Diagnosing X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy after Implementation of Newborn Screening: A Reference Laboratory Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Laboratory Studies
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Statistics
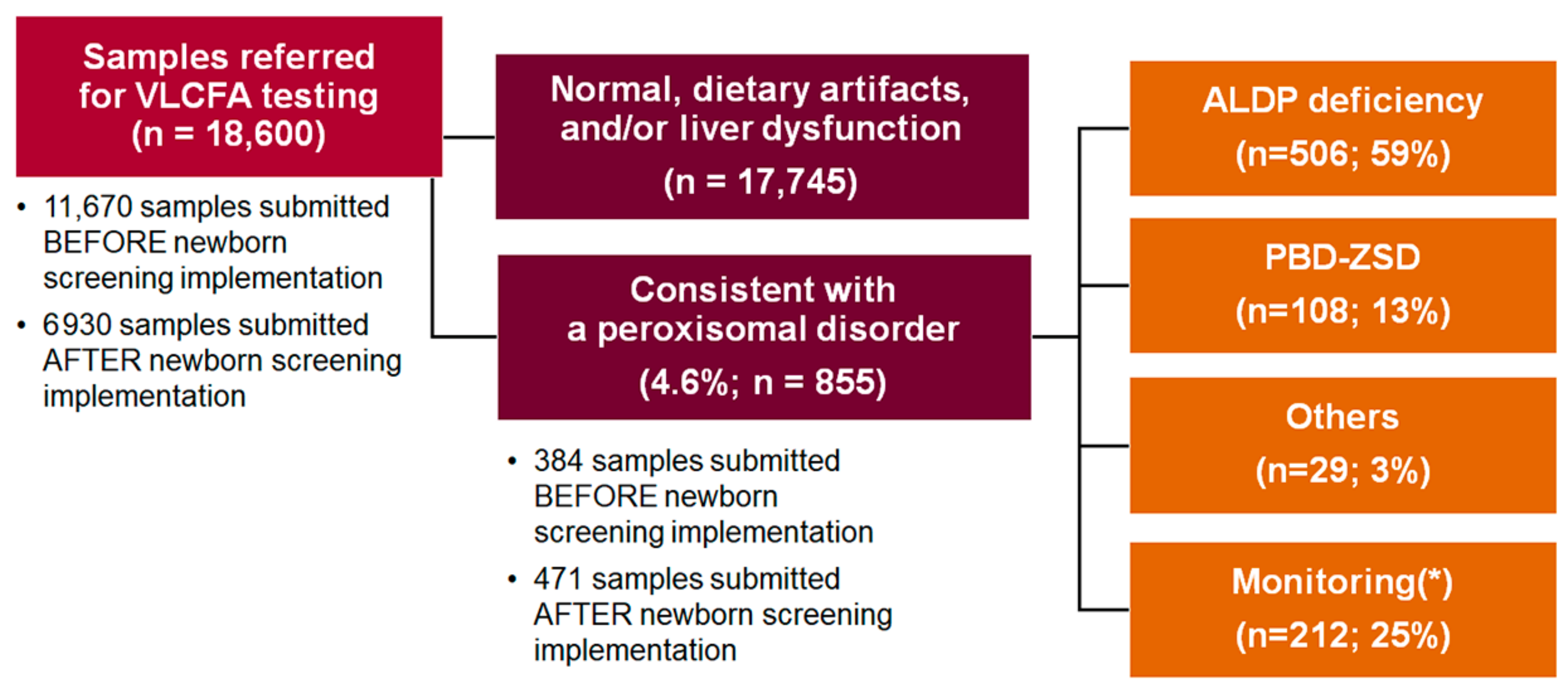
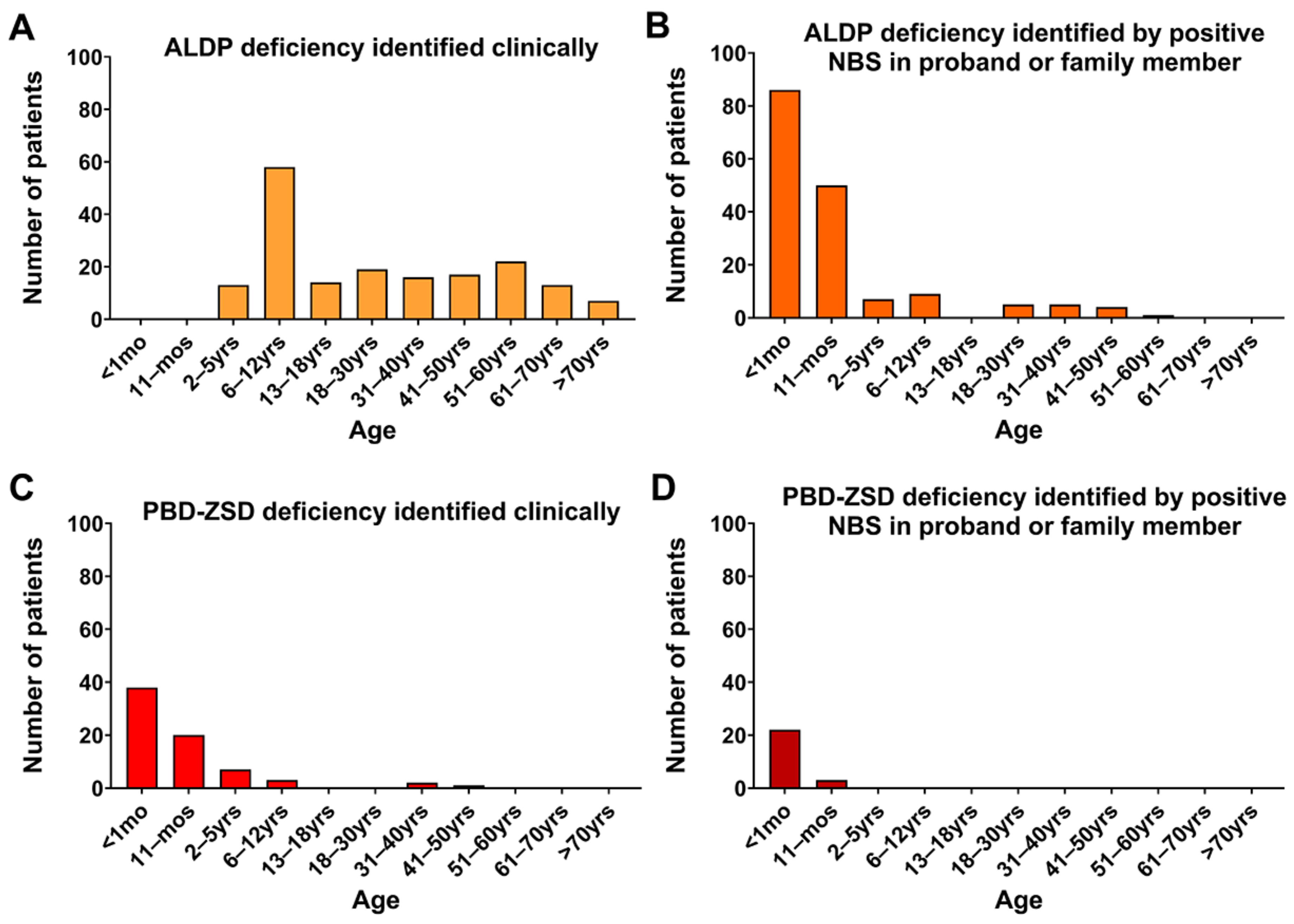
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosser, J.; Douar, A.M.; Sarde, C.O.; Kioschis, P.; Feil, R.; Moser, H.; Poustka, A.M.; Mandel, J.L.; Aubourg, P. Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters. Nature 1993, 361, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, S.; Pujol, A.; Waterham, H.R.; van Geel, B.M.; Boehm, C.D.; Raymond, G.V.; Cutting, G.R.; Wanders, R.J.; Moser, H.W. ABCD1 mutations and the X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy mutation database: Role in diagnosis and clinical correlations. Hum. Mutat. 2001, 18, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, S.; Wanders, R.J. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: Very long-chain fatty acid metabolism, ABC half-transporters and the complicated route to treatment. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2007, 90, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, S.; Berger, J.; Aubourg, P. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: Clinical, metabolic, genetic and pathophysiological aspects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.; Moser, H.W.; Moser, A.B.; Kishimoto, Y. Adrenoleukodystrophy: Impaired oxidation of long chain fatty acids in cultured skin fibroblasts an adrenal cortex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1981, 102, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, A.B.; Kreiter, N.; Bezman, L.; Lu, S.; Raymond, G.V.; Naidu, S.; Moser, H.W. Plasma very long chain fatty acids in 3000 peroxisome disease patients and 29,000 controls. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Biase, I.; Tortorelli, S.; Kratz, L.; Steinberg, S.J.; Cusmano-Ozog, K.; Braverman, N. Laboratory diagnosis of disorders of peroxisomal biogenesis and function: A technical standard of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Anesthesia Analg. 2020, 22, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezman, L.; Moser, A.B.; Raymond, G.V.; Rinaldo, P.; Watkins, P.A.; Smith, K.D.; Kass, N.E.; Moser, H.W. Adrenoleukodystrophy: Incidence, new mutation rate, and results of extended family screening. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 49, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, A.B.; Jones, R.O.; Hubbard, W.C.; Tortorelli, S.; Orsini, J.J.; Caggana, M.; Vogel, B.H.; Raymond, G.V. Newborn Screening for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2016, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteson, J.; Sciortino, S.; Feuchtbaum, L.; Bishop, T.; Olney, R.S.; Tang, H. Adrenoleukodystrophy Newborn Screening in California Since 2016: Programmatic Outcomes and Follow-Up. