Abstract
Quantum computing challenges the mathematical problems anchoring the security of the classical public key algorithms. For quantum-resistant public key algorithms, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has undergone a multi-year standardization process and selected the post-quantum cryptography (PQC) public key digital signatures of Dilithium, Falcon, and SPHINCS+. Finding common ground to compare these algorithms can be difficult because of their design differences, including the fundamental math problems (lattice-based vs. hash-based). We use a visualization model to show the key/signature size vs. security trade-offs for all PQC algorithms. Our performance analyses compare the algorithms’ computational loads in the execution time. Building on the individual algorithms’ analyses, we analyze the communication costs and implementation overheads when integrated with Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and with Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)/Internet Protocol (IP). Our results show that the lattice-based algorithms of Dilithium and Falcon induce lower computational overheads than the hash-based algorithms of SPHINCS+. In addition, the lattice-based PQC can outperform the classical algorithm with comparable security strength; for example, Dilithium 2 and Falcon 512 outperform RSA 4096 in the TLS handshake time duration.
1. Introduction
Public key digital signatures provide authentication and integrity protection and are critical in securing digital systems. The security of the most-used present-day digital signature standards like Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA) [1] and the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) [2] are based on the computational hardness problems such as prime factorization and the discrete logarithm problem. Shor’s polynomial-time algorithm effectively solves these problems when equipped with a powerful quantum computer [3]. Securing digital communication against attackers that have access to quantum computing resources [4] requires new public key cryptographic algorithms that can withstand such quantum attackers.
Recent advancements in quantum computing and quantum computers (Section 3) yield a need for transitioning to post-quantum cryptography (quantum-resistant cryptography). This involves identifying the relevant hardness problems and designing and constructing quantum-resistant algorithms for securing digital communications.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) launched the Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) standardization project to establish and standardize quantum-resistant algorithms. The NIST has a track record of preparing for the impending cryptanalysis and breaks on cryptographic algorithms and is preparing for the post-quantum era before the emergence of practical quantum computer implementations capable of breaking current systems. The NIST’s involvement in cryptography has global and lasting impacts on digital systems, as demonstrated by their involvement in standardizing DES in the 1970s and AES in the late 1990s. The standardization process starts with an open public call that lists the requirements of the algorithms. All the submission algorithms are openly published and subjected to analyses, and, after the analyses, an algorithm is selected for standardization. The PQC standardization project follows the same process and requests that the interested parties provide submissions for quantum-resistant cryptographic candidates.
We study the security and performances of the NIST digital signature algorithms selected for standardization. The selected three digital signature algorithms are Crystals–Dilithium (Dilithium), Falcon, and SPHINCS+. The design principles and hardness problems underlying these digital signature algorithms come from lattice-based and hash-based cryptography (Section 4).
Contributions and Paper Organization
We compare the PQC digital signature schemes in both security and performance. We first focus on the algorithms before their integration into the TCP/TLS protocol and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). Our security analyses of the PQC algorithms include the adoption of a model for visual representations to compare the size–security trade-offs of digital signature algorithms (Section 5). These include the security offered by the digital signature algorithms with respect to public key length and signature length. We then analyze the individual algorithm performances in the execution time and its scalability in message sizes for key-pair generation, signature generation, and signature verification (Section 6). Our work additionally extends beyond the analyses of the individual algorithms and to the integration into the TCP/TLS protocol and PKI. We analyze the computational overheads involved in integration with PKI in terms of certificate generation and certificate verification times (Section 7) and the communication/handshake overheads for TLS 1.3 and TCP/IPv4 connection when integrating the signature algorithms (Section 8). Our analyses show that, with comparable security strengths, the lattice-based PQC algorithms (Dilithium and Falcon) can even outperform the classical RSA algorithm, while the hash-based SPHINCS+ generally takes longer than Dilithium and Falcon.
2. Materials and Methods
Methodologies and Approaches
For the performance analyses of the PQC schemes, we implement prototypes and empirically measure performances between the schemes. While the post-quantum era prepares for adversaries equipped with quantum computing, the PQC schemes are designed to be implemented on classical computers to defend common users. We build on the algorithm implementations from liboqs and openssl by Open Quantum Safe [5] and deploy them on a virtual machine with 4 processing cores and 8 GB of RAM on a computer equipped with an 8-core 16-thread AMD Ryzen 7 1700X processor with a 3.4 GHz processor frequency and 32 GB RAM. While the absolute performance costs vary depending on the computer platform and its hardware specifications, we focus on the comparison results in this paper so that our results and insights are applicable to classical non-quantum computers beyond our platform. We run each experiment to collect 1000 data values and use the average value for our analysis. We compare the performance costs of the algorithms by themselves in Section 6, when integrated into PKI in Section 7, and when integrated with TLS 1.3 and TCP/IP in Section 8.
3. Background: PQC History and NIST
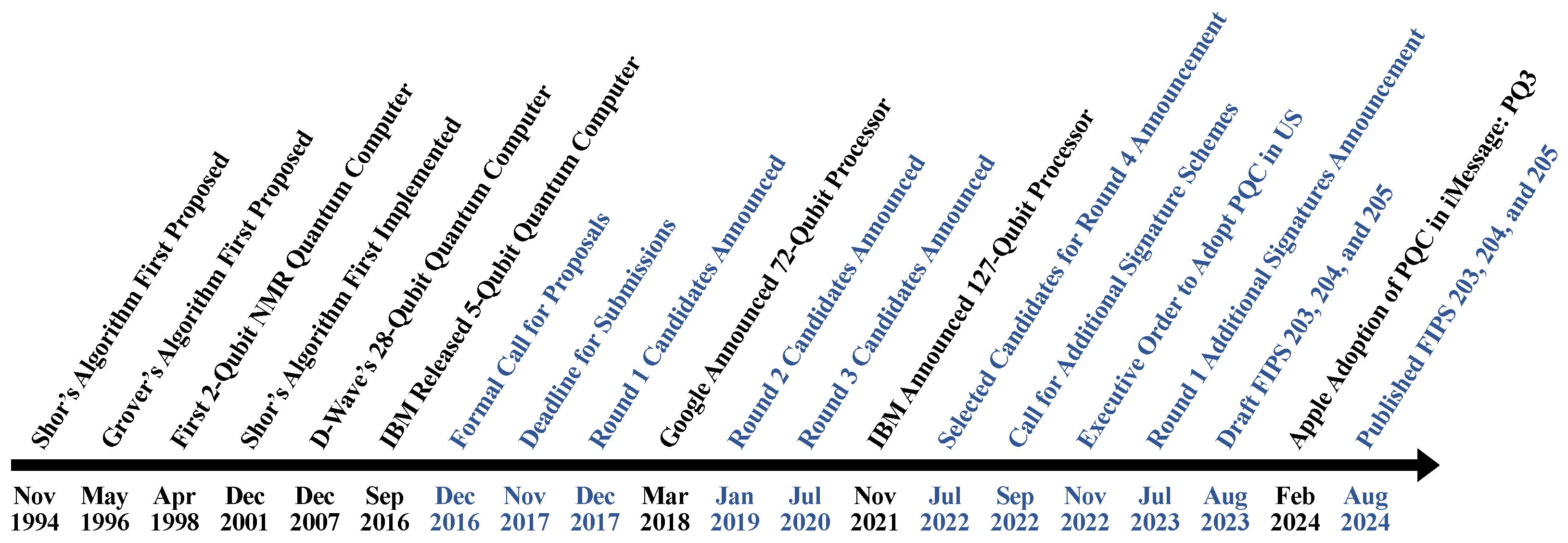
We describe the PQC history and the NIST involvement to motivate our work in this section, and Figure 1 shows the timeline of events regarding cryptography and quantum computing. Cryptography provides the backbone to secure digital systems in our society. While practical quantum computers currently only support a small number of qubits and remain at proof-of-concept stages, theoretical algorithms building on quantum computing have emerged to expedite the solving of computational hardness problems anchoring the security of current public–key algorithms. Shor’s algorithm [3], invented in 1994, provides a polynomial-time algorithm in quantum computing for solving the prime factorization and discrete log problem, threatening the security of public key algorithms such as RSA and Diffie–Hellman Key Exchange. Grover’s algorithm [6], invented in 1996, expedites the brute-force search of the general problems, such as the original database search problem and hash collision finding. The first successful implementation of quantum searching was performed, in 1998, on a two-qubit Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) quantum computer. It used Grover’s algorithm to search for a system that has four states [7]. Followed by Grover’s implementation, in 2001, a seven-qubit NMR quantum computer [8] used Shor’s algorithm to find prime factors for the number 15.
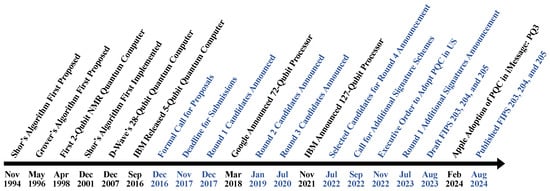
Figure 1.
PQC history and the events leading up to NIST’s standardization. Highlighted in blue are the events involving NIST.
Inspired by the extraordinary opportunities in quantum computing, major tech giants started research into quantum computers. The first was D-Wave Systems, using quantum annealing concepts, which cannot run Shor’s algorithm and is built for specific applications like combinatorial optimization problems. In 2019, D-Wave unveiled a 5000 qubit processor [9]. On the other hand, Google and International Business Machines (IBM) follow the universal quantum gate model, which can run Shor’s algorithm. In 2018, Google announced a 72-qubit quantum processor [10]. IBM showed significant progress from a 5-qubit processor [11] to a 127-qubit processor and announced details on futuristic 433- and 1121-qubit processors. IBM’s quantum experience provides access to up to 32-qubit processor quantum computers for registered users free of cost [12]. With steady growth in practical quantum computers and raising concerns in cryptography, the NIST initiated the PQC standardization project. The NIST requested nominations in December 2016 for public key post-quantum cryptographic algorithms [13]. The NIST’s PQC standardization project aims to replace the present recommended digital signature standards of RSA and ECDSA [14] with post-quantum algorithms. Instead of measuring the security in bits, all these post-quantum algorithms are referenced with security categories defined by the NIST (Table 1). Each of these categories sets the minimum required computational resources to break well-known symmetric block cipher or hash functions. Breaking a symmetric block cipher indicates a successful brute-force key search attack, and breaking a hash function means a successful brute-force collision attack. Computational resources can be restricted by a new parameter, defined by NIST, called MAXDEPTH. It can be used to limit the quantum attacks to a fixed run time or circuit depth. PQC standardization is a multi-year process and involves multiple rounds of analyses and scrutiny for the maturity of algorithm design before standardization.

Table 1.
NIST security categories, where X is the MAXDEPTH.
In response to the open public call for the PQC standardization proposal [13], the NIST received 82 submissions, and only 69 of the submissions satisfied the minimum required conditions. The first round of the PQC standardization project started in December 2017 and selected 26 candidate algorithms. With fewer algorithms to analyze, the second round of the PQC standardization project started in January 2019 and selected 15 algorithms for the third round [16]. In July 2022, the NIST announced the end of the third round and selected candidates for standardization. A public key encryption/KEM and three digital signatures were selected for standardization. In August 2024, the NIST released three standards including (i) KEM: FIPS 203 based on Kyber, and (ii) digital signatures: FIPS 204 based on Dilithium and 205 based on SPHINCS+ for public comments. The NIST has yet to release FIPS 206 based on FALCON. The PQC standardization effort has continued to round 4 for identifying additional KEM standards. In September 2022, the NIST started a new search for digital signatures and released an additional call for proposals. This effort is currently in its round 2 and is analyzing fourteen candidates for digital signatures [17]. Notable exceptions of the NIST finalist algorithm family candidates from the third round that did not get selected were the multivariate-based algorithms. While surviving the first three rounds, during the third round, the key-recovery attack [18], rectangular MinRank attack [19], and hybrid combinatorial/algebraic attack [20] were discovered as being able to break the multivariate-based mathematical problem in polynomial time (e.g., Rainbow—I got broken and the key compromised in days).
