Near 15 times and at Far 15 times | 15 (27 ± 8) | Near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses Near 15 times and at Far 15 times | Accommodative/vergence response (refractor) Heart rate variability (electrocardiography; electromyography) Trapezius muscle activity (electromyography) |
| Zetterberg et al., 2013 (Sweden) [12] FN: Yes | 66 (54/12) | Ne: neck/shoulder pain in the last 12 weeks Nc: healthy symptom | 33 (median age 39 [range 20–47]) | Visually demanding near work at a computer screen under different visual conditions | 1 ses 4 series of 7 min | 33 (median age 39 [range 20–47]) | Visually demanding near work at a computer screen under different visual conditions | 1 ses 4 series of 7 min | Accommodative/vergence response (refractor) Heart rate variability (electrocardiography; electromyography) Trapezius muscle activity (electromyography) |
| Richter et al., 2015 (Sweden) [16] FN: Yes | 66 (54/12) | Ne: chronic neck pain Nc: healthy symptom | 33 (median age 39 [range 20–47]) | Four near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses 4 series of 7 min | 33 (median age 39 [range 20–47]) | Four near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses 4 series of 7 min | Accommodative/vergence response (refractor) Heart rate variability (electrocardiography; electromyography) Trapezius muscle activity (electromyography) |
| Zetterberg et al., 2015 (Sweden) [11] FN: Yes | 26 (17/9) | Ne: chronic neck pain and/or professional oculomotor problems (asthenopia) Nc: healthy symptom | 12 (26 ± 8) 26 ± 8 | Near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses of 2.5 min | 14 (32 ± 7) | Near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses of 2.5 min | Accommodative/vergence response (refractor) Heart rate variability (electrocardiography; electromyography) Trapezius muscle activity (electromyography) |
| Zetterberg et al., 2017 (Sweden) [17] FN: Yes | 66 (54/12) | Ne: chronic neck pain Nc: healthy symptom | 33 (median age 39 [range 20–47]) | Four near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses of 7 min | 33 (median age 39 [range 20–47]) | Four near-to-far vision tasks under different visual conditions | 1 ses of 7 min | Accommodative/vergence response (refractor) Heart rate variability (electrocardiography; electromyography) Ocular and cervical fatigue (Borg CR-10 scale) |
| Author | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Richter et al., 2010 [14] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 5 |
| Richter et al., 2011 [15] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 5 |
| Forsman et al., 2012 [13] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 5 |
| Zetterberg et al., 2013 [12] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 5 |
| Zetterberg et al., 2015 [11] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 5 |
| Richter et al., 2015 [16] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 5 |
| Zetterberg et al., 2017 [17] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 5 |
| Reference | Variable/Condition | Main Results (Experimental Group) |
|---|---|---|
| Richter et al., 2010 [14] | Accommodative error (D)/EMG (% RVE) | Binocular with −3.5 D: r2 =0.38; p = 0.0012 Binocular with 0.0 D: r2 = 0.003; p = 0.79 Binocular with 1–2 Prism D: r2 = 0.07; p = 0.203 Binocular with +3.5 D: r2 = 0.316; p = 0.0022 |
| Richter et al., 2011 [15] | Response diopters (D)/EMG (% RVE) | Binocular with −3.5 D: r2 = 0.25; p = 0.013 |
| Binocular with 0.0 D: r2 = 0.016; p = 0.563 | ||
| Accommodative error (D)/EMG (% RVE) | Binocular with −3.5 D: r2 = 0.3686 p = 0.001 | |
| Binocular with 0.0 D: r2 = 0.0018; p = 0.845 | ||
| Forsman et al., 2012 [13] | EMG/refraction signals | R(tau) = 0.019; p = 0.001 |
| Zetterberg et al., 2013 [12] | Accommodation response (D)/EMG (%RVE) | Binocular with −3.5: r = 0.377; p = 0.017 |
| Monocular with −3.5: r = 0.147; p = 0.326 | ||
| Monocular neutral with 0.0 D: r = −0.018; p = 0.897 | ||
| Monocular with +3.5: r = 0.088; p = 0.524 | ||
| Zetterberg et al., 2015 [11] | Trapezius muscle activity (in %RVE) | Neutral lenses: 1.82 [0.79, 2.86]; p = 0.034 Negative −3.5 D lenses: 2.36 [0.72, 3.99]; p > 0.1 Positive +3.5 D lenses: 1.74 [0.28, 3.21]; p = p > 0.1 |
| Richter et al., 2015 [16] | Trapezius muscle activity (% RVE) during the visual tasks | Binocular −3.5 D: p = 0.007 Monocular −3.5 D: p = 0.048 Monocular 0 D: p = 0.043 Monocular +3.5 D: p > 0.5 |
| Zetterberg et al., 2017 [17] | Accommodation response | Binocular −3.5 D: 3.39 (2.09) Monocular −3.5 D: 3.68 (2.00) Monocular 0 D: 1.51 (0.74) Monocular +3.5 D: 0.97 (0.99) |
| BOR’s scale internal eye discomfort | Binocular −3.5 D: 3.0 (0 ± 9.0) * Monocular −3.5 D: 2.0 (0 ± 7.0) Monocular 0 D: 2.0 (0 ± 7.0) Monocular +3.5 D: 3.0 (0 ± 9.0) | |
| BOR’s scale external eye discomfort | Binocular −3.5 D: 3.0 (0 ± 7.0) Monocular −3.5 D: 2.5 (0.3 ± 7.0) Monocular 0 D: 2.0 (0 ± 7.0) Monocular +3.5 D: 2.5 (0 ± 7.0) | |
| BOR’s scale neck/shoulder discomfort | Binocular −3.5 D: 3.0 (1.0 ± 9.0) Monocular −3.5 D: 3.0 (0.5 ± 10.0) Monocular 0 D: 3.0 (1.0 ± 10.0) Monocular +3.5 D: 3.0 (0.5 ± 9.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lérida-Ponce, M.Á.; Lérida-Ortega, M.Á.; Sedeño-Vidal, A.; Ibáñez-Vera, A.J. Associations Between Visual Accommodation and Cervical Muscle Activity and Symptomatology: A Systematic Review. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030252
Lérida-Ponce MÁ, Lérida-Ortega MÁ, Sedeño-Vidal A, Ibáñez-Vera AJ. Associations Between Visual Accommodation and Cervical Muscle Activity and Symptomatology: A Systematic Review. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(3):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030252
Chicago/Turabian StyleLérida-Ponce, Miguel Ángel, Miguel Ángel Lérida-Ortega, Ana Sedeño-Vidal, and Alfonso Javier Ibáñez-Vera. 2025. "Associations Between Visual Accommodation and Cervical Muscle Activity and Symptomatology: A Systematic Review" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 3: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030252
APA StyleLérida-Ponce, M. Á., Lérida-Ortega, M. Á., Sedeño-Vidal, A., & Ibáñez-Vera, A. J. (2025). Associations Between Visual Accommodation and Cervical Muscle Activity and Symptomatology: A Systematic Review. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(3), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030252








