TiO2/Au/TiO2 Plasmonic Photocatalysts: The Influence of Titania Matrix and Gold Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Photocatalyst Preparation
2.2.1. Simple Photodeposition Method of Gold on Titania (Au/TiO2)
2.2.2. Preparation of TiO2/Au/TiO2 Photocatalysts
- (1)
- Physical mixing of two gold-modified samples containing both fine and large titania crystals was carried out by mild grounding of 80 wt% of Au/TiO2 (large) with 20 wt% of Au/TiO2 (fine) in an agate mortar. These samples are named as “(Au/TiO2 + Au/TiO2)”, where “R”, “r”, “A”, and “a” are used according to the selected TiO2. For example, (Au/R + Au/r) means the sample prepared by physical mixing of two gold-modified rutile samples containing large (80 wt%) and fine (20 wt%) rutile crystallites.
- (2)
- Subsequent photodeposition is defined as gold deposition on the mixture of bare and gold-modified titania samples. Various combinations of titania were tested (same as those in the case of simple physical mixing), and obtained samples were named as “Au/(TiO2(1) + Au/TiO2(2))”, i.e., gold was deposited on the mixture of bare titania (1) and gold-modified titania (2). The codes of “R”, “r”, “A”, and “a” are used in the sample names respective to the selected titania (instead of TiO2(1) and TiO2(2)).
Photocatalyst Characterization
Photocatalytic Activity Testing
3. Results
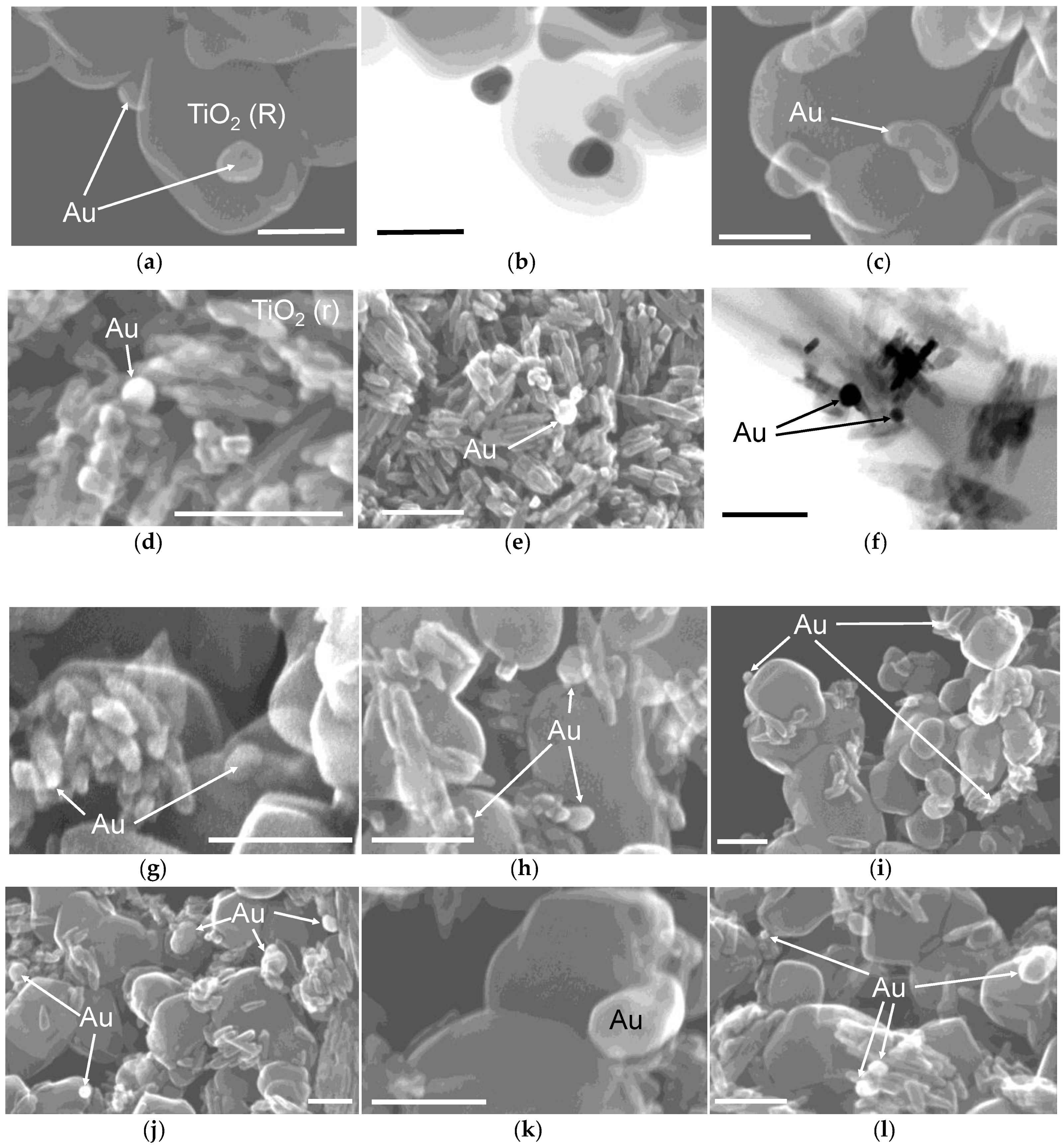
3.1. Preparation of Gold-Modified Titania Samples
3.2. Properties of Au/TiO2 and TiO2/Au/TiO2 Samples
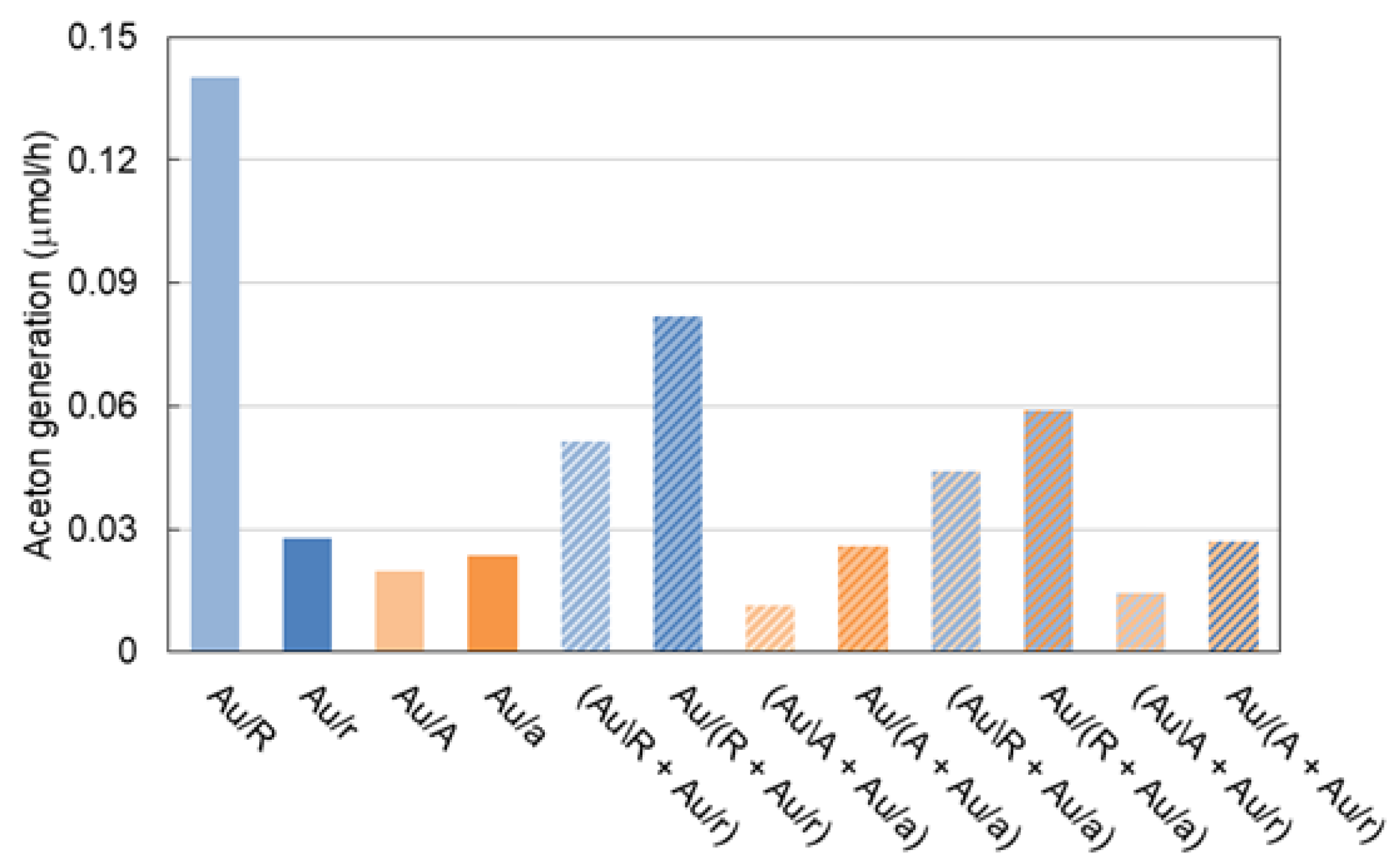
3.3. Photocatalytic Activity under UV/Vis and Vis Irradiation by Au/TiO2 and TiO2/Au/TiO2 Photocatalysts
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Y.; Tatsuma, T. Mechanisms and Applications of Plasmon-Induced Charge Separation at TiO2 Films Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7632–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja-Mogan, T.; Ohtani, B.; Kowalska, E. Photonic crystals for plasmonic photocatalysis. Catalysts 2020, 10, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Janczarek, M.; Wang, K.; Zheng, S.; Kowalska, E. Morphology-governed performance of plasmonic photocatalysts. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, S.W. TiO2 photocatalysis for the degradation of pollutants in gas phase: From morphological design to plasmonic enhancement. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2015, 24, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asapu, R.; Claes, N.; Ciocarlan, R.G.; Minjauw, M.; Detavernier, C.; Cool, P.; Bals, S.; Verbruggen, S.W. Electron Transfer and Near-Field Mechanisms in Plasmonic Gold-Nanoparticle-Modified TiO2 Photocatalytic Systems. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 4067–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretti, I.; Keulemans, M.; Verbruggen, S.W.; Lenaerts, S.; Van Doorslaer, S. Light-Induced Processes in Plasmonic Gold/TiO2 Photocatalysts Studied by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. Top. Catal. 2015, 58, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L.J.; Purcell-Milton, F.; Salmeron, A.S.; Zhang, H.; Govorov, A.O.; Fedorov, A.V.