Assessment of Hepatic Enzyme Biomarkers in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) from Lotic and Lentic Freshwater Habitats: Implications for Monitoring Metal Pollution and Ecological Stress in Aquatic Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling of Fish
2.2. Elemental Analysis
2.3. Hepatic Enzymes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters in Water
3.2. Fish Length, Weight and Fulton’s Condition Factor
3.3. Element Concentrations in Water
3.4. Differences in Hepatic Element Concentrations and Enzyme Activities in All Fish Specimens (Males and Females) Between Reservoirs and River Ecosystem
3.5. Differences in Hepatic Element Concentrations and Enzymes Between Females and Males
3.6. Correlation Analysis of Metal and Enzyme Concentrations in Northern Pike Liver
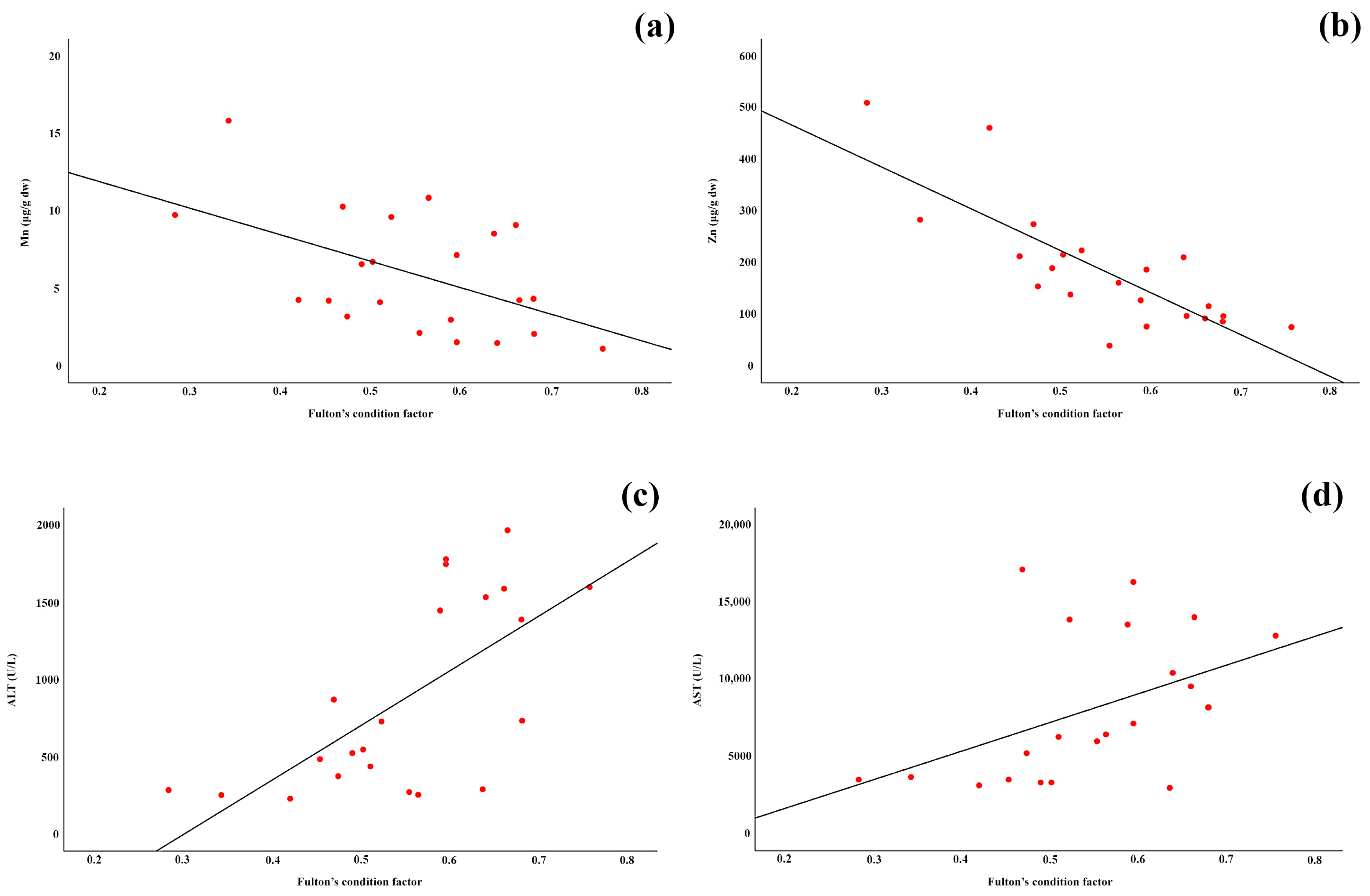
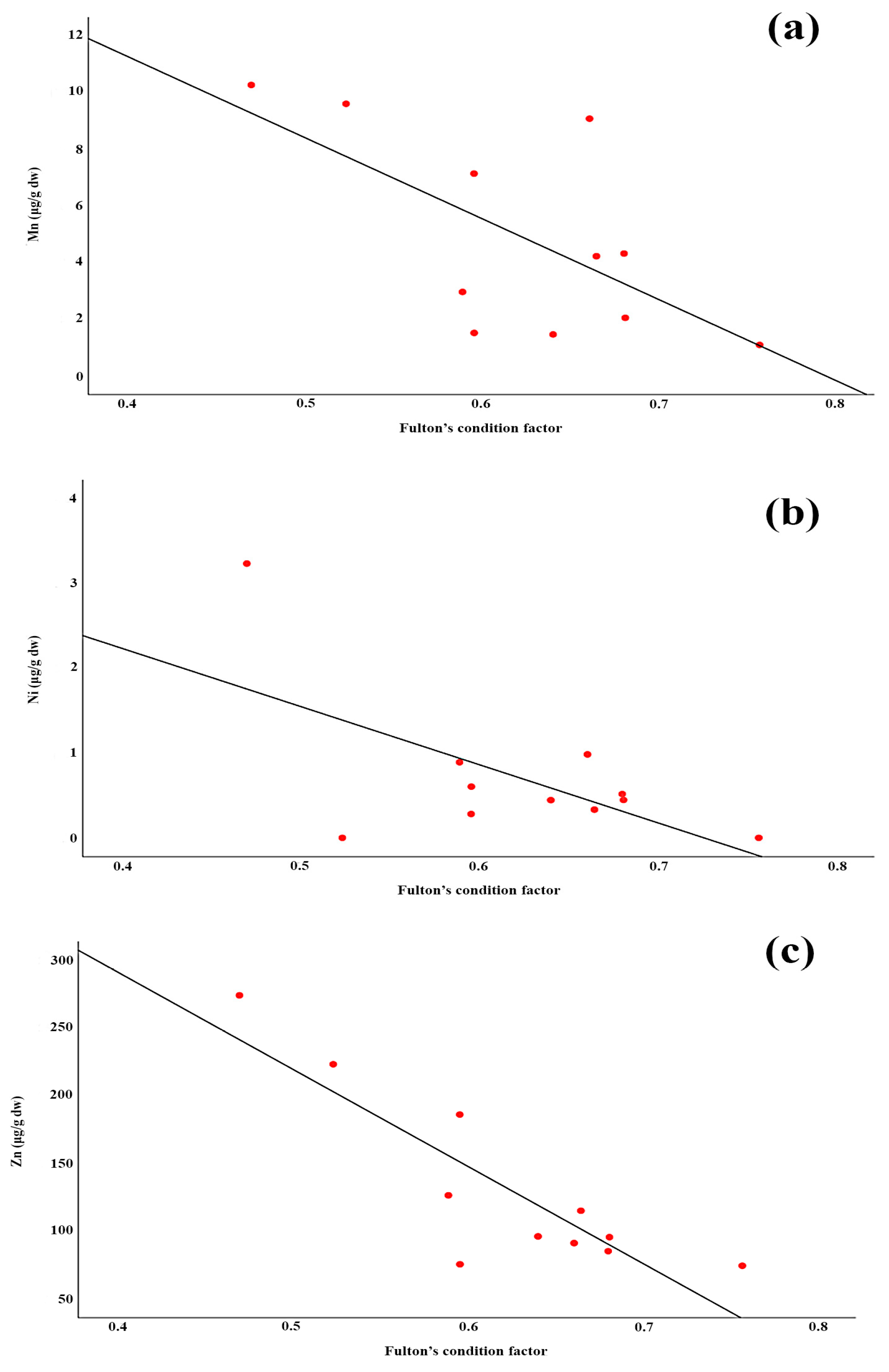
3.7. Regression of Hepatic Element Concentration and Enzyme Activities with Fish Condition Factor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, W.; Su, L.; Craig, N.J.; Du, F.; Wu, C.; Shi, H. Comparison of microplastic pollution in different water bodies from urban creeks to coastal waters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Kumari, N. Impact assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface water bodies. In Metals in Water: Global Sources, Significance, and Treatment; Shukla, S.K., Kumar, S., Madhav, S., Mishra, P.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 129–154. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, P.; Saravanan, V.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Arnica, G.; Rajasimman, M.; Gurunathan, B.; Pugazhendhi, A. Comprehensive review on toxic heavy metals in the aquatic system: Sources, identification, treatment strategies, and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2024, 249, 119440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štrbac, S.; Kašanin Grubin, M.; Vasić, N. Importance of background values in assessing the impact of heavy metals in river ecosystems: Case study of Tisza River, Serbia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1247–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Ye, S.; Yuan, H.; Ding, X.; Wang, J. Surface sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 2966–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Ordiales, E.; Esbrí, J.M.; Covelli, S.; López-Berdonces, M.A.; Higueras, P.L.; Loredo, J. Heavy metal contamination in sediments of an artificial reservoir impacted by long-term mining activity in the Almadén mercury district (Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6024–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Barabach, J.; Ptak, M.; Zhu, S. Heavy metals in lake surface sediments in protected areas in Poland: Concentration, pollution, ecological risk, sources, and spatial distribution. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boškov, J. Impact of tourism on spatial transformation: A case study of the Bela Crkva municipality (Serbia). Eur. J. Econ. Stud. 2015, 3, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, A.; Said, K.; Messaoudi, I. Cadmium: Bioaccumulation, histopathology, and detoxifying mechanisms in fish. Am. J. Res. Commun. 2013, 1, 60–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wannas, A.K.; Mohammed, S.H. The role of environmental stress in fish health: A review. