No Long-Term Superiority of Cord-Derived PRP over Autologous PRP in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alessio-Mazzola, M.; Felli, L.; Trentini, R.; Formica, M.; Capello, A.G.; Lovisolo, S.; Maffulli, N. Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Grade 3 Symptomatic Degenerative Meniscal Lesions: A 1-Year Follow-up Prospective Study. Sports Health 2022, 14, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Coviello, M.; Abate, A.; Ippolito, F.; Nappi, V.; Maddalena, R.; Maccagnano, G.; Noia, G.; Caiaffa, V. Continuous Cold Flow Device Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: Myths and Reality. Medicina 2022, 58, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cole, B.J.; Karas, V.; Hussey, K.; Pilz, K.; Fortier, L.A. Hyaluronic Acid Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Prospective, Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Clinical Outcomes and Effects on Intra-articular Biology for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 339–346, Erratum in: Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, NP10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, L.; Bizzoca, D.; Geronimo, A.; Moretti, F.L.; Monaco, E.; Solarino, G.; Moretti, B. Towards Precision Medicine for Osteoarthritis: Focus on the Synovial Fluid Proteome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Di Martino, A.; Di Matteo, B.; Papio, T.; Tentoni, F.; Selleri, F.; Cenacchi, A.; Kon, E.; Filardo, G. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid Injections for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: Results at 5 Years of a Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasai, S.; Sato, M.; Maehara, M.; Toyoda, E.; Uchiyama, R.; Takahashi, T.; Okada, E.; Iwasaki, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Watanabe, M. Characteristics of autologous protein solution and leucocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Prodromidis, A.D.; Charalambous, C.P.; Moran, E.; Venkatesh, R.; Pandit, H. The role of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) intraarticular injections in restoring articular cartilage of osteoarthritic knees. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open. 2022, 4, 100318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Coşkun, H.S.; Yurtbay, A.; Say, F. Platelet Rich Plasma Versus Autologous Conditioned Serum in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Clinical Results of a Five-Year Retrospective Study. Cureus 2022, 14, e24500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Horie, M.; Choi, H.; Lee, R.H.; Reger, R.L.; Ylostalo, J.; Muneta, T.; Sekiya, I.; Prockop, D.J. Intraarticular injection of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) promotes rat meniscal regeneration by being activated to express Indian hedgehog that enhances expression of type II collagen. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Pinto, N.R.; Pereda, A.; Jimenez, P.; Corso, M.D.; Kang, B.S.; Nally, M.; Lanata, N.; Wang, H.L.; Quirynen, M. The impact of the centrifuge characteristics and centrifugation protocols on the cells, growth factors, and fibrin architecture of a leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) clot and membrane. Platelets 2018, 29, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.B.; Blashki, D.; Buchanan, R.M.; Yazdi, I.K.; Ferrari, M.; Simmons, P.J.; Tasciotti, E. Adult and umbilical cord blood-derived platelet-rich plasma for mesenchymal stem cell proliferation, chemotaxis, and cryo-preservation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5308–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, E.; Mandelbaum, B.; Buda, R.; Filardo, G.; Delcogliano, M.; Timoncini, A.; Fornasari, P.M.; Giannini, S.; Marcacci, M. Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular injection versus hyaluronic acid viscosupplementation as treatments for cartilage pathology: From early degeneration to osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy 2011, 27, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belk, J.W.; Kraeutler, M.J.; Houck, D.A.; Goodrich, J.A.; Dragoo, J.L.; McCarty, E.C. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, T.; Mosier, B.A.; Bryant, T.; Minas, T. A 20-year follow-up after first-generation autologous chondrocyte implantation. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 2751–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaková, T.; Rosocha, J.; Lacko, M.; Harvanová, D.; Gharaibeh, A. Treatment of knee joint osteoarthritis with autologous platelet-rich plasma in comparison with hyaluronic acid. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzotta, A.; Pennello, E.; Stagni, C.; Del Piccolo, N.; Boffa, A.; Cenacchi, A.; Buzzi, M.; Filardo, G.; Dallari, D. Umbilical Cord PRP vs. Autologous PRP for the Treatment of Hip Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Annaniemi, J.A.; Pere, J.; Giordano, S. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Therapy in Obese versus Non-Obese Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Comparative Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.H.; Gong, S.G.; Song, J.; Wu, P.P.; Hu, W.L. Effect of mesenchymal stromal cells transplantation on the outcomes of patients with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Res. 2024, 42, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Niu, J.; Huang, J.; Ke, Y.; Tang, X.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Li, H.; Zhi, X.; Wang, K.; et al. Knee osteoarthritis and all-cause mortality: The Wuchuan Osteoarthritis Study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardo, G.; Di Matteo, B.; Di Martino, A.; Merli, M.L.; Cenacchi, A.; Fornasari, P.; Marcacci, M.; Kon, E. Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular knee injections show no superiority versus viscosupplementation: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 43, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellegren, J.H.; Lawrence, J.S. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 16, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebulla, P.; Pupella, S.; Santodirocco, M.; Greppi, N.; Villanova, I.; Buzzi, M.; De Fazio, N.; Grazzini, G.; Italian Cord Blood Platelet Gel Study Group. Multicentre standardisation of a clinical grade procedure for the preparation of allogeneic platelet concentrates from umbilical cord blood. Blood Transfus. 2016, 14, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gould, D.; Kelly, D.; Goldstone, L.; Gammon, J. Visual Analogue Scale (VAS). J. Clin. Nurs. 2001, 10, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WOMAC Osteoarthritis Index. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003, pp. 511–560. Available online: http://www.uppharma.it/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/scale-valutazione-osteoartrite-WOMAC.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Roos, E.M.; Roos, H.P.; Lohmander, L.S.; Ekdahl, C.; Beynnon, B.D. Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS)--development of a self-administered outcome measure. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1998, 28, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiaffa, V.; Ippolito, F.; Abate, A.; Nappi, V.; Santodirocco, M.; Visceglie, D. Allogenic platelet concentrates from umbilical cord blood for knee osteoarthritis: Preliminary results. Med. Glas. 2021, 18, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villafañe, J.H.; Valdes, K.; Pedersini, P.; Berjano, P. Osteoarthritis: A call for research on central pain mechanism and personalized prevention strategies. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessio-Mazzola, M.; Lovisolo, S.; Sonzogni, B.; Capello, A.G.; Repetto, I.; Formica, M.; Felli, L. Clinical outcome and risk factor predictive for failure of autologous PRP injections for low-to-moderate knee osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 29, 23094990211021922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, H.; Leon, J.; Pont, J.L.; Wilson, D.A.; Bansal, A.; Agarwal, D.; Preoteasa, I. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in osteoarthritis (OA) knee: Correct dose critical for long term clinical efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3971, Erratum in: Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khurana, A.; Goyal, A.; Kirubakaran, P.; Akhand, G.; Gupta, R.; Goel, N. Efficacy of Autologous Conditioned Serum (ACS), Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), Hyaluronic Acid (HA) and Steroid for Early Osteoarthritis Knee: A Comparative Analysis. Indian J. Orthop. 2020, 55 (Suppl. 1), 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Filardo, G.; Kon, E.; Buda, R.; Timoncini, A.; Di Martino, A.; Cenacchi, A.; Fornasari, P.M.; Giannini, S.; Marcacci, M. Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular knee injections for the treatment of degenerative cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
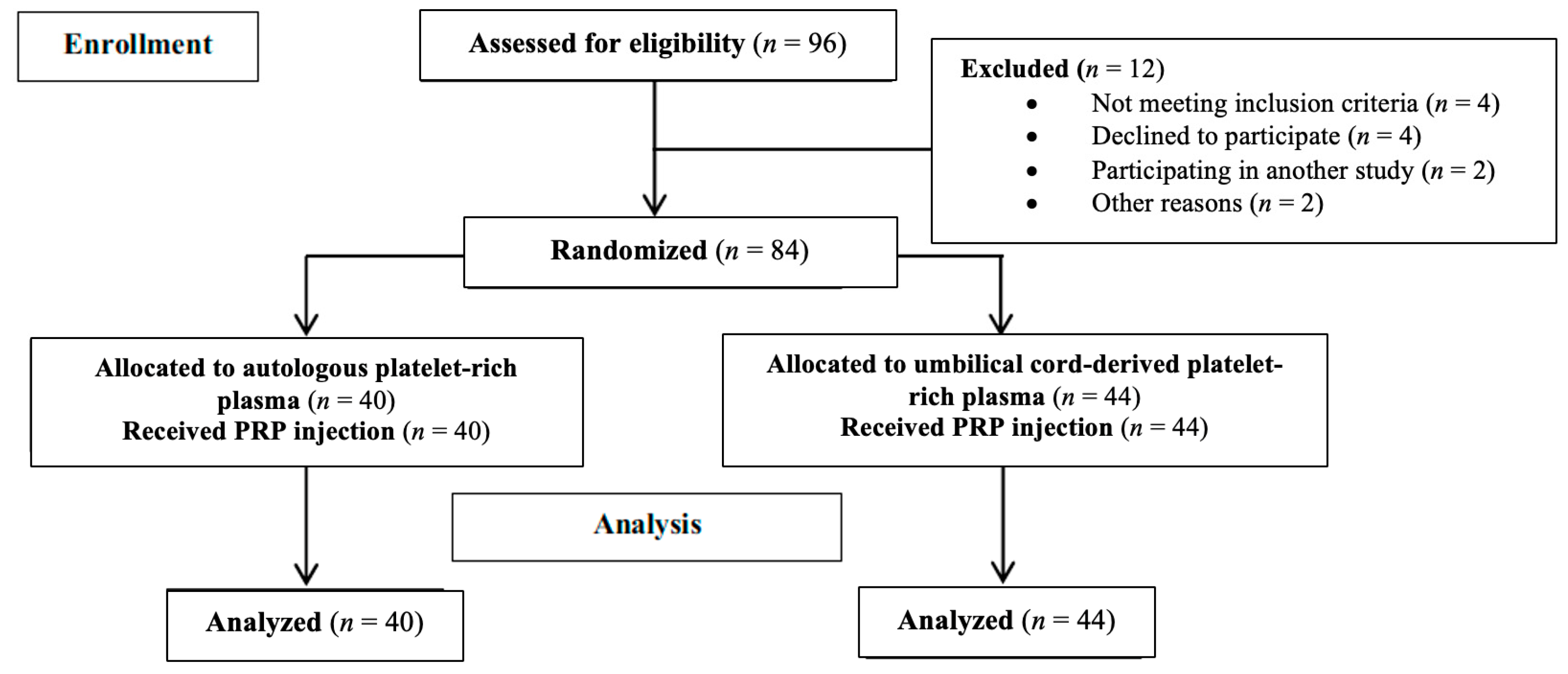

| Preoperative Features | C-PRP Group (n = 44) | A-PRP Group (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 58.36 ± 8.51 | 60.19 ± 9.21 | 0.23 |
| Gender (female) | 20 (45.5%) | 22 (55%) | 0.38 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 25.19 ± 5.27 | 25.36 ± 3.92 | 0.59 |
| Side (left) | 19 (43.2%) | 15 (37.5%) | 0.86 |
| Kellgren–Lawrence | 0.71 | ||
| I | 9 (20.5%) | 10 (25%) | |
| II | 20 (45.5%) | 17 (42.5%) | |
