Abstract
The Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis, YFP) possesses the ability to detect distance through echolocation signals, and its sonar signal signature is adjusted to detect different targets. In order to understand the vocal characteristics of YFPs in different behavioral states and their differential performance, we recorded the vocal activities of YFPs in captivity during free-swimming, feeding, and nighttime resting and quantified their signal characteristic parameters for statistical analysis and comparison. The results showed that the number of vocalizations of the YFPs in the daytime free-swimming state was lower than that in the feeding and nighttime resting states, and the echolocation signals emitted in these three states showed significant differences in the −10 dB duration, −3 dB bandwidth, −10 dB bandwidth, and root-mean-square (RMS) bandwidth. Analysis of the resolution of the echolocation signals of the YFPs using the ambiguity function indicated that their distance resolution could reach the millimeter level. These results indicate that the echolocation signal characteristics of YFPs present diurnal differences and that they can be adjusted with changes in their detection targets. The results of this study can provide certain scientific references and foundations for the studies of tooth whale behavioral acoustics, and provide relevant scientific guidance for the conservation and management of YFPs.
Keywords:
Yangtze finless porpoise; echolocation signal; behavioral state; diurnal variation; ambiguity function Key Contribution:
In this study, we analyzed and compared the vocalization pattern and echolocation signal characteristics of the Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis) in captivity during free-swimming, feeding, and nighttime resting, as well as the discriminative ability of their echolocation signals, to explore the differences in the changes in the echolocation signals of the YFPs in different behavioral states with a view to providing certain references for acoustic studies of the YFPs’ biological behaviors.
1. Introduction
The Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis, YFP) is a small toothed whale endemic to China. It is distributed in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, as well as Dongting Lake and Poyang Lake. It serves as an important indicator species for the health of the freshwater ecosystem of the Yangtze River and the status of its biodiversity [1]. YFPs were listed as critically endangered (CR) by the Species Survival Commission of the World Conservation Union (IUCN/SSC) in 2013 [2]. With only 1249 of their species remaining in the wild by 2022, their conservation remains important [3]. YFPs have evolved an effective echolocation system to adapt to the freshwater living environment, which mainly allows them to carry out activities necessary for survival such as localization and navigation, inter-individual communication and exchange, prey hunting, and escaping from enemies [4,5,6]. However, a number of human water-related activities generate tremendous noise [7,8], which affect YFPs’ sonar activities to a certain extent and even threaten their survival activities. There is an urgent need to study the echolocation behavior of this group of toothed whales, which are frequently affected by human activities and are in endangered conditions.
In recent years, it has been demonstrated that harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) use different echolocation strategies and biosonar parameters in two different environments for solving an otherwise identical target approach task, thus highlighting that biosonar adjustments are both range- and context-dependent [9]. Fang et al. demonstrated that the echolocation signal parameters of the YFPs differed among the three environments: a captive tank, a netted pen, and field water of the Yangtze River, indicating that the YFPs adapted to their echolocation signals depending on their surroundings [10]. Acoustic monitoring of YFPs in some field waters of the Yangtze River revealed that their nighttime sonar activities were greater than those of daytime, which may be related to their nocturnal foraging [11,12]. It has also been shown that the sonar activity of YFPs may be related to the changes in their surrounding environments [13]. However, little is known about whether YFPs adjust their sonar signal activity in response to behavioral activities or diurnal variations.
In addition, one study used differently spaced objects to allow harbor porpoises to discriminate between detections, and they were found to be able to resolve and discriminate closely spaced targets, suggesting a clutter rejection zone much shorter than their auditory integration time and that such clutter rejection is greatly aided by spatial filtering with their directional biosonar beam [14]. Ambiguity functions for processing radar signals have also been used to study the discriminatory ability of echolocation signals in toothed whales [15]. Studies on the ability to discriminate sonar signals have mainly focused on toothed whales living in the ocean, while studies on the YFPs in this area have not yet been reported.
Studying the echolocation signal activity and characteristics of YFPs in different behavioral states is crucial for understanding their survival strategies. Due to the large spatial extent of the field waters, the turbidity of the water, and the small body size of the YFPs, the implementation of acoustic monitoring and behavioral observations had limitations that were not conducive to the conduct of this study. Therefore, we studied the sonar activity patterns and signal characteristics of the YFPs in different behavioral states in a relatively controlled environment in captivity. This will help to understand the vocalization patterns and changing characteristics of the YFPs and provide a reference basis for the relevant departments to formulate targeted management policies and protection measures for the YFPs based on the patterns and characteristics of their sonar activities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
The experimental research subjects were two male YFPs in the captive breeding base, and the data collection period was from March to April 2023.
2.2. Experimental Procedure
Data acquisition equipment: ① A fixed underwater high-frequency acoustic event recorder (i.e., A-tag, ML200-AS8 Marine Micro Technology, Saitama, Japan) was used for the monitoring of the YFPs vocalization events. Only specific high-frequency acoustic signal events were recorded during operation and were detected at a distance of approximately 300 m [16]. The sensitivity of the hydrophone is close to the main frequency of YFPs vocalization at 120 kHz [17]; electronic bandpass filtering is 55–235 kHz to eliminate underwater noise signals outside the frequency band of YFPs sonar signals; The sampling rate was set to 2 kHz, i.e., the pulse signal was recorded every 0.5 ms [18].
