A Hypothetical Protein Fragment from Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Demonstrates Significant Activity Against Both Bacterial and Parasite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Construction of B. subtilis Engineered Strain
2.4. Screening of Candidate Antibacterial Genes
2.5. Extracellular Protein Acquisition
2.6. Antibacterial Experiment of Extracellular Protein
2.7. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Antimicrobial Peptides
2.8. Bioinformatics Tools Were Used to Analyze and Screen Antimicrobial Peptides
2.9. Analysis of Antibacterial Activity of rLc149
2.9.1. Antibacterial Activity Assay by Agar Diffusion Method
2.9.2. MIC and MBC Detection
2.9.3. Bactericidal Kinetics Curve
2.10. Antibacterial Mechanism Analysis
2.10.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.10.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
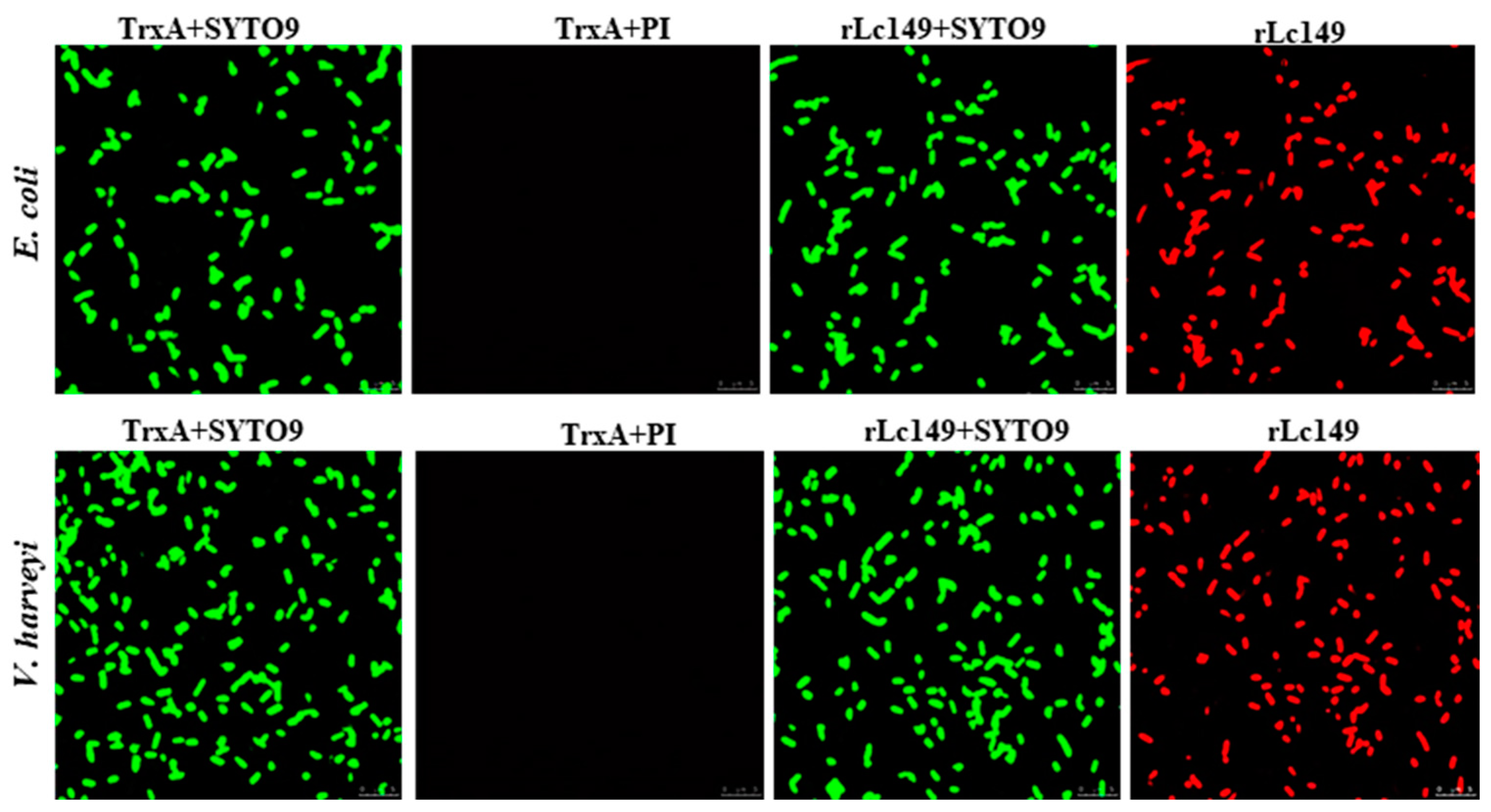
2.10.3. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) Analysis
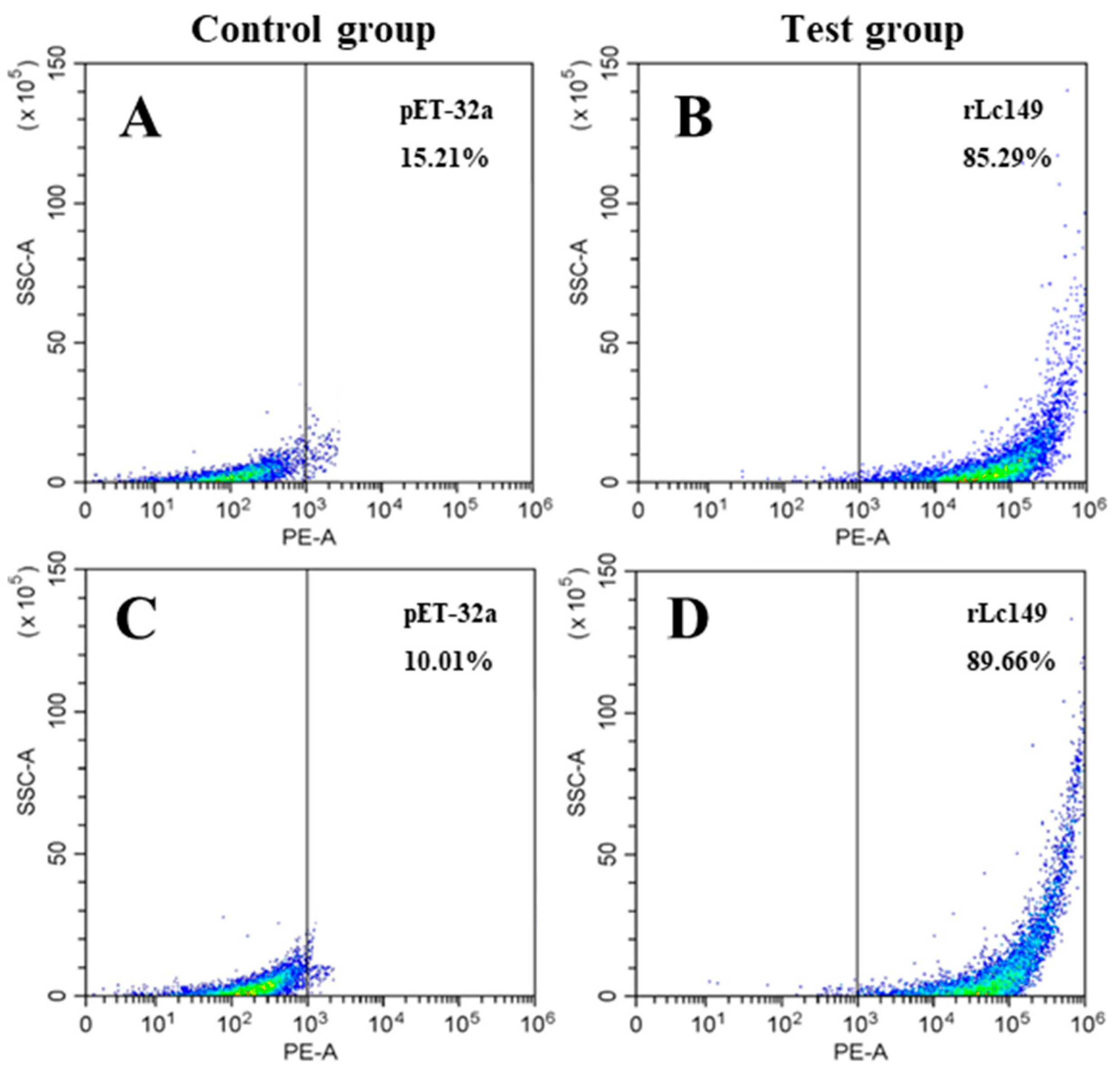
2.10.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.10.5. Gel Retardation Analysis
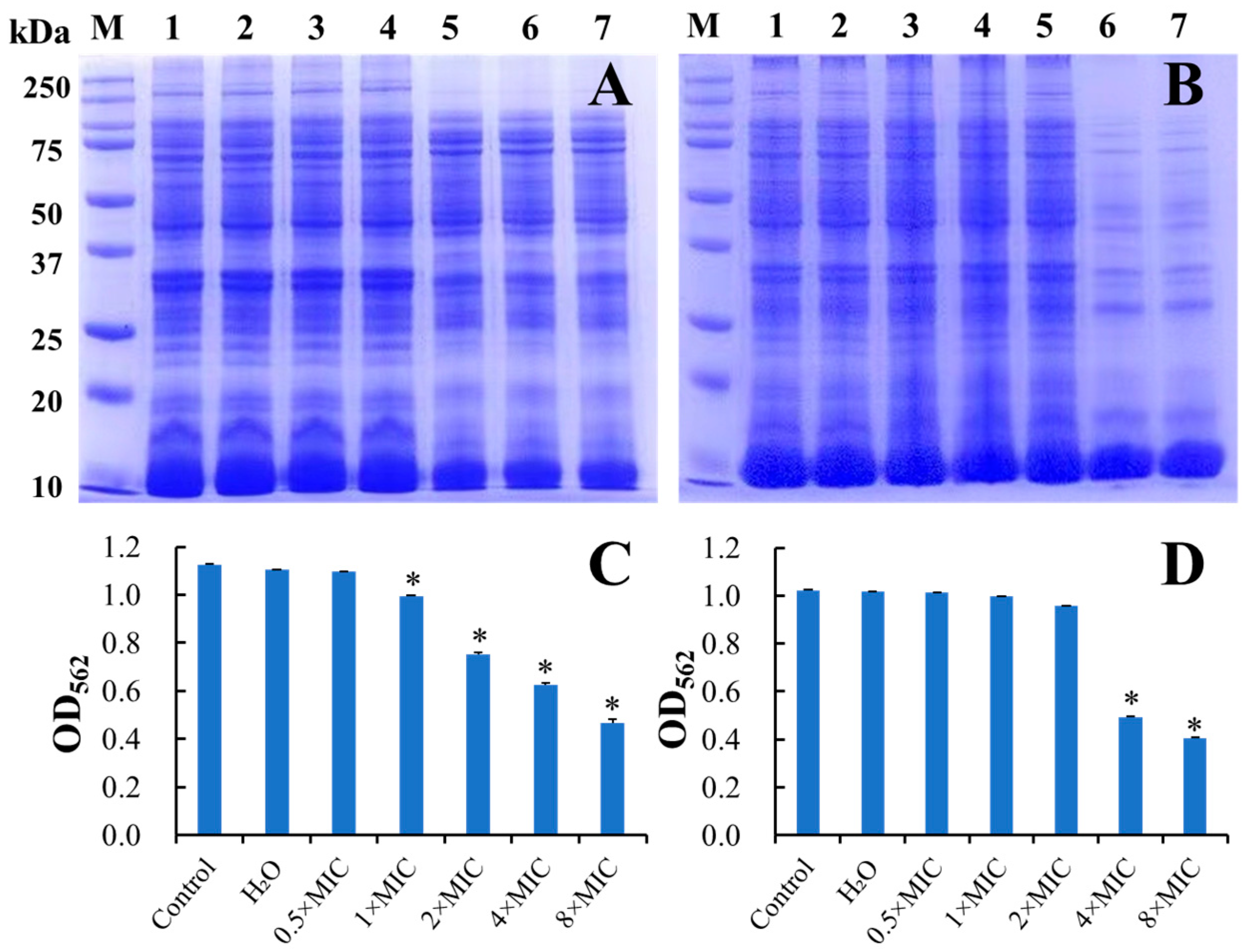
2.10.6. Bacterial Protein Content Analysis
2.11. rLc149 Activity Against Parasite
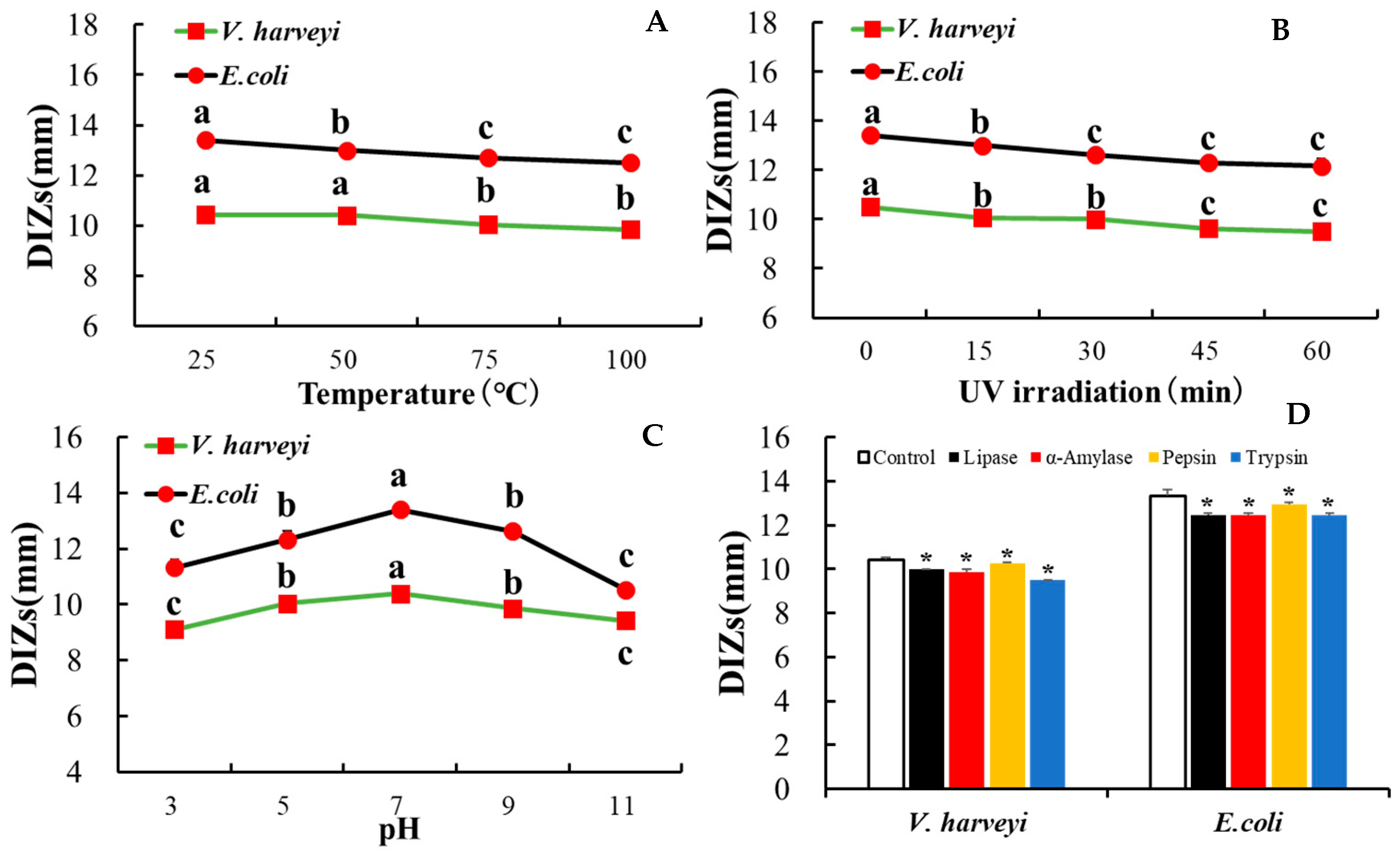
2.12. Stability Assay
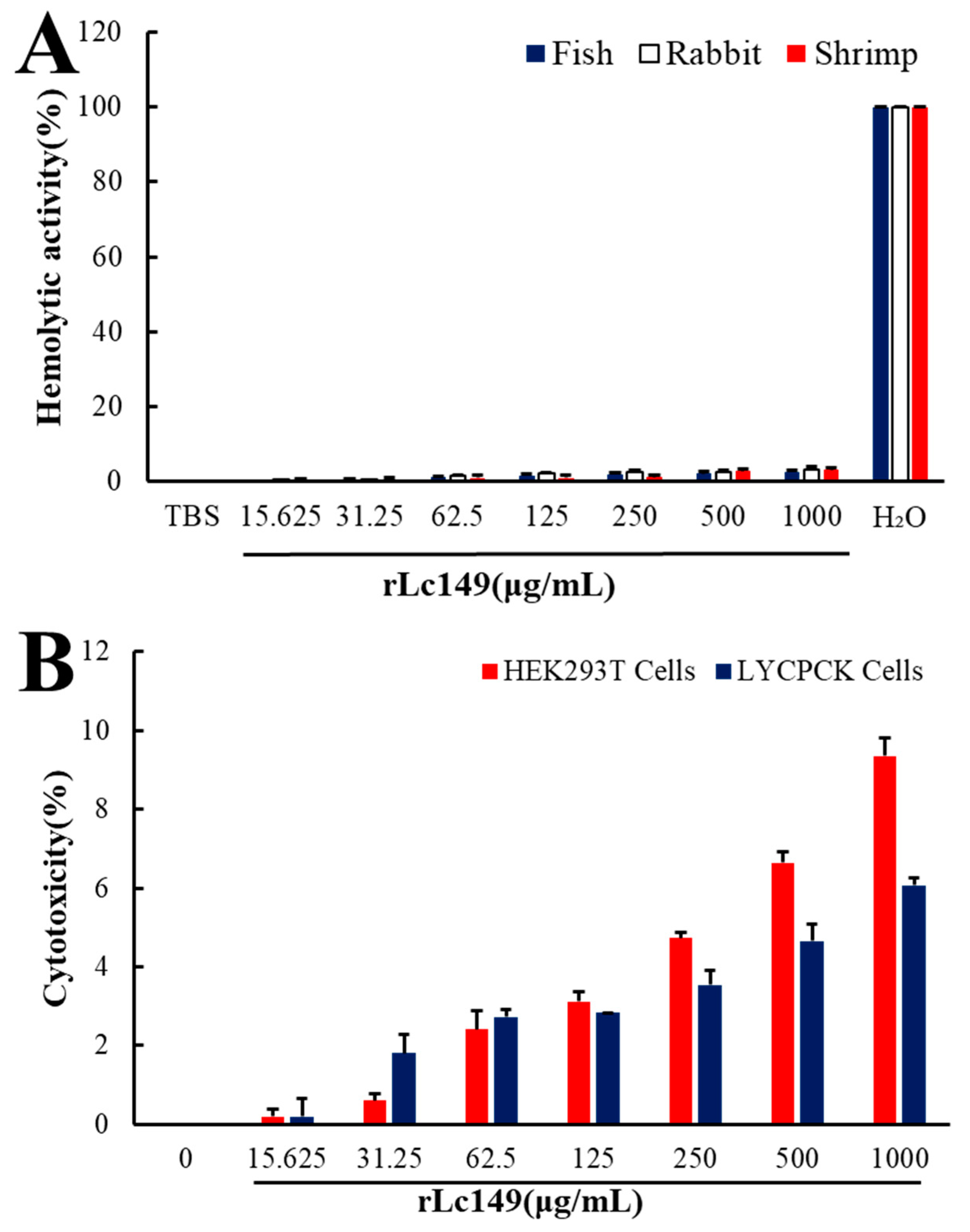
2.13. Hemolytic Analysis
2.14. Cytotoxic Analysis
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
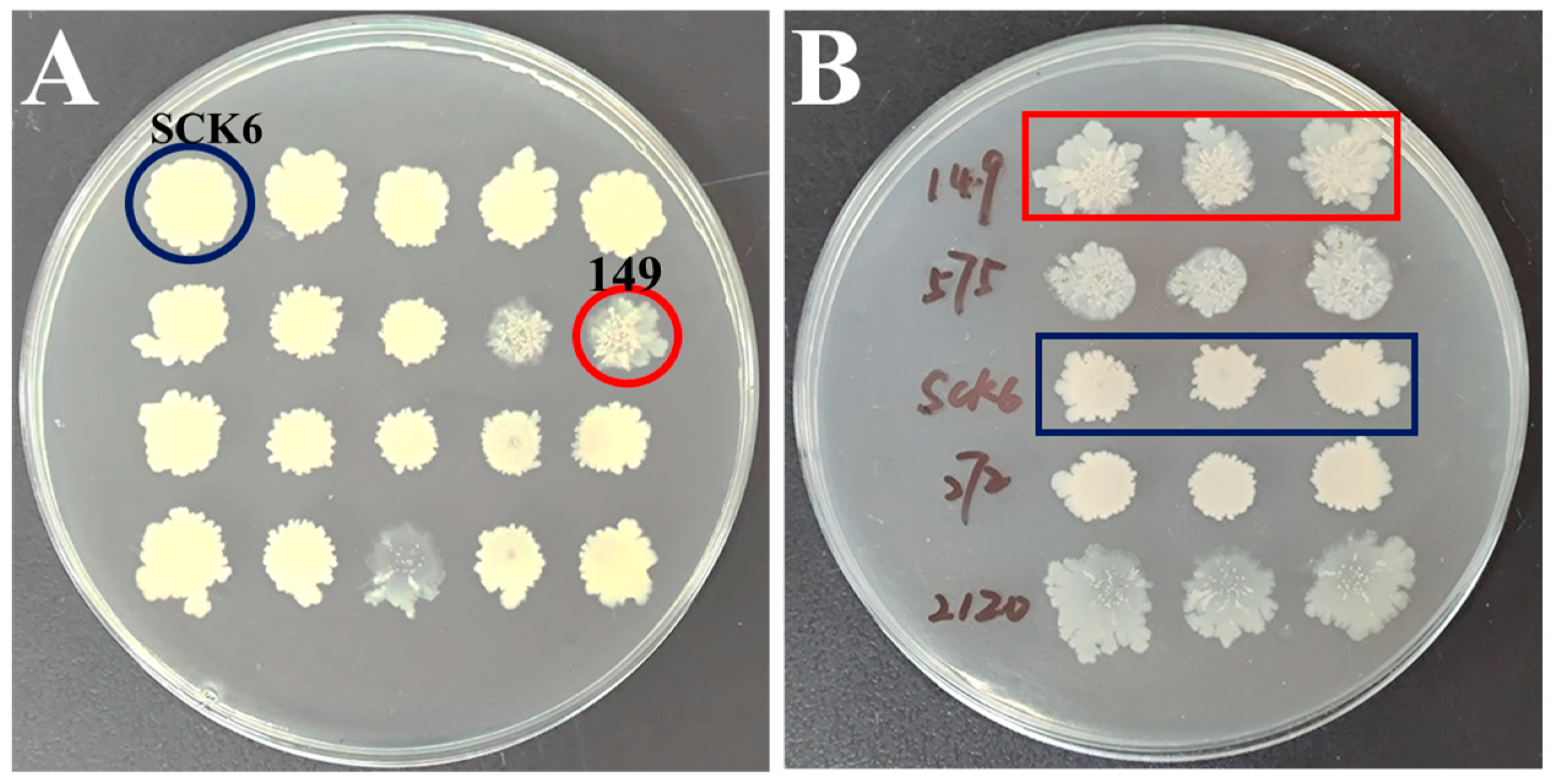
3.1. Construction of B. subtilis Engineered Strain 149
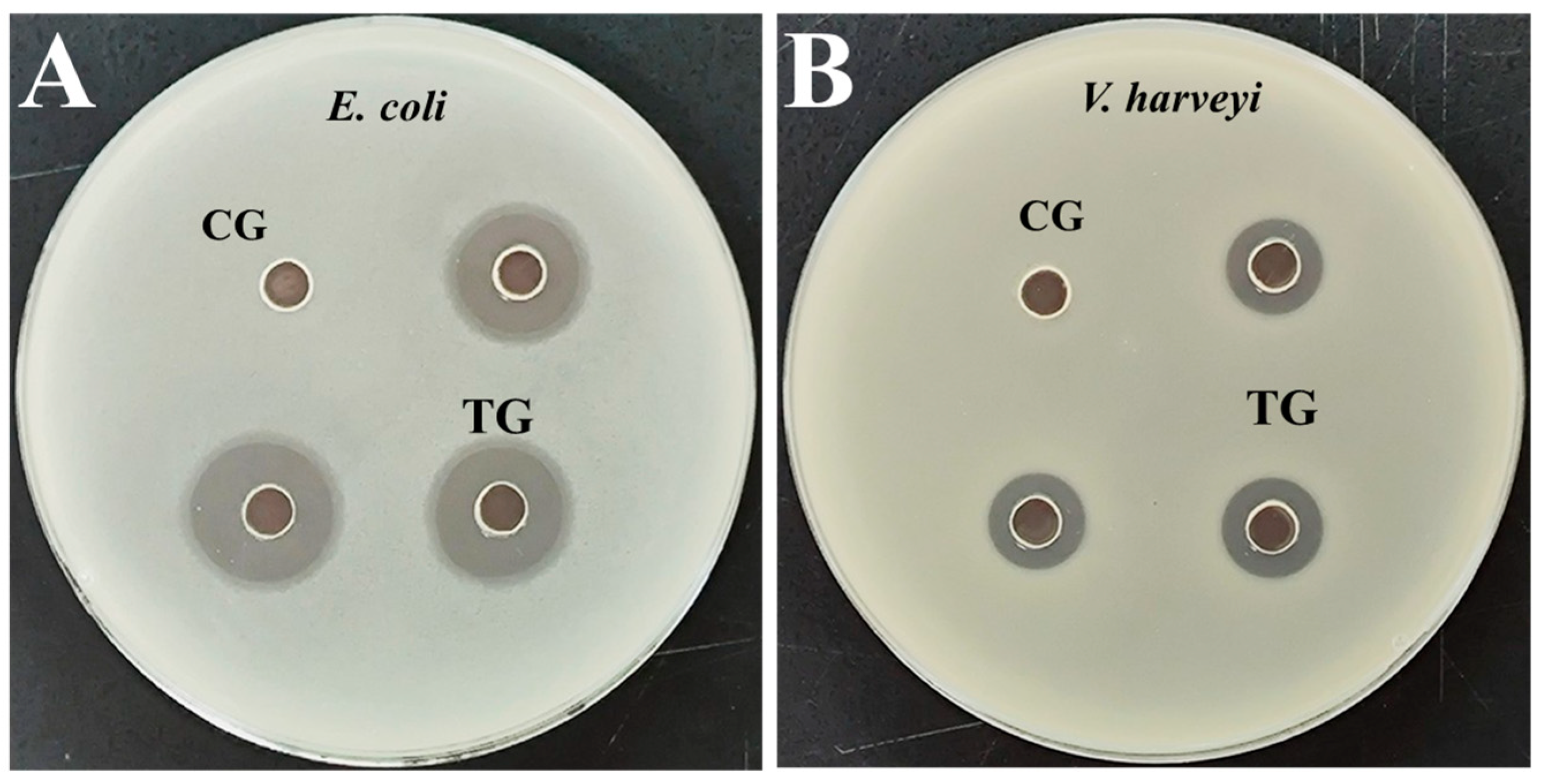
3.2. Antibacterial Activity Analysis of Extracellular Protein
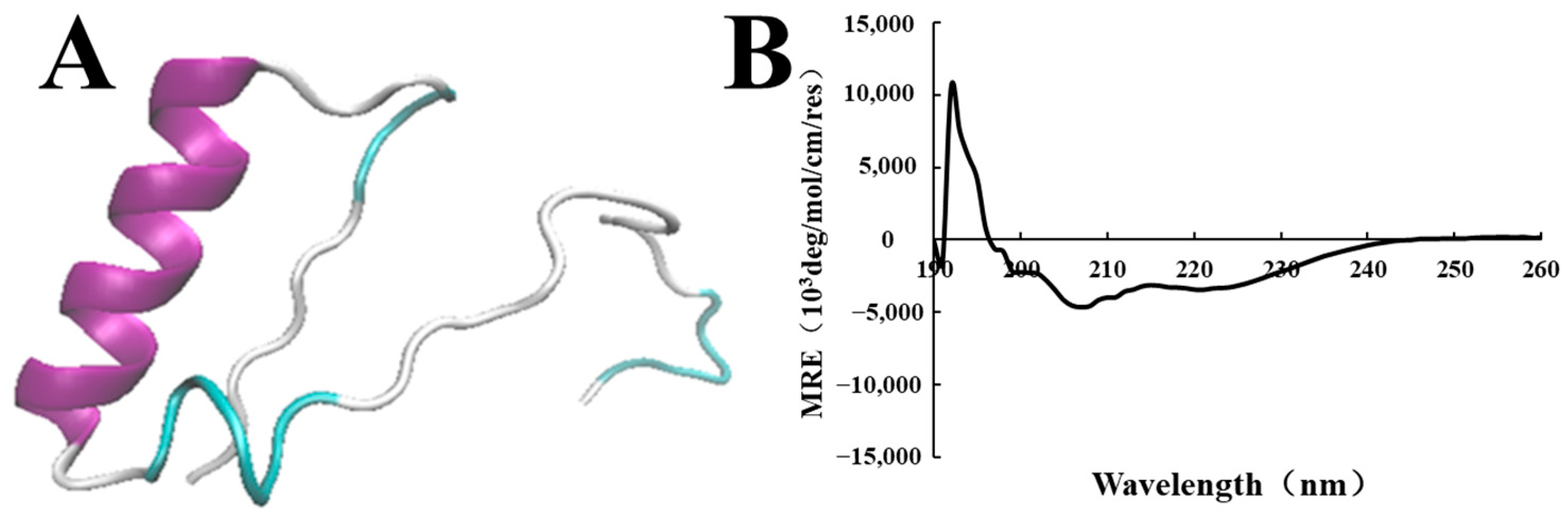
