Abstract
As a member of the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) class, scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SRB1) plays a key role in innate immunity. Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) ranks among the most extensively cultivated freshwater aquaculture species in China. However, little is known about the function of SRB1 in C. idellus. In this research study, a SRB1 gene was identified in C. idellus, named CiSRB1. The full-length cDNA of CiSRB1 is 2486 bp long, with an open reading frame (ORF) of 2486 bp encoding a 497 amino acid (aa) protein containing a conserved CD36 domain. The identified genomic DNA length of CiSRB1 is 20,042 bp, including 12 exons and 11 introns. The predictive analysis of protein interactions revealed that CiSRB1 could interact with the outer capsid proteins of typical GCRV strains. The tissue distribution of CiSRB1 exhibited age-dependent characteristics. CiSRB1 displayed the highest expression in the intestines and moderate levels in muscle, spleen, liver, and brain of one-year-old grass carp while maintaining relatively low levels in three-year-old grass carp. Following grass carp reovirus (GCRV) infection, notable upregulation of CiSRB1 transcripts was observed in major immune tissues (gills, intestines, spleen, and liver). Furthermore, significant differences were found between one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp, with lower CiSRB1 expression levels being detected in the older group. Additionally, a distinct response to GCRV infection was observed in one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp. It was found that one-year-old individuals had a mortality rate of up to 84% 6 days post-infection (dpi), whereas all three-year-old counterparts survived after GCRV infection. The analysis of GCRV copy numbers across tissues revealed substantially higher levels in one-year-old grass carp compared with their older counterparts, confirming the existence of age-dependent susceptibility to GCRV infection in grass carp. Combined with these results, it was speculated that the decline in cell-surface CiSRB1 expression with age may impede reovirus binding to host cells, potentially explaining why older grass carp demonstrated enhanced resistance to GCRV infection. This observation accentuates the importance of CiSRB1 in the context of GCRV infection and provides insights into age-dependent susceptibility to reovirus.
Key Contribution:
The CiSRB1 gene, identified in economically important grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus), exhibited age-dependent expression patterns. In one-year-old grass carp, CiSRB1 was highly expressed in the intestines and moderately so in muscle, spleen, liver, and brain, while levels were relatively low in three-year-old carp. Upon GCRV infection, there was a significant increase in CiSRB1 transcripts in immune tissues, with lower levels observed being in three-year-old fish compared with one-year-olds. Notably, higher mortality and GCRV copy numbers were seen in one-year-old fish, indicating age-related susceptibility to GCRV. The predictive analysis of protein interactions revealed that CiSRB1 could interact with the outer capsid proteins of typical GCRV strains. This suggests that age may impact the cell-surface expression of CiSRB1 post-GCRV infection, potentially affecting reovirus binding to target cells. These findings shed light on age-related restrictions in reovirus infection in grass carp.
1. Introduction
Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) is one of the most extensively cultivated freshwater aquaculture species in China, significantly contributing to the agricultural economy []. However, the production of C. idellus has experienced a decline due to various infectious diseases, leading to substantial financial losses annually. One of the most severe and prevalent diseases is grass carp hemorrhage disease, caused by grass carp reovirus (GCRV) []. GCRV, a double-stranded RNA virus, typically induces intestinal and muscle bleeding, often resulting in death upon infection. It is estimated that GCRV accounts for an economic loss of approximately 20% of the total grass carp production []. Unfortunately, there are currently no optimal methods for preventing GCRV infection or curing hemorrhagic disease in C. idellus []. Hence, the identification of factors in C. idellus linked to host immune defense is crucial to developing antiviral drugs and improving fish breeding programs.
In teleosts, the innate immune system heavily relies on pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) to identify conserved domains []. Among these PRRs, scavenger receptors (SRs) play a pivotal role in the immune system, encompassing functions such as phagocytosis, antigen presentation, clearance of apoptotic cells, and activation of various signaling pathways []. The expansive family of scavenger receptors (SRs) is categorized into ten classes (classes A-J) based on structural characteristics and functional domains, and the majority of SRs are present on macrophages to mediate lipid transport and immune defense [].
Within the SRBs, there are three members: cluster differentiation-36 (CD36), scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SRB1), and lysosomal integral membrane protein type 2 (LIMP2) []. SRB1, a high-density lipoprotein (HDL) receptor crucial for HDL metabolism [], has been associated with the entry of multiple viruses into host cells, including hepatitis C virus (HCV) [,,], dengue virus (DV) [], malaria parasite [], SARS-CoV-2 [], and GCRV [,]. Extensive research on SRB1 has been conducted across different species, such as humans (Homo sapiens) [], mice (Mus musculus) [], orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) [], rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) [], and turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) []. Transcriptome analysis of GCRV-infected C. idellus kidney (CIK) cells reveals the upregulation of SRB1 between 8 and 24 h post-infection (hpi), indicating its potential role in GCRV cell entry []. Despite these insights, the specific action of SRB1 during GCRV infection in C. idellus remains unknown. This study aims to clone the SRB1 gene and explore its functions during grass carp hemorrhage, shedding light on the role of SRB1 in virus entry into host cells and contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of fish SRB1 function.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish and Sampling
Healthy one-year-old (n = 200; weight, 80.3 ± 10.1 g; length, 18.1 ± 3.5 cm) and three-year-old (n = 150; weight, 1500.8 ± 500.4 g; length, 70.7 ± 10.3 cm) grass carp were adapted to 4 × 4 × 2 m3 indoor concrete ponds with dechlorinated and aerated water at 28.0 ± 1.0 °C at the Fangcun Experimental Station, Pearl River Fisheries Research Institute (Guangzhou, China). These fish were fed commercial feed from Guangdong Bairong Aquatic Varieties Group Co., Ltd. (FoShan, China), twice daily. After a one-week acclimatization period with no observed abnormalities, the grass carp were prepared for further experimentation.
For tissue distribution experiments, nine tissues (gills, head kidney, heart, intestines, brain middle kidney, liver, muscle, and spleen) were collected from healthy one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp (n = 3 per age group). All tissues were promptly homogenized in TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) and stored at −80 °C until RNA extraction. Further, tail tissues were obtained and fixed in 95% ethanol.
