Abstract
Hybridization is common among minnows and shiners in the family Leuciscidae, and mitonuclear discordance can reveal evidence of historical hybridization and introgression events that have shaped extant species and populations. We have identified a notable case of serial mitogenome replacement in populations of two shiner species, Luxilus zonatus and L. chrysocephalus, which are syntopic in drainages throughout the northern and eastern Ozark Interior Highlands of North America. These mitogenome replacement events involved L. zonatus acquiring the mitogenome of L. chrysocephalus, and populations of L. chrysocephalus acquiring the mitogenome of an allopatric congeneric species, L. cornutus. The latter species has a more northern distribution that was likely shifted southward by glacial advances during the Pleistocene. The geographic extent of mitogenome replacements in both species spans multiple separate drainages encompassing most of the major river systems that comprise the northern and eastern Ozark Highlands. We attribute these patterns to shifting species distributions, which were impacted by multiple glacial advances and coincident geomorphological changes to Ozark Highland drainages throughout the Pleistocene. The serial nature of mitogenome replacements in L. zonatus and L. chrysocephalus may exclude a role for natural selection in these introgression events, but the dynamic shifts in species distributions and gene flow connections throughout the Pleistocene may have favored an invasion-with-hybridization model that predicts massive asymmetric introgression between invading and resident species. These results have applied significance for eDNA metabarcoding methods of biodiversity assessment in Ozark streams, as they are dependent on mitogenome detections.
Keywords:
hybrid introgression; mitonuclear discordance; Ozark Highlands; Luxilus; Leuciscidae; Pleistocene Key Contribution:
Pleistocene hybrid introgression has led to two congeneric minnow species experiencing mitogenome replacement across largely congruent Ozark Highland drainages.
1. Introduction
Hybridization and introgression occur frequently in nature and can be an important source of genetic variation in species [1,2,3,4,5]. Discordant patterns of mitonuclear introgression, which in the most extreme cases can result in mitogenome replacement even in the absence of measurable nuclear introgression, are well documented [6,7,8]. Furthermore, the evidence of historical hybrid zones that have moved or disappeared is often apparent from genetic traces of introgression in the extant populations of impacted species [9].
Introgression may be driven by deterministic factors. Natural selection may favor introgression of locally adapted mitogenomes when species encounter novel or extreme environments or drive genetic rescue when mitogenomes have accumulated mutation load [8,10,11,12]. Mitochondrial replacement also may be nonadaptive and driven by sex-biased fitness of hybrid offspring [12,13,14,15,16]. Alternatively, introgression may be driven as an outcome of range shifts and species invasion. When range shifts lead to invading species encountering congeneric species and engaging in hybridization, the outcome can lead to massive introgression in the genome of the invading species as a purely neutral demographic process [17,18].
Hybridization is common in fishes [19], and particularly prevalent in minnows and shiners of the family Leuciscidae [20,21,22]. Multi-species unguarded nesting behaviors are common among minnows and shiners [23] and are associated with high rates of hybridization [24]. Discordant mitonuclear introgression patterns have been extensively reported among fish species, with examples of complete mitogenome replacement at the population level reported in salmonids [25,26,27], cichlids [28], darters [29], killifishes [30,31,32], and shiners in the genus Luxilus [33].
The genus Luxilus comprises nine North American shiner species [34]. Studies have demonstrated the frequent occurrence of hybridization among sympatric Luxilus species [35,36,37], and members of the genus commonly spawn in heterospecific groups that can include multiple congeners [23,38]. Within the zone of extant sympatry between L. chrysocephalus and L. cornutus, mechanisms of reproductive isolation and the dynamics of hybridization vary among populations isolated in separate drainages [13,39,40]. In the Ozark Interior Highlands, outside the zone of extant species sympatry, historical hybrid introgression has resulted in L. chrysocephalus populations in drainages throughout the region appearing monomorphic for L. cornutus mitogenomes [33].
Recently, it was discovered that L. zonatus populations in some Ozark drainages exhibit L. chrysocephalus mitogenomes [41]. What makes this particularly noteworthy is that in the river drainages where L. zonatus exhibits L. chrysocephalus mitogenomes, the L. chrysocephalus populations themselves are monomorphic for L. cornutus mitogenomes [33], suggesting a complex history of hybridization, introgression, and serial mitogenome replacement among Luxilus species in the Ozarks [41]. The geographic extent of mitogenome introgression informs our understanding of the Pleistocene biogeography of aquatic riverine communities throughout the Ozark Highlands. Mitogenome introgression also has applied significance for the use of environmental DNA metabarcode detection techniques, which most often target mtDNA, and are dependent on accurate reference datasets for species detections and biodiversity assessments [42,43]. The objective of our study was to determine the geographic extent of mitogenome introgression among L. zonatus populations, determine which drainages were impacted, and interpret these introgression events in a historical phylogeographic context.
2. Materials and Methods
The genus Luxilus is a relatively common minnow found throughout the eastern United States, including the cornutus and zonatus species groups. The cornutus group comprises four species, L. chrysocephalus, L. cornutus, L. cerasinus, and L. albeolus [37]. Luxilus chrysocephalus is one of the most widely distributed members of this group with a range that spans the southern Great Lakes and the eastern two-thirds of the Mississippi River basin, as well as south into Gulf Coast drainages. Luxilus cornutus has a similarly large range but is more northern in its distribution, including the northwestern portion of the Mississippi River basin, through the Great Lakes basin, and extending east to Atlantic drainages from Nova Scotia to the mid-Atlantic coast. A zone of extant sympatry between the species spans drainages of the Great Lakes, the upper Illinois River, and portions of the upper Ohio River basin. The other two species of the group are more narrowly distributed in mid-Atlantic drainages, with L. albeolus ranging from the Roanoke River of Virginia, southward to the Cape Fear River of North Carolina, while L. cerasinus is found primarily in the Roanoke and New rivers.