We focus on the digital signature algorithms in this paper, while the NIST solicits and plans to standardize both key exchange/key encapsulation mechanisms and digital signature algorithms. Our work focuses on the NIST-selected signature schemes/algorithms: Dilithium, Falcon, and SPHINCS+.
4. PQC Signature Schemes
The NIST-selected digital signature schemes for standardization are Dilithium, Falcon, and SPHINCS+. These families of algorithms can be categorized into two different schemes, listed in Table 2, based on the hardness problems on which they rely. These include lattice-based signature schemes (Dilithium and Falcon) described in Section 4.1 and hash-based signature schemes (SPHINCS+) described in Section 4.2.

Table 2.
NIST-selected digital signature algorithms and respective parameter sets with security levels.
Within each algorithm family (Dilithium, Falcon, and SPHINCS+), there are multiple algorithms depending on the parameter choices for the security level control. The parameters affect the public key length and the private-key length as well as the signature length for the PQC signature algorithms, and the security strengths increase as the length increase (using greater number/options to yield greater entropy), as we study in Section 5. The public key and the signature lengths for the different algorithms are also listed in the horizontal axis in Figure 2. For example, Dilithium 2 has a public key length of 1312 Bytes, Dilithium 3 with 1952 Bytes, and Dilithium 5 with 2592 Bytes. Thus, Dilithium 5 is designed to have greater security strength than Dilithium 3, and Dilithium 3 greater than Dilithium 2. This section describes the overview of the PQC schemes without the scheme-specific details, such as the actual parameters/variables to control for the different algorithms within the family; we refer readers interested in the scheme-specific design details to the design documents for Dilithium [21], Falcon [22], and SPHINCS+ [23].
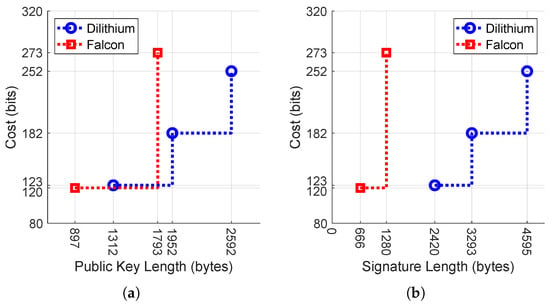
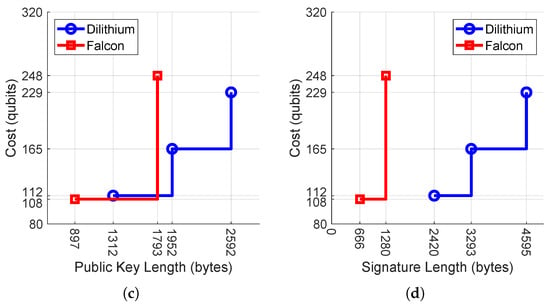
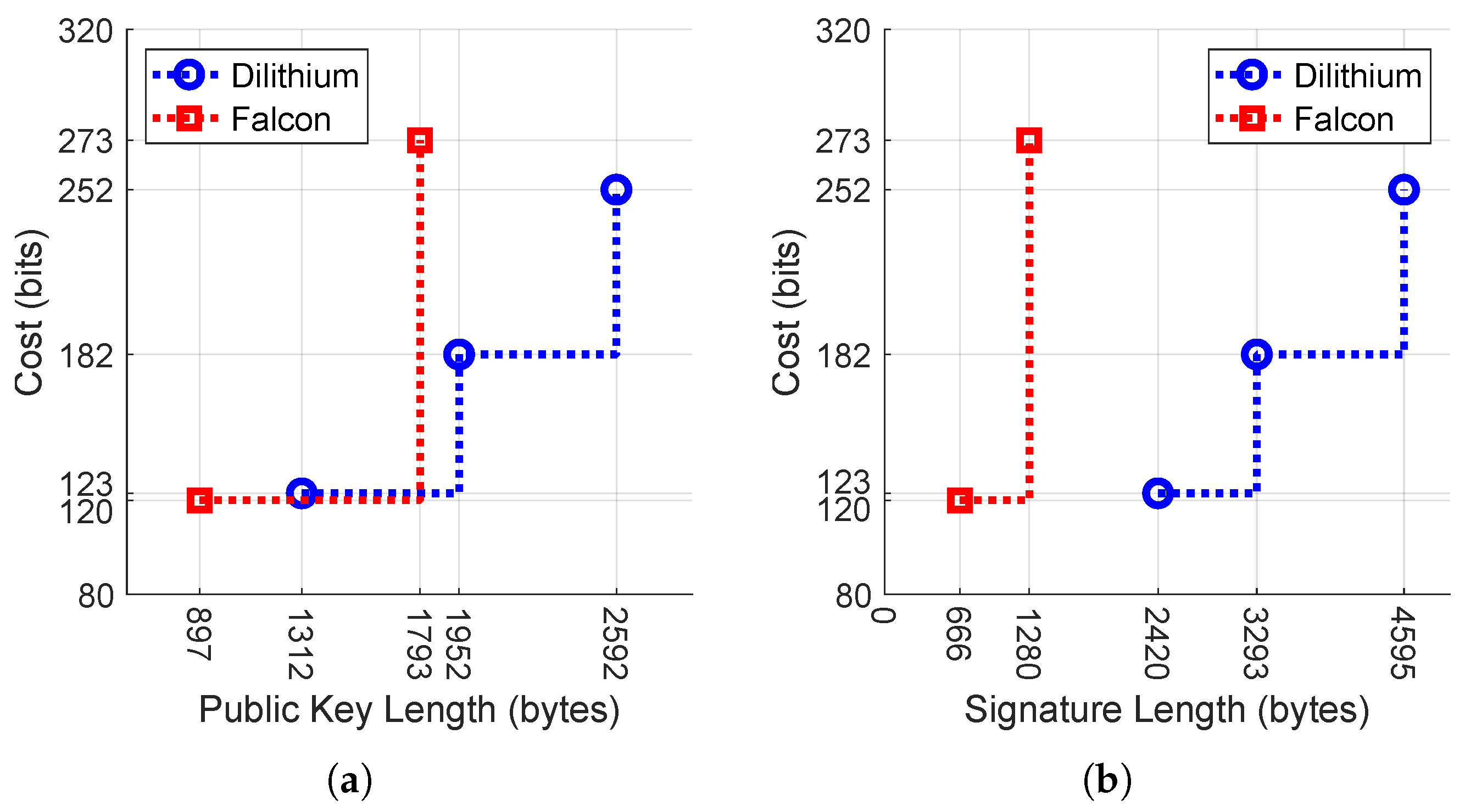
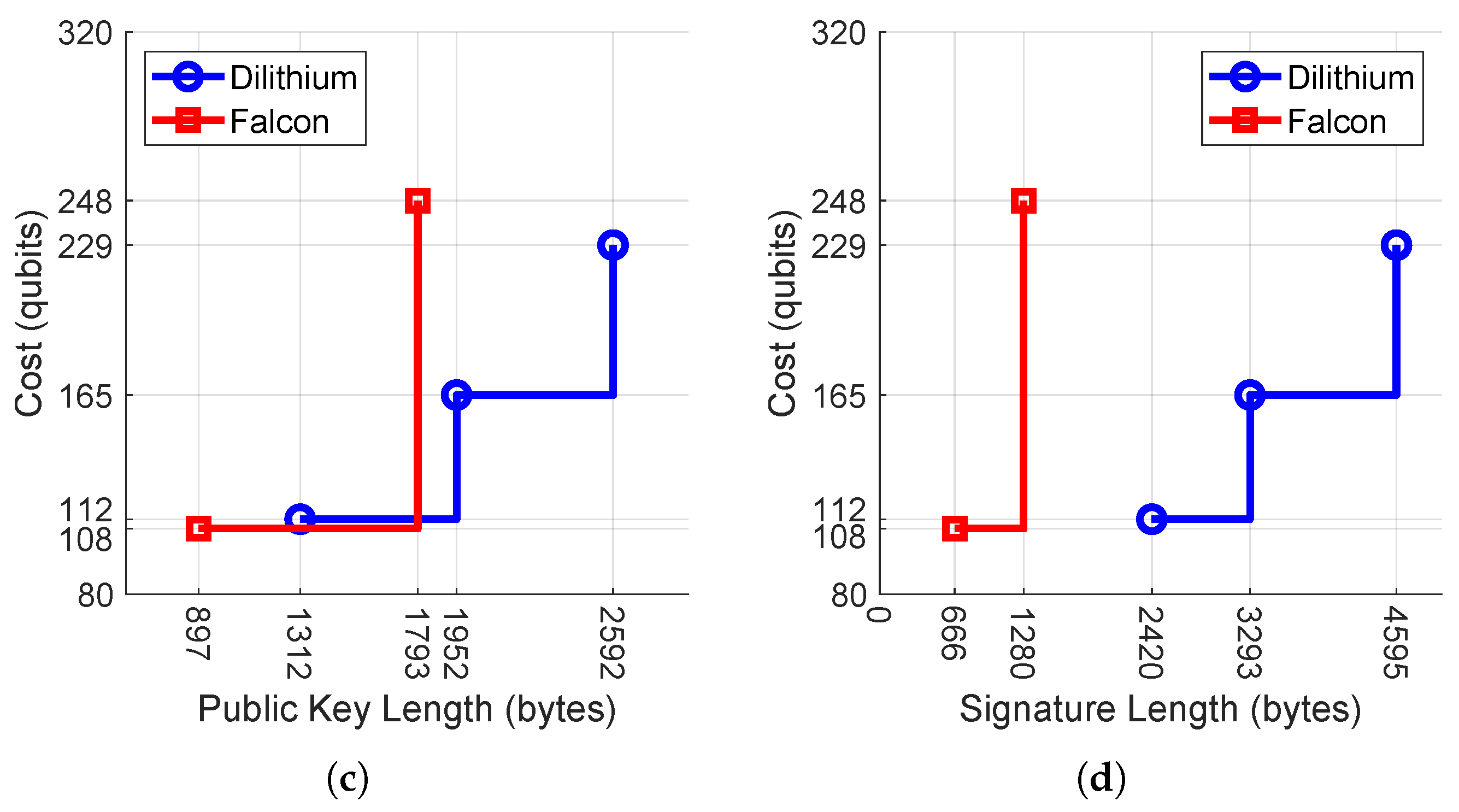
Figure 2.
Security costs for lattice-based signatures. The dotted line shows the classical bit security level (the top two figures), whereas the solid line shows the quantum bit security level (the bottom two figures). The vertical scales are consistent across the figures. (a) Security in bits vs. public key length. (b) Security in bits vs. signature length. (c) Security in qubits vs. public key length. (d) Security in qubits vs. signature length.