2.2. Gene Cloning and Sequence Analysis of SRB1 in C. idellus
Total RNA was extracted from healthy samples of one-year-old fish by using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. The ReverTra Ace kit (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan) was used to synthesize the first-strand cDNA by using an oligo dT primer (Takara, Kyoto, Japan). Fragments of SRB1 in C. idellus, designated as CiSRB1, were obtained by blasting the sequence of SRB1 in G. rarus (GrSRB1, GenBank accession No. MK436208) against the draft genome of grass carp (SRA accession No. PRJEB5920) []. Partial cDNA fragments of the CiSRB1 gene were amplified by specific primers (Table 1). Subsequently, specific and adaptor primers (Table 1) were designed to obtain the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) by using the SMARTTM RACE cDNA Amplification Kit (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, USA). The full-length cDNA sequence of CiSRB1 was amplified by using primers CiSRB1-F2 and CiSRB1-R2 (Table 1) targeting the 5′ and 3′ UTRs, respectively. Then, a Gel Extraction Kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA) was used to purify the PCR products, which were then ligated into pMD19-T vectors (Takara, Japan) and transformed into competent Escherichia coli DH5α cells (TransGen, Beijing, China). Positive colonies of the target fragment were sequenced by a commercial company (Tianyi huiyuan, Guangzhou, China).

Table 1.
Primers for full-length cDNA cloning and qPCR.
The sequences of CiSRB1 were analyzed by using Sequence Manipulation Suite (STS) (http://www.bio-soft.net/sms/, accessed on 15 March 2024), and Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (SMART) (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/, accessed on 15 March 2024) was utilized to predict the protein domains. The NetNglyc 1.0 server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetNGlyc/, accessed on 16 March 2024) predicted potential N-glycosylation sites. SRB1 sequences from other species were acquired from BLASTP (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blastp.cgi, accessed on 16 March 2024), and multiple-sequence alignments were conducted by using ClustalW 2.1 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/tools/clustalw2.1, accessed on 16 March 2024). The phylogenetic tree based on the amino acid sequences was constructed by utilizing Mega 7.0 (http://www.megasoftware.net/index.html, accessed on 16 March 2024) with the neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm and a bootstrapping procedure with a minimum of 1000 bootstraps.
The genomic DNA sequences of CiSRB1 were predicted from the grass carp draft genome based on cDNA sequences, and specific primers (Table 2) were designed accordingly. Genomic DNA was extracted from the tail tissue of one-year-old fish by using the Universal Genomic DNA Kit (CWBio, Beijing, China). PCR amplification was performed by using the extracted genomic DNA as a template, and the resulting PCR products were sequenced to obtain the genomic DNA sequences of CiSRB1. Exons and introns were determined by comparing the genomic DNA sequences with the cDNA sequences.

Table 2.
Primers for the amplification of genomic DNA sequences.
AlphaFold Server (https://alphafoldserver.com, accessed on 30 June 2024) [] was used to predict the potential interaction between CiSRB1 and GCRV particles, which play key roles in viral attachment and infection [,]. The outer capsid proteins of several typical GCRV strains were analyzed, including the VP5 protein from the GCRV-873 strain (GenBank accession No. AAG17823.1), the VP7 protein from the GCRV-873 strain (GenBank accession No. AAM92742.1), the VP5 protein from the HZ08 strain (GenBank accession No. ADJ75337.1, designated as VP5H in this paper), and the VP7 protein from the GCRV-GD108 strain (GenBank accession No. ADT79738.1, designated as VP7G in this paper). UCSF ChimeraX (http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera/, accessed on 15 March 2024) [] was then utilized to visualize the results predicted by AlphaFold Server.
2.3. GCRV Challenge and Sampling
The acquisition of the GCRV and GCRV challenge was based on [] with modifications. In brief, two hundred fish were divided into four groups (Groups I–IV), each consisting of 50 fish. Group I, containing one-year-old fish, and Group II, containing three-year-old fish, were intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected with 20 µL/g body weight of 0.7% NaCl as the control treatments. Samples of gills, spleen, intestines, and liver were collected from three individuals in each group, respectively. Meanwhile, Group III, containing one-year-old fish, and Group IV, containing three-year-old fish, were i.p. injected with 20 µL/g body weight of GCRV (HZ08 strain) at a titer of 2.97 × 103 copy/µL. These injected fish were maintained under the same conditions as mentioned above. Afterwards, three individuals from each challenge group were euthanized, and samples of gills, spleen, intestines, and liver were collected 6, 12, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, and 144 h post-injection (hpi). All samples were immediately homogenized in TRIzol reagent and stored at −80 °C until RNA extraction for further analysis. The total mortality of these four groups was assessed by recording the number of dead fish daily. The experiment ended when no deaths were recorded for two consecutive weeks, and the total mortality was calculated at that point.
2.4. Quantification of Gene Expression
Total RNAs were extracted from various tissues of healthy one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp, including gills, head kidney, heart, intestines, brain middle kidney, liver, muscle, and spleen. First-strand cDNA synthesis was performed by using ReverTra Ace® qPCR RT Master Mix with gDNA Remover (Toyobo, Japan). Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) was conducted by using SYBR® Green Realtime PCR Master Mix (Toyobo, Japan) on the StepOnePlus™ Real-Time PCR System (ABI, Los Angeles, CA, USA), with three replicates performed per sample. The β-actin gene in C. idellus (GenBank accession No. M25013.1) served as an internal control for cDNA normalization. Gene expression levels were calculated by using the 2−∆∆Ct method []. The expression level in the gills from healthy one-year-old grass carp was set as the baseline (1.00) for tissue distribution, and the relative gene expression was calculated as the ratio of gene expression in each tissue relative to that in the gills from one-year-old grass carp.
To determine the effects of viral infection on CiSRB1 transcripts, three individuals were sampled from each group. Four representative immune tissues, gills, spleen, intestines, and liver were collected 6, 12, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, and 144 hpi. The mRNA expression levels of CiSRB1 at 0 h in healthy one-year-old fish were set to 1.00, and β-actin was used as an internal control to normalize the relative CiSRB1 transcripts in different tissues in response to GCRV infection. To determine dynamic changes in GCRV levels in the infected fish, the relative GCRV copy numbers were examined by specific primers (Table 1) for the M6 segment of the GCRV-HZ08 strain []. For convenience, the relative copy number of GCRV 1 dpi in the gills of one-year-old infected fish was used for normalization, and GCRV relative copy numbers of one-year-old and three-year-old infected fish in gills, spleen, intestines, and liver were calculated 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 dpi.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The experimental data were expressed as the means ± standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. Significant differences were subjected to one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test by using SPSS Statistics 22.0, with p < 0.05 being considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Features of CiSRB1
The full-length cDNA sequence of CiSRB1 (GenBank accession No. MT643909) was obtained via RT-PCR and RACE, measuring 2486 bp in length. It comprised a 1494 bp ORF encoding 497 amino acids (aa), a 310 bp 5’-UTR and a 682 bp 3′-UTR with three RNA instability motifs (ATTTA), five polyadenylation signal sequences (ATTAA), and a poly(A) tail (Figure 1). Structure analysis revealed that the CiSRB1 protein contained two primary putative transmembrane domains of 23 aa each (residues 7~29 and 442~464) and six putative N-glycosylation sites (residues 101, 107, 211, 309, 329, and 382). Additionally, a CD36 domain spanning aa 14 to 462 (E-value = 9.5 × 10−155) was discovered.
