GeV-Class Two-Fold CW Linac Driven by an Arc-Compressor
Abstract
1. Introduction
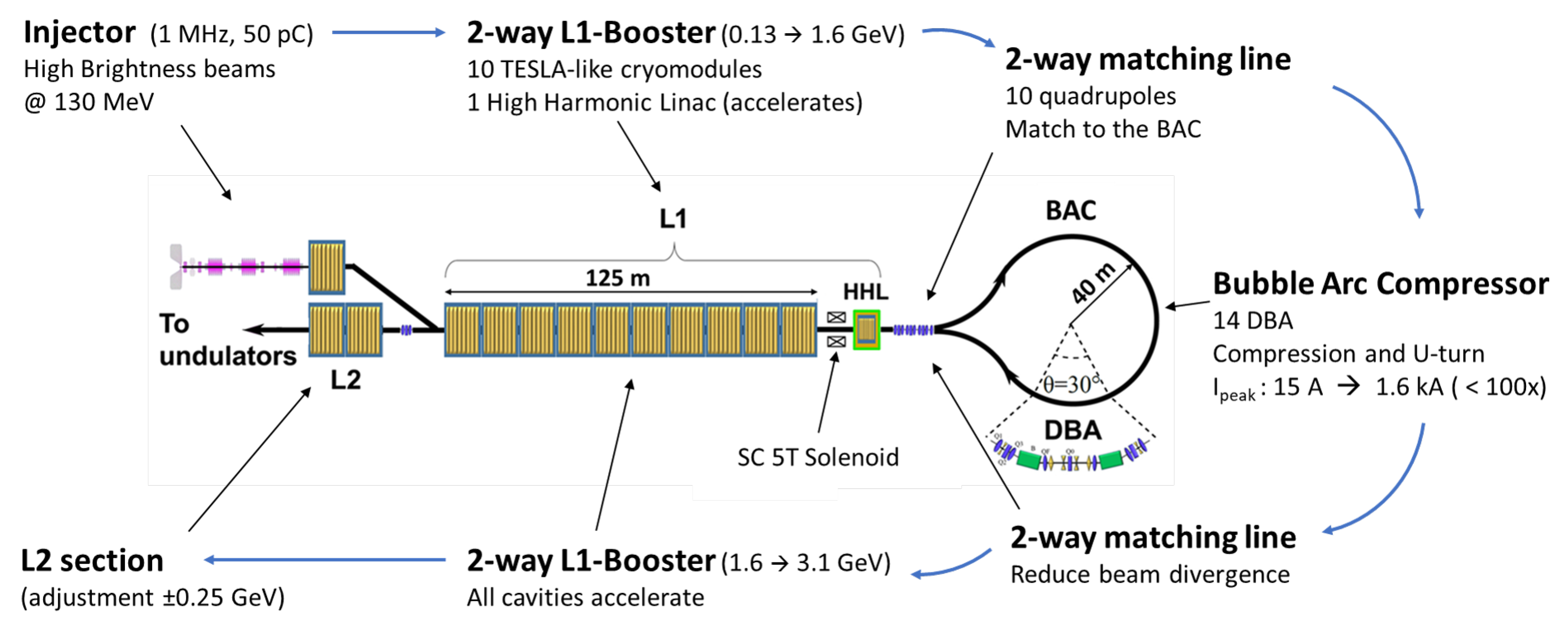
2. Machine Layout
- The injector about 20 m long is composed as follows: a 1.3 GHz normal conducting NC two 2-cells buncher; a cryomodule about 3 m long with inside a 7-cells 1.3 GHz acceleration cavity, a 3-cells 3.9 GHz higher harmonic cavity, for longitudinal phase space (LPS) shaping, and a second 7-cells 1.3 GHz cavity, at the cryomodule exit the bunch is pre-compressed and with an energy of about 6 MeV; an about 1.5 m drift used for emittance compensation; a 1 m 9-cells TESLA-like cavity where the bunch is accelerated at 10 MeV and undergoes a mild velocity bunching VB [10,11]; a TESLA-cyomodule, bringing eight 9-cells cavity that damp the last emittance oscillation and deliver a ∼130 MeV high brightness bunch.
- Downstream the injector, a dogleg line brings the beam to the linac booster. In this line, if needed, a laser heater device to suppress the microbunching instabilities (MBI) [12,13] can be hosted. The MBI driven by coherent syncrotron radiation CSR and longitudinal space charge LSC in the bubble arc has been preliminarily evaluated, resulting in a moderate effect and not a show-stopper for lasing.
