Environmental DNA Detects Remaining Populations of Endangered Stream Salmon (Sichuan Taimen: Hucho bleekeri Kimura Salmonidae) in the Qinling Mountains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Species
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Field Surveys
2.3.1. First Phase: Detection Rate of eDNA in Different Seasons
2.3.2. Second Phase: Determine Distribution Range of the Sichuan Taimen
3. Results
3.1. Detection Rate of Sichuan Taimen eDNA in Different Seasons
3.2. Creel Survey Results
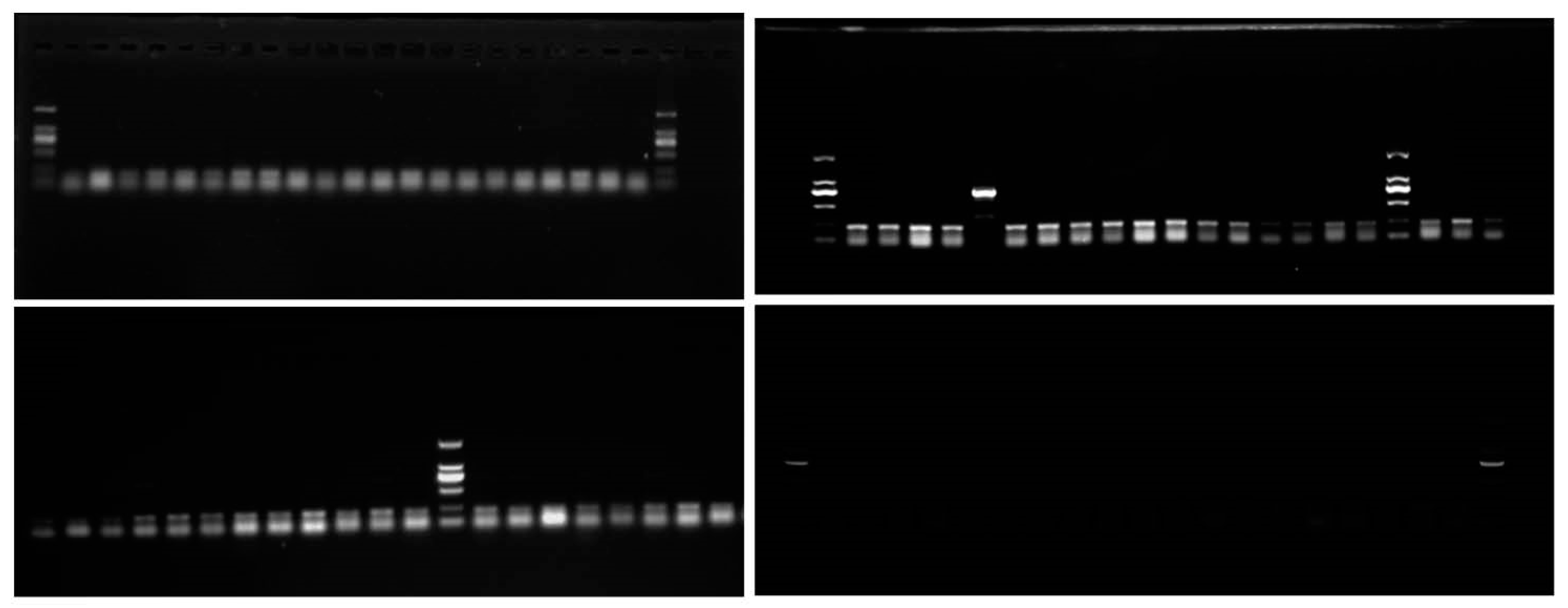
3.3. eDNA Survey Results
3.4. Distribution Range of Sichuan Taimen in Qinling Moutains
4. Discussion
4.1. Optimal Season for Monitoring Sichuan Taimen
4.2. High Detection Capacity of eDNA
4.3. Distribution of Sichuan Taimen in the Qinling Mountains
4.4. Low eDNA Concentration in the Taibai River
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Snyder, D.E. Invited overview: Conclusions from a review of electrofishing and its harmful effects on fish. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2003, 13, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, L.; Grenouillet, G. Do stream fish track climate change? Assessing distribution shifts in recent decades. Ecography 2013, 36, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, H.C.; Maddison, B.C.; Middleditch, D.J.; Patmore, J.R.M.; Gough, K.C. REVIEW: The detection of aquatic animal species using environmental DNA—A review of eDNA as a survey tool in ecology. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA—An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmann, K.; Evans, A.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Knapp, M.; Yu, D.W.; de Bruyn, M. Environmental DNA for wildlife biology and biodiversity monitoring. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beng, K.C.; Corlett, R.T. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in ecology and conservation: Opportunities, challenges and prospects. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2089–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Inui, R.; Matsuoka, S.; Akamatsu, Y.; Goto, M.; Kono, T. Estimation of biodiversity metrics by environmental DNA metabarcoding compared with visual and capture surveys of river fish communities. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. “Sight-unseen” detection of rare aquatic species using environmental DNA. Conserv. Lett. 2011, 4, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laramie, M.B.; Pilliod, D.S.; Goldberg, C.S. Characterizing the distribution of an endangered salmonid using environmental DNA analysis. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, A.O.; Kelly, R.P.; O’Donnell, J.L.; Park, L.; Schwenke, P.; Greene, C.; Henderson, R.A.; Beamer, E.M. Environmental DNA provides quantitative estimates of a threatened salmon species. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 237, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigsgaard, E.E.; Carl, H.; Møller, P.R.; Thomsen, P.F. Monitoring the near-extinct European weather loach in Denmark based on environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelzle, M.C.; Kinziger, A.P. Using occupancy modelling to compare environmental DNA to traditional field methods for regional-scale monitoring of an endangered aquatic species. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, P.S. Current global status of taimen and the need to implement aggressive conservation measures to avoid population and species-level extinction. Arch. Pol. Fish. 2013, 21, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.H. The Fishes of Sichuan, China; Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology: Chengdu, China, 1994; Volume 641. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.Q.; Chen, Y.Y. China Red Data Book of Endangered Animals (Pisces); Science Press: Beijing, China; Hong Kong, China; New York, NY, USA, 1998. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, R.H.; Gui, L.H.; Li, M.; Luo, Q.H. Protective Biology of Hucho bleekeri in the Upper Changjiang River, China. J. Guangxi Normal Univ. 2010, 28, 96–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Ding, R.H. Protection biology of Hucho bleekeri IV. Estimating of its resource and cause of being faced with danger of extinction. Sichuan J. Zool. 1995, 14, 101–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z. Hucho bleekeri. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.3. 2012. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/13151680/174797529 (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Hu, M.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Cao, L.; Xiong, B.X. Threatened fishes of the world: Hucho bleekeri Kimura, 1934 (Salmonidae). Environ. Boil. Fish. 2008, 82, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.J.; Li, K.M.; Shen, Z.X. Hucho bleekeri, a precious fish. Fish. Sci. 2006, 25, 261–262. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Li, L.X.; Wei, Q.W.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Sun, Q.L.; Yang, X.G.; Li, L. The rediscovery of Hucho bleekeri in the Taibai River, the upper tributary of the Hanjiang River, China. Chin. J. Zool. 2014, 3, 414. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.G.; Wei, Q.W.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, X.Q.; Cheng, B.L. The distribution actuality and protecting countermeasure of rare aquatic animals in Xushui River of Qinling Mountains. J. Fish. Sci. China 1999, 6, 123–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Luo, Z. The Yangtze River Dictionary; Wuhan Publishing House: Wuhan, China, 1997. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, H.X.; Wang, Q.J.; Kong, F.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, W. An optimized environmental DNA method to improve detectability of the endangered Sichuan Taimen (Hucho bleekeri). Fishes 2023, 8, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, R.A.; Merkes, C.M.; Jackson, C.A.; Goforth, R.R.; Amberg, J.J. Seasonal trends in eDNA detection and occupancy of bigheaded carps. J. Great Lakes Res. 2017, 43, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, S.F.; Groves, J.D.; Williams, L.A.; Waits, L.P. Using environmental DNA methods to improve detectability in a hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis) monitoring program. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, A.S.; Groomb Ridge, J.J.; Zakaria, N.B.; Griffiths, R.A. Seasonal variation in environmental DNA in relation to population size and environmental factors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, V.; Aman, J.; York, G.; Kinnison, M.T. Environmental DNA detects Spawning Habitat of an ephemeral migrant fish (Anadromous Rainbow Smelt: Osmerus mordax). BMC Ecol. Evol. 2022, 22, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilliod, D.S.; Goldberg, C.S.; Arkle, R.S.; Waits, L.P. Estimating occupancy and abundance of stream amphibians using environmental DNA from filtered water samples. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 70, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Sun, Z.Y.; Fu, J.R.; Guo, Y.S. Status and conservation of fish resources in the upper reaches of Qingyi River. Fish. Sci. 2017, 36, 504–508. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Yan, T.; Huang, Y.Y.; Long, Z.H.; Yan, J.G.; Zhao, F.Q.; Chen, Y.S.; He, Z.D.; Du, J. Analysis of fish resources status in the upper reaches of the Dadu River. Freshw. Fish. 2021, 51, 35–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yan, J.G.; Zhao, F.