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Hot plasmonic electrons for generation of enhanced photocurrent in gold-TiO2 nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueno, K.; Misawa, H. Surface plasmon-enhanced photochemical reactions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2013, 15, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, S.K.; Li, J.T.; Meng, F.K.; Senty, T.R.; Suri, S.; Zhi, M.J.; Li, M.; Bristow, A.D.; Wu, N.Q. Photocatalytic Activity Enhanced by Plasmonic Resonant Energy Transfer from Metal to Semiconductor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15033–15041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cushing, S.K.; Meng, F.; Senty, T.R.; Bristow, A.D.; Wu, N. Plasmon-induced resonance energy transfer for solar energy conversion. Nat. Photon. 2015, 9, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, D.B.; Christopher, P.; Bauer, J.L.; Linic, S. Predictive Model for the Design of Plasmonic Metal/Semiconductor Composite Photocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Fujiwara, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Tatsuma, T. Plasmon-resonance-based generation of cathodic photocurrent at electrodeposited gold nanoparticles coated with TiO2 films. ChemPhysChem 2009, 10, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furube, A.; Du, L.; Hara, K.; Katoh, R.; Tachiya, M. Ulltrafast plasmon-induced electron transfer from gold nanodots into TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14852–14853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, E.; Abe, R.; Ohtani, B. Visible light-induced photocatalytic reaction of gold-modified titanium(IV) oxide particles: Action spectrum analysis. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, E.; Janczarek, M.; Rosa, L.; Juodkazi, S.; Ohtani, B. Mono- and bi-metallic plasmonic photocatalysts for degradation of organic compounds under UV and visible light irradiation. Catal. Today 2014, 230, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominami, H.; Tanaka, A.; Hashimoto, K. Mineralization of organic acids in aqueous suspension of gold nanoparticles supported on cerium(IV) oxide powder under visible light irradiation. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1287–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priebe, J.B.; Radnik, J.; Lennox, A.J.J.; Pohl, M.M.; Karnahl, M.; Hollmann, D.; Grabow, K.; Bentrup, U.; Junge, H.; Beller, M.; et al. Solar Hydrogen Production by Plasmonic Au-TiO2 Catalysts: Impact of Synthesis Protocol and TiO2 Phase on Charge Transfer Efficiency and H2 Evolution Rates. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2137–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, Y.; Kanda, T.; Torigoe, K.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M. Preparation of Gold/Silver/Titania Trilayered Nanorods and Their Photocatalytic Activities. Langmuir 2014, 30, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Zhao, J.-C.; Zheng, Z.-F.; Gao, X.-P. Visible-light-driven oxidation of organic contaminants in air with gold nanoparticle catalysts on oxide supports. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5353–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Ranasingha, O.; Natesakhawat, S.; Ohodnicki, P.R.; Andio, M.; Lewis, J.P.; Matranga, C. Visible light plasmonic heating of Au-ZnO for the catalytic reduction of CO2. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6968–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominami, H.; Tanaka, A.; Hashimoto, K. Gold nanoparticles supported on cerium(IV) oxide powder for mineralization of organic acids in aqueous suspensions under irradiation of visible light of λ = 530 nm. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 397, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, S.W.; Keulemans, M.; Goris, B.; Blommaerts, N.; Bals, S.; Martens, J.A.; Lenaerts, S. Plasmonic ‘rainbow’ photocatalyst with broadband solar light response for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 188, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malankowska, A.; Kobylanski, M.P.; Mikolajczyk, A.; Cavdar, O.; Nowaczyk, G.; Jarek, M.; Lisowski, W.; Michalska, M.; Kowalska, E.; Ohtani, B.; et al. TiO2 and NaTaO3 Decorated by Trimetallic Au/Pd/Pt Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Photocatalysts: Experimental and Computational Studies. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16665–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska-Jurek, A.; Wei, Z.; Wysocka, I.; Szweda, P.; Kowalska, E. The effect of nanoparticles size on photocatalytic and antimicrobial properties of Ag-Pt/TiO2 photocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 353, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zielińska-Jurek, A.; Kowalska, E.; Sobczak, J.W.; Lisowski, W.; Ohtani, B.; Zaleska, A. Preparation and characterization of monometallic (Au) and bimetallic (Ag/Au) modified-titania photocatalysts activated by visible light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 101, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielan, Z.; Kowalska, E.; Dudziak, S.; Wang, K.; Ohtani, B.; Zielinska-Jurek, A. Mono- and bimetallic (Pt/Cu) titanium(IV) oxide core–shell photocatalysts with UV/Vis light activity and magnetic separability. Catal. Today 2021, 361, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Yuan, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Mori, K.; Yamashita, H. Enhancement of plasmonic activity by Pt/Ag bimetallic nanocatalyst supported on mesoporous silica in the hydrogen production from hydrogen storage material. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 223, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, J.; Barbosa, E.C.M.; Araujo, T.P.; Fiorio, J.L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zou, Y.-C.; Mou, T.; Alves, T.V.; de Oliveira, D.C.; Wang, B.; et al. Controlling Reaction Selectivity over Hybrid Plasmonic Nanocatalysts. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 7289–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, S.; Wei, Z.; Yoshiiri, K.; Braumuller, M.; Ohtani, B.; Rau, S.; Kowalska, E. Titania modification with ruthenium(II) complex and gold nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2016, 15, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalska, E.; Yoshiiri, K.; Wei, Z.; Zheng, S.; Kastl, E.; Remita, H.; Ohtani, B.; Rau, S. Hybrid photocatalysts composed of titania modified with plasmonic nanoparticles and ruthenium complexes for decomposition of organic compounds. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 178, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendez-Medrano, M.G.; Kowalska, E.; Lehoux, A.; Herissan, A.; Ohtani, B.; Bahena, D.; Briois, V.