② The underwater eco-acoustic recorder (SoundTrap 300HF, Ocean Instruments Ltd., Auckland, New Zealand) was used to collect the YFPs echolocation signals, with the Sample Rate set to 576 kHz, the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) at 16 bits, and the Preamp gain set to high.
These two types of underwater sound recorders have been widely used in passive acoustic studies of YFPs [19,20,21]. During data collection, one SoundTrap 300HF and one A-tag were placed 1.5 m from the surface of the water in one corner of the rearing tank. Acoustic signal acquisition in this study was carried out uninterruptedly during the observation period, and the accompanying law enforcement recorder was used for recording; audible event acquisition continued uninterruptedly for 24 h. The hydrophones did not affect the daily activities of the YFPs, ensuring that the animals were free to move around and eliminating human interference as much as possible.
Nine days were randomly selected for the study of temporal changes in the number of vocalization events, and the 24 h were roughly divided into three categories based on the state of the YFPs appearing in one hour (e.g., Table 1). Divers would clean and vacuum the rearing pool from 8:00 to 9:00 daily, which was excluded due to the presence of anthropogenic disturbance. The feeding baits were all live Hemiculter leucisculus, and toy balls were provided daily in the captive tank.

Table 1.
Time period (hours) of the YFPs activity in three states.
The echolocation signals of the YFPs were collected under three experimental conditions: the first was the free-swimming condition (i.e., when no one was interfering in the daytime, the two YFPs were in a variety of swimming postures, mostly swimming counterclockwise along the edge of the feeding pool in pairs with uniform swimming speeds.); the second was the feeding condition (i.e., when the feeders were feeding them live fish during the daytime, the two YFPs exhibited more complex behavior, with alternating feeding periods). (We picked up the signals emitted during its detection of live fish.) and the third was the nighttime resting condition (i.e., when no one was interfering at night, the behavior of the two YFPs was mostly accompanied by swimming, and their swimming speed was uniform and slowed down.).
2.3. Data Acquisition and Analytical Processing
① Data analysis of vocal events: The acoustic data collected with the A-tag were exported and converted into a format using the Logger tools (v5.03) software, and the acoustic signal events of the YFPs were extracted from the background noise events using a customized program based on the Igor Pro 7 (WaveMetrics, Lake Oswego, OR, USA) software. Usually, the echolocation signals of YFPs are expressed in the form of pulse sequences, and one pulse sequence emitted will contain five to hundreds of pulses [22], and sound pressure levels vary uniformly, and the inter-click intervals (ICIs) vary between 20 and 70 ms, whereas the changes in the sound pressure levels and ICIs of the underwater noise are irregular, so that the recorded acoustic signal pulse characteristics can be used to determine the vocalization events of YFPs [23]; In addition, the durations of the YFPs pulse sequences are generally less than 130 ms [24]. We screened the YFPs signals according to the above rule.
② Echolocation signal characterization: The data collected using SoundTrap were decompressed into .wav format files and imported into its accompanying analysis software, dBwav 1.3, and the data were calibrated according to the end-to-end sensitivity provided on the official website (http://www.oceaninstruments.co.nz/, accessed on 6 August 2023). According to the high energy distribution of echolocation signals in YFPs, the corresponding audio clips were intercepted against the spectrogram, and the information was exported.
In order to select the echolocation signal as closely as possible to the propagation axis, we referred to some criteria set in previous studies [17,25,26]. The main steps to further selecting and analyzing the dBwav 1.3 intercepted audio clips include: (1) As far as possible, ensure that the audio was selected to be recorded with the animal’s head facing the hydrophone; (2) Echolocation signal sequence sequences were independent signal sequences, excluding the superposition of multiple signal sequences; (3) The single pulse signal with the highest amplitude and typical characteristics of a toothed whale’s waveform was selected, and the part with a clear sinusoidal waveform and smooth envelope structure was intercepted, while the rest of the reverberating structure was eliminated; (4) The intercepted echolocation signals with signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) higher than 5 dB were calculated using a MatLab R2022a customized code for further analysis [27].
Using the above methods, the author selected 300 single-pulse echolocation signals for the YFPs in the three different behavioral states: free-swimming, feeding, and nighttime resting, for a total of 900 echolocation signals. The peak frequency (which is the frequency that corresponds to the energy maximum of the signal spectrum), the −3 dB bandwidth (−3 dB_BW, which is the frequency range bandwidth at 3 dB less than the peak power), and the −10 dB bandwidth (−10 dB_BW, which is the frequency range bandwidth at 10 dB less than the peak power) of the intercepted echolocation signals were manually processed using Praat6211; the centroid frequency (which is the frequency at which the power spectrum is divided into two equal parts), the root-mean-square bandwidth (RMS_BW, which is the spectral standard deviation of the centroid frequency), and −10 dB duration (which is the duration between two points that are −10 dB below the peak of the signal waveform) of the signals were processed using custom MatLab code [28,29]. The bandwidth of the signal can be parameterized using −3 dB_BW and −10 dB_BW as well as RMS_BW [6,28,29]. The parameters of the spectrum setting in Praat were as follows: the visible frequency range was 0~288 kHz, the analysis mode was Fourier, the window function type was Hanning, and the window length was 0.0002 s.
