Expression of Recombinant Hirudin in Bacteria and Yeast: A Comparative Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Expression of Recombinant Hirudin HV1 and HLF1V in E. coli
2.2. Expression of Recombinant Hirudin HV1 in P. pastoris
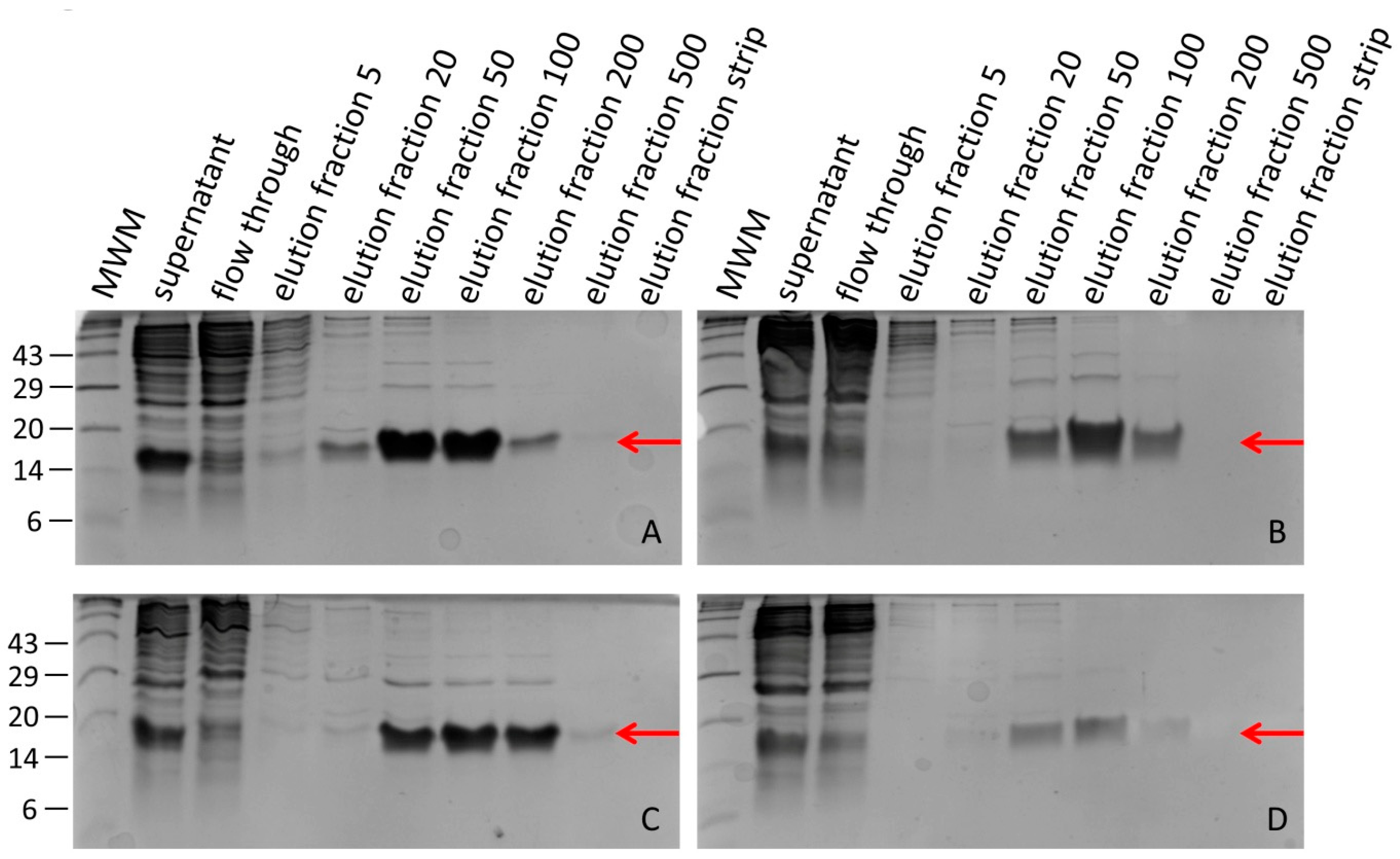
2.3. Purification of Recombinant Hirudins HV1 and HLF1V
2.4. Blood Coagulation Assays
3. Results
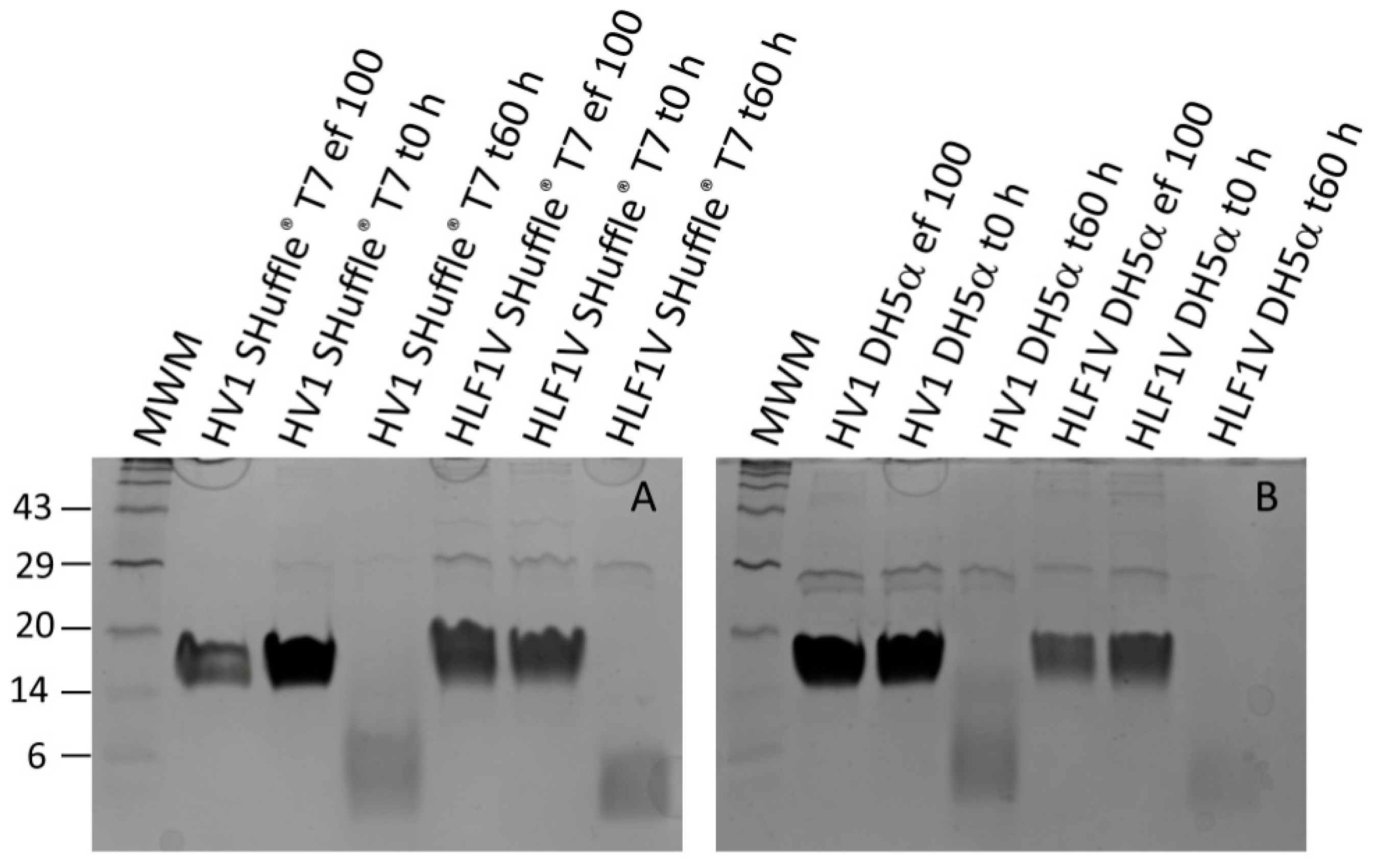
3.1. Expression of Recombinant Hirudin HV1 and HLF1V in Escherichia coli Strains
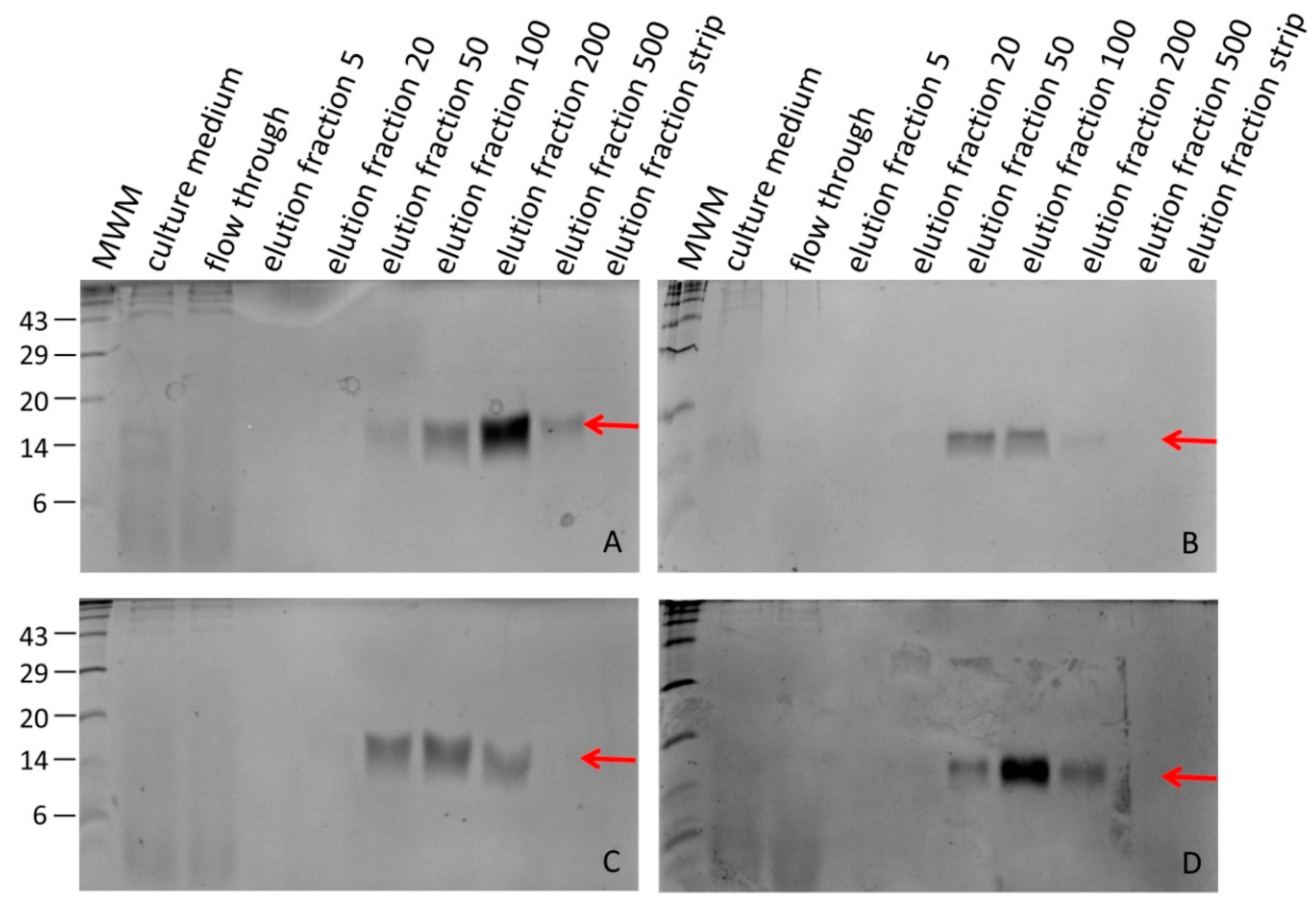
3.2. Processing Recombinant Hirudin HV1 and HLF1V
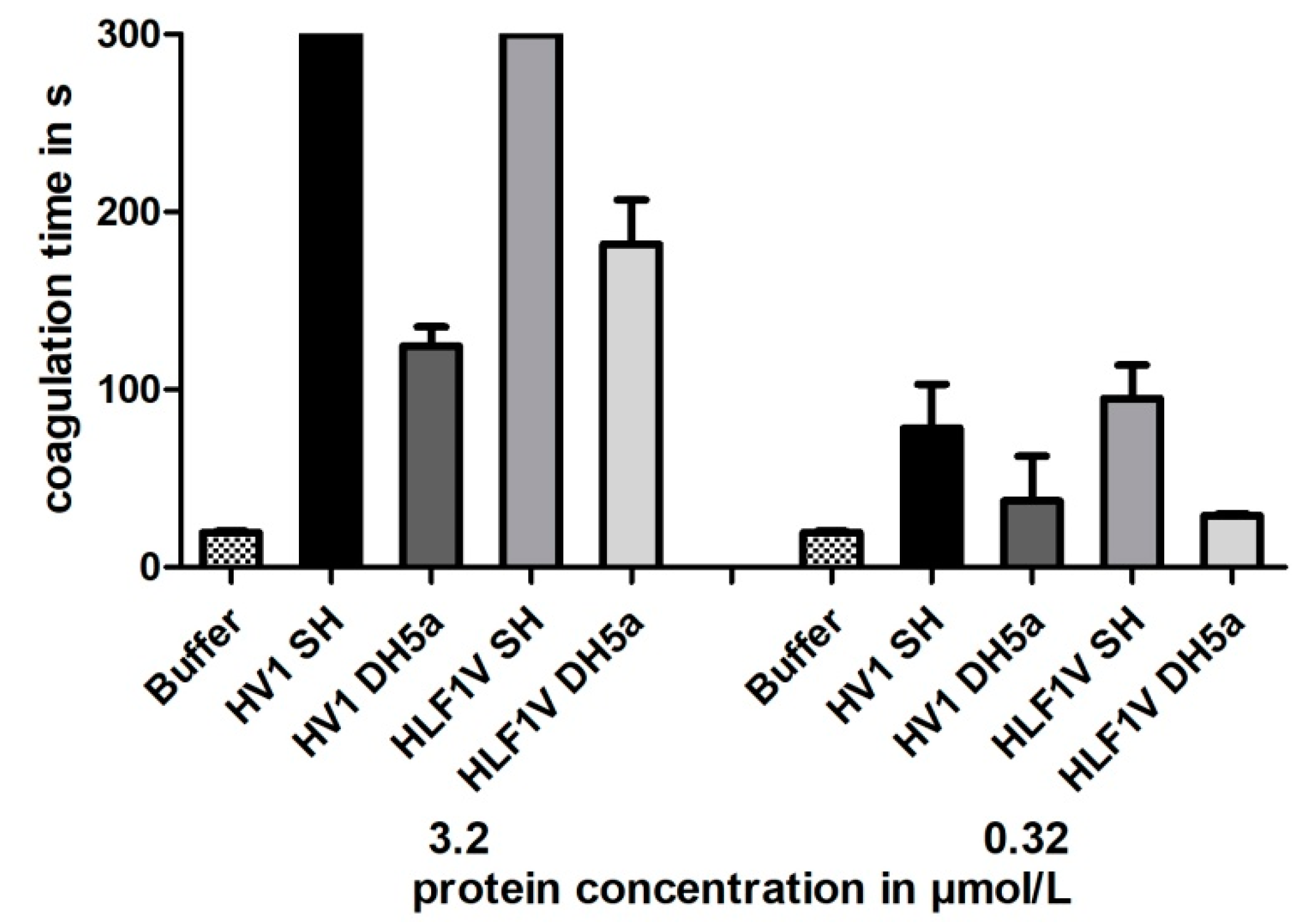
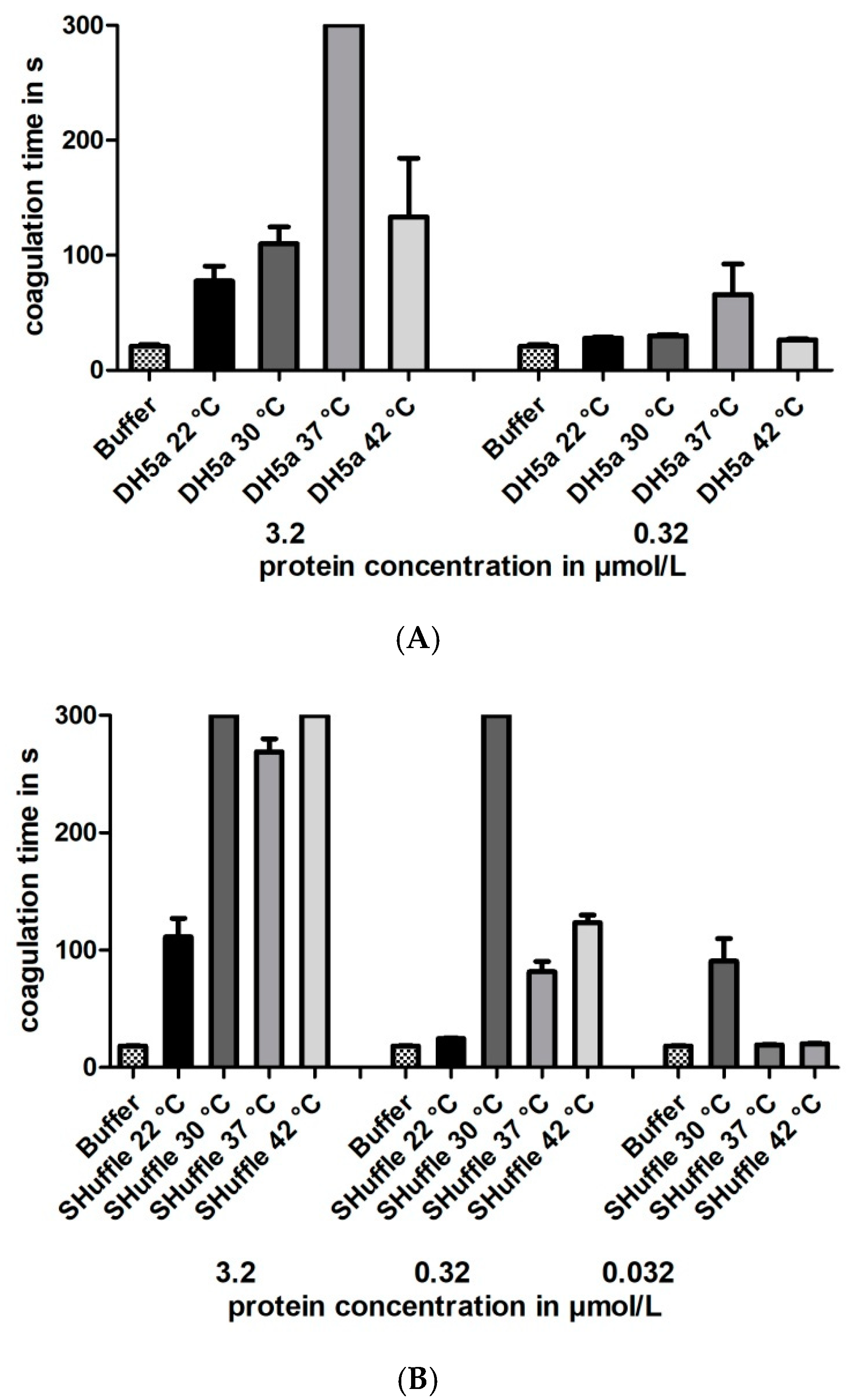
3.3. Functional Characterization of Hirudin HV1 and HLF1V Expressed in E. coli Strains
3.4. Expression of Recombinant Hirudin HV1 in P. pastoris GS115
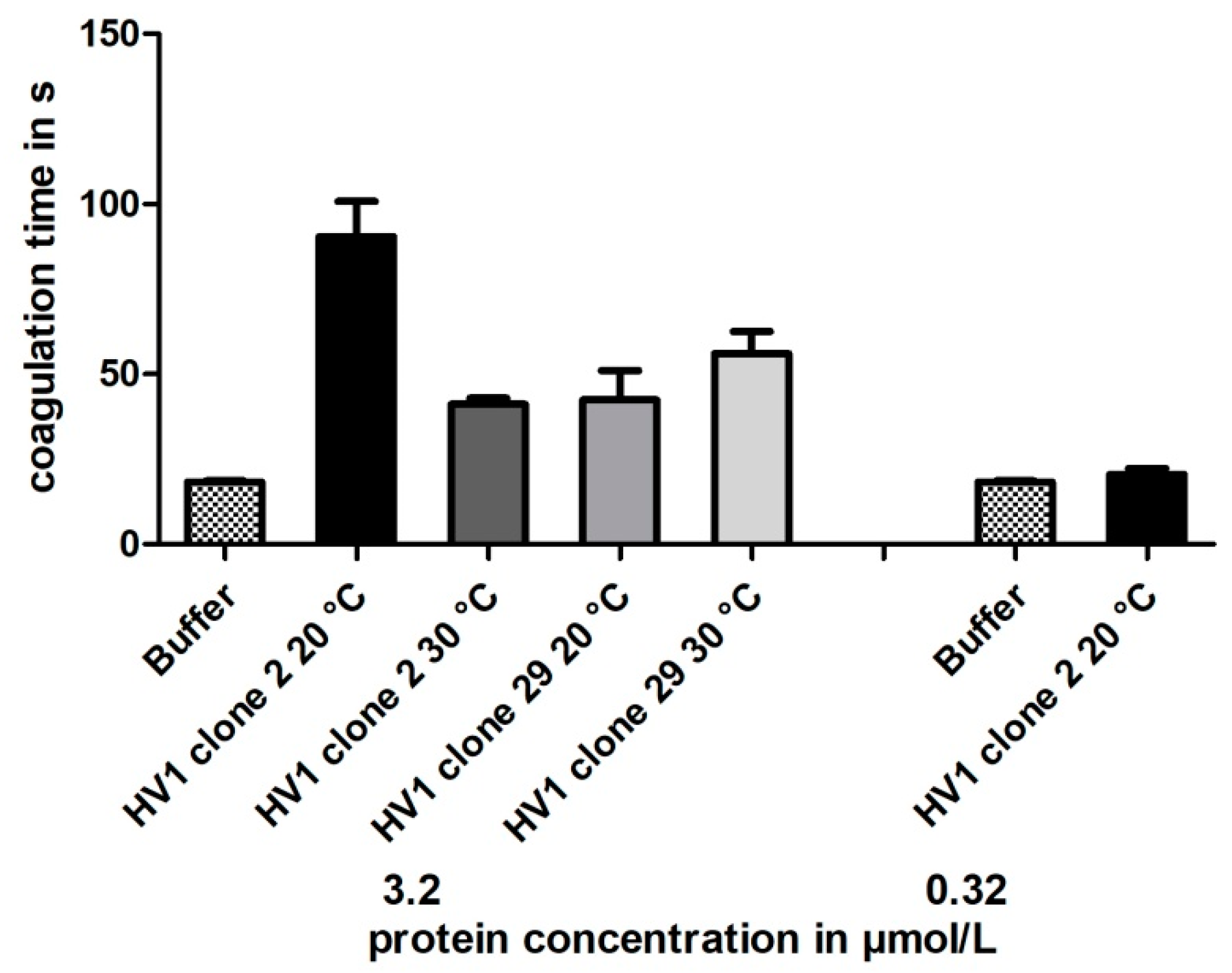
3.5. Functional Characterization of Hirudin HV1 Expressed in P. pastoris GS115
4. Discussion
5. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dodt, J.; Müller, H.-P.; Seemüller, U.; Chang, J.-Y. The complete amino acid sequence of hirudin, a thrombin specific inhibitor: Application of colour carboxymethylation. FEBS Lett. 1984, 165, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwardt, F. Hirudin as an inhibitor of thrombin. Method. Enzym. 1970, 19, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwardt, F. Development of hirudin as an antithrombotic agent. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1989, 15, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.H. Hirudin: Clinical potential of a thrombin inhibitor. Annu. Rev. Med. 1994, 45, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Warkentin, T.E. The direct thrombin inhibitor hirudin. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodt, J.; Seemüller, U.; Maschler, R.; Fritz, H. The complete covalent structure of hirudin. Localization of the disulfide bonds. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1985, 366, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydel, T.J.; Ravichandran, K.G.; Tulinsky, A.; Bode, W.; Huber, R.; Roitsch, C.; Fenton, J.W., 2nd. The structure of a complex of recombinant hirudin and human alpha-thrombin. Science 1990, 249, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydel, T.J.; Tulinsky, A.; Bode, W.; Huber, R. Refined structure of the hirudin-thrombin complex. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 221, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, T.E. Bivalent direct thrombin inhibitors: Hirudin and bivalirudin. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2004, 17, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Lukas, P.; Böhmert, M.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. Hirudin or hirudin-like factor—That is the question: Insights from the analyses of natural and synthetic HLF variants. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.P.; Degryse, E.; Stefani, L.; Schamber, F.; Cazenave, J.P.; Courtney, M.; Tolstoshev, P.; Lecocq, J.P. Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for the anticoagulant hirudin from the bloodsucking leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodt, J.; Machleidt, W.; Seemüller, U.; Maschler, R.; Fritz, H. Isolation and characterization of hirudin isoinhibitors and sequence analysis of hirudin PA. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1986, 367, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.; Mescke, K.; Liebig, S.; Mahfoud, H.; Lemke, S.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. More than just one: Multiplicity of Hirudins and Hirudin-like Factors in the Medicinal Leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.; Haase, M.; Lemke, S.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. Hirudins and hirudin-like factors in Hirudinidae: Implications for function and phylogenetic relationships. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Lukas, P.; Sponholz, D.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. The hirudin-like factors HLF3 and HLF4- hidden hirudins of European medicinal leeches. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ahmed, R.; Abilov, A.; Müller, C. Diversity of hirudin and hirudin-like factor genes in the North-African medicinal leech, Hirudo troctina. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdualkader, A.M.; Ghawi, A.M.; Alaama, M.; Awang, M.; Merzouk, A. Leech therapeutic applications. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Sig, A.K.; Guney, M.; Guclu, A.U.; Ozmen, E. Medicinal leech therapy—An overall perspective. Integr. Med. Res. 2017, 6, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Ren, J.-X.; Wang, J.-J.; Ding, L.-S.; Zhao, J.-J.; Liu, S.-Y.; Gao, H.-M. Chinese medicinal leech: Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 7895935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Lingna, W.; Jinghong, H.; Yongqing, Z. Oral administration of leeches (Shuizhi): A review of the mechanisms of action on antiplatelet aggregation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 232, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Völpel, H.; Janssens, U.; Hach-Wunderle, V.; Kemkes-Matthes, B.; Eichler, P.; Mueller-Velten, H.G.; Pötzsch, B. Recombinant hirudin (lepirudin) provides safe and effective anticoagulation in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: A prospective study. Circulation 1999, 99, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubenow, N.; Greinacher, A. Hirudin in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2002, 28, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riehl-Bellon, N.; Carvallo, D.; Acker, M.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Marquet, M.; Loison, G.; Lemoine, Y.; Brown, S.W.; Courtney, M.; Roitsch, C. Purification and biochemical characterization of recombinant hirudin produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 2941–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, S.A.; Nadeau, D.; Tirado, J.; Hollis, G.F.; Knabb, R.M.; Jia, S. Production and purification of recombinant hirudin expressed in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 1996, 8, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochanowski, R.; Kotłowski, R.; Szweda, P. Novel method of expression and purification of hirudin based on pBAD TOPO, pTYB12 vectors and gene synthesis. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 50, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, G. Pharmacology of recombinant hirudin. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2002, 28, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüstenhagen, D.A.; Lukas, P.; Müller, C.; Aubele, S.A.; Hildebrandt, J.-P.; Kubick, S. Cell-free synthesis of the hirudin variant 1 of the blood-sucking leech Hirudo medicinalis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Techniques for transformation of E. coli. In DNA Cloning: A Practical Approach; Glover, D.M., Ed.; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1985; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lobstein, J.; Emrich, C.A.; Jeans, C.; Faulkner, M.; Riggs, R.; Berkmen, M. SHuffle, a novel Escherichia coli protein expression strain capable of correctly folding disulfide bonded proteins in its cytoplasm. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 4th ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.C.; von Hippel, P.H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 182, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, C.N.; Vajdos, F.; Fee, L.; Grimsley, G.; Gray, T. How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 2411–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yang, L.; Guo, Y.; Fang, F.; Wang, D.; Li, R.; Jiang, M.; Kang, W.; Ma, J.; Sun, J.; et al. High-temperature cultivation of recombinant Pichia pastoris increases endoplasmic reticulum stress and decreases production of human interleukin-10. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Leandro, L.; Colasante, M.; Pitari, G.; Ippoliti, R. Hosts and heterologous expression strategies of recombinant toxins for therapeutic purposes. Toxins (Basel) 2023, 15, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakrishnan, A.; Rosli, W.R.W.; Tahir, A.R.M.; Razak, F.S.A.; Kee, P.E.; Ng, H.S.; Chew, Y.