Cloning, Characterization and Functional Analysis of Caspase 8-like Gene in Apoptosis of Crassostrea hongkongensis Response to Hyper-Salinity Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. cDNA Cloning and Sequence Analysis
2.4. Salt Stress Experiment and Sampling
2.5. RNA Interference (RNAi) Experiment
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.7. Caspase 8 and Caspase 3 Activity Analysis in Gills of C. hongkongensis
2.8. TUNEL Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
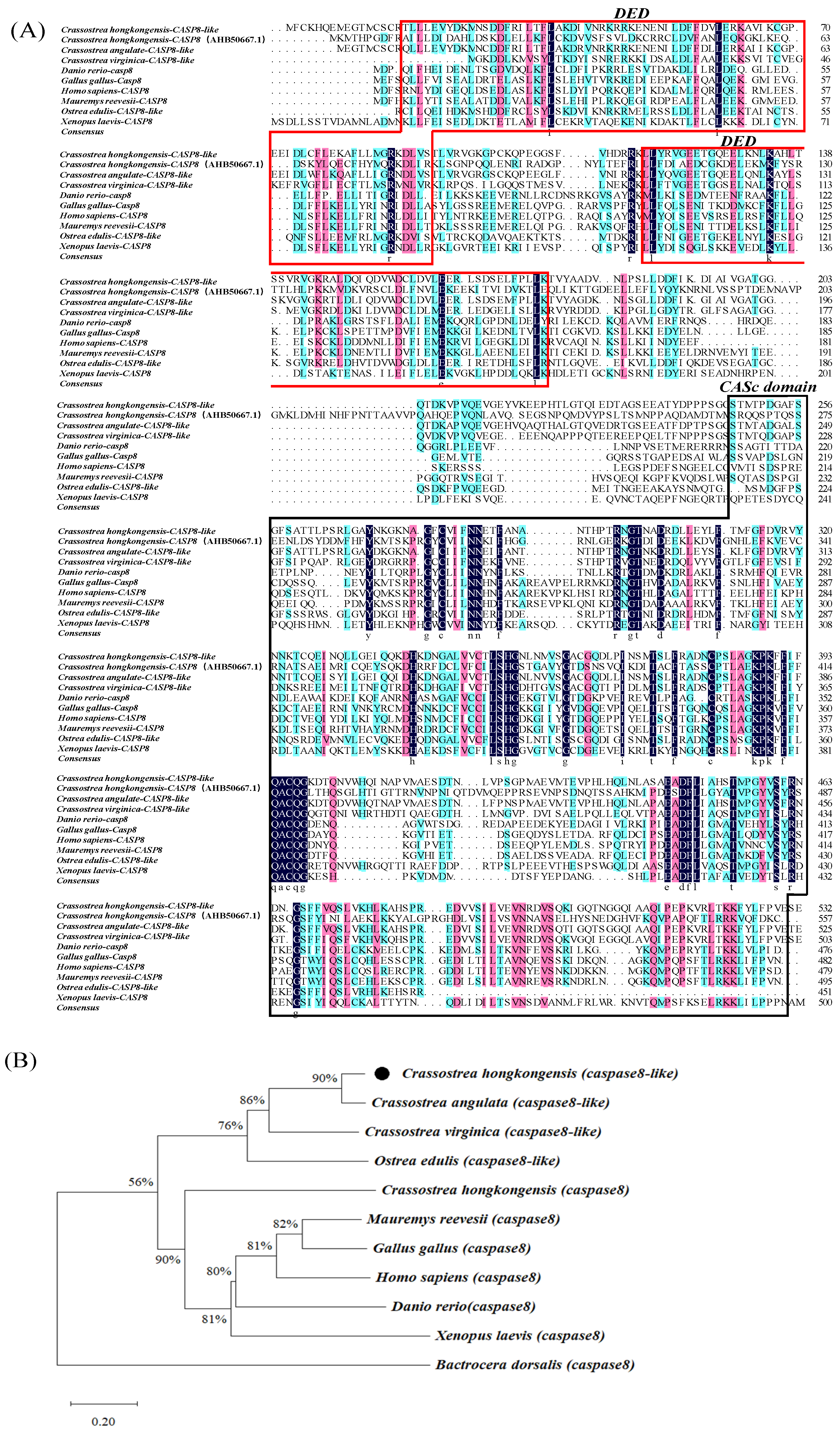
3.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Caspase8-like from C. hongkongensis
3.2. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
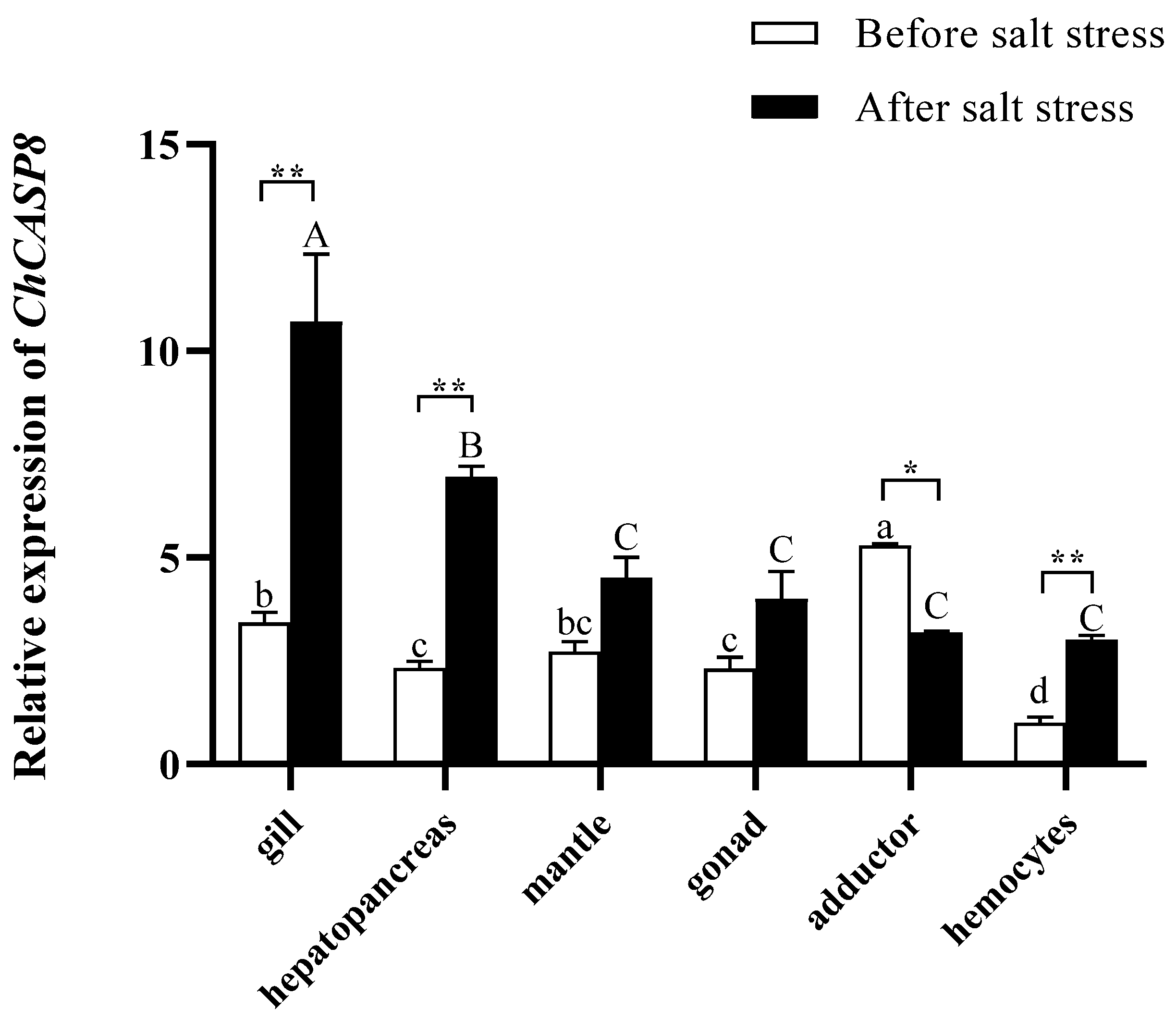
3.3. ChCASP8-like Expression Profile in Different Tissues
3.4. The Transcriptions of Apoptosis-Related Genes Were Stimulated by Hyper-Salinity Stress, but Were Inhibited by ChCASP8-like Silence
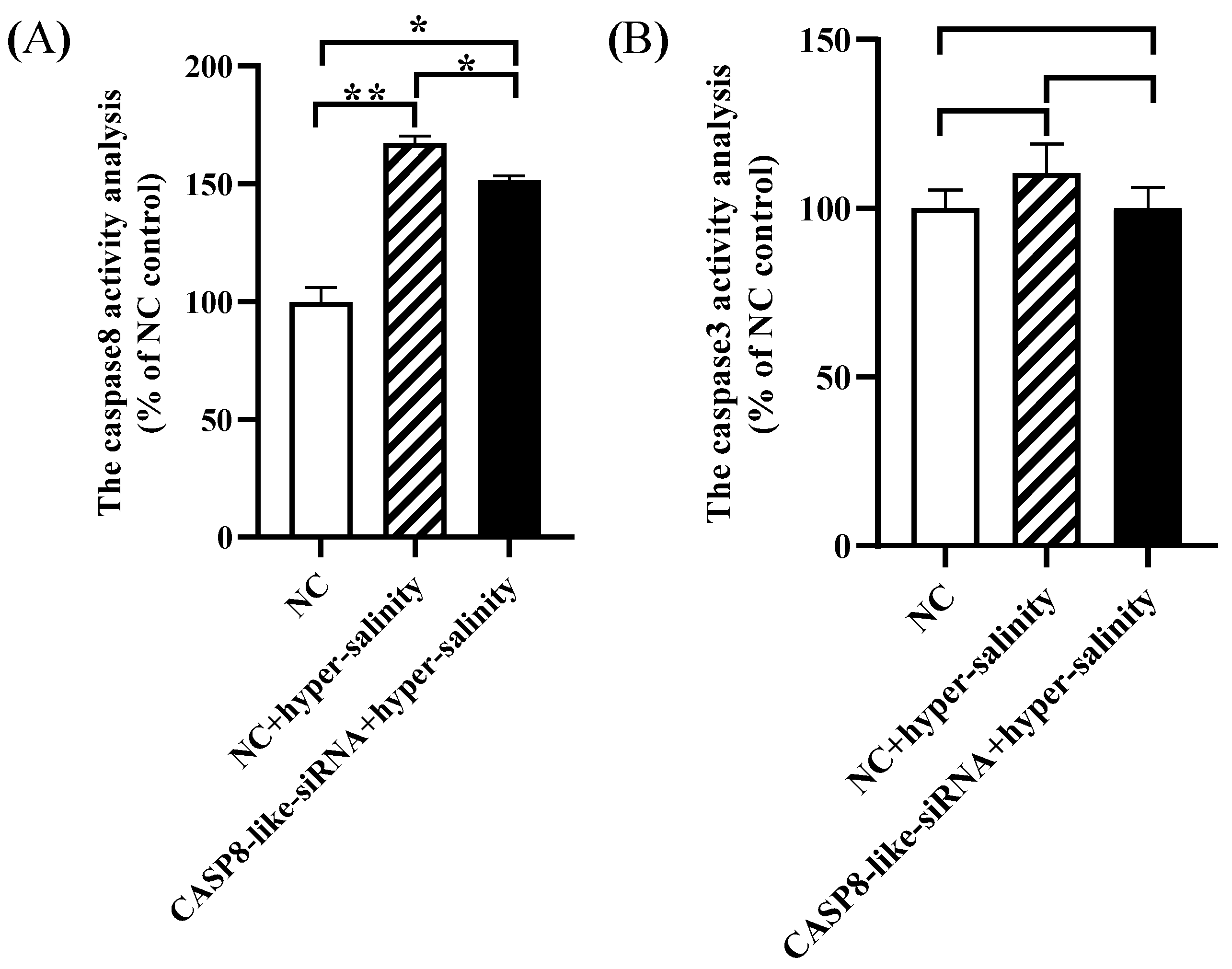
3.5. The Caspase 8 Activity Was Increased by Hyper-Salinity Stress, but Was Inhibited by ChCASP8-like Silence
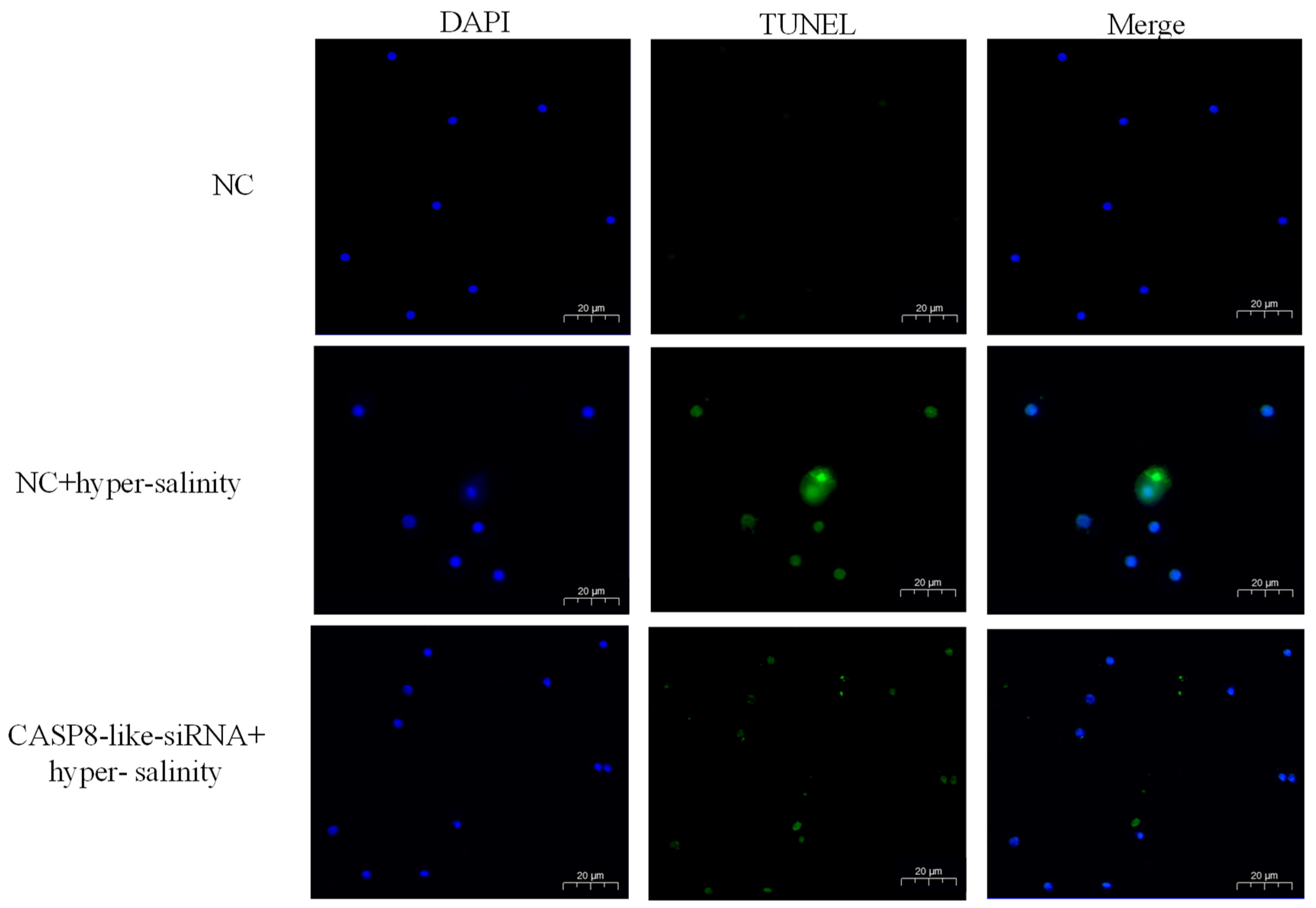
3.6. ChCASP8-like Silencing Alleviated the Apoptosis Resulted from Hyper-Salinity Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holley, M.C. Application of new biological approaches to stimulate sensory repair and protection. Br. Med. Bull. 2002, 63, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raff, M.C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature 1992, 356, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.A.; Gores, G.J. Physiology and pathophysiology of apoptosis in epithelial cells of the liver, pancreas, and intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, G1174–G1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Qu, T.; Huang, B.; Ji, P.; Huang, W.; Que, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, G. Cloning and characterization of a novel caspase-8-like gene in Crassostrea gigas. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2015, 46, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.R.; Llambi, F. Cell Death Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a006080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamaki, K.; Shimizu, K.; Iwata, H.; Imai, K.; Satou, Y.; Funayama, N.; Nozaki, M.; Yajima, M.; Nishimura, O.; Higuchi, M.; et al. The apoptotic initiator caspase-8: Its functional ubiquity and genetic diversity during animal evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 3282–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, T.; Takayasu, M.; Mizuno, M.; Yoshimoto, M.; Yoshida, J. Caspase activation in neuronal and glial apoptosis following spinal cord injury in mice. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2003, 43, 20–29, Discussion 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Qu, F.; Qi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, Y.; Yu, Z. Cloning, characterization and expression analysis of a caspase-8 like gene from the Hong Kong oyster, Crassostrea hongkongensis. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 35, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wei, D.; Pan, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, F. BmCaspase-8-like regulates autophagy by suppressing BmDREDD-mediated cleavage of BmATG6. Insect Sci. 2023, 30, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wong, N.K.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Mo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z. Analysis of in situ Transcriptomes Reveals Divergent Adaptive Response to Hyper- and Hypo-Salinity in the Hong Kong Oyster, Crassostrea hongkongensis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, H.; ElHady, M.; Alcivar-Warren, A.; Allen, S.; Al-Tobasei, R.; Bao, L.; Beck, B.; Blackburn, H.; Bosworth, B.; Buchanan, J.; et al. Aquaculture genomics, genetics and breeding in the United States: Current status, challenges, and priorities for future research. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, K.G.; Bain, L.J.; Baldwin, W.S.; Callard, G.V.; Cohen, S.; Di Giulio, R.T.; Evans, D.H.; Gómez-Chiarri, M.; Hahn, M.E.; Hoover, C.A.; et al. Fundulus as the premier teleost model in environmental biology: Opportunities for new insights using genomics. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2007, 2, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kültz, D. Physiological mechanisms used by fish to cope with salinity stress. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.S.; Chang, A.L.; Deck, A.; Ferner, M.C. Atmospheric rivers and the mass mortality of wild oysters: Insight into an extreme future? Proc. Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20161462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoste, A.; Malham, S.K.; Gélébart, F.; Cueff, A.; Poulet, S.A. Stress-induced immune changes in the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2002, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Pan, Z.; Qu, B.; Yu, X.; Xu, K.; Deng, Y.; Liang, F. Identification of a tyrosinase gene and its functional analysis in melanin synthesis of Pteria penguin. Gene 2018, 656, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Qian, J.; Tu, Z.; Yang, C.; Deng, Y.; Xue, Y.; Shang, Y.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Effects of diel-cycling hypoxia and salinity on lipid metabolism and fatty acid composition of the oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 191, 106124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Li, L.; She, Z.; Huang, B.; Zhang, G. Genome and transcriptome analyses provide insight into the euryhaline adaptation mechanism of Crassostrea gigas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Figueira, E.; Soares, A.; Freitas, R. Salinity influences the biochemical response of Crassostrea angulata to Arsenic. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Yu, F.F.; Zhong, Z.M.; Liang, Q.W.; Pang, H.Y.; Wu, S.Y. Transcriptome analysis reveals the function of TLR4-MyD88 pathway in immune response of Crassostrea hongkongensis against Vibrio Parahemolyticus. Aquacult Rep. 2022, 25, 101253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Lee, H.; Han, M.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, S.O.; Jeong, S.J.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, G.Y.; Park, E.K.; Jeon, Y.J.; et al. Cytoprotective effects of fermented oyster extracts against oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and apoptosis through activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Excli J. 2020, 19, 1102–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrylkova, K.; Kyryachenko, S.; Leid, M.; Kioussi, C. Detection of apoptosis by TUNEL assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 887, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimprich, K.A.; Cortez, D. ATR: An essential regulator of genome integrity. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, R.L.; Zou, L. ATR: A master conductor of cellular responses to DNA replication stress. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, E.A.; Cortez, D. ATR signalling: More than meeting at the fork. Biochem. J. 2011, 436, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummers, B.; Mari, L.; Guy, C.S.; Heckmann, B.L.; Rodriguez, D.A.; Rühl, S.; Moretti, J.; Crawford, J.C.; Fitzgerald, P.; Kanneganti, T.D.; et al. Caspase-8-Dependent Inflammatory Responses Are Controlled by Its Adaptor, FADD, and Necroptosis. Immunity 2020, 52, 994–1006.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brentnall, M.