There are three allopatric species in the L. zonatus species group, restricted mostly to the Ozark Highlands [44]. They include L. cardinalis in the Arkansas River drainage, L. pilsbryi in the White River drainage, and L. zonatus in Missouri and Mississippi River tributaries that drain the Ozarks, including the Osage, Gasconade, and Meramec River drainages in the northern Ozark Highlands, and the Black and St. Francis River drainages in the southeastern Ozark Highlands [44]. All three species in the L. zonatus complex are sympatric with L. chrysocephalus.
We sampled L. zonatus from eleven sites in each of five major Ozark river drainages where they are found, along with L. pilsbryi from three sites in the White River drainage, and L. cardinalis from two sites in the Arkansas River drainage (Table 1). Sample sizes for each species and collection site are reported in Table 2. Specimens were collected by seining moderate to strong flowing currents in the main channels of creeks and rivers. We also collected L. chrysocephalus from ten sites within the Ozark Highland study area (Table 1 and Table 2) and combined current with previously reported results [33] for the species in this region. Additional reference sequences of Luxilus species outside the Ozark Highlands study area were [34,45] obtained from GenBank (National Center for Biotechnology Information).

Table 1.
Ozark Highlands sample locations, drainages, and species collected.

Table 2.
Summary of numbers of individuals of each species exhibiting each mtDNA haplogroup (clade according to Figure 1) at each sampled site.
Fin clips were preserved in 95% ethanol (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and voucher specimens were preserved in 10% formalin ((ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). All specimens were identified to species based on diagnostic morphological features [38]. Ozark Highlands samples collected for this study were extracted using Blood and Tissue extraction columns (Qiagen, Venlo, The Netherlands). Subunit 2 of the NADH dehydrogenase gene (ND2) of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) exhibited sufficient interspecific variation to delineate relationships among species and major phylogenetic clades of members of the Luxilus genus. This region was isolated by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using primers designed from an L. chrysocephalus reference sequence using Geneious Prime 2024.0 (Dotmatics, Boston, MA, USA). The primers were LuxND2_4010F 5′-GCCCATACCCCGAACATGAC-3′ and LuxND2_5145R 5′-TCTGCTTAGAGCTTTGAAGGCT-3′. PCR was conducted combining 1 ng DNA and 1 µM each primer with Thermo Scientific PCR Master Mix (2×) (Thermo Fischer, Waltham, MA, USA), and cycling conditions of an initial denaturing step at 95 °C for 4 min, 35 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 58 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 45 s, followed by 72 °C for 4 min. PCR products were prepared for Sanger Sequencing using HighPrep PCR magnetic beads (Magbio Genomics, Gaithersburg, MD, USA). Sanger Sequencing of forward and reverse strands was conducted at the MU Genomic Technology Core (https://mugenomicscore.missouri.edu/, accessed on 20 August 2025) using the PCR primers. Chromatograms were assembled and aligned using Geneious Prime 2024.0 (Dotmatics, Boston, MA, USA). Additional samples of Luxilus species were provided from unpublished archived sequences (T.E. Dowling) prepared using similar PCR and Sanger sequencing methods as previously described [34].
A phylogeny was generated using the maximum likelihood (ML) method employed in the IQ-TREE web server (https://iqtree.github.io/, accessed on 20 August 2025) [46]. The appropriate substitution model (GTR + F + I + G4) was selected based on the Akaike information criterion by employing ModelFinder [47], and the ML algorithm was run for 1000 bootstrap replicates. Internal node support was assessed using the ultrafast bootstrap and the aBayes tests [46]. Notropis atherinoides was selected as the outgroup for the genus Luxilus based on Ref. [48]. Nucleotide diversity (π) and nucleotide divergence (Dxy) parameters were estimated from ND2 sequence alignments using DnaSP 6.12.03 [49].
Molecular divergence times of mitochondrial lineages were estimated with a Bayesian analysis using the suite of programs from BEAST 2.7.8 [50] and reported as mean divergence time +/− 95% HPDs. Fossil-based calibration is confounded in Leuciscids by a poor fossil record. Therefore, we conservatively employed a uniform prior distribution of divergence rates to generate estimates of divergence time. This approach has been developed by examining a diversity of fossils to generate molecular estimates of divergence time for a variety of minnows and suckers [51,52,53,54,55]. Estabrook et al. [56] reported a relationship between body size and rates of mtDNA evolution in fishes, leading to development of a general relationship between body mass and rates of mtDNA evolution for minnows and suckers [53]. Luxilus minnows (3–100 g) lie at the low end of the size range for the family, with a corresponding expected rate of 2.5–3.5% pairwise divergence per million years [56]. Input files were generated using BEAUti 2 and the Bayesian analysis was run with a species tree relaxed clock with a log-normal rate distribution spanning the rate range reported by Smith and Larson. Analyses were run for 20 million generations with parameters logged every 1000 generations. Multiple runs were conducted, and outputs were examined in Tracer 1.7.2 [57] to verify that key parameters had effective sample sizes of 200 or greater. Log and tree files from four runs were combined using LogCombiner 2.7.3 [57] with a 10% burnin. Mean age estimates and topology were based on the maximum clade credibility using common ancestor heights from our combined trees using TreeAnnotator 2.7.3 and the tree was visualized in FigTree 1.4.4.