-L.; Lee, S.-K.; Ramasamy, M.; Tan, C.S.; et al. Evolving paradigms of recombinant protein production in pharmaceutical industry: A rigorous review. Sci. 2024, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.J.; Vega, M.C. Choose a suitable expression host: A survey of available protein production platforms. In Advanced Technologies for Protein Complex Production and Characterization. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Vega, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.R.; Byregowda, S.M.; Veeregowda, B.M.; Balamurugan, V. An overview of heterologous expression host systems for the production of recombinant proteins. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2016, 4, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, A.; Bernhard, F.; Berrow, N.; Buyel, J.F.; Ferreira-da-Silva, F.; Haustraete, J.; van den Heuvel, J.; Hoffmann, J.-E.; de Marco, A.; Peleg, Y.; et al. A concise guide to choosing suitable gene expression systems for recombinant protein production. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 102572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Marco, A. Strategies for successful recombinant expression of disulfide bond-dependent proteins in Escherichia coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkmen, M. Production of disulfide-bonded proteins in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouresmaeil, M.; Azizi-Dargahlou, S. Factors involved in heterologous expression of proteins in E. coli host. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaranen, M.J.; Ruddock, L.W. Applications of catalyzed cytoplasmic disulfide bond formation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Miralles, N.; Garcia-Fruitós, E. Heterologous expression of difficult to produce proteins in bacterial systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatahet, F.; Nguyen, V.D.; Salo, K.E.H.; Ruddock, L.W. Disruption of reducing pathways is not essential for efficient disulfide bond formation in the cytoplasm of E. coli. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2010, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Hatahet, F.; Salo, K.E.H.; Enlund, E.; Zhang, C.; Ruddock, L.W. Pre-expression of a sulfhydryl oxidase significantly increases the yields of eukaryotic disulfide bond containing proteins expressed in the cytoplasm of E.coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gąciarz, A.; Veijola, J.; Uchida, Y.; Saaranen, M.J.; Wang, C.; Hörkkö, S.; Ruddock, L.W. Systematic screening of soluble expression of antibody fragments in the cytoplasm of E. coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Corujo, A.; Uchida, Y.; Saaranen, M.J.; Ruddock, L.W. Escherichia coli cytoplasmic expression of disulfide-bonded proteins: Side-by-side comparison between two competing strategies. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Wang, Z.; Hamann, M.; Sponholz, D.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. Life without blood: Molecular and functional analysis of hirudins and hirudin-like factors of the Asian non- hematophagous leech Whitmania pigra. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 1808–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, C.; Rimkus, N.; Skala, F.F.O.; Merouze, M.; Böttcher, D.; Dörr, M.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Improved recombinant expression of soluble cathepsin B and L in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, A.R.; Trahan, N.D.; Son, M.S. Growth and maintenance of Escherichia coli laboratory strains. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.M.; Page, R. Strategies to optimize protein expression in E. coli. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2010, 61, 5.24.1–5.24.29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combet, C.; Blanchet, C.; Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. NPS@: Network protein sequence analysis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, C.; Noteborn, M. Formation of soluble recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli is favored by lower growth temperature. Nat. Biotechnol. 