4.1. Lattice-Based Signature Schemes
Lattice-based signature schemes are based on a set of points in an n-dimensional space with a periodic structure [24]. The security of lattice-based cryptography comes from the use of NP-hard problems such as (i) Short Vector Problems (SVPs), which involve finding the shortest non-zero vector, (ii) Closed Vector Problems (CVPs), which involve finding the shortest vector, (iii) Learning With Errors (LWE), which is computationally intensive as it requires a linear function over a finite ring of given samples, (iv) Short Integer Solutions (SISs), which are based on Ajtai’s theorem, where if polynomial-time algorithm A solves the SIS problem, then there exists an Algorithm B that can solve the Short Vector Integer Problem (SVIP), (v) Learning With Rounding (LWR), which is the non-rounding variant of LWE. LWR is more efficient than LWE as it removes LWE’s complex randomization elements [25]. Both Dilithium and Falcon are lattice-based algorithms selected for standardization.
4.1.1. Dilithium
Dilithium relies on the Fiat–Shamir and Aborts framework and SVPs for its security [21]. Dilithium introduces three algorithms (Table 2) in Dilithium 2, Dilithium 3, and Dilithium 5 corresponding to 2, 3, and 5 of the NIST’s post-quantum security categories, respectively.
4.1.2. Falcon
Falcon is based on fast Fourier lattice-based compact signatures over an N-th Degree Truncated Polynomial Ring (NTRU) [22]. Falcon relies on the NTRU for key generation, encryption and decryption data, Short Integer Problems (SISs), Floating-Point arithmetic, and Gaussian sampling floating-point arithmetic for its security. Falcon parameter sets (Table 2) include Falcon 512 and Falcon 1024 algorithms corresponding to 1 and 5 of the NIST’s post-quantum security strengths, respectively.
4.2. Hash-Based Signature Schemes
Hash-based signatures are based on one-time signatures [26] or many-time signatures [27]. Their security relies on the collision and preimage resistance of the underlying hash function. Previously available standards like LMS and XMSS are stateful where the state of the private key needs to be remembered for single use and does not meet ideal digital signature requirements [13]. SPHINCS+ is stateless and builds on both one-time signature schemes as well as few-time signature schemes.
SPHINCS+
SPHINCS+ uses Winternitz One-Time Signature Plus (WOTS+) and a Forest of Random Subsets (FORS) for signature generation. SPHINCS+ parameter sets are designed to be small/size-optimized (s) or fast/speed-optimized (f). Each of the SPHINCS+ parameter sets in Table 2 has 3 more variants based on the underlying hash function. For example, SPHINCS+128s can be based on the SHA-256 (SPHINCS+-SHA-256-128s) or SHAKE256 (SPHINCS+-SHAKE256-128s) or Haraka (SPHINCS+-Haraka-128s) hash functions. Each of these can again be sub-categorized based on the type of construction as ’robust’, where XORs message with pseudo-random bitmasks, or ’simple’, where bitmasks are omitted [23]. For example, SPHINCS+-SHA-256-128s is available as SPHINCS+-SHA-256-128s-robust and SPHINCS+-SHA-256-128s-simple.
5. Security Analysis Using Visualization Model
In this section, we analyze the size–security trade-offs of the NIST-selected signature schemes using the attacker’s security cost in qubits. The metric qubit used to measure the security strength is relatively new and depends on the quantum computer physics and hardware architecture, which are in active research and development.
5.1. Metrics: Qubits
In classical computing, the state of a particular bit is always known. In the quantum case, before the measurement is carried out, the state of a qubit is unknown. Although a qubit resembles a classical bit after the measurement, it takes two possible values and additionally can exploit the interference effects; before the measurement, a qubit can be in a superposition of these two states described by the wave function. The classical brute-force attacker searches blindly and cannot distinguish if some particular value is closer or further from the key being searched, while checking if the key is found may only generate a binary result of “true” or “false”. In the quantum case, a brute-force attacker always has an overlap of the wave function of the current state of qubits and the key, and this overlap is bigger if some particular state of qubits is closer to the key being searched. Even if the algorithm’s structure is unknown to the attacker, interference helps to move in the direction towards the key, enabling a faster search.
Qubit Cost
Qubit cost indicates the number of qubits the attacker needs to break the algorithm assuming a sufficient number of gates. For Dilithium, qubit cost represents the cost of solving an SVP, which is exponential relative to Block–Korkine–Zolotarev (BKZ) algorithm’s block-size (b) [21]. For Falcon, core SVP hardness indicates the cost for one call to the SVP oracle in dimension b [22,28].
5.2. Lattice-Based Signatures Security and Length Trade-Off
Figure 2 shows the classical and quantum security cost trade-offs with respect to the public key length and the signature length of lattice-based signature algorithms. Public key length and signature length are important parameters controlling the trade-off between security strength and communication overhead in digital communications. For example, when Alice sends a signed message to Bob, Bob uses Alice’s public key and signature to verify the message. The public key and signature are the overheads in the communication. Many real-world applications use the same private/public key-pair to sign/verify multiple messages rather than using One Time Pad/Ephemeral Keys, resulting in the transfer of signatures more often than public keys. A low signature size and low public key lengths help in reducing communication costs. In Figure 2, an ideal algorithm will have a small communication cost (left in the plot) and provide strong security (top).
Dilithium and Falcon, the two lattice-based NIST finalists schemes, display the security vs. overhead/length trade-off, and the security costs measured in (classical) bits or qubits increase as the public key length or the signature length increases. Figure 2a analyzes the classical security cost to public key length trade-offs. With 123 and 120 bit costs targeting level 1 security, Dilithium’s public key size is 46.26% bigger than Falcon. Falcon at 1793 bytes offers level 5 security with 91 bits more security and has an 8.14% smaller public key size than Dilithium, offering level 3 security at 1952 bytes. Falcon with 273 bit cost targeting level 5 security has a 30.82% smaller public key size than Dilithium with 252 bit cost targeting level 5 security. As discussed before, low signature sizes are preferable and from Figure 2b,d it is evident that Falcon has low signature sizes compared to Dilithium for both classical and quantum security levels. Figure 2b analyzes the classical security cost to signature length trade-offs. With 123 and 120 bit costs targeting level 1 security, Dilithium’s signature size is 263.36% bigger than Falcon. Falcon with a 273 bit cost targeting level 5 security has a 72.14% smaller signature size than Dilithium with a 252 bit cost targeting level 5 security. Figure 2c analyzes the quantum security cost to public key length trade-offs. Falcon at a 248 qubit cost targeting level 5 security has a 99.88% bigger signature size than its level 1 parameter set with a 108 qubit cost.
For applications targeting security levels 2 and 3, Falcon does not have any parameter sets and yet it is advantageous to use the Falcon 1024 parameter set as it provides better security and less overhead compared to Dilithium parameter sets.
5.3. Hash-Based Signatures Security and Length Trade-Off
Figure 3 shows the classical and quantum security trade-offs with respect to the public key length and the signature length of the hash-based signature algorithm SPHINCS+. Hash-based signature algorithms generate smaller public keys and larger signatures compared to the lattice-based schemes in Section 5.2.
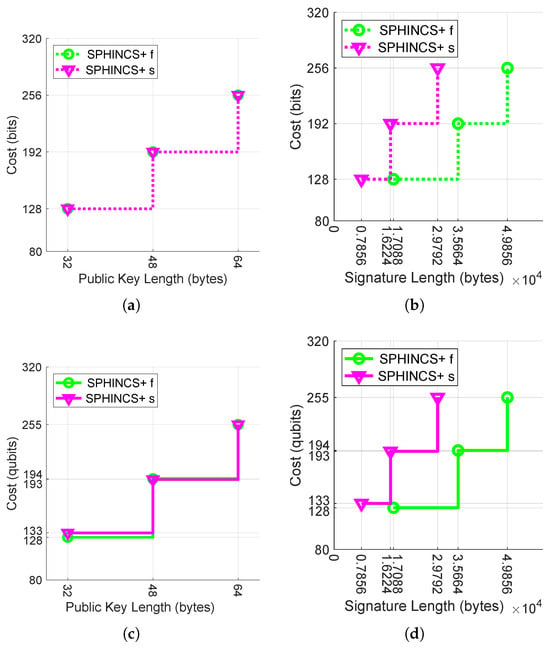
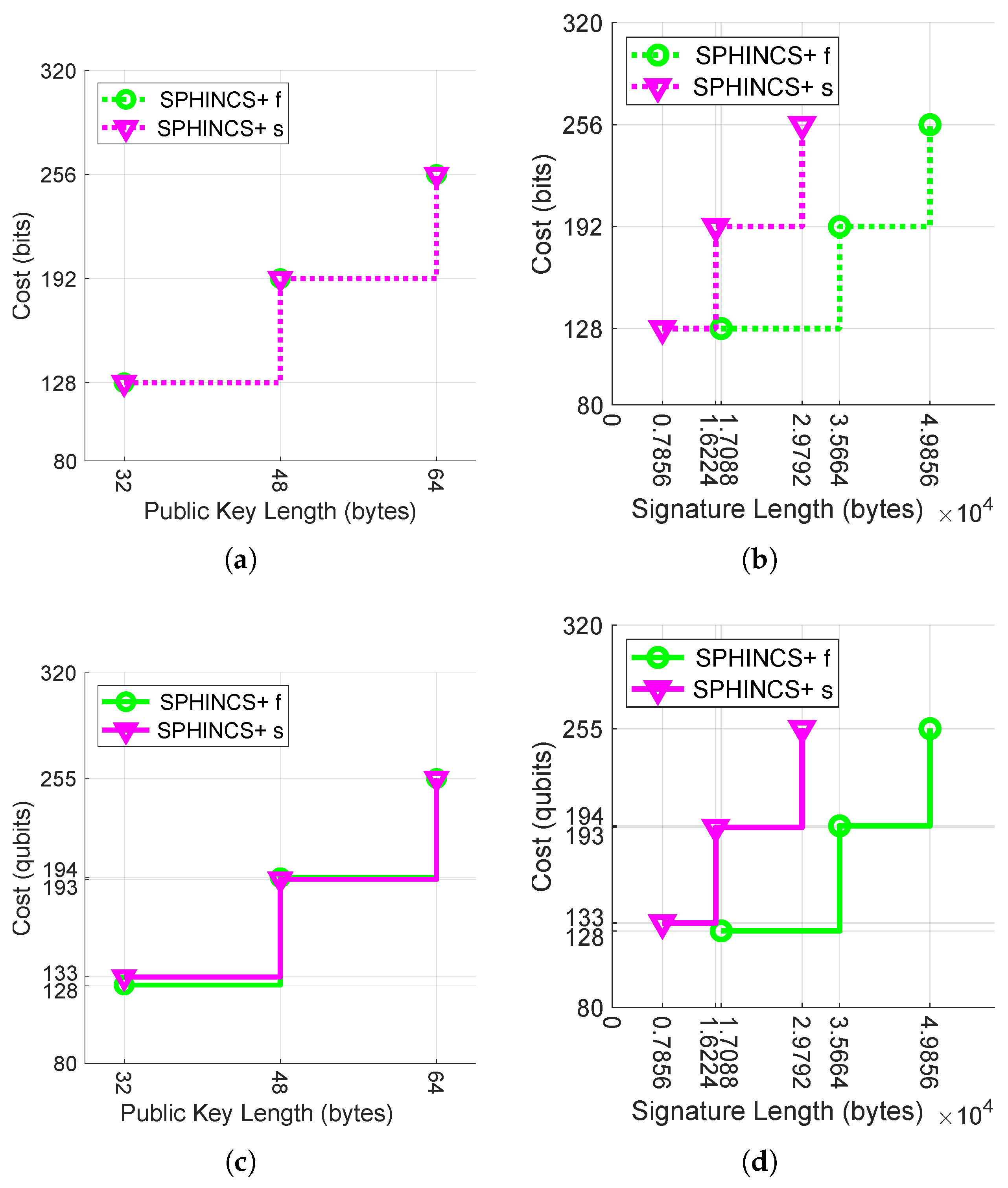
Figure 3.