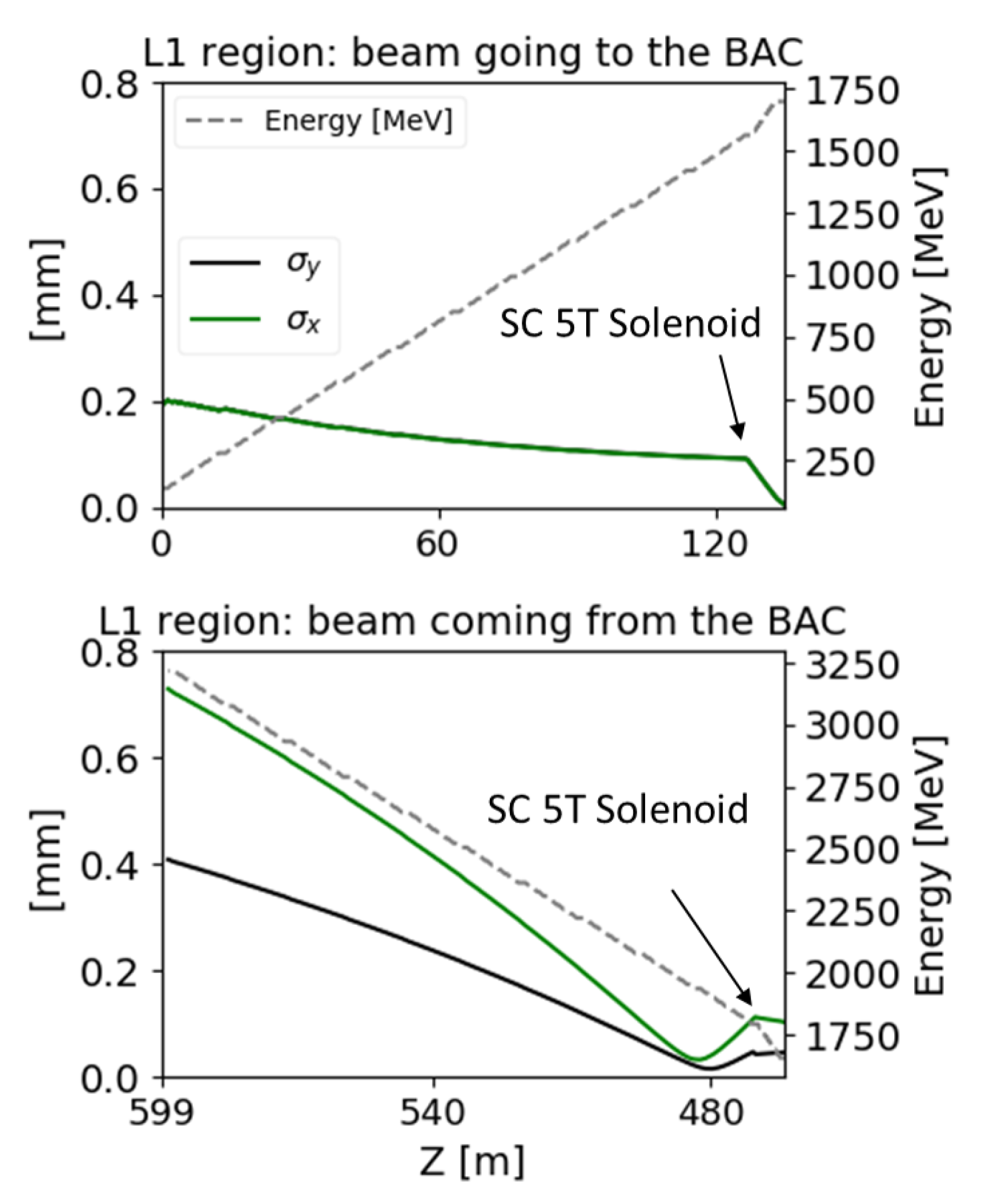
- The Linac booster, 10 TESLA-like cryomodules for about 125 m, provides an energy increase up to 1.6 GeV. The injection phase that guarantees the correct chirp ad hoc for the of the BAC maximum compression is about 6 degree out of the RF crest.
