Changes in Foot Shape after Long-Distance Running
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Data Collection
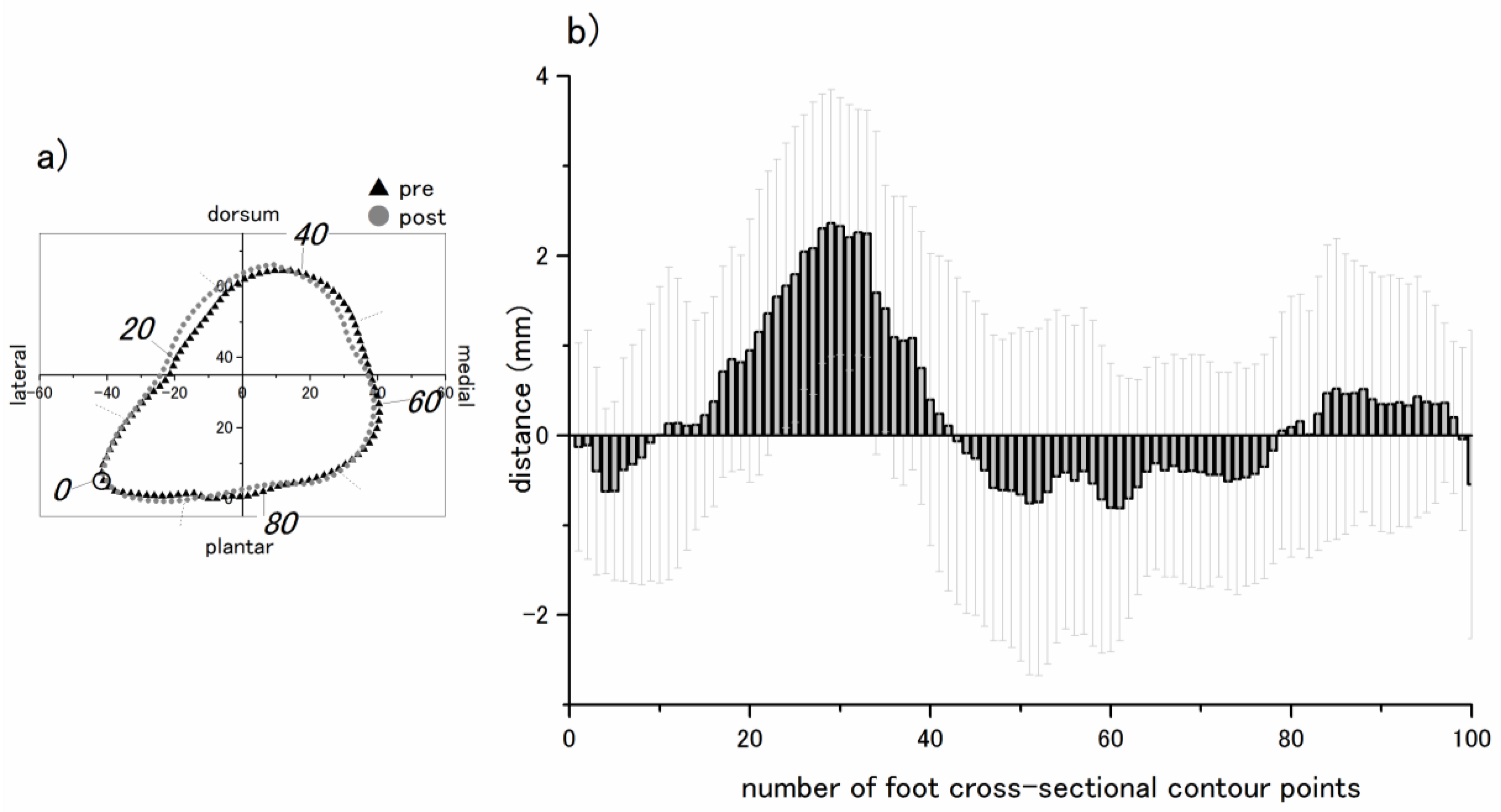
2.3. Data Processing
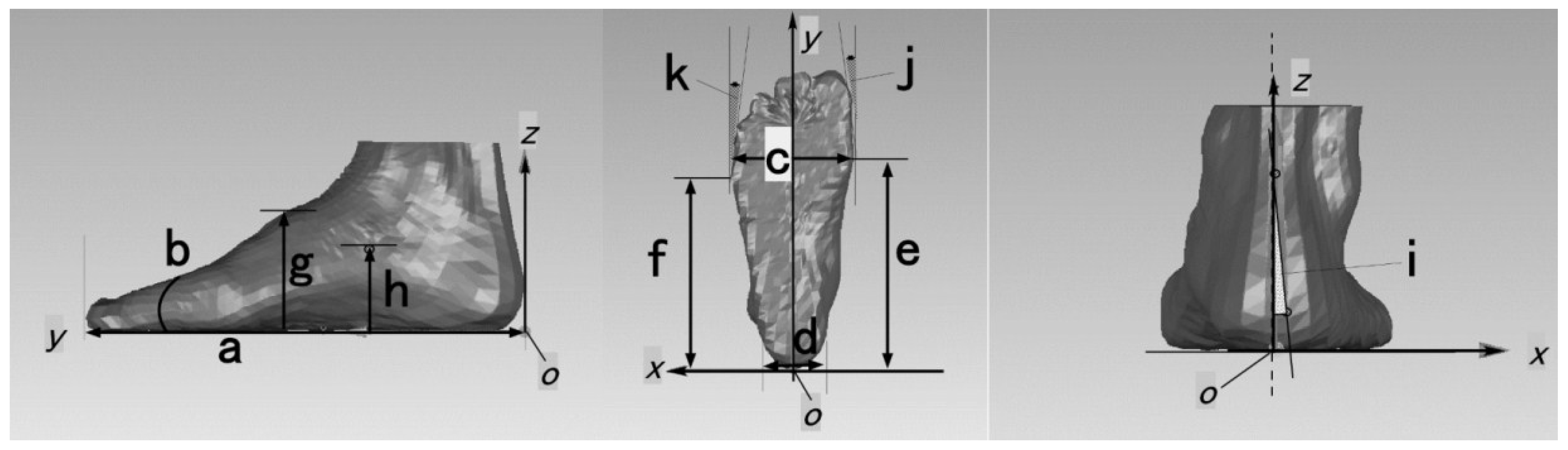
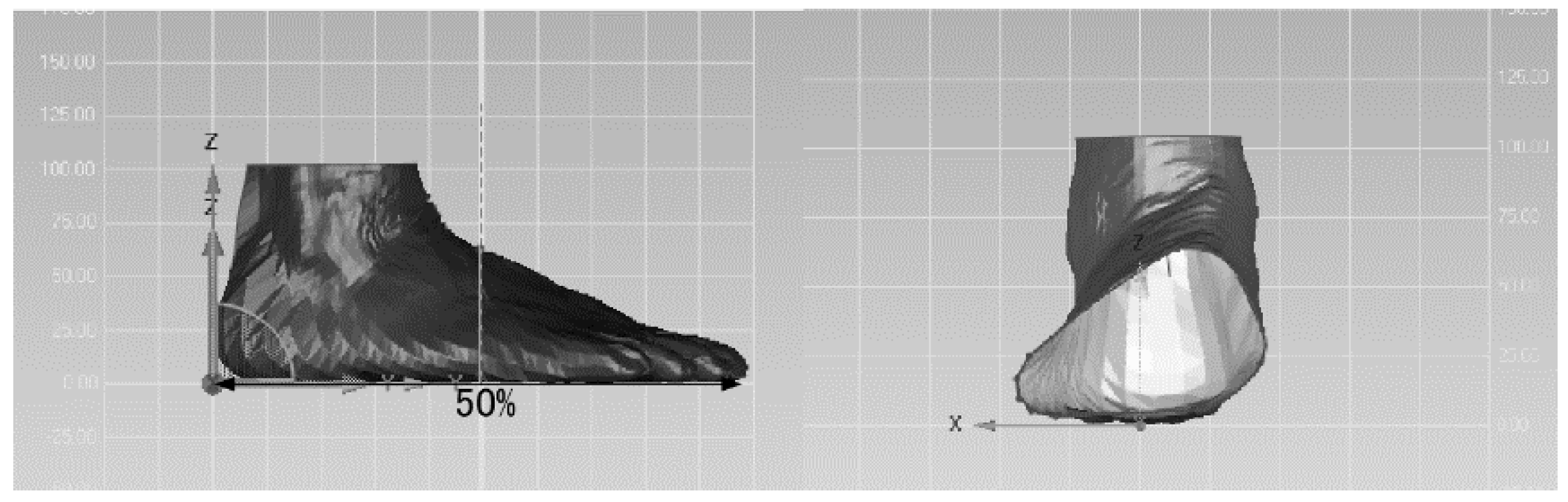
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
| Condition | Pre-run | Post-run | Difference | p Value | Effect Size (r) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean | (SD) | Mean | (SD) | ||||
| foot length (mm) | 253.6 | 8.7 | 254.0 | 8.5 | −0.4 | ns | 0.26 | 0.25 |
| ball girth (mm) | 244.3 | 9.8 | 243.5 | 9.8 | 0.8 | ns | 0.28 | 0.24 |
| ball width (mm) | 99.5 | 4.2 | 99.6 | 4.4 | −0.1 | ns | 0.72 | 0.08 |
| heel width (mm) | 60.6 | 3.1 | 60.5 | 3.0 | 0.1 | ns | 0.20 | 0.29 |
| medial length (mm) | 183.6 | 7.0 | 183.7 | 6.7 | −0.1 | ns | 0.85 | 0.26 |
| lateral length (mm) | 160.2 | 5.7 | 160.2 | 5.5 | 0.0 | ns | 0.99 | 0.00 |
| dorsal height (mm) | 58.9 | 4.0 | 57.6 | 4.1 | 1.3 | ** | 0.00 | 0.77 |
| navicular height (mm) | 38.6 | 6.2 | 37.1 | 5.6 | 1.5 | ** | 0.00 | 0.62 |
| arch height ratio (%) | 15.2 | 2.4 | 14.6 | 2.2 | 0.6 | ** | 0.00 | 0.65 |
| heel angle (deg) | 3.7 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 5.3 | 0.3 | ns | 0.78 | 0.07 |
| toe 1 angle (deg) | 7.5 | 3.3 | 9.6 | 2.8 | −2.1 | * | 0.02 | 0.69 |
| toe 5 angle (deg) | 13.7 | 3.1 | 13.6 | 3.4 | 0.1 | ns | 0.69 | 0.09 |
| volume (mm3) | 827,759.6 | 72,068.3 | 814,073.2 | 70,207.4 | 13,686.4 | * | 0.03 | 0.70 |
| Medial Side of the Foot (Number of Feet) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deformation Pattern | Lateral | None | Medial | Total | |
| Lateral Dorsum of the Foot (Number of Feet) | Lateral | 1 | 7 | 8 | 16 |
| None | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Medial | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 | |
