A Roadmap to Newborn Screening for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Abstract
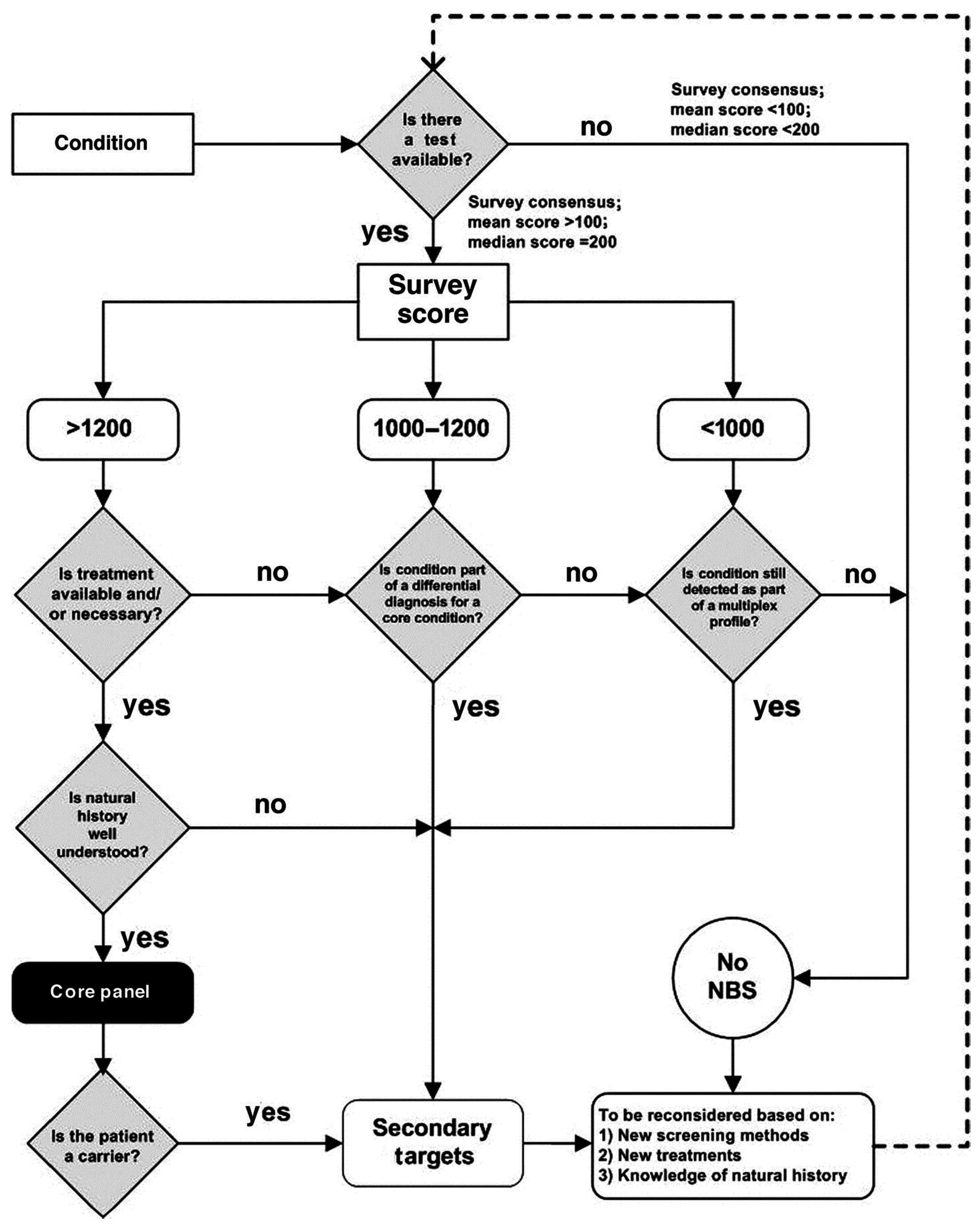
:1. Statement of Problem
Background
2. Achieving the Goal of State-Based Universal NBS
3. The Ohio Newborn Screening Pilot
4. Addressing the Barriers and Building the Infrastructure
4.1. Outreach and Education of Healthcare Providers and the Patient Community
4.2. Laboratory Test Validation and Refinement, including Screening Algorithm Development
4.3. Clinical Care Considerations for Pre-Symptomatically Identified Infants with DMD
4.4. Long-Term Follow-Up
4.5. Bioethical, Social, and Legal Considerations
4.6. Evidence Review
5. Path Forward: Assessment of Current Treatments and Next Steps
5.1. Current Treatments
5.2. Disease-Modifying Approaches Nearing Approval
5.3. Future Landscape (CRISPR)
6. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendell, J.R.; Shilling, C.; Leslie, N.D.; Flanigan, K.M.; al-Dahhak, R.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Kneile, K.; Dunn, D.M.; Duval, B.; Aoyagi, A.; et al. Evidence-based path to newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, M.; Hoffman, E.P.; Bertelson, C.J.; Monaco, A.P.; Feener, C.; Kunkel, L.M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell 1987, 50, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldane, J.B.S. The rate of spontaneous mutation of a human gene. J. Genetics 1935, 31, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, T.; Kress, W.; Meng, G.; Muller, C.R. Risk assessment and genetic counseling in families with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Acta Myol. 2012, 31, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soltanzadeh, P.; Friez, M.J.; Dunn, D.; von Niederhausern, A.; Gurvich, O.L.; Swoboda, K.J.; Sampson, J.B.; Pestronk, A.; Connolly, A.M.; Florence, J.M.; et al. Clinical and genetic characterization of manifesting carriers of DMD mutations. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2010, 20, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirski, K.T.; Crawford, T.O. Motor and cognitive delay in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Implication for early diagnosis. J. Pediatr. 2014, 165, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.T.; Silverstein Fadlon, C.A.; Ulm, J.W.; Jankovic, I.; Eskin, A.; Lu, A.; Miller, V.R.; Cantor, R.M.; Li, N.; Elashoff, R.; et al. Online self-report data for duchenne muscular dystrophy confirms natural history and can be used to assess for therapeutic benefits. PLoS Curr. 2014, 6. pii:ecurrents.md.e1e8f2be7c949f9ffe81ec6fca1cce6a. [Google Scholar]