3. Results
A mtDNA ML phylogeny (Figure 1) was consistent with previously reported species relationships in the genus Luxilus [34,48], with most labeled nodes achieving 100% bootstrap and 1.0 posterior probability (100/1) support (Figure 1). Samples of the L. zonatus group (L. pilsbryi, L. cardinalis, and L. zonatus) formed a monophyletic clade (100/1). Within the L. zonatus species group, L. cardinalis and L. pilsbryi were most closely related (98/1), followed by L. zonatus as expected [34,44]. However, among morphologically identified L. zonatus populations, the L. zonatus mtDNA haplogroup was only found in specimens from a portion of its range, in the Black/Current River drainage (Table 2, Figure 2A).
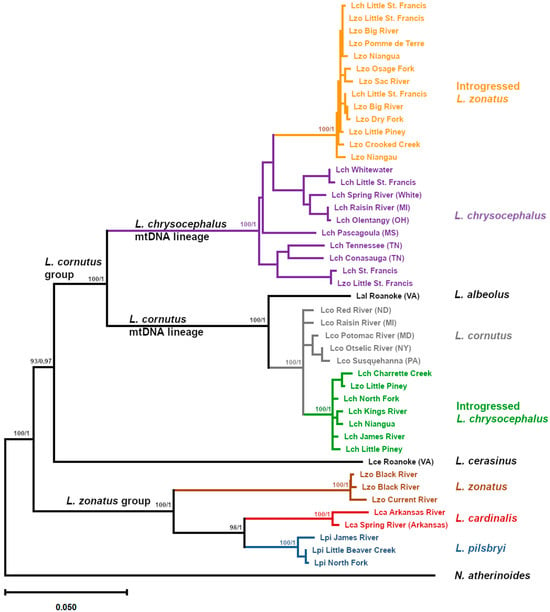
Figure 1.
Maximum Likelihood phylogeny of mitochondrial ND2 sequences of Luxilus spp. identified by sample location (Table 1). Morphological species abbreviations: L. chrysocephalus Lch, L. cornutus Lco, L. zonatus Lzo, L. cardinalis Lca, L. pilsbryi Lpi, L. albeolus Lal, L. cerasinus Lce. Clades are labeled according to predominant species and highlighted by separate colors. Reference specimens from outside the Ozark Highlands are identified by drainage and state, and duplicate river names are clarified by corresponding drainage. The L. cornutus and L. zonatus groups, and nested L. chrysocephalus and L. cornutus mtDNA lineages are labeled along interior branches, and bootstrap support and aBayes posterior probabilities are shown at labeled clade interior nodes. Notropis atherinoides was used as the outgroup.
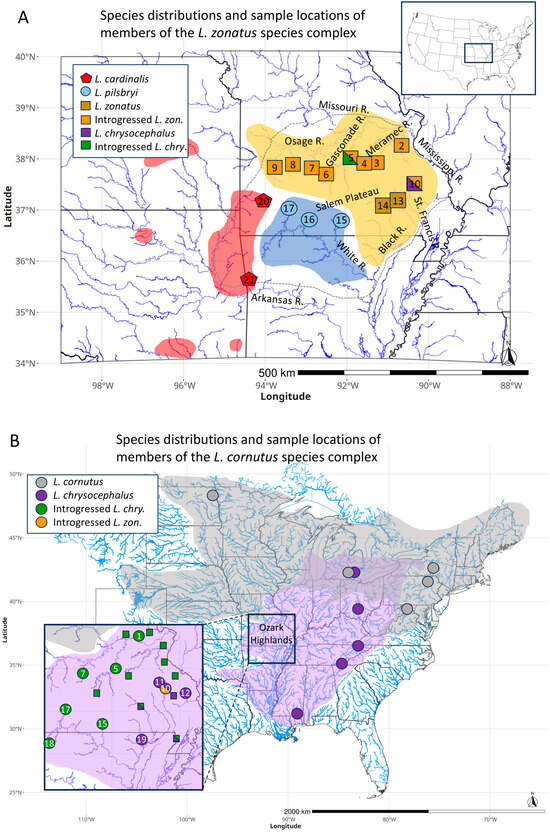
Figure 2.
Distribution of species and mitochondrial linages for morphologically assigned members of the (A) L. zonatus group and (B) L. cornutus group. Shaded areas delineate species distributions, and symbols with colors indicate mitochondrial lineages. Split symbols indicate sample mitochondrial polymorphism. Numbered sample locations are identified according to Table 1. The dotted line in (A) marks the boundary of the Ozark Interior Highlands. Small square symbols in (B) reproduce data first reported in Ref. [33]. Mitochondrial lineage colors match clades in Figure 1.
The cornutus group, excluding L. cerasinus (i.e., L. cornutus, L. albeolus, and L. chrysocephalus), formed a second monophyletic clade (100/1), with Luxilus cerasinus sister to the rest of the cornutus group (93/0.97). There were two mtDNA lineages within the cornutus group, one contained the L. cornutus mtDNA lineage, including L. albeolus (100/1) while the other contained the L. chrysocephalus mtDNA lineage (100/1).
Comparison of mtDNA results with morphological species assignments identified considerable introgression among these taxa. A well-defined mtDNA lineage of morphologically identified L. zonatus (100/1) was nested within the range-wide L. chrysocephalus mtDNA lineage, indicating that this distinct lineage (hereafter ‘introgressed L. zonatus’) resulted from mitochondrial introgression from L. chrysocephalus into L. zonatus. These morphologically identified introgressed L. zonatus were from the St. Francis, Meramec, Gasconade, and Osage river drainages. Most individuals sampled from these populations exhibited the introgressed L. zonatus mtDNA haplogroup (Table 2). The paraphyletic L. chrysocephalus range-wide mtDNA clade, exclusive of introgressed L. zonatus, exhibited nucleotide diversity (π) of 0.033. Nucleotide diversity for the monophyletic introgressed L. zonatus lineage was nearly an order of magnitude lower at 0.004.