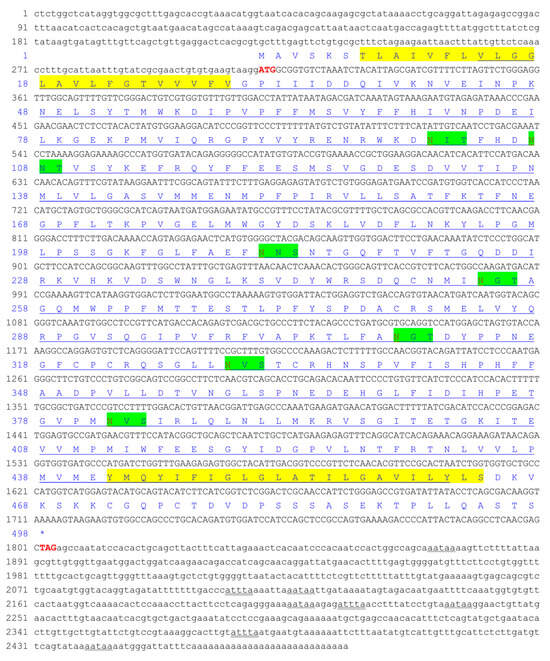
Figure 1.
Nucleotide and putative amino acid sequences of CiSRB1. Nucleotide (lower row) and putative amino acid (upper row) sequence numbers are shown on the left. The start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TAG) are highlighted in bold red. The mRNA instability motif (ATTTA) is double-underscored, and the poly-adenylation signal sequence (AATAA) is shown with a wavy line. Transmembrane regions are marked with yellow backgrounds. The CD36 domain is underscored. Asn-Xaa-Ser/Thr sequons are highlighted in green background, and Asn residues predicted to be N-linked glycosylation sites are highlighted in red. * indicates that amino acids stop being produced.
The full-length genomic DNA sequence of CiSRB1 was 20,042 bp in length, with a schematic diagram depicted in Figure 2. CiSRB1 contained 12 exons and 11 introns, adhering to the consensus GT/AG rule. Comparison with previous research indicated conserved lengths of most exons (1~7) between CiSRB1 (Figure 2a) and GrSRB1 (Figure 2b), with distinctions starting from exon 8. Furthermore, significant differences were observed in the intron lengths, with CiSRB1 spanning 20,042 bp and GrSRB1 only 10,792 bp.
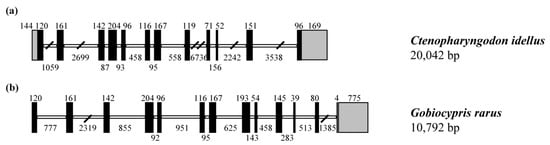
Figure 2.
Genomic structure of SRB1 genes. (a) CiSRB1 and (b) GrSRB1. Exons are represented by dark bars and introns by white boxes, while 5′-UTR and 3′-UTR are indicated by dark bars with a diagonal line. The number of nucleotides in each exon or intron is shown above or below the corresponding element.
3.2. Homology Analysis of CiSRB1
The deduced amino acid sequence of CiSRB1 showed 86.56%, 80.32%, 80.15%, 72.19%, 54.06%, 54.04%, 52.28%, 50.39%, and 50.00% identity with the SRB1 homologs from G. rarus, D. rerio, Cyprinus carpio, Oreochromis niloticus, Gallus gallus, H. sapiens, Xenopus laevis, Bos Taurus, and M. musculus, respectively (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Multiple-sequence alignments of SRB1 proteins from different species. The dark shade indicates 100% identity, and the gray shade indicates 50% identity. The CD36 domain is highlighted in a red box. CiSRB1 denotes SRB1 in C. idellus, GrSRB1 denotes SRB1 in G. rarus, DrSRB1 denotes SRB1 in D. rerio, CcSRB1 denotes SRB1 in C. carpio, OnSRB1 denotes SRB1 in O. niloticus, GgSRB1 denotes SRB1 in G. gallus, XlSRB1denotes SRB1 in X. laevis, HmSRB1 denotes SRB1 in H. sapiens, BtSRB1 denotes SRB1 in B. taurus, and MmSRB1 denotes SRB1 in M. musculus.
The phylogenetic tree indicated that homologous SRB1 proteins from various vertebrate species clustered into four groups: mammals, birds, amphibians, and fish. All fish SRB1 proteins clustered together, with SRB1 from C. idellus branching most closely to SRB1 from G. rarus (Figure 4), reflecting a genetic relationship consistent with the evolution of species.
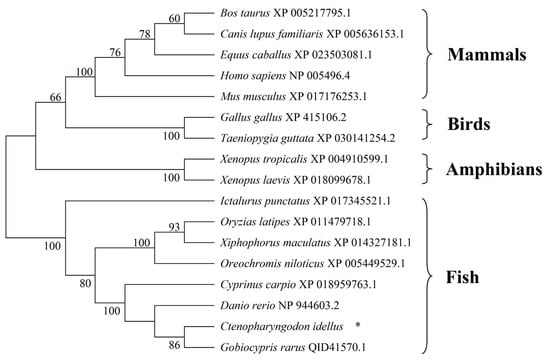
Figure 4.
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree analysis of SRB1 proteins in vertebrates. The tree was constructed based on amino acid sequences of grass carp SRB1 and 16 orthologs by using MEGA 7.0 software. The GenBank accession numbers of the SRB1 proteins are given after the species names in the tree. * represents SRB1 in C. idellus.