| III | 15 (34.1%) | 13 (32.5%) | |
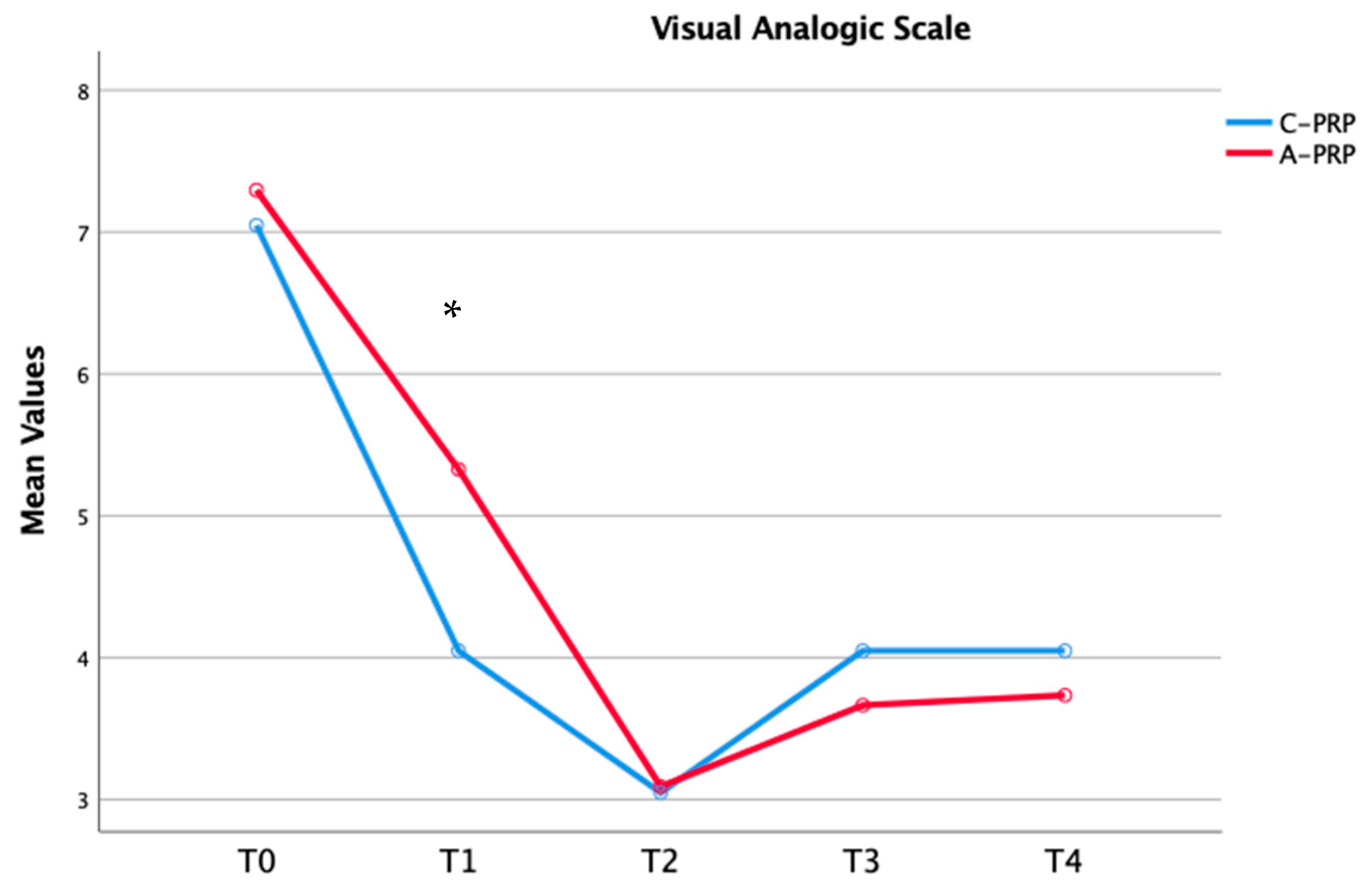
| VAS_T0 | 7.05 ± 1.31 | 7.29 ± 1.91 | 0.43 |
| WOMAC_T0 | 50.93 ± 9.49 | 53.30 ± 13.43 | 0.39 |
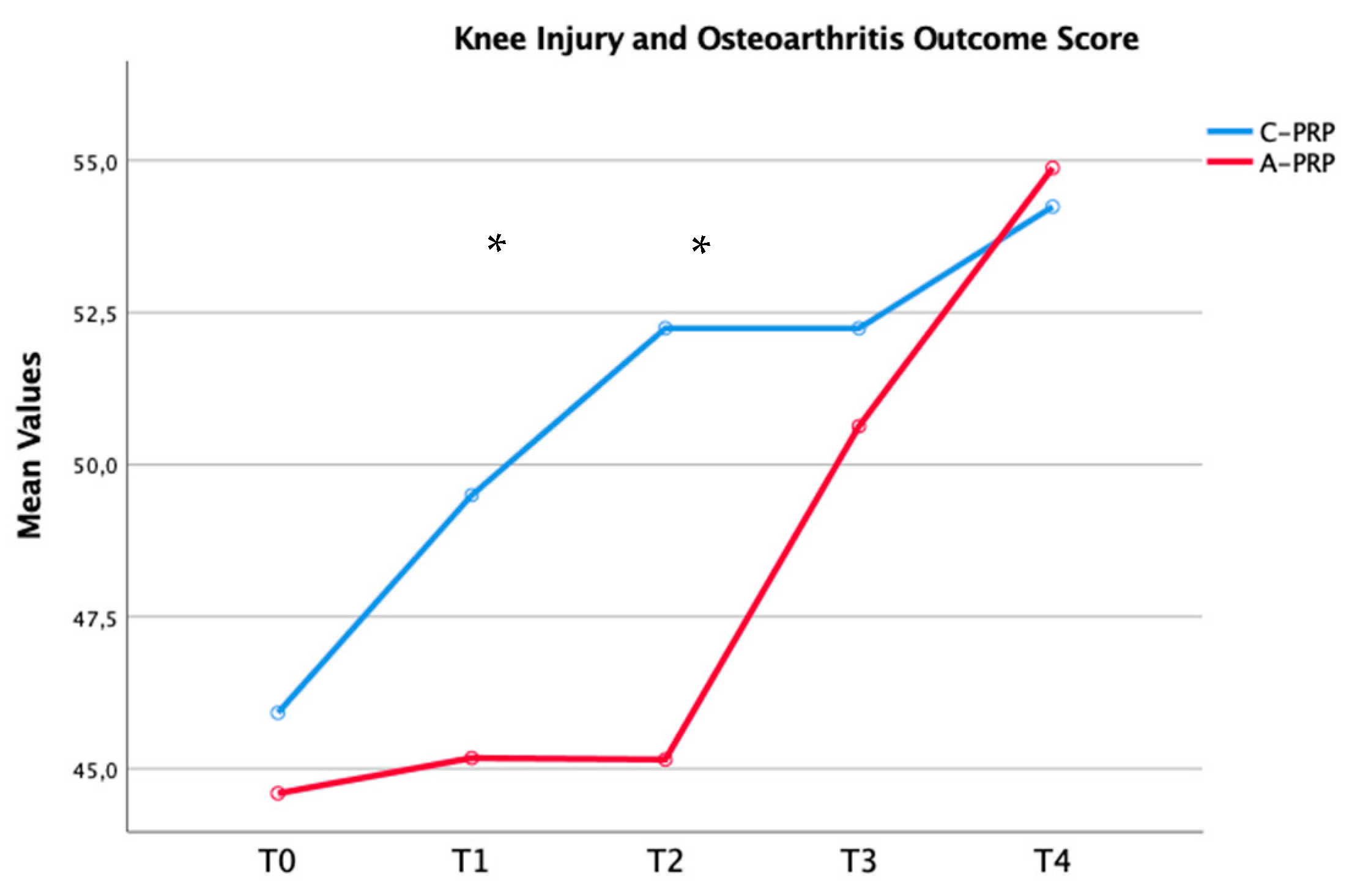
| KOOS_T0 | 45.92 ± 6.02 | 44.59 ± 4.15 | 0.75 |
| IKDC_T0 | 40.24 ± 6.59 | 39.44 ± 4.53 | 0.61 |
| C-PRP Group (n = 44) | A-PRP Group (n = 40) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS | ||||
| T1 | 4.05 ± 1.23 | 5.23 ± 2.22 | 0.03 | |
| T2 | 3.05 ± 0.94 | 3.09 ± 0.98 | 0.85 | |
| T3 | 4.05 ± 0.89 | 3.66 ± 1.30 | 0.29 | |
| T4 | 4.01 ± 0.68 | 3.73 ± 0.96 | 0.35 | |
| WOMAC | ||||
| T1 | 28.78 ± 4.85 | 36.92 ± 10.15 | 0.01 | |
| T2 | 35.18 ± 4.47 | 40.30 ± 13.43 | 0.03 | |
| T3 | 42.48 ± 11.31 | 42.30 ± 12.42 | 0.94 | |
| T4 | 41.78 ± 5.16 | 44.30 ± 13.35 | 0.29 | |
| KOOS | ||||
| T1 | 49.50 ± 6.15 | 45.17 ± 4.41 | 0.01 | |
| T2 | 52.24 ± 6.58 | 45.15 ± 6.71 | 0.01 | |
| T3 | 52.12 ± 5.29 | 50.63 ± 7.21 | 0.20 | |
| T4 | 54.24 ± 6.34 | 54.88 ± 6.70 | 0.54 | |
| IKDC | ||||
| T1 | 53.24 ± 6.29 | 49.40 ± 5.48 | 0.07 | |
| T2 | 53.67 ± 4.22 | 50.15 ± 6.71 | 0.01 | |
| T3 | 48.78 ± 5.13 | 47.15 ± 6.74 | 0.70 | |
| T4 | 47.25 ± 5.43 | 47.56 ± 8.31 | 0.88 |
| Preoperative | Last Follow Up | Mean Difference | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-PRP Group (n = 44) | ||||
| VAS | 7.05 ± 1.31 | 4.01 ± 0.68 | −3.04 ± 0.63 | 0.01 |
| WOMAC | 50.93 ± 9.49 | 41.78 ± 5.16 | −9.23 ± 4.33 | 0.01 |
| KOOS | 45.92 ± 6.02 | 54.24 ± 6.34 | 8.32 ± 0.32 | 0.01 |
| IKDC | 40.24 ± 6.59 | 47.25 ± 5.43 | 7.01 ± 1.16 | 0.01 |
| A-PRP Group (n = 40) | ||||
| VAS | 7.29 ± 1.91 | 3.73 ± 0.96 | −3.56 ± 0.95 | 0.01 |
| WOMAC | 53.30 ± 13.43 | 44.30 ± 13.35 | −11.00 ± 0.08 | 0.01 |
| KOOS | 44.59 ± 4.15 | 54.24 ± 6.34 | 9.65 ± 2.19 | 0.01 |
| IKDC | 39.44 ± 4.53 | 47.56 ± 8.31 | 8.12 ± 3.78 | 0.01 |
| OR | 95% CI | SE | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-PRP Group (n = 44) | ||||
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 2.99 | 0.42–21.41 | 0.3 | 0.01 |
| Kellgren–Lawrence | 64.52 | 11.27–369.35 | 1.4 | 0.01 |
| A-PRP Group (n = 40) | ||||
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 3.56 | 0.98–32.29 | 0.6 | 0.01 |
| Kellgren–Lawrence | 59.46 | 10.13–289.78 | 1.2 | 0.01 |
| Aspect | Autologous PRP (A-PRP) | Cord Blood-Derived PRP (C-PRP) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost of Preparation | €164 per session | €196 per session |