- Mathews, K.D.; Cunniff, C.; Kantamneni, J.R.; Ciafaloni, E.; Miller, T.; Matthews, D.; Cwik, V.; Druschel, C.; Miller, L.; Meaney, F.J.; et al. Muscular Dystrophy Surveillance Tracking and Research Network (MD STARnet): Case definition in surveillance for childhood-onset Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy. J. Child Neurol. 2010, 25, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciafaloni, E.; Fox, D.J.; Pandya, S.; Westfield, C.P.; Puzhankara, S.; Romitti, P.A.; Mathews, K.D.; Miller, T.M.; Matthews, D.J.; Miller, L.A.; et al. Delayed diagnosis in duchenne muscular dystrophy: Data from the Muscular Dystrophy Surveillance, Tracking, and Research Network (MD STARnet). J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubowitz, V. Intellectual Impairment in Muscular Dystrophy. Arch. Dis. Child 1965, 40, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner-Medwin, D.; Bundey, S.; Green, S. Early diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Lancet 1978, 1, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A.; Sibert, J.R.; Harper, P.S. Early development of boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1990, 32, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, A.M.; Florence, J.M.; Cradock, M.M.; Malkus, E.C.; Schierbecker, J.R.; Siener, C.A.; Wulf, C.O.; Anand, P.; Golumbek, P.T.; Zaidman, C.M.; et al. Motor and cognitive assessment of infants and young boys with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Results from the Muscular Dystrophy Association DMD Clinical Research Network. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2013, 23, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- About ChildMuscleWeakness. Available online: http://www.childmuscleweakness.org/index.php/about-us (accessed on 5 April 2017).
- Silversides, C.K.; Webb, G.D.; Harris, V.A.; Biggar, D.W. Effects of deflazacort on left ventricular function in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AAP; Newborn Screening Task Force. Newborn screening: A blueprint for the future—A call for a national agenda on state newborn screening programs. Pediatrics 2000, 106, 389–427. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd-Puryear, M.A.; Tonniges, T.; van Dyck, P.C.; Mann, M.Y.; Brin, A.; Johnson, K.; McPherson, M. American Academy of Pediatrics Newborn Screening Task Force recommendations: How far have we come? Pediatrics 2006, 117, S194–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newborn screening: Toward a uniform screening panel and system—Executive summary. Pediatrics 2006, 117, S296–S307.