The acoustic parameters of the signals in each state were statistically analyzed using SigmaPlot 14.0, and significant differences were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and the Mann–Whitney U-test. The results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and the data were plotted using SigmaPlot 14.0. For the description of the characteristic distributions of echolocation signal parameters, reference was made to the descriptions of the histogram distributions in previous studies of YFPs [10,17].
Referring to Li et al. [30] and Chen et al. [31], the echolocation signals’ discriminative ability of YFPs was analyzed by custom MatLab code using the ambiguity function. The function describes the time-frequency characteristics of the echolocation signal. It is commonly used for the characterization of sonar signals and is expressed as
where τ is the signal time delay and ξ is the signal Doppler shift.
The results of the ambiguity function’s characterization of the signal are mainly in the form of a 3D ambiguity plot expressing the degree of ambiguity of the neighboring targets and its 2D cross-section at the peak drop to 70.7%, which is called the ambiguity plot. The two jointly reflect the signal’s resolving power for distance (time delay value) and velocity (Doppler shift) of neighboring targets and the detection accuracy of the distance and velocity quantities. The time delay resolving power is the time difference Δτ = 2τ0 between two intersections of the ambiguity plot and the τ-axis, while the frequency shift resolving power is the frequency shift difference Δξ = 2ξ0 between two intersections of the ambiguity map and the ξ-axis. The detection accuracy is then half of the resolving power (i.e., τ0 and ξ0). Therefore, the steeper the 3D ambiguity function plot surface and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the ambiguity plot, the easier it is to discriminate between neighboring targets [32].
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Vocalization Number Characteristics of the YFPs in Three Behavioral States
Screening of the YFPs vocalization events over a 9-day period and counting the percentage of each hour’s vocalization to the 24 h total showed that the YFPs vocalization activity changed at different hours of the day. The number of vocalization events of the YFPs in a 24 h period showed significant peaks in five periods: 12:00–13:00, 16:00–17:00, 19:00–20:00, 21:00–22:00, and 0:00–1:00, indicating strong vocalization activities (see Figure 1). Excluding the condition of special human interference (suction by divers from 8:00 to 9:00 a.m.), the three states show that the average proportion of vocalizations per hour in the 24 h total was lower during the daytime free swimming period (3.60%) than during feeding (5.09%) and the nighttime resting period (4.20%), and was highest during the feeding state (see Figure 2).
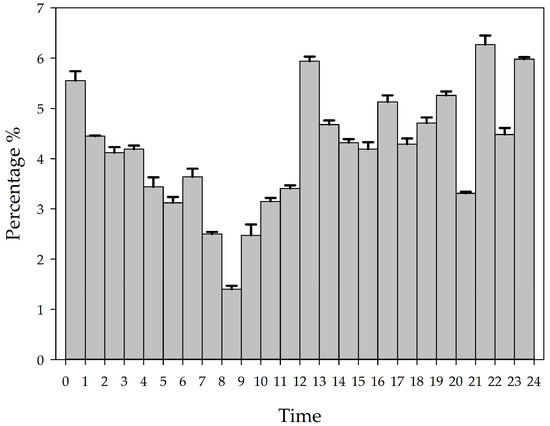
Figure 1.
Temporal characteristics of the intensity of vocalization events of the YFPs.
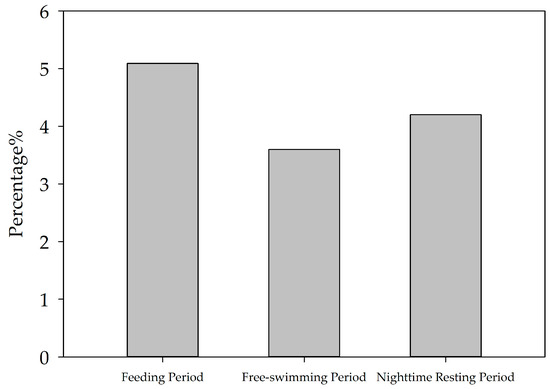
Figure 2.
Intensity characteristics of vocalization events in three states of the YFPs.
3.2. Comparison of Echolocation Signal Parameters of the YFPs under Three Behavioral States
The acoustic parameters such as peak frequency, centroid frequency, signal bandwidth, and −10 dB duration of the echolocation signals under the three states were quantified and counted, and the parameters of the three groups were compared and analyzed using one-way ANOVA and then analyzed using the Mann–Whitney U-test for the differences among the groups. The acoustic parameters of the echolocation signals of the YFPs showed variability in the signal bandwidths (−3 dB_BW, −10 dB_BW, and RMS_BW) and the −10 dB duration under the three behavioral states, and the results of their one-way ANOVA are shown in Table 2. The mean, standard deviation, and variability of the echolocation signal parameters for each activity state are listed in Table 3, and the distribution is shown in Figure 3. The peak frequency of the echolocation signals was predominantly distributed at 125–135 kHz in all three states of free-swimming, feeding, and nighttime resting, accounting for 67%, 65%, and 66.67%, respectively. In the distribution of the −10 dB duration, two peaks of 30–40 µs and 50–60 µs were observed in the signal distribution during both the free-swimming and nighttime resting conditions, which accounted for 21%, 19.67%, 24.33%, and 23%, respectively, while the echolocation signals of the YFPs during feeding were mainly distributed in the range of 60–70 µs. In the distribution of −3 dB_BW, a peak of 15–25 kHz was observed in the signal distribution during the nighttime resting condition, while a peak of 10–20 kHz was observed in the signal distribution during the free-swimming and feeding states, which was 57.66% in the free-swimming state and 65.33% in the feeding state. The RMS_BW of the echolocation signals in the three states of free-swimming, feeding, and nighttime resting were mainly distributed in the range of 10–20 kHz, which accounted for 32%, 44%, and 38.33%, respectively. The distribution of the echolocation signals during feeding was higher in the number of low bandwidth values compared to the other two states and lower in the number of low −10 dB durations than the other two states.

