C-2p Spin-Polarizations along with Two Mechanisms in Extended Carbon Multilayers: Insight from First Principles
Abstract
1. Introduction and Context
- Keeping an isolated atomic behavior—as for Gd (4f)—characterized by two unpaired carbon p electrons in an appropriate crystal–chemical host, and leading eventually to their polarization and the expectation of M(C) = 2 μB. We assess this within an intraband spin polarization mechanism;
- Checking for the hypothesis of interband spin polarization mechanism by involving two carbon neighbors at a distance which allows electronic interactions between them. The subsequent bonding involves a spin pairing and a loss of the magnetization magnitude. The expectation is a magnitude of M(C) close to 1 μB.
2. Brief Presentation of the Computational Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geometry Optimization and Energy-Dependent Results
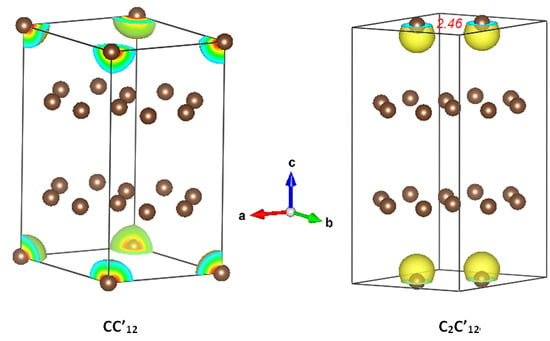
