Molecular Characterization and Expression of the LAP3 Gene and Its Association with Growth Traits in the Blood Clam Tegillarca granosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Cloning and Characterization of Tg-LAP3
2.3. Analysis of Nucleotide and Amino Acid Sequences
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis of Tg-LAP3
2.5. Association Analysis of SNPs with Growth Trait in T. granosa
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
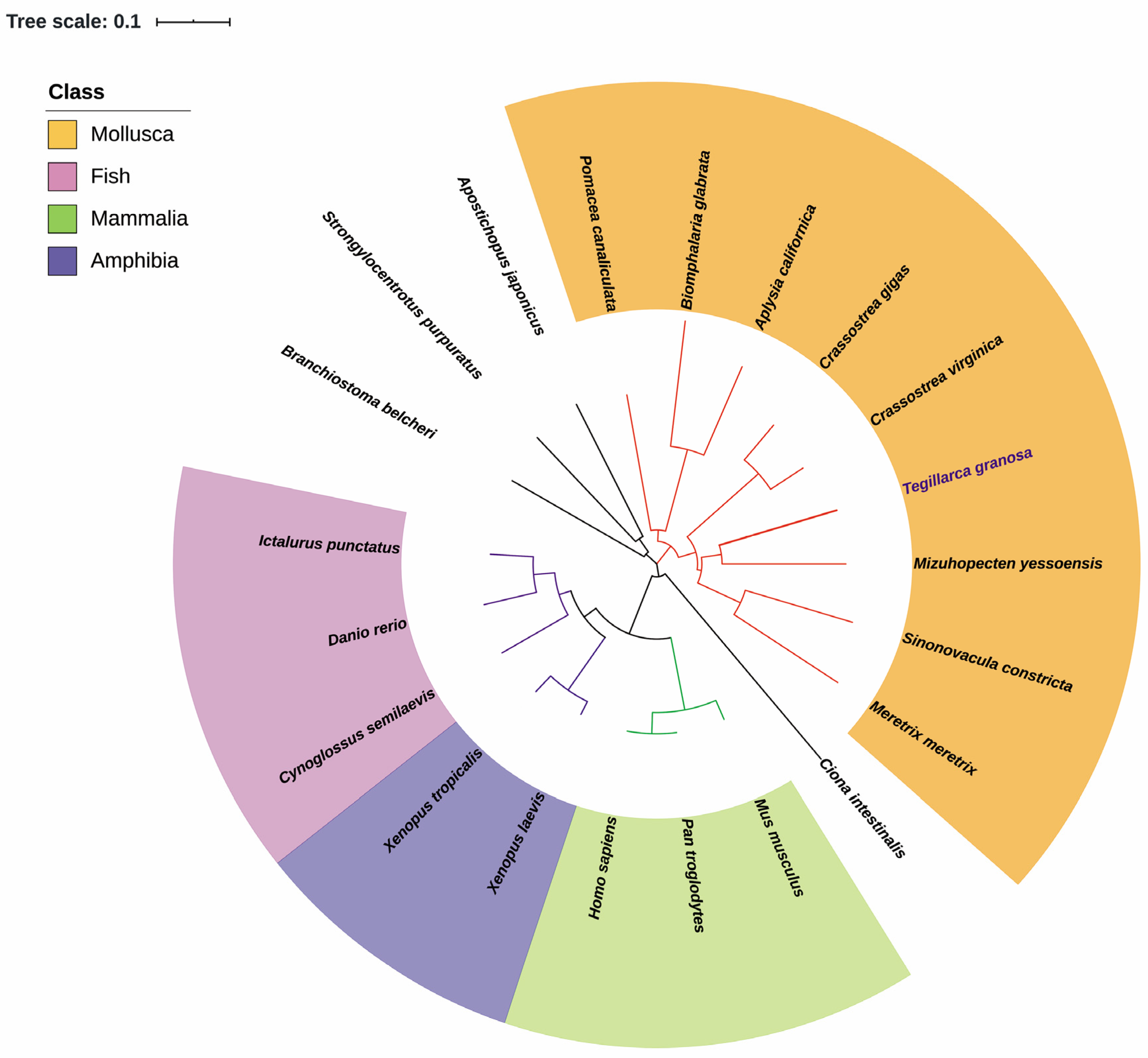
3.1. Gene Structure and Characterization of Tg-LAP3
3.2. Analysis of the Deduced Amino Acid Sequence of Tg-LAP3
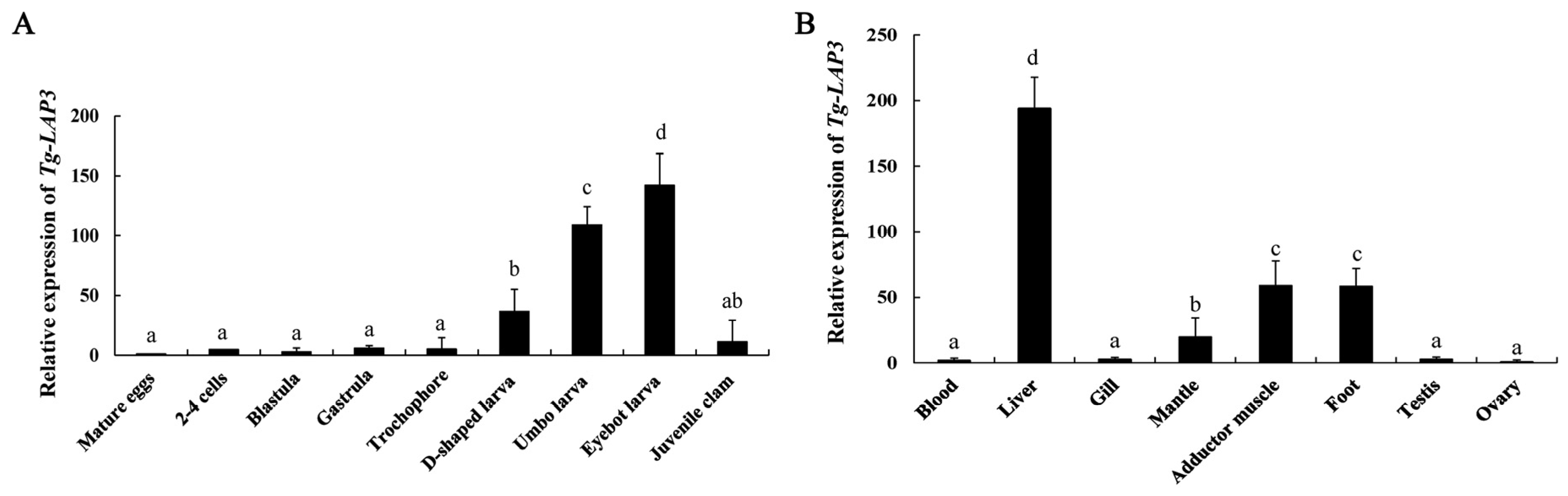
3.3. Quantitative Expression Analysis of Tg-LAP3
3.4. Association Analysis of SNPs with Growth Traits
4. Discussion
4.1. Tg-LAP3 Gene and Amino Acid Sequence Features
4.2. Quantitative Expression Analysis of Tg-LAP3
4.3. Association Analysis between SNPs of Tg-LAP3 Gene and Growth Traits
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsujimoto, M.; Goto, Y.; Maruyama, M.; Hattori, A. Biochemical and enzymatic properties of the M1 family of aminopeptidases involved in the regulation of blood pressure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2008, 13, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuypers, H.T.; Loon-Klaassen, L.A.; Egberts, W.T.; Jong, W.W.; Bloemendal, H. The primary structure of leucine aminopeptidase from bovine eye lens. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 25, 7077–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloetzel, P.M.; Ossendorp, F. Proteasome and peptidase function in MHC-class-I-mediated antigen presentation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Fowler, J.H.; Walling, L.L. Leucine aminopeptidases: Diversity in structure and function. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.S.; Gu, Y.Q.; Pautot, V.; Bray, E.A.; Walling, L.L. Leucine aminopeptidase RNAs, proteins, and activities increase in response to water deficit, salinity, and the wound signals systemin, methyl jasmonate, and abscisic acid. Plant Physiol. 1999, 120, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanover, A.; Schwartz, A.L. The ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway: Mechanisms of recognition of the proteolytic substrate and involvement in the degradation of native cellular proteins. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, A.J.S.; Day, A.J. The metabolic basis of genetic differences in growth efficiency among marine animals. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 203, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.J.; Reid, D.D.; Nell, J.A. Growth characteristics of Sydney rock oysters Saccostrea commercialis in relation to size and temperature. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1998, 227, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ju, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.L.; Huang, J.M.; Zhang, A.W.; Zhong, J.F.; Wang, C.F. Single nucleotide polymorphisms, haplotypes and combined genotypes of LAP3 gene in bovine and their association with milk production traits. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 4053–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.F. Cloning and expression of growth candidate genes and their SNPs association with growth traits in sheep. Master’s Thesis, Gansu Agriculture University, Lanzhou, China, 29 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Koehn, R.K.; Hilbish, T.J. The adaptive importance of genetic variation. Am. Sci. 1987, 75, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, A.J.S.; Day, A.J. Metabolic interrelations underlying the physiological and evolutionary advantages of genetic diversity. Am. Zool. 1999, 39, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharam, S.D.; Wardill, T.J.; Goddard, V.; Donald, K.M.; Parry, H.; Pascore, P.; Pickerill, P.; Smerdon, G.; Hawkins, A.J.S. A Leucine aminopeptidase gene of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas exhibits an unusually high level of sequence variation, predicted to affect structure, and hence activity, of the enzyme. J. Shellfish Res. 2008, 27, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.H.; Liu, C.S.; Lin, D.H.; Liu, S.; Lin, Z.H.; Dong, Y.H. Polymorphisms of LAP3 gene and their association with the growth traits in the razor clam Sinonovacula constricta. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, K.M.; Day, A.J.; Smerdon, G.R.; Cross, L.J.; Hawkins, A.J. Quantification of gene transcription and enzyme activity for functionally important proteolytic enzymes during early development in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Comp. Biochem Phys. B 2003, 136, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.B.; Dong, Y.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Liu, C.S.; Lin, D.H.; Lin, Z.H. Gene cloning and expression analysis of leucine aminopeptidaselap3 genes in different development stages of larvae and different tissues of adult of Meretrix meretrix. Acta. Oceannol. Sin. 2017, 2, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.H. Transcriptome analysis using 454 pyrosequencing and cloning and expression of growth-related genes for the blood clam Tegillarca granosa. Ph.D Thesis, Ocean Univiversity of China, Qingdao, China, 6 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.H.; Xiang, X.; Yao, H.H.; Bao, Y.B.; Sun, C.S.; Lin, Z.H. Cloning and expression of GRB2 gene from the blood clam Tegillarca granosa. Oceannol. Limnol. Sin. 2013, 44, 937–943. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, F.Z.; Yao, H.H.; Dong, Y.H.; Zhou, X.L.; Lin, Z.H. cDNA, introns cloning and spatiotemporal expression analysis of HDAC1 gene in Tegillarca granosa. Acta Oceannol. Sin. 2016, 38, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.J.; Dong, Y.H.; Yao, H.H.; Lin, Z.H. Cloning and spatiotemporal expression analysis of Smad1/5 gene in the blood clam Tegillarca granosa. J. Fish China 2015, 39, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.J. Cloning and spatiotemporal expression analysis of Smad1/5, BMP2/4 gene and growth traits related SNP screening in the Tegillarca granosa. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University of China, Shanghai, China, 1 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, F.Z.; Yao, H.H.; Qian, X.J.; Lin, Z.H.; Dong, Y.H. Cloning and expression analysis of IGF 1 R gene in Tegillarca granosa. J. Fish. China 2017, 41, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, F.Z. The genetic structure of IGF1R, HDAC1, LAP3 and association analysis with growth traits in the Tegillarca granosa. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University of China, Shanghai, China, 10 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cartharius, K.; Frech, K.; Klocke, B.; Haltmeier, M.; Klingenhoff, A.; Frisch, M.; Bayerlein, M.; Werner, T. MatInspector and beyond: Promoter analysis based on transcription factor binding sites. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; Mcgettigan, P.A.; Mcwilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, A.; Lopez, R.; Thompsom, J.D.; et al. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2010, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhir, K.; Glen, S.; Koichiro, T. MEGA: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol.Biol. Evol. 2010, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Albiston, A.L.; Ye, S.; Chai, S.Y. Membrane bound members of the M1 family: More than aminopeptidases. Protein Pept. Lett. 2004, 11, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell 1981, 23, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Maier, S.; Nimmrich, I.; Yan, P.S.; Caldwell, C.W.; Olek, A.; Huang, T.H. Oligonucleotide-based microarray for DNA methylation analysis: Principles and applications. J. Cell Biochem. 2003, 88, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Tsunoda, T.; Sese, J.; Taira, H.; Mizushima-Sugano, J.; Hata, H.; Ota, T.; Isogai, T.; Tanaka, T.