Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by a Short Isometric Exercise Session Versus Combined Exercise in Hypertensive Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
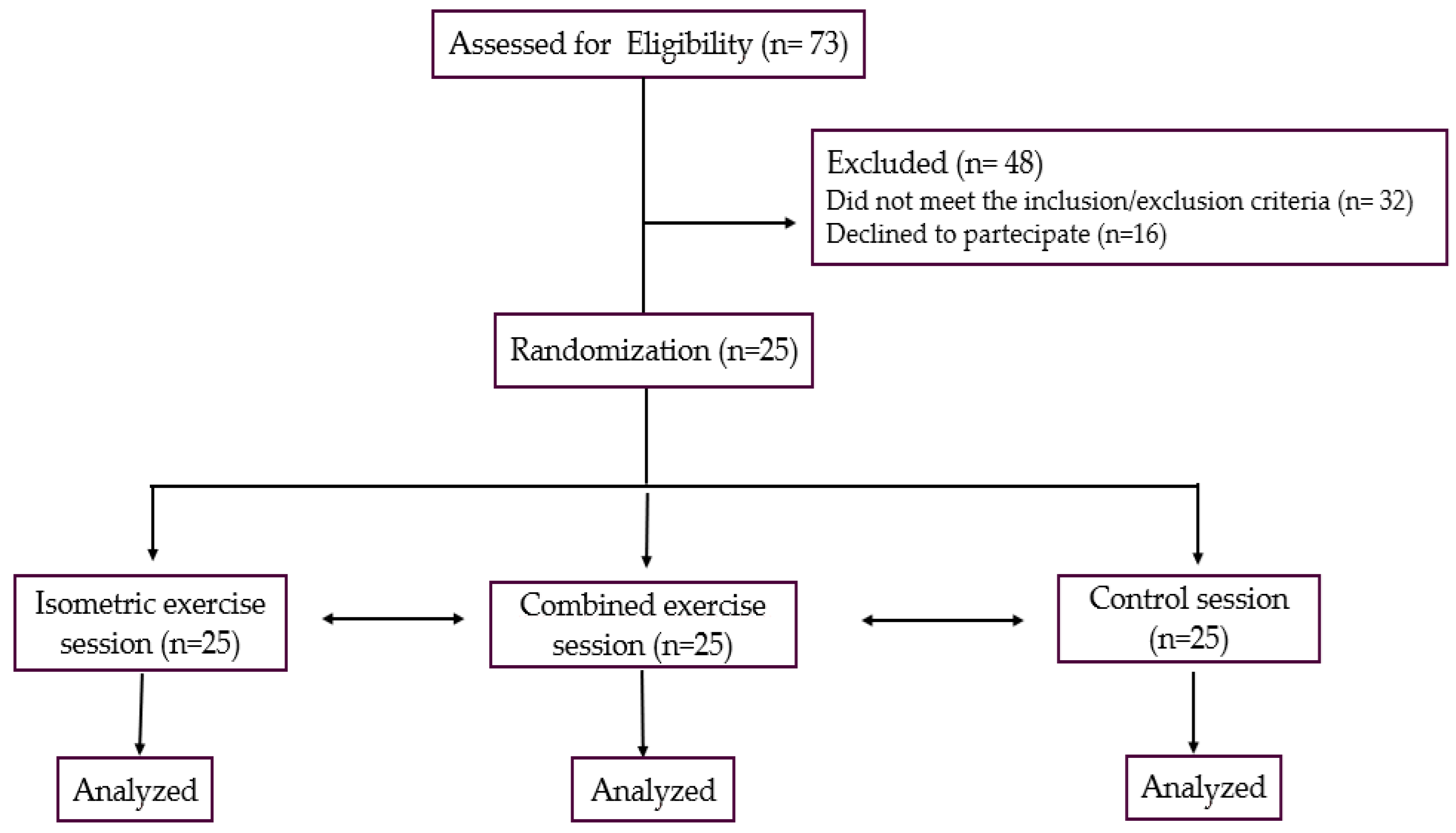
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Exercise Settings
2.4. Experimental Sessions
2.5. Statistical Analysis
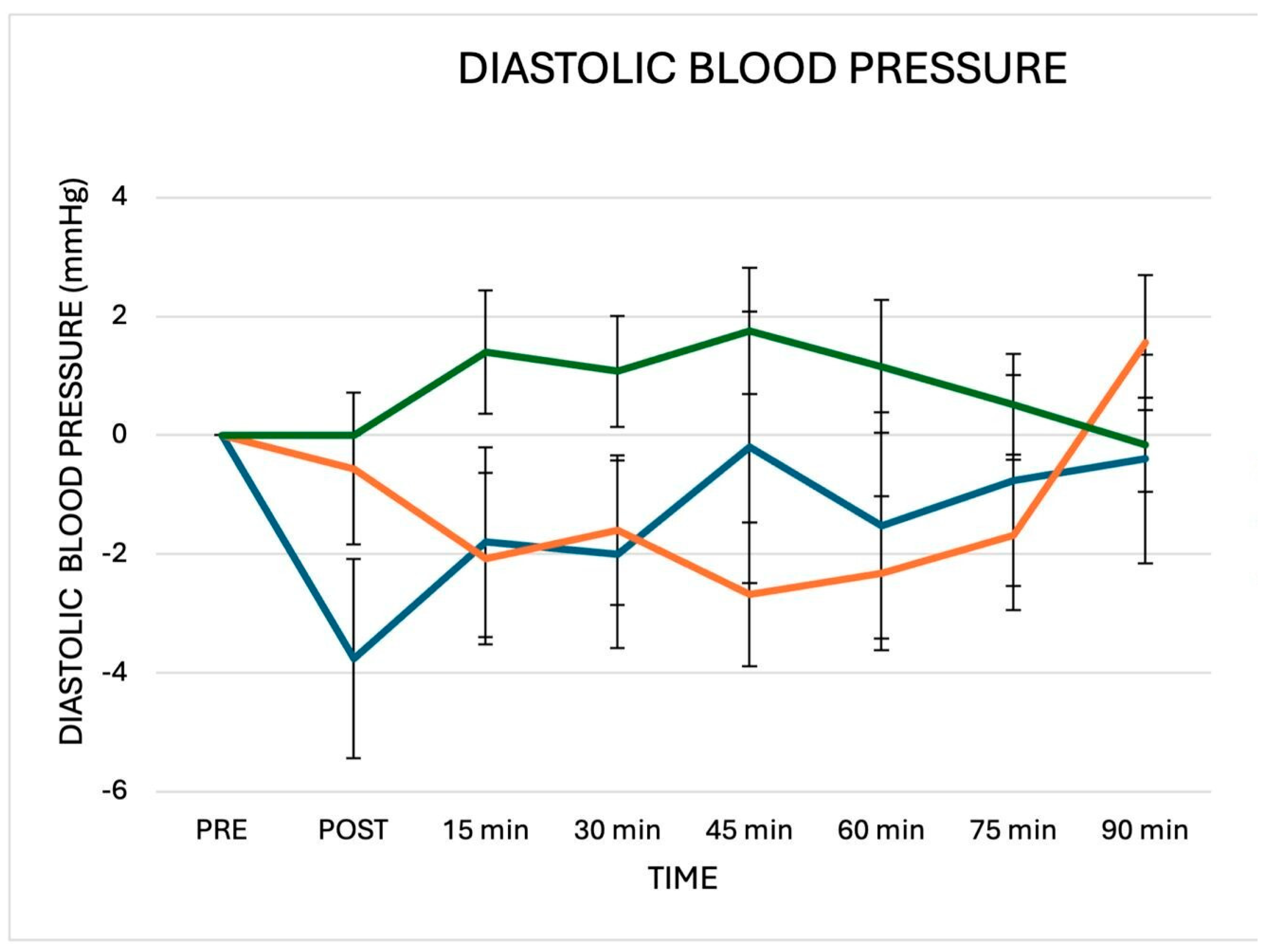
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornelissen, V.A.; Smart, N.A. Exercise training for blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e004473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescatello, L.S.; Buchner, D.M.; Jakicic, J.M.; Powell, K.E.; Kraus, W.E.; Bloodgood, B.; Campbell, W.W.; Dietz, S.; Dipietro, L.; George, S.M.; et al. Physical Activity to Prevent and Treat Hypertension: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarzadeh Ganjeh, B.; Zeraattalab-Motlagh, S.; Jayedi, A.; Daneshvar, M.; Gohari, Z.; Norouziasl, R.; Ghaemi, S.; Selk-Ghaffari, M.; Moghadam, N.; Kordi, R.; et al. Effects of aerobic exercise on blood pressure in patients with hypertension: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized trials. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Li, X.; Yan, P.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, K. The effectiveness of aerobic exercise for hypertensive population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, H.; Boardman, H.; Deiseroth, A.; Moholdt, T.; Simonenko, M.; Kränkel, N.; Niebauer, J.; Tiberi, M.; Abreu, A.; Solberg, E.E.; et al. Personalized exercise prescription in the prevention and treatment of arterial hypertension: A Consensus Document from the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC) and the ESC Council on Hypertension. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.J.; Dieberg, G.; Hess, N.C.; Millar, P.J.; Smart, N.A. Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.J.; Deenmamode, A.H.P.; Griffiths, M.; Arnold, O.; Cooper, N.J.; Wiles, J.D.; O’Driscoll, J.M. Exercise training and resting blood pressure: A large-scale pairwise and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.J.; Coleman, D.A.; Ritti-Dias, R.M.; Farah, B.Q.; Stensel, D.J.; Lucas, S.J.E.; Millar, P.J.; Gordon, B.D.H.; Cornelissen, V.; Smart, N.A.; et al. Isometric Exercise Training and Arterial Hypertension: An Updated Review. Sports Med. 2024, 54, 1459–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S. Evidence for exercise therapies including isometric handgrip training for hypertensive patients. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 48, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDougall, J.D.; McKelvie, R.S.; Moroz, D.E.; Sale, D.G.; McCartney, N.; Buick, F. Factors affecting blood pressure during heavy weight lifting and static contractions. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1992, 73, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.A.; Wiles, J.D.; Coleman, D.D.; Sharma, R.; O’driscoll, J.M. Continuous cardiac autonomic hemodynamic responses to isometric exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, P.; Nagle, F. Isometric exercise: Cardiovascular responses in normal and cardiac populations. Cardiol. Clin. 1987, 5, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishor Keshari, K.; Kumar, T.; Lnu, S.; Kumar, C.; Kumar, M. Evaluation of Cardiovascular Response to Isometric Handgrip Exercise in Obese Individuals. Cureus 2023, 15, e41898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminiti, G.; Marazzi, G.; Volterrani, M.; D’Antoni, V.; Fecondo, S.; Vadalà, S.; Sposato, B.; Giamundo, D.M.; Vitarelli, M.; Morsella, V.; et al. Effect of Different Isometric Exercise Modalities on Myocardial Work in Trained Hypertensive Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Randomized Pilot Study. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagonas, N.; Vlatsas, S.; Bauer, F.; Seibert, F.S.; Zidek, W.; Babel, N.; Schlattmann, P.; Westhoff, T.H. Aerobic versus isometric handgrip exercise in hypertension: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goessler, K.; Buys, R.; Cornelissen, V.A. Low-intensity isometric handgrip exercise has no transient effect on blood pressure in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2016, 10, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Silva, L.; Fecchio, R.Y.; Silva Junior, N.D.D.; Pio-Abreu, A.; Silva, G.V.D.; Drager, L.F.; Silva de Sousa, J.C.; Forjaz, C.L.M. Post-dynamic, isometric and combined resistance exercise responses in medicated hypertensive men. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2024, 38, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, K.; Yeung, P.K. Post-Exercise Hypotension: An. Alternative Management Strategy for Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, P.C.; Dipp, T.; Waclawovsky, G.; Lehnen, A.M. Post-isometric exercise hypotension occurs irrespective of muscle mass in adults with hypertension: A randomized clinical trial. Clinics 2025, 80, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G.A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, D.; Cahalane, E.; Conroy, R.; Fitzgerald, D.; Hardiman, O. Maximum voluntary isometric contraction: Reference values and clinical application. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2007, 8, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiadomski, W.; Laskowska, D.; Gąsiorowska, A.; Cybulski, G.; Strasz, A.; Józef Langfort, J. Determination and Prediction of One Repetition Maximum (1RM): Safety Considerations. J. Hum. Kinet. 