- Downstream the Linac there is a 3.9 GHz TESLA linac (named HHL into Figure 1), which is used to give an extra LPS RF curvature needed to pre-compensate CSR effects arising into the BAC.
- The quadrupole matching line between the main linac (L1) and the BAC (10 quadrupoles) exploits the symmetric focusing effect of a SC solenoid [14] positioned before HHL. This quadrupoles matching line, being crossed back and forth by bunches, has not a trivial behavior. If it is not properly set considering the returning bunch dynamics, it increases the bunch transverse size, turning on chromatic effects that inside solenoids scale quadratically with the bunch dimension. This effect, if not kept under control, is very detrimental in terms of emittance increase. Consequently, the quadrupoles accomplish two tasks: to match the bunch to the BAC and to constraint the beam envelope within acceptable limits when, coming back, it enters a second time the SC solenoid.
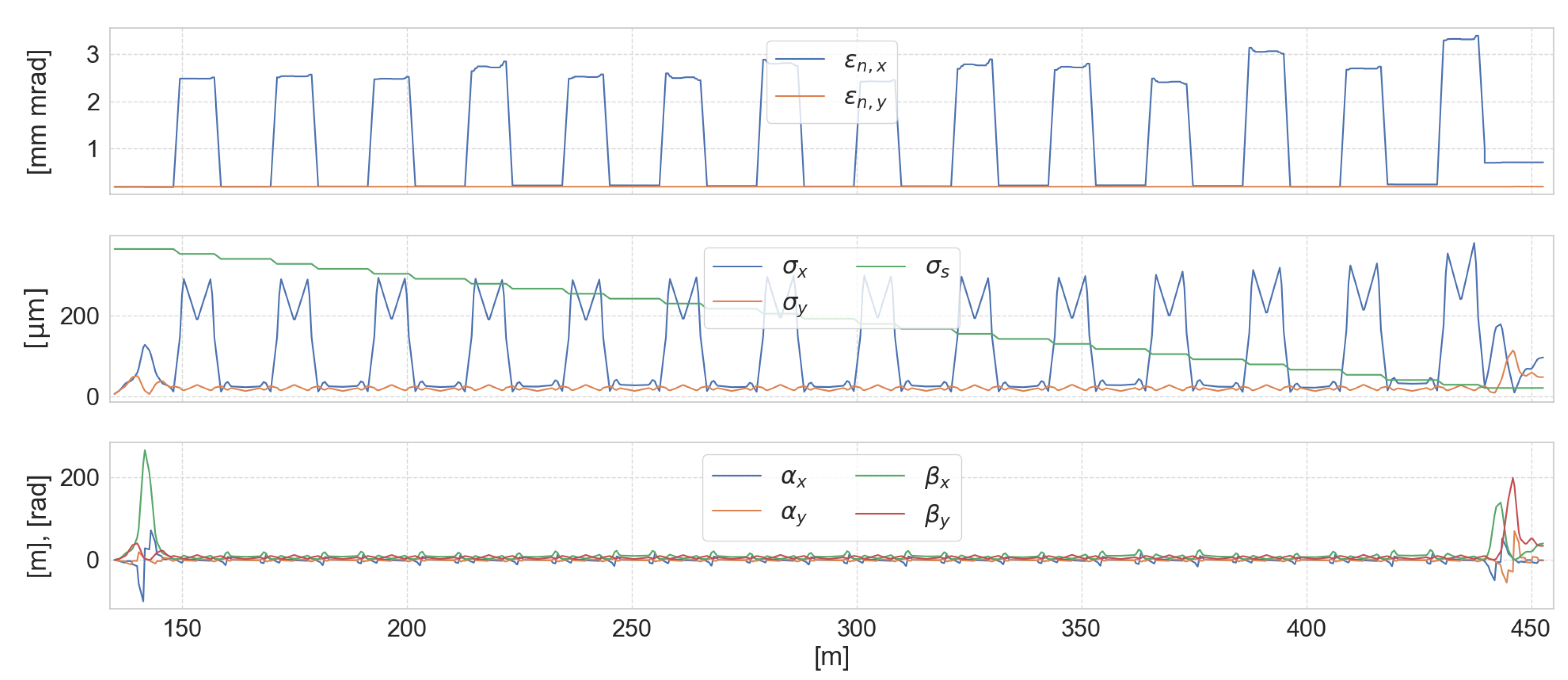
- The BAC is a long dispersive path used to increase the beam current peak while it is U-turned, preserving the transverse slice emittance, even in the presence of important Coherent Synchrotron Radiation (CSR) emissions. The lattice arc is based on the work described in [5]. It is composed by 14 Double Bend Achromat (DBA) cells, each one bending the beam of 30; Table 1 contains its main parameters.