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2021, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, K.; Berry, S.A.; Choi, H.; Gaviglio, A.; Gupta, A.; Hietala, A.; Kenney-Jung, D.; Lund, T.; Miller, W.; Pierpont, E.I.; et al. A report on state-wide implementation of newborn screening for X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy. Am. J. Med Genet. Part A 2019, 179, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Clinard, K.; Young, S.P.; Rehder, C.W.; Fan, Z.; Calikoglu, A.S.; Bali, D.S.; Bailey, D.B., Jr.; Gehtland, L.M.; Millington, D.S.; et al. Evaluation of X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy Newborn Screening in North Carolina. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1920356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, P.L.; Li, H.; Hagar, A.F.; Jerris, S.C.; Wittenauer, A.; Wilcox, W. Newborn Screening for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy in Georgia: Experiences from a Pilot Study Screening of 51,081 Newborns. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, B.K.; Hickey, R.; Hitchins, L.; Shively, V.; Ehrhardt, J.; Ashbaugh, L.; Peng, Y.; Basheeruddin, K. Newborn Screening for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: The Initial Illinois Experience. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2022, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priestley, J.R.C.; Adang, L.A.; Drewes Williams, S.; Lichter-Konecki, U.; Menello, C.; Engelhardt, N.M.; DiPerna, J.C.; DiBoscio, B.; Ahrens-Nicklas, R.C.; Edmondson, A.C.; et al. Newborn Screening for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: Review of Data and Outcomes in Pennsylvania. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2022, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenke, G.C.; Fuchs, S.; Krasemann, E.; Doerr, H.G.; Wilichowski, E.; Hunneman, D.H.; Hanefeld, F. Cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) in only one of monozygotic twins with an identical ALD genotype. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 40, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, M.; Kemp, S.; de Visser, M.; van Geel, B.M.; Wanders, R.J.; Aubourg, P.; Poll-The, B.T. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD): Clinical presentation and guidelines for diagnosis, follow-up and management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.; Patel, J.; Stacy, H.; Mamak, E.G.; Faghfoury, H.; Raiman, J.; Clarke, J.T.R.; Blaser, S.; Mercimek-Mahmutoglu, S. Long-term outcome of patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: A retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. EJPN Off. J. Eur. Paediatr. Neurol. Soc. 2017, 21, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, H.W.; Mahmood, A.; Raymond, G.V. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Nat. Clin. Pr. Neurol. 