Farmed Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi) Coinfected with Parasites and Oomycete Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diseased Fish
2.2. Parasite and Pathogen Collection
2.3. Oomycete Isolation and Purification
2.4. Histopathology
2.5. DNA Extraction and Viral Detction
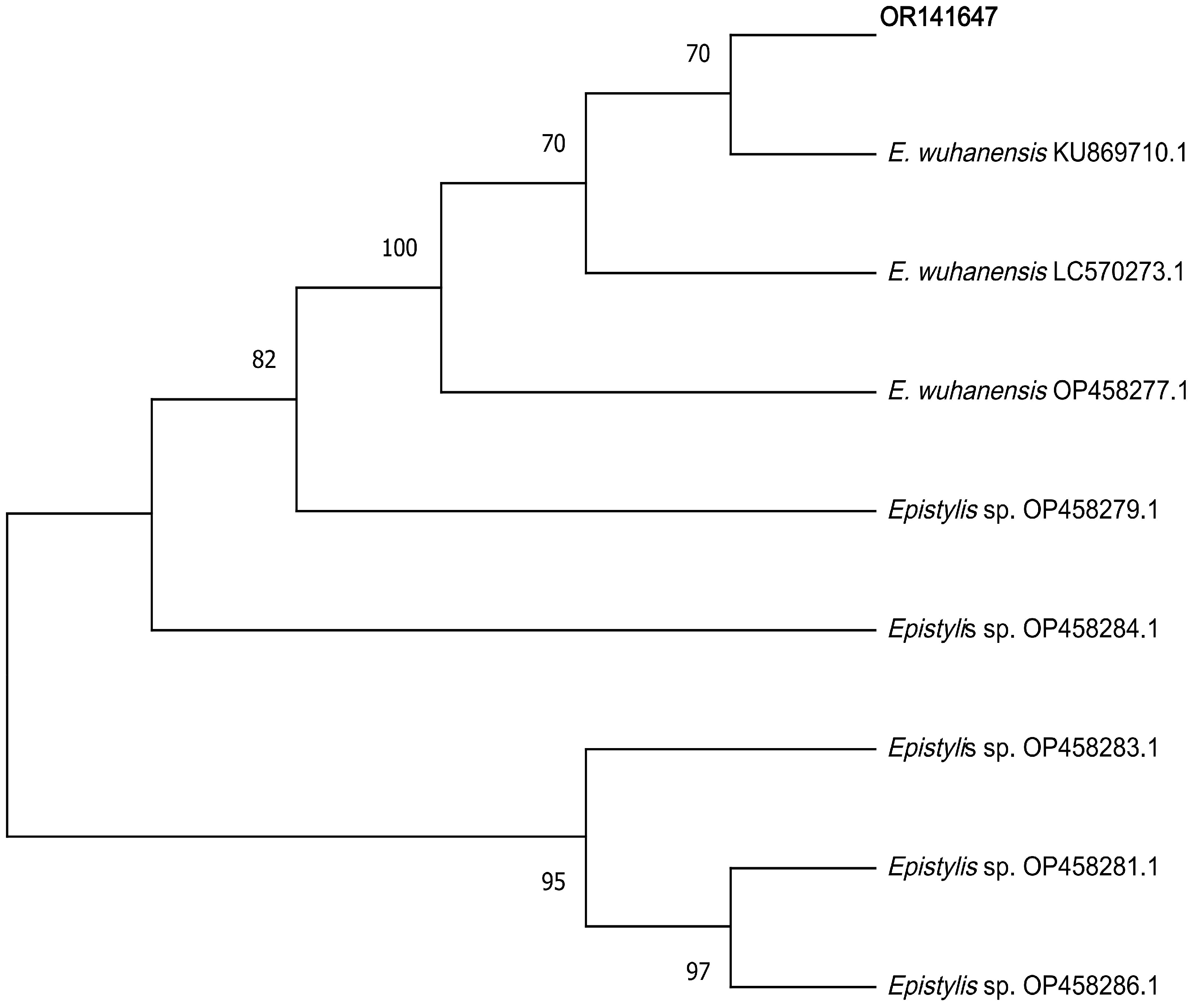
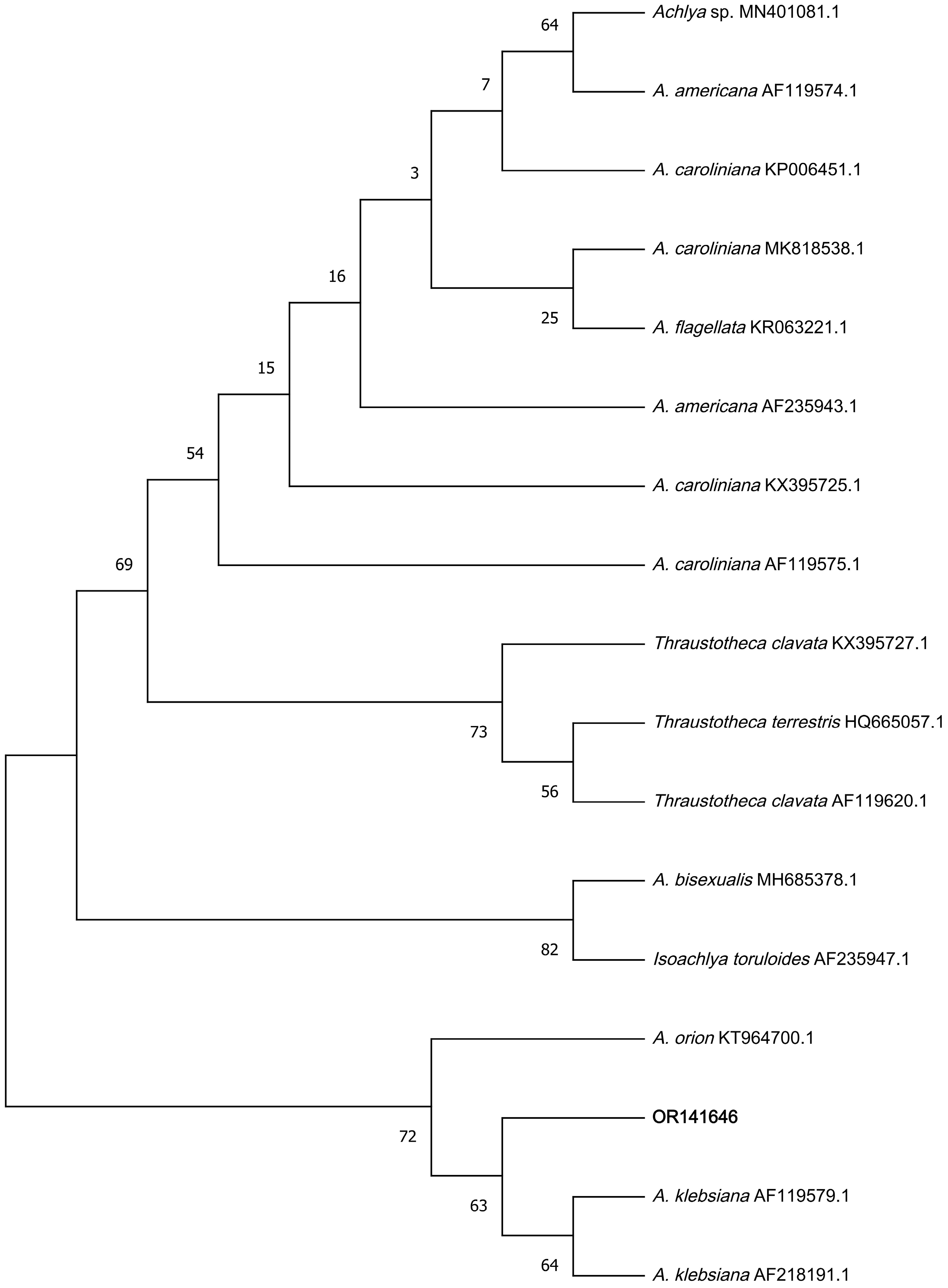
2.6. Cluster Analysis
3. Results
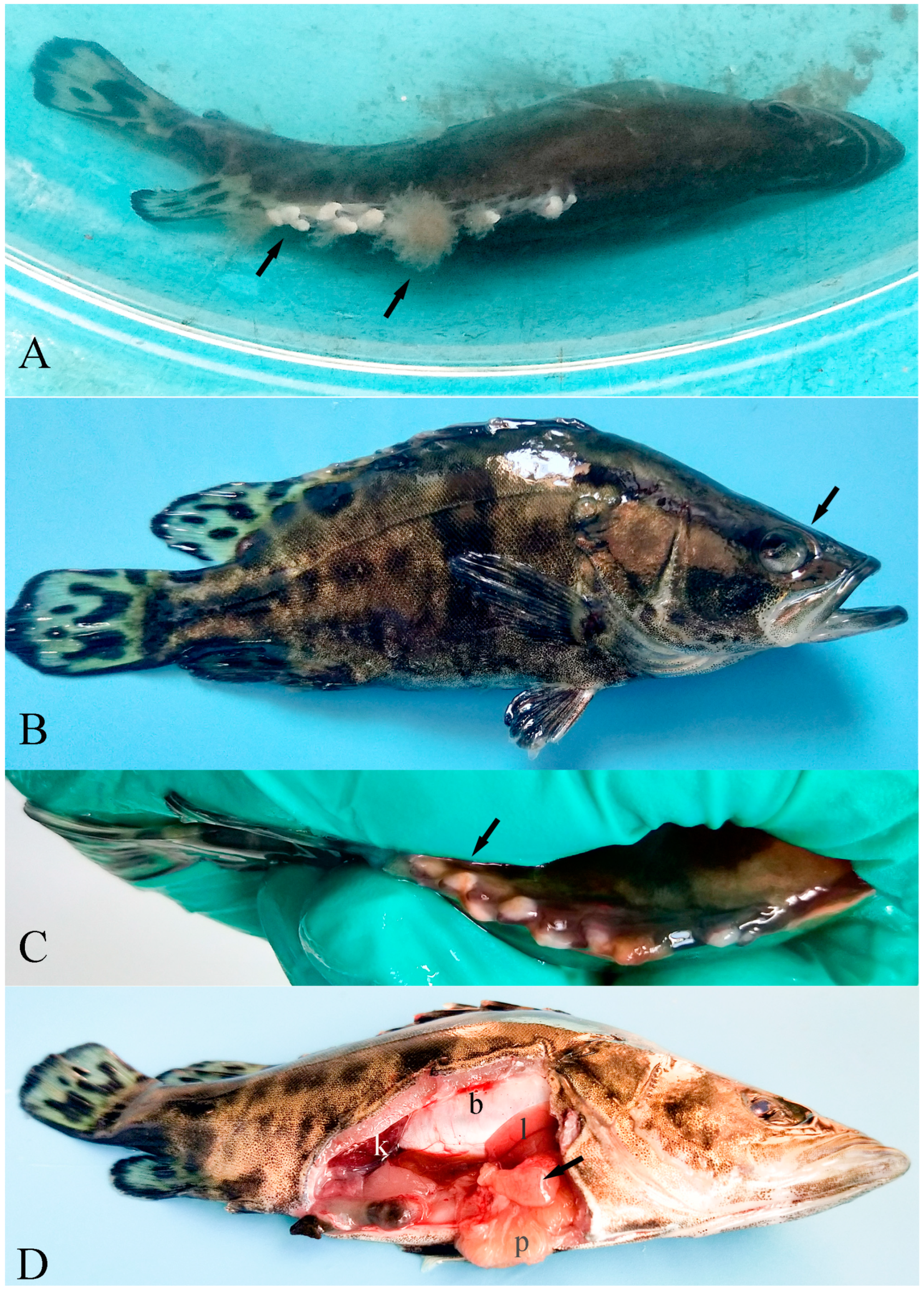
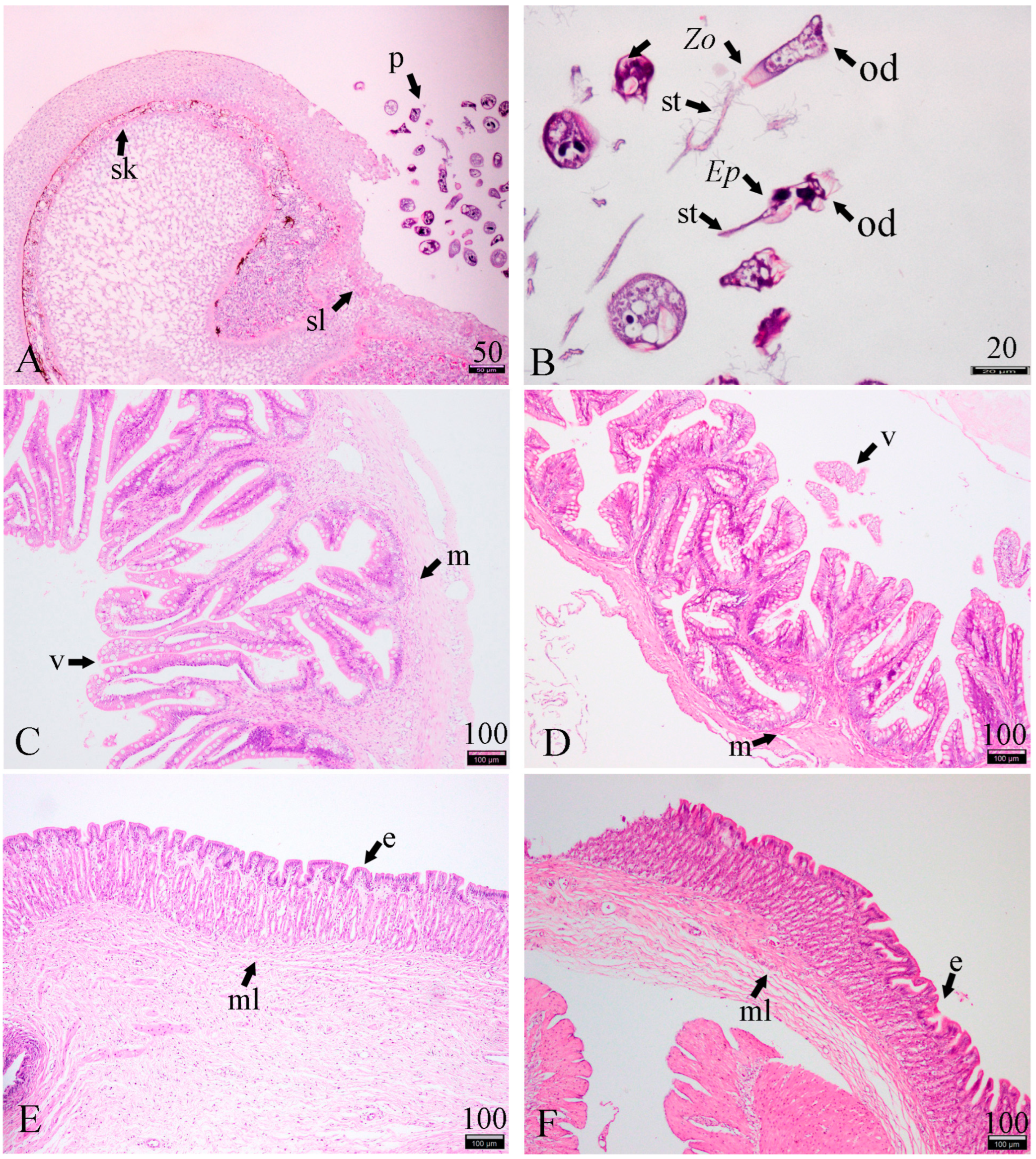
3.1. Clinical Signs of Diseased Fish
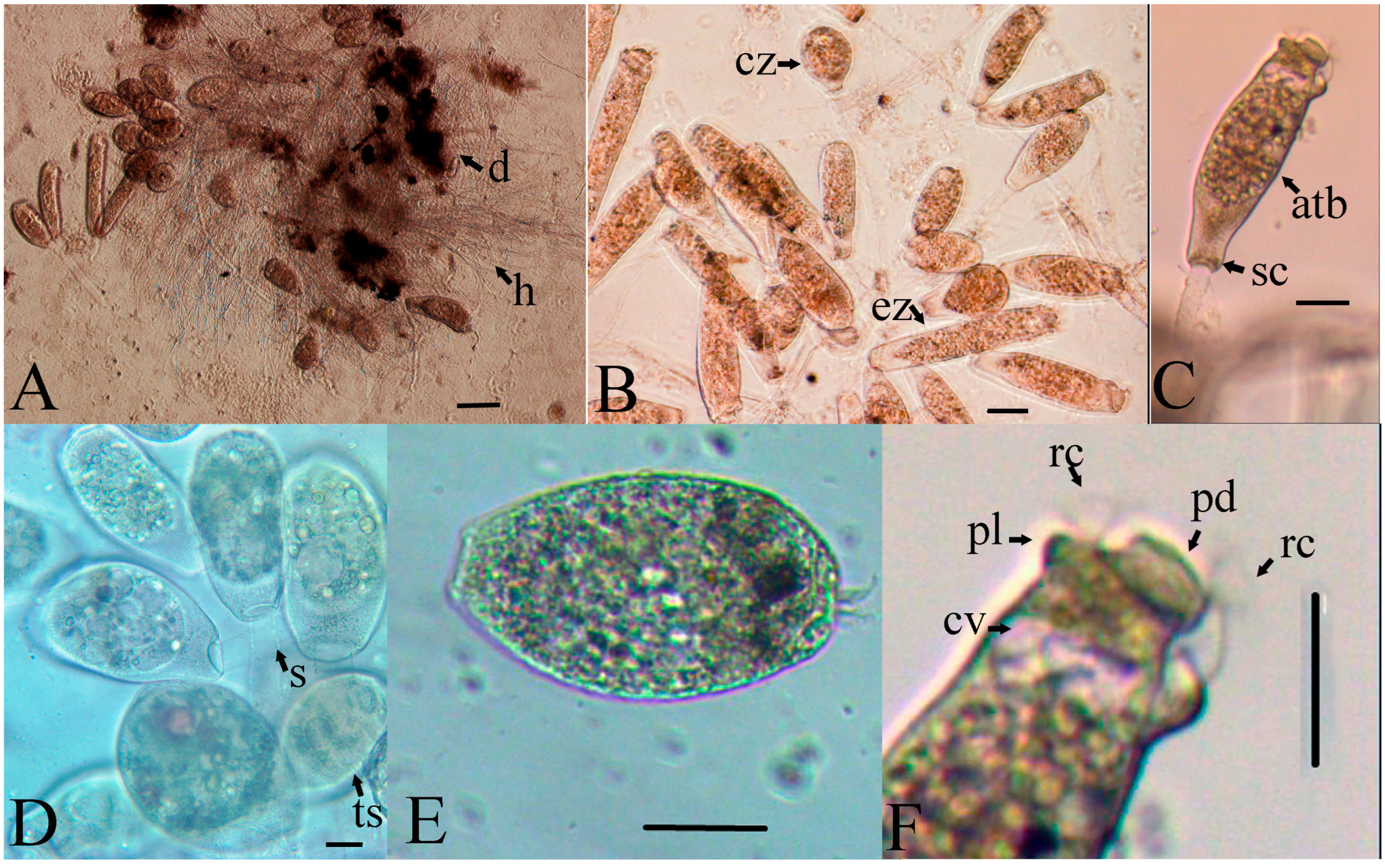
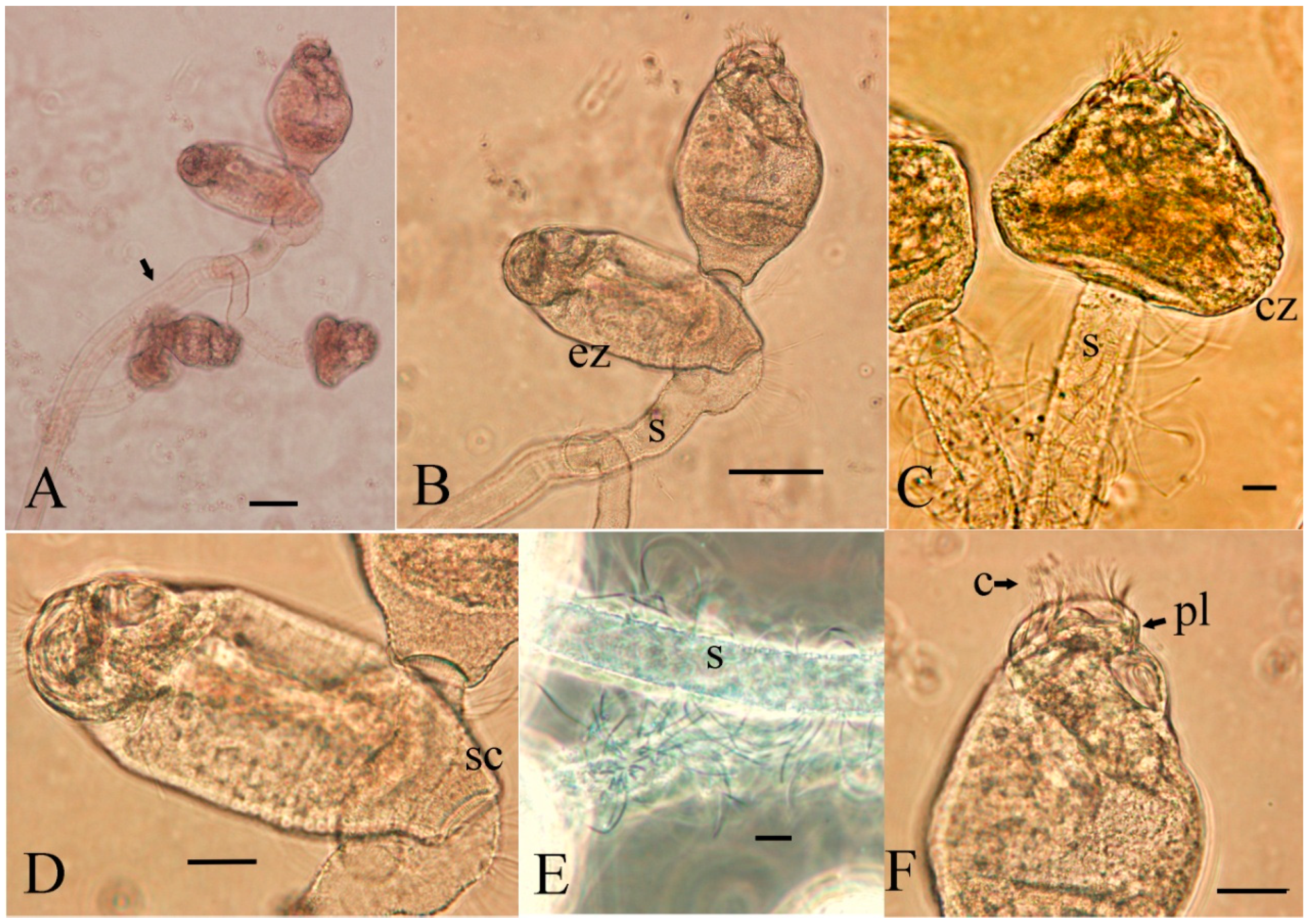
3.2. Parasite Morphology
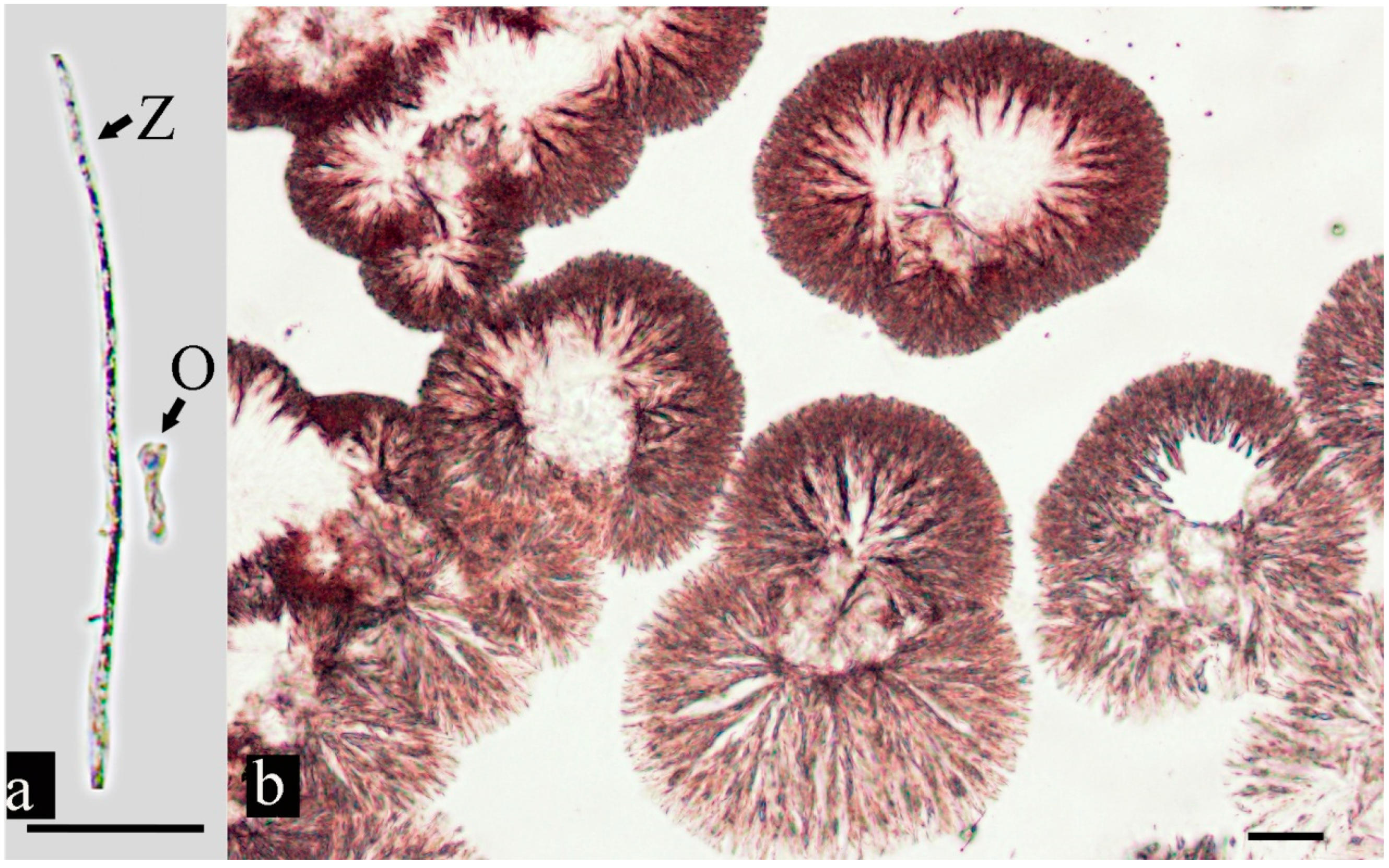
3.3. Oomycete Morphology
3.4. Tissue Histopathology
3.5. Sequence Alignment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, Y.; Xiong, M.T.; Yu, J.X.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, T.L. Effects of artificial submersed vegetation on consumption and growth of mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky) foraging on live prey. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2019, 34, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisheries and Fisheries Administration of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2023. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2023/indexeh.htm (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- He, S.; You, J.J.; Liang, X.F.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.P. Transcriptome sequencing and metabolome analysis of food habits domestication from live prey fish to artificial diets in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Yi, H.D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.Q.; Liu, X.G.; Bi, S.; Lai, H.