| Total | 3 | 10 | 8 | 21 | |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gijon-Nogueron, G.A.; Gavilan-Diaz, M.; Valle-Funes, V.; Jimenez-Cebrian, A.M.; Cervera-Marin, J.A.; Morales-Asencio, J.M. Anthropometric foot changes during pregnancy: A pilot study. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2013, 103, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWhorter, J.W. The effects of loaded versus unloaded activities on foot volumetrics in older healthy adults. N. Am. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2008, 3, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M.; Mochimaru, M.; Kanade, T. 3D measurement of feature cross-sections of foot while walking. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2011, 22, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, A.K.; Trucco, E.; Salvi, J.; Wang, W.; Abboud, R.J. Dynamic 3D shape of the plantar surface of the foot using coded structured light: A technical report. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouchi, M.; Kimura, M.; Mochimaru, M. Deformation of foot cross-section shapes during walking. Gait Posture 2009, 30, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, B.; Mozina, J.; Jezersek, M. 3D laser measurements of bare and shod feet during walking. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailler-Savage, E.A.; Adams, B.B. Skin manifestations of running. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tiggelen, D.; Wickes, S.; Coorevits, P.; Dumalin, M.; Witvrouw, E. Sock systems to prevent foot blisters and the impact on overuse injuries of the knee joint. Mil. Med. 2009, 174, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telfer, S.; Woodburn, J. The use of 3D surface scanning for the measurement and assessment of the human foot. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2010, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, E.R.; Ward, E.D.; Derrick, T.R. Medial longitudinal arch mechanics before and after a 45-minute run. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2014, 104, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, E.; Marsden, J. The effects of prolonged running on foot posture: A repeated measures study of half marathon runners using the foot posture index and navicular height. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headlee, D.L.; Leonard, J.L.; Hart, J.M.; Ingersoll, C.D.; Hertel, J. Fatigue of the plantar intrinsic foot muscles increases navicular drop. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiolkowski, P.; Brunt, D.; Bishop, M.; Woo, R.; Horodyski, M. Intrinsic pedal musculature support of the medial longitudinal arch: An electromyography study. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2003, 42, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, K.M.; Hamill, J. The role of selected extrinsic foot muscles during running. Clin. Biomech. 2004, 19, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaoka, H.B.; Luo, Z.P.; An, K.N. Effect of the posterior tibial tendon on the arch of the foot during simulated weightbearing: Biomechanical analysis. Foot Ankle Int. 1997, 18, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, J.T.; Zhang, M.; An, K.N. Effects of plantar fascia stiffness on the biomechanical responses of the ankle-foot complex. Clin. Biomech. 2004, 19, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gefen, A. Biomechanical analysis of fatigue-related foot injury mechanisms in athletes and recruits during intensive marching. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2002, 40, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukano, M.; Iso, S. Changes in Foot Shape after Long-Distance Running. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2016, 1, 30-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk1010030
Fukano M, Iso S. Changes in Foot Shape after Long-Distance Running. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2016; 1(1):30-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk1010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukano, Mako, and Shigeo Iso. 2016. "Changes in Foot Shape after Long-Distance Running" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 1, no. 1: 30-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk1010030
APA StyleFukano, M., & Iso, S. (2016). Changes in Foot Shape after Long-Distance Running. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 1(1), 30-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk1010030