Security costs for hash-based signatures. The dotted line shows the classical bit security level (the top two figures), whereas the solid line shows the quantum bit security level (the bottom two figures). The vertical scales are consistent across the figures. (a) Security in bits vs. public key length. (b) Security in bits vs. signature length. (c) Security in qubits vs. public key length. (d) Security in qubits vs. signature length.
Figure 3a analyzes the classical bit cost to public key length trade-offs. Both SPHINCS+s and SPHINCS+f have the same bit cost for the same public key sizes. This is due to the fact that in the classical case, the underlying hash function determines the security costs of the algorithm. Figure 3b analyzes the classical bit cost to signature length trade-offs. At a 128 bit cost, SPHINCS+s generates a 54.02% smaller signature than SPHINCS+f. As the security costs increases, this difference remains significant and is 40.24% at a 256 bit cost. Figure 3c analyzes the quantum bit cost to public key length trade-offs. For the same public key lengths of 32 bytes, SPHINCS+s provides 3.9% more security than SPHINCS+f. Figure 3d analyzes the quantum bit cost to signature length trade-offs. SPHINCS+f with a 1 qubit cost more than SPHINCS+s at 193 produces 119% more in signature length. Overall, SPHINCS+s parameter sets with smaller signature lengths are preferable over SPHINCS+f parameter sets.
6. Performance Analysis of PQC Digital Signature Algorithms
In this section, we analyze the execution times of each selected algorithm for key-pair generation, signature generation (signing), and signature verification (verifying). We use the liboqs version 0.7.2 library to analyze the performance of the algorithms. Using our benchmark software, each of the algorithms is sampled to calculate the average time duration for key-pair generation, signing a message, and verifying the messages. We also vary the message lengths with random data to measure the algorithm performances with respect to message scalability. Each data point is averaged over 1000 runs, and the results are plotted.
6.1. Algorithm Performances
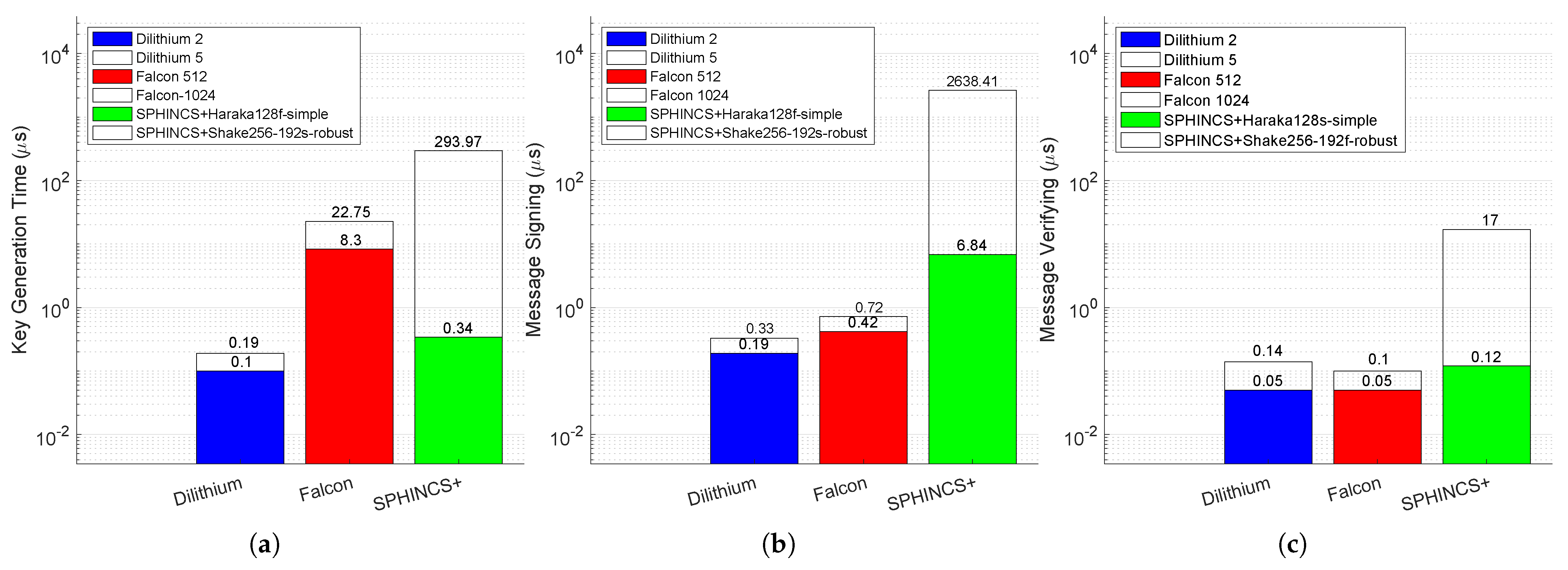
Figure 4 shows the computing costs for every algorithm of each family. While we experiment with all algorithms, our presentation/plot focuses on the slowest from each algorithm family (outlined bar) and the fastest from each algorithm family to show the performance span across Dilithium (D), Falcon (F), and SPHINCS+ (S).
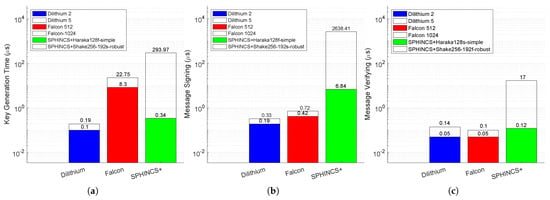
Figure 4.
Performance analysis of the fastest (colored bar) and slowest (outlined bar) signature candidates from each family across the three signature algorithms. The 95% confidence interval values are small (i.e., less than 2.6% of the average values) and are thus omitted from the plot. (a) Key generation time. (b) Message signing time. (c) Message verifying time.
We analyze the performances within each PQC family of algorithms in order to compare the performances between the algorithms and their respective parameter sets. We introduce the intra-family performance ratio, where i specifies the algorithm family, i.e., . For example, is the ratio between the execution time for the slowest Dilithium algorithm and the time for the quickest Dilithium algorithm. By definition, . By dividing the slowest algorithm’s duration with the fastest for each family of algorithms, the key generation data (Figure 4a) shows that , , and . For the message signing phase (Figure 4b), , , and . For message verification (Figure 4c), , , and . This makes it clear that Dilithium, when compared to Falcon and SPHINCS+, shows optimal behavior with regards to the time taken to run the algorithms from each family.
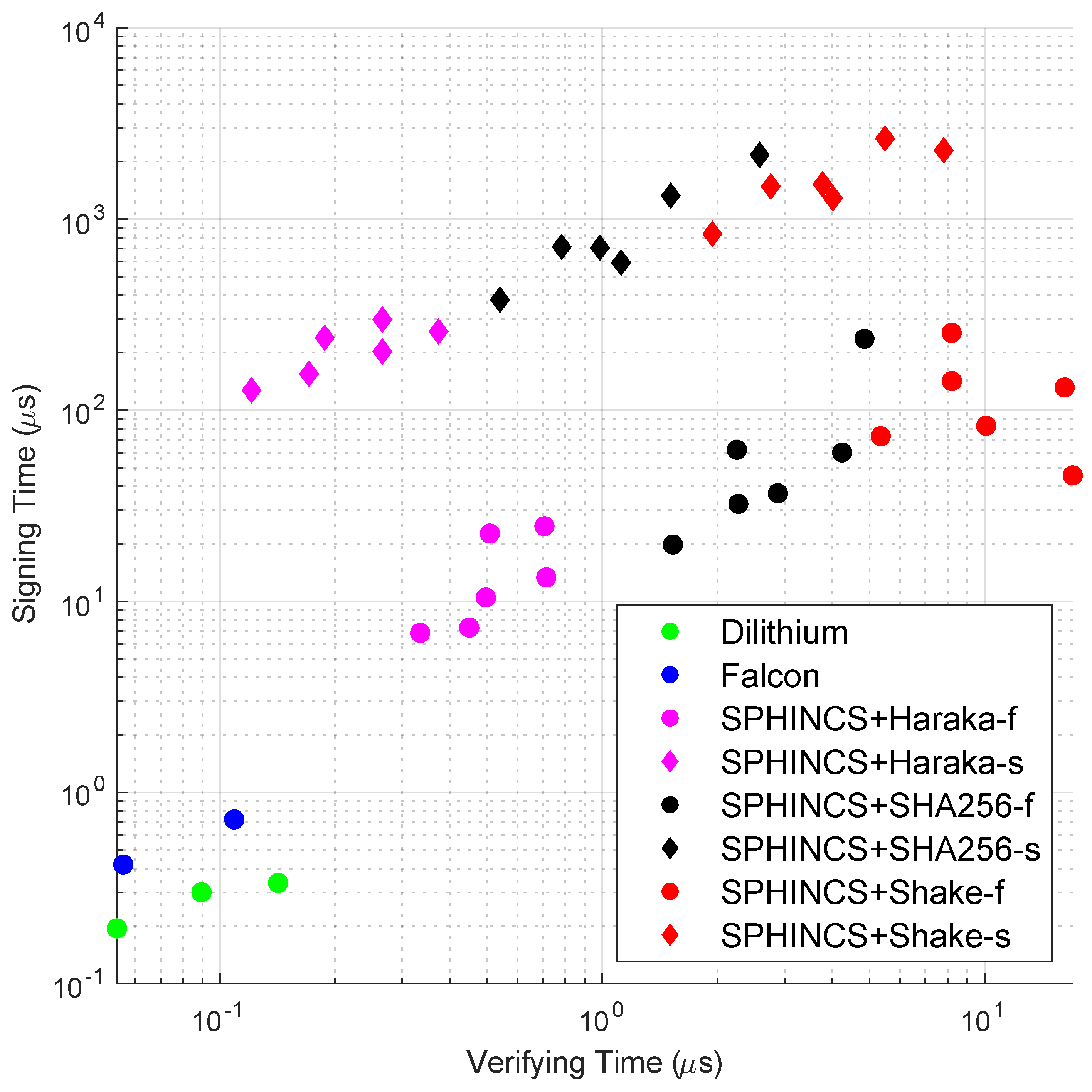
While the intra-family comparison analysis helps in understanding how each algorithm in a family performs independently, an inter-family comparison analysis provides additional insights when comparing the algorithms from other families. For key generation, our data shows that Dilithium is at least 43.68 times faster than Falcon and 1.78 times faster than SPHINCS+ algorithms. Similar to key generation, Dilithium outperforms Falcon by at least 1.27 times and SPHINCS+ by 20.72 times in message signing. For message verification, both Dilithium and Falcon parameter sets targeting level 1 security are the most effective with the same verification time, which is 2.4 times faster than the SPHINCS+ parameter set targeting the same security level. Falcons’ slowest algorithm (Falcon 1024) is 1.4 times faster than Dilithium’s slowest algorithm (Dilithium 5). Dilithium 5 and Falcon 1024 are 121.42 and 170 times faster than the slowest SPHINCS+ algorithm. From our intra-family and inter-family comparisons, we conclude that lattice-based algorithms are efficient compared to hash-based algorithms in key generation, message signing, and message verification. Figure 5 plots all the parameter sets used in our analysis. It focuses on the signing vs. verifying trade-off and an ideal algorithm with the lowest overheads is positioned at the left bottom of the plot. Figure 5 shows that lattice-based algorithms are closer to this point than hash-based algorithms. In hash-based algorithms, SPHINCS+ algorithms with Haraka as the underlying hash function are closer to the ideal position. Overall, Dilithium is the fastest in execution times across the NIST-selected digital signature algorithms. We extend the analysis to algorithm scalability by using variable message lengths to compare how the performance changes when the input size increases.