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Li, G.F. Promotion of pellet-feed feeding in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus is influenced by immune and intestinal flora. Aquaculture 2021, 52, 736864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.W.; Li, H.Y.; Zhao, J.L.; Tang, S.J.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, Y.H.; Chen, X.W. The digestive system of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) can adapt to domestication by feeding with artificial diet. Aquaculture 2021, 538, 736546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruyet, J.P.; Labbé, L.; Le Bayon, N.; Sévère, A.; Le Roux, A.; Le Delliou, H.; Quéméner, L. Combined effects of water quality and stocking density on welfare and growth of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Living Resour. 2008, 21, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birolo, M.; Bordignon, F.; Trocino, A.; Fasolato, L.; Pascual, A.; Godoy, S.; Nicoletto, C.; Maucieri, C.; Xiccato, G. Effects of stocking density on the growth and flesh quality of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) reared in a low-tech aquaponic system. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Bunte, R.M.; Carty, A.J. Evaluation of rapid cooling and tricaine methanesulfonate (MS222) as methods of euthanasia in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2009, 48, 785–789. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Fu, X.; Li, N.; Wan, Q.; Chen, W.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Lin, L. Co-infections of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus and Siniperca chuatsi rhabdovirus in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Impact of Aeromonas hydrophila and infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus infections on susceptibility and host immune response in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 105, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Song, W.; Clamp, J.C.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Q. Reconsideration of systematic relationships within the order Euplotida (Protista, Ciliophora) using new sequences of the gene coding for small-subunit rRNA and testing the use of combined data sets to construct phylogenies of the Diophrys-complex. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 50, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, M.C.; Guillot, J.; Deville, M. Taxonomic and phylogenetic analysis of Saprolegniaceae (Oomycetes) inferred from LSU rDNA and ITS sequence comparisons. Anton. Leeuw. 2000, 77, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Guo, Q.; Gu, Z. Description of a New Freshwater Ciliate Epistylis wuhanensis n. sp. (Ciliophora, Peritrichia) from China, with a Focus on Phylogenetic Relationships within Family Epistylididae. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, L.; Lv, L.Y.; Cai, W.J.; Dou, Y.Q.; Li, J.; Tang, S.L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Mandarin fish (Sinipercidae) genomes provide insights into innate predatory feeding. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Gu, Z. Morphological and molecular identification of epibiontic sessilid Epistylis semiciculus n. sp. (ciliophora, Peritrichia) from Procambarus clarkia (Crustacea, Decapoda) in China. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 10, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksepka, S.P.; Bullard, S.A. Morphology, phylogenetics and pathology of “red sore disease” (coinfection by Epistylis cf. wuhanensis and Aeromonas hydrophila) on sportfishes from reservoirs in the South-Eastern United States. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet. Res. 2017, 47, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Pattanayak, S.; Sahoo, M.; Kumar, P.R.; Kumar, R.; Sahoo, P.K. Co-infection of bacterial and parasitic pathogens including the myxosporean Zschokkella auratis infecting brain in farmed striped murrel Channa striata (Bloch, 1793) causing large scale mortality. Indian J. Fish. 2020, 67, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Guo, G.; Yang, N.; Li, Q.; Yin, F.; Wang, P.; Zheng, J.; Zeng, J. Three species of Aeromonas (A. dhakensis, A. hydrophila and A. jandaei) isolated from freshwater crocodiles (Crocodylus siamensis) with pneumonia and septicemia. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.; Rodríguez Saint-Jean, S.; Pérez-Prieto, S.I. Virulence of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus and Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus coinfection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and nucleotide sequence analysis of the IHNV glycoprotein gene. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 1507–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemme, I.; Louhi, K.R.; Karvonen, A. Host infection history modifies co-infection success of multiple parasite genotypes. J. Anim. Ecol. 2016, 85, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Cai, S.H.; Jian, J.C.; Liu, G.F.; Xu, L.W. Co-infection of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus and Francisella sp. in farmed pearl gentian grouper (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂E. lanceolatus) in China—A case report. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogut, H.; Cavus, N. A comparison of ectoparasite prevalence and occurrence of viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) in whiting Merlangius merlangus euxinus. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanog. 2014, 49, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Densmore, C.I.; Ottinger, C.A.; Blazer, V.S.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Smith, D.R. Immunomodulation and disease resistance in postyearling rainbow trout infected with Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of whirling disease. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2004, 16, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutuli, M.T.; Gibello, A.; Rodriguez-Bertos, A.; Blanco, M.M.; Villarroel, M.; Giraldo, A.; Guarro, J. Skin and subcutaneous mycoses in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) caused by Fusarium oxysporum in coinfection with Aeromonas hydrophila. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2015, 9, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.J.; Anderson, V.L.; Robertson, E.J.; Secombes, C.J.; van West, P. New insights into animal pathogenic oomycetes. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozlan, R.E.; Marshall, W.L.; Lilje, O.; Jessop, C.N.; Gleason, F.H.; Andreou, D. Current ecological understanding of fungal-like pathogens of fish: What lies beneath? Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Carrasco, N.K.; Perissinotto, R.; Vosloo, A. Association of the epibiont Epistylis sp. with a calanoid copepod in the St Lucia Estuary, South Africa. J. Plankton Res. 2016, 38, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kühner, S.; Simão, T.L.; Safi, L.S.; Gazulha, F.B.; Eizirik, E.; Utz, L.R. Epistylis portoalegrensis n. sp. (Ciliophora, Peritrichia): A New Freshwater Ciliate Species from Southern Brazil. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2016, 63, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, N.; Albarouki, E.; Schirawski, J. Comparative Methods for Molecular Determination of Host-Specificity Factors in Plant-Pathogenic Fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Meng, Q.; Liu, G.; Qi, G.; Jiang, C.; Meng, X.; Warren, A. Morphology and morphogenesis of Epistylis plicatilis ehrenberg, 1831 (Ciliophora, Peritrichia) from Wuhan, China. J. Morphol. 2014, 275, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.; Yu, Y.H.; Shen, Y.F. Phylogenetic relationships of the subclass Peritrichia (Oligohymenophorea, Ciliophora) with emphasis on the genus Epistylis, inferred from small subunit rRNA gene sequences. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2001, 48, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.; Fen, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y. Phylogenetic relationships of the subclass Peritrichia (Oligohymenophorea, Ciliophora) inferred from small subunit rRNA gene sequences. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, D. The Ciliated Protozoa: Characterization, Classification, and Guide to the Literature; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Yang, H.; Gu, Z.M. First diagnosis of ectoparasitic ciliates (Trichodina and Chilodonella) on farmed juvenile yellow catfish, Tachysurus fulvidraco in China. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 14285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Nguyen, T.; Nam, B.; Lee, H.B. Characterization of Achlya americana and A. bisexualis (Saprolegniales, Oomycota) isolated from freshwater environments in Korea. Mycobiology 2019, 2, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, K.R.; Halliday, F.W.; Jones, C.D.; Carbone, I.; Mitchell, C.E. Parasites, niche modification and the host microbiome: A field survey of multiple parasites. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 2404–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, W.; Ge, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Huang, F.; Liu, H. First report of Epistylis unioi Gong 1986 (Sessilida: Epistylididae) infecting fry of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco in Hubei, China. Zootaxa 2012, 3556, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Prime | Protein or Virulent Factors | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | 5.8S ribosomal RNA gene, and internal transcribed spacer 2 | F:GTAGGTGAACCTGCGGAAGGATCATTA R:TACTGATATGCTTAAGTTCAGCGG | 50 | 500 | [11] |
| C1/D1 | 28S large subunit ribosomal RNA gene | F:ACCCGCTGATTTAAGCAT R:TCCGTGTTTCAAGACGG | 59 | 600 | [12] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, L.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, W. Farmed Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi) Coinfected with Parasites and Oomycete Pathogens. Fishes 2024, 9, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030097
Xu X, Zhang Y, Ding L, Huang J, Zhou Z, Chen W. Farmed Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi) Coinfected with Parasites and Oomycete Pathogens. Fishes. 2024; 9(3):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030097
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiandong, Yanping Zhang, Liyun Ding, Jiangfeng Huang, Zhiyong Zhou, and Wenjing Chen. 2024. "Farmed Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi) Coinfected with Parasites and Oomycete Pathogens" Fishes 9, no. 3: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030097
APA StyleXu, X., Zhang, Y., Ding, L., Huang, J., Zhou, Z., & Chen, W. (2024). Farmed Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi) Coinfected with Parasites and Oomycete Pathogens. Fishes, 9(3), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9030097