3.3. Predictive Analysis of Protein Interactions between CiSRB1 and GCRV Particles
In AlphaFold3, the modified local distance difference test (pLDDT) is a per-atom confidence estimate on a scale of 0–100, and the predicted aligned error (PAE) indicates model confidence in the relative orientations of the protein parts. Higher pLDDT or PAE values indicate greater confidence in the prediction []. High pLDDT and PAE values were observed between CiSRB1 and VP5, VP7, VP5H, and VP7G (Figure S1), confirming the reliability of our predictions. These results, predicted by AlphaFold3, were then visualized by using ChimeraX. In ChimeraX, three methods are used to analyze the interactions between protein structures: “Clashes” (unfavorable interactions due to close proximity), “Contacts” (various polar and nonpolar interactions), and “H-Bonds” (hydrogen bond analysis) []. The interaction between the CiSRB1 protein and the outer capsid protein of GCRV depends on amino acid residues at their interaction interface. There were 3 hydrogen bonds and 63 contacts between CiSRB1 and VP5, 8 hydrogen bonds and 108 contacts between CiSRB1 and VP7, 3 hydrogen bonds and 66 contacts between CiSRB1 and VP5H, and 11 hydrogen bonds and 687 contacts between CiSRB1 and VP7G (Figure 5).
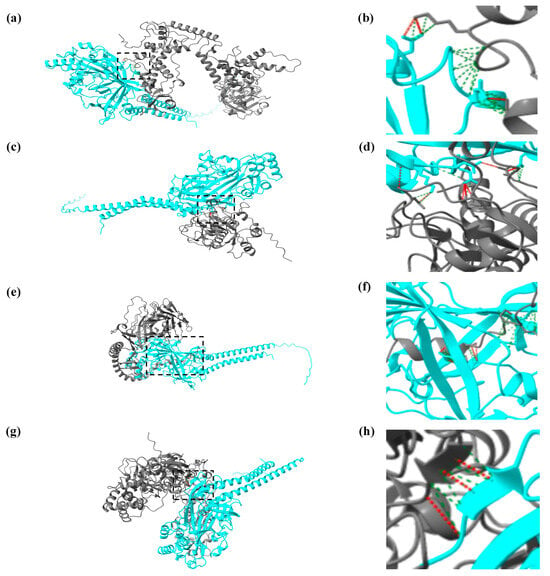
Figure 5.
Visualized results of protein interactions between CiSRB1 and GCRV particles by UCSF ChimeraX. The interactions are depicted as follows: (a) CiSRB1 and VP5, (c) CiSRB1 and VP7, (e) CiSRB1 and VP7G, and (g) CiSRB1 and VP5H; panels (b), (d), (f), and (h) are magnifications of panels (a), (c), (e), and (g), respectively. In the visualizations, the blue protein chain represents the CiSRB1 protein, and the gray protein chain represents the outer capsid protein from different typical GCRV strains. The red dashed lines between the two protein chains represent hydrogen bonds, and the green dashed lines indicate various polar and nonpolar interactions between the molecules.
3.4. Tissue Distribution of CiSRB1 in Healthy Grass Carp
In healthy one-year-old grass carp, CiSRB1 expression was detected in all tested tissues, with the highest expression being in the intestines (16.48 ± 1.33 fold change), followed by muscle (6.06 ± 0.15 fold change), spleen (5.98 ± 0.06 fold change), liver (5.14 ± 0.32 fold change), and brain (4.68 ± 0.36 fold change). Lower expression levels were observed in the middle kidney (3.10 ± 0.11 fold change), heart (2.75 ± 0.04 fold change), and head kidney (2.03 ± 0.11 fold change), with the lowest being in the gills (1.00 ± 0.06 fold change). Conversely, in healthy three-year-old grass carp, CiSRB1 exhibited high expression levels in the intestines (2.72 ± 0.10 fold change) and gills (2.20 ± 0.04 fold change), intermediate levels in the liver (1.89 ± 0.05 fold change), and low levels in the other tissues, with the lowest expression being observed in the spleen (0.17 ± 0.00 fold change). Overall, CiSRB1 transcripts in the tested tissues of three-year-old individuals were significantly lower compared with one-year-old individuals, except for gills (p < 0.05) (Figure 6).
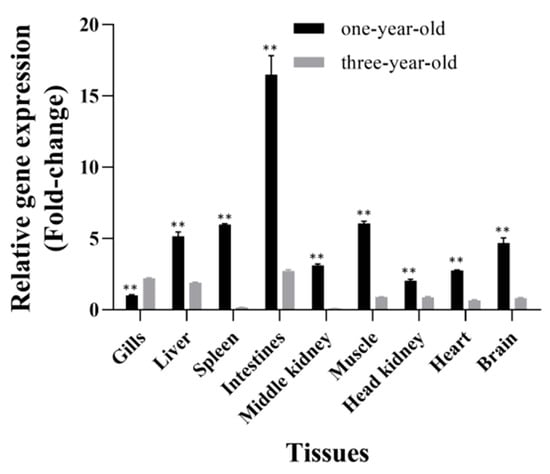
Figure 6.
Tissue distribution of CiSRB1 in healthy one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp. Data are expressed as the ratios of CiSRB1 mRNA expression in each tissue relative to its expression in the gills from one-year-old fish. Significant differences in CiSRB1 expression between samples from one-year-old and three-year-old fish were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test. ** indicates p < 0.01.
3.5. Mortality of Grass Carp after GCRV Infection
One-year-old and three-year-old grass carp were injected with either 0.7% NaCl or GCRV virus, and the mortality of both control (Groups I and II) and experimental (Groups III and IV) groups was evaluated after infection. No clinical disease symptoms were detected in the control fish (Group I: one-year-old fish; Group II: three-year-old fish). However, among the one-year-old grass carp injected with GCRV (Group III), mortality was observed from 6 dpi and continued up to 13 dpi (Figure 7). The total mortality of one-year-old grass carp infected with GCRV was 84% (42/50), with all deceased fish exhibiting typical symptoms of muscular or intestinal hemorrhage. In contrast, throughout the entire infection period, three-year-old grass carp infected with GCRV (Group IV) remained asymptomatic, with no mortality recorded.
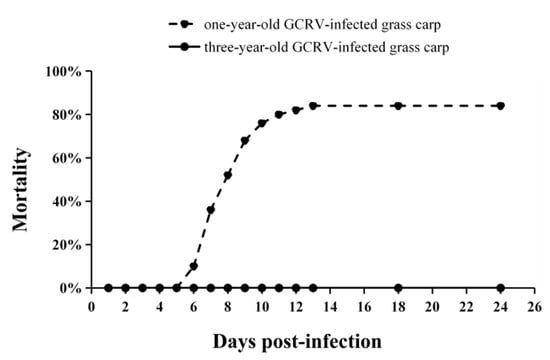
Figure 7.
Mortality rates of one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp after GCRV infection. The number of deceased grass carp in each group was monitored daily until no deaths were recorded for two consecutive weeks.