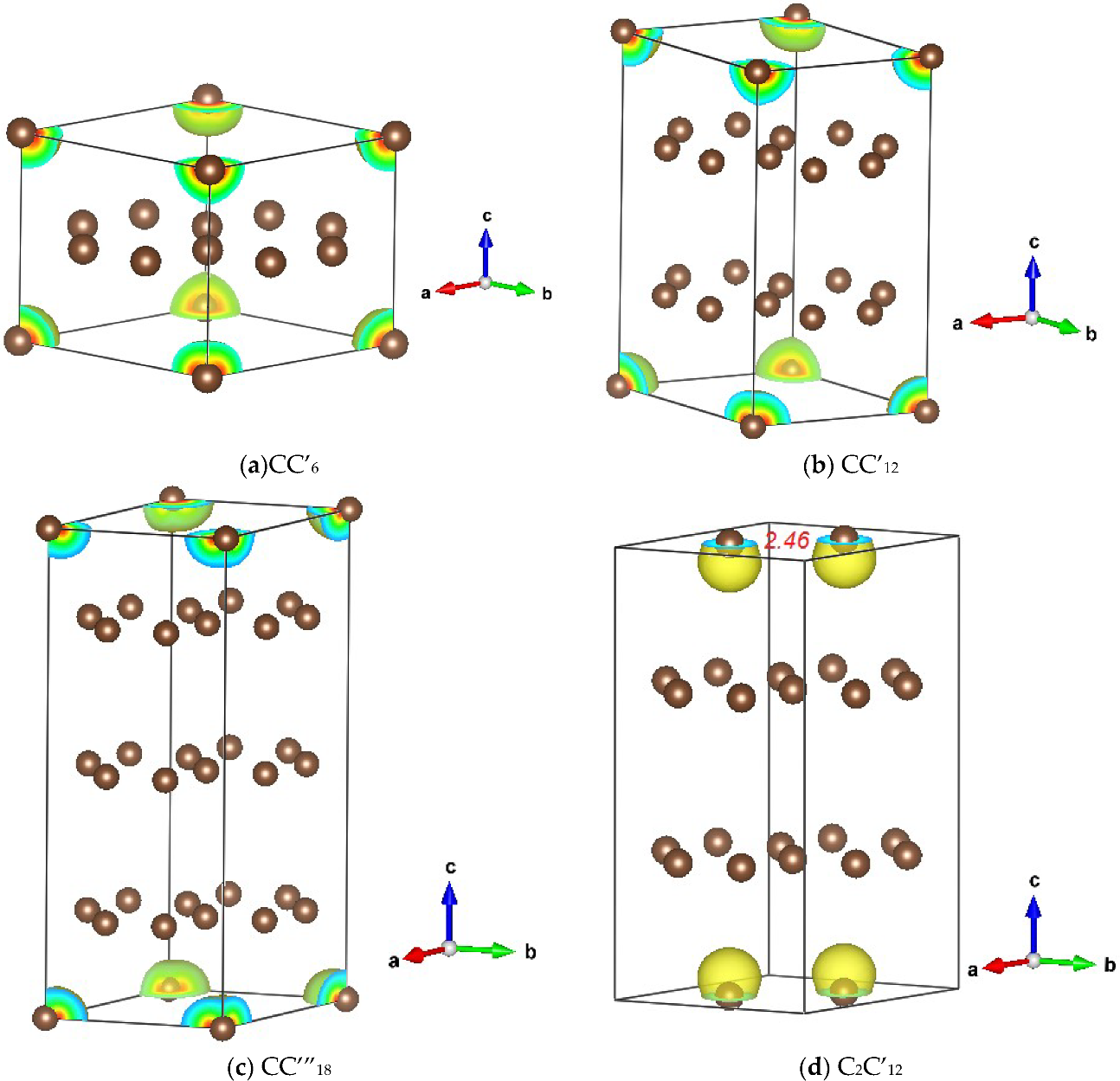
3.1.1. CC’n (n = 6, 12 and 18)
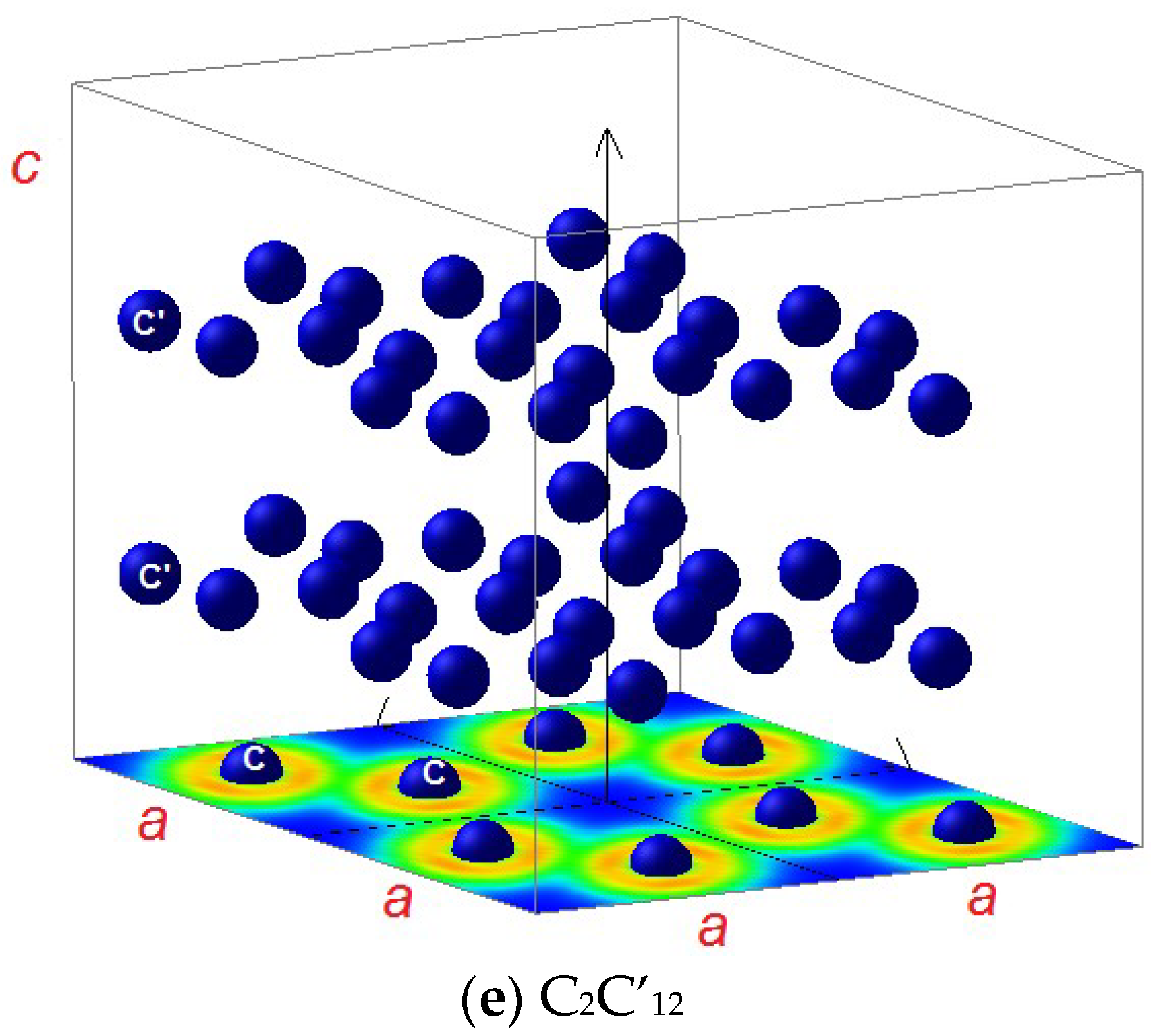
3.1.2. C2C’12
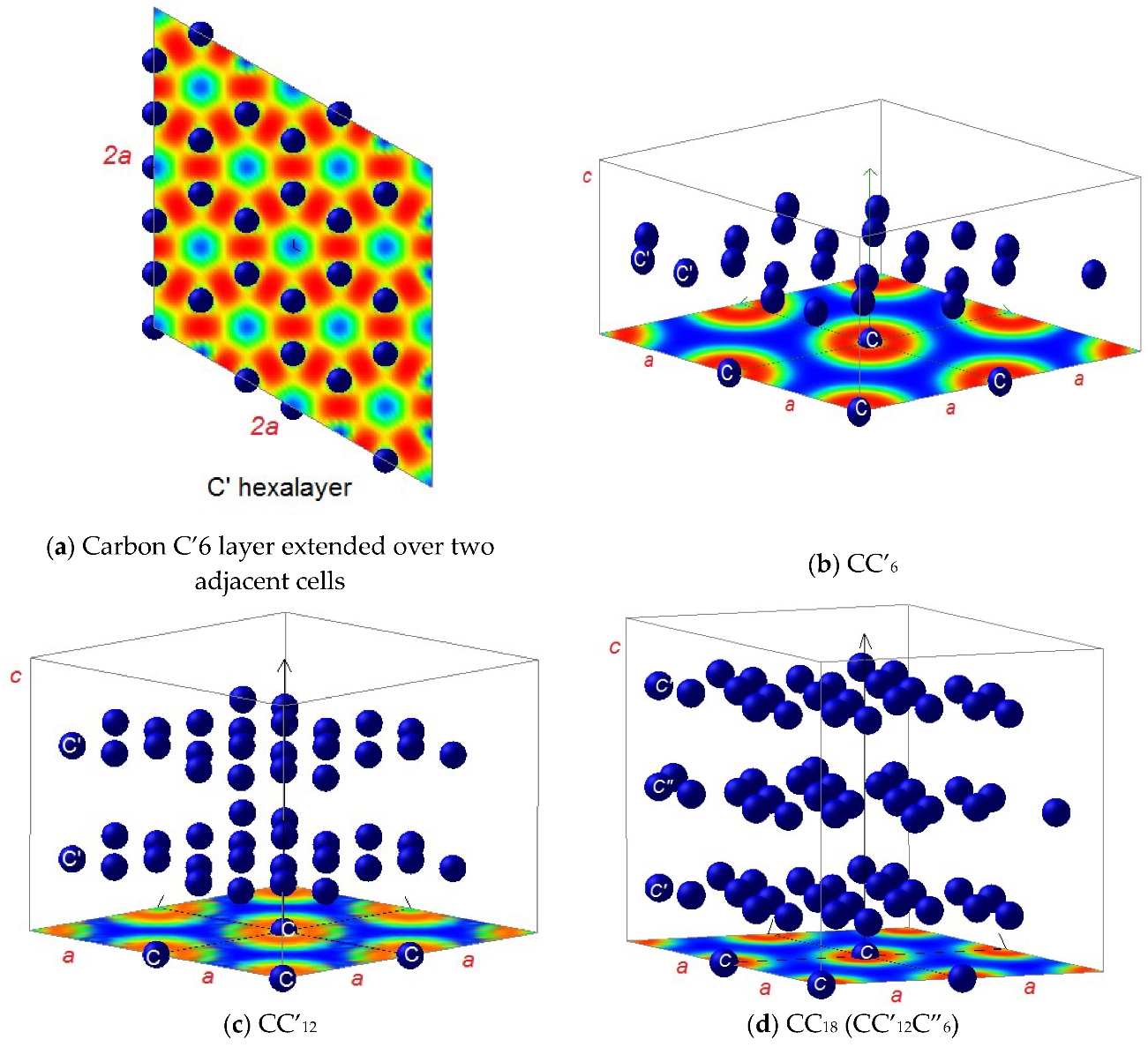
3.2. Magnetic Charge Density
3.3. Electron Localization Function ELF
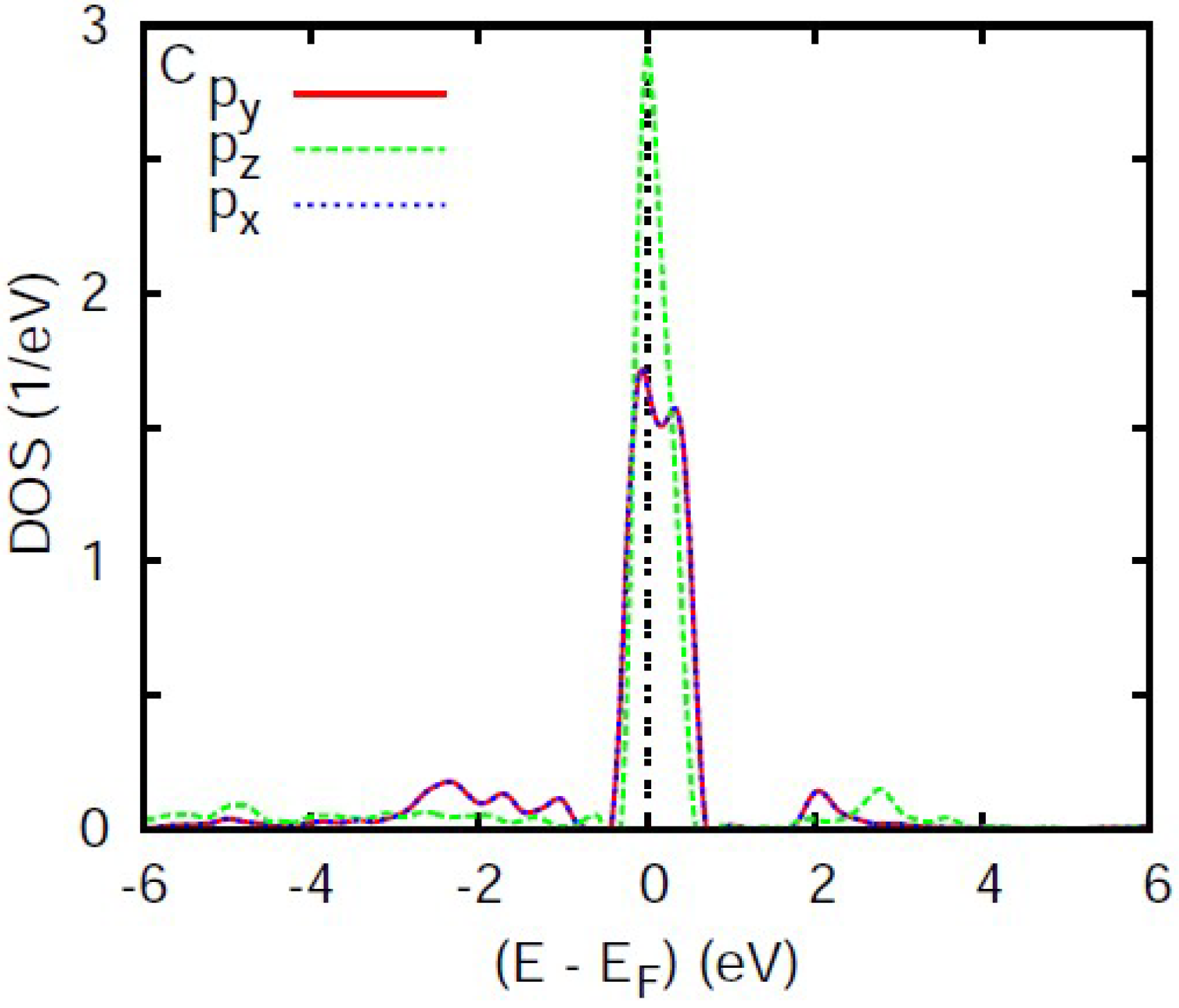
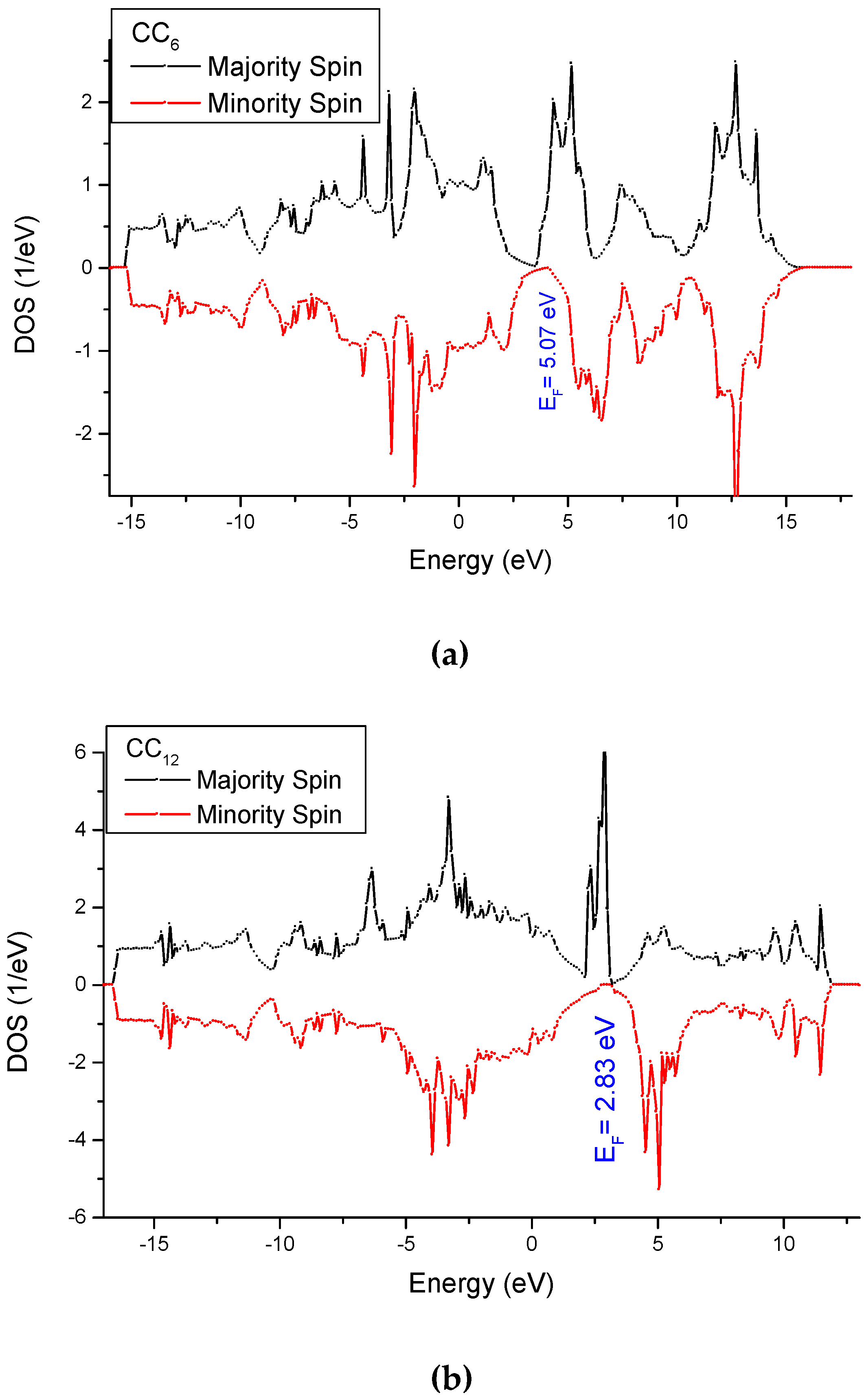
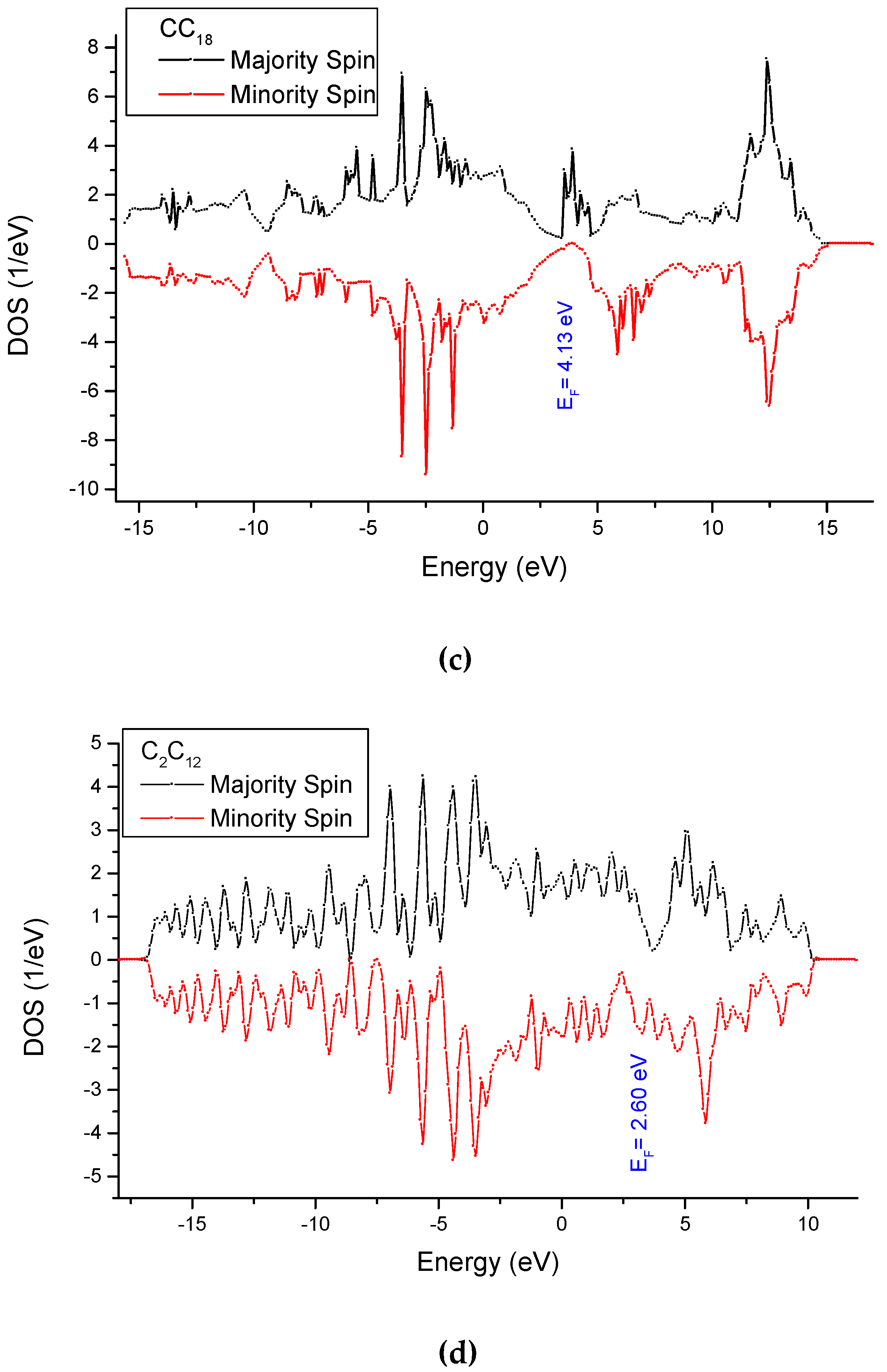
3.4. Analysis of the Electronic Density of States
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohn, P. Magnetism in the Solid State—An Introduction; Springer Series in Solid-State Sciences; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133–A1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, S.F.; Etourneau, J. (CaO)nIrO2 (n = 1, 2, 4) family: Chemical scissors effects of CaO on structural characteristics correlated to physical properties. Ab initio study. J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 255, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, S.F.; Eyert, V.; Mavromaras, A.; Najm, S.; Chevalier, B.; Etourneau, J. Chemical