Table 2.
One Way ANOVA results of acoustic parameters of echolocation signals of the YFPs in three states.

Table 3.
Calculated echolocation signal characteristics of the YFPs in three states.
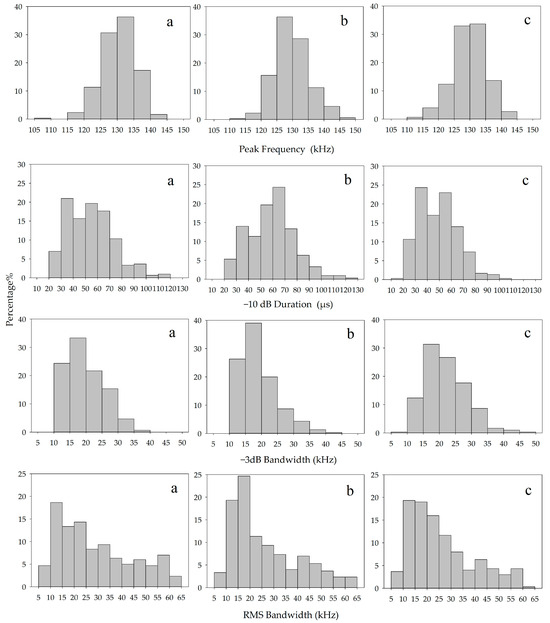
Figure 3.
Histograms of echolocation signal characteristics of the YFPs (Free-swimming (a); Feeding (b); Nighttime Resting (c)).
3.3. Echolocation Signal Resolution of the YFPs
To describe the discriminative ability of YFP echolocation signals, a typical sequence of the YFPs echolocation signals (see Figure 4a) was selected, for which Figure 4b shows the time frequency characteristic map. The single-pulse signal with the largest amplitude (see Figure 4c) was intercepted and analyzed. The 3D ambiguity function plot and ambiguity plot of the echolocation signal of the YFPs are shown in Figure 5, and the peak in the 3D ambiguity plot is obvious. From the actual data of the ambiguity plot (see Figure 5b), it can be seen that the time-delay measurement accuracy τ0 of the YFP sonar signal was about 0.569 μs, the distance resolution ability of the signal to the target was ρ = c·τ0, and the speed of sound in the Yangtze River was 1465.93 m·s−1 (water temperature of 15 °C, water depth of 5 m); thus, ρ = 0.834 mm. Notably, the distance resolution was still quite high. The time-delay accuracy measurements of the YFP echolocation signal sequence (see Figure 4a) show that the time-delay accuracy of the individual echolocation signals varied between 0.5 and 0.9 μs (see Figure 6). Figure 7 shows the 3D ambiguity function plots and ambiguity plots of typical echolocation signals for the three behavioral states, and the results show that they reached the millimeter level in all three states.
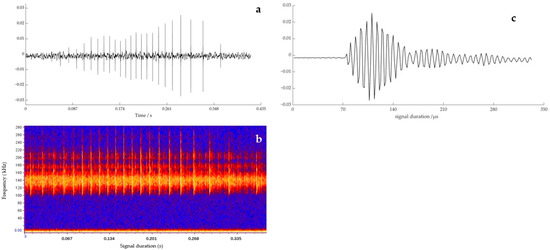
Figure 4.
Characteristics of the echolocation signal sequence of the YFP (Waveform diagram (a); Time frequency characteristic (b); Single pulse waveform (c)).
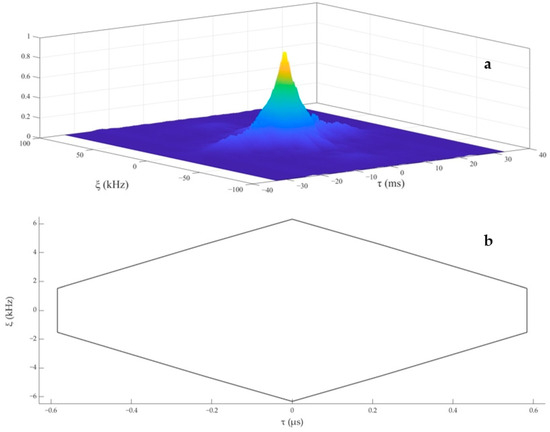
Figure 5.
The 3D ambiguity function plot (a) and ambiguity plot (b) of a single echolocation signal of the YFP.