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Identification and characterization of the potential promoter regions of 1031 kinds of human genes. Genome Res. 2011, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.; Chua, N.H. ASF-2: A factor that binds to the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter and a conserved GATA motif in cab promoters. Plant Cell 1989, 1, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, E.; McGrew, M.J.; Nguyen, T.; Grieshammer, U.; Horgan, D.; Hughes, S.H.; Rosenthal, N. An E box comprises a positional sensor for regional differences in skeletal muscle gene expression and methylation. Dev. Biol. 1999, 213, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.V.; Donoghue, M.J.; Merlie, J.P.; Sanes, J.R. Distinct regulatory elements control muscle-specific, fiber-type-selective, and axially graded expression of a myosin light-chain gene in transgenic mice. Mol. Cell Biol. 1996, 16, 3909–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Sul, H.S. Upstream stimulatory factor binding to the E-box at-65 is required for insulin regulation of the fatty acid synthase promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26367–26374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.N.; Koehn, R.K.; Bayne, B.L. Leucine aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase-I), N-acetyl-b-hexosamidase and lysosomes in the mussel, Mytilus edulis, in salinity changes. J. Exp. Zool. 1980, 214, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, A.J.S. Protein turnover: A functional appraisal. Funct. Ecol. 1991, 5, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.L.; Guo, H.H.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.T.; Roy, S.W.; Lu, W.; Hu, J.J.; et al. Molecular characterization of myostatin gene from Zhikong scallop Chlamys farreri (Jones et Preston 1904). Genes Genet. Syst. 2010, 85, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer Name | Sequence from 5′ to 3′ | Information of Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Tg-LAP3-GSP1 | CCCCCTGACCTTCCAGCGTTACCAATGT | 5’-RACE |
| Tg-LAP3-GSP2 | AAACAGGTGACAGAATGTGGAGAATGCC | 3’-RACE |
| Tg-LN1-F | TAAGCGACTCAAAATGGCAG | Cloning of intron 1 |
| Tg-LN1-R | TGTTCATCAAATTTTTGTGC | |
| Tg-LN2-F | GCACAAAAATTTGATGAACA | Cloning of intron 2 |
| Tg-LN2-R | ATCCTTCACCTTGCTTTCCC | |
| Tg-LN3/4-F | ACCCGAGTATTTTATGGATT | Cloning of intron 3 and 4 |
| Tg-LN3/4-R | GTTATTACCTATCTGCTACA | |
| Tg-LN5-F | TTGTTATCTCAGTTTGTGTA | Cloning of intron 5 |
| Tg-LN5-R | CTGTGGAGTAAGTTTATTTG | |
| Tg-LN6-F | TTGTTATCTCAGTTTGTGTA | Cloning of intron 6 |
| Tg-LN6-R | TGTGAACCTTGAGCAACTGA | |
| Tg-LN7-F | TTATCAGTTGCTCAAGGTTC | Cloning of intron 7 |
| Tg-LN7-R | AACAGCAAACAGTGTCCCAG | |
| Tg-LN8-F | CAGTCAAACCTGGTGATGTA | Cloning of intron 8 |
| Tg-LN8-R | TCAGGGTTCAGTTCAGATAG | |
| Tg-LN9-F | ACAGGTTGACAATACAGATG | Cloning of intron 9 |