3.6. Expression Profiles of CiSRB1 following GCRV Infection
To assess the potential involvement of the CiSRB1 gene in GCRV cell entry across different age groups, the mRNA levels of CiSRB1 in immune-related tissues, including gills, spleen, intestines and liver, were determined.
In the gills of one-year-old grass carp, robust upregulation of CiSRB1 expression was observed upon GCRV stimulation (Figure 8a). CiSRB1 mRNA levels peaked 12 hpi (3.48 ± 0.15 fold change) and then quickly dropped back to the original levels by 48 hpi, with slight fluctuations thereafter. In three-year-old individuals, CiSRB1 exhibited a different expression pattern, with transcript levels steadily declining from the peak 0 hpi (2.85 ± 0.08 fold change) to the lowest point 120 hpi (0.72 ± 0.05 fold change).
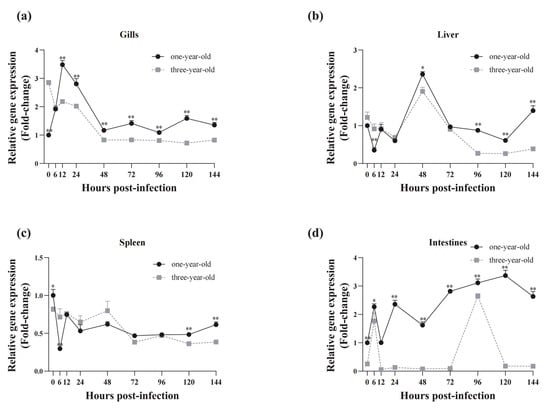
Figure 8.
Temporal expression analysis of CiSRB1 in immune tissues from one-year-old and three-year-old carp after GCRV infection. The mRNA levels of CiSRB1 in the gills (a), liver (b), spleen (c), and intestines (d) 0~144 hpi were subjected to qPCR analysis. Expression levels of CiSRB1 in the healthy samples from one-year-old fish (0 hpi) were set to 1.00, and β-actin served as an internal control to normalize the relative expression levels of the target genes. The results are based on three independent experiments and are expressed as means ± SD. Significant differences in CiSRB1 expression between the samples from the one-year-old and three-year-old fish were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test. ** indicates p < 0.01, and * indicates p < 0.05.
In the liver of one-year-old grass carp, CiSRB1 expression reached its lowest level 6 hpi (0.35 ± 0.07 fold change), followed by a gradual upregulation to peak levels (2.36 ± 0.07 fold change) 48 hpi, before declining again from 72 to 120 hpi (0.61 ± 0.07 fold change). A similar trend was observed in three-year-old grass carp, with CiSRB1 transcripts gradually decreasing to a nadir 24 hpi (0.69 ± 0.06 fold change) (Figure 8b), followed by an increase to peak levels (1.90 folds ± 0.11 fold change). This was succeeded by a significant decline to the lowest point (0.26 ± 0.03 fold change) 120 hpi, followed by a gradual increase 144 hpi.
In the spleen of one-year-old grass carp, CiSRB1 mRNA expression exhibited rapid downregulation, reaching its lowest level 6 hpi (0.30 ± 0.01 fold change), followed by slight variations and fluctuating patterns from 12 to 144 hpi. This fluctuating expression pattern was also observed in the spleen of three-year-old individuals infected with GCRV (Figure 8c).
In the intestines of one-year-old grass carp, CiSRB1 mRNA expression levels demonstrated unstable changes following GCRV challenge. After GCRV exposure, CiSRB1 expression gradually increased 6 hpi (2.36 ± 0.14 fold change), then slowly declined to baseline levels 12 hpi. Subsequently, CiSRB1 expression was upregulated again, reaching its peak levels (3.37 ± 0.19 fold change) 120 hpi. In three-year-old grass carp stimulated with GCRV, a 1.76 to 2.65 fold-change increase in CiSRB1 expression was observed 6 hpi and 96 hpi in the intestines, with lower transcription levels of CiSRB1 being observed at other tested timepoints (Figure 8d).
3.7. Relative Copy Numbers of GCRV RNA in Infected Grass Carp
The relative GCRV copy numbers in four tissues (gills, liver, spleen, and intestines) were examined by qPCR by using specific primers for the M6 segment of the GCRV-HZ08 strain to determine the GCRV infection status of GCRV-infected grass carp. Minor differences in the GCRV copy numbers of gills, liver, and spleen were observed between one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp 1 dpi, indicating that the GCRV dose used for injection was appropriate (Figure 9). In one-year-old infected fish, the GCRV relative copy numbers in gills (Figure 9a), spleen (Figure 9c), and intestines (Figure 8d) showed an increasing trend and peaked 6 dpi during the tested period. However, the GCRV relative copy numbers in the liver followed a parabolic trend, reaching a maximum 3 dpi and then decreasing to the original level 6 dpi (Figure 9b). In three-year-old carp, the GCRV levels remained quite low in the gills throughout the infection (Figure 9a), and a similar parabolic curve was observed for the liver (Figure 9b). The GCRV copy numbers in the spleen increased after infection in the three-year-old fish, although they were significantly lower than those in the one-year-old fish. Similarly, the GCRV RNA levels gradually increased to their peak in the intestines 5 dpi before declining 6 dpi (Figure 9d). In general, the relative copy numbers of GCRV in the tissues of the three-year-old grass carp were significantly lower than those in the one-year-old grass carp after GCRV infection.
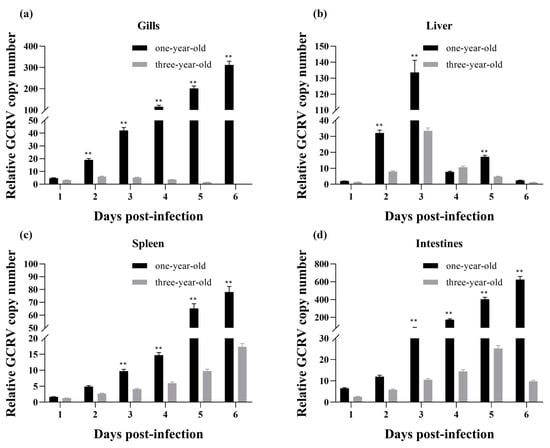
Figure 9.
Relative GCRV copy numbers in infected one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp. The relative GCRV copy numbers were examined by using specific primers targeting the M6 segment of the GCRV-HZ08 strain. (a) The relative GCRV copy number in gills; (b) The relative GCRV copy number in liver; (c) The relative GCRV copy number in spleen; (d) The relative GCRV copy number in intestines. The copy number of GCRV 1 dpi in the gills of one-year-old infected fish was used for normalization. The data (expressed as means ± SD) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test. ** indicates p < 0.01.
