Acute Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Warm-Up on Performance and Cardiorespiratory Parameters of Scuba Divers—A Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.2.1. Inspiratory Muscle Warm-Up (IMW)
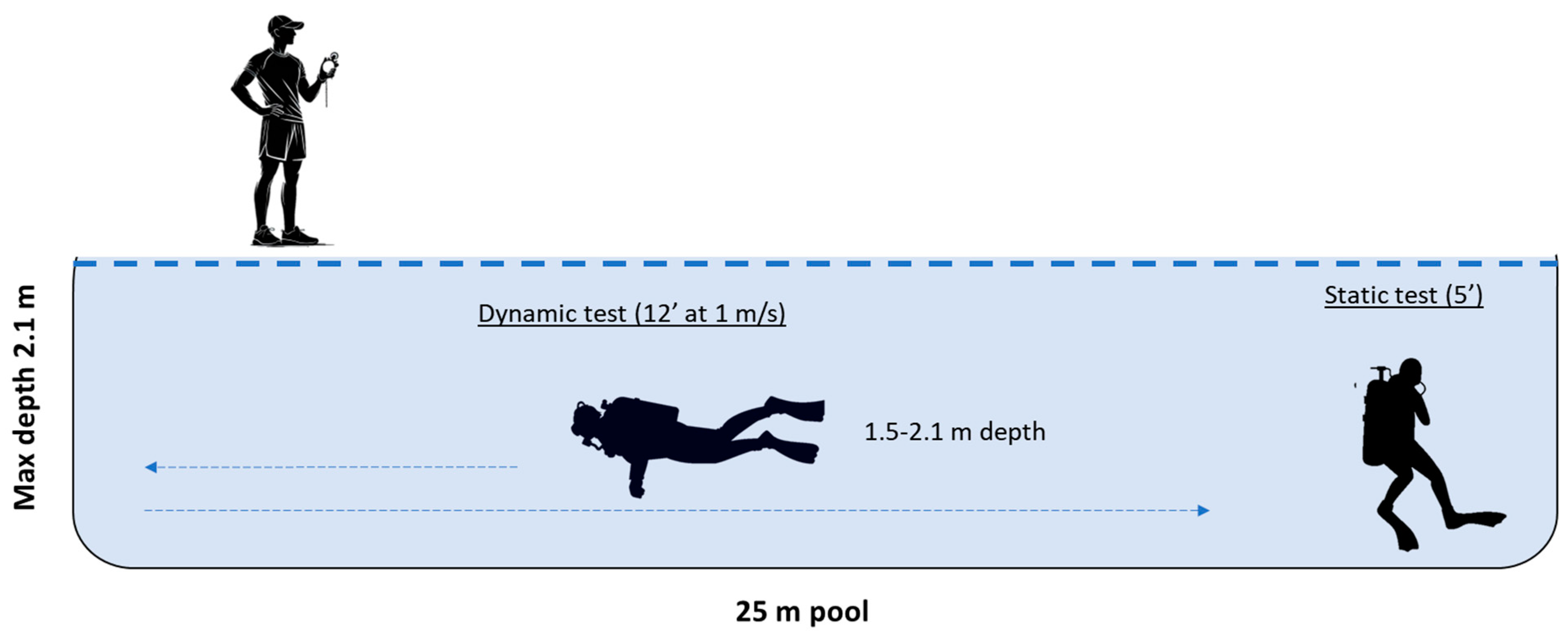
2.2.2. Immersion Protocols: Static and Dynamic Immersion Test
2.3. Outcomes
2.3.1. Gas Consumption
2.3.2. Forced Spirometry (FS)
2.3.3. Oxygen Saturation (SO2) and Heart Rate (HR)
2.3.4. Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IMW | inspiratory muscle warm-up |
| SO2 | oxygen saturation |
| RPE | rate of perceived exertion |
| HR | heart rate |
| MIP | maximal inspiratory pressure |
| FS | forced spirometry |
| BPM | beats per minute |
References
- Fúnez, M.L.; Casadesús, J.M.; Aguirre, F.; Carrera, A.; Reina, F. Practice guideline for multidisciplinary investigation of diving fatalities. Rev. Esp. Med. Leg. 2024, 50, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, D.R.; Lundgren, C.E.G. The underwater environment: Cardiopulmonary, thermal, and energetic demands. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalat, G.; Coquart, J.; Castres, I.; Joulia, F.; Sirost, O.; Clua, E.; Lemaître, F. The oxygen-conserving potential of the diving response: A kinetic-based analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2017, 35, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, J.C.L.; Sepúlveda, I.C.; Sánchez, E.S.M.; Duque, J.E.M.; Benítez, J.F.C. Physiology responses at baseline and subsequent dynamic apnea in underwater athletes. Rev. Peru. Cienc. Act. Fis. Dep. 2023, 10, 1717–1737. [Google Scholar]
- de Asís-Fernández, F.; Del Corral, T.; López-De-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Effects of inspiratory muscle training versus high intensity interval training on the recovery capacity after a maximal dynamic apnoea in breath-hold divers: A randomised crossover trial. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2020, 50, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Escudero, P.; Cabanas, A.M.; Fuentes-Ferrer, M.; Galindo-Canales, M. Oxygen saturation behavior by pulse oximetry in female athletes: Breaking myths. Biosensors 2021, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Kawamura, T.; Akiyama, H.; Chang, L.; Iwata, R.; Muraoka, I. Effects of sex differences on breath-hold diving performance. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2021, 293, 103721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorini, L.; Rodio, A.; Di Libero, T.; Ieno, C.; Tranfo, G.; Pigini, D.; Pinto, A.; Marchetti, E. Hyperbaric effects on heart rate in professional SCUBA divers in thermal water. Front. Sports Act. Living 2024, 6, 1429732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, N.A.; Giallauria, F.; Dieberg, G. Efficacy of inspiratory muscle training in chronic heart failure patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 1502–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Corchete, L.A.; García, J.F.; Jerves Donoso, D.; Lantarón-Caeiro, E.; Cobreros Mielgo, R.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Gallego-Gallego, D.; Seco-Calvo, J. Effects on respiratory pressures, spirometry biomarkers, and sports performance after inspiratory muscle training in a physically active population by Powerbreath®: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biology 2022, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajghanbari, B.; Yamabayashi, C.; Buna, T.R.; Coelho, J.D.; Freedman, K.D.; Morton, T.A.; Palmer, S.A.; Toy, M.A.; Walsh, C.; Sheel, A.W.; et al. Effects of respiratory muscle training on performance in athletes: A systematic review with meta-analyses. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 1643–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Gallego-Gallego, D.; Corchete, L.A.; Fernández Zoppino, D.; González-Bernal, J.J.; García Gómez, B.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J. Inspiratory muscle training program using the PowerBreath®: Does it have ergogenic potential for respiratory and/or athletic performance? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, M.; Forget, P.; Couturaud, F.; Reychler, G. Effects of inspiratory muscle training in COPD patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 2178–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, C.; Marostegan, A.B.; Hartz, C.S.; Moreno, M.A.; Gobatto, C.A.; Manchado-Gobatto, F.B. Effects of inspiratory muscle warm-up on physical exercise: A systematic review. Biology 2023, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdal, M.; Bostanci, Ö. Influence of inspiratory muscle warm-up on aerobic performance during incremental exercise. Isokinet. Exerc. Sci. 2018, 26, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdal, M.; Bostanci, Ö.; Dağlioğlu, Ö.; Ağaoğlu, S.A.; Kabadayi, M. Effect of respiratory warm-up on anaerobic power. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriverdi, A.; Kahraman, B.O.; Ozsoy, I.; Ozpelit, E.; Savci, S. Acute effects of inspiratory muscle training at different intensities in healthy young people. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 190, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepomuceno Júnior, V.; Borges Gómez, T.; Gomes Neto, M. Use of Powerbreathe® in inspiratory muscle training for athletes: Systematic review. Fisioter. Mov. 2016, 29, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Koizumi, J.; Ohya, T. Effects of high-intensity inspiratory muscle warm-up on inspiratory muscle strength and accessory inspiratory muscle activity. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2023, 313, 104069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.E.; McKeever, T.M.; Lobb, C.; Sherriff, T.; Gupta, L.; Hearson, G.; Martin, N.; Lindley, M.R.; Shaw, D.E. Respiratory muscle specific warm-up and elite swimming performance. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, E.F.; Sanders, M.E.; Shafer, A.; Barone Gibbs, B.; Nagle, J.A.; Deldin, A.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Robertson, R.J. Energy expenditure, cardiorespiratory, and perceptual responses to shallow-water aquatic exercise in young adult women. Phys. Sportsmed. 2013, 41, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Science, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kilding, A.E.; Brown, S.; McConnell, A.K. Inspiratory muscle training improves 100 and 200 m swimming performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal-Tello, N.; Ortega, J.G.; Caballero-Lozada, A.F.; Devia-Quiñonez, M.J.; González-Calzada, I.; Rojas-Hernández, D.; Segura-Ordoñez, A. Effects of inspiratory muscle training on lung function parameter in swimmers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Sports Act. Living 2024, 16, 1429902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, J.; Ohya, T. Effects of High-Intensity Inspiratory Muscle Warm-Up on High-Intensity Exercise Performance and Muscle Oxygenation. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2024, 19, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, Á.H.; Galdames, S.; Barrilao, R.G.; Serrano, P.A.C.; Arancibia, A.P.A.; Argandoña, P.D.S. Influence of intermittent aerobic performance on the variables of static and dynamic apnea performances. Arch. Med. Deporte 2017, 34, 274–279. [Google Scholar]