3.3. Characterization of the Lc149 Structure
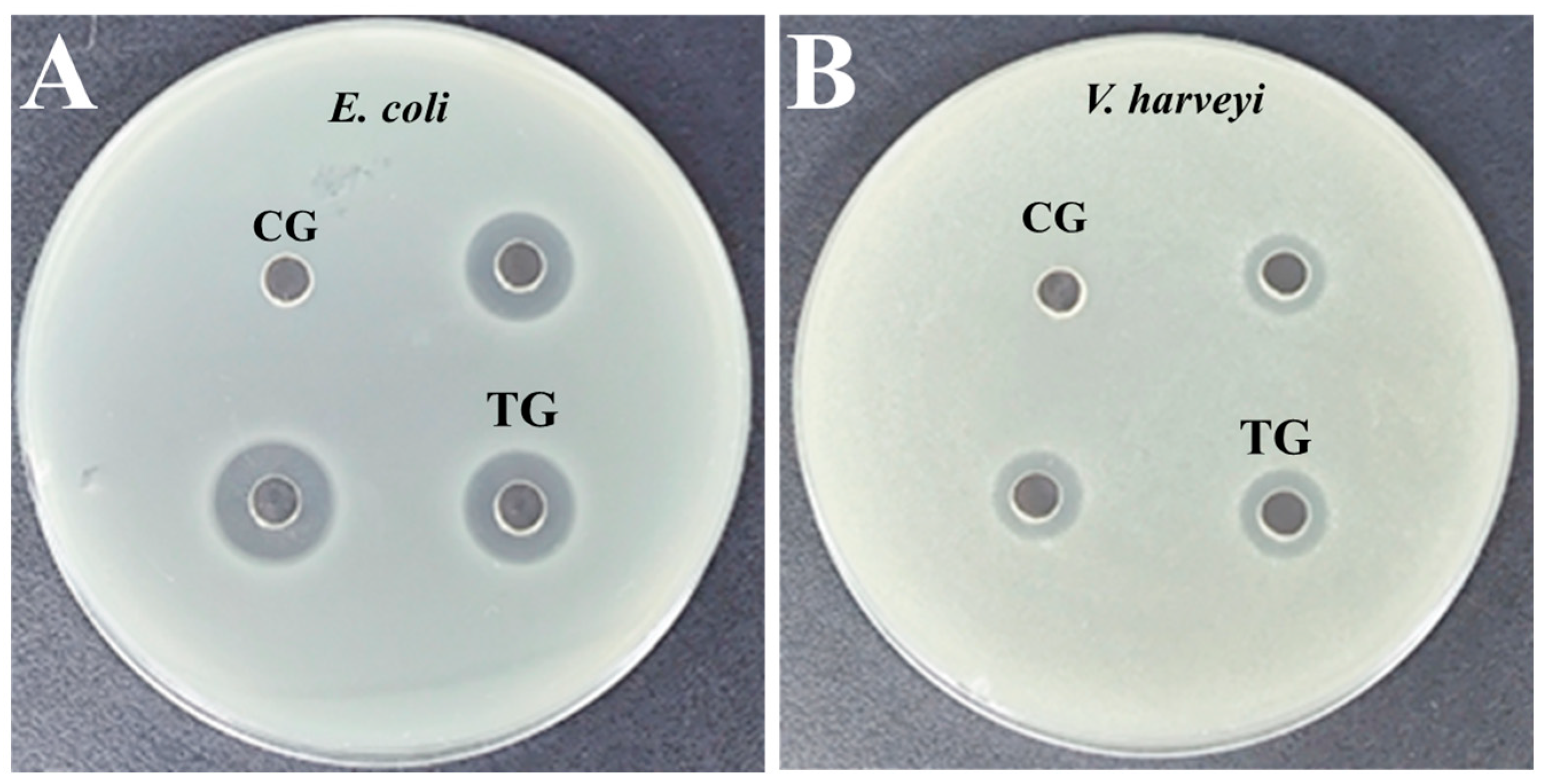
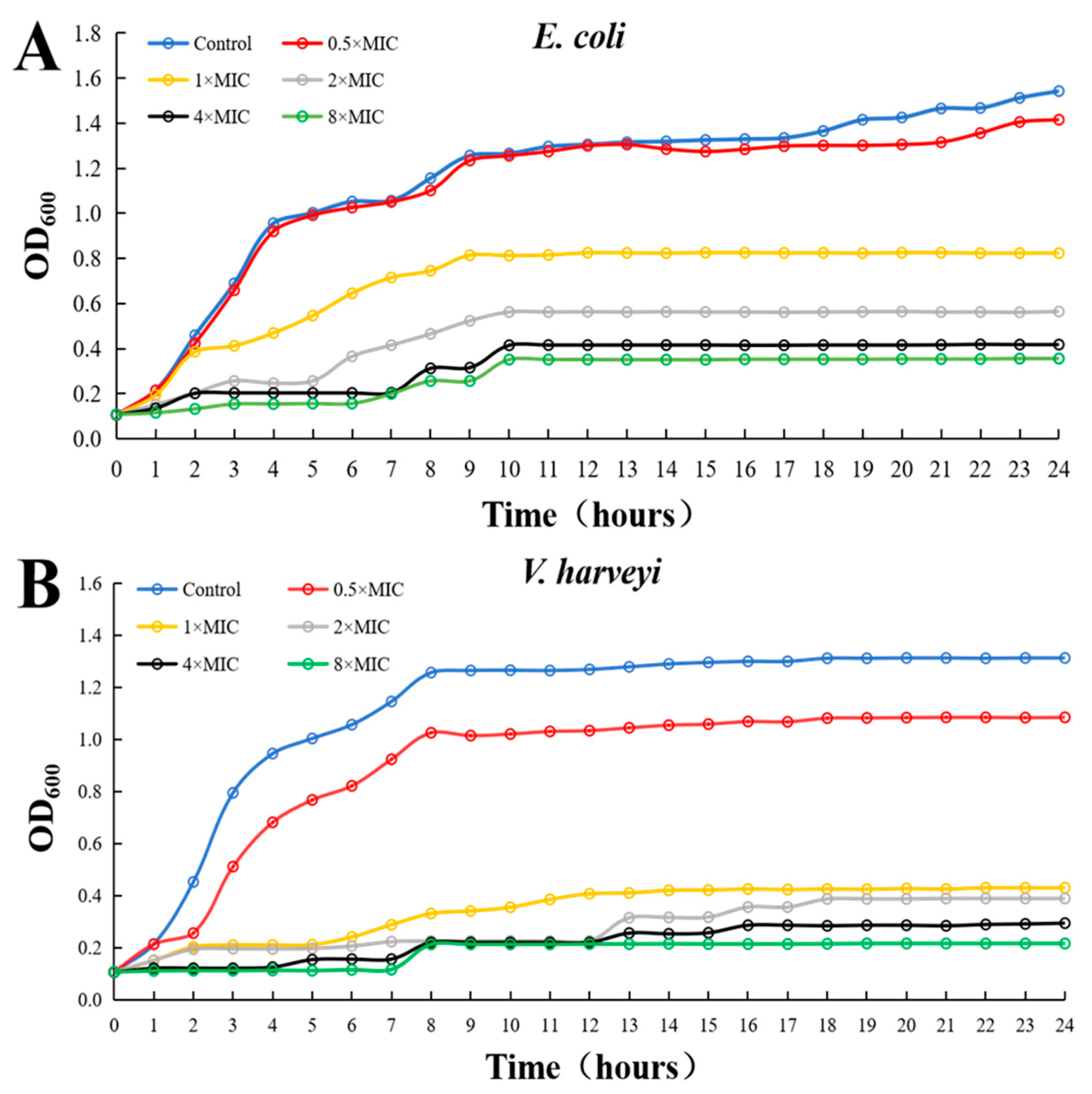
3.4. Antibacterial Activity Monitoring of rLc149
3.5. Analysis of the Antibacterial Mechanism of Lc149
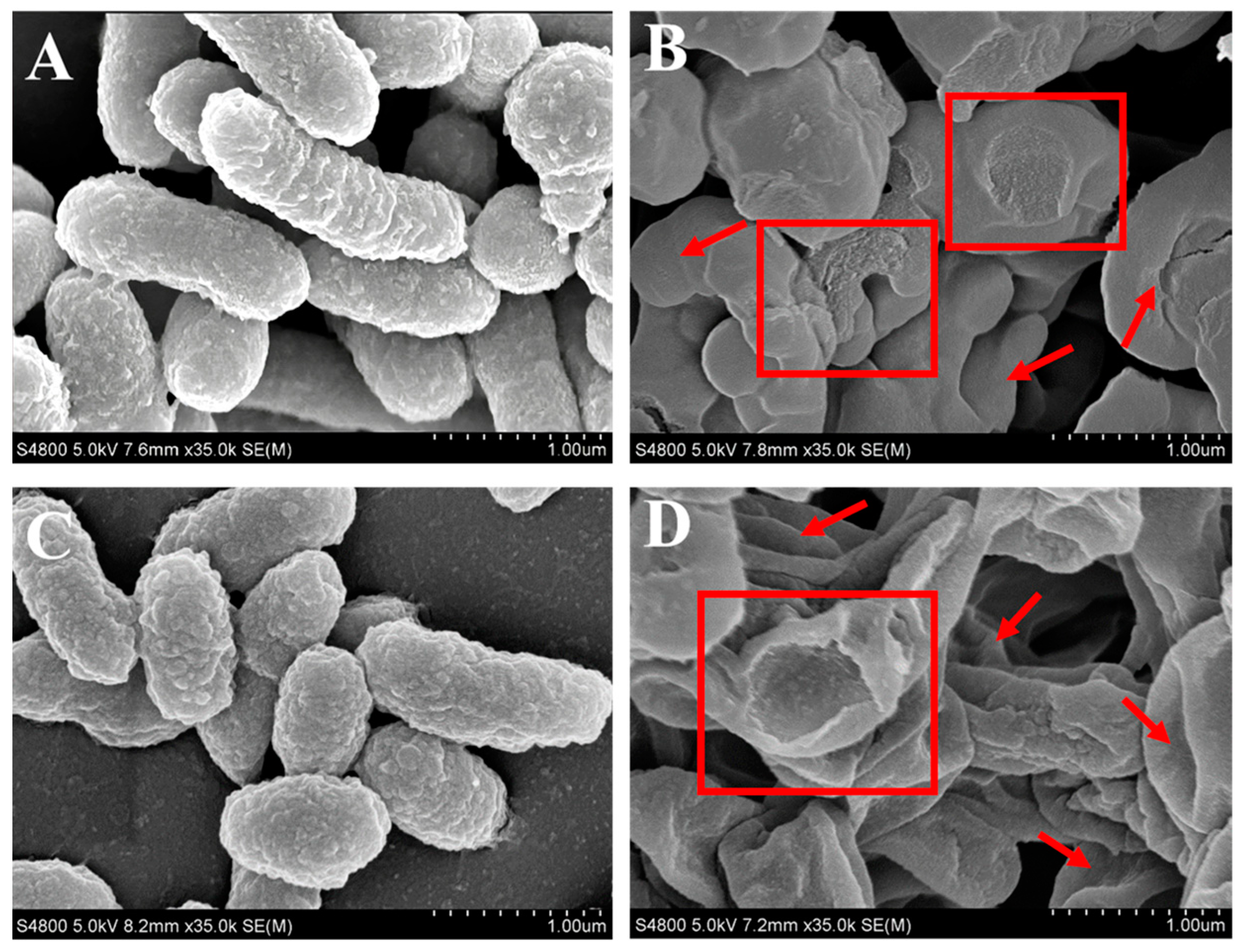
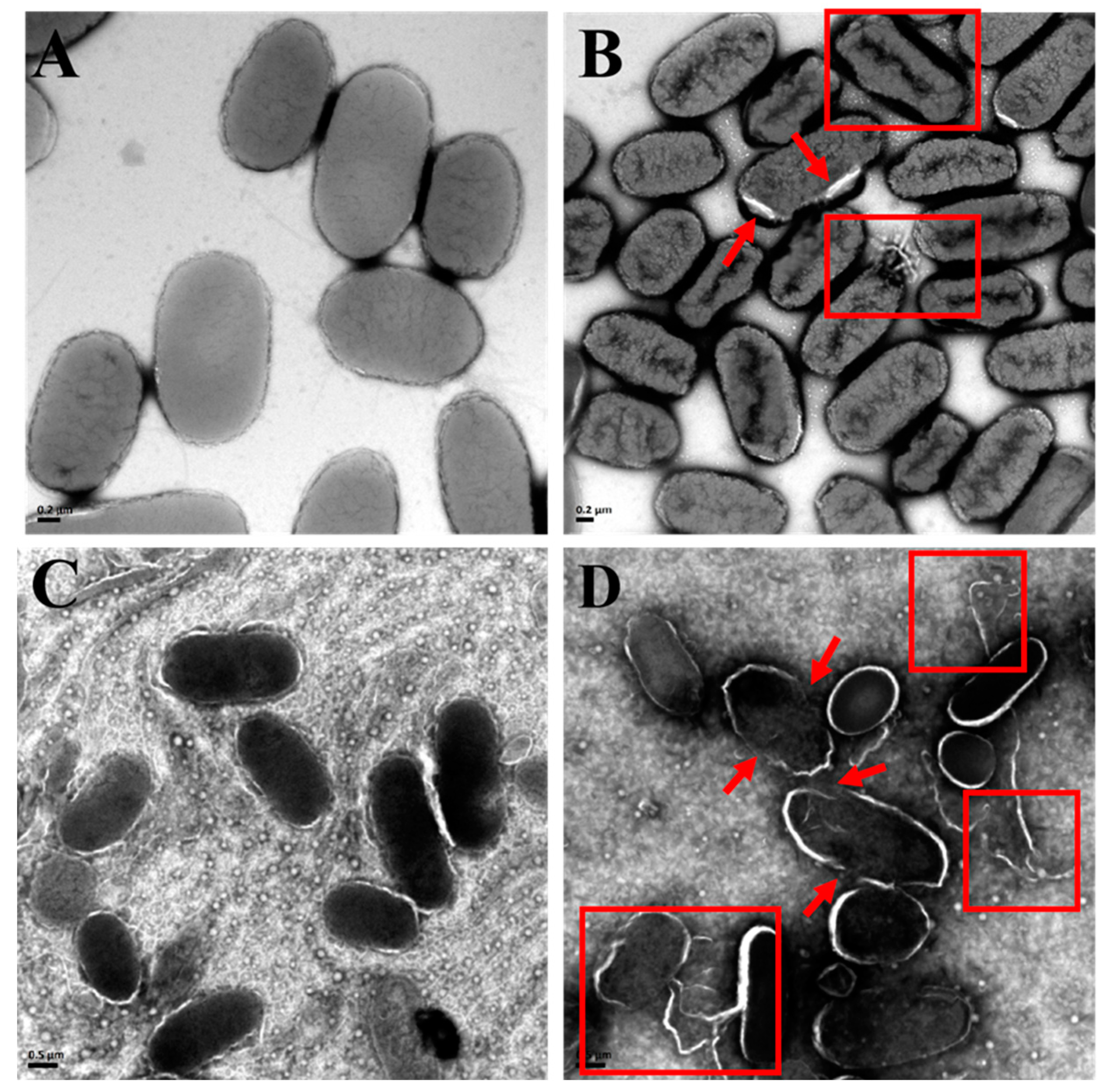
3.5.1. Disruption of Bacterial Structures
3.5.2. Inhibition of the Bacterial Biofilm Formation
3.5.3. Inhibition of the Bacterial Protein Synthesis
3.6. A Significant Parasite Killing Activity of rLc149
3.7. rLc149 Exhibits Relatively Stable Characteristics
3.8. Safety Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, H.; Singh, R.; Kaur, S.; Dhaka, P.; Bedi, J.S.; Gill, J.P.S.; Gongal, G. Review of antibiotic use and resistance in food animal production in WHO south-east asia region. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. Publisher correction: A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 595, E36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, D. Intelligent fish farm-the future of aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 2681–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schar, D.; Klein, E.Y.; Laxminarayan, R.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Krafft, T.; Martens, P. The interaction between climate change and marine fisheries: Review, challenges, and gaps. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 259, 107479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.K.; Patel, A.B.; Singh, S.K.; Mehta, N.K.; Anand, V.; Lal, J.; Dekari, D.; Devi, N.C. Climate change effects on aquaculture production and its sustainable management through climate-resilient adaptation strategies: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 31731–31751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Ge, M.; Feng, J.; Wei, X.; Tan, H.; Liang, Z.; Tong, G. Epidemiological investigation on diseases of larimichthys crocea in ningbo culture area. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1420995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo Lagno, A.; Lara, M.; Cornejo, J. Aquatic animal health: History, present and future. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2024, Special Edition, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, K.S.; Paley, R.K.; Batista, F.M.; Bass, D.; Peeler, E.J. Advances in aquatic animal health within the framework of the world organisation for animal health. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2024, 159–167, Special Edition. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem Büyükkiraz, M.; Kesmen, Z. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): A promising class of antimicrobial compounds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 1573–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; An, F.; Zhang, T.; Lou, M.; Guo, J.; Liu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, R. Antimicrobial peptides: An alternative to traditional antibiotics. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 265, 116072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Song, Y. Mechanism of antimicrobial peptides: Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antibiofilm activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.C.D.; Guimarães, J.M.; Pereira, S.D.S.; Mariúba, L.A.M. The multifunctionality of expression systems in bacillus subtilis: Emerging devices for the production of recombinant proteins. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 2443–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Synthetic biology toolbox and chassis development in bacillus subtilis. Trends. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Q.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, D. [Research progress and industrial application of bacillus subtilis in systematic and synthetic biotechnology]. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 923–938. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Han, L.; Suo, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Z. Exploitation of bacillus subtilis as a robust workhorse for production of heterologous proteins and beyond. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, Z.; Yan, C.; Tang, X.; Fang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D. Centrosomal protein of 192 kda (cep192) fragment possesses bactericidal and parasiticidal activities in larimichthys crocea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folgueira, I.; Lamas, J.; Sueiro, R.A.; Leiro, J.M. Molecular characterization and gene expression modulation of the alternative oxidase in a scuticociliate parasite by hypoxia and mitochondrial respiration inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, P.A.; Salinas, N.; Álvarez, C.A.; Mercado, L.A.; Guzmán, F. Alpha-helical domain from IL-8 of salmonids: Mechanism of action and identification of a novel antimicrobial function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.; Carpio, Y.; Valdés, I.; Velázquez, J.; Zamora, Y.; Morales, R.; Morales, A.; Rodríguez, E.; Estrada, M.P. Co-administration of tilapia alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides with subunit antigens boost immunogenicity in mice and tilapia (oreochromis niloticus). Vaccine 2014, 32, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffredo, M.R.; Casciaro, B.; Bellavita, R.; Troiano, C.; Brancaccio, D.; Cappiello, F.; Merlino, F.; Galdiero, S.; Fabrizi, G.; Grieco, P.; et al. Strategic single-residue substitution in the antimicrobial peptide esc (1-21) confers activity against staphylococcus aureus, including drug-resistant and biofilm phenotype. ACS Infect. Dis. 2024, 10, 2403–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.H.; Wong, S.R.; Lee, S.H. The therapeutic anticancer potential of marine-derived bioactive peptides: A highlight on pardaxin. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2023, 29, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorny, A.; Almeida, P.F. The antibiotic peptide daptomycin functions by reorganizing the membrane. The Journal of Membrane Biology 2021, 254, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.W. DAPTOMYCIN, its membrane-active mechanism vs. That of other antimicrobial peptides. Biochimica Biophysica Acta. Biomembranes 2020, 1862, 183395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schittek, B.; Hipfel, R.; Sauer, B.; Bauer, J.; Kalbacher, H.; Stevanovic, S.; Schirle, M.; Schroeder, K.; Blin, N.; Meier, F.; et al. Dermcidin: A novel human antibiotic peptide secreted by sweat glands. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieg, S.; Seeber, S.; Steffen, H.; Humeny, A.; Kalbacher, H.; Stevanovic, S.; Kimura, A.; Garbe, C.; Schittek, B. Generation of multiple stable dermcidin-derived antimicrobial peptides in sweat of different body sites. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.; Liu, H.; Hui Lee, W.; Zhang, Y. An anionic antimicrobial peptide from toad bombina maxima. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 295, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Lin, N.; Liu, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D. A novel antimicrobial peptide screened by a bacillus subtilis expression system, derived from larimichthys crocea ferritin h, exerting bactericidal and parasiticidal activities. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1168517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikapitiya, C.; Dananjaya, S.H.S.; Chandrarathna, H.P.S.U.; De Zoysa, M.; Whang, I. Octominin: A novel synthetic anticandidal peptide derived from defense protein of octopus minor. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodam Hazrati, M.; Vácha, R. Membrane adsorption enhances translocation of antimicrobial peptide buforin 2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 8469–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, M.P.; Kolodkin, N.I.; Kolobov, A.A.; Afonin, V.G.; Afonina, I.V.; Stefanenko, L.I.; Shpen’, V.M.; Shamova, O.V.; Kolobov, A.A. Indolicidin analogs with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and low hemolytic activity. Peptides 2020, 132, 170356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.J.; Kang, N.H.; Kim, M.K.; Park, J.; Park, E.; Park, G.H.; Kang, T.W.; Na, D.E.; Park, J.B.; Yi, Y.E.; et al. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity, and mechanism of action of pleurocidin against drug resistant staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajish, C.; Yang, S.; Kumar, S.D.; Shin, S.Y. Proadrenomedullin n-terminal 20 peptide (PAMP) and its c-terminal 12-residue peptide, PAMP(9-20): Cell selectivity and antimicrobial mechanism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imjongjirak, C.; Amphaiphan, P.; Charoensapsri, W.; Amparyup, P. Characterization and antimicrobial evaluation of SpPR-AMP1, a proline-rich antimicrobial peptide from the mud crab scylla paramamosain. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 74, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Guan, S.; Sun, W.; Fu, H. Melittin, the major pain-producing substance of bee venom. Neurosci. Bull. 2016, 32, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, R.; Hakemi Vala, M.; Hashemi, A.; Aghazadeh, H.; Sabatier, J.; Pooshang Bagheri, K. Action mechanism of melittin-derived antimicrobial peptides, MDP1 and MDP2, de novo designed against multidrug resistant bacteria. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergaoui, I.; Zaïri, A.; Gharsallah, H.; Aouni, M.; Hammami, A.; Hani, K.; Selmi, B. The in vitro evaluation of anti-chlamydial and cytotoxic properties of dermaseptin s4 and derivatives: Peptides from amphibian skin. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 6096–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Gwak, J.W.; Kamarajan, P.; Fenno, J.C.; Rickard, A.H.; Kapila, Y.L. Biomedical applications of nisin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primer Name | Sequences (5′-3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| pET-32a-F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG | Universal primer |
| pET-32a-R | TGCTAGTTATTGCTCAGCGG | |
| rLc149-F | gctgatatcggatccgaattcGAATTCATGAACATCAACATCGACA | cDNA cloning |