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 32, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezierska, B.; Witeska, M. The metal uptake and accumulation in fish living in polluted waters. In Soil and Water Pollution Monitoring, Protection and Remediation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Avigliano, E.; Monferrán, M.V.; Sánchez, S.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Gastaminza, J.; Volpedo, A.V. Distribution and bioaccumulation of 12 trace elements in water, sediment, and tissues of the main fishery from different environments of the La Plata basin (South America): Risk assessment for human consumption. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, G.Y.; Eissa, H.A.; Zaghloul, A.Y.; Kelany, M.S.; Hamed, M.A.; Moselhy, K.M.E. Impact of some heavy metal accumulation in different organs on fish quality from Bardawil Lake and human health risks assessment. Geochem. Trans. 2024, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M.; Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes; Publications Kottelat, Cornol and Freyhof: Berlin, Germany, 2007; p. 646. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolić, D.; Skorić, S.; Janković, S.; Hegediš, A.; Djikanović, V. Age-specific accumulation of toxic metal(loid)s in northern pike (Esox lucius) juveniles. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusek, L.; Svobodova, Z.; Janouskova, D.; Vykusova, B.; Jarkovsky, J.; Smid, R.; Pavlis, P. Bioaccumulation of mercury in muscle tissue of fish in the Elbe River (Czech Republic): Multispecies monitoring study 1991–1996. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pinho, A.P.; Guimarães, J.R.D.; Martins, A.S.; Costa, P.A.S.; Olavo, G.; Valentin, J. Total mercury in muscle tissue of five shark species from Brazilian offshore waters: Effects of feeding habit, sex, and length. Environ. Res. 2002, 89, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavia, L.; da Silva, A.P.; Carneiro, M.C.; Kmecick, M.; Pozzan, R.; Esquivel-Muelbert, J.; Isaac, L.; Prodocimo, M.M. Health status biomarkers and hemato-biochemical indices in Nile tilapia. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 7, 200168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalefa, H.S.; AbuBakr, H.O.; Aljuaydi, S.H.; Kotp, Y.H.; Al-Mokaddem, A.K.; Abdel-Moneam, D.A. Aquatic assessment of the chelating ability of silica-stabilized magnetite nanocomposite to lead nitrate toxicity with emphasis on their impact on hepatorenal, oxidative stress, genotoxicity, histopathological, and bioaccumulation parameters in Oreochromis niloticus and Clarias gariepinus. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 262. [Google Scholar]
- Shahsavani, D.; Baghshani, H.; Nourian, K. Impact of betaine and allicin against circulating oxidative and biochemical alterations induced by cadmium intoxication in common carp. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 3637–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begun, G. In vivo biochemical changes in liver and gill of Clarias batrachus during cypermethrin exposure and following cessation of exposure. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 82, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Scotti, L.; Siqueira, D.; Zanini, R.; do Amaral, F.; Jurinitz, D.; Wassermann, G. Changes in hematological and serum biochemical values in jundiá (Rhamdia quelen) due to sub-lethal toxicity of cypermethrin. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.; Mushigeri, S.B.; Shivakumar, R.; Philip, G.H. Response of Cyprinus carpio (Linn) to sublethal concentration of cypermethrin: Alterations in protein metabolic profiles. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmeyer, H.U.; Bowers, G.N., Jr.; Horder, M.; Moss, D.W. Provisional recommendations on IFCC methods for the measurement of catalytic concentrations of enzymes. Part 2. IFCC method for aspartate aminotransferase. Clin. Chim. Acta 1976, 70, F19–F29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, W.E. Computation and interpretation of the biological statistics of fish populations. Bull. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1975, 191, 10019384629. [Google Scholar]
- Sakan, S.; Gržetić, I.; Đorđević, D. Distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in the Tisa (Tisza) River sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2007, 14, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanović, A.; Milijašević, D.; Brankov, J. Assessment of polluting effects and surface water quality using water pollution index: A case study of Hydro-system Danube-Tisa-Danube, Serbia. Carpath. J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2011, 6, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Stojanović, Ž. Agriculture in Serbia. In The Geography of Serbia; Manić, E., Nikitović, V., Djurović, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 269–288. [Google Scholar]
- Mitić, D.-L.; Živković, M.; Teofilović, V. Tragovi teških metala u vodama belocrkvanskih jezera (in Serbian). In Proceedings of the 27th Conference on Biotechnology with International Participation, Čačak, Srbija, 25–26 March 2022; pp. 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Report on the Measurement of Surface Waters of the “Belocrkvan Lakes” on 8th August 2024. Available online: https://www.jezera.rs/obavestenja/52-a-8-8-2024 (accessed on 3 September 2025). (In Serbian).
- Nguyen, H.L.; Braun, M.; Szaloki, I.; Baeyens, W.; Grieken, R.V.; Leermakers, M. Tracing the metal pollution history of the Tisza River through the analysis of a sediment depth profile. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 200, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apeagyei, E.; Bank, M.S.; Spengler, J.D. Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ni, S.J.; He, Z.W.; Zhang, C.J.; Nan, X.; Kong, B.; Weng, Z.Y. Analysis of the spatial relationship between heavy metals in soil and human activities based on landscape geochemical interpretation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 146, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapalia, A.; Borrok, D.M.; Van Metre, P.C.; Wilson, J. Zinc isotopic signatures in eight lake sediment cores from across the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, K.; Kandemir, Ş.; Doğru, M.I.; Doğru, A.; Şimşek, I.; Yılmaz, S.; Örün, G.; Altaş, L.; Yazıcıoğlu, A.; Korkmaz, N.; et al. The effects of seasonal heavy-metal pollution of Ladik Lake on pike fish (Esox lucius). Biol. Rhythm Res. 2021, 52, 821–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algül, F.; Beyhan, M. Concentrations and sources of heavy metals in shallow sediments in Lake Bafa, Turkey. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, M.; Zain, M.; Shakoor, N.; Ahmad, M.A.; Azeem, I.; Aziz, M.A.; Tulcan, R.X.S.; Rathore, A.; Tahir, M.; Horton, R.; et al. Global navigation of lithium in water bodies and emerging human health crisis. npj Clean Water 2023, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamat, N.; Movahedinia, A.; Etemadi-Deylami, E.; Mohammadi, Y. Pike (Esox lucius) bio-indicator of heavy metal pollution in Anzali Wetland. Water Qual. Expos. Health 2015, 7, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamunde, C.; Wood, C.M. The influence of ration size on copper homeostasis during sublethal dietary copper exposure in juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.Y.; Gitlin, J.D. Hepatic copper metabolism: Insights from genetic disease. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosell, M.; McGeer, J.C.; Wood, C.M. Plasma copper clearance and biliary copper excretion are stimulated in copper-acclimated trout. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 280, R796–R806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosell, M.; McDonald, M.D.; Walsh, P.J.; Wood, C.M. Effects of prolonged copper exposure in the marine gulf toadfish (Opsanus beta) II: Copper accumulation, drinking rate and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in osmoregulatory tissues. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štrbac, S.; Kašanin-Grubin, M.; Jovančićević, B.; Simonović, P. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and microelements in silver bream (Brama brama L.), northern pike (Esox lucius L.), sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus L.), and common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) from Tisza River, Serbia. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2015, 78, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris-Palacios, S.; Biagianti-Risbourg, S.; Vernet, G. Biochemical and (ultra)structural hepatic perturbations of Brachydanio rerio (Teleostei, Cyprinidae) exposed to two sublethal concentrations of copper sulfate. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 50, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, N.; Ger, T.R.; Uapipatanakul, B.; Huang, J.C.; Chen, K.H.; Hsiao, C.D. Review of Copper and Copper Nanoparticle Toxicity in Fish. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Cui, A.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W. Effects of copper exposure and recovery in juvenile yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi): Histological, physiological and molecular responses. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 31, 101669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarek-Gwiazda, E.; Amirowicz, A. Bioaccumulation of trace elements in roach, silver bream, Rudd, and perch living in an inundated opencast sulphur mine. Aquat. Ecol. 2006, 40, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshkarchy, S.S.; Raesen, A.K.; Najim, S.M. Effect of heavy metals on physiological and histological status in liver of common carp Cyprinus carpio, reared in cages and wild in the Euphrates River, Babil/Iraq. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 779, 012066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salem, Z.; Capelli, N.; Laffray, X.; Elise, G.; Ayadi, H.; Aleya, L. Seasonal variation of heavy metals in water, sediment and roach tissues in a landfill draining system pond (Etueffont, France). Ecol. Eng. 2014, 69, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yousuf, M.H.