| Tg-LN9-R | CCAGCCTGTTGTAAGGTATT | |
| Tg-LN10-F | ATTGATGTTGCTCTTGGCTC | Cloning of intron 10 |
| Tg-LN10-R | TGACCTTCCAGCGTTACCAA | |
| Tg-LN11-F | ACATTGGTAACGCTGGAAGG | Cloning of intron 11 |
| Tg-LN11-R | AGCTAGATAAGGAATTTCTG | |
| Tg-LN12-F | ATAAAAACTGGTTACATCTA | Cloning of intron 12 |
| Tg-LN12-R | TTAGTTGTCTATTGTATGTC | |
| GSP1 | TCCACTAAATGGGGTTTTCTAATAAC | Cloning of proximal promoter sequence |
| GSP2 | TGGGGGCTGCCATTTTGAGTCGCTTACA | |
| GSP3 | TTACTCTACTCCACTTCACTCCAAAT | |
| GW-F | GAAGTGGAGTAGAGTAATGC | Verification of proximal promoter sequence |
| GW-R | TTGGGAGGTCCTGGTTCTTG | |
| SNP-F1 | TGTTCTGCTAAGCTGGGT | HRM primer |
| SNP-R1 | CACAGGAATGCTAACGCT | |
| SNP-F2 | AGTTACAAGTTAGGGGAC | HRM primer |
| SNP-R2 | ACATTTTCGTCTGATTAG | |
| SNP-F3 | GTTTTTATTATTTGTGAC | HRM primer |
| SNP-R3 | AAGTTATCAGGTTACATT | |
| LAP3-real-F | GATGTTGCTCTTGGCTCAGG | qRT-PCR |
| LAP3-real-R | TCCCGTATTGTTATTTTTCGTCACT | |
| 18S rRNA-real-F | CGTGCTCGTCCACCTTGGAG | qRT-PCR |
| 18S rRNA-real-R | GAACTCGTCGAGCTGCATCTTG |
| Intron Name | Starting Postion(bp) | Length (bp) | Characteristy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tg-LN1 | 111 | 615 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN2 | 233 | 1040 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN3 | 394 | 540 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN4 | 463 | 864 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN5 | 575 | 1042 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN6 | 737 | 1127 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN7 | 899 | 581 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN8 | 1113 | 1105 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN9 | 1216 | 1853 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN10 | 1296 | 1567 | GC-AG |
| Tg-LN11 | 1446 | 378 | GT-AG |
| Tg-LN12 | 1540 | 1345 | GT-AG |
| Common Name | Species | GenBank No. | Size (aa) | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood clam | Tegillarca granosa | AFP57676 | 530 | - |
| Yesso scallop | Mizuhopecten yessoensis | XP_021371955 | 529 | 73.4 |
| Eastern oyster | Crassostrea virginica | XP_022345091 | 529 | 70.7 |
| Razor clam | Sinonovacula constricta | MF687490 | 519 | 70.4 |
| Pacific oyster | Crassostrea gigas | ACJ05337 | 529 | 71.7 |
| Hard clam | Meretrix meretrix | KU678388 | 417 | 58.0 |
| Golden apple snail | Pomacea canaliculata | XP_025095362 | 523 | 69.2 |
| Sea hare | Aplysia californica | XP_012937771 | 527 | 64.4 |
| Freshwater snail | Biomphalaria glabrata | XP_013075022 | 497 | 62.2 |
| Sea squirt | Ciona intestinalis | XP_00213156 | 529 | 55.2 |
| Sea cucumber | Apostichopus japonicas | PIK48812 | 547 | 59.8 |
| Sea urchin | Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | XP_030841514 | 527 | 66.1 |