| rLc149-R | gtggtggtggtggtgctcgagCTCGAGGAGTGACAGATGAGAGC |
| Bacteria | DIZs (mm) |
|---|---|
| E. coli | 15.50 ± 0.90 |
| V. harveyi | 11.00 ± 0.10 |
| Bacterial Species | DIZs (mm) | MIC (µg/mL) | MBC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | 12.83 ± 0.58 | 31.25 | 62.50 |
| V. harveyi | 10.17 ± 0.29 | 62.50 | 62.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, C.; Chen, M.; Xu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D. A Hypothetical Protein Fragment from Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Demonstrates Significant Activity Against Both Bacterial and Parasite. Fishes 2025, 10, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030109
Yan C, Chen M, Xu H, Jin J, Liu X, Wang Z, Zhang D. A Hypothetical Protein Fragment from Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Demonstrates Significant Activity Against Both Bacterial and Parasite. Fishes. 2025; 10(3):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030109
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Chunmei, Meiling Chen, Hao Xu, Jian Jin, Xiande Liu, Zhiyong Wang, and Dongling Zhang. 2025. "A Hypothetical Protein Fragment from Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Demonstrates Significant Activity Against Both Bacterial and Parasite" Fishes 10, no. 3: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030109
APA StyleYan, C., Chen, M., Xu, H., Jin, J., Liu, X., Wang, Z., & Zhang, D. (2025). A Hypothetical Protein Fragment from Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Demonstrates Significant Activity Against Both Bacterial and Parasite. Fishes, 10(3), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030109