2008, 19, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, J.D.; Goldring, N.; Coleman, D. Home-based isometric exercise training induced reductions resting blood pressure. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidi, M.; Ahmadizad, S.; Argani, H.; Najafi, A.; Ebrahim, K.; Salehi, N.; Javidi, Y.; Pescatello, L.S.; Jowhari, A.; Hackett, D.A. Effect of Lower- versus Higher-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Training in Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminiti, G.; Volterrani, M.; Iellamo, F.; Marazzi, G.; D’Antoni, V.; Calandri, C.; Vadalà, S.; Catena, M.; Di Biasio, D.; Manzi, V.; et al. Acute Changes in Myocardial Work during Isometric Exercise in Hypertensive Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inder, J.D.; Carlson, D.J.; Dieberg, G.; McFarlane, J.R.; Hess, N.C.; Smart, N.A. Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: A systematic review and meta-analysis to optimize benefit. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiza-Betancur, A.F.; Pérez Bedoya, E.; Montoya Dávila, J.; Chulvi-Medrano, I. Effect of Isometric Resistance Training on Blood Pressure Values in a Group of Normotensive Participants: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Health 2020, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baross, A.W.; Wiles, J.D.; Swaine, I.L. Effects of the intensity of leg isometric training on the vasculature of trained and untrained limbs and resting blood pressure in middle-aged men. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2012, 2012, 964697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baross, A.W.; Wiles, J.D.; Swaine, I.L. Double-leg isometric exercise training in older men. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2013, 4, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, J.D.; Coleman, D.A.; Swaine, I.L. The effects of performing isometric training at two exercise intensities in healthy young males. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, G.I.; Taylor, B.A.; Thompson, P.D.; MacDonald, H.V.; Lamberti, L.; Chen, M.H.; Farinatti, P.; Kraemer, W.J.; Panza, G.A.; Zaleski, A.L.; et al. The antihypertensive effects of aerobic versus isometric handgrip resistance exercise. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somani, Y.B.; Baross, A.W.; Brook, R.D.; Milne, K.J.; McGowan, C.L.; Swaine, I.L. Acute response to a 2-min isometric exercise test predicts the blood pressure-lowering efficacy of isometric resistance training in young adults. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Age, years | 65.9 ± 8.2. |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 28.1 ± 8.2 |