The L. cornutus mtDNA haplogroup also exhibited evidence of introgression as previously reported [33]. Sampled populations of morphologically identified L. chrysocephalus from drainages throughout the northern Ozark Highlands, as well as the White River drainage in the southern Ozark Highlands, all exhibited a monophyletic clade of introgressed mtDNA (100/1) derived from L. cornutus (hereafter ‘introgressed L. chrysocephalus’) (Table 2, Figure 2B), rendering the range-wide L. cornutus clade paraphyletic. The L. cornutus clade (exclusive of the introgressed L. chrysocephalus clade) exhibited nucleotide diversity of 0.010 compared to 0.006 for the introgressed L. chrysocephalus clade. Samples of morphologically identified L. chrysocephalus taken from the St. Francis River and Whitewater River exhibited range-wide L. chrysocephalus haplotypes, while the Little St. Francis River sample included both range-wide L. chrysocephalus and introgressed L. zonatus haplotypes (Table 2, Figure 2B).
Among all sampled L. zonatus individuals, the only ones that did not exhibit the L. zonatus haplogroup or the here-defined introgressed L. zonatus haplogroup were one individual in the Little Piney, a tributary of the Gasconade River, which exhibited an introgressed L. chrysocephalus haplotype, and one L. zonatus individual from the Little St. Francis River exhibiting an L. chrysocephalus haplotype (Table 2, Figure 2A).
Our Bayesian phylogenetic analysis yielded the same tree topology as the ML analysis, with the exception that there was weak evidence for reciprocal monophyly between L. cornutus and introgressed L. chrysocephalus sequences (Figure 3). This calibrated phylogeny exhibited very large HPD confidence intervals in part due to calibration uncertainty built into the analysis. Nevertheless, confidence intervals placed the coalescent ages of most clades of interest within the Pleistocene (2.6 to 0.01 Ma). Our analysis placed the most likely age of the most recent shared ancestor between L. cornutus and L. chrysocephalus as pre-Pleistocene, at 5.05 Ma (0.61–11.77 Ma), and the L. zonatus group (L. zonatus, L. pilsbryi, L. cardinalis) at 4.75 Ma (0.59–11.07) (Figure 3). The coalescent age of all samples in the L. chrysocephalus mtDNA lineage was 1.98 Ma (0.24–4.62 Ma), and the introgressed L. zonatus clade within the L. chrysocephalus mtDNA lineage was 0.30 Ma (0.03–0.72 Ma). Nucleotide divergence (Dxy) between the introgressed L. zonatus clade and the next most closely related L. chrysocephalus haplotype was 0.049 with an estimated age of 1.52 Ma (0.16–3.57 Ma). The age of the ancestor of the L. cornutus and introgressed L. chrysocephalus mtDNA lineage (i.e., excluding L. albeolus) was 0.73 Ma (0.07–1.72 Ma), with an age for the nested range-wide L. cornutus clade estimated at 0.42 Ma (0.04–1.02 Ma), and the introgressed L. chrysocephalus clade estimated at 0.31 Ma (0.03–0.74 Ma), respectively.
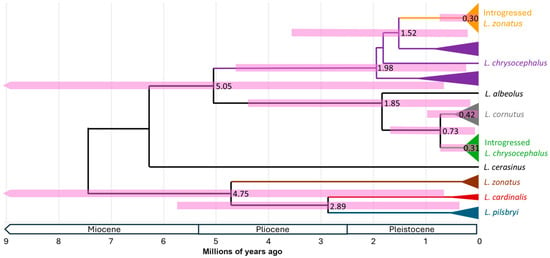
Figure 3.
Time-calibrated phylogeny resulting from Bayesian analysis in BEAST. Mean ages are shown at each node, and horizontal bars present the 95% highest posterior density (HPD) intervals for the estimated divergence times. Clade colors match those in Figure 1.
4. Discussion
Discordant mitonuclear introgression has been widely documented in many organisms [6,8,10,11]. The features that make our study exceptional are, first, that mitogenome replacement appears to have occurred twice in succession involving three congeneric shiner species. Second, the ranges of impacted populations in the two affected species are largely congruent and cover multiple isolated drainages that span the northern and eastern Ozark Highlands. The phylogeographic patterns of mitogenome introgression of both L. chrysocephalus and L. zonatus require at least two separate incidences of mitonuclear introgression that are Pleistocene in age, leading to mitogenome replacement in ancestral populations of both species. The broad, congruent geographic overlap of impacted populations, involving numerous Ozark Highland drainages, may reflect the impact of shifting distributions of both species associated with Pleistocene glacial cycles, and coincident with Ozark Highlands geomorphological processes. These results inform our understanding of Pleistocene biogeography of Ozark Highland riverine systems and have applied significance for the use of environmental DNA metabarcoding applications in Ozark Highland streams [58].
Glaciation in North America west of the present-day Mississippi River valley was marked by the Laurentide Ice Sheet advancing as far south as the vicinity of the Missouri River Valley at the northern edge of the unglaciated Ozark Highlands. Five glacial advances occurred in this region prior to the Illinoian stage at approximately 2.4, 1.3, 0.8, 0.4, and 0.2 Ma [59]. These events modified the course of rivers in the region, pushing the range of affected species southward [60]. Periglacial lakes along the glacial front would have increased in size as glaciers melted. This would have also increased connection of periglacial lakes along the glacial front, and overflow of meltwater may have allowed for east–west dispersal of fishes along the northern border region of the Ozark Highlands [60].