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; He, B. Investigation and analysis of fish resource in Minjiang River. Acta Ecol. Anim. Domastici 2022, 43, 43–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Katano, I.; Harada, K.; Doi, H.; Souma, R.; Minamoto, T. Environmental DNA method for estimating salamander distribution in headwater streams, and a comparison of water sampling methods. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, H.; Mitsuzuka, T.; Araki, H. An Environmental DNA Survey on Distribution of an Endangered Salmonid Species, Parahucho perryi, in Hokkaido, Japan. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 569425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, R.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Wen, J.T. Experimental study on the response relationship between environmental DNA concentration and biomass of Schizothorax prenanti in still water. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 972680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample ID | Stream Name | Longitude (0) | Latitude (0) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xushui River basin | ||||
| S21 | Hetaoping Stream | 107.67271 | 33.81472 | 1535 |
| S20 | Hetaoping Stream | 107.67643 | 33.81398 | 1540 |
| S19 | Hetaoping Stream | 107.67777 | 33.81178 | 1542 |
| S13 | Dajian Stream | 107.59071 | 33.76663 | 1714 |
| S14 | Dajian Stream | 107.58762 | 33.76532 | 1659 |
| S15 | Dajian Stream | 107.56453 | 33.76874 | 1532 |
| S3 | Xiaojian Stream | 107.49081 | 33.74385 | 1274 |
| S1 | Xiaojian Stream | 107.49025 | 33.74397 | 1276 |
| S2 | Xiaojian Stream | 107.49981 | 33.74382 | 1254 |
| S4 | Xiaojian Stream | 107.48938 | 33.743417 | 1310 |
| S12 | Maoer Stream | 107.45415 | 33.73392 | 1069 |
| S11 | Niuwei Stream | 107.35985 | 33.69751 | 1059 |
| S22 | Heixiazi Stream | 107.34712 | 33.69592 | 951 |
| Taibai River basin | ||||
| S6 | Sujia Stream | 107.36523 | 33.91537 | 1613 |
| S7 | Sujia Stream | 107.32536 | 33.91416 | 1628 |
| S8 | Sujia Stream | 107.3298 | 33.9019 | 1632 |
| S5 | Sujia Stream | 107.34709 | 33.90674 | 1692 |
| S10 | Sujia Stream | 107.36503 | 33.90343 | 1733 |
| S9 | Sujia Stream | 107.36512 | 33.90425 | 1756 |
| S16 | Taibai River | 1235 | ||
| S17 | Taibai River | 1227 | ||
| S18 | Taibai River | 1224 | ||
| Positive control | Fish pond | |||
| Negative control | Xianyi River | 106.59852 | 34.82904 | |
| Blank control | distilled water | |||
| Stream Name | Site | Sample | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taibai River | S1 | S1-1 | × | × | √ | × |
| S1-2 | × | × | √ | × | ||
| S1-3 | × | × | √ | × | ||
| Taibai River | S2 | S2-1 | × | √ | √ | √ |
| S2-2 | × | √ | × | √ | ||
| S2-3 | × | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Taibai River | S3 | S3-1 | × | √ | √ | √ |
| S3-2 | × | √ | √ | √ | ||
| S3-3 | × | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Taibai River | S4 | S4-1 | × | × | √ | × |
| S4-2 | × | × | √ | √ | ||
| S4-3 | × | × | √ | √ | ||
| Taibai River | S5 | S5-1 | × | × | √ | × |
| S5-2 | × | × | × | √ | ||
| S5-3 | × | × | √ | × | ||
| Taibai River | S6 | S6-1 | √ | × | √ | × |
| S6-2 | × | × | √ | √ | ||
| S6-3 | × | √ | √ | × | ||
| Fish pond | Positive control | C+ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Xianyi River | Negative control | C- | × | × | × | × |
| distilled water | Blank control | BC | × | × | × | × |
| Species | Number | Weight (g) | Length (cm) | Quantity Percentage (%) | Weight Percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed Value | Average Value | Observed Value | Average Value | ||||
| Taibai River | |||||||
| Hucho bleekeri | 1 | 1.94 | 1.94 | 5 | 5 | 0.76 | 0.15 |
| Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 125 | 3.76–43.67 | 17.86 ± 3.87 | 4.5–15.5 | 10.31 ± 3.87 | 94.70 | 98.35 |