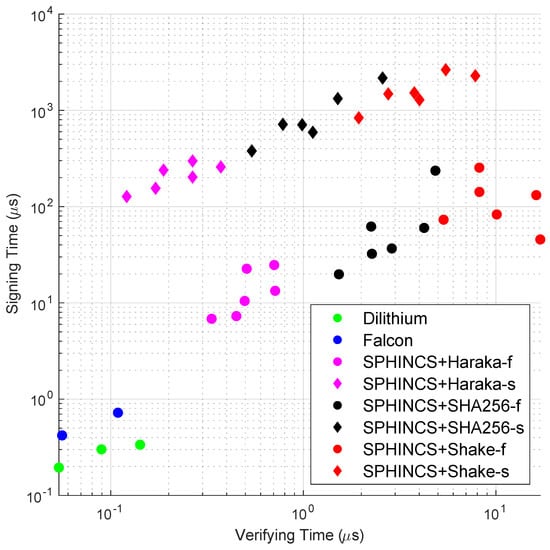
Figure 5.
Signing vs. verifying times.
6.2. Message Scalability Performances
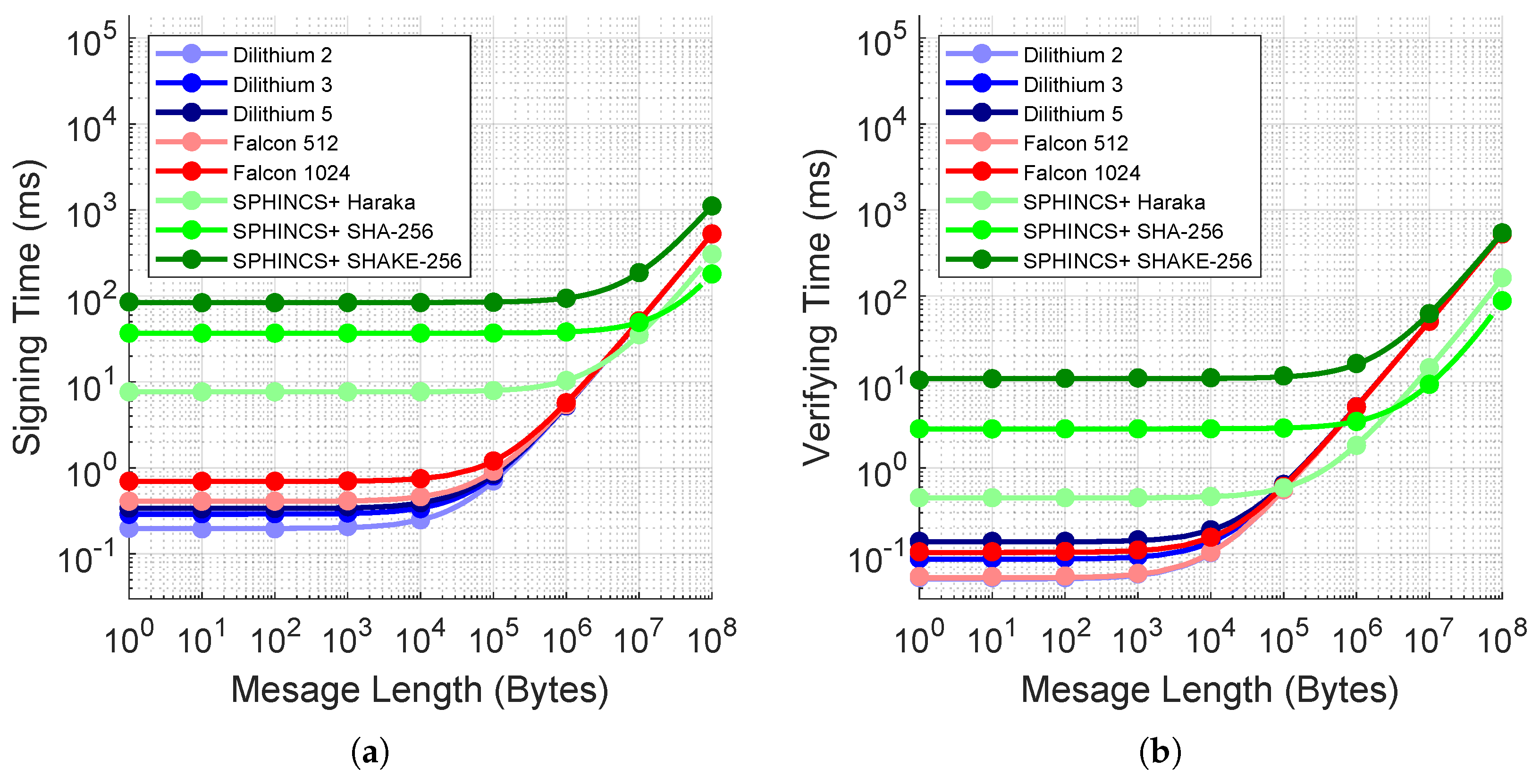
We measure the signing and verifying performances of the PQC algorithms when the message length varies from 1 Byte to 100 MB to analyze the message scalability. Using our results in Figure 6, the dots represent our empirically measured data values while the line estimates the polynomial line of best fit (LoBF) based on minimizing the mean squared error to enable greater precision in our analysis. Table 3 includes the LoBF estimations in their equation form, and Figure 6 includes the plot for each equation.
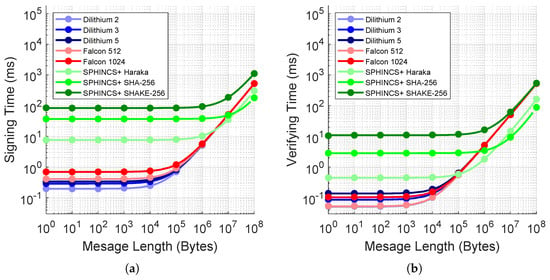
Figure 6.
Performance analysis for the fastest and slowest candidates from each family. The horizontal axis is in logarithmic scale. The dots show the discrete experimental data, and the solid lines are our LoBF estimates. The plot shows the default enabled SPHINCS+-128f-robust variant algorithms of SPHINCS+ only. (a) Message signing time with varying message lengths. (b) Message verifying time with varying message lengths.

Table 3.
The line of best fit (LoBF) estimations for the signing time and verifying time in milliseconds, where x is the message length in Bytes. Table lists the default enabled SPHINCS+-128f-robust variant algorithms of SPHINCS+ only.
From this data, we find that the fastest algorithm for message signing is Dilithium 2 when message sizes are less than 3.256 MB. For message sizes greater than 3.256 MB but less than 19 MB, we find that SPHINCS+-Haraka-128f-robust yields the fastest signing time, and for message sizes greater than 19 MB, SPHINCS+-SHA-256-128f-robust is the fastest at signing. For verification, we find that Dilithium 2 is similar to Falcon 512, with Dilithium 2 being just 0.1339 ms faster, on average. For message sizes less than 0.1088 MB, Dilithium 2 is fastest, but for message sizes greater than 0.1088 MB and less than 3.138 MB, we find that SPHINCS+-Haraka-128f-robust has the fastest verification, and for message sizes greater than 3.138, SPHINCS+-SHA-256-128f-robust is fastest.
6.3. Application Dependency
The choice of the PQC algorithm depends on its application since the application determines the usage frequencies of the signing vs. verifying and the message payload size. The frequency discrepancy between signing and verifying a message varies significantly according to the application. For example, in cryptocurrency applications, once a transaction is created, it gets signed a single time. In contrast, as the transaction propagates across the network, every node verifies that the message is genuine [29], thus the signing-to-verifying ratio is close to zero in this case. We aim to prioritize the algorithm with fast message verification. In addition, the message payload size provided by the application requirement affects the performance prioritization and the algorithm selection. Our results show that Dilithium 2 is the most execution-time-efficient if the application message length is short and SPHINCS+-Haraka-128f-robust and SPHINCS+-SHA-256-128f-robust are the fastest for verifying when the message lengths are larger.
7. Performance Analysis of Integration with Public Key Infrastructure
Public key infrastructure (PKI) is critical in digital networking systems since it provides trust in the public key, which can be used for security protocols or for establishing symmetric keys. Because of its importance for digital and internet networking, we study the effects of transitioning to post-quantum algorithms in PKI and how it affects the performance of digital networking systems. In this section, we focus on the PKI integration of the post-quantum algorithms and conduct an empirical implementation-based study for our analyses of the NIST post-quantum algorithms. More specifically, we study and analyze the feasibility and the performances of the NIST PQC standardization project’s digital signature algorithms when integrated into PKI. Our work focuses on computational efficiency for the following reasons. First, transitioning to post-quantum PKI implementations affects computing the most. Second, we generalize the computational overheads caused by the post-quantum algorithms across the PKI architecture and implementation scenarios.