- After the BAC, where the bunch shows a current peak up to 100 times higher, it passes a second time into the qudrupoles matching line, into the SC solenoid and finally it is accelerated a second time by the SC linac booster in the backward direction overpassing 3 GeV energy.
- Leaving L1 on the way back, the bunch enters two extra cryomodules, named L2, needed to tune the final beam energy (±300 MeV) before the beam is matched to undulators. A quadrupoles triplet before L2 provides a soft focuses kick that brings the beam rms transverse size at few tens of microns at the FEL undulators transfer lines entrance.
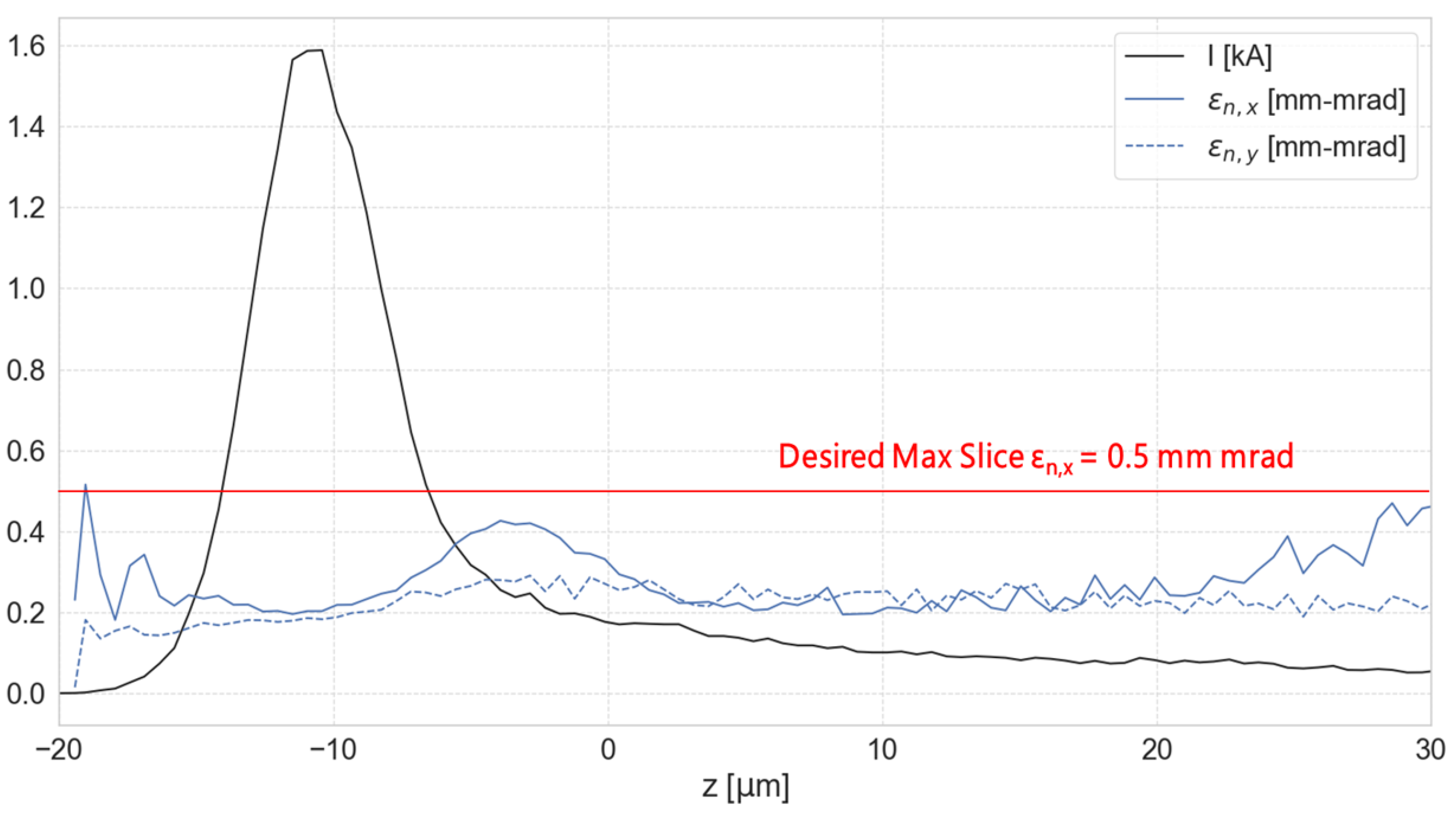
3. Start to End Simulation and Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, L.; Ueda, K.; Gühr, M.; Bucksbaum, P.H.; Simon, M.; Mukamel, S.; Rohringer, N.; Prince, K.C.; Masciovecchio, C.; Meyer, M.; et al. Roadmap of ultrafast x-ray atomic and molecular physics. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2018, 51, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, L.; Bacci, A.; Bellandi, A.; Bertucci, M.; Bolognesi, M.; Bosotti, A.; Broggi, F.; Calandrino, R.; Camera, F.; Canella, F.; et al. MariX, an advanced MHz-class repetition rate X-ray source for linear regime time-resolved spectroscopy and photon scattering. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2019, 930, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigner, M. A possible apparatus for electron clashing-beam experiments. Il Nuovo Cimento (1955–1965) 1965, 37, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekutowicz, J.; Bogacz, S.; Douglas, D.; Kneisel, P.; Williams, G.; Ferrario, M.; Ben-Zvi, I.; Rose, J.; Smedley, J.; Srinivasan-Rao, T.; et al. Proposed continuous wave energy recovery operation of an x-ray free electron laser. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top.-Accel. Beams 2005, 8, 010701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mitri, S.; Cornacchia, M. Transverse emittance-preserving arc compressor for high-brightness electron beam-based light sources and colliders. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2015, 109, 62002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.P.; Ghiorso, W.; Staples, J.; Huang, T.M.; Sannibale, F.; Kramasz, T.D. Mechanical design and fabrication of the VHF-gun, the Berkeley normal-conducting continuous-wave high-brightness electron source. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 023302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LASA Website. Available online: http://wwwlasa.mi.infn.it/ttfcathodes/ (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Sertore, D.; Favia, D.; Michelato, P.; Monaco, L.; Pierini, P. Cesium telluride and metals photoelectron thermal emittance measurements using a time-of-flight spectrometer. In Proceedings of the 9th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC), Lucerne, Switzerland, 5–9 July 2004; pp. 408–410. [Google Scholar]