- Arend, M.; Kivastik, J.; Mäestu, J. Maximal inspiratory pressure is influenced by intensity of the warm-up protocol. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2016, 230, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorca-Santiago, J.; Jiménez, S.L.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Lorenzo, A. Inspiratory muscle training in intermittent sports modalities: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NO IMW | IMW | ANOVA | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Effect | IMW Effect | Time × IMW Effect | ||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p | d | F | p | η2p | F | p | η2p | F | p | η2p | ||
| Gas consumption (bar) | 13.75 ± 3.77 | 10.00 ± 2.31 | 0.034 | 1.19 | ||||||||||
| O2 saturation (%) | Pre | 98.12 ± 0.99 | 98.37 ± 0.74 | 0.458 | 0.28 | 7.364 | 0.030 | 0.513 | 1.647 | 0.240 | 0.190 | 0.563 | 0.478 | 0.074 |
| Post | 95.00 ± 4.27 | 96.62 ± 1.50 * | 0.233 | 0.5 | ||||||||||
| Spirometry (L/min) | Pre | 567.50 ± 185.40 | 620.00 ± 150.02 | 0.73 | 0.31 | 0.312 | 0.594 | 0.043 | 18.152 | 0.004 | 0.722 | 6.081 | 0.063 | 0.326 |
| Post | 539.37 ± 203.72 | 600.00 ± 161.75 | 0.025 | 0.33 | ||||||||||
| HR (bpm) | Pre | 84.25 ± 12.57 | 90.00 ± 9.70 | 0.293 | 0.51 | 0.246 | 0.635 | 0.034 | 10.112 | 0.013 | 0.714 | 5.341 | 0.054 | 0.433 |
| Post | 78.12 ± 7.39 | 94.00 ± 11.04 | 0.005 | 1.69 | ||||||||||
| RPE | 2.37 ± 2.72 | 1.50 ± 1.60 | 0.059 | 0.3 | ||||||||||
| NO IMW | IMW | ANOVA | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Effect | IMW Effect | Time × IMW Effect | |||||||||||||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p | d | F | p | η2p | F | p | η2p | F | p | η2p | |||
| Gas consumption (bar) | 59.37 ± 15.90 | 51.25 ± 15.05 | 0.001 | 0.526 | |||||||||||
| O2 saturation (%) | Pre | 96.37 ± 3.15 | 96.12 ± 2.79 | 0.888 | 0.008 | 177.144 | <0.001 | 0.962 | 0.012 | 0.915 | 0.002 | 0.732 | 0.420 | 0.095 | |
| Post | 92.25 ± 3.10 * | 93.12 ± 3.97 * | 0.345 | 0.244 | |||||||||||
| Spirometry (l/min) | Pre | 561.25 ±176.97 | 625.00 ± 142.60 | 0.006 | 0.56 | 1.714 | 0.232 | 0.197 | 37.741 | 0.003 | 0.872 | 6.581 | 0.052 | 0.349 | |
| Post | 563.75 ± 155.35 | 590.00 ± 167.90 | 0.121 | 0.44 | |||||||||||
| HR (bpm) | Pre | 81.25 ± 10.01 | 91.37 ± 10.01 | 0.001 | 1.01 | 10.915 | 0.013 | 0.609 | 16.024 | 0.005 | 0.696 | 0.048 | 0.834 | 0.007 | |
| Post | 87.37 ± 14.16 * | 96.62 ± 8.99 | 0.054 | 0.77 | |||||||||||
| RPE | 4.37 ± 1.30 | 5.56 ± 1.29 | 0.012 | 0.91 | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alberola-Blanes, R.; Alacid, F.; Quero-Calero, C.D.; López-Plaza, D. Acute Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Warm-Up on Performance and Cardiorespiratory Parameters of Scuba Divers—A Preliminary Study. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020105
Alberola-Blanes R, Alacid F, Quero-Calero CD, López-Plaza D. Acute Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Warm-Up on Performance and Cardiorespiratory Parameters of Scuba Divers—A Preliminary Study. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(2):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020105
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlberola-Blanes, Ricardo, Fernando Alacid, Carmen Daniela Quero-Calero, and Daniel López-Plaza. 2025. "Acute Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Warm-Up on Performance and Cardiorespiratory Parameters of Scuba Divers—A Preliminary Study" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 2: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020105
APA StyleAlberola-Blanes, R., Alacid, F., Quero-Calero, C. D., & López-Plaza, D. (2025). Acute Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Warm-Up on Performance and Cardiorespiratory Parameters of Scuba Divers—A Preliminary Study. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(2), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020105