1988, 6, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Miguel, T.; Pérez-Bermúdez, P.; Gavidia, I. Production of soluble eukaryotic recombinant proteins in E. coli is favoured in early log-phase cultures induced at low temperature. Springerplus 2013, 2, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, M.; Mo, W. Expression, purification, and mass spectrometric analysis of 15N, 13C-labeled RGD-hirudin, expressed in Pichia pastoris, for NMR studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, J.-H.; Lee, S.-K.; Choi, E.-S.; Rhee, S.-K. Gene expression and secretion of the anticoagulant hirudin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1991, 1, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.D.; Rhee, S.K.; Seo, J.H. Enhanced production of anticoagulant hirudin in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae by chromosomal delta-integration. J. Biotechnol. 2001, 85, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraj, R.; Smooker, P.M. So you need a protein—A guide to the production of recombinant proteins. Open Vet. Sci. J. 2009, 3, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastberg, L.L.B.; Ard, R.; Jensen, M.K.; Workman, C.T. Burden imposed by heterologous protein production in two major industrial yeast cell factories: Identifying sources and mitigation strategies. Front. Fungal. Biol. 2022, 3, 827704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, V.; Knecht, R.; Gruetter, M.; Raschdorf, F.; Gassmann, E.; Maschler, R. Isolation and purification of novel hirudins from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 1990, 530, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, V.; Knecht, R.; Börnsen, K.O.; Gassmann, E.; Stone, S.R.; Raschdorf, F.; Schlaeppi, J.M.; Maschler, R. Primary structure and function of novel O-glycosylated hirudins from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 2294–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.S.Y.; Wijeyewickrema, L.C.; Wilkinson, B.L.; Pike, R.N.; Payne, R.J. Total synthesis of homogeneous variants of hirudin P6: A post-translationally modified anti-thrombotic leech- derived protein. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 3947–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, K.-K.; Le, N.M.T.; Nguyen, N.-L.; Kim, D.-H. Improving expression and assembly of difficult- to-express heterologous proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by culturing at a sub-physiological temperature. Microb. Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Expression System | Hirudin HV1 | HLF1V |
|---|---|---|
| SHuffle® T7 | 17.6 | 11.5 |
| DH5α | 21.2 | 13.8 |
| Expression System | Hirudin HV1 | HLF1V |
|---|---|---|
| SHuffle® T7 | 132.4 µmol/L (931 µg/mL) | 154.9 µmol/L (1011 µg/mL) |
| DH5α | 190.9 µmol/L (1341 µg/mL) | 128.2 µmol/L (842 µg/mL) |
| Cultivation Temperature | Clone 2 | Clone 29 |
|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 59.3 µmol/L (416 µg/mL) | 50.7 µmol/L (356 µg/mL) |
| 30 °C | 11.3 µmol/L (79 µg/mL) | 34.3 µmol/L (241 µg/mL) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Böttcher, D.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Müller, C. Expression of Recombinant Hirudin in Bacteria and Yeast: A Comparative Approach. Methods Protoc. 2025, 8, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8040089
Wang Z, Böttcher D, Bornscheuer UT, Müller C. Expression of Recombinant Hirudin in Bacteria and Yeast: A Comparative Approach. Methods and Protocols. 2025; 8(4):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8040089
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhongjie, Dominique Böttcher, Uwe T. Bornscheuer, and Christian Müller. 2025. "Expression of Recombinant Hirudin in Bacteria and Yeast: A Comparative Approach" Methods and Protocols 8, no. 4: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8040089
APA StyleWang, Z., Böttcher, D., Bornscheuer, U. T., & Müller, C. (2025). Expression of Recombinant Hirudin in Bacteria and Yeast: A Comparative Approach. Methods and Protocols, 8(4), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8040089