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Rodriguez-Lopez, J.; Remita, H. Surface modification of TiO2 with Ag nanoparticles and CuO nanoclusters for applications in photocatalysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 5143–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczarek, M.; Wei, Z.; Endo, M.; Ohtani, B.; Kowalska, E. Silver- and copper-modified decahedral anatase tiania particles as visible light-responsive plasmonic photocatalyst. J. Photon. Energy 2017, 7, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endo-Kimura, M.; Kowalska, E. Plasmonic Photocatalysts for Microbiological Applications. Catalysts 2020, 10, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.F.; Tachikawa, T.; Zhang, P.; Fujitsuka, M.; Majima, T. Au/TiO2 Superstructure-Based Plasmonic Photocatalysts Exhibiting Efficient Charge Separation and Unprecedented Activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, X.G.; Zhao, L.; Lan, X.F.; Shi, J.S. An efficient inverse opal (IO)-TiO2-MoO3−x for photocatalytic H2 evolution and RhB degradation—The synergy effect of IO structure and plasmonic MoO3−x. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 527, 146726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Sun, N.; Tang, D.Y.; Jing, L.Q. Dimension-matched plasmonic Au/TiO2/BiVO4 nanocomposites as efficient wide-visible-light photocatalysts to convert CO2 and mechanistic insights. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 11838–11845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; An, T.; Yamashita, H. Fabrication of Au/TiO2 nanowires@carbon fiber paper ternary composite for visible-light photocatalytic degradation of gaseous styrene. Catal. Today 2017, 281, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, K.; Dong, B. A Nonmetal Plasmonic Z-Scheme Photocatalyst with UV- to NIR-Driven Photocatalytic Protons Reduction. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, A.; Fan, F.; Li, C. Achieving overall water splitting on plasmon-based solid Z-scheme photocatalysts free of redox mediators. J. Catal. 2017, 354, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, Y.; Dou, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Bao, N. Rational design of Z-scheme Bi12O17Cl2/plasmonic Ag/anoxic TiO2 composites for efficient visible light photocatalysis. Powder Technol. 2021, 384, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudo, E.; Tanaka, A.; Kominami, H. Bifunctions of a Cr hydroxide layer for water splitting over a platinized Au/TiO2 plasmonic photocatalyst under visible light irradiation. Catal. Today, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, F.; Peer, I.; Jain, P.K.; Amirav, L. Plasmon-Enhanced Multicarrier Photocatalysis. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4370–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobadi, T.G.U.; Ghobadi, A.; Ozbay, E.; Karadas, F. Strategies for Plasmonic Hot-Electron-Driven Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. ChemPhotoChem 2018, 2, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yoshiiri, K.; Rosa, L.; Wei, Z.; Juodkazis, S.; Ohtani, B.; Kowalska, E. TiO2/Au/TiO2 plasmonic photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability under visible-light irradiation. Catal. Today 2022, 397–399, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, H.; Keulemans, M.; Nuyts, G.; Vanmeert, F.; Li, C.; Minjauw, M.; Detavernier, C.; Bals, S.; Lenaerts, S.; Verbruggen, S.W. Plasmonic gold-embedded TiO2 thin films as photocatalytic self-cleaning coatings. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 267, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, M.; Mittal, D.; Rao, V.G. Plasmon-induced hot-hole generation and extraction at nano-heterointerfaces for photocatalysis. Commun. Mater. 