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; De Guevara, R.L.; Cepero, E.; Boise, L.H. Caspase-9, caspase-3 and caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, A.; She, Z.; Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Li, L. Adaptive divergence and underlying mechanisms in response to salinity gradients between two Crassostrea oysters revealed by phenotypic and transcriptomic analyses. Evol. Appl. 2023, 16, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.B.; Ren, H.L.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Xu, D.-D.; Qiao, K.; Wang, K.-J. First molecular cloning of a molluscan caspase from variously colored abalone (Haliotis diversicolor) and gene expression analysis with bacterial challenge. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2010, 28, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, H.W.; Yao, C.L. Molecular and acute temperature stress response characterizations of caspase-8 gene in two mussels, Mytilus coruscus and Mytilus galloprovincialis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 177–178, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.J.; Han, L.H.; Cong, R.S.; Liang, J. Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2005, 37, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbetts, M.D.; Zheng, L.; Lenardo, M.J. The death effector domain protein family: Regulators of cellular homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scatena, R.; Bottoni, P.; Botta, G.; Martorana, G.E.; Giardina, B. The role of mitochondria in pharmacotoxicology: A reevaluation of an old, newly emerging topic. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 293, C12–C21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häcker, G.; Paschen, S.A. Therapeutic targets in the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, K.; Bratton, S.B.; Cohen, G.M. The Apaf-1 apoptosome: A large caspase-activating complex. Biochimie 2002, 84, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, M.E.; Krammer, P.H. The CD95(APO-1/Fas) DISC and beyond. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, A.; O’Connor, L.; Dixit, V.M. Apoptosis signaling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 217–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; He, L.; Fu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, J.; Liu, L.; Zhong, Q. Molecular characterization of caspase-8-like and its expression induced by microcystin-LR in grass carp (Ctenopharygodon idella). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 89, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzayans, R.; Murray, D. Do TUNEL and Other Apoptosis Assays Detect Cell Death in Preclinical Studies? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer | Forward Primer/Reverse Primer (5′–3′) | Application | Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChCASP8-outer-F | CCAGTGGTCCTATGGCGGAAGTGATG | 3′RACE | 667 |
| ChCASP8-inner-F | TGACAATGGGTCTTTCTTCGTTCAATCC | nest-3′RACE | 543 |
| ChCASP8-outer-R | CAGCAACGGAAACAGT | 5′RACE | 606 |
| ChCASP8-inner-R | GTCCAGACAGTCCCACACG | nest-5′RACE | 561 |
| UPM | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT | RACE | |
| NUP | AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT | RACE universal primer | |
| ChCASP8-test-F | TCGTGTGGGACTGTCTGGA | cDNA test | 1689 |
| ChCASP8-test-R | TGCCTAGACCTCGCTTTCAA | cDNA test | |
| ChCASP8-siRNA-F | GCGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGATTCTGCGTCATCTTCA | RNA interference | 469 |
| ChCASP8-siRNA-R | GCGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGACTTCCGTCATCACTTCC | RNA interference | |
| GFP-siRNA-F | GATCACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGATGGTGAGCAAGGGCGAGGA | RNA interference | 717 |
| GFP-siRNA-R | GATCACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTTACTTGTACAGCTCGTCCA | RNA interference | |
| β-actin-F | GTGCTACGTTGCCCTGGACTT | qRT-PCR | 110 |
| β-actin-R | TCGCTCGTTGCCAATGGTGAT | qRT-PCR | |
| ChCASP8-F | AACTGTTTCCGTTGCTGA | qRT-PCR | 89 |