4. Discussion
SRs are pivotal for immune defense, functioning as PRRs. Among them, SRB1, renowned as an HDL receptor, performs vital functions in viral entry into host cells [,,,,,,], immune regulation [], phagocytosis of apoptotic cells [], and more. In this study, the SRB1 gene was discerned from C. idellus, designated as CiSRB1. The CiSRB1 protein contained a CD36 domain, two transmembrane regions, and two cytoplasmic tails (Figure 1), resembling observations in other species []. Alignment and structural analysis of diverse SRB1 orthologs from different species unveiled that fish SRB1 proteins share notable similarities of at least 72%, clustering together in a distinct clade within the phylogenetic tree.
The genomic architecture of the SRB1 gene varies across species. In G. rarus [], C. carpio (Gene ID: 109090404), and S. maximus [], the SRB1 gene comprises 13 exons and 12 introns. However, CiSRB1, as discovered in this study, consists of 12 exons and 11 introns, akin to the genomic structure observed in H. sapiens (Gene ID: 949) and Bos taurus (Gene ID: 282346). Comparing the sequences of GrSRB1 and CiSRB1, the cDNA sequences demonstrated substantial similarity, sharing up to 88.76%. Notably, differences in the size of the CiSRB1 genomic sequence compared with that of GrSRB1 primarily stemmed from variations in intron length. Research suggests that introns are involved in regulating gene expression, with DNA methylation within introns playing an important role in this regulatory process []. The role of introns in gene expression regulation, particularly in the context of GCRV mortality, warrants further investigation.
CiSRB1 exhibited a widespread distribution in various tissues with varying expression levels in healthy grass carp, predominantly expressed in the intestines, akin to reports in S. maximus [], E. coioides [], and Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) []. However, a novel paralog of SCARB1 (SCARB1-2) in S. salar was equally expressed in muscle, liver, and midgut []. Furthermore, it was reported that SRB1 exhibited the highest expression in the liver and steroidogenic tissues in mammals or nonmammals, such as M. musculus [], D. rerio [], goldfish (Carassius auratus) [], and G. rarus []. This suggests that the tissue distribution of SRB1 varies across different species. It is possible that SRB1 emerged relatively early in vertebrate evolution, possessing several metabolic functions [].
Lower levels of CiSRB1 transcript were detected in most tested tissues of three-year-old grass carp compared with one-year-old individuals, except for the gills. These findings paralleled the expression pattern observed for JAM-A in grass carp, a potential receptor for GCRV infection, where JAM-A exhibited higher expression levels in one-year-old grass carp compared with three-year-old individuals []. Furthermore, it was found that one-year-old grass carp had a mortality rate of up to 84% 6 dpi, whereas all three-year-old grass carp survived after GCRV infection (Figure 6), consistently with previous research [,,]. Similar age-dependent patterns of susceptibility to viral infection have been documented in various species, such as spring viremia of carp virus (SVCV) challenge in North American fish species [] and European common carp (Cyprinus carpio carpio) [], as well as nervous necrosis virus (NNV) challenge in barramundi (Lates calcarifer) [] and gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) []. It is possible that the immunity of young individuals, including the expression of antiviral, inflammatory, and cell-mediated cytotoxicity genes, renders them more susceptible to viral infection [,].
SRB1 serves as an essential factor in the entry of multiple viruses. It can interact directly with HCV particles or indirectly via ApoB or HDL to promote HCV entry into cells [,,]. The interaction of ApoA-I and SRB1 facilitates the attachment and entry of DV into cells []. SR-B1 mediates the interaction of cholesterol with the spike of SARS-CoV-2, thereby facilitating the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into host cells []. SRB1 also plays a crucial role in the innate immunity of teleost fish. In large yellow croakers (Larimichthys crocea), notable upregulation of SRB1 was observed after Pseudomonas plecoglossicida infection []. Similarly, SRB1 is implicated in the immune response of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against Vibrio anguillarum infection []. In S. salar, two distinct paralogues (SRB1-a and SRB1-b) show similar responses to viral mimic (dsRNA: pIC) []. This suggests that SRB1 influences both bacterial and viral infection. To explore the role of CiSRB1 during GCRV infection in grass carp, challenges were conducted across different age groups to evaluate responses. Notable upregulation of CiSRB1 transcripts was observed in major immune tissues (gills, liver, spleen, and intestines) following GCRV challenge. This result corroborates our previous transcriptome analysis, which demonstrates that the expression of phagosome pathway-related gene SRB1 in CIK cells is upregulated from 8 to 24 h after GCRV infection []. Similar findings have been confirmed for CiSRB2a and CiSRB2b, the alternative splicing products of SRB1, whose expression levels are elevated in the gills and spleen following GCRV infection []. This suggests that SRB1 plays a crucial role in the immune regulation of C. idellus in response to GCRV challenge. In G. rarus, a model fish used to analyze the mechanism of GCRV infection, GrSRB1 expression is upregulated in the gills, spleen, liver, and intestines after GCRV infection. Furthermore, co-immunoprecipitation assays reveal that GrSRB1 can interact with GCRV particles, such as VP5 and VP7 proteins from the GCRV-873 strain and the VP7 protein from the GCRV-GD108 strain []. The protein sequence similarity between GrSRB1 and CiSRB1 was approximately 90%, indicating that both likely play a similar role in GCRV infection. Additionally, protein interactions between CiSRB1 and GCRV particles were predicted by AlphaFold3 and visualized by using ChimeraX. These predictions indicated that CiSRB1 interacts with the outer capsid proteins of typical GCRV strains (VP5 and VP7 proteins from the GCRV-873 strain, VP5 protein from the HZ08 strain, and VP7 protein from the GCRV-GD108 strain) through hydrogen bonding as well as various polar and nonpolar interactions. These findings preliminarily infer that SRB1 may interact with the outer capsid proteins of GCRV and then facilitates the entry of GCRV into host cells via endocytosis, similarly to other reported viral attachment protein [,,]. These research findings provide support for our subsequent studies on the specific mechanisms of CiSRB1 in GCRV infection. Further research is needed to determine whether CiSRB1 can be directly or indirectly associated with GCRV particles to facilitate entry into host cells, such as knockdown or overexpression of CiSRB1 in CIK cells.