| Waist circumference, cm | 106.2 ± 31.6 |
| Male/female, n | 23/2 |
| Previous PCI/CABG, n | 19/10 |
| EF, (%) | 52.7 ± 6.7 |
| NT-proBNP, ng/pL | 124.2 ± 31.6 |
| Comorbidities | |
| Carotid artery disease, n (%) | 14 (56) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 7 (24) |
| Hypercholesterolemia, n (%) | 22 (88) |
| Previous Smoke habit, n (%) | 15 (60) |
| Ergometric test | |
| Time of exercise, s | 295.8 ± 87.3 |
| MET | 5.8 ± 1.6 |
| Treatment | |
| Anti-platelets agents, n (%) | 25 (100) |
| ACE-Is/ARBs, n (%) | 22 (88) |
| Betablockers, n (%) | 21 (84) |
| CCBs, n (%) | 11 (44) |
| SGLT2-I, n (%) | 7 (28) |
| Diuretics, n (%) | 8 (32) |
| Statins, n (%) | 25 (100) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vitarelli, M.; Laterza, F.; Peñín-Grandes, S.; Perrone, M.A.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Volterrani, M.; Marazzi, G.; Manzi, V.; Padua, E.; Sposato, B.; et al. Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by a Short Isometric Exercise Session Versus Combined Exercise in Hypertensive Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Pilot Study. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020189
Vitarelli M, Laterza F, Peñín-Grandes S, Perrone MA, Santos-Lozano A, Volterrani M, Marazzi G, Manzi V, Padua E, Sposato B, et al. Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by a Short Isometric Exercise Session Versus Combined Exercise in Hypertensive Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Pilot Study. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(2):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020189
Chicago/Turabian StyleVitarelli, Matteo, Francesco Laterza, Saúl Peñín-Grandes, Marco Alfonso Perrone, Alejandro Santos-Lozano, Maurizio Volterrani, Giuseppe Marazzi, Vincenzo Manzi, Elvira Padua, Barbara Sposato, and et al. 2025. "Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by a Short Isometric Exercise Session Versus Combined Exercise in Hypertensive Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Pilot Study" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 2: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020189
APA StyleVitarelli, M., Laterza, F., Peñín-Grandes, S., Perrone, M. A., Santos-Lozano, A., Volterrani, M., Marazzi, G., Manzi, V., Padua, E., Sposato, B., Morsella, V., Iellamo, F., & Caminiti, G. (2025). Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by a Short Isometric Exercise Session Versus Combined Exercise in Hypertensive Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Pilot Study. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(2), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020189













