The Effects of Different Concentrations of Hydrogen-Rich Water on the Growth Performance, Digestive Ability, Antioxidant Capacity, Glucose Metabolism Pathway, mTOR Signaling Pathway, and Gut Microbiota of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Fish Culture
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Biological Analyses in Largemouth Bass Tissues
2.5. DNA Extraction and 16s rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.6. RNA Extraction and qPCR Amplification
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Effect of Hydrogen on the Growth Performance of Largemouth Bass
3.2. Histological Observation
3.3. Effect of Hydrogen on Biochemical Indicators of Largemouth Bass
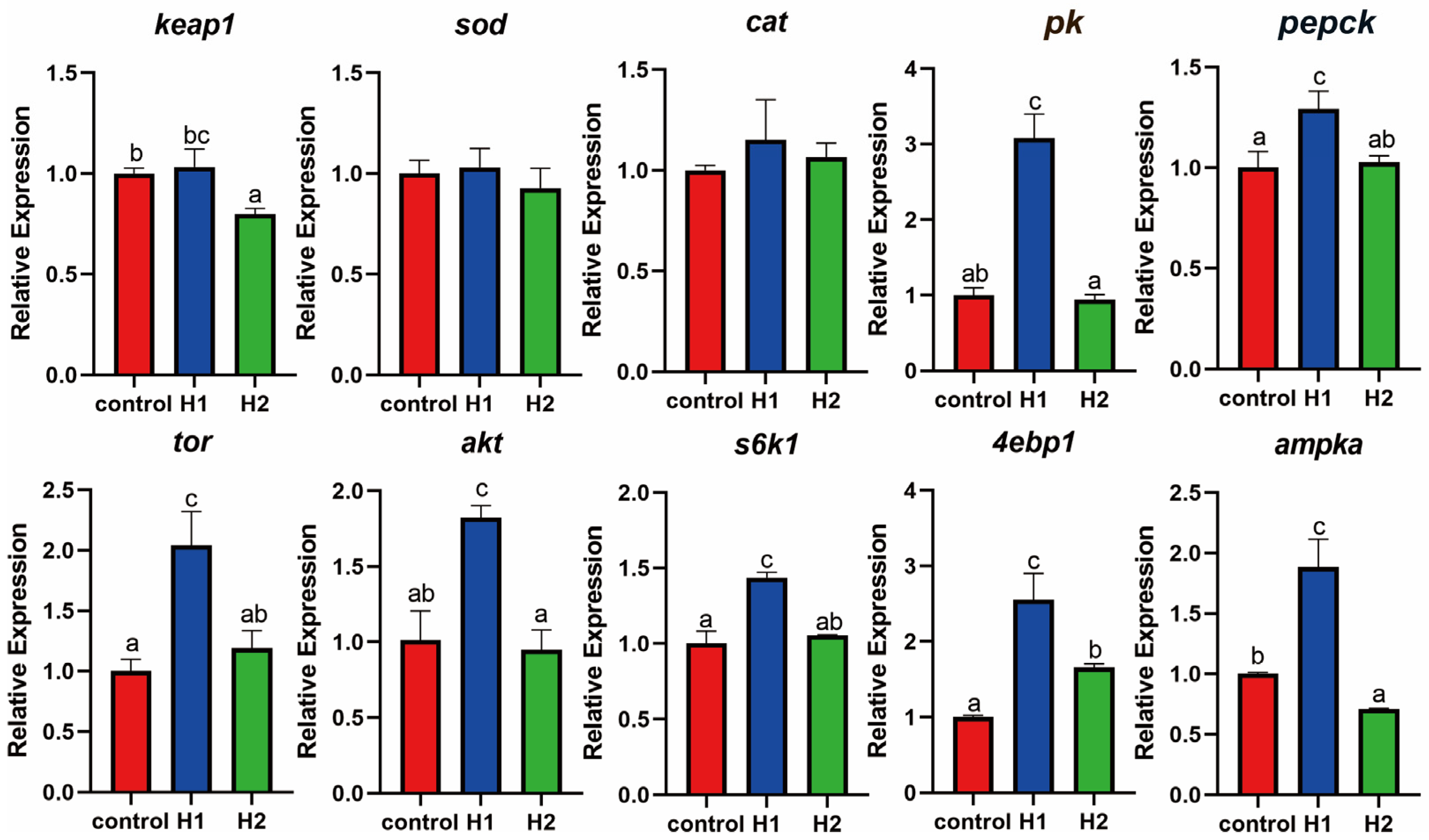
3.4. Effects of Hydrogen on the Oxidative Stress System, Carbohydrate Metabolism, and TOR Pathway of Largemouth Bass
3.5. Effects of Hydrogen on Microbial Diversity
3.6. Effect of Hydrogen on the Difference in Microbial Community Composition of Phylum Level and Genus Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bohnes, F.A.; Hauschild, M.Z.; Schlundt, J.; Nielsen, M.; Laurent, A. Environmental sustainability of future aquaculture production: Analysis of Singaporean and Norwegian policies. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wen, Z.Y.; Zou, Y.C.; Qin, C.J.; Yuan, D.Y. Largemouth bass pond culture in China: A review. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Res. 2017, 3, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chu, S.; Zhou, P. A critical review for hydrogen application in agriculture: Recent advances and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 54, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yin, C.K.; Zhong, D.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Qi, T.; Liu, G.H.; Li, X.B. Formic acid as a potential on-board hydrogen storage method: Development of homogeneous noble metal catalysts for dehydrogenation reactions. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 2655–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lou, W.; Kong, L.; Shen, W. Hydrogen commonly applicable from medicine to agriculture: From molecular mechanisms to the field. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.-I.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, R.; Shen, W.; Yang, J. Hydrogen-rich water alleviates salt stress in rice during seed germination. Plant Soil 2013, 370, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Shen, W. Molecular hydrogen positively influences lateral root formation by regulating hydrogen peroxide signaling. Plant Sci. 2022, 325, 111500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, M.; Sobue, S.; Ito, M.; Ito, M.; Hirayama, M.; Ohno, K. Beneficial biological effects and the underlying mechanisms of molecular hydrogen-comprehensive review of 321 original articles. Med. Gas Res. 2015, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Q.; Du, W.; Wei, Q.; Yao, W. Hydrogen-Rich Water and Lactulose Protect Against Growth Suppression and Oxidative Stress in Female Piglets Fed Fusarium Toxins Contaminated Diets. Toxins 2018, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L.; Jiao, J.; Yan, H.W. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates steroid-associated femoral head necrosis through inhibition of oxidative stress in a rabbit model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, C.; Zang, Y.; Bing, S.; Mo, Q.; Shu, D. Drinking with electrolyzed reduced hydrogen-rich water alters egg quality, intestinal morphology, and antioxidant activities in heat-stressed layers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2022, 31, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wu, B.; Meng, F.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhao, H. Impact of molecular hydrogen treatments on the innate immune activity and survival of zebrafish (Danio rerio) challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Lai, M.; Li, X.; Lin, Y.; Sun, Y. Hydrogen administration improves the growth performance of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) by increasing feed intake, reducing serum lipids, activating mTOR and Nrf2 signaling pathways, and altering the intestinal microbiota. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Storey, K.B. mTOR Signaling in Metabolic Stress Adaptation. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, A.; Neidhofer, S.; Matthias, T. The gut microbiome feelings of the brain: A perspective for non-microbiologists. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, W.; Si, Y.; Zhao, T.; Lai, X.; Guo, Z. Molecular hydrogen regulates PTEN-AKT-mTOR signaling via ROS to alleviate peritoneal dialysis-related peritoneal fibrosis. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4134–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Shi, L.; Du, D.Y.; Li, H.; Yi, N.; Long, J.G. Hydrogen-rich water ameliorates metabolic disorder via modifying gut microbiota in impaired fasting glucose patients: A randomized controlled study. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Z.M.; Zhao, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, F.D.; He, J.; Yao, T.T.; Zhang, X.K.; Yi, Y.; Ma, S.N.; Zhao, P.X.; et al. Effects of long-term hydrogen intervention on the physiological function of rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önalan, Ş.; Bulut, M.; Alwazeer, D. Evaluation of the Potential Use of Oxy-Hydrogen Gas for the Treatment of Lactococcus garvieae Infected- Zebrafish in Hydrogen-Rich Water Aquarium. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2023, 66, e23220750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnovali, M.; Mariotti, M.; Banfi, G. Molecular hydrogen enhances osteogenesis in Danio rerio embryos. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkovski, S. Digestive enzymes in fish larvae and juveniles-implications and applications to formulated diets. Aquaculture 2001, 200, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsdóttir, Á.; Pálsdóttir, H.M. Atlantic cod trypsins: From basic research to practical applications. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoncu, R.; Efeyan, A.; Sabatini, D.M. Zoncu R, Efeyan A, Sabatini DM. mTOR: From growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, C.; Woo, J.T.; Lindner, J.; Shelton, K.D.; Magnuson, M.A. Multiallelic Disruption of the rictor Gene in Mice Reveals that mTOR Complex 2 Is Essential for Fetal Growth and Viability. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Jiang, W.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. Supplementation of enzyme-treated soy protein saves dietary protein and promotes digestive and absorptive ability referring to TOR signaling in juvenile fish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1657–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Luo, K.; Rao, W.; Chen, P.; Lei, K.; Liu, C.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Effects of replacing dietary fish meal with enzyme-treated soybean meal on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, immunity and mTOR pathway in abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 130, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a novel antioxidant: Overview of the advantages of hydrogen for medical applications. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 555, 289. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Yu, G.; Liu, S.Y.; Li, J.B.; Wang, J.F.; Bo, L.L.; Qian, L.R.; Sun, X.J.; Deng, X.M. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Protects Against Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injuryin Rats. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 167, e339–e344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Yang, T.; Liu, W.; Deng, Y.; Xu, B. Sulforaphane Prevents Methylmercury-Induced Oxidative Damage and Excitotoxicity Through Activation of the Nrf2-ARE Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamanalp, M.; Kirici, M.; Kirici, M.; Alwazeer, D.; Kocaman, M.; Uçar, A.; Parlak, V.; Özcan, S.; Alak, G. Does hydrogen-rich water mitigate MP toxicity in rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss)? Monitoring with hematology, DNA damage, and apoptosis via ROS/GSH/MDA pathway. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2023, 52, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chou, G.; Li, Q. Cardioprotective role of azafrin in against myocardial injury in rats via activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Phytomedicine 2018, 47, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Liu, F. Effect of hydrogen-rich water on the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2019, 51, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Yu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Hou, L.; Chen, S.; Xiong, L.; Wang, G. Protective effects of hydrogen gas on murine polymicrobial sepsis via reducing oxidative stress and HMGB1 release. Shock 2010, 34, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, F.; Russell, G.; Hancock, J.T. Molecular hydrogen in agriculture. Planta 2021, 254, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: Initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kura, B.; Szantova, M.; LeBaron, T.W.; Mojto, V.; Barancik, M.; Szeiffova Bacova, B.; Kalocayova, B.; Sykora, M.; Okruhlicova, L.; Tribulova, N. Biological effects of hydrogen water on subjects with NAFLD: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalam, B.S.; Medale, F.; Panserat, S. Utilisation of dietary carbohydrates in farmed fishes: New insights on influencing factors, biological limitations and future strategies. Aquaculture 2017, 467, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Lei, Q.; Zhao, S.; Guan, K. Regulation of Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis by Acetylation of PKM and PEPCK; Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2011; p. a010942. [Google Scholar]
- Conde-Sieira, M.; Soengas, J.L.; Valente, L.M. Potential capacity of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) to use carbohydrates: Metabolic responses to hypo-and hyper-glycaemia. Aquaculture 2015, 438, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Singh, R. Probiotics in aquaculture: A promising emerging alternative approach. Symbiosis 2019, 77, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, N.; Shen, M.; Zhang, K.; Pan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Y. Drinking hydrogen-rich water alleviates chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain through the regulation of gut microbiota. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Shi, Q.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Yue, C.-P.; He, Z.-J.; Li, X.-X.; He, Q.-J.; Liu, Q.; Du, X.-B. Hydrogen-rich water ameliorates neuropathological impairments in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease through reducing neuroinflammation and modulating intestinal microbiota. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 409. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yang, T.; Tan, L.; Lv, P.; Xu, Q.; Tao, G.; Qin, S.; Lu, X.; He, Q. Nanocapsule-mediated sustained H2 release in the gut ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, C.; Dong, B.; Li, Y.; Luo, N.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y. Effect of molecular hydrogen treatment on Sepsis-Associated encephalopathy in mice based on gut microbiota. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mao, B.; Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Cui, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Blautia-a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1875796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Accession Number | Primer Sequence | Tm (°C) | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| keap1 | XM_038713665.1 | F: CAGCATTACATGGCCGCATC | 62.1 | 86 |
| R: CTTCTCTGGGTCGTAAGACTCC | ||||
| sod | MK614711.1 | F: CCACCAGAGGTCTCACAGCA | 58.7 | 158 |
| R: CCACTGAACCGAAGAAGGACT | ||||