Significant differences were observed between one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp after GCRV challenge, with lower CiSRB1 expression levels being detected in the older group. Similarly, the relative copy numbers of GCRV across tissues revealed substantially higher levels in one-year-old grass carp compared with their older counterparts, consistently with prior findings [,]. This indicates that CiSRB1 is positively correlated with the degree of GCRV infection in one-year-old grass carp. The overexpression analysis of CiSRB2a and CiSRB2b in CIK cells also supports this, showing increased GCRV copy numbers following overexpression of CiSR-B2a and CiSR-B2b []. As a potential receptor for GCRV infection, higher levels of endogenous SRB1 may facilitate increased interactions with the viral outer capsid proteins, thereby promoting the rapid entry of GCRV into host cells via endocytosis, resulting in a greater number of GCRV copies within the host cells. Our previous study finds that the accumulation of GCRV copy numbers up to a certain threshold may lead to hemorrhagic disease, leading to organ malfunction and death [,]. In this study, the GCRV copy numbers peaked 6 dpi, coinciding with observed mortality from 6 dpi in one-year-old grass carp, indicating that the viral load had reached a fatal threshold. Conversely, the GCRV copy numbers in three-year-old grass carp were far lower those in the one-year-old individuals. Moreover, multi-omics sequencing indicates that three-year-old grass carp recognize the virus immediately, rapidly activate the immune response, and enhance host translation machinery to defend against viruses []. This coincides with our finding that GCRV copy numbers decreased from 2 dpi in the gills, 3 dpi in the liver, and 5 dpi in the intestines in the three-year-old individuals. Overall, although SRB1 is also expressed in three-year-old grass carp, allowing GCRV to enter, their immune system rapidly recognizes the virus and activates the immune response against it. Consequently, the viral load is not enough to cause hemorrhagic disease, preventing organ malfunction and death, allowing three-year-old grass carp to survive after GCRV infection. This observation accentuates the importance of CiSRB1 in the context of GCRV infection and provides insights into age-dependent susceptibility to reovirus.
5. Conclusions
In this study, CiSRB1 was identified, and its gene structure and expression levels were thoroughly analyzed. It was unveiled that CiSRB1 closely resembles SRB1 in other vertebrates, exhibiting the conserved CD36 domain. The predictive analysis of protein interactions revealed that CiSRB1 interact with the outer capsid proteins of typical GCRV strains through hydrogen bonding as well as various polar and nonpolar interactions. Tissue distributions exhibited age-dependent characteristics, with CiSRB1 being highly expressed in the intestines and moderately in the muscle, spleen, liver, and brain of one-year-old grass carp, while maintaining relatively low levels in three-year-old grass carp. Notable upregulation of CiSRB1 transcripts was observed in major immune tissues (gills, spleen, liver, and intestines) following GCRV challenge. Furthermore, significant differences were found between one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp, with lower CiSRB1 expression levels being detected in the older group. Additionally, higher mortality and more GCRV copy numbers were observed in one-year-old grass carp compared with their three-year-old counterparts, confirming the existence of age-related restriction to GCRV in grass carp. These results suggest that the cell-surface expression of CiSRB1 may decrease with age following GCRV infection, potentially acting as the reovirus receptor and reducing reovirus binding to target cells. This sets the stage for further investigations into the mechanisms underlying viral infection in fish.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes9070276/s1, Figure S1: The predicted results of protein interactions between CiSRB1 and GCRV particles by AlphaFold3. The interactions are depicted as follows: (a) CiSRB1 and VP5, (b) CiSRB1 and VP7, (c) CiSRB1 and VP5H, and (d) CiSRB1 and VP7G. Predictions colored according to pLDDT (orange: pLDDT ≤ 50; yellow: 50 < pLDDT ≤ 70; light blue: 70 < pLDDT ≤ 90; and dark blue: 90 ≤ pLDDT < 100) and PAE matrix of same prediction (darker color means more confident).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. and J.S.; Methodology, Y.L. and Q.L.; Investigation, Y.Z., P.C. and R.H.; Data Curation, M.O.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, K.C., J.Z. and J.S.; Writing—Review and Editing, Y.Z., Y.W. and Y.L.; Visualization, Q.L., P.C. and R.H.; Supervision, K.C., J.Z., Y.W. and M.O.; Project Administration, M.O.; Funding Acquisition, J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (2023TD37), China-ASEAN Maritime Cooperation Fund (CAMC-2018F), and National Freshwater Genetic Resource Center (FGRC18537).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All fish experiments in the present study were approved by the Pearl River Fisheries Research Institute and the Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences under contract LAEC-PRFRI-2020-01-01, and the experimental process complied with the protocols of international guidelines for the ethical use of animals in research.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Xiong, L.; Xiao, T.; Liu, Q. Identification of the C1qDC gene family in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and the response of C1qA, C1qB, and C1qC to GCRV infection in vivo and in vitro. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 148, 109477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Su, J. Type II grass carp reovirus infects leukocytes but not erythrocytes and thrombocytes in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Viruses 2021, 13, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ji, N.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Xiao, T.; Wang, J.; Zou, J. Analysis of tissue tropism of GCRV-II infection in grass carp using a VP35 monoclonal antibody. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2024, 157, 105189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Liao, L.; Xu, Q.; He, Z.; Xiao, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, B.; Yan, Q. Host–Microbiota Interactions and Responses to Grass Carp Reovirus Infection in Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, G.; Yuan, L.; Xia, X.-Q.; Zhang, W.; Shi, M. Transcriptomes of zebrafish in early stages of multiple viral invasions reveal the role of sterols in innate immune switch-on. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Martin, L.C.; Krishnan, M.; Kumaresan, M.; Manikandan, B.; Ramar, M. Interactions between macrophage membrane and lipid mediators during cardiovascular diseases with the implications of scavenger receptors. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2024, 258, 105362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Brunner, J.S.; Hajto, A.; Sharif, O.; Schabbauer, G. Lipid scavenging macrophages and inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2022, 1867, 159066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huby, T.; Le Goff, W. Macrophage SR-B1 in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2022, 33, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, H.; Schnober, E.K.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Thumann, C.; Zeisel, M.B.; Diepolder, H.M.; Hu, Z.; Liang, T.J.; Blum, H.E.; Thimme, R.; et al. Scavenger receptor class B is required for hepatitis C virus uptake and cross-presentation by human dendritic cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3466–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpitts, C.C.; Baumert, T.F. SCARB1 variants and HCV infection: Host susceptibility is lost in translation. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennelle, L.T.; Magoro, T.; Angelucci, A.R.; Dandekar, A.; Hahn, Y.S. Hepatitis C virus alters macrophage cholesterol metabolism through interaction with scavenger receptors. Viral Immunol. 2022, 35, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kakinami, C.; Li, Q.; Yang, B.; Li, H. Human apolipoprotein A-I is associated with dengue virus and enhances virus infection through SR-BI. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, A.