| Availability | Widely available in most orthopedic clinics and hospitals | Limited availability; requires specialized centers or biobanks |
| Processing Complexity | Simple; involves blood collection and centrifugation | Complex; involves umbilical cord blood collection, screening, and advanced processing |
| Logistical Issues | Minimal; processed at point of care, no need for external sourcing | High; requires specialized facilities, donor screening, cryopreservation, and transport |
| Regulatory Considerations | Minimal; standard blood processing regulations | Stringent; requires compliance with ethical, regulatory, and safety standards for human tissues |
| Standardization | Dependent on patient’s platelet count and blood quality | More standardized, with consistent quality due to controlled sourcing and processing |
| Time to Preparation | Relatively quick, usually within the same treatment session | Longer; involves additional steps such as donor screening, processing, and potential cryopreservation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coviello, M.; Abate, A.; Maccagnano, G.; Geronimo, A.; Caiaffa, E.; Nappi, V.; Caiaffa, V.; Solarino, G. No Long-Term Superiority of Cord-Derived PRP over Autologous PRP in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020138
Coviello M, Abate A, Maccagnano G, Geronimo A, Caiaffa E, Nappi V, Caiaffa V, Solarino G. No Long-Term Superiority of Cord-Derived PRP over Autologous PRP in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(2):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020138
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoviello, Michele, Antonella Abate, Giuseppe Maccagnano, Alessandro Geronimo, Elio Caiaffa, Vittorio Nappi, Vincenzo Caiaffa, and Giuseppe Solarino. 2025. "No Long-Term Superiority of Cord-Derived PRP over Autologous PRP in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 2: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020138
APA StyleCoviello, M., Abate, A., Maccagnano, G., Geronimo, A., Caiaffa, E., Nappi, V., Caiaffa, V., & Solarino, G. (2025). No Long-Term Superiority of Cord-Derived PRP over Autologous PRP in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(2), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020138