The major drainages of the Ozark Highlands radiate out of the Salem Plateau. Biogeographically, drainages north of the Salem Plateau (e.g., Osage, Gasconade, Meramec) have similar ichthyofaunal species assemblages that differ in notable respects from drainages south of the Salem Plateau (e.g., St. Francis, Black, White). These biogeographic differences are evident in some Leuciscids (Campostoma spp., Cyprinella spp., Notropis spp.), Centrarchids (Ambloplites spp., Lepomis spp.), Ictalurids (Noturus spp.) [38], and phylogeography of the Etheostoma caeruleum [61], and Etheostoma spectabile [29] complexes. There is also evidence that connections occurred occasionally between drainages that were otherwise isolated by the Salem Plateau. A population genetic study of the topminnow, Fundulus olivaceus, identified gene flow between the Big and St. Francis rivers, the Meramec and Black rivers, the Big Piney and North Fork rivers, and the Meramec and Gasconade rivers [62]. Study of fluvial geomorphology in the Ozark Highlands offers evidence that headwaters on opposite sides of the Salem Plateau have commingled historically through numerous stream capture events [63], creating opportunities for faunal exchanges among drainages.
The L. zonatus species group (L. cardinalis, L. pilsbryi, and L. zonatus) diversified in isolated drainages, likely beginning in the Pliocene (common ancestor estimated here at 4.7 Ma), and the phylogeographic distribution of these three species is consistent with their origin in the southern Ozark Highlands, followed by a range expansion of L. zonatus into the more northern drainages within its range. Those northern L. zonatus populations appear monophyletic for the introgressed mitogenome acquired from L. chrysocephalus. Among L. zonatus populations, mitogenome introgression has impacted at least four of the five major Ozark drainages encompassed by the extant species distribution, such that, range-wide, far more L. zonatus individuals exhibit introgressed than non-introgressed mitogenomes. The distribution of mitogenome replacement in northern L. zonatus populations is consistent with massive introgression predicted by an invasion-with-hybridization model [18] driven by demographic inequality at a northward invasion front. According to this prediction, as L. zonatus expanded its range into eastern and northern portions of the Ozark Highlands where L. chrysocephalus was already present, the demographic inequality alone between resident and invading populations could have been sufficient to drive asymmetric mtDNA introgression [17,18]. The reduced nucleotide diversity and monophyly of the introgressed L. zonatus clade relative to other range-wide L. chrysocephalus haplotypes may indicate that this mitogenome replacement event coincided with a founder event initially within a small geographic region (e.g., within one drainage) and then expanded into other drainages through continued L. zonatus range expansion. The broad extant syntopy of L. zonatus and L. chrysocephalus throughout the Ozark Highlands suggests a northward expansion of L. zonatus without competition or species replacement.
The age of the split between L. cornutus and L. chrysocephalus is similarly dated to the Pliocene (5.05 Ma). With a northern L. cornutus range that was almost completely formerly glaciated, the presence of introgressed L. cornutus mitogenomes in Ozark L. chrysocephalus populations provides evidence for range overlap within or in the vicinity of the Ozark Highlands at least sometime during the Pleistocene [33]. The divergence between introgressed haplotypes found in Ozark L. chrysocephalus and the range-wide L. cornutus species haplogroup is dated to approximately mid-late Pleistocene (0.73 Ma). Evidence that hybrid introgression resulted in L. chrysocephalus mitogenome replacement from an L. cornutus donor spans all drainages originating in the Ozark Highlands, with most drainages appearing monophyletic for the introgressed haplogroup, and only drainages in the southeastern Ozark Highlands (Black, St. Francis, and Whitewater Rivers) exhibiting predominantly non-introgressed L. chrysocephalus mitogenomes [33].
Our phylogenetic analysis shows that, after introgression, range-wide L. cornutus and introgressed Ozark L. chrysocephalus populations achieved comparable levels of nucleotide diversity, suggesting that an L. cornutus range-wide expansion was similarly Pleistocene in age and occurred on a similar time frame to when the Ozark L. chrysocephalus introgression event occurred. The relatively limited range-wide nucleotide diversity in the northerly distributed L. cornutus compared to the more southerly distributed L. chrysocephalus is consistent with contrasting and disproportionate impacts of Pleistocene glaciation on these species in their respective extant latitudinal distributions.
The notable feature of these overlapping patterns of introgression is that in multiple drainages where L. zonatus appears monomorphic for an introgressed haplogroup from an L. chrysocephalus donor, sympatric L. chrysocephalus populations appear monomorphic for a different introgressed haplogroup from an L. cornutus donor. This dual mitogenome replacement pattern was observed in all drainages north of the Salem Plateau, including all samples in the Osage, Gasconade, and Meramec River drainages. The coalescent ages of the introgressed L. chrysocephalus and L. zonatus haplogroup clades are both pre-Illinoian late Pleistocene, and with essentially the same age estimates (310 and 297 kya, respectively), suggesting that introgressed populations of both species may have established nearly concurrently via either range expansions or gene flow. However, L. zonatus introgression would have had to precede L. chrysocephalus introgression, or else introgressed L. zonatus populations would exhibit L. cornutus-lineage haplotypes instead of L. chrysocephalus-lineage haplotypes.
The phylogeographic distribution of mitogenome replacement events across multiple isolated drainages may suggest a deterministic driver operating similarly in separate drainages throughout the Ozark Highlands. However, the concurrent prevalence of introgressed mitogenomes in populations of both L. chrysocephalus and L. zonatus presents challenges to the invocation of natural selection as a driving factor. If mitogenome replacement was prevalent across multiple Ozark drainages because natural selection favored introgression of locally adapted mitogenomes in both species, then this does not account for why natural selection would favor different non-native mitogenomes in sympatric populations of each species. Similarly, if the driver of selection favoring introgressed mitogenomes was to alleviate some form of accumulated mutation load, as might have been caused by founder effects resulting from shifting ranges driven by glacial cycles, then that would not address the multi-drainage pattern of introgression or explain why introgressed mitogenomes were more fit than native mitogenomes in both species. A population genetic study of nuclear genetic variation could detail population relationships, and historical patterns of connection and gene flow among drainages, detect nuclear introgression if it has occurred, and inform hypotheses regarding the role of natural selection as a driver of introgression in this system.