-C.; Marinach, C.; Manzoni, G.; Silvie, O. Plasmodium sporozoites can invade hepatocytic cells independently of the ephrin receptor A2. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Qin, X.; Ye, J.; Shen, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, P. Possible mechanisms of cholesterol elevation aggravating COVID-19. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 3533–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; He, L.; Luo, L.; Huang, R.; Liao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Transcriptomics sequencing provides insights into understanding the mechanism of grass carp reovirus infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, M.; Huang, R.; Luo, Q.; Xiong, L.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y. Characterisation of scavenger receptor class B type 1 in rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.-J.; Asthana, S.; Kraemer, F.B.; Azhar, S. Thematic review series: Lipid transfer proteins scavenger receptor B type 1: Expression, molecular regulation, and cholesterol transport function. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1114–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Ji, A.; de Beer, F.C.; Tannock, L.R.; van der Westhuyzen, D.R. SR-BI protects against endotoxemia in mice through its roles in glucocorticoid production and hepatic clearance. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Qin, Q.; Wei, S. Identification and characterization of scavenger receptor class B type 1 in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ge, X.; Su, B.; Fu, Q.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Ren, Y.; Song, L.; Yang, N. Characterization of class B scavenger receptor type 1 (SRB1) in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, H.; Huang, R.; Xia, X.; Feng, Q.; et al. The draft genome of the grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) provides insights into its evolution and vegetarian adaptation. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Fang, Q.; Shah, S.; Atanasov, I.C.; Zhou, Z.H. Subnanometer-resolution structures of the grass carp reovirus core and virion. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 382, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, L.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S.; Fang, Q. VP5 autocleavage is required for efficient infection by in vitro-recoated aquareovirus particles. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1795–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.C.; Goddard, T.D.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Pearson, Z.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Tools for structure building and analysis. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Su, J.; Huang, R.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Cloning and preliminary functional studies of the JAM-A gene in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Xiong, L.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Huang, R.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Different responses in one-year-old and three-year-old grass carp reveal the mechanism of age restriction of GCRV infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, Y.; Sunatani, T.; Kim, I.-S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Shiratsuchi, A. Signalling pathway involving GULP, MAPK and Rac1 for SR-BI-induced phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. J. Biochem. 2009, 145, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.G.; Littlejohn, M.D.; Meier, S.; Roche, J.R.; Mitchell, M.D. DNA methylation is correlated with gene expression during early pregnancy in Bos taurus. Physiol. Genom. 2013, 45, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleveland, E.J.; Syvertsen, B.L.; Ruyter, B.; Vegusdal, A.; Jørgensen, S.M.; Gjøen, T. Characterization of scavenger receptor class B, type I in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Lipids 2006, 41, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundvold, H.; Helgeland, H.; Baranski, M.; Omholt, S.W.; Våge, D. Characterisation of a novel paralog of scavenger receptor class B member I (SCARB1) in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). BMC Genet. 2011, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundert, M.; Ewert, A.; Heeren, J.; Behrendt, B.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Greten, H.; Merkel, M.; Rinninger, F. Scavenger receptor class B type I mediates the selective uptake of high-density lipoprotein–associated cholesteryl ester by the liver in mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwilligen, R.A.F.; Mulder, L.; Araújo, P.M.; Carneiro, M.; Bussmann, J.; Hoekstra, M.; Van Eck, M. Zebrafish as outgroup model to study evolution of scavenger receptor class B type I functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2023, 1868, 159308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, A.E.; Marie, R.S.; Callard, I.P. Expression of SR-BI (scavenger receptor class B type I) in turtle (Chrysemys picta) tissues and other nonmammalian vertebrates. J. Exp. Zool. 2002, 292, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhu, D.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Liao, L.; Yang, C.; Huang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Multi-Omics sequencing provides insights into age-dependent susceptibility of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) to reovirus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 694965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmenegger, E.J.; Sanders, G.E.; Conway, C.M.; Binkowski, F.P.; Winton, J.R.; Kurath, G. Experimental infection of six North American fish species with the North Carolina strain of spring viremia of carp virus. Aquaculture 2016, 450, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embregts, C.W.E.; Rigaudeau, D.; Veselý, T.; Pokorová, D.; Lorenzen, N.; Petit, J.; Houel, A.; Dauber, M.; Schütze, H.; Boudinot, P.; et al. Intramuscular DNA vaccination of juvenile carp against spring viremia of carp virus induces full protection and establishes a virus-specific B and T cell response. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, D.; Hick, P.; Whittington, R.J. Age dependency of nervous necrosis virus infection in barramundi Lates Calcarifer (Bloch). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Álvarez, M.Á.; Arizcun, M.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A. Profile of innate immunity in gilthead seabream larvae reflects mortality upon betanodavirus reassortant infection and replication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bao, N.; Rui, C.; Xue, Y.; Fang, Q.; Zheng, T.; Lin, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Identification of large yellow croakers (Larimichthys crocea) scavenger receptor genes: Involvement in immune response to Pseudomonas plecoglossicida infection and hypoxia-exposure experiments. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 144, 109307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Sun, L. Gene network analysis reveals a core set of genes involved in the immune response of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against vibrio anguillarum infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslamloo, K.; Xue, X.; Hall, J.R.; Smith, N.C.; Caballero-Solares, A.; Parrish, C.C.; Taylor, R.G.; Rise, M.L. Transcriptome profiling of antiviral immune and dietary fatty acid dependent responses of Atlantic salmon macrophage-like cells. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, L.; He, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Characterization of SR-B2a and SR-B2b genes and their ability to promote GCRV infection in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 124, 104202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Yu, F.; Lu, L. Disruption of clathrin-dependent trafficking results in the failure of grass carp reovirus cellular entry. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Fang, Q. Identification of the caveolae/raft-mediated endocytosis as the primary entry pathway for aquareovirus. Virology 2018, 513, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, D.M.; Strebl, M.; Koehler, M.; Welsh, O.L.; Yu, X.; Hu, L.; Dos Santos Natividade, R.; Knowlton, J.J.; Taylor, G.M.; Moreno, R.A.; et al. NgR1 binding to reovirus reveals an unusual bivalent interaction and a new viral attachment protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2219404120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).