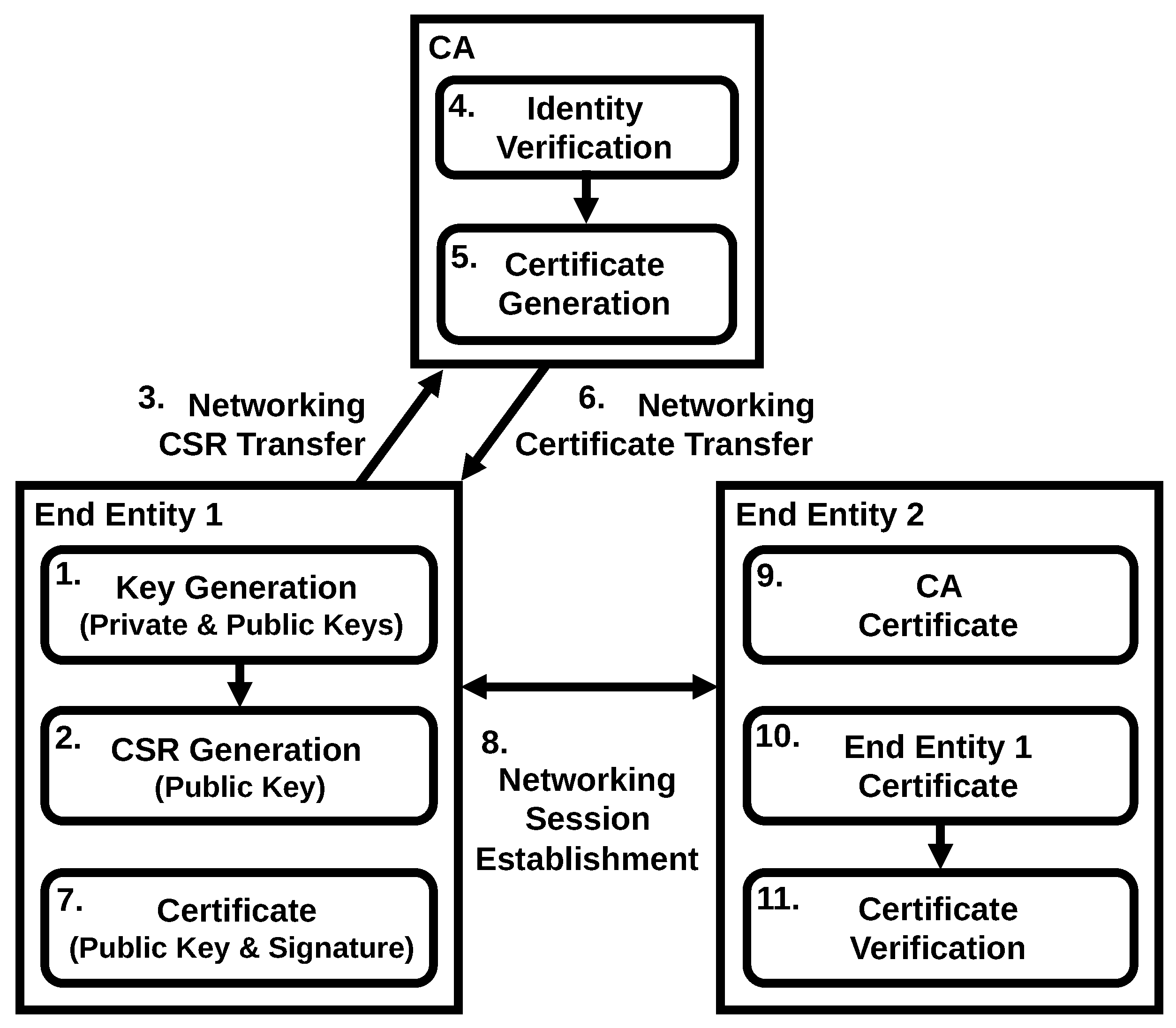
Figure 7 shows the PKI certification process. In Step 1, the Key-Pair Generation for the public–private key-pair is achieved locally for the subject end-entity, End-Entity 1. The private key does not leave the local node, while the public key is shared with the others, including the CA for certification and later End-Entity 2 for communicating data. In Step 2, End-Entity 1 creates a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) using the public key and sends it to the CA in Step 3. In Step 4, the CA verifies the identity of End-Entity 1 and generates a certificate in Step 5. This certificate contains the public key of End-Entity 1 and a signature generated by the CA using its private key. In Step 6, the certificate is transferred to End-Entity 1. In Step 7, End-Entity 1 verifies and configures the certificate for future communications. In Step 8, the certificate is transferred from End-Entity 1 to End-Entity 2 for authentication. End-Entity 2 obtains the CA and End-Entity 1 certificates in Steps 9 and 10, respectively, for verification. In Step 11, End-Entity 2 verifies the certificate of End-Entity 1. This verification includes the use of the CA’s public key from the CA certificate to verify the signature on the End-Entity 1 certificate. Once verification is successful, a session is established between End-Entity 1 and End-Entity 2 for communicating data.
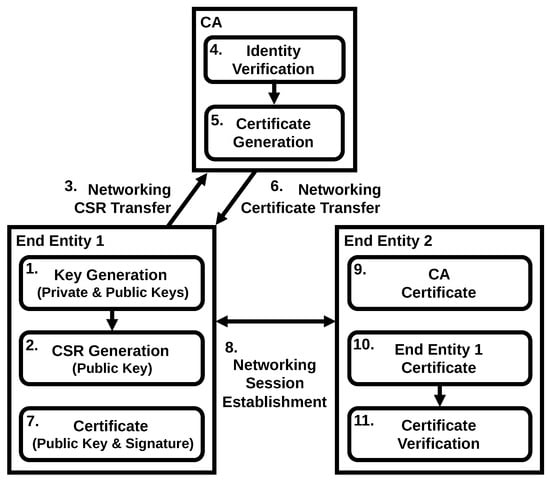
Figure 7.
The PKI process focusing on the networking/computing between the end-entity (the beneficiary of the PKI service) and the CA (PKI service provider). The PKI backend, such as that for registration, is not included in this diagram.
The functions described in this section and shown in Figure 7 are the essential functions for the PKI process. In addition to its popular applications to provide the root of trust for authenticating web servers for more conventional internet applications, PKI and digital certificate management are applied for ad hoc networking where the data networking between the end-entities does not go through traditional internet core domain networking, e.g., a Security Credential Management System (SCMS) for vehicular/V2X/VANET networking [30,31,32]. Our work is applicable in such ad hoc networking contexts in principle because the PKI designs for such applications are often more complex due to the requirements of the end-entities and the additional security/privacy objectives, which build on the PKI functions targeted for our analyses.
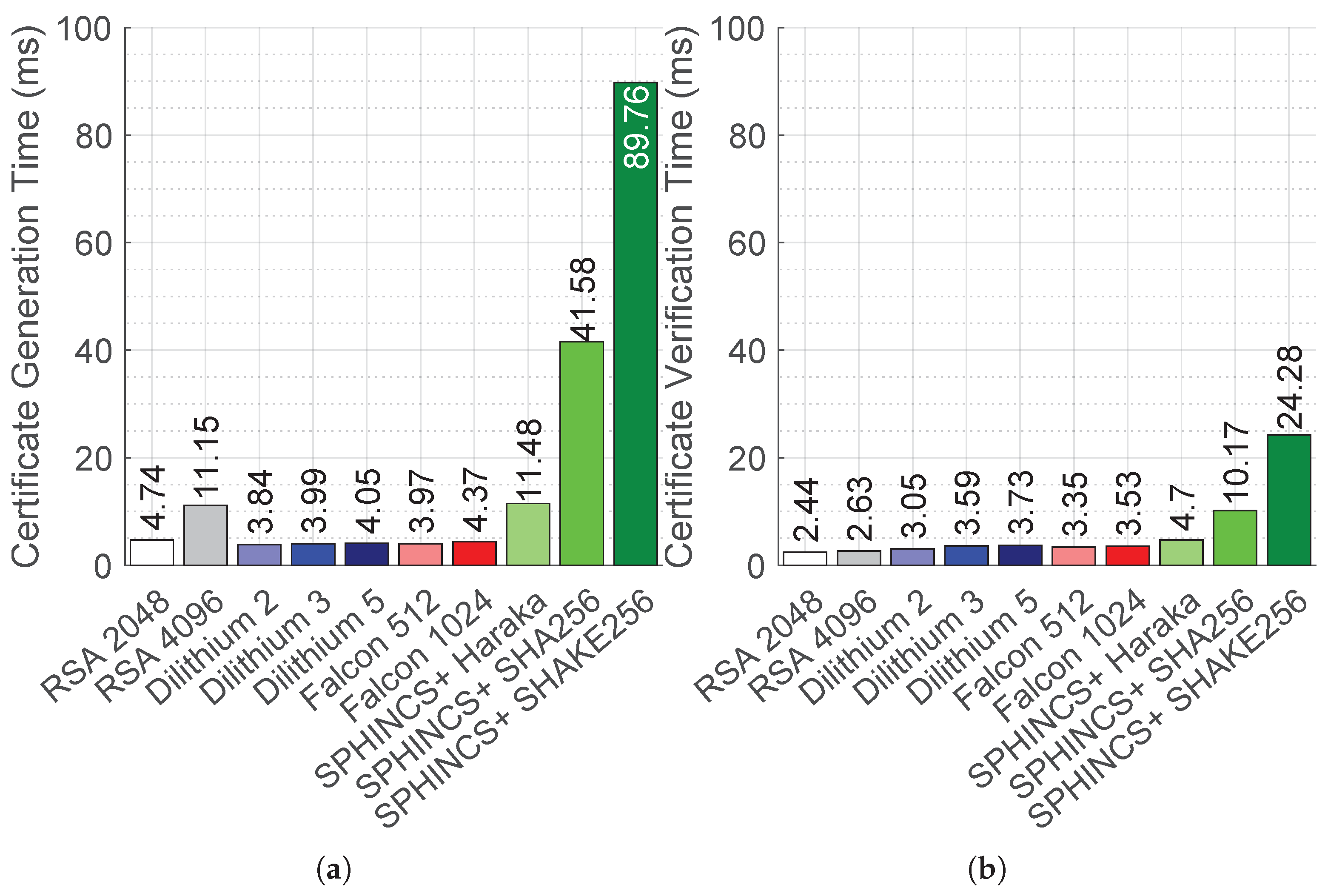
Figure 8a plots the average time taken for certificate generation using classical RSA and NIST-selected post-quantum digital signature algorithms. All Dilithium and Falcon algorithms outperform RSA in certificate generation times. Dilithium 2 and Falcon 512 are 18.98% and 16.24% faster than RSA 2048, while they are 65.56% and 64.39% faster than RSA 4096, respectively. Dilithium 2 is the fastest post-quantum algorithm and is 3.27% faster than Falcon 512, which is the second fastest post-quantum algorithm. At security level 5, Dilithium 5 is 7.32% faster than Falcon 1024. Hash-based SPHINCS+ algorithms take longer time than any other classical or post-quantum algorithms. SPHINCS+-Haraka-128f-robust takes 2.9%, 198.95%, and 189.16% more certificate generation time than RSA 4096, Dilithium 2, and Falcon 512, respectively. SPHINCS+-Haraka-128f-robust is the most efficient in the SPHINCS+ family and is 72.39% and 87.21% faster than SPHINCS+-SHA-256-128f-robust and SPHINCS+-SHAKE256-128f-robust, respectively. Overall, Dilithium algorithms are the most effective in terms of certificate generation time.
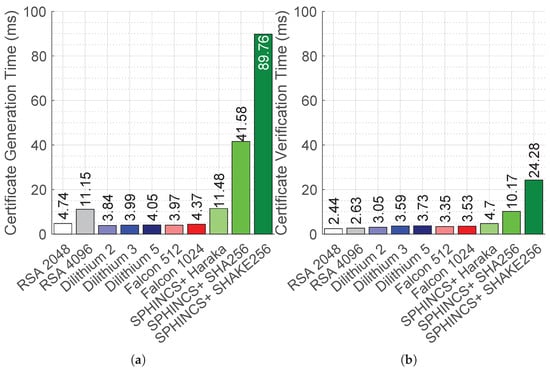
Figure 8.
Performance of PKI integrated with PQC. The plots show the default enabled SPHINCS+-128f-robust variant algorithms of SPHINCS+ only. The 95% confidence interval values are small (i.e., less than 0.93% of the average values) and are thus omitted from the plot. (a) Certificate generation time. (b) Certificate verification time.
Figure 8b plots the average time taken for certificate verification using classical RSA and NIST-selected post-quantum digital signature algorithms. In contrast to the certificate generation times, classical RSA is the most effective in terms of certification verification times. SPHINCS+ algorithms continue to remain the heaviest in terms of certification verification times, too. Dilithium 2 and Falcon 512 take 25% and 37.29% longer than RSA 2048, while they take 15.96% and 27.37% longer than RSA 4096, respectively. Dilithium 2 is 15% and 18.23% faster than Dilithium 3 and Dilithium 5, respectively. Falcon 1024 takes 5.37% longer than Falcon 512 for the certificate verification. Similar to certificate generation, with certificate verification, SPHINCS+-Haraka-128f-robust is the most efficient in the SPHINCS+ family and is 53.78% and 80.64% faster than SPHINCS+-SHA-256-128f-robust and SPHINCS+-SHAKE256-128f-robust, respectively. Overall, post-quantum algorithms increase the certificate verification times compared to classical RSA. Lattice-based Dilithium and Falcon are efficient compared to the hash-based SPHINCS+ algorithms.