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Al-Ghais, S.M. Trace metals in liver, skin and muscle of Lethrinus lentjan fish species in relation to body length and sex. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 256, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkowska, M.; Protasowicki, M. Distribution of metals (Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu) in fish tissues in two lakes of different trophy in Northwestern Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošković, A.; Dojčinović, B.; Simić, S.; Pavlović, M.; Simić, V. Heavy metal and trace element bioaccumulation in target tissues of three edible predatory fish species from Bovan Reservoir (Serbia). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, N.; Sun, S.; An, Q.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W. Trends and health risk of trace metals in fishes in Liaodong Bay, China, from 2015 to 2020. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyeste, K.; Zulkipli, N.; Uzochukwu, I.E.; Somogyi, D.; Nagy, L.; Czeglédi, I.; Harangi, S.; Baranyai, E.; Simon, E.; Nagy, S.A.; et al. Assessment of trace and macroelement accumulation in cyprinid juveniles as bioindicators of aquatic pollution: Effects of diets and habitat preferences. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Kim, W.R.; Poterucha, J.J. Evaluation of elevated liver enzymes. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakan, M.S.; Đorđević, D.S.; Manojlović, D.D.; Polić, S.P. Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3337–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, W.A.; Srivastava, K.; Nasibullah, M.; Khan, M.F. Reactive oxygen species (ROS): Sources, generation, disease pathophysiology, and antioxidants. Discov. Chem. 2025, 2, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allameh, A.; Niayesh-Mehr, R.; Aliarab, A.; Sebastiani, G.; Pantopoulos, K. Oxidative Stress in Liver Pathophysiology and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, M.D. Alkaline phosphatase pathophysiology with emphasis on its role in the homeostasis of the enzyme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3144. [Google Scholar]
- Huseen, H.M.; Mohammed, A.J. Heavy Metals Causing Toxicity in Fishes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1294, 062028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, G.; Seneff, S. Gamma-Glutamyltransferase: A Predictive Biomarker of Cellular Antioxidant Inadequacy and Disease Risk. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 818570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgaml, S.A.; Khalil, R.; Hashish, E.A.; El-Murr, A. Protective effects of selenium and alpha-tocopherol against lead-induced hepatic and renal toxicity in Oreochromis niloticus. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mohiseni, M.; Asayesh, S.; ShafieeBazarnoie, S.; Mohseni, F.; Moradi, N.; Matouri, M.; Mirzaee, N. Biochemical alteration induced by cadmium and lead in common carp via an experimental food chain. Iran J. Toxicol. 2016, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourian, K.; Baghshani, H.; Shahsavani, D. The effect of vitamin C on lead-induced plasma biochemical alterations in fish, Cyprinus carpio. Iran J. Toxicol. 