Distributions of mitochondrial haplogroups between L. zonatus and L. chrysocephalus are further complicated in the St. Francis River drainage in the southeastern Ozark Highlands. The L. chrysocephalus sampled in the St. Francis River drainage in this study exhibited exceptional mitochondrial sequence diversity that reflected the entire range-wide mitogenome diversity of L. chrysocephalus (Figure 1). Results reported here are consistent with those reported by Ref. [33] except that the earlier study relied on a PCR-RFLP assay that only resolved L. cornutus and L. chrysocephalus mtDNA lineages, and did not delineate differences between the introgressed L. zonatus haplogroup and all other range-wide L. chrysocephalus haplotypes.
In the Little St. Francis River, both L. zonatus and L. chrysocephalus were polymorphic for L. chrysocephalus haplotypes, including a predominance of the introgressed L. zonatus haplogroup in both species. The prevalence of the introgressed L. zonatus haplogroup could be indicative of an ancestral polymorphism in the Little St. Francis L. chrysocephalus population that has been shared with L. zonatus through introgressive hybridization. The St. Francis River L. chrysocephalus could be the source of the introgressed L. zonatus haplogroup that subsequently expanded into other Ozark Highland drainages. Alternatively, the shared mitochondrial polymorphisms between L. zonatus and L. chrysocephalus in the Little St. Francis River could indicate more recent, ongoing hybridization between the species. Though the morphologies of L. zonatus and L. chrysocephalus are distinct [38], the use of morphological traits for assigning species has limitations. The identification of hybrids, and particularly, multi-generation backcross individuals, requires nuclear genetic data [20,64,65]. Further sampling within this drainage, and particularly, the inclusion of nuclear genetic data, is needed before conclusions can be drawn regarding historical phylogeography versus ongoing hybridization. Either way, this level of interspecies haplogroup sharing is distinctive within this system and was not encountered to the same extent in other drainages. In the Osage, Gasconade, and Meramec drainages, where L. chrysocephalus and L. zonatus are syntopic and both essentially monomorphic for introgressed haplogroups, there is little evidence of recent or ongoing hybridization between the species beyond the St. Francis River drainage, except for one L. zonatus individual from Little Piney Creek in the Gasconade River drainage that exhibited the introgressed L. chrysocephalus mitogenome.
5. Conclusions
The concurrent patterns of mitogenome introgression among Luxilus species within the Ozark Highlands offer an exceptional example of mitonuclear discordance impacting multiple species and provide unique insights into Pleistocene-era impacts of gene flow and range shifts driven or facilitated by glacial advances and geomorphological processes occurring in the Ozark Highlands during this period. Furthermore, these results have applied significance for the establishment of accurate reference database sequences used in environmental DNA metabarcoding throughout the Ozark Highlands region.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.D.D. and T.E.D.; data curation, D.D.D.; formal analysis, D.D.D. and A.J.W.; funding acquisition, D.D.D. and T.E.D.; investigation, D.D.D., C.A. and S.K.; project administration, D.D.D.; writing—original draft, D.D.D.; writing—review and editing, A.J.W. and T.E.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by institutional funds from MST and WSU. Some samples were funded by previous NSF awards to TED. This study was initiated as part of an effort to build an eDNA metabarcoding database for Missouri under cooperative agreement no. 460 to DDD with the Missouri Department of Conservation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Missouri University of Science and Technology (No. 182-21, 4 June 2021). Fish specimens were collected under the issuance of a Wildlife Collector Permit from the Missouri Department of Conservation (Permit No. 64265, 14 February 2024).
Data Availability Statement
All DNA sequences are available in GenBank under accession numbers PV549218-PV549283, OR552081, AP012079, EF613564, MG570447, MT667242, NC084090, NC033925, OR552079, and OR492267.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the Opportunities for Undergraduate Research Experiences program run in the Experiential Learning Office at the Missouri University of Science and Technology for supporting CA and SK.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| mtDNA | Mitochondrial DNA |
| ML | Maximum Likelihood |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RFLP | Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism |
| HPD | Highest Posterior Density |
References
- Arnold, M.L. Natural Hybridization and Evolution; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, T.E.; Secor, C.L. The Role of Hybridization and Introgression in the Diversification of Animals. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1997, 28, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, N.B.; Mallet, J. Prevalence and Adaptive Impact of Introgression. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2025, 55, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, P.W. Adaptive Introgression in Animals: Examples and Comparison to New Mutation and Standing Variation as Sources of Adaptive Variation. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 4606–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, J. Hybridization as an Invasion of the Genome. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toews, D.P.L.; Brelsford, A. The Biogeography of Mitochondrial and Nuclear Discordance in Animals. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3907–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, V.A.; Lavrenchenko, L.A. Approaches to the Detection of Hybridization Events and Genetic Introgression upon Phylogenetic Incongruence. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2022, 12, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, T.; Leblois, R.; Rousset, F.; Crochet, P.A. A Reassessment of Explanations for Discordant Introgressions of Mitochondrial and Nuclear Genomes. Evolution 2017, 71, 2140–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielstra, B. Historical Hybrid Zone Movement: More Pervasive than Appreciated. J. Biogeogr. 2019, 46, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, D.B.; Havird, J.C.; Sharbrough, J. The On-Again, off-Again Relationship between Mitochondrial Genomes and Species Boundaries. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 2212–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, G.E. Reconciling the Mitonuclear Compatibility Species Concept with Rampant Mitochondrial Introgression. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2019, 59, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, R.S. The Role of Mitonuclear Incompatibilities in Allopatric Speciation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, T.E.; Hoeh, W.R. The Extent of Introgression Outside the Contact Zone between Notropis cornutus and Notropis chrysocephalus (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Evolution 1991, 45, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, A.S.; Loggins, R.; Kumar, S.; Dowling, T.E. Does Nonneutral Evolution Shape Observed Patterns of DNA Variation in Animal Mitochondrial Genomes? Annu. Rev. Genet. 2001, 35, 539–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacPherson, N.; Champion, C.P.; Weir, L.K.; Dalziel, A.C. Reproductive Isolating Mechanisms Contributing to Asymmetric Hybridization in Killifishes (Fundulus spp.). J. Evol. Biol. 2023, 36, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfennig, K.S. Biased Hybridization and Its Impact on Adaptive Introgression. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielstra, B.; Arntzen, J.W. Postglacial Species Displacement in Triturus Newts Deduced from Asymmetrically Introgressed Mitochondrial DNA and Ecological Niche Models. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currat, M.; Ruedi, M.; Petit, R.J.; Excoffier, L. The Hidden Side of Invasions: Massive Introgression by Local Genes. Evolution 2008, 62, 1908–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbs, C.L. Society of Systematic Biologists Hybridization between Fish Species in Nature. Syst. Zool. 1955, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbinden, Z.D.; Douglas, M.R.; Chafin, T.K.; Douglas, M.E. A Community Genomics Approach to Natural Hybridization. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 290, 20230768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribner, K.T.; Page, K.S.; Bartron, M.L. Hybridization in Freshwater Fishes: A Review of Case Studies and Cytonuclear Methods of Biological Inference. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2001, 10, 293–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuser, A.V.; Pitura, A.R.; McFarlane, S.E.; Mandeville, E.G.D. Extensive multi-species hybridization between Leuciscidae minnow species. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, O.; Kvarnemo, C. How Sexual and Natural Selection Interact and Shape the Evolution of Nests and Nesting Behaviour in Fishes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 378, 20220139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corush, J.B.; Fitzpatrick, B.M.; Wolfe, E.L.; Keck, B.P. Breeding Behaviour Predicts Patterns of Natural Hybridization in North American Minnows (Cyprinidae). J. Evol. Biol. 2021, 34, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.C.; Bernatchez, L. The Ghost of Hybrids Past: Fixation of Arctic Charr (Salvelinus alpinus) Mitochondrial DNA in an Introgressed Population of Lake Trout (S. namaycush). Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doiron, S.; Bernatchez, L.; Blier, P.U. A Comparative Mitogenomic Analysis of the Potential Adaptive Value of Arctic Charr MtDNA Introgression in Brook Charr Populations (Salvelinus fontinalis Mitchill). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1902–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englmaier, G.K.; Rodríguez, N.V.; Bravničar, J.; Zangl, L.; Persat, H.; Marić, S.; Ratschan, C.; Delling, B.; Gonçalves, D.V.; Secci-Petretto, G.; et al. SNP-Based Analysis of European Thymallus spp. (Salmonidae) Reveals Extensive Mito-Nuclear Discordance Relevant for Biogeographic Inferences, Taxonomy and Conservation. Divers. Distrib. 2024, 30, e13845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevado, B.; KoblmÜller, S.; Sturmbauer, C.; Snoeks, J.; Usano-Alemany, J.; Verheyen, E. Complete Mitochondrial DNA Replacement in a Lake Tanganyika Cichlid Fish. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4240–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossu, C.M.; Near, T.J. Gene Trees Reveal Repeated Instances of Mitochondrial DNA Introgression in Orangethroat Darters (Percidae: Etheostoma). Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvernell, D.D.; Schaefer, J.F. Variation in Contact Zone Dynamics between Two Species of Topminnows, Fundulus notatus and F. olivaceus, across Isolated Drainage Systems. Evol. Ecol. 2014, 28, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbel-Filho, W.M.; Pacheco, G.; Tatarenkov, A.; Lira, M.G.; Garcia de Leaniz, C.; Rodríguez López, C.M.; Lima, S.M.Q.; Consuegra, S. Phylogenomics Reveals Extensive Introgression and a Case of Mito-Nuclear Discordance in the Killifish Genus Kryptolebias. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2022, 177, 107617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, E.W.; Dowling, T.E. Influence of Hydrogeographic History and Hybridization on the Distribution of Genetic Variation in the Pupfishes Cyprinodon atrorus and C. bifasciatus. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvernell, D.D.; Aspinwall, N. Introgression of Luxilus cornutus MtDNA into Allopatric Populations of Luxilus chrysocephalus (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in Missouri and Arkansas. Mol. Ecol. 1995, 4, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, T.E.; Naylor, G.J.P. Evolutionary Relationships of Minnows in the Genus Luxilus (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) as Determined from Cytochrome b Sequences. Copeia 1997, 1997, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, T.E.; Moore, W.S. Level of Reproductive Isolation between Two Cyprinid Fishes, Notropis cornutus and N. chrysocephalus. Copeia 1984, 1984, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, T.E.; Smith, G.R.; Brown, W.M. Reproductive Isolation and Introgression between Notropis cornutus and Notropis chrysocephalus (Family Cyprinidae): Comparison of Morphology, Allozymes, and Mitochondrial DNA. Evolution 1989, 43, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, S.; Dowling, T.E. Hybridization between the Cyprinid Fishes Luxilus albeolus, L. cornutus, and L. cerasinus with Comments on the Proposed Hybrid Origin of L. albeolus. Copeia 1991, 1991, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflieger, W.L. The Fishes of Missouri, 2nd ed.; Missouri Department of Conservation: Jefferson City, MO, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, C.A.; Berra, T.M. Demonstration of Reproductive Isolation and Observation of Mismatings in Luxilus. Copeia 1993, 1993, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, T.E.; Broughton, R.E.; Demarais, B.D. Significant Role for Historical Effects in the Evolution of Reproductive Isolation: Evidence from Patterns of Introgression between the Cyprinid Fishes, Luxilus cornutus and Luxilus chrysocephalus. Evolution 1997, 51, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halas, D. Assessing the Prevalence of Common Patterns and Unique Events in the Formation of Biotas: A Study of Fish Taxa of the North American Central Highlands. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Campbell, T.; McElroy, M.E.; Pin, K.; Childress, J.N.; Armstrong, M.N.; Zehnpfennig, J.R.; Kelson, S.J.; Koning, A.A.; et al. Are Genetic Reference Libraries Sufficient for Environmental DNA Metabarcoding of Mekong River Basin Fish? Water 2021, 13, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, E.; Sidlauskas, B.; Cronn, R.; Anthony, J.; Cornwell, T.; Friesen, T.A.; Konstantinidis, P.; Penaluna, B.E.; Stein, S.; Levi, T. Creating, Curating and Evaluating a Mitogenomic Reference Database to Improve Regional Species Identification Using Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 23, 1880–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayden, R.L. Systematics of the Notropis zonatus Species Group, with Description of a New Species from the Interior Highlands of North America. Copeia 1988, 1988, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, T.E.; Hoeh, W.R.; Smith, G.R.; Brown, W.M. Evolutionary Relationships of Shiners in the Genus Luxilus (Cyprinidae) as Determined by Analysis of Mitochondrial DNA. Copeia 1992, 1992, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A Fast Online Phylogenetic Tool for Maximum Likelihood Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, C.; Schonhuth, S.; Mayden, R.; Garrison, N.L.; Armbruster, J.W. Phylogenomics and Classification of Notropis and Related Shiners (Cypriniformes: Leuciscidae) and the Utility of Exon Capture on Lower Taxonomic Groups. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sanchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sanchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchêne, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kühnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An Advanced Software Platform for Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.R.; Dowling, T.E.; Gobalet, K.W.; Lugaski, T.; Shiozawa, D.K.; Evans, R.P. Biogeography and Rates of Evolution of Great Basin Fishes. In Great Basin Aquatic Systems History; Her, R., Madsen, D.B., Currey, D.R., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 175–234. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, G.R.; Dowling, T.E. Correlating Hydrographic Events and Divergence Times of Speckled Dace (Rhinichthys: Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in the Colorado River Drainage. In Proceedings of the Special Paper of the Geological Society of America; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008; Volume 439, pp. 301–317. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, J.E.; Smith, G.R.; Dowling, T.E. Middle to Late Cenozoic Geology, Hydrography, and Fish Evolution in the American Southwest. In Proceedings of the Special Paper of the Geological Society of America; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008; Volume 439, pp. 279–299. [Google Scholar]
- Unmack, P.J.; Dowling, T.E.; Laitinen, N.J.; Secor, C.L.; Mayden, R.L.; Shiozawa, D.K.; Smith, G.R. Influence of Introgression and Geological Processes on Phylogenetic Relationships of Western North American Mountain Suckers (Pantosteus, Catostomidae). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.R.; Chow, J.; Unmack, P.J.; Markle, D.F.; Dowling, T.E.; Arbor, A. Evolution of the Rhinichthys osculus Complex (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in Western North America. In Fishes of the Mio-Pliocene Western Snake River Plain and Vicinity; Miscellaneous Publications Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 45–84. [Google Scholar]
- Estabrook, G.F.; Smith, G.R.; Dowling, T.E. Body Mass and Temperature Influence Rates of Mitochondrial DNA Evolution in North American Cyprinid Fish. Evolution 2007, 61, 1176–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis by Sampling Trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.M.; Berkman, L.K.; Geheber, A.D.; Landwer, B.; Ludwig, E.J.; Duvernell, D.D. Putting EDNA to the Test: A Field Comparison of EDNA Metabarcoding to Established Protocols for Assessing Biodiversity in Missouri’s Ozark Highland Streams. Environ. DNA 2024, 6, e510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovey, C.W.I.; Balco, G. Summary of Early and Middle Pleistocene Glaciations in Northern Missouri, USA. In Developments in Quarternary Sciences; Ehlers, J., Gibbard, P.L., Hughes, P.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 15, pp. 553–561. [Google Scholar]
- Robison, H.W. Zoogeographic Implications of the Mississippi River Basin. In The Zoogeography of North American Freshwater Fishes; Hocutt, E.H., Wiley, E.O., Eds.; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 267–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, J.M.; Wood, R.M.; Simons, A.M. Phylogeography and Post-Glacial Colonization Patterns of the Rainbow Darter, Etheostoma caeruleum (Teleostei: Percidae). J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvernell, D.D.; Westhafer, E.; Schaefer, J.F. Late Pleistocene Range Expansion of North American Topminnows Accompanied by Admixture and Introgression. J. Biogeogr. 2019, 46, 2126–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeson, H.W.; McCoy, S.W.; Keen-Zebert, A. Geometric Disequilibrium of River Basins Produces Long-Lived Transient Landscapes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 475, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbins, M.S.; Hahn, M.W. Phylogenomic Approaches to Detecting and Characterizing Introgression. Genetics 2022, 220, iyab173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teletchea, F. Molecular Identification Methods of Fish Species: Reassessment and Possible Applications. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2009, 19, 265–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).