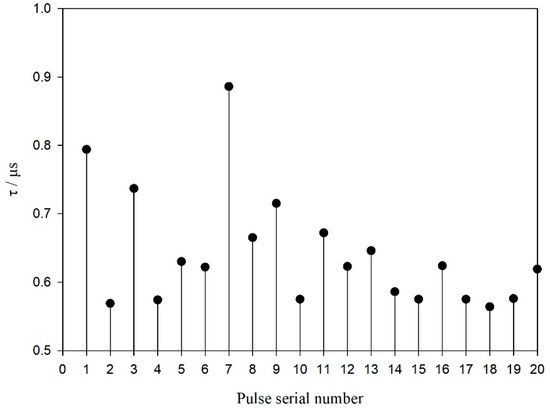
Figure 6.
Variation in time delay measurement accuracy of the echolocation signal sequence of the YFP.
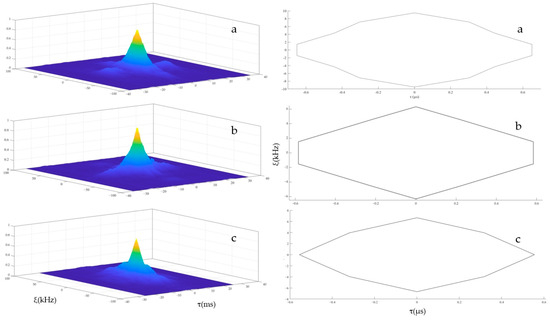
Figure 7.
The 3D ambiguity function plots and ambiguity plots of individual echolocation signals of the YFPs (Free-swimming (a), Feeding (b), Nighttime Resting (c)).
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the Diurnal Variation Pattern of the Number of Vocalization Events of the YFPs
In this study, the 9-day monitoring results of the vocalization events of the YFPs showed that there were diurnal variations in their vocal activity, with five peak time periods (12:00–13:00, 16:00–17:00, 19:00–20:00, 21:00–22:00, and 0:00–1:00) corresponding to the five feeding periods. The YFPs emitted echolocation signals significantly more frequently during feeding than in the free-swimming condition, a phenomenon that has also been observed in studies of toothed whales such as beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas) [33], and bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) [34]. This may be related to the fact that YFPs emit predatory signals during feeding, especially buzz signals when catching prey [20], leading to a significant increase in pulse signals; it is also possible that the presence of live bait during feeding caused the YFPs to increase the frequency of emitting echolocation signals. In their study on the factors influencing the frequency of vocalizations of YFPs, Serres et al. found that the YFPs emitted the highest number of echolocation signals under the condition of the presence of live fish [13].
The results of this experiment showed that the average number of vocalization events per hour during nighttime resting accounted for a higher percentage than during the daytime in the free-swimming condition and that four periods of higher vocalization existed at night, mainly at 18:00–19:00, 23:00–24:00, 1:00–2:00, and 3:00–4:00. In studies of YFPs in the field, it has also been found that more vocalization activities of YFPs were monitored at night [8,11,12,20], and it is believed that such phenomena are related to the tendency of YFPs to prefer nocturnal foraging activities. However, the nighttime feeding period was eliminated from this study, no food was provided, and the animals spent most of their time in an undisturbed resting state. Regarding the reasons for the high percentage of average hourly vocalizations during nighttime resting, the authors believe that first, the animal may have been in the clear water body of the captive tank and, so, some visual aids were present for observation, which could reduce vocal activities. Second, it is possible that the vocal behaviors were increased prior to the nighttime resting for the purpose of communicating with their companions, promoting the synchronization of slow swimming and detection of the surrounding environment. Cetacean sleep is characterized by single-hemisphere slow-wave sleep, and the sleep cycle is around 1 h, which explains the results in the present study of nocturnal resting with periods of higher vocalizations and their intervals of around 1–2 h [35]. A similar phenomenon has been seen in studies of bottlenose dolphin vocalizations, where bottlenose dolphins increase vocal interactions before resting to ensure synchrony in slow swimming [36,37].
The YFP is a highly social animal that requires vocal behavior in order to perform functions such as socialization, orientation, and the transmission of information. The number of vocal events of YFPs changes under different behavioral states, which reflects their physiological and psychological states in different contexts [13,38]. The frequency of vocalizations of YFPs shows seasonal variations due to breeding activities, which may be attributed to their need to use their voices to attract the opposite sex and establish pair bonding [13,39]. Toothed whales also vocalize differently to provide feedback in the face of negative external noise threat stimuli [13]. In this study, the YFPs increased their vocal behavior during their feeding and nocturnal resting periods. This provides a number of references for the formulation of conservation policies. For example, strategies such as controlling the speed of vessels or even temporarily restricting travel are implemented in the waters where porpoises frequently feed in the wild, as well as during preferred foraging hours or night resting hours, in order to reduce the impacts of anthropogenic water-related activities. However, only a sample size of nine days from March to April was selected for the study, not covering the four seasons of the year. Therefore, selecting a sample size with a larger seasonal span and a larger number of days to carry out further studies will help to comprehensively understand the sonar activity patterns of the YFPs and facilitate scientific management in a captive environment.