2019, 2, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.G.; AbouelFadl, K.Y.; Abd El Baset, M.; Mahmoud, U.M.; Kloas, W.; Moustafa, M.A. Blood biomarkers in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus and African catfish Clarias gariepinus to evaluate water quality of the River Nile. J. Fish Sci. Com. 2018, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrez, S.; Zughaibi, T.A.; Javed, M. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and their toxicity assessment in Mystus species. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Liao, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yao, X.; Du, C.; Wang, Y.; Song, F.; Deng, S.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, X.; et al. Independent and combined associations of urinary metals exposure with markers of liver injury: Results from the NHANES 2013–2016. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarski, B.; Witeska, M.; Kondera, E. Blood biochemical biomarkers in fish toxicology—A review. Animals 2025, 15, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, A.R.; Yeltekin, A. Metal levels in the liver, muscle, gill, intestine, and gonad of Lake Van fish (Chalcalburnus tarichi) with abnormal gonad. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 159, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, M.; Kaçar, E.; Karadede Akın, H. Accumulation of trace elements in muscle, gill and liver of fish species (Capoeta umbla and Luciobarbus mystaceus) in the Tigris River (Turkey), and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Cai, M.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, D.; Chen, K.; Lin, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, M.; et al. Metals in fishes from Yongshu Island, southern South China Sea: Human health risk assessment. J. Toxicol. 2017, 2017, 2458293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.; Davies, P.M. Body composition of northern pike (Esox lucius L.) in relation to body size and condition factor. Fish. Res. 1994, 19, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazicioğlu, O.; Yilmaz, S.; Polat, N. The growth feature of pike, Esox lucius L., 1758 inhabiting Lake Ladik. Acta Biol. Turc. 2024, 37, J4:1–J4:8. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, M.C.; Torronteras, R.; Córdoba, F.; Canalejo, A. Acute toxicity of manganese in goldfish Carassius auratus is associated with oxidative stress and organ specific antioxidant responses. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łuczyńska, J.; Tońska, E.; Paszczyk, B.; Łuczyński, M. The relationship between biotic factors and the content of chosen heavy metals (Zn, Fe, Cu and Mn) in six wild freshwater fish species collected from two lakes (Łańskie and Pluszne) located in northeastern Poland. Iran J. Fish Sci. 2020, 19, 421–442. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, M.; Kaçar, E. Bioaccumulation of metals in various tissues of fish species in relation to fish size and gender and health risk assessment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2023, 9, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musharraf, M.; Khan, M. Dietary manganese requirement of fingerling Indian major carp, Labeo rohita (Hamilton) estimated by growth, tissue manganese concentration and hepatic manganese-superoxide dismutase activity. Aquaculture 2021, 736, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Lin, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W. Effects of dietary zinc levels on growth performance, digestive enzyme activities, plasma physiological response, hepatic antioxidant responses and metallothionein gene expression in juvenile spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bervoets, L.; Blust, R. Metal concentrations in water, sediment and gudgeon (Gobio gobio) from a pollution gradient: Relationship with fish condition factor. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 126, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Chatha, A.M.M. Metals mixture effects on growth performance and their bioaccumulation in fish. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2022, 21, 601–614. [Google Scholar]
- Kasimoglu, C. The Effect of Fish Size, Age and Condition Factor on the Contents of Seven Essential Elements in Anguilla nguilla from Tersakan Stream Mugla (Turkey). J. Pollut. Eff. Cont. 2014, 2, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Das, D.; Sarbajna, A.; Chakraborty, S.B. Zinc modulates hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal-liver axis to impair reproduction in female Mystus vittatus (Bloch, 1794). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 42212–42229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharwat, M.; Almundarij, T.I.; Marzok, M. Diseases and disorders of trace elements deficiency in farm animals: An illustrated review. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2025, 14, 624–640. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, J.A.; Haque, A.; Akter, N.; Akter, S.; Satter, A.; Sarker, P.K.; Marshall, D.J.; Paray, B.A.; Hossain, M.B. Effects of dietary supplementation of Zn-nanoparticles on the growth performance and nutritional quality of Asian catfish, Clarias batrachus. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1410557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Khan, N.; Fatima, M.; Haque, N.U.; Davies, S.J. Bioavailability of zinc from different organic zinc chelates and their effect on the growth, whole body, tissue zinc content, enzymes activity and proximate composition of Labeo rohita. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0314146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, P.; Bergagna, S.; Dezzutto, D.; Barbero, R.; Righetti, M.; Pagliasso, G.; Gasco, L.; Gennero, M.S.; Pizzul, E.; Dondo, A.; et al. Long-term assessment of baseline blood biochemistry parameters in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) maintained under controlled conditions. Animals 2020, 10, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H.; Su, Y.; Ren, M.; Zhu, J.; Ge, X. Serum biochemistry, liver histology and transcriptome profiling of bighead carp Aristichthys nobilis following different dietary protein levels. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
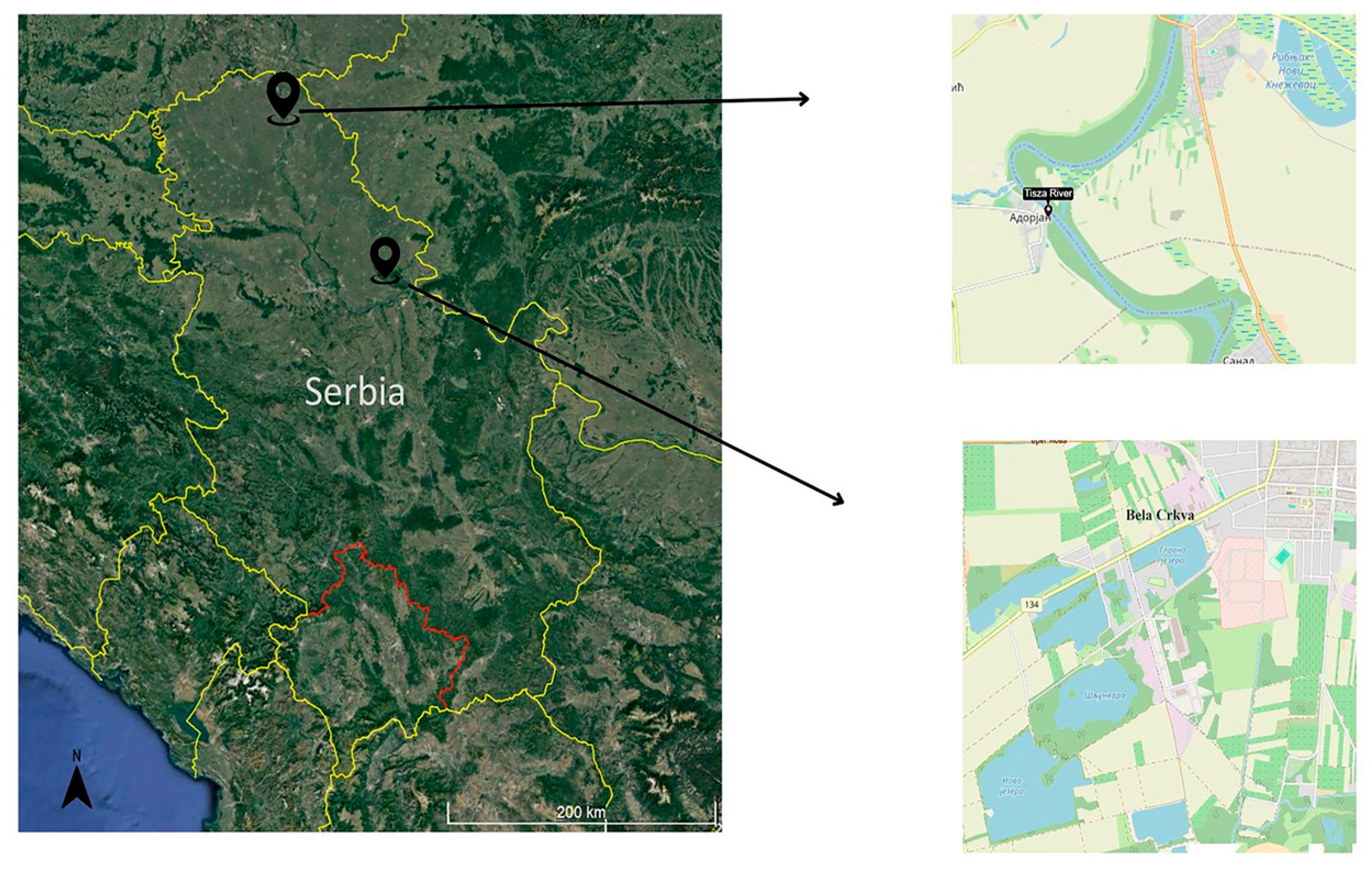

| Parameters | Bela Crkva Reservoirs Values (Min–Max) | Tisza River Values |
|---|---|---|
| O2 (mg/L) | 7.35–9.02 | 7.7 |
| O2 (%) | 72.4–85.8 | 72.9 |
| Temperature (°C) | 12.6–13.1 | 12.9 |
| pH | 7.68–7.9 | 7.49 |
| Conductivity (µS/cm−1) | 398–483 | 588 |
| Transmittance (cm) | 125–170 | 100 |
| TL (cm) | W (g) | Age | FCF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoirs | 30.23 ± 8.0 * | 163.85 ± 183.1 * | 1+–2+ | 0.48 ± 0.1 * |