2007, 3, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffnagel, I.C.; Laheji, F.K.; Aziz-Bose, R.; Tritos, N.A.; Marino, R.; Linthorst, G.E.; Kemp, S.; Engelen, M.; Eichler, F. The Natural History of Adrenal Insufficiency in X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: An International Collaboration. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el-Deiry, S.S.; Naidu, S.; Blevins, L.S.; Ladenson, P.W. Assessment of adrenal function in women heterozygous for adrenoleukodystrophy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, M.; Barbier, M.; Dijkstra, I.M.; Schur, R.; de Bie, R.M.; Verhamme, C.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Aubourg, P.A.; Wanders, R.J.; van Geel, B.M.; et al. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in women: A cross-sectional cohort study. Brain 2014, 137, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffnagel, I.C.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W.; Janssens, G.E.; van Weeghel, M.; van Geel, B.M.; Poll-The, B.T.; Kemp, S.; Engelen, M. Disease progression in women with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy is slow. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, S.; Huffnagel, I.C.; Linthorst, G.E.; Wanders, R.J.; Engelen, M. Adrenoleukodystrophy—Neuroendocrine pathogenesis and redefinition of natural history. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, G.V.; Moser, A.B.; Fatemi, A. X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy. In GeneReviews((R)); Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, B.H.; Bradley, S.E.; Adams, D.J.; D’Aco, K.; Erbe, R.W.; Fong, C.; Iglesias, A.; Kronn, D.; Levy, P.; Morrissey, M.; et al. Newborn screening for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in New York State: Diagnostic protocol, surveillance protocol and treatment guidelines. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2015, 114, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ojodu, J.; Kemper, A.R.; Lam, W.K.K.; Grosse, S.D. Implementation of Newborn Screening for Conditions in the United States First Recommended during 2010–2018. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2023, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braverman, N.E.; Raymond, G.V.; Rizzo, W.B.; Moser, A.B.; Wilkinson, M.E.; Stone, E.M.; Steinberg, S.J.; Wangler, M.F.; Rush, E.T.; Hacia, J.G.; et al. Peroxisome biogenesis disorders in the Zellweger spectrum: An overview of current diagnosis, clinical manifestations, and treatment guidelines. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 117, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Biase, I.; Pasquali, M. Quantification of Very-Long-Chain and Branched-Chain Fatty Acids in Plasma by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2546, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currier, R.J. Newborn Screening Is on a Collision Course with Public Health Ethics. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2022, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallack, E.J.; Turk, B.R.; Yan, H.; Price, C.; Demetres, M.; Moser, A.B.; Becker, C.; Hollandsworth, K.; Adang, L.; Vanderver, A.; et al. MRI surveillance of boys with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy identified by newborn screening: Meta-analysis and consensus guidelines. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattay, T.W.; Rautenberg, M.; Sohn, A.S.; Hengel, H.; Traschutz, A.; Roben, B.; Hayer, S.N.; Schule, R.; Wiethoff, S.; Zeltner, L.; et al. Defining diagnostic cutoffs in neurological patients for serum very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) in genetically confirmed X-Adrenoleukodystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffnagel, I.C.; van de Beek, M.C.; Showers, A.L.; Orsini, J.J.; Klouwer, F.C.C.; Dijkstra, I.M.E.; Schielen, P.C.; van Lenthe, H.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Vaz, F.M.; et al. Comparison of C26:0-carnitine and C26:0-lysophosphatidylcholine as diagnostic markers in dried blood spots from newborns and patients with adrenoleukodystrophy. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspers, Y.R.J.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Dijkstra, I.M.E.; Barendsen, R.W.; van Lenthe, H.; Kulik, W.; Engelen, M.; Goorden, S.M.I.; Vaz, F.M.; Kemp, S. Comparison of the Diagnostic Performance of C26:0-Lysophosphatidylcholine and Very Long-Chain Fatty Acids Analysis for Peroxisomal Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| State | Included | Start Date | State | Included | Start Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | No (*) | Montana | No | ||
| Alaska | No | Nebraska | Yes | 1 July 2018 | |
| Arizona | Yes | 1 January 2022 | Nevada | No | |
| Arkansas | Yes | 15 November 2021 | New Hampshire | Yes | 26 August 2020 |
| California [10] | Yes | (a) 21 September 2016 | New Jersey | Yes | 8 July 2019 |
| Colorado | No(*) | New Mexico | Yes | 1 January 2023 | |
| Connecticut | Yes | 1 July 2016 a | New York [9] | Yes | 30 December 2013 |
| Delaware | Yes | January 2020 | North Carolina [12] | Yes | 2 January 2018 |
| District of Columbia | Yes | September 2018 | North Dakota | No | |
| Florida | Yes | 1 May 2018 | Ohio | Yes | October 2022 |
| Georgia [13] | Yes | May 2020 | Oklahoma | Yes | March 2021 |
| Hawaii | No | Oregon | Yes | 1 January 2023 | |
| Idaho | Yes | 1 February 2022 | Pennsylvania [15] | Yes | April 2017 |
| Illinois [14] | Yes | 18 June 2019 | Rhode Island | Yes | 1 October 2018 |
| Indiana | Yes | 1 July 2021 | South Carolina | No | |
| Iowa | No | South Dakota | No | ||
| Kansas | No | Tennessee | Yes | 30 April 2018 | |
| Kentucky | Yes | 9 July 2018 | Texas | Yes | 5 August 2019 |
| Louisiana | No | Utah | Yes | 20 September 2020 | |
| Maine | Yes | 1 April 2022 | Vermont | Yes | 1 May 2019 |