4.2. Analysis of Echolocation Signals Characterization of the YFPs in Three Behavioral States
The YFPs’ echolocation signals showed significant differences in the −10 dB duration, −3 dB_BW, −10 dB_BW, and RMS_BW values during the free-swimming, feeding, and nighttime resting conditions. The bandwidth averages (−3 dB_BW, −10 dB_BW, and RMS_BW) for the echolocation signals of the YFPs in the feeding state were lower than those in the free-swimming state, while the −10 dB duration averages of the signals were higher than the other two states. The author suggests that the reason for these differences may be the inconsistency in the detection targets required for the YFPs in the three behavioral states. The live bait targets that need to be detected in the feeding state are more finely tuned and variable in location than the surroundings that need to be detected during free swimming and nighttime resting. Studies have shown that the characteristics of the echolocation signals of toothed whales can be adjusted according to their detection target range. A reduction in the signal bandwidth facilitates the animal to extract the signal from the noise and improve the SNR, while an increase in the signal duration enhances the energy of the detected signal without increasing the signal amplitude [40]. The YFPs actively emit echolocation signals with low bandwidth and high duration during feeding to adjust the SNR and energy of the signals to improve their detection accuracy.
The echolocation signal characteristics of the YFPs in this study showed differences between the nighttime resting and the free-swimming state during the daytime, with an overall high bandwidth and low mean duration of their nighttime signals, which reduced the energy of the detected signal [40]. In their research on melon-headed whales (Peponocephala electra), foreign scholars have found that their echolocation signals were adjusted according to day and night, possibly to adapt to changes in ambient noise or to enhance the detection of targets [41]. However, no investigation of diurnal ambient background noise was conducted in this study in order to confirm whether this was related to their adaptation to changes. The author suggests that the differences in the signal characteristics of this type of YFPs may have arisen as an adaptation to the behavioral pattern of resting and socializing at night.
In their research on the vocalization and behavior of toothed whales, Wei et al. studied the characteristics of communication signals (low-frequency signals) of bottlenose dolphins in a free-swimming state and a training state and found that there was a significant change in the proportion of communication signal categories (low-frequency signals) of bottlenose dolphins in the two behavioral states; furthermore, there was a variability in the acoustic parameters of the signals, indicating that there was an inevitable connection between their vocalization and behavior [42]. We provided further evidence that toothed whale vocalizations are tuned to behavioral traits in terms of high-frequency signals. However, in this study, only one single hydrophone was used for acoustic signal acquisition, and despite the author’s rigorous signal selection, it was still impossible to avoid recording signals that deviate from the propagation axis, which may bias the results to some extent. Thus, further studies of signals from porpoises in different behavioral states using a range of receivers (e.g., hydrophone arrays) will help to increase the understanding of the acoustics of porpoise behavior and provide more insight into the use of sonar signals.
4.3. Analysis of Echolocation Signal Resolution of the YFPs
In the study of YFPs echolocation system for target detection, scholars have found that YFPs perform echolocation vocalizations once every 5.1 s on average, and their detection distance was projected based on the vocalization interval, which showed that 90% of the acoustic detection distances are less than 77 m [16]. However, the resolving power of the echolocation signals of YFPs has not been investigated. We analyzed their resolving power and detection accuracy in terms of the time domain, frequency domain, time frequency analysis, and ambiguity function.
In this study, the echolocation signals of the YFPs in all three behavioral states indicated strong anti-reverberation ability and high distance resolution. Compared to the results of Li et al. on bottlenose dolphins, beluga whales, and sperm whales (Pseudorca crassidens) in captivity, the distance discrimination of YFPs is at the same level as that of these three toothed whales [30]. Chen et al. conducted a study on the bionic bottlenose dolphin echolocation signal, and the results showed that the length of the bottlenose dolphin echolocation signal in the natural environment is shorter, which improves its speed discrimination. In an artificial breeding environment, for the bottlenose dolphin echolocation signal, the peak frequency was lower, the bandwidth was narrower, and the side flap of the 3D ambiguity function was smaller, which is beneficial for anti-reverberation and distance discrimination [31]. The YFPs constantly changed the characteristics of each pulsed signal during signaling vocalizations, as in the case of bottlenose dolphins and sperm whales [30]. Qing studied and analyzed the echolocation signal sequence strings of beluga whales and bottlenose dolphins, and the results proved that they may achieve target-optimized detection and identification through transmitting pulse strings with different types of energy distribution [43]. This also indicates that YFPs can achieve optimal detection and identification of a target by continuously changing the echolocation signal characteristics during target detection.