| cat | XM_038704976.1 | F: GTTCCCGTCCTTCATCCACT | 58.5 | 85 |
| R: CAGGCTCCAGAAGTCCCACA | ||||
| pk | XM_038700626.1 | F: CTCTTTCATCCGCAAAGC | 53.8 | 172 |
| R: AATTCCCAGGTCACCACG | ||||
| pepck | XM_038696646.1 | F: GGAAACGGCCAACATTCT | 55.3 | 151 |
| R: GCCAACCAGCAGTTCTCAT | ||||
| tor | XM_038723321.1 | F: TCAGGACCTCTTCTCATTGGC | 59.1 | 208 |
| R: CCTCTCCCACCATGTITCTCT | ||||
| akt | XM_038729214.1 | F: ATGGACTCCTCTCCAGACCC | 57.4 | 164 |
| R: TTCATGGCGTACTAGCGTCC | ||||
| s6k1 | XM_038713349.1 | F: GCCAATCTCAGCGTTCTCAAC | 59.8 | 156 |
| R: CTGCCTAACATCATCCTCCTT | ||||
| 4ebp1 | XM_038709593.1 | F: AGCAGGAACITICGGTCATA | 50.2 | 168 |
| R: GTCAATGGGCAGTCAGAAGA | ||||
| ampkα | XM_038734014.1 | F: CACATGAATGCCAAGATTG | 52.1 | 131 |
| R: GGACCAGCATATAACCTTC | ||||
| Β-actin | XM_038695351.1 | F: AAAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC | 59.9 | 184 |
| R: AAGGAAGGCTGGAAGAGGG |
| Index | Control | H1 | H2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial body weight (IBW, g) | 13.67 ± 0.16 a | 13.69 ± 0.14 a | 13.85 ± 0.03 a |
| Final body weight (FBW, g) | 416.53 ± 22.41 a | 492.78 ± 25.82 b | 481.59 ± 6.42 b |
| feed intake (FI, g) | 7225.15 ± 280.13 a | 7967.58 ± 497.33 a | 7818.32 ± 158.24 a |
| Survival rate (SR, %) | 90.00 ± 2.00 a | 96.00 ± 2.00 b | 94.67 ± 3.06 ab |
| Weight gain rate (WGR, %) | 2949.42 ± 201.59 a | 3499.72 ± 162.39 b | 3377.17 ± 43.95 b |
| Specific growth rate (SGR, %) | 6.10 ± 0.12 a | 6.40 ± 0.08 b | 6.34 ± 0.12 b |
| Feed conversion ratio (FCR) | 1.79 ± 0.04 c | 1.66 ± 0.03 ab | 1.63 ± 0.03 a |
| Item | Control | H1 | H2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amylase (U/mgprot) | 0.13 ± 0.09 a | 0.13 ± 0.09 a | 0.23 ± 0.03 a |
| Trypsin (U/mgprot) | 141.50 ± 15.33 a | 246.53 ± 38.06 b | 171.10 ± 12.29 a |
| Lipase (U/mgprot) | 1.56 ± 0.36 b | 1.03 ± 0.69 ab | 0.45 ± 0.19 a |
| SOD (U/mgprot) | 32.54 ± 2.71 a | 38.87 ± 15.37 a | 22.97 ± 3.57 a |
| GSH-PX (U/mL) | 21.42 ± 15.80 a | 22.91 ± 14.15 a | 19.91 ± 7.23 a |
| CAT (U/mgprot) | 4.41 ± 0.08 a | 2.35 ± 1.14 a | 3.44 ± 0.27 a |
| MDA (nmol/mgprot) | 3.62 ± 1.09 a | 3.97 ± 1.21 a | 6.78 ± 1.65 b |
| H2O2 (mmol/gprot) | 26.45 ± 11.61 b | 13.16 ± 5.25 a | 21.15 ± 2.48 ab |
| NO (umol/gprot) | 7.03 ± 1.83 b | 5.02 ± 1.10 ab | 4.67 ± 1.06 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Peng, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y. The Effects of Different Concentrations of Hydrogen-Rich Water on the Growth Performance, Digestive Ability, Antioxidant Capacity, Glucose Metabolism Pathway, mTOR Signaling Pathway, and Gut Microbiota of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes 2024, 9, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060210
Yuan Y, Li H, Chen S, Lin Y, Peng J, Hu J, Wang Y. The Effects of Different Concentrations of Hydrogen-Rich Water on the Growth Performance, Digestive Ability, Antioxidant Capacity, Glucose Metabolism Pathway, mTOR Signaling Pathway, and Gut Microbiota of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes. 2024; 9(6):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060210
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yin, Huixiang Li, Songwei Chen, Yongchun Lin, Jiangyuan Peng, Junru Hu, and Yongsheng Wang. 2024. "The Effects of Different Concentrations of Hydrogen-Rich Water on the Growth Performance, Digestive Ability, Antioxidant Capacity, Glucose Metabolism Pathway, mTOR Signaling Pathway, and Gut Microbiota of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides)" Fishes 9, no. 6: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060210
APA StyleYuan, Y., Li, H., Chen, S., Lin, Y., Peng, J., Hu, J., & Wang, Y. (2024). The Effects of Different Concentrations of Hydrogen-Rich Water on the Growth Performance, Digestive Ability, Antioxidant Capacity, Glucose Metabolism Pathway, mTOR Signaling Pathway, and Gut Microbiota of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes, 9(6), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060210