| ChCASP8-R | TACTCGCCGACTTCTTGT | qRT-PCR | |
| ChCASP3-F | AGGCTGGCTGATTATGGG | qRT-PCR | 120 |
| ChCASP3-R | TCGTTTGTGACGGTTTGC | qRT-PCR | |
| ChATR-F | CCTTCCCAACAGACCCAA | qRT-PCR | 130 |
| ChATR-R | TCGCTGCCGTTCATCGTG | qRT-PCR | |
| CASP9-F | CGAGGTGGAAAGGAGAAC | qRT-PCR | 146 |
| CASP9-R | CTGGGTCAGACTGGAAAGA | qRT-PCR | |
| ChCHK1-F | CACACGAAAGGAGTTACCCACAGAG | qRT-PCR | 105 |
| ChCHK1-R | TCGAAACACAGTAGCCAGTCCAAAG | qRT-PCR | |
| ChBCL-XL-F | ACTCGTGGACTCTATCGTGGACTG | qRT-PCR | 99 |
| ChBCL-XL-R | GCAATTCTAAGCGACTCCCATCCC | qRT-PCR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.; Yu, Z.; Leng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Y. Cloning, Characterization and Functional Analysis of Caspase 8-like Gene in Apoptosis of Crassostrea hongkongensis Response to Hyper-Salinity Stress. Fishes 2024, 9, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050172
Lin J, Yu Z, Leng Y, Zhu J, Yu F, Lu Y, Chen J, He W, Zhang Y, Wen Y. Cloning, Characterization and Functional Analysis of Caspase 8-like Gene in Apoptosis of Crassostrea hongkongensis Response to Hyper-Salinity Stress. Fishes. 2024; 9(5):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050172
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jinji, Ziqi Yu, Yang Leng, Jiexiong Zhu, Feifei Yu, Yishan Lu, Jiayu Chen, Wenhao He, Yixin Zhang, and Yaoshen Wen. 2024. "Cloning, Characterization and Functional Analysis of Caspase 8-like Gene in Apoptosis of Crassostrea hongkongensis Response to Hyper-Salinity Stress" Fishes 9, no. 5: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050172
APA StyleLin, J., Yu, Z., Leng, Y., Zhu, J., Yu, F., Lu, Y., Chen, J., He, W., Zhang, Y., & Wen, Y. (2024). Cloning, Characterization and Functional Analysis of Caspase 8-like Gene in Apoptosis of Crassostrea hongkongensis Response to Hyper-Salinity Stress. Fishes, 9(5), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9050172