2021, 2, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Son, H.Y.; Nam, Y.S. Multilayered Plasmonic Heterostructure of Gold and Titania Nanoparticles for Solar Fuel Production. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, A.; Takase, M.; Takashima, M.; Murakamid, N.; Ohtani, B. A fingerprint of metal-oxide powders: Energy-resolved distribution of electron traps. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12096–12099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshiiri, K.; Karabiyik, B.; Wang, K.; Wei, Z.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Kowalska, E. The property-governed activity of silver-modified titania photocatalysts: The influence of titania matrix. J. Chem. Phys. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, E.; Mahaney, O.O.P.; Abe, R.; Ohtani, B. Visible-light-induced photocatalysis through surface plasmon excitation of gold on titania surfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalska, E.; Rau, S. Photoreactors for wastewater treatment: A review. Recent Pat. Eng. 2010, 4, 242–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Endo, M.; Wang, K.; Charbit, E.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Ohtani, B.; Kowalska, E. Noble metal-modified octahedral anatase titania particles with enhanced activity for decomposition of chemical and microbiological pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 318, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, E.; Rau, S.; Ohtani, B. Plasmonic Titania Photocatalysts Active under UV and Visible-Light Irradiation: Influence of Gold Amount, Size, and Shape. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2012, 361853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prieto-Mahaney, O.O.; Murakami, N.; Abe, R.; Ohtani, B. Correlation between photocatalytic activities and structural and physical properties of titanium(IV) oxide powders. Chem. Lett. 2009, 38, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Wei, Z.S.; Ohtani, B.; Kowalska, E. Interparticle electron transfer in methanol dehydrogenation on platinum-loaded titania particles prepared from P25. Catal. Today 2018, 303, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.K.; Wallace, W.T.; Goodman, D.W. Support effects on the nucleation, growth, and morphology of gold nano-clusters. Surf. Sci. 2006, 600, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, N.; Abe, R.; Ohtani, B. In situ observation of photocatalytic reaction by photoacoustic spectroscopy: Detection of heat of exothermic photocatalytic reaction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 451, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.N.; Halas, N.J. Shape-controlled synthesis and surface plasmonic properties of metallic nanostructures. MRS Bull. 2005, 30, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, L.Q.; Zhao, J.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhao, Y.R.; Hao, L.M.; Lu, Y.M. Shape dependent resonance light scattering properties of gold nanorods. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2005, 121, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murazawa, N.; Ueono, K.; Mizeikis, V.; Juodkazis, S.; Misawa, H. Spatially Selective Nonlinear Photopolymerization Induced by the Near-Field of Surface Plasmons Localized on Rectangular Gold Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaor, D.A.H.; Sorrell, C.C. Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janes, R.; Knightley, L.J.; Harding, C.J. Structural and spectroscopic studies of iron (III) doped titania powders prepared by sol-gel synthesis and hydrothermal processing. Dyes Pigments 2004, 62, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, C. High Temperature Stable Anatase Phase Titanium Dioxide Films Synthesized by Mist Chemical Vapor Deposition. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janczarek, M.; Kowalska, E.; Ohtani, B. Decahedral-shaped anatase titania photocatalyst particles: Synthesis in a newly developed coaxial-flow gas-phase reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debnath, R.; Chaudhuri, J. Mutual phase stabilization of aluminium phosphate and titania in AlPO4-TiO2 binary system. Bull. Mater. Sci. 1992, 15, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, N.; Nakashima, T.; Yamamoto, K. Metastability of anatase: Size dependent and irreversible anatase-rutile phase transition in atomic-level precise titania. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Wei, Z.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Nitta, A.; Kowalska, E. P25 and its components—Electronic properties and photocatalytic activities. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 31, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, N.; Chenakin, S. XPS characterization of Au/TiO2 catalysts: Binding energy assessment and irradiation effects. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 391, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossnagel, S.M.; Sites, J.R. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of ion beam sputter deposited silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, and tantalum pentoxide. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1984, 2, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H.; Soloviev, A.; Li, Z.S.; Sogaard, E.G. XPS and FTIR investigation of the surface properties of different prepared titania nano-powders. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 246, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.G.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhao, Q.N. Effect of surface structure on photocatalytic activity of TiO2 thin films prepared by sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 2000, 379, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayotov, D.; McEntee, M.; Burrows, S.; Driscoll, D.; Tang, W.; Neurock, M.; Morris, J. Infrared studies of propene and propene oxide adsorption on nanoparticulate Au/TiO2. Surf. Sci. 2016, 652, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrétien, S.; Metiu, H. Density functional study of the interaction between small Au clusters, Aun (n = 1–7) and the rutile TiO2 surface. I. Adsorption on the stoichiometric surface. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 084704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Kohyama, M.; Tanaka, S.; Takeda, S. Structure and stability of Au rods on TiO2(110) surfaces by first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 155413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Janczarek, M.; Endo, M.; Wang, K.L.; Balcytis, A.; Nitta, A.; Mendez-Medrano, M.G.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Juodkazis, S.; Ohtani, B.; et al. Noble metal-modified faceted anatase titania photocatalysts: Octahedron versus decahedron. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 237, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchalska, M.; Kobielusz, M.; Matuszek, A.; Pacia, A.; Wojtyla, S.; Macyk, W. On Oxygen Activation at Rutile- and Anatase-TiO2. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 7424–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichat, P.; Mozzanega, M.N.; Disdier, J.; Herrmann, J.M. Platinum content and temperature effects on the photocatalytic hydrogen production from aliphatic alcohols over platinum/titanium dioxide. Nouv. J. Chim. 1982, 6, 559–564. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto, S.I.; Ohtani, B.; Kagiya, T. Photocatalytic Dehydrogenation of Aliphatic-Alcohols by Aqueous Suspensions of Platinized Titanium-Dioxide. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1985, 81, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; White, J.M. Photodecomposition of water over platinum/titanium dioxide catalysts. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1980, 72, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, F.H.; Rudham, R. Photocatalytic dehydrogenation of liquid alcohols by platinized anatase. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1987, 83, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyulavári, T.; Kovács, K.; Kovács, Z.; Bárdos, E.; Kovács, G.; Baán, K.; Magyari, K.; Veréb, G.; Pap, Z.; Hernadi, K. Preparation and characterization of noble metal modified titanium dioxide hollow spheres—New insights concerning the light trapping efficiency. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 534, 147327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, Z.-R.; Kovács, G.; Hernádi, K.; Baia, L.; Pap, Z. The investigation of the photocatalytic efficiency of spherical gold nanocages/TiO2 and silver nanospheres/TiO2 composites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 183, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, G.; Baia, L.; Vulpoi, A.; Radu, T.; Karácsonyi, É.; Dombi, A.; Hernádi, K.; Danciu, V.; Simon, S.; Pap, Z. TiO2/WO3/Au nanoarchitectures’ photocatalytic activity, “from degradation intermediates to catalysts’ structural peculiarities”, Part I: Aeroxide P25 based composites. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 147, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veréb, G.; Ambrus, Z.; Pap, Z.; Kmetykó, Á.; Dombi, A.; Danciu, V.; Cheesman, A.; Mogyorósi, K. Comparative study on UV and visible light sensitive bare and doped titanium dioxide photocatalysts for the decomposition of environmental pollutants in water. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 417–418, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczarek, M.; Endo, M.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K.; Kowalska, E. Enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial prformance of cuprous oxide/titania: The effect of titania matrix. Materials 2018, 11, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Miao, S.; Liu, T.; Mu, L.; Li, R.; Fan, F.; Li, C. Positioning the Water Oxidation Reaction Sites in Plasmonic Photocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 11771–11778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
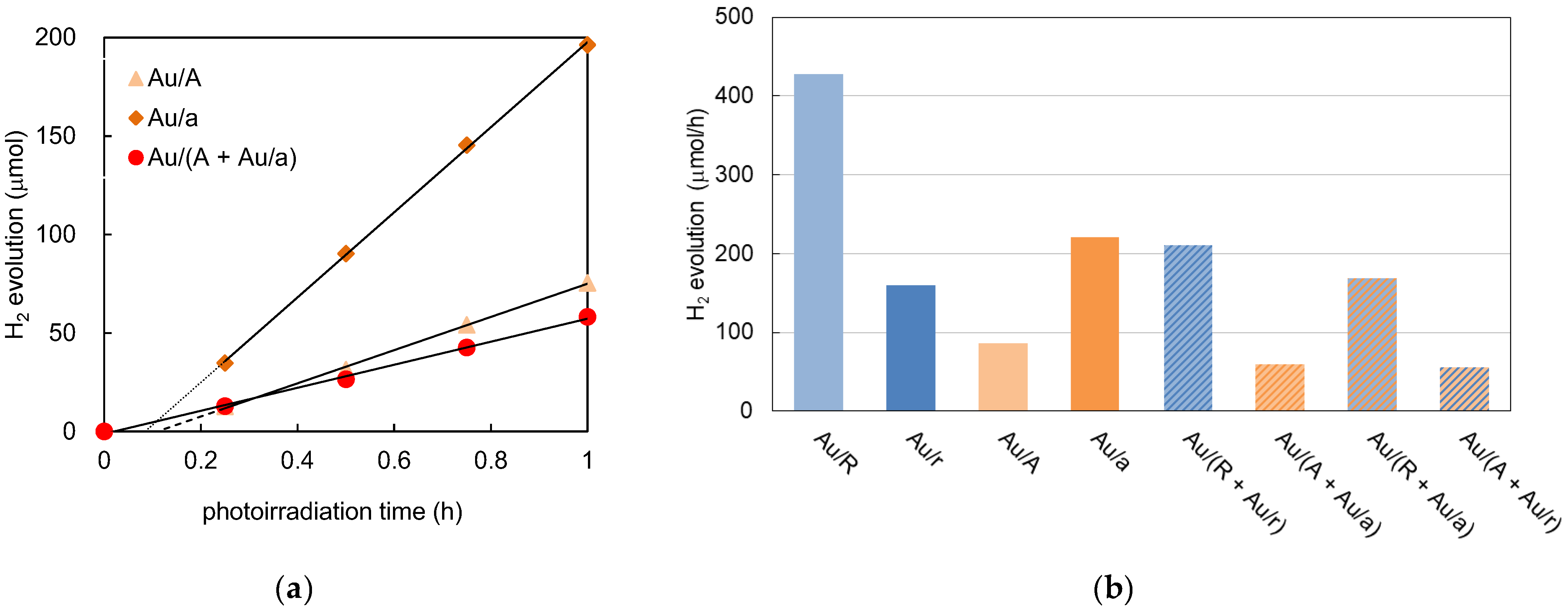

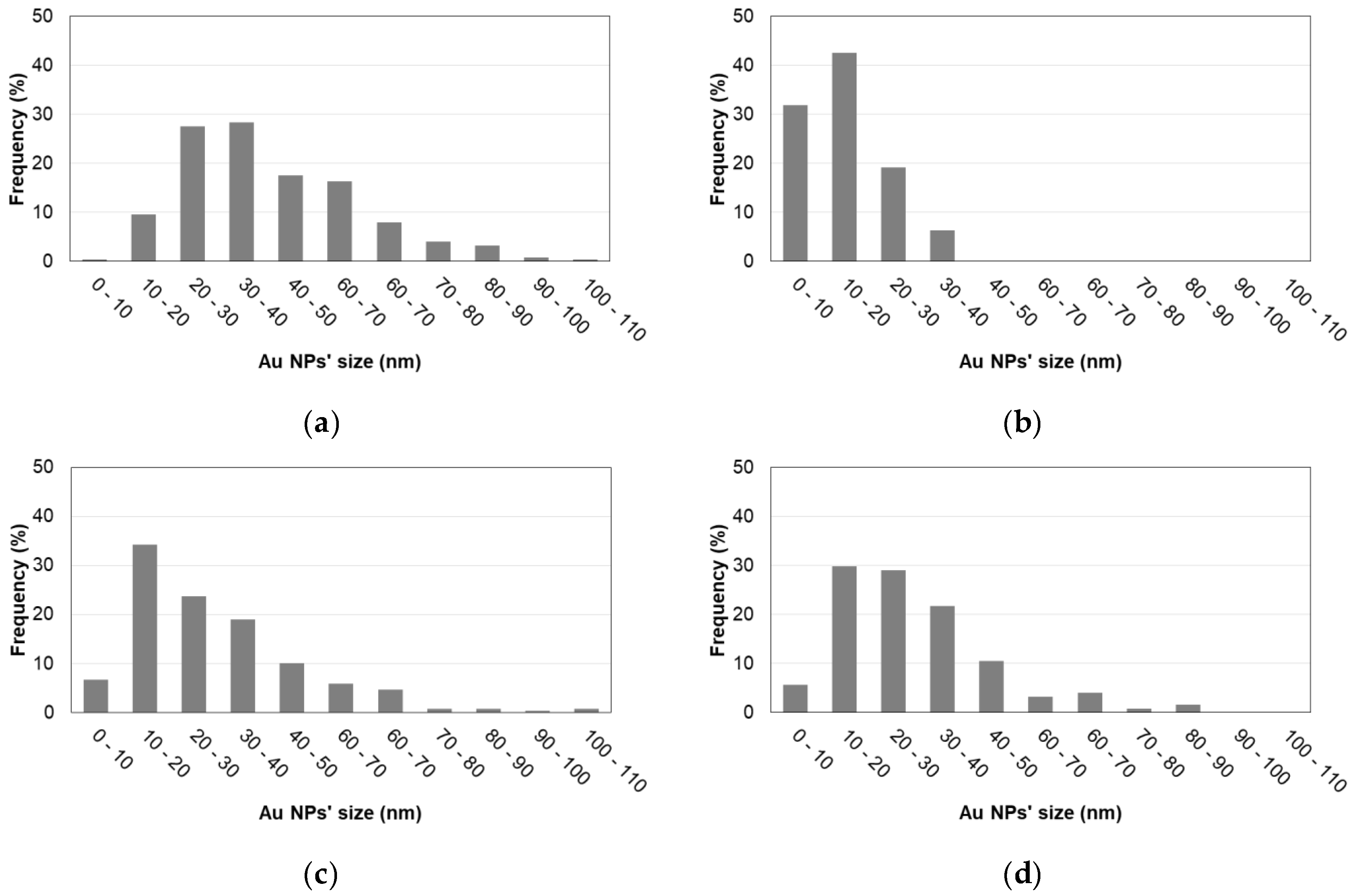