- Vecchione, T.; Ben-Zvi, I.; Dowell, D.; Feng, J.; Rao, T.; Smedley, J.; Wan, W.; Padmore, H. A low emittance and high efficiency visible light photocathode for high brightness accelerator-based X-ray light sources. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 034103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, L.; Ferrario, M. Velocity bunching in photo-injectors. In Proceedings of the American Institute of Physics (AIP) Conference, College Park, MD, USA, 28 September 2001; Volume 581, pp. 87–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario, M.; Alesini, D.; Bacci, A.; Bellaveglia, M.; Boni, R.; Boscolo, M.; Castellano, M.; Chiadroni, E.; Cianchi, A.; Cultrera, L.; et al. Experimental demonstration of emittance compensation with velocity bunching. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 054801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Borland, M.; Emma, P.; Wu, J.; Limborg, C.; Stupakov, G.; Welch, J. Suppression of microbunching instability in the linac coherent light source. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top.-Accel. Beams 2004, 7, 074401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, J.; Ding, Y.; Emma, P.; Huang, Z.; Ratner, D.; Raubenheimer, T.; Venturini, M.; Zhou, F. Start-to-end simulation of the shot-noise driven microbunching instability experiment at the Linac Coherent Light Source. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 2017, 20, 054402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.; Kashikhin, V.; Page, T.; Terechkine, I.; Tompkins, J.; Wokas, T. Designing focusing solenoids for superconducting RF accelerators. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2007, 17, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, L.; Rosenzweig, J.B. Envelope analysis of intense relativistic quasilaminar beams in rf photoinjectors: MA theory of emittance compensation. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 55, 7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, M.; Alesini, D.; Bacci, A.; Bellaveglia, M.; Boni, R.; Boscolo, M.; Castellano, M.; Catani, L.; Chiadroni, E.; Cialdi, S.; et al. Direct measurement of the double emittance minimum in the beam dynamics of the sparc high-brightness photoinjector. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 234801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, A.; Alesini, D.; Antici, P.; Bellaveglia, M.; Boni, R.; Chiadroni, E.; Cianchi, A.; Curatolo, C.; Di Pirro, G.; Esposito, A.; et al. Electron Linac design to drive bright Compton back-scattering gamma-ray sources. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 194508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, A.; Petrillo, V.; Rossetti Conti, M. GIOTTO: A Genetic Code for Demanding Beam-dynamics Optimizations. In Proceedings of the 7th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC 2016), Busan, Korea, 8–13 May 2016; pp. 3073–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floettmann, K. ASTRA: A Space Charge Tracking Algorithm; DESY: Hamburg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Borland, M. Elegant: A flexible SDDS-Compliant code for accelerator simulation. In Proceedings of the 6th International Computational Accelerator Physics Conference (ICAP 2000), Darmstadt, Germany, 11–14 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Galayda, J. The Linac Coherent Light Source-II Project. In Proceedings of the 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC’14), Dresden, Germany, 15–20 June 2014; JACoW: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- XFEL. DESY. Available online: https://www.xfel.eu/ (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Di Mitri, S. Maximum brightness of linac-driven electron beams in the presence of collective effects. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top.-Accel. Beams 2013, 16, 050701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MariX Initiative Official Website. Available online: https://marix.eu (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Serafini, L.; Rossi, G.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Bacci, A.; Bellandi, A.; Bertucci, M.; Bolognesi, M.; Bosotti, A.; Broggi, F.; Calandrino, R.; et al. MariX Conceptual Design Report. 2019. Available online: https://repodip.fisica.unimi.it/marix/MariX_CDR.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2019).

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Cell length | m |
| Dipole bending angle | |
| Dipole length | m |
| per DBA cell | 35 mm |
| # of dipoles per DBA | 2 |
| # of quadrupoles per DBA | 9 |
| # of sextupoles per DBA | 6 |
| # of DBA cells in the BAC | 14 |
| Total in the BAC | 490 mm |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 0.2 mm-mrad | |
| 365 m | |
| E | ∼130 MeV |
| Passage | Par. | Final val. |
|---|---|---|
| 1st pass | 3.179 | |
| 1st pass | ||
| 1st pass | 2.152 m | |
| 1st pass | 10.016 m | |
| 2nd pass | 2.02 rad | |
| 2nd pass | 1.19 rad |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| m | |
| m | |
| m | |
| mm mrad | |
| mm mrad | |
| ( GeV) | |
| 50 pC | |
| kA | |
| Slices @ | mm mrad |
| Slices @ | mm mrad |
| Slices @ |
| Parameter | Cut Bunch 31pC |
|---|---|
| m | |
| mm mrad | |
| mm mrad | |
| E | GeV |
| kA | |
| Best Slice | <0.2 mm mrad |
| Best Slice | <0.2 mm mrad |
| Slices @ | ∼ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bacci, A.; Bosotti, A.; Di Mitri, S.; Drebot, I.; Faillace, L.; Michelato, P.; Monaco, L.; Opromolla, M.; Paparella, R.; Petrillo, V.; et al. GeV-Class Two-Fold CW Linac Driven by an Arc-Compressor. Instruments 2019, 3, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments3040054
Bacci A, Bosotti A, Di Mitri S, Drebot I, Faillace L, Michelato P, Monaco L, Opromolla M, Paparella R, Petrillo V, et al. GeV-Class Two-Fold CW Linac Driven by an Arc-Compressor. Instruments. 2019; 3(4):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments3040054
Chicago/Turabian StyleBacci, Alberto, Angelo Bosotti, Simone Di Mitri, Illya Drebot, Luigi Faillace, Paolo Michelato, Laura Monaco, Michele Opromolla, Rocco Paparella, Vittoria Petrillo, and et al. 2019. "GeV-Class Two-Fold CW Linac Driven by an Arc-Compressor" Instruments 3, no. 4: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments3040054
APA StyleBacci, A., Bosotti, A., Di Mitri, S., Drebot, I., Faillace, L., Michelato, P., Monaco, L., Opromolla, M., Paparella, R., Petrillo, V., Rossetti Conti, M., Rossi, A. R., Serafini, L., & Sertore, D. (2019). GeV-Class Two-Fold CW Linac Driven by an Arc-Compressor. Instruments, 3(4), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments3040054