| Tisza River | 42.81 ± 15.0 * | 693.16 ± 911.1 * | 1+–5+ | 0.62 ± 0.1 * |
| Females | 37.17 ± 17.5 | 552.08 ± 1032.9 | 1+–5+ | 0.56 ± 0.1 |
| Males | 36.07 ± 10.4 | 342.96 ± 342.8 | 1+–3+ | 0.55 ± 0.1 |
| Liver | Reservoirs | Tisza River | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | As | 0.47 ± 0.5 | 0.22 ± 0.4 | ns |
| Cr | 0.35 ± 0.2 | 0.38 ± 0.2 | ns | |
| Cu | 7.78 ± 3.1 * | 41.92 ± 35.8 * | 0.000 | |
| Fe | 151.59 ± 153.3 * | 862.73 ± 516.5 * | 0.001 | |
| Li | 0.09 ± 0.1 | 0.08 ± 0.1 | ns | |
| Ni | 1.78 ± 5.1 | 0.70 ± 0.9 | ns | |
| Mn | 6.91 ± 4.1 | 4.88 ± 3.5 | ns | |
| Pb | 1.11 ± 0.6 | 1.24 ± 0.5 | ns | |
| Zn | 233.59 ± 138.8 * | 131.17 ± 66.9 * | 0.034 | |
| Enzyme | ALT | 359.20 ± 119.5 * | 1397.91 ± 430.3 * | 0.000 |
| AST | 4302.84 ± 1376.3 * | 11,923.59 ± 3413.1 * | 0.000 | |
| AP | 990.68 ± 324.9 | 988.22 ± 287.2 | ns | |
| GGT | 5.20 ± 1.9 * | 3.46 ± 0.8 * | 0.016 |
| Liver | Females | Males | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element (μg g−1 dw) | As | 0.36 ± 0.5 | 0.33 ± 0.5 | ns |
| Cr | 0.43 ± 0.3 | 0.32 ± 0.2 | ns | |
| Cu | 31.71 ± 44.3 | 20.10 ± 15.5 | ns | |
| Fe | 532.99 ± 571.6 | 489.28 ± 504.9 | ns | |
| Li | 0.14 ± 0.1 * | 0.05 ± 0.1 * | 0.011 | |
| Ni | 0.62 ± 1.0 | 1.67 ± 4.7 | ns | |
| Mn | 7.87 ± 2.7 * | 4.53 ± 4.0 * | 0.030 | |
| Pb | 1.02 ± 0.5 | 1.28 ± 0.5 | ns | |
| Zn | 176.41 ± 71.7 | 186.51 ± 145.3 | ns | |
| Enzyme (UL−1) | ALT | 757.86 ± 557.6 | 962.11 ± 659.5 | ns |
| AST | 8762.01 ± 5692.3 | 7664.05 ± 3971.0 | ns | |
| AP | 908.55 ± 271.8 | 1045.46 ± 314.9 | ns | |
| GGT | 4.39 ± 1.7 | 4.28 ± 1.7 | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jovičić, K.; Đikanović, V.; Subotić, S.; Dimitrijević, M.; Kovačević, S.; Miljanović, B.; Vranković, J.S. Assessment of Hepatic Enzyme Biomarkers in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) from Lotic and Lentic Freshwater Habitats: Implications for Monitoring Metal Pollution and Ecological Stress in Aquatic Ecosystems. Fishes 2025, 10, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110541
Jovičić K, Đikanović V, Subotić S, Dimitrijević M, Kovačević S, Miljanović B, Vranković JS. Assessment of Hepatic Enzyme Biomarkers in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) from Lotic and Lentic Freshwater Habitats: Implications for Monitoring Metal Pollution and Ecological Stress in Aquatic Ecosystems. Fishes. 2025; 10(11):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110541
Chicago/Turabian StyleJovičić, Katarina, Vesna Đikanović, Srđan Subotić, Milena Dimitrijević, Snežana Kovačević, Branko Miljanović, and Jelena S. Vranković. 2025. "Assessment of Hepatic Enzyme Biomarkers in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) from Lotic and Lentic Freshwater Habitats: Implications for Monitoring Metal Pollution and Ecological Stress in Aquatic Ecosystems" Fishes 10, no. 11: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110541
APA StyleJovičić, K., Đikanović, V., Subotić, S., Dimitrijević, M., Kovačević, S., Miljanović, B., & Vranković, J. S. (2025). Assessment of Hepatic Enzyme Biomarkers in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) from Lotic and Lentic Freshwater Habitats: Implications for Monitoring Metal Pollution and Ecological Stress in Aquatic Ecosystems. Fishes, 10(11), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110541