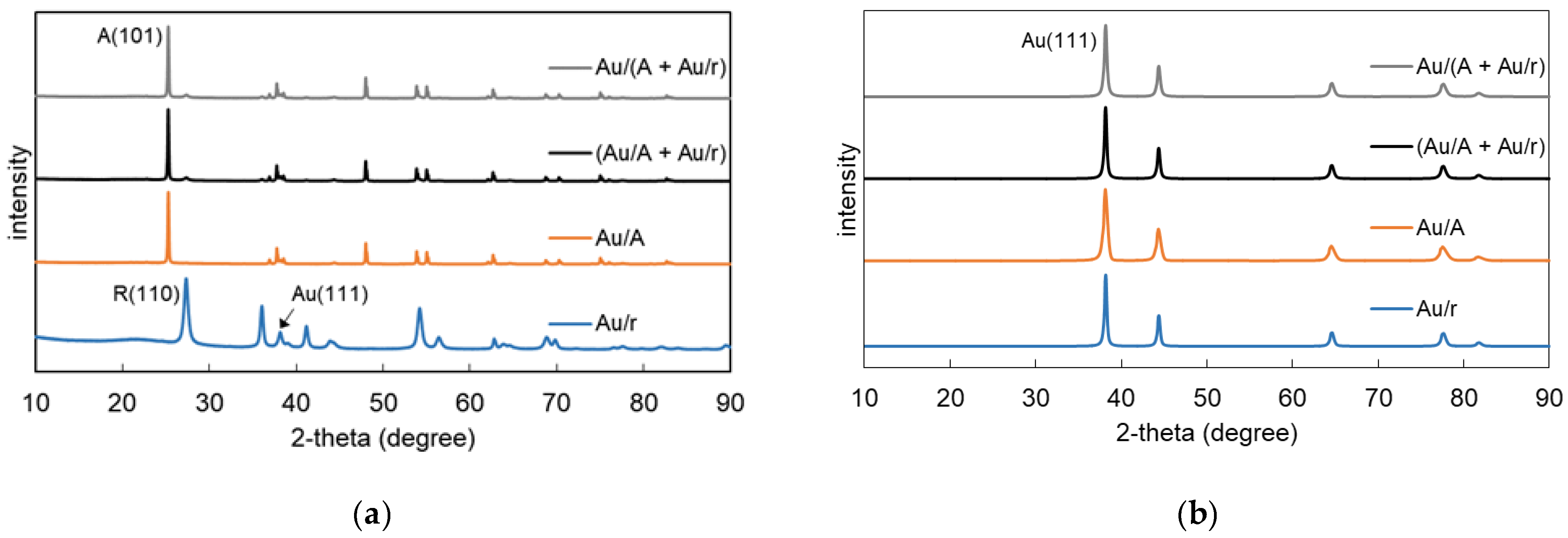
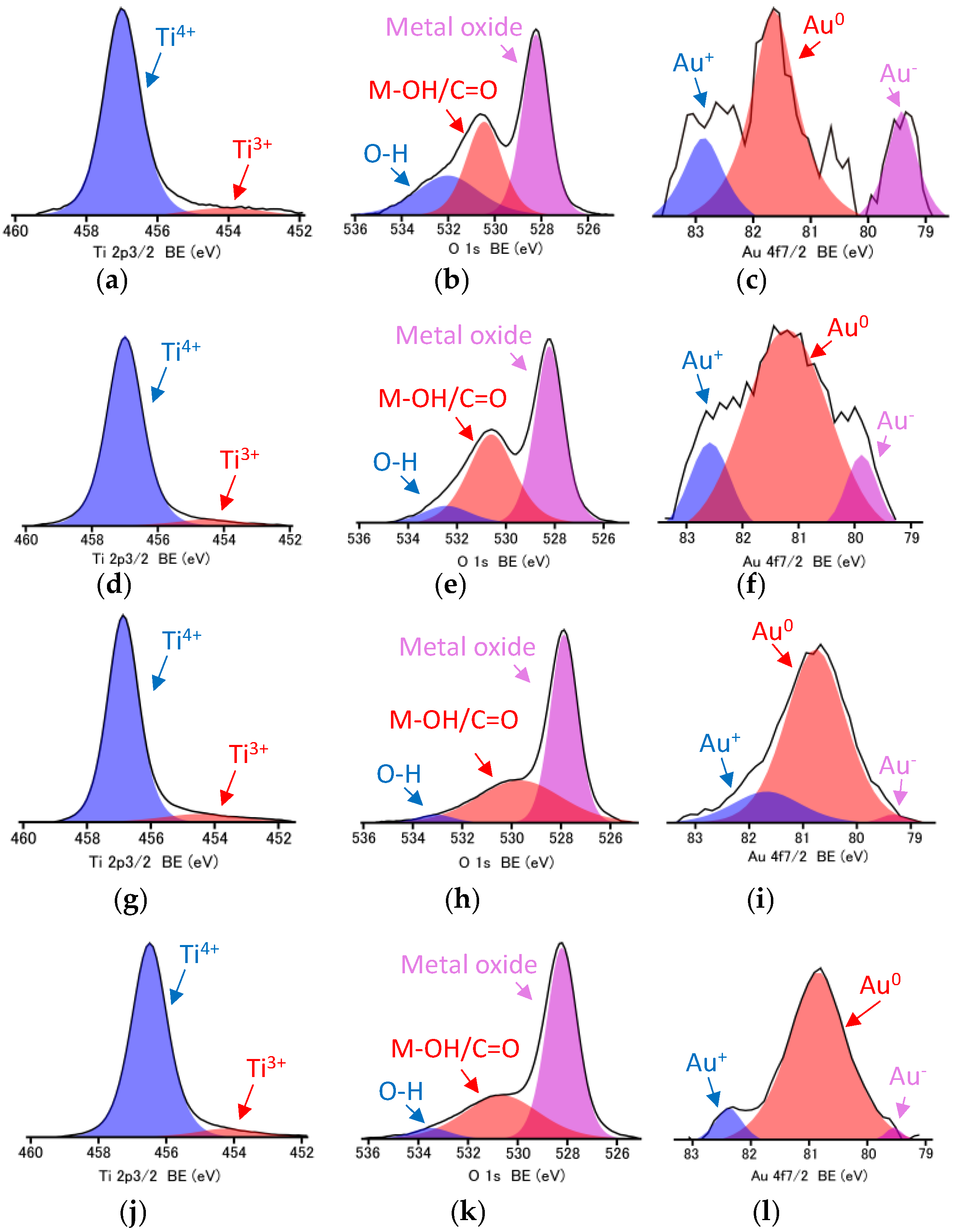

| Name | Code | Supplier | Composition (%) | Crystallite Size */nm | SSA/m2 g−1 | ETs/μmol g−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatase | Rutile | NC | ||||||
| ST F-10 | R | Showa Denko Ceramics (Shiojiri, Japan) | 4.0 | 93.0 | 3.0 | 60.6 | 13 | 55 |
| MT-150A | r | Tayca (Osaka, Japan) | 0.0 | 81.9 | 18.1 | 14.8 | 114 | 221 |
| ST41 | A | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha (Osaka, Japan) | 98.2 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 76.2 | 11 | 13 |
| TKP-102 | a | Tayca | 89.3 | 0.0 | 10.7 | 16.7 | 114 | 77 |
| Sample Code TiO2(1) + TiO2(2) | LSPR Peak/nm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2(1) | TiO2(2) | (Au/TiO2(1) + Au/TiO2(2)) | Au/(TiO2(1) + Au/TiO2(2)) | |
| R + r | 578 | 549 | 567 | 562 |
| A + a | 572 | 550 | 571 | 569 |
| R + a | 578 | 550 | 573 | 565 |
| A + r | 572 | 549 | 569 | 566 |
| Sample | Crystallite Size (nm) | Crystalline Composition (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatase | Rutile | Gold | Anatase | Rutile | Gold | |
| Au/R | 38.7 | 60.4 | 24.6 | 6.6 | 91.2 | 2.3 |
| Au/r | 14.8 | 18.9 | 0.0 | 97.7 | 2.3 | |
| Au/A | 76.2 | 103.6 | 31.1 | 97.5 | 0.5 | 2.0 |
| Au/a | 16.7 | 13.7 | 97.7 | 0.0 | 2.3 | |
| (Au/R + Au/r) | 40.2 | 63.0 | 24.5 | 5.4 | 92.2 | 2.4 |
| Au/(R + Au/r) | 39.3 | 62.9 | 20.5 | 5.5 | 92.2 | 2.3 |
| (Au/A + Au/a) | 86.6 | 131.9 | 27.4 | 96.8 | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| Au/(A + Au/a) | 89.5 | 76.0 | 23.3 | 94.8 | 3.2 | 2.0 |
| (Au/R + Au/a) | 23.0 | 60.2 | 26.7 | 23.3 | 74.4 | 2.3 |
| Au/(R + Au/a) | 23.8 | 60.5 | 23.3 | 22.3 | 75.5 | 2.2 |
| (Au/A + Au/r) | 77.9 | 16.9 | 30.9 | 80.6 | 17.3 | 2.1 |
| Au/(A + Au/r) | 79.9 | 17.5 | 27.3 | 81.6 | 16.4 | 2.0 |
| Sample | Titanium (%) | Oxygen (%) | Gold (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti4+ | Ti3+ | OH | CO/M-OH | TiO2 | Au+ | Au0 | Au− | |
| Au/R | 88.0 | 12.0 | 24.0 | 27.9 | 48.1 | 22.0 | 56.9 | 21.1 |
| Au/r | 94.0 | 6.0 | 15.4 | 40.8 | 43.8 | 10.9 | 79.9 | 9.2 |
| Au/a | 94.4 | 5.6 | 8.7 | 41.1 | 50.2 | 15.2 | 75.3 | 9.5 |
| (Au/R + Au/r) | 85.8 | 14.2 | 3.2 | 31.1 | 65.7 | 10.1 | 80.5 | 9.4 |
| Au/(R + Au/r) | 94.0 | 6.0 | 12.9 | 42.5 | 44.6 | 20.3 | 68.6 | 11.1 |
| (Au/R + Au/a) | 89.5 | 10.5 | 1.3 | 43.0 | 55.7 | 17.7 | 81.0 | 1.3 |
| Au/(R + Au/a) | 93.2 | 6.8 | 2.5 | 36.7 | 60.8 | 7.0 | 91.6 | 1.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshiiri, K.; Wang, K.; Kowalska, E. TiO2/Au/TiO2 Plasmonic Photocatalysts: The Influence of Titania Matrix and Gold Properties. Inventions 2022, 7, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions7030054
Yoshiiri K, Wang K, Kowalska E. TiO2/Au/TiO2 Plasmonic Photocatalysts: The Influence of Titania Matrix and Gold Properties. Inventions. 2022; 7(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions7030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshiiri, Kenta, Kunlei Wang, and Ewa Kowalska. 2022. "TiO2/Au/TiO2 Plasmonic Photocatalysts: The Influence of Titania Matrix and Gold Properties" Inventions 7, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions7030054
APA StyleYoshiiri, K., Wang, K., & Kowalska, E. (2022). TiO2/Au/TiO2 Plasmonic Photocatalysts: The Influence of Titania Matrix and Gold Properties. Inventions, 7(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions7030054