| Amphioxus | Branchiostoma belcheri | XP_019624998 | 531 | 63.5 |
| Channel catfish | Ictalurus punctatus | XP_017316877 | 518 | 62.4 |
| Zebrafish | Danio rerio | CAM13051 | 517 | 62.3 |
| Half-smooth tongue sole | Cynoglossus semilaevis | XP_008315686 | 520 | 61.4 |
| Western clawed frog | Xenopus tropicalis | AAH84523 | 520 | 60.8 |
| African clawed frog | Xenopus laevis | NP_001084691 | 495 | 61.6 |
| Human | Homo sapiens | CAG33409 | 519 | 61.6 |
| Chimpanzees | Pan troglodytes | JAA04696 | 519 | 61.6 |
| Mouse | Mus musculus | CAJ18509 | 519 | 61.4 |
| Locus | Genotype | Number | Frequency (%) | Body Weight (g) | Shell Length (mm) | Shell Width (mm) | Shell Height (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g.-488A > G | AA | 6 | 10.34 | 8.51 ± 1.91 | 28.37 ± 2.36 | 21.96 ± 1.82 | 19.61 ± 1.45 |
| AG | 28 | 48.28 | 9.16 ± 2.36 | 29.35 ± 2.68 | 22.37 ± 2.12 | 19.93 ± 1.65 | |
| GG | 24 | 41.34 | 9.74 ± 2.75 | 29.86 ± 2.60 | 22.97 ± 2.00 | 20.14 ± 1.54 | |
| g.-1123C > T | CC | 30 | 49.18 | 8.17 ± 2.45 | 27.88 ± 2.88 | 21.72 ± 2.21 | 19.23 ± 1.78 |
| CT | 26 | 42.62 | 9.42 ± 1.84 | 29.71 ± 1.98 | 22.60 ± 1.45 | 20.16 ± 1.29 | |
| TT | 5 | 8.20 | 8.83 ± 1.88 | 29.20 ± 2.21 | 22.22 ± 1.76 | 19.84 ± 1.68 | |
| g.-1304C > A | CC | 39 | 72.22 | 7.78 ± 1.75 | 27.66 ± 2.36 | 21.21 ± 1.66 | 19.11 ± 1.38 |
| CA | 13 | 22.22 | 9.64 ± 2.23 | 29.75 ± 2.46 | 22.89 ± 2.07 | 20.09 ± 1.55 | |
| AA | 3 | 5.56 | 9.66 ± 0.46 | 30.48 ± 0.99 | 22.95 ± 0.38 | 20.26 ± 0.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, H.; Ren, F.; Bao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Lin, Z. Molecular Characterization and Expression of the LAP3 Gene and Its Association with Growth Traits in the Blood Clam Tegillarca granosa. Fishes 2021, 6, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040054
Yao H, Ren F, Bao Y, Dong Y, Lin Z. Molecular Characterization and Expression of the LAP3 Gene and Its Association with Growth Traits in the Blood Clam Tegillarca granosa. Fishes. 2021; 6(4):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040054
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Hanhan, Fuzhen Ren, Yongbo Bao, Yinghui Dong, and Zhihua Lin. 2021. "Molecular Characterization and Expression of the LAP3 Gene and Its Association with Growth Traits in the Blood Clam Tegillarca granosa" Fishes 6, no. 4: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040054
APA StyleYao, H., Ren, F., Bao, Y., Dong, Y., & Lin, Z. (2021). Molecular Characterization and Expression of the LAP3 Gene and Its Association with Growth Traits in the Blood Clam Tegillarca granosa. Fishes, 6(4), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6040054