8. Performance Analysis of Integration with TCP/IP and TLS
In this section, we analyze the communication/handshake overhead of the PQC algorithms at the packet level when integrated with TLS 1.3 and TCP/IPv4. We focus on handshake duration time because PQC authentication impacts TLS 1.3 only during the handshake process and helps in deriving session keys that are used for transferring the payload. The handshake connection involves multiple transmissions between the client and the server, where the client initiates the connection by sending a client hello packet to the server and the server responds with server hello carrying the certificate signed by the Certificate Authority (CA), which contains the public key (post-quantum) of the server and the signature (post-quantum). The client then verifies the signature and sends a finished message to the server indicating the end of the handshake. After a successful handshake, application data is securely transferred using the derived session key. Our analysis focuses on packet-level overhead as opposed to the broader networking overhead between the two hosts. We use local virtual machines loaded with OQS-OpenSSL_1_1_1 [5] acting as a client and server to establish a TLS 1.3 connection using PQC authentication. We use tcpdump [33] to capture the TLS and TCP/IP handshake packets and Wireshark [34] to analyze the packet data. More details about the experimental setup are provided below.
We established the TLS 1.3 connection 1000 times for the experimental samples and ran and compared the performances with RSA (not quantum-resistant) to provide a reference.
Table 4 shows the algorithms, time, CPU usage, Certificate Size (CS), total TCP Segment Size (TSS), number of Server Hello Packets (SHPs), Server Hello Size (SHS), and number of Handshake Packets (HPs). Time refers to the average handshake time elapsed for a connection, CPU usage represents the highest percentage logged during connection establishment, and CS provides the size of the certificate generated using the algorithms listed. We observed that Server Hello with large certificates uses TCP segmentation. SHP represents the number of packets used to transfer the Server Hello message. TSS provides the total data transferred by TCP segments. SHS represents the total Server Hello size in bytes that contains the certificate and TLS extensions. HP represents the total number of packets used to establish the connection (counted to client’s finished message).

Table 4.
TLS performance with different digital signature algorithms, including CPU usage with a 95% confidence interval, certificate size, TCP segment size, number of server hello packets, server hello size, and number of handshake packets. Table lists the default enabled SPHINCS+-128f-robust variant algorithms of SPHINCS+ only.
8.1. Packet-Level Handshake Analysis: Time Overhead
This section analyzes the handshake overheads in the unit of average connection time and processing (CPU utilization). Our results in Table 4 show that Dilithium 2 outperforms the other quantum-resistant algorithms in average handshake time. Falcon 512 is the next fastest pqc algorithm in handshake establishment and takes 3.23% more time than Dilithium 2. Dilithium 2 and Falcon 512 are 7.22% and 10.6% slower than RSA 2048, while they are 68.12% and 67.09% faster than RSA 4096, respectively.
SPHINCS+-Haraka-128f-robust takes 286.52% and 274.41% more than Dilithium 2 and Falcon 512, respectively. SPHINCS+-SHAKE256-128f-robust takes the longest time for a TLS connection establishment and is two orders larger in magnitude than Dilithium or Falcon’s connection establishment times.
8.2. Packet-Level Handshake Analysis: Certificate Size and Server Hello
This section analyzes the overhead caused by the CS and SHS on the connection handshake. Falcon 512’s CS (2358 B) is 55.94% smaller than Dilithium 2 (5340 B). Falcon 512 is the only post-quantum algorithm that transfers its Server Hello message in a single packet and is suitable for devices capable of handling only small certificate sizes due to small buffer sizes. We compute the fraction that the CS takes up inside the Server Hello with . This provides the additional extension overhead that each algorithm enforces on the TLS connection. Falcon 1024 has a percentage of 93.7%, causing only 6.3% overhead. Except for Falcon 512, all other post-quantum algorithms use TCP segmentation for their Server Hello message, indicating the additional overhead within the handshake. Fraction implicates the effect of the post-quantum certificate in the Server Hello of the handshake. A handshake using Falcon 512 is composed of 12.4% Server Hello, while the other post-quantum algorithms have a percentage of 20% or more.
8.3. PQC Algorithm Choices with TLS Integration
From our analysis, Dilithium 2 has the fastest connection time among the PQC algorithms. Falcon 512 is a better alternative to the Dilithium family due to its low CS and similar packet overheads to RSA.
9. Takeaways and Discussion
We analyze the PQC algorithms in security and performance in this paper and summarize our choices and recommendations based on the analyses in this section. In security costs, Falcon 512/1024 incurs the most computational effort against a quantum-equipped cryptanalyst among the lattice-based algorithms in qubits (Section 5.2). Our performance analyses focusing on the algorithms only (Section 6) yield that Dilithium 2 is the quickest for signing for messages shorter than 3.256 MB and that SPHINCS+-Haraka-128f-robust is the quickest for signing messages longer than 3.256 MB. When the PQC algorithm is integrated with TLS and TCP/IP (Section 8), Dilithium 2 is the best both in connection handshake time and in CPU processing, while Falcon 512 has the shortest certificate size affecting the payload and memory.
The choice of the PQC digital signature algorithm depends on both the PQC application requirements and the R&D in quantum computing and cryptanalysis. Our PQC recommendations are based on standard practices in networking security. For example, the key exchange occurs more sporadically than the message communication frequency (if they are comparable, using a one-time pad can be an option for information-theoretic security resistant against (quantum-)computationally capable adversaries), and therefore we prioritize the recommendations based on the signature length as opposed to the public key length in Section 5.2. Other choices depend on the application domains and properties, including the application-layer message size affecting the efficiency performance comparison in the PQC algorithms in Section 6 and the signing frequency vs. verifying frequency providing different prioritization. For example, the cryptocurrency blockchain utilizing digital signatures for the transaction integrity would prioritize the verifying efficiency (since, for every signing to generate a transaction, numerous miners would verify the signature/transaction) and has a message input size less than 460 kB (e.g., Bitcoin has transaction sizes in the order of hundreds to thousands of Bytes), so the performance-focused PQC choice would be Dilithium 2. For networking-constrained applications, the algorithm can also be chosen in order to minimize the number of transmitted packets, which depends on the algorithm’s certificate size and the networking protocol’s packet specification including the field length. For example, if the PQC is used for TLS and TCP/IP in constrained environment, then Falcon 512 would be the choice as studied in Section 8.
10. Related Work in PQC Analyses
In this section, we discuss more work related to our research, including post-quantum algorithm performance studies, cryptanalysis, and security studies.
10.1. PQC Digital Signature Performance Analyses in TLS and TCP/IP and Beyond
Sikeridis et al. [35] provided a performance study on the post-quantum digital signature algorithm candidates of the NIST’s PQC standardization project. The few selected parameters of seven out of the nine algorithms in the second round were integrated with TLS 1.3 and analyzed for networking latency for the respective algorithms. The authors also proposed a scheme to use different post-quantum algorithms regarding Certificate Authority (CA) and Intermediate Certificate Authority (ICA) to improve the overall handshake speed and throughput. Our work is comparable to this work in that it includes performance analyses when the PQC algorithms are integrated with TLS. However, our work provides the performance analyses with finer granularity at the packet level, enabling richer analyses (e.g., analyzing the required number of packet transmissions to capture the relationship between the certificate size and the protocol’s segmentation).
Basu et al. conducted a hardware evaluation study on the signature candidates, including Dilithium, in [36]. Out of the three signature algorithms they analyzed, only Dilithium advanced to the third round of the NIST’s PQC standardization project. Based on implementations in Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) and Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), their analysis recommends the use of Dilithium in server implementations with low latency.
Beyond TLS and TCP/IP, other research showed that post-quantum digital signatures are feasible and provided performance analyses in widely used networking protocols, including QUIC (a more advanced protocol to replace TCP/TLS) [37,38,39,40], power analysis [41], email or S/MIME [42,43], DNS/DNSSEC [44,45], and 4G/5G eSIM provision [46,47].
10.2. Cryptanalysis and Security Analyses
Lattice-based cryptanalysis is provided in [48,49]. The authors in [48] provided a software toolkit named Sage 9.0 to perform side-channel attacks on lattice-based cryptography. They also proposed a cryptanalysis framework that can take advantage of side information or hints to perform lattice reduction attacks. Their analysis shows a significant cost reduction in performing cryptanalysis that utilizes hints. In [49], the authors performed cryptanalysis based on skip-addition fault attacks. They made use of the determinism in the signature algorithm and injected a single fault targeting the signing operation. A portion of the secret key was extracted and used by the proposed forgery algorithm to generate signatures. Their analyses included skip-addition attacks on Dilithium and zero-cost mitigations.
10.3. Hardware-Based PQC Analyses
As lattice-based and hash-based cryptography differ in the underlying design, many researchers have looked at developing special-purpose hardware to speed up the underlying arithmetic operations and improve the algorithm performances. These include special hardware design implementations or accelerators for Dilithium [50,51,52,53,54,55], Falcon [56,57,58,59], and SPHINCS+ [60,61,62,63,64].
Our PQC implementations are software-based—i.e., the different cryptographic ciphers are implemented in software, while fixing the hardware. The hardware is fixed—i.e., we use the same device platform to test across the PQC algorithms, for fair comparison. Furthermore, our work does not aim to advance or optimize the efficiency of the cipher computations, in contrast to the aforementioned previous work using hardware to improve efficiency.
11. Conclusions
This paper presents security comparisons and performance analyses of NIST-selected post-quantum digital signature algorithms. In our security comparisons, we use a visualization model to analyze the trade-off between the key/signature size vs. security. In our performance analyses, we analyze the performances of the NIST-selected PQC digital signature schemes for key generation, signing, and verifying signatures. To measure the PQC implementation costs and the overheads in communication, time, and processing, we also integrate the PQC algorithms with PKI and TLS 1.3. Our analyses results show that the lattice-based algorithms are computational efficient compared to the hash-based algorithms. Our results from integration with TLS 1.3 show that, at comparable security strengths, Dilithium 2 and Falcon 512 outperform RSA 4096 in handshake time duration by 68.12% and 67.09%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R., Q.K., Y.B. and S.-Y.C.; methodology, M.R.; software, S.W. and P.C.; validation, M.R.; formal analysis, M.R., Q.K., Y.B. and S.W.; investigation, M.R., Q.K., Y.B. and S.W.; resources, M.R. and S.W.; data curation, S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.R., Q.K. and S.W.; writing—review and editing, M.R. and S.-Y.C.; visualization, S.W.; supervision, S.-Y.C.; project administration, S.-Y.C.; funding acquisition, S.-Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation—grant number 1922410.