| Botia superciliaris | 3 | 2.3–6.43 | 4.74 ± 2.17 | 7–10 | 8.83 ± 1.61 | 2.27 | 1.08 |
| Sarcocheilichthys nigripinnis | 3 | 1.28–2.62 | 1.86 ± 0.76 | 5–6.5 | 5.83 ± 0.76 | 2.27 | 0.42 |
| Sujia Stream | |||||||
| Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis | 3 | 15.09–163 | 74.95 ± 77.88 | 11.5–26 | 17.88 ± 7.42 | 3.26 | 24.94 |
| Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 86 | 2.8–31 | 14.26 ± 7.12 | 4–11.5 | 9.06 ± 2.79 | 93.48 | 71.63 |
| Cobitis sinensis | 3 | 7.1–13.22 | 10.32 ± 3.07 | 9–11.5 | 10.50 ± 1.32 | 3.26 | 3.43 |
| Hetaoping Stream | |||||||
| Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis | 3 | 38–43 | 40.83 ± 2.57 | 11–15 | 13 ± 2 | 50 | 79.28 |
| Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 3 | 9–13 | 10.67 ± 2.08 | 4.5–6.5 | 5.17 ± 0.76 | 50 | 20.71 |
| Dajian Stream | |||||||
| Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis | 17 | 22–305 | 63.12 ± 69.13 | 5–29 | 13.06 ± 6.95 | 94.44 | 99.28 |
| Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 1 | 6.5 | 5 | 5.56 | 0.72 | ||
| Xiaojian Stream | |||||||
| Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis | 7 | 33.96–129 | 63.98 ± 31.6 | 15.2–21 | 18.03 ± 2.03 | 2.88 | 26.81 |
| Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 235 | 4–26.4 | 17.86 ± 2.87 | 4.5–15.2 | 10.11 ± 3.27 | 96.71 | 72.33 |
| Paracobitis variegatus | 1 | 14.44 | 14.44 | 17 | 17 | 0.41 | 0.86 |
| Maoer Stream | |||||||
| Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis | 4 | 40.24–204 | 84.8 ± 79.55 | 16–26 | 18.88 ± 4.77 | 9.30 | 51.99 |
| Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 39 | 3.4–33.5 | 7.48 ± 2.35 | 2–15 | 6.45 ± 5.62 | 90.70 | 48.01 |
| Niuwei Stream | |||||||
| Zacco platypus | 7 | 8.37–21.3 | 14.15 ± 5.13 | 9–20 | 12.43 ± 3.54 | 10.61 | 10.50 |
| Gnathopogon imberbis | 5 | 4.26–16.35 | 9.71 ± 5.7 | 8.5–11.5 | 9.7 ± 1.44 | 7.58 | 5.14 |
| Pseudogobio vaillanti | 50 | 13.67–51.63 | 28.13 ± 11.12 | 12–19 | 14.86 ± 1.85 | 75.76 | 74.54 |
| Trilophysa bleekeri | 1 | 3.37 | 3.37 | 4 | 4 | 1.51 | 0.35 |
| Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis | 1 | 57.25 | 57.25 | 18 | 18 | 1.51 | 6.06 |
| Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 1 | 26.55 | 26.55 | 15 | 15 | 1.51 | 2.81 |
| Varicorhinus macrolepis | 1 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 8 | 8 | 1.51 | 0.58 |
| Heixiazi Stream (non catch were obtained) | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Kong, F.; Deng, J.; Fang, C.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. Environmental DNA Detects Remaining Populations of Endangered Stream Salmon (Sichuan Taimen: Hucho bleekeri Kimura Salmonidae) in the Qinling Mountains. Fishes 2023, 8, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120570
Zhao H, Zhang J, Wang Q, Ma H, Zhang H, Kong F, Deng J, Fang C, Zhang H, Jiang W. Environmental DNA Detects Remaining Populations of Endangered Stream Salmon (Sichuan Taimen: Hucho bleekeri Kimura Salmonidae) in the Qinling Mountains. Fishes. 2023; 8(12):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120570
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hu, Jianlu Zhang, Qijun Wang, Hongying Ma, Han Zhang, Fei Kong, Jie Deng, Cheng Fang, Hongxing Zhang, and Wei Jiang. 2023. "Environmental DNA Detects Remaining Populations of Endangered Stream Salmon (Sichuan Taimen: Hucho bleekeri Kimura Salmonidae) in the Qinling Mountains" Fishes 8, no. 12: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120570
APA StyleZhao, H., Zhang, J., Wang, Q., Ma, H., Zhang, H., Kong, F., Deng, J., Fang, C., Zhang, H., & Jiang, W. (2023). Environmental DNA Detects Remaining Populations of Endangered Stream Salmon (Sichuan Taimen: Hucho bleekeri Kimura Salmonidae) in the Qinling Mountains. Fishes, 8(12), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120570