bonding and magnetism in the ternary germanides UT2Ge2 (T = 3d transition metal) from local spin density functional calculations. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1997, 174, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorneles, L.S.; Venkatesan, M.; Moliner, M.; Lunney, J.G.; Coey, J.M.D. Magnetism in thin films of CaB6 and SrB6. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 6377–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedolla, P.O.; Gruber, C.; Mohn, P.; Redinger, J. p-electron magnetism in CdS doped with main group elements p-electron magnetism in CdS doped with main group elements. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2012, 24, 476002–476005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatami, A.; Tachibana, M.; Yagi, T.; Murakami, M. Preparation of multilayer graphene sheets and their applications for particle accelerators. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1962, 030005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total-energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, J. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented wave. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. The projected augmented wave method. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. The Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Press, W.H.; Flannery, B.P.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T. Numerical Recipes; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Blöchl, P.E.; Jepsen, O.; Anderson, O.K. Improved tetrahedron method for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 16223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special k-points for Brillouin Zone integration. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, D.; Edgecombe, K.E. A simple measure of electron localization. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 92, 5397–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, A.; Jepsen, O.; Flad, J.; Andersen, K.O.; Preuss, H.; von Schnering, H.G. The ELF perspective of chemical bonding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1992, 31, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolotko, O.; Senyshyn, A.; Mühlbauer, M.J.; Nikolowski, K.; Ehrenberg, H. Understanding structural changes in NMC Li-ion cells by in situ neutron diffraction. J. Power Sources 2014, 255, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V. Observation of critical magnetic behavior in 2D carbon based composites. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2001, 44, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (a). CC’6. | ||
| Magn. Config. | NSP | SP |
| a | 4.285 | 4.272 |
| c/a | 0.933 | 1.183 |
| d(C’-C’) | 1.41–1.43 | 1.42-1.43 |
| C’(6k) x, 0, ½ | 0.335 | 0.333 |