| Maryland | No | Virginia | Yes | March 2022 | |
| Massachusetts | Yes | 29 January 2018 | Washington | Yes | 1 March 2018 |
| Michigan | Yes | October 2019 | West Virginia | Yes | April 2020 |
| Minnesota [11] | Yes | 6 February 2017 | Wisconsin | No | |
| Mississippi | No | Wyoming | No | ||
| Missouri | Yes | 1 December 2021 |
| Phenotype | ALDP Deficiency | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients (Males/Females) | Age in Years (Median; Range) | |
| Asymptomatic | 138 (80/58) | 0.11; 0.01–73 |
| Primary adrenal insufficiency (only) | 23 (22/1) | 9.3; 1.8–62 |
| Myelopathy with or without peripheral neuropathy (adrenomyeloneuropathy, AMN) | 80 (50/30) | 46; 5.3–78 |
| Rapidly progressive, inflammatory white matter demyelination (cerebral ALD) | 38 (38/0) | 8.9; 5.2–60 |
| Reason for Referral | ALDP Deficiency | PBD-ZSD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients (Males/Females) | Age in Years (Median; Range) | Number of Patients (Males/Females) | Age in Years (Median; Range) | |
| Clinical findings | 179 (145/34) | 21; 1.2–78 | 71 (40/31) | 0.07; 0–50 |
| Family history | 58 (26/32) | 23; 0.27–74 | 4 (2/2) | 1.2; 0–4.4 |
| Positive NBS in proband | 137 (70/67) | 0.07; 0.01–2.5 | 25 (12/13) | 0.03; 0–0.42 |
| Positive NBS in family member | 30 (24/6) | 15; 0.06–61 | 0 | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prinzi, J.; Pasquali, M.; Hobert, J.A.; Palmquist, R.; Wong, K.N.; Francis, S.; De Biase, I. Diagnosing X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy after Implementation of Newborn Screening: A Reference Laboratory Perspective. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2023, 9, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns9040064
Prinzi J, Pasquali M, Hobert JA, Palmquist R, Wong KN, Francis S, De Biase I. Diagnosing X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy after Implementation of Newborn Screening: A Reference Laboratory Perspective. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2023; 9(4):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns9040064
Chicago/Turabian StylePrinzi, Julia, Marzia Pasquali, Judith A. Hobert, Rachel Palmquist, Kristen N. Wong, Stephanie Francis, and Irene De Biase. 2023. "Diagnosing X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy after Implementation of Newborn Screening: A Reference Laboratory Perspective" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 9, no. 4: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns9040064
APA StylePrinzi, J., Pasquali, M., Hobert, J. A., Palmquist, R., Wong, K. N., Francis, S., & De Biase, I. (2023). Diagnosing X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy after Implementation of Newborn Screening: A Reference Laboratory Perspective. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 9(4), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns9040064






