Bioactive Substance Derived from Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor) Potentially Induces Immune Performance of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Analysis
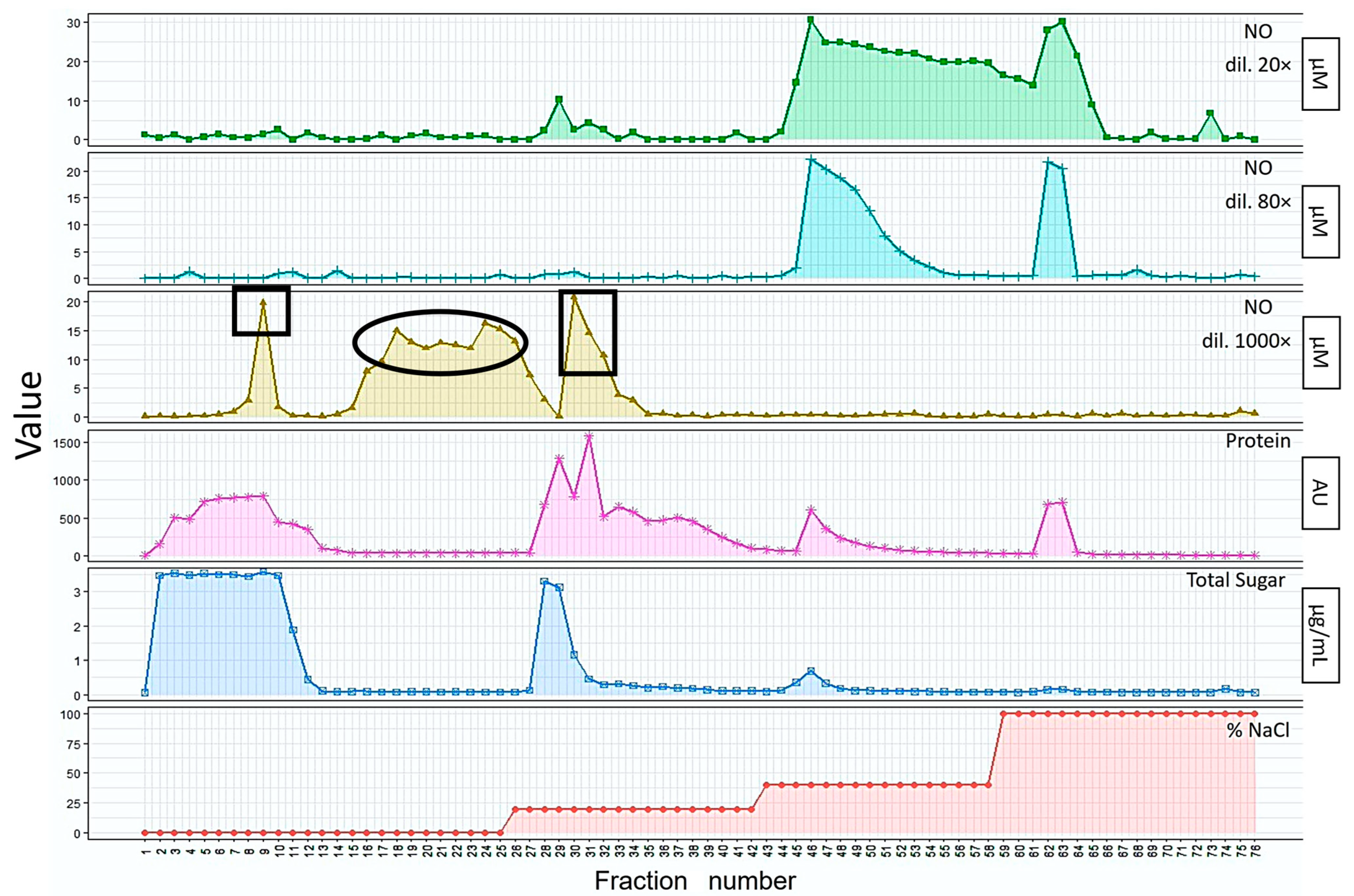
2.1.1. Extraction and Isolation of Bioactive Substances from Mealworm Larvae
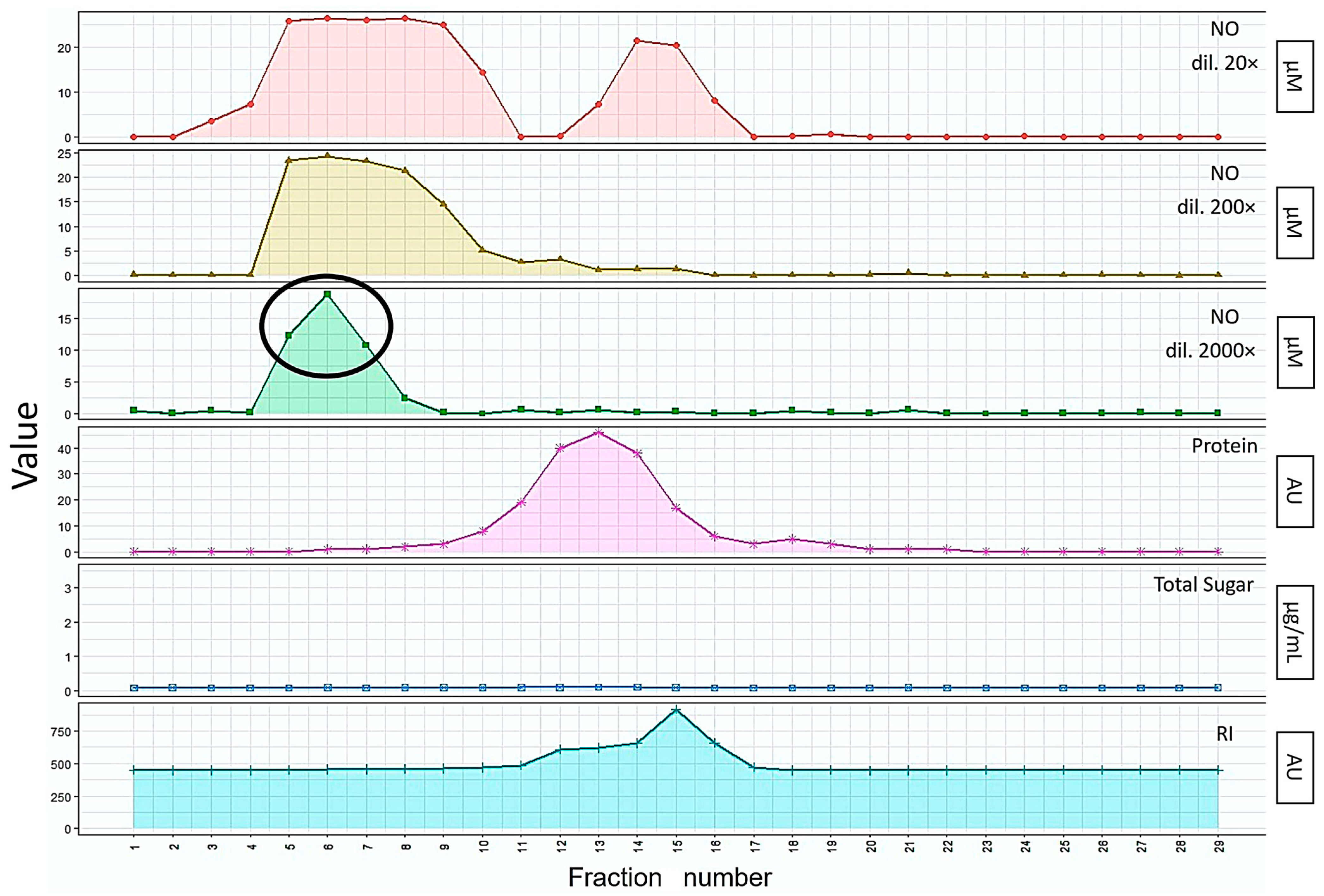
2.1.2. Purification of Bioactive Substances from Mealworm Larvae Extract
2.1.3. RAW264.7 Cell Culture
2.1.4. NO Activity Assay
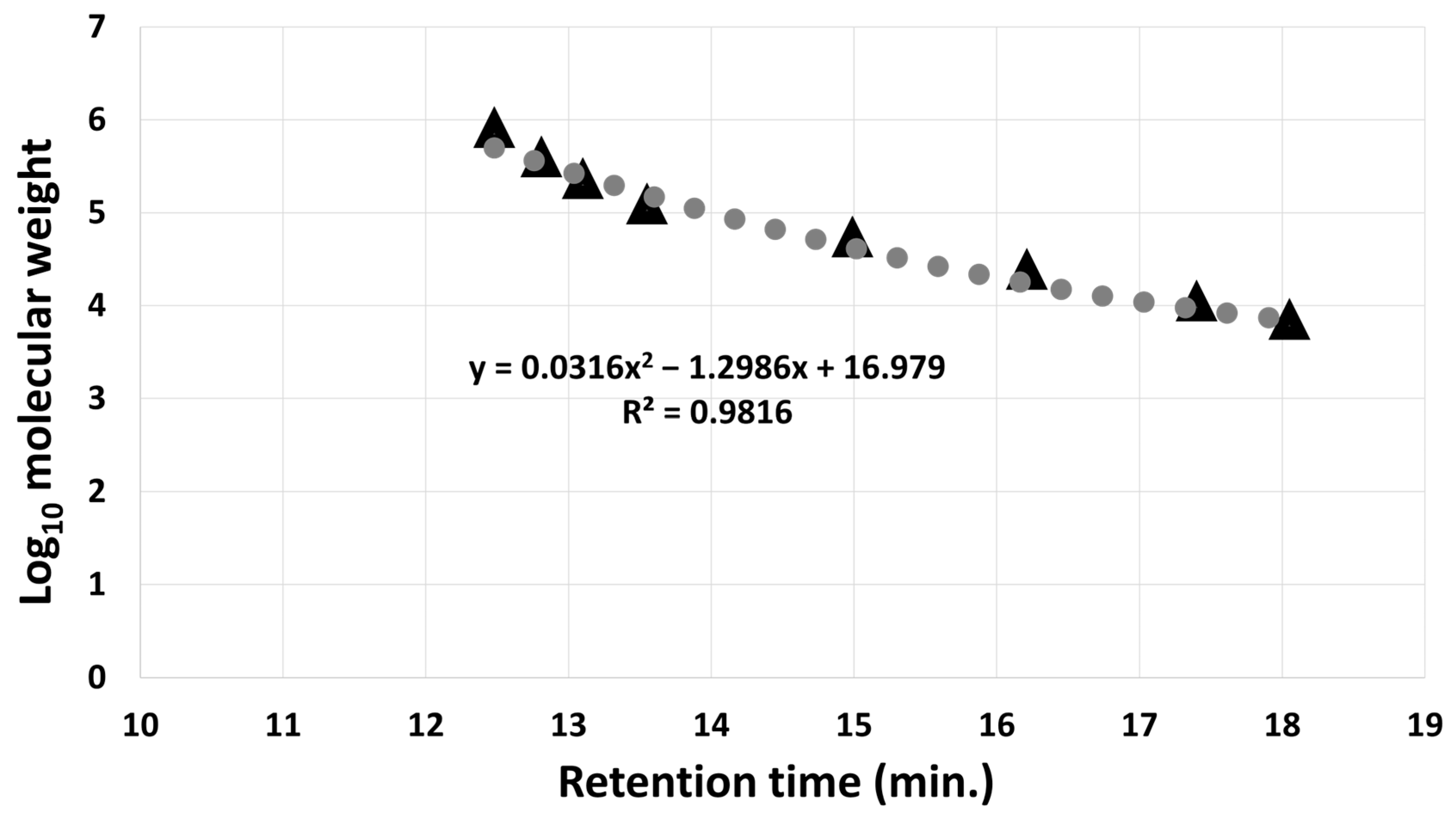
2.1.5. Determination of the Molecular Weight of the Mealworm-Derived Bioactive Substance
2.2. In Vivo Analysis
2.2.1. Experimental Zebrafish
2.2.2. Preparation of the Mealworm-Derived Bioactive Substance Diet
2.2.3. Evaluation of Zebrafish Cytokines Using qRT-PCR to Confirm mRNA (Messenger Ribonucleic Acid) Sequencing After Dietary Treatment with the Mealworm-Derived Bioactive Substance
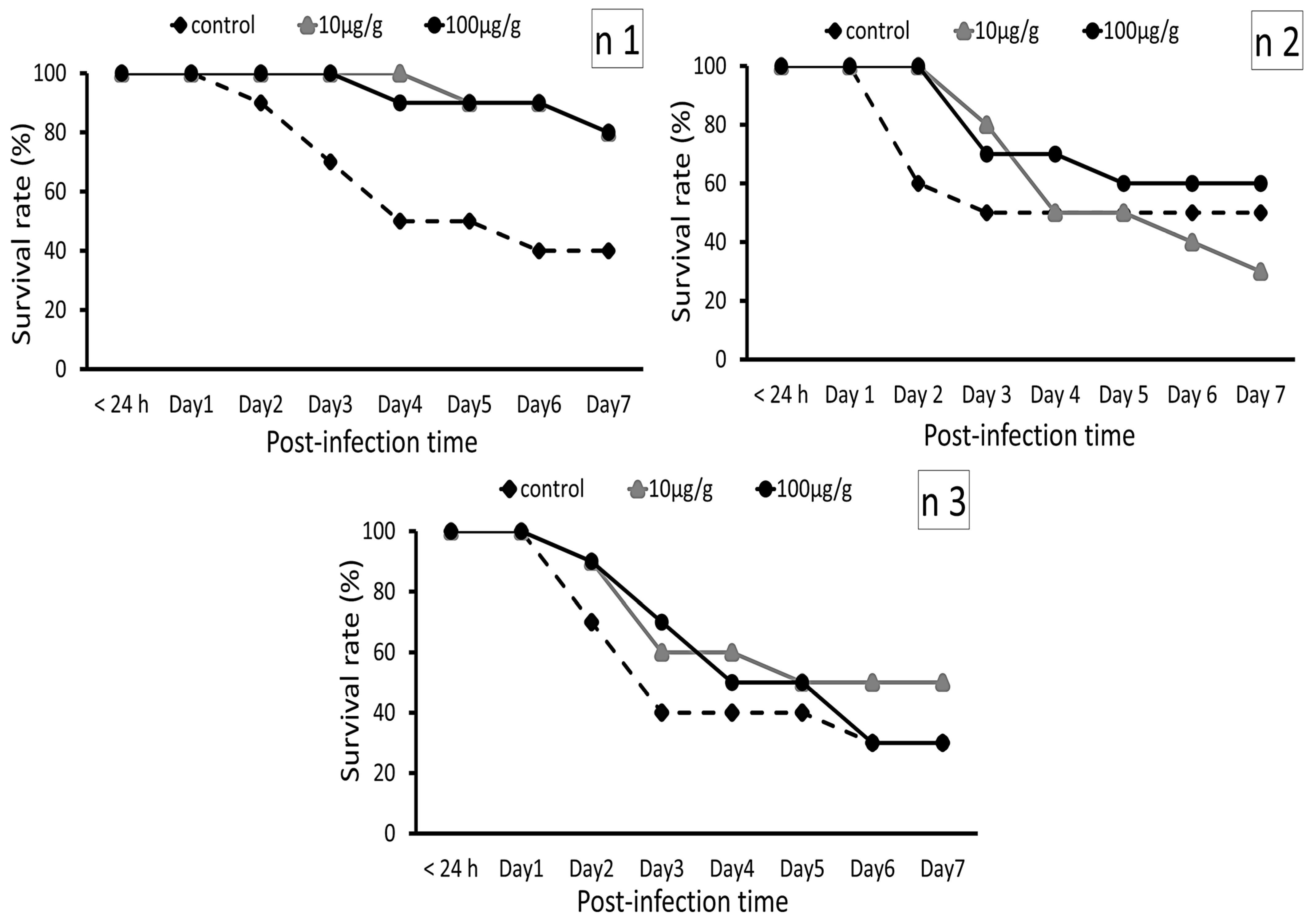
2.2.4. Zebrafish Challenge Test Using Edwardsiella tarda
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Analysis
3.1.1. Extraction and Isolation of the Bioactive Substances from Mealworm Larvae
3.1.2. Molecular Weight Determination of Mealworm Bioactive Substance
3.2. In Vivo Analysis
3.2.1. Zebrafish Post-Challenge Evaluation
3.2.2. RNA Sequencing Analysis of Zebrafish After Receiving Dietary Mealworm-Derived Bioactive Substance Treatment
3.2.3. Differentially Expressed Genes in Response to Dietary Mealworm-Derived Bioactive Substance
3.2.4. Differentially Expressed Genes and Functional Enrichment Obtained via Gene Ontology Analysis
3.2.5. Determination of Differentially Expressed Genes Associated with Immune Responses
3.2.6. KEGG Pathway Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
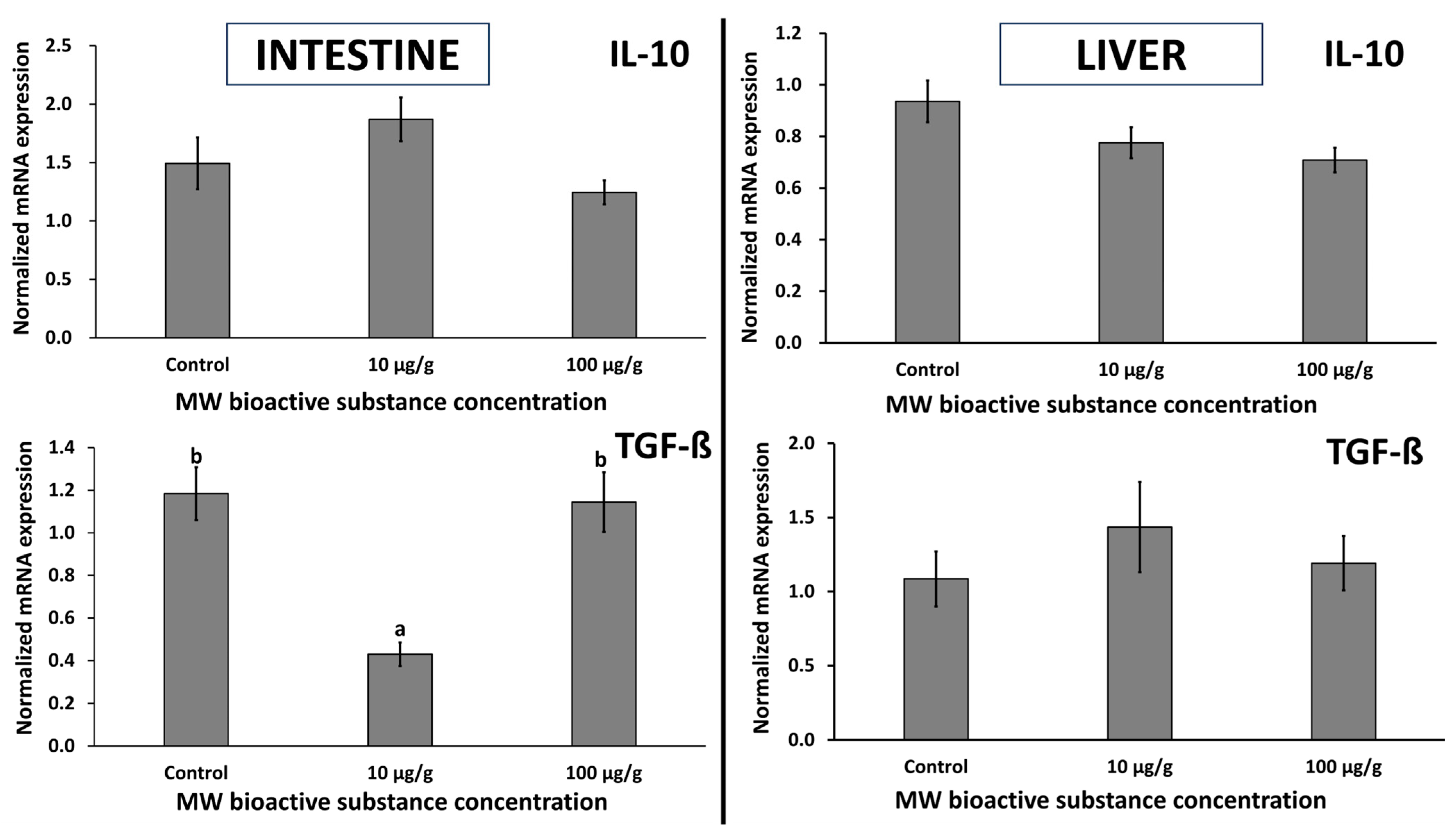
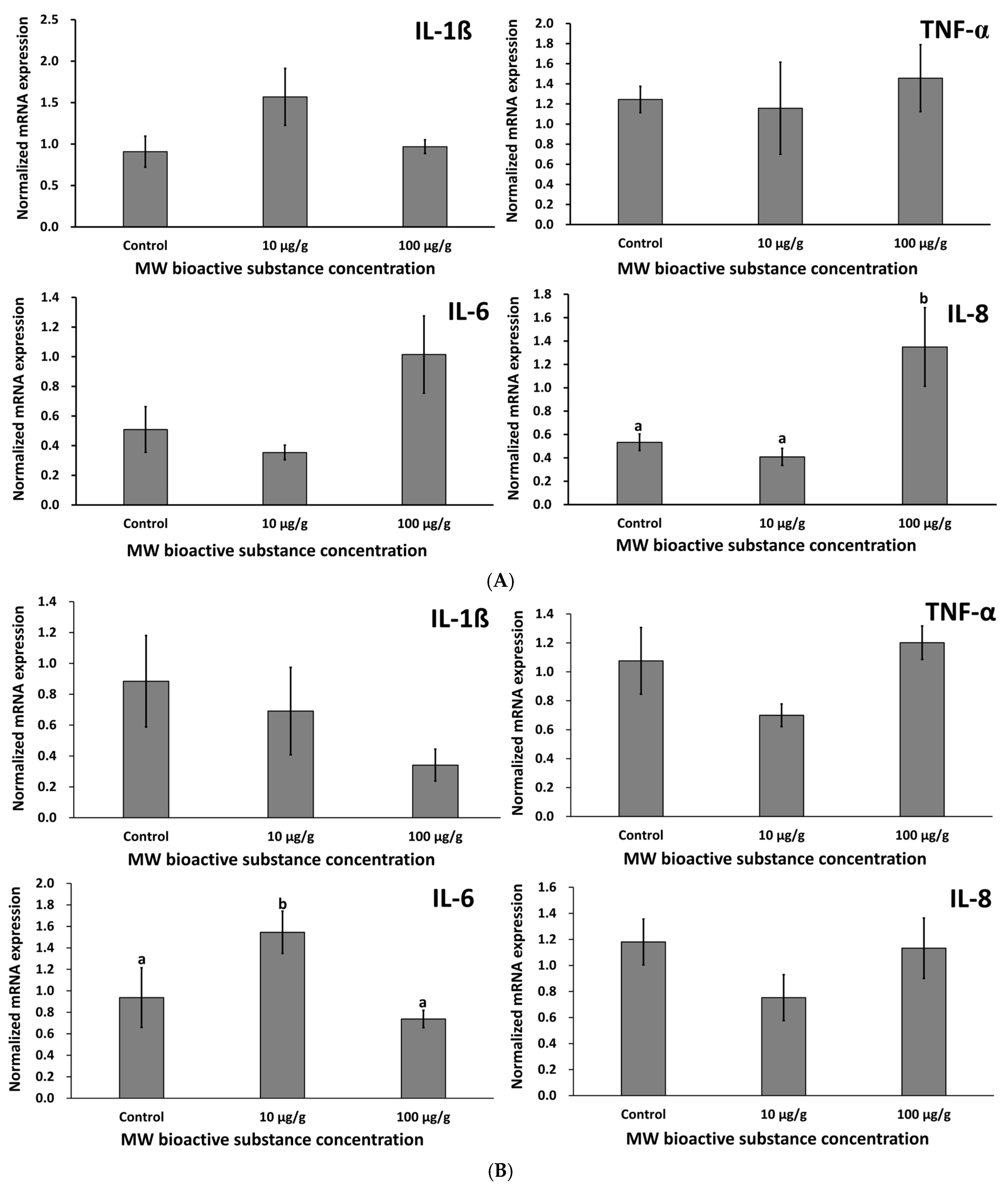
3.2.7. Evaluation of Zebrafish Cytokines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ratcliffe, N.; Azambuja, P.; Mello, C.B. Recent advances in developing insect natural products as potential modern day medicines. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 904958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.I.; Kim, J.W.; Yoe, S.M. Purification and characterization of a novel antibacterial peptide from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 52, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, O.; Zhou, D.; Song, Q.; Soomro, A.A.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Screening, expression, purification and functional characterization of novel antimicrobial peptide genes from Hermetia illucens (L.). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, L.; Finke, M.; van Huis, A. Can diets containing insects promote animal health? J. Insects Food Feed 2018, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, N.; Ishikawa, Y.; Takaoki, M.; Yamashita, M.; Nakayama, S.; Kiguchi, K.; Kok, R.; Wada, H.; Mitsuhashi, J.; Space Agriculture Task Force. Entomophagy: A key to space agriculture. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 41, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, T.; Ido, A.; Kusano, K.; Miura, C.; Miura, T. A novel polysaccharide in insects activates the innate immune system in mouse macrophage RAW264 cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.J.; Hwang, I.K.; Nho, C.W.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, S.H. Determination of carbohydrate composition in mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.) larvae and characterization of mealworm chitin and chitosan. Foods 2021, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Masri, J.; Perez, V.; Maya, C.; Zhao, J. Growth performance and nutrient composition of mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) fed on fresh plant materials-supplemented diets. Foods 2020, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, I.; Józefiak, A.; Henry, M. Beyond the protein concept: Health aspects of using edible insects on animals. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 715–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Gong, Y.; Cao, S.; Lu, F.; Hand, D.; Liu, H.; Jin, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xie, S. Effects of dietary Tenebrio molitor meal on the growth performance, immune response and disease resistance of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 69, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankian, Z.; Khosravi, S.; Kim, Y.O.; Lee, S.M. Effects of dietary inclusion of yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) meal on growth performance, feed utilization, body composition, plasma biochemical indices, selected immune parameters and antioxidant enzyme activities of mandarin fish (Siniperca scherzeri) juveniles. Aquaculture 2018, 496, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, J.D.; Park, C.; Park, J.H.; Chung, T.H. Replacing fish meal by mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) on the growth performance and immunologic responses of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Acta Sci. Anim. Sci. 2018, 40, e35015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte, C.; Rios, A.; Lefebvre, T.; Do, H.; Henry, M.; Jintasataporn, O. Replacing fish meal with defatted insect meal (yellow mealworm Tenebrio molitor) improves the growth and immunity of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Animals 2019, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, M.A.; Gai, F.; Enes, P.; Peréz-Jiménez, A.; Gasco, L. Effect of partial dietary replacement of fishmeal by yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) larvae meal on the innate immune response and intestinal antioxidant enzymes of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.M.; Khosravi, S.; Mauliasari, I.R.; Lee, S.M. Dietary inclusion of mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) meal as an alternative protein source in practical diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fry. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.Z.; Ohta, T.; Ido, A.; Miura, C.; Miura, T. The dipterose of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) induces innate immune response through toll-like receptor pathway in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, T.; Kusano, K.; Ido, A.; Miura, C.; Miura, T. Silkrose: A novel acidic polysaccharide from the silkmoth that can stimulate the innate immune response. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.Z.; Yasin, I.A.; Ohta, T.; Hashizume, A.; Ido, A.; Takahashi, T.; Miura, C.; Miura, T. The silkrose of Bombyx mori effectively prevent vibriosis in penaeid prawns via the activation of innate immunity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Hansson, G.K. Innate immunity, macrophage activation, and atherosclerosis. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 219, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, M. Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.Z.; Kameda, K.; Kondo, F.; Iwai, T.; Kurniawan, R.A.; Ohta, T.; Ido, A.; Takahashi, T.; Miura, C.; Miura, T. Effects of dietary silkrose of Antheraea yamamai on gene expression profiling and disease resistance to Edwardsiella tarda in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 114, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurley, A.T.; Callard, G.V. Characterization of housekeeping genes in zebrafish: Male-female differences and effects of tissue type, developmental stage and chemical treatment. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Nishiyama, T.; Shimizu, K.; Kadota, K. TCC: An R package for comparing tag count data with robust normalization strategies. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, L. Ggplot2: Elegant graphic for data analysis by WICKHAM, H. Biometerics 2011, 67, 678–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulos, P.; Hatzis, P. Systematic integration of RNA-Seq statistical algorithms for accurate detection of differential gene expression patterns. Nucleid Acid Res. 2015, 43, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar-Roiné, S.; Matsui, M.; Reybier, K.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Pauillac, S.; Laurent, D. Ability of certain plant extracts traditionally used to treat ciguatera fish poisoning to inhibit nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.P.; Zhang, D.D.; Ke, Y.; Bian, K. The vasodilatory effects of anti-inflammatory herb medications: A comparison study of four botanical extracts. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1021284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Otsu, Y.; Ali, M.F.Z.; Hashizume, A.; Miura, C. The effects of silkworm-derived polysaccharide (silkrose) on ectoparasitic infestations in yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata) and white trevally (Pseudocaranx dentex). Fishes 2022, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiguchi, H.; Suryadi, I.B.B.; Ali, M.F.Z.; Miura, C.; Miura, T. Dietary black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens)—Dipterose-BSF—Enhanced zebrafish innate immunity gene expression and resistance to Edwardsiella tarda infection. Insects 2024, 15, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Kawai, T.; Obinata, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Horiuchi, T.; Saeki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Furusawa, M. Production of human α-interferon in silkworm using a baculovirus vector. Nature 1985, 315, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, Y.C.; Tocilj, A.; Davies, P.L.; Jia, Z. Mimicry of ice structure by surface hydroxyls and water of a β-helix antifreeze protein. Nature 2000, 406, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, Y.; Ohta, E.; Kawai, Y.; Ohta, S. Dorsamin-A’s, glycerolipids carrying a dehydrophenylalanine ester moiety from the seed-eating larvae of the bruchid beetle Bruchidius dorsalis. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, N.; Hijikata, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Yamori, T.; Tsuruo, T.; Natori, S. Anti-tumor effect of N-beta-alanyl-5-S-glutathionyldihydroxyphenylalanine (5-S-GAD), a novel anti-bacterial substance from an insect. Anticancer Res. 2000, 20, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chernysh, S.; Kim, S.I.; Bekker, G.; Pleskach, V.A.; Filatova, N.A.; Anikin, V.B.; Platonov, V.G.; Bulet, P. Antiviral and antitumor peptides from insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12628–12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Abe, S.; Zhao, Y.P.; An, Y.; Suzuki, K. Growth suppression of rat hepatoma cells by a pentapeptide from Antheraea yamamai. J. Insect Biotechnol. Sericology 2004, 73, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawuyi, I.G.; Heo, E.; Jeong, M.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.J.; Chae, J.; Gwon, S.; Lee, S.D.; Kim, H.; Ojulari, O.V.; et al. Acidic polysaccharide from the edible insect Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis activates antiviral immunity to suppress norovirus infection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 347, 122587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, E.S.; Xiong, J.; de Medeiros, F.G.M.; Grace, M.; Moncada, M.; Lila, M.A.; Hoskin, R.T. Spray dried insect protein-polyphenol particles deliver health-relevant value-added food ingredients. Future Foods 2024, 9, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarneri, A.; Triunfo, M.; Ianniciello, D.; Tedesco, F.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Schmitt, E.; Capece, A.; Falabella, P. Insect-derived chitosan, a biopolymer for the increased shelf life of white and red grapes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Lin, Q.; Shao, F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, K.; Wu, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; et al. Insect cuticle-inspired design of sustainably sourced composite bioplastics with enhanced strength, toughness and stretch-strengthening behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 333, 121970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirk, B.D.; Heichel, D.L.; Eccles, L.E.; Rodgers, L.I.; Lateef, A.H.; Burke, K.A.; Stoppel, W.L. Modifying naturally occurring, nonmammalian-sourced biopolymers for biomedical applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 5915–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugumaran, M.; Evans, J.J. Catecholamine derivatives as novel crosslinkers for the synthesis of versatile biopolymers. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mente, E. Insects: An alternative for fish and human nutrition. Public Health Toxicol. 2022, 2, A27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlaugotne, B.; Pubule, J.; Blumberga, D. Advantages and disadvantages of using more sustainable ingredients in fish feed. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifinia, M.; Bahmanbeigloo, Z.A.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Khanjani, M.H.; Daliri, M.; Koochacknejad, E.; Jasour, M.S. Fishmeal replacement by mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) in diet of farmed Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei): Effects on growth performance, serum biochemistry, and immune response. Aquat. Living Resour. 2023, 36, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, A.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhu, A.; Shen, L.; Ming, Q.; Feng, Z. Comparative analysis of the acute response of zebrafish Danio rerio skin to two different bacterial infections. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2013, 25, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwick, L.; Bayne, C.J. The acute phase response and innate immunity of fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, D.; Taggart, J.B.; Ireland, J.H.; McAndrew, B.J.; Starkey, W.G.; Haley, C.S.; Hamilton, A.; Guy, D.R.; Mota-Velasco, J.C.; Gheyas, A.A.; et al. Gene expression comparison of resistant and susceptible Atlantic salmon fry challenged with infectious pancreatic necrosis virus reveals a marked contrast in immune response. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, F.; Torraca, V.; Meijer, A.H. Chemokine receptors and phagocyte biology in zebrafish. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreda, D.R.; Soliman, A.M. The acute inflammatory response of teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 146, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadiso, T.M.; Krasnov, A.; Skugor, S.; Afanasyef, S.; Hordvik, I.; Nilsen, F. Gene expression analyses of immune responses in Atlantic salmon during early stages of infection by salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) revealed bi-phasic responses coinciding with the copepod-chalimus transition. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiesen, C.L.; Hu, L.; Torslev, A.S.; Poulsen, E.T.; Larsen, U.G.; Kjaer-Sorensen, K.; Thomsen, J.S.; Brüel, A.; Enghild, J.J.; Oxvig, C.; et al. Superoxide dismutase 3 is expressed in bone tissue and required for normal bone homeostasis and mineralization. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 164, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Noman, A.; Zhang, C.; Al-Bukhaiti, W.; Abed, S.M. Effect of fish-heavy metals contamination on the generation of reactive oxygen species and its implications on human health: A review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1500870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Boiti, A.; Vallone, D.; Foulkes, N.S. Reactive oxygen species signaling and oxidative stress: Transcriptional regulation and evolution. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, C.; Santos, P.; Passos, R.; Vaz, M.; Azeredo, R.; Machado, M.; Fernández-Boo, S.; Baptista, T.; Costas, B. Functional and molecular immune response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) following challenge with Yersinia ruckeri. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3096. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35328519/ (accessed on 30 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Reis, E.S.; Mastellos, D.C.; Gros, P.; Lambris, J.D. Complement component C3—The “Swiss Army Knife” of innate immunity and host defense. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 274, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delvaeye, M.; Conway, E.M. Coagulation and innate immune responses: Can we view them separately? Blood 2009, 114, 2367–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, N.C.; Rise, M.L.; Christian, S.L. A comparison of the innate and adaptive immune systems in cartilaginous fish, ray-finned fish, and lobe-finned fish. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlie-Silva, I.; Klein, A.; Gomes, J.M.M.; Prado, E.J.R.; Moraes, A.C.; Eto, S.F.; Fernandes, D.C.; Fagliari, J.J.; Junior, J.D.C.; Lima, C.; et al. Acute-phase proteins during inflammatory reaction by bacterial infection: Fish-model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Han, S.; Jiang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y. Effect of dietary phenylalanine on growth performance and intestinal health of triploid rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in low fishmeal diets. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1008822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Liang, H.; Huang, D.; Yu, H.; Xue, C.; Gu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, M.; Zhang, L. Phenylalanine plays important roles in regulating the capacity of intestinal immunity, antioxidants and apoptosis in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Animals 2023, 13, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Shi, X.; Pei, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Kong, X. The role of ferroptosis in fish inflammation. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 15, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Yang, L.; Xing, Y.; Li, Z. The effects of quercetin on immunity, antioxidant indices, and disease resistance in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 46, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymuszka, A.; Adaszek, Å. Pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokine expression in carp blood and head kidney leukocytes exposed to cyanotoxin stress—An in vitro study. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, C.A.; Kennedy-Stoskopf, S.; Horne, W.A.; Fuller, F.J.; Tompkins, W.A.F. Cloning and sequencing hybrid striped bass (Morone saxatilis x M. chrysops) transforming growth factor-ß (TGF-ß), and development of a reverse transcription quantitative competitive polymerase chain reaction (RT-qcPCR) assay to measure TGF-ß mRNA of teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2000, 10, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, R.K.A.; Zaccone, G.; Capillo, G.; Albano, M.; Mokhtar, D.M. Structural and functional aspects of the spleen in molly fish Poecilia sphenops (Valenciennes, 1846): Synergistic interactions of stem cells, neurons, and immune cells. Biology 2022, 11, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, C.G.; Freitas, D.D.A.; Riberio, P.A.P.; Teixeira, R.R.C.; da Silva, R.F.; Gamarano, P.G.; de AraÚjo, R.D.; Prado, V.G.L.; Guilherme, H.D.O.; Paulino, R.P.; et al. Impact of replacing fish meal with black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) meal on diet acceptability in juvenile nile tilapia: Palatability and nutritional and health considerations for dietary preference. Aquac. Res. 2024, 2024, 3409955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, S.J.; Libby, P. Human vascular smooth muscle cells. Target for and source of tumor necrosis factor. J. Immunol. 1989, 142, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, S.C. Identification and expression analysis of two pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-a and IL-8, in cobia (Rachycentron canadum L.) in response to Streptococcus dysgalactiae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggestøl, H.Ø.; Lunde, H.S.; Haugland, G.T. The proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) -identification, molecular characterization, phylogeny and gene expression analyses. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 105, 103608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Lin, H.T.; Foung, Y.F.; Lin, J.H.Y. The bioactivity of teleost IL-6: IL-6 protein in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) induces Th2 cell differentiation pathway and antibody production. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.; Zou, J.; Savan, R.; Kono, T.; Sakai, M.; Woo, J.; Secombes, C. Characterisation and expression analysis of an interleukin 6 homologue in the Japanese pufferfish, Fugu rubripes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellana, B.; Iliev, D.B.; Sepulcre, M.P.; Mackenzie, S.; Goetz, F.W.; Mulero, V.; Planas, J.V. Molecular characterization of interleukin-6 in the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3363–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ran, C.; Teame, T.; Ding, Q.; Hoseinifar, H.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Olsen, R.E.; Gatlin III, D.M.; et al. Research progress on gut health of farmers teleost fish: A viewpoint concerning the intestinal mucosal barrier and the impact of its damage. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2020, 30, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, S.; Avunje, S.; Jung, S.J. Differential expression profile of innate immune genes in the liver of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV) at host susceptible and non-susceptible temperatures. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafalla, C.; Coll, J.; Secombes, C.J. Expression of genes related to the early immune response in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; He, C.; Baoprasertkul, P.; Xu, P.; Li, P.; Serapion, J.; Waldbieser, G.; Wolters, W.; Liu, Z. Analysis of a catfish gene resembling interleukin-8: cDNA cloning, gene structure, and expression after infection with Edwardsiella ictaluri. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covello, J.M.; Bird, S.; Morrison, R.N.; Battaglene, S.C.; Secombes, C.J.; Nowak, B.F. Cloning and expression analysis of three striped trumpeter (Latris lineata) pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-8, in response to infection by the ectoparasitic, Chondracanthus goldsmidi. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, F.; Tacke, F. Immunology in the liver—From homeostasis to disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.D.; Wang, Y.H.; Chang, C.; Gershwin, M.E.; Lian, Z.X. The intestinal microbiota and microenvironment in liver. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickmeier, I.; Seidel, D.; Grün, J.R.; Derkow, K.; Lehnardt, S.; Kühl, A.A.; Hamann, A.; Schott, E. Influence of CD8 T cell priming in liver and gut on the enterohepatic circulation. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipka, S.; Bruckner, G. The immunomodulatory role of bile acids. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 165, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suryadi, I.B.B.; Ali, M.F.Z.; Nishiguchi, H.; Akanuma, S.; Miura, C.; Miura, T. Bioactive Substance Derived from Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor) Potentially Induces Immune Performance of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes 2025, 10, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060285
Suryadi IBB, Ali MFZ, Nishiguchi H, Akanuma S, Miura C, Miura T. Bioactive Substance Derived from Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor) Potentially Induces Immune Performance of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes. 2025; 10(6):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060285
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuryadi, Ibnu Bangkit Bioshina, Muhammad Fariz Zahir Ali, Haruki Nishiguchi, Saita Akanuma, Chiemi Miura, and Takeshi Miura. 2025. "Bioactive Substance Derived from Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor) Potentially Induces Immune Performance of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)" Fishes 10, no. 6: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060285
APA StyleSuryadi, I. B. B., Ali, M. F. Z., Nishiguchi, H., Akanuma, S., Miura, C., & Miura, T. (2025). Bioactive Substance Derived from Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor) Potentially Induces Immune Performance of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes, 10(6), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10060285