Data Availability Statement
All the crypto libraries used in this study are opensource and available on Github. Open Quantum Safe https://github.com/open-quantum-safe (accessed on 1 June 2025). The data presented in this study are openly available in pq-openssl-research at https://github.com/Simewu/pq-openssl-research (accessed on 1 June 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| PQC | Post-Quantum Cryptography |
| PKI | Public Key Infrastructure |
| TLS | Transport Layer Security |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
References
- Rivest, R.L.; Shamir, A.; Adleman, L. A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 1978, 21, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caelli, W.J.; Dawson, E.P.; Rea, S.A. PKI, elliptic curve cryptography, and digital signatures. Comput. Secur. 1999, 18, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, P.W. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 1999, 41, 303–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, T. Quantum Computing and Cryptography; Entrust Inc.: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stebila, D.; Mosca, M. Post-quantum key exchange for the internet and the open quantum safe project. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Selected Areas in Cryptography, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 10–12 August 2016; pp. 14–37. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, L.K. A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 22–24 May 1996; pp. 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, I.L.; Gershenfeld, N.; Kubinec, M. Experimental implementation of fast quantum searching. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandersypen, L.M.; Steffen, M.; Breyta, G.; Yannoni, C.S.; Sherwood, M.H.; Chuang, I.L. Experimental realization of Shor’s quantum factoring algorithm using nuclear magnetic resonance. Nature 2001, 414, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheatley, M. D-Wave debuts new 5000-qubit quantum computer. 2019. Available online: https://www.dwavequantum.com/company/newsroom/media-coverage/techrepublic-d-wave-announces-5-000-qubit-fifth-generation-quantum-annealer/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Kelly, J. A preview of Bristlecone, Google’s new quantum processor. Google Research Blog. 2018. Available online: https://research.google/blog/a-preview-of-bristlecone-googles-new-quantum-processor/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Alsina, D.; Latorre, J.I. Experimental test of Mermin inequalities on a five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 012314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelvecchi, D. IBM’s quantum cloud computer goes commercial. Nat. News 2017, 543, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagic, G.; Alagic, G.; Alperin-Sheriff, J.; Apon, D.; Cooper, D.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.K.; Miller, C.; Moody, D.; Peralta, R.; et al. Status Report on the First Round of the NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization Process; US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fips, P. 186-4: Federal Information Processing Standards Publication. Digital Signature Standard (DSS); Information Technology Laboratory, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2013; pp. 20899–20900. [Google Scholar]
- Brassard, G.; Høyer, P.; Tapp, A. Quantum cryptanalysis of hash and claw-free functions. ACM Sigact News 1997, 28, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Alagic, G.; Alperin-Sheriff, J.; Apon, D.; Cooper, D.; Dang, Q.; Kelsey, J.; Liu, Y.K.; Miller, C.; Moody, D.; Peralta, R.; et al. Status Report on the Second Round of the NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization Process; US Department of Commerce, NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Status Report on the First Round of the Additional Digital Signature Schemes for the NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization Process. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/ir/2024/NIST.IR.8528.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Tao, C.; Petzoldt, A.; Ding, J. Efficient key recovery for all HFE signature variants. In Proceedings of the Annual International Cryptology Conference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 70–93. [Google Scholar]
- Beullens, W. Improved cryptanalysis of UOV and rainbow. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Zagreb, Croatia, 17–21 October 2021; pp. 348–373. [Google Scholar]
- Beullens, W.; Breaking rainbow takes a weekend on a laptop. Cryptology ePrint Archive. 2022. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2022/214 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Ducas, L.; Kiltz, E.; Lepoint, T.; Lyubashevsky, V.; Schwabe, P.; Seiler, G.; Stehlé, D. Crystals-dilithium: A lattice-based digital signature scheme. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. 2018, 2018, 238–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouque, P.A.; Hoffstein, J.; Kirchner, P.; Lyubashevsky, V.; Pornin, T.; Prest, T.; Ricosset, T.; Seiler, G.; Whyte, W.; Zhang, Z. Falcon: Fast-Fourier Lattice-Based Compact Signatures over NTRU; Submission to the NIST’s post-quantum cryptography standardization process; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, D.J.; Hülsing, A.; Kölbl, S.; Niederhagen, R.; Rijneveld, J.; Schwabe, P. The SPHINCS+ signature framework. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 2129–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Regev, O. Lattice-based cryptography. In Annual International Cryptology Conference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Nejatollahi, H.; Dutt, N.; Ray, S.; Regazzoni, F.; Banerjee, I.; Cammarota, R. Post-quantum lattice-based cryptography implementations: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2019, 51, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, L. Constructing digital signatures from a one way function. 1979. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Constructing-Digital-Signatures-from-a-One-Way-Function.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Merkle, R.C. A certified digital signature. In Proceedings of the Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 218–238. [Google Scholar]
- Alkim, E.; Ducas, L.; Pöppelmann, T.; Schwabe, P. Post-quantum key exchange—A new hope. In Proceedings of the 25th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 16), Austin, TX, USA, 10–12 August 2016; pp. 327–343. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.L.; Chen, X.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Sun, Y.; Niu, X.X.; Yang, Y.X. A secure cryptocurrency scheme based on post-quantum blockchain. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 27205–27213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, W.; Weimerskirch, A.; Kumar, V.; Hehn, T. A security credential management system for V2V communications. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Vehicular Networking Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 16–18 December 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chang, S.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y. Protecting vehicular networks privacy in the presence of a single adversarial authority. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–11 October 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecht, B.; Therriault, D.; Weimerskirch, A.; Whyte, W.; Kumar, V.; Hehn, T.; Goudy, R. A Security Credential Management System for V2X Communications. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 3850–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, V.; Leres, C.; McCanne, S. TCPDUMP Public Repository 2003. Available online: https://www.tcpdump.org/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Wireshark Tool. Available online: https://www.wireshark.org (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Sikeridis, D.; Kampanakis, P.; Devetsikiotis, M. Post-Quantum Authentication in TLS 1.3: A Performance Study. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive. 2020. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/071 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Basu, K.; Soni, D.; Nabeel, M.; Karri, R. NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography-A Hardware Evaluation Study. Cryptology ePrint Archive. 2019. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2019/047 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Raavi, M.; Wuthier, S.; Zhou, X.; Chang, S.Y. Post-Quantum QUIC Protocol in Cloud Networking. In Proceedings of the 2023 Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications & 6G Summit (EuCNC/6G Summit), Gothenburg, Sweden, 6–9 June 2023; pp. 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raavi, M.; Wuthier, S.; Chandramouli, P.; Zhou, X.; Chang, S.Y. QUIC Protocol with Post-quantum Authentication. In International Conference on Information Security; Susilo, W., Chen, X., Guo, F., Zhang, Y., Intan, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Raavi, M.; Wuthier, S.; Chandramouli, P.; Balytskyi, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chang, S.Y. Security comparisons and performance analyses of post-quantum signature algorithms. In International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 424–447. [Google Scholar]
- Raavi, M.; Chandramouli, P.; Wuthier, S.; Zhou, X.; Chang, S.Y. Performance Characterization of Post-Quantum Digital Certificates. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), Athens, Greece, 19–22 July 2021; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hines, K.; Raavi, M.; Villeneuve, J.; Wuthier, S.; Moreno-Colin, J.; Bai, Y.; Chang, S. Post-quantum cipher power analysis in lightweight devices. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM Conference on Security and Privacy in Wireless and Mobile Networks, San Antonio, TX, USA, 16–19 May 2022; pp. 282–284. [Google Scholar]
- Döberl, C.; Eibner, W.; Gärtner, S.; Kos, M.; Kutschera, F.; Ramacher, S. Quantum-resistant End-to-End Secure Messaging and Email Communication. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security, 2023, ARES ’23, New York, NY, USA, 29 August–1 September 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandev, R.; Kavun, E.B. Performance Comparison of Post-Quantum Signature Algorithms Through An Android Email Application Plug-in. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Omni-layer Intelligent Systems (COINS), Berlin, Germany, 23–25 July 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raavi, M.; Wuthier, S.; Chang, S. Securing Post-Quantum DNSSEC Against Fragmentation Mis-Association Threat. In Proceedings of the ICC 2024—IEEE International Conference on Communications, Denver, CO, USA, 9–13 June 2024; pp. 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertzen, J.; Stebila, D. Post-Quantum Signatures in DNSSEC via Request-Based Fragmentation. In International Conference on Post-Quantum Cryptography; Johansson, T., Smith-Tone, D., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 535–564. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Q.; Purification, S.; Cheruiyot, R.; Kim, J.; Kim, I.; Chang, S.Y. Post-Quantum Digital Signature and Authentication for eSIM in 5G Mobile Networking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Silicon Valley Cybersecurity Conference (SVCC), Fremont, CA, USA, 23–25 June 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bettale, L.; Dottax, E.; Grémy, L. Post-Quantum Secure Channel Protocols for eSIMs; Cryptology ePrint Archive 2024. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2024/2005 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Dachman-Soled, D.; Ducas, L.; Gong, H.; Rossi, M. LWE with Side Information: Attacks and Concrete Security Estimation. IACR Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2020, 2020, 292. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, P.; Jhanwar, M.P.; Howe, J.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Bhasin, S. Exploiting determinism in lattice-based signatures: Practical fault attacks on pqm4 implementations of NIST candidates. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Auckland, New Zealand, 9–12 July 2019; pp. 427–440. [Google Scholar]
- Aikata, A.; Mert, A.C.; Imran, M.; Pagliarini, S.; Roy, S.S. KaLi: A Crystal for Post-Quantum Security Using Kyber and Dilithium. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckwith, L.; Nguyen, D.T.; Gaj, K. Hardware Accelerators for Digital Signature Algorithms Dilithium and FALCON. IEEE Des. Test 2024, 41, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteo, S.D.; Sarno, I.; Saponara, S. CRYPHTOR: A Memory-Unified NTT-Based Hardware Accelerator for Post-Quantum CRYSTALS Algorithms. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 25501–25511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckwith, L.; Nguyen, D.T.; Gaj, K. High-Performance Hardware Implementation of CRYSTALS-Dilithium. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Field-Programmable Technology (ICFPT), Auckland, New Zealand, 6–10 December 2021; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, G.; Sasdrich, P.; Güneysu, T. A Hard Crystal-Implementing Dilithium on Reconfigurable Hardware. In Proceedings of the Smart Card Research and Advanced Applications, Birmingham, UK, 7–9 November 2022; Grosso, V., Pöppelmann, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 210–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Peng, W. An Efficient Hardware Implementation of Crystal-Dilithium on FPGA. In Proceedings of the Information Security and Privacy; Zhu, T., Li, Y., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 64–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Youn, J.; Nam, K.; Jung, H.H.; Cho, M.; Na, J.; Park, J.Y.; Jeon, S.; Kang, B.G.; Oh, H.; et al. An Efficient Hardware/Software Co-Design for FALCON on Low-End Embedded Systems. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 57947–57958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Amiet, D.; Wendler, J.; Zbinden, P.; Wei, T. Falcon Takes Off—A Hardware Implementation of the Falcon Signature Scheme; Cryptology ePrint Archive 2023. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2023/1885 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Alsuhli, G.; Saleh, H.; Al-Qutayri, M.; Mohammad, B.; Stouraitis, T. Area and Power Efficient FFT/IFFT Processor for FALCON Post-Quantum Cryptography. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Tao, Q.; Zhu, M.; Wei, S.; Liu, L. FalconSign: An Efficient and High-Throughput Hardware Architecture for Falcon Signature Generation. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. 2025, 2025, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Song, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, Z. High-Throughput Hardware Implementation for Haraka in SPHINCS+. In Proceedings of the 2023 24th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–7 April 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, P.; Schupp, J.; Sigl, G. The Impact of Hash Primitives and Communication Overhead for Hardware-Accelerated SPHINCS+. In Proceedings of the Constructive Side-Channel Analysis and Secure Design; Wacquez, R., Homma, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiet, D.; Leuenberger, L.; Curiger, A.; Zbinden, P. FPGA-based SPHINCS+ Implementations: Mind the Glitch. In Proceedings of the 2020 23rd Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), Kranj, Slovenia, 26–28 August 2020; pp. 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, Q.; Upegui, A.; Gantel, L.; Duc, A.; Traverso, G. An Area-Efficient SPHINCS+ Post-Quantum Signature Coprocessor. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW), Portland, OR, USA, 17–21 June 2021; pp. 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Valdivieso, J.; Cumplido, R. Design and Implementation of Hardware-Software Architecture Based on Hashes for SPHINCS+. ACM Trans. Reconfig. Technol. Syst. 2024, 17, 54:1–54:22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).