| Tot. Energy | 56.23 | −56.91 |
| Ecoh. /at. | −0.932 | −1.021 |
| M (μB) | - | 2.01 |
| (b). CC’12. | ||
| Magn. Config. | NSP | SP |
| a | 4.278 | 4.265 |
| c/a | 1.820 | 2.060 |
| d(C’-C’) | 1.42–1.43 | 1.42–1.43 |
| C’(12n) x, 0, z | 0.334/0.280 | 0.333/0.297 |
| Tot. Energy | 111.46 | −112.16 |
| Ecoh. /at. | −1.464 | −1.518 |
| M (μB) | - | 2.01 |
| (c). CC”’18 (CC’12C”6). | ||
| Magn. Config. | NSP | SP |
| a | 4.275 | 4.265 |
| c/a | 2.57 | 2.68 |
| d(C’-C’)(C”-C”) | 1.41–1.42 | 1.41–1.42 |
| C’(12n) x, 0, z | 0.334/0.183 | 0.333/0.196 |
| C”(6k) x, 0, ½ | 0.333 | 0.334 |
| Tot. Energy | 166.57 | −167.22 |
| Ecoh. /at. | −1.657 | −1.691 |
| M (μB) | - | 1.980 |
| (d). C2C’12. | ||
| Magn. Config. | NSP | SP |
| a | 4.220 | 4.230 |
| c/a | 2.238 | 2.458 |
| d(C’-C’) | 1.41 | 1.41 |
| C’(12n) x, 0, z | 0.333/0.319 | 0.333/0.308 |
| Tot. Energy | 116.46 | −116.60 |
| Ecoh. /at. | −1.20 | −1.22 |
| M (μB) | - | 1.97 (2 C) |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matar, S.F. C-2p Spin-Polarizations along with Two Mechanisms in Extended Carbon Multilayers: Insight from First Principles. Condens. Matter 2020, 5, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat5030048
Matar SF. C-2p Spin-Polarizations along with Two Mechanisms in Extended Carbon Multilayers: Insight from First Principles. Condensed Matter. 2020; 5(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat5030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatar, Samir F. 2020. "C-2p Spin-Polarizations along with Two Mechanisms in Extended Carbon Multilayers: Insight from First Principles" Condensed Matter 5, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat5030048
APA StyleMatar, S. F. (2020). C-2p Spin-Polarizations along with Two Mechanisms in Extended Carbon Multilayers: Insight from First Principles. Condensed Matter, 5(3), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat5030048