YFPs are often found in shallow water depths and are therefore subject to a great deal of unwanted echo interference. However, porpoises can still become entangled or drown in nets that their biosonar is capable of detecting [44], and we understand that the YFPs are also threatened in this way. The distance discrimination of the YFPs in this study demonstrated that their echolocation signals were able to discriminate nets, which is consistent with the results of other toothed whale net detection experiments [45]. When a task is difficult and attention-demanding, foraging performance can be constrained, and the detection of threats may be hindered [46]. The YFPs are similarly less alert to threatening objects, such as nets, when performing focused detection tasks. Although a ten-year fishing ban has been fully implemented in the Yangtze River since 2021, the remaining pollution, such as discarded fishing nets, still exists. It is extremely important to manage the ecological environment of the YFPs’ frequented waters and cultivate the public’s awareness.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we analyzed the vocalization patterns and signal characteristics of YFPs during free swimming, feeding, and nighttime resting, and gained a more in-depth understanding of their habits, such as active time, resting time, and feeding habits, which will enhance the accuracy of the field acoustic monitoring results and contribute to the monitoring and protection of the wild populations. This will provide relevant scientific guidance for the development of protection measures for YFPs, which will better manage anthropogenic water-related activities and effectively protect YFPs from threats. As a next step, the behavioral acoustic characteristics of YFPs in different habitats should be studied in depth over a longer time span using hydrophone arrays to investigate the relationship between their vocalizations and behavioral status in different habitats, as well as the effects of diurnal variations in the seasons on their sonar activities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L. (Danqing Lin) and K.L.; Data curation, J.C., H.L. and J.Z.; Data analysis, J.C., W.L. and H.L.; Funding acquisition, D.L. (Danqing Lin) and K.L.; Investigation, J.C.; Methodology, J.C. and D.L. (Danqing Lin); Project administration, K.L.; Resources, D.L. (Danqing Lin) and K.L.; Software, J.C., K.Y. and D.L. (Dong Li); Supervision, K.L.; Validation, D.L. (Danqing Lin), D.L. (Dong Li) and K.L.; Writing—original draft, J.C.; Writing—review and editing, D.L. (Danqing Lin) and K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was financed by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (NO. 2023TD11); Protection of the Yangtze Finless Porpoise; and Publicizing Science (17230149).
Institutional Review Board Statement
We strictly followed the national regulations and policies for animal protection in China. The medical examinations and related experiments conducted were approved by competent authorities of the Department of Resource Environmental Protection, Yangtze River Basin Fisheries Regulation and Management Office, Ministry of Agriculture. Which reviewed and approved the procedures for animal observation and passive acoustic monitoring (2017 [185] and 2018 [183]).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhou, X.; Guang, X.; Sun, D.; Xu, S.; Yang, G. Population genomics of finless porpoises reveal an incipient cetacean species adapted to freshwater. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Turvey, S.; Zhao, X.; Mei, Z. Neophocaena asiaeorientalis ssp. asiaeorientalis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; Version 3.1; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland; Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.J.; Yu, W.J. The Yangtze finless porpoise population has rebounded to 1249. Xinhua Daily Telegraph, 1 March 2023; p. 006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.X.; Wang, D. Characteristics and Functions of Sound of the Yangtze Finless Porpolse (Neophocaena phocaenoides) in Captivity. Tech. Acoust. 1999, 18, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. A preliminary study on sound and acoustic behavior of the Yangtze Finless Porpoise, Neophocaena Phocaenoides. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1996, 20, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Busnel, R. (Ed.) Animal Sonar Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.C.; Ju, T.; Li, S.H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.T.; Wang, K.X. Navigation noise property of large vessels in Hechangzhou region of the Yangtze River and its potential effects on the Yangtze finless porpoise. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2018, 38, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, P.X.; Wang, Z.T.; Akamatsu, T.; Tregenza, N.; Li, G.Y.; Wang, K.X.; Wang, D. Anthropogenic activity, hydrological regime, and light level jointly influence temporal patterns in biosonar activity of the Yangtze finless porpoise at the junction of the Yangtze River and Poyang Lake, China. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, L.; Peter, T.M. Context-dependent biosonar adjustments during active target approaches in echolocating harbour porpoises. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb206169. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Pine, M.K.; Wang, K.X.; Li, S.H. The source parameters of echolocation clicks from captive and free-ranging Yangtze finless porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Akamatsu, T.; Wang, K.; Wang, D. The diel rhythms of biosonar behavior in the Yangtze Finless Porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis) in the port of the Yangtze River: The correlation between prey availability and boat traffic. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yu, D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Z. Seasonal and diel activities of the Yangtze finless porpoise in natural and highly disturbed habitats: Implications for conservation planning of freshwater cetaceans. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2022, 32, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serres, A.; Xu, C.; Hao, Y.G.; Wang, D. The click production of captive Yangtze Finless Porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaorientalis) is influenced by social and environmental factors. Animals 2021, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chloe, E.M.; Laia, R.-D.; Peter, T.M. Directional biosonar beams allow echolocating harbour porpoises to actively discriminate and intercept closely-spaced targets. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb242779. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, C.W.; Bates, R.H.; Dawson, S.M. Intrinsic echolocation capability of Hector’s dolphin, Cephalorhynchus hectori. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 90, 2931–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, T.; Wang, D.; Wang, K.; Li, S.; Dong, S.; Zhao, X.; Barlow, J.; Stewart, B.S.; Richlen, M. Estimation of the detection probability for Yangtze finless porpoises (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis) with a passive acoustic method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 4403–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Wang, K.X.; Wang, D.; Akamatsu, T. Echolocation signals of the free-ranging Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientialis). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 3288–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Wang, D.; Wang, K.X.; Taylor, E.A.; Cros, E.; Shi, W.J.; Wang, Z.T.; Fang, L.; Chen, Y.F.; Kong, F.M. Evoked-potential audiogram of an Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin (Sousa chinensis). J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215 Pt 17, 3055–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Akamatsu, T.; Dong, L.; Wang, K.; Wang, D.; Kimura, S. Widespread passive acoustic detection of Yangtze finless porpoise using miniature stereo acoustic data-loggers: A review. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Akamatsu, T.; Mei, Z.; Dong, L.; Imaizumi, T.; Wang, K.; Wang, D. Frequent and prolonged nocturnal occupation of port areas by Yangtze finless porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis): Forced choice for feeding? Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, P.; Xia, D.J.; Li, Z.H.; Wu, Z.; Yu, D.P.; Chen, M.M. Study on the utilization pattern of island-type habitat patches by Yangtze finless porpoise and analysis of potential factors. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2023, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki-Yamamoto, Y.; Akamatsu, T.; Ura, T.; Sugimatsu, H.; Kojima, J.; Bahl, R.; Behera, S.; Kohshima, S. Diel changes in the movement patterns of Ganges River dolphins monitored using stationed stereo acoustic data loggers. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2013, 29, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, T.; Wang, D.; Wang, K.X.; Naito, Y. Biosonar behaviour of free-ranging porpoises. Proc. R. Soc. B 2005, 272, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, T.; Teilmann, J.; Miller, L.A.; Tougaard, J.; Dietz, R.; Wang, D.; Siebert, U.; Naito, Y. Comparison of echolocation behaviour between coastal and riverine porpoises. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.; Würsig, B. Echolocation signals of dusky dolphins (Lagenorhynchus obscurus) in Kaikoura, New Zealand. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 115, 2307–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Shi, W.; Wang, D. Echolocation signals of free-ranging Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) in Sanniang Bay, China. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; XU, X.H.; Song, Z.Z.; Yang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of echolocation from Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin (Sousa chinensis) and finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis sunmeri). Acta Acust. 2021, 46, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, P.T.; Carder, D.A.; Bedholm, K.; Ridgway, S.H. Porpoise clicks from a sperm whale nose—Convergent evolution of 130 kHz pulses in toothed whale sonars? Bioacoustics 2005, 15, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.T.; Wahlberg, M. Recording and quantification of ultrasonic echolocation clicks from free-ranging toothed whales. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2007, 54, 1421–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, D.Z.; Lin, J.H.; Chi, J. Analyses of click signal characteristics of captive bottlenose dolphins, beluga whales and false killer whales. Tech. Acoust. 2019, 38, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Niu, F.Q.; Lin, C.L.; Liu, W. Click signal of bottlenose dolphin and its simulation analysis under different environments. Tech. Acoust. 2019, 38, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, T. Sonar Technology, 2nd ed.; Harbin Engineering University Press: Harbin, China, 2010; pp. 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fish, M.P.; Mowbray, W.H. Production of underwater sound by the white whale or beluga, Delphinapterus leucas (Pallas). J. Mar. Res. 1962, 20, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.Q.; Yang, Y.M.; Wen, H.T.; Liu, Z.W. Vocalization and signal characteristic of bottlenose dolphin. Tech. Acoust. 2011, 30, 148–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lyamin, O.I.; Manger, P.R.; Ridgway, S.H.; Mukhametov, L.M.; Siegel, J.M. Cetacean sleep: An unusual form of mammalian sleep. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 1451–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremers, D.; Jaramillo, M.B.; Böye, M.; Lemasson, A.; Hausberger, M. Nocturnal vocal activity in captive bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus): Could dolphins have presleep choruses? Anim. Behav. Cogn. 2014, 1, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Therrien, S.C.; Thomas, J.A.; Therrien, R.E.; Stacey, R. Time of Day and Social Change Affect Underwater Sound Production by Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) at the Brookfield Zoo. Aquat. Mamm. 2012, 38, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serres, A.; Hao, Y.G.; Wang, D. Swimming features in captive odontocetes: Indicative of animals’ emotional state? Behav. Process. 2020, 170, 103998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, K.X.; Chen, D.Q.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Wang, X. Observation on some sexual behavior of the Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaerientals) in captivity. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2004, 24, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Morisaka, T.; Karczmarski, L.; Akamatsu, T.; Sakai, M.; Dawson, S.; Thornton, M. Echolocation signals of Heaviside’s dolphins (Cephalorhynchus heavisidii). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; Roch, M.A.; Wiggins, S.M.; Schnitzler, H.U.; Hildebrand, J.A. Acoustic behavior of melon-headed whales varies on a diel cycle. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2015, 69, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Xu, X.M.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, F.Q. Comparison study on whistle characteristics of captive bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops turncatus) during swimming and under training. Acta Acust. 2014, 39, 452–458. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qing, X. Research on the Mechanisms of Biosonar Operation in the Representative Hunting Behaviour of Cetaceans; Harbin Engineering University: Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Read, A.J.; Drinker, P.; Northridge, S. Bycatch of marine mammals in U.S. and global fisheries. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastelein, R.A.; Au, W.W.L.; de Haan, D. Detection distances of bottom-set gillnets by harbour porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) and bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Mar. Environ. Res. 2000, 49, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukas, R.; Kamil, A.C. The cost of limited attention in blue jays. Behav. Ecol. 2000, 11, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).