- Mendell, J.R.; Lloyd-Puryear, M. Report of MDA muscle disease symposium on newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle & Nerve 2013, 48, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, S.A.; Shilling, C.J.; Westra, S.; Wall, C.; Wicklund, M.P.; Stolle, C.; Brown, C.A.; Michele, D.E.; Piccolo, F.; Winder, T.L.; et al. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy in the United States. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfanos, A.P.; Naylor, E.W. A rapid screening test for Duchenne muscular dystrophy using dried blood specimens. Clin. Chim Acta 1984, 138, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatheridge, M.A.; Kwon, J.M.; Mendell, J.M.; Scheuerbrandt, G.; Moat, S.J.; Eyskens, F.; Rockman-Greenberg, C.; Drousiotou, A.; Griggs, R.C. Identifying Non-Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy-Positive and False Negative Results in Prior Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Newborn Screening Programs: A Review. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, R.; Emery, A.E.; Scheuerbrandt, G.; Syme, J. Feasibility of neonatal screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J. Med. Genet. 1982, 19, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moat, S.J.; Bradley, D.M.; Salmon, R.; Clarke, A.; Hartley, L. Newborn bloodspot screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: 21 years experience in Wales (UK). Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 21, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moat, S.J.; Korpimaki, T.; Furu, P.; Hakala, H.; Polari, H.; Merio, L.; Makinen, P.; Weeks, I. Characterization of a Blood Spot Creatine Kinase Skeletal Muscle Isoform Immunoassay for High-Throughput Newborn Screening of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Clin. Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendell, J.R.; Moxley, R.T.; Griggs, R.C.; Brooke, M.H.; Fenichel, G.M.; Miller, J.P.; King, W.; Signore, L.; Pandya, S.; Florence, J.; et al. Randomized, double-blind six-month trial of prednisone in Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggar, W.D.; Gingras, M.; Fehlings, D.L.; Harris, V.A.; Steele, C.A. Deflazacort treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escolar, D.M.; Hache, L.P.; Clemens, P.R.; Cnaan, A.; McDonald, C.M.; Viswanathan, V.; Kornberg, A.J.; Bertorini, T.E.; Nevo, Y.; Lotze, T.; et al. Randomized, blinded trial of weekend vs daily prednisone in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology 2011, 77, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, W.M.; Ruttencutter, R.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Matkovic, V.; Landoll, J.; Hoyle, C.; Mendell, J.R.; Kissel, J.T. Orthopedic outcomes of long-term daily corticosteroid treatment in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology 2007, 68, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; van Ommen, G.J. Antisense-mediated exon skipping: A versatile tool with therapeutic and research applications. RNA 2007, 13, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinali, M.; Arechavala-Gomeza, V.; Feng, L.; Cirak, S.; Hunt, D.; Adkin, C.; Guglieri, M.; Ashton, E.; Abbs, S.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.; et al. Local restoration of dystrophin expression with the morpholino oligomer AVI-4658 in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: A single-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation, proof-of-concept study. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendell, J.R.; Goemans, N.; Lowes, L.P.; Alfano, L.N.; Berry, K.; Shao, J.; Kaye, E.M.; Mercuri, E. Longitudinal effect of eteplirsen versus historical control on ambulation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, E.M.; Barton, E.R.; Zhuo, J.; Tomizawa, Y.; Friesen, W.J.; Trifillis, P.; Paushkin, S.; Patel, M.; Trotta, C.R.; Hwang, S.; et al. PTC124 targets genetic disorders caused by nonsense mutations. Nature 2007, 447, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, J.; Xiao, X. Adeno-associated virus vector carrying human minidystrophin genes effectively ameliorates muscular dystrophy in mdx mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13714–13719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watchko, J.; O’Day, T.; Wang, B.; Zhou, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, X. Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated minidystrophin gene therapy improves dystrophic muscle contractile function in MDX mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.; Amoasii, L.; Mireault, A.A.; McAnally, J.R.; Li, H.; Sanchez-Ortiz, E.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Shelton, J.M.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. Postnatal genome editing partially restores dystrophin expression in a mouse model of muscular dystrophy. Science 2016, 351, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, C.E.; Hakim, C.H.; Ousterout, D.G.; Thakore, P.I.; Moreb, E.A.; Castellanos Rivera, R.M.; Madhavan, S.; Pan, X.; Ran, F.A.; Yan, W.X.; et al. In vivo genome editing improves muscle function in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Science 2016, 351, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabebordbar, M.; Zhu, K.; Cheng, J.K.; Chew, W.L.; Widrick, J.J.; Yan, W.X.; Maesner, C.; Wu, E.Y.; Xiao, R.; Ran, F.A.; et al. In vivo gene editing in dystrophic mouse muscle and muscle stem cells. Science 2016, 351, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Zaidy, S.A.; Lloyd-Puryear, M.; Kennedy, A.; Lopez, V.; Mendell, J.R. A Roadmap to Newborn Screening for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2017, 3, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns3020008
Al-Zaidy SA, Lloyd-Puryear M, Kennedy A, Lopez V, Mendell JR. A Roadmap to Newborn Screening for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2017; 3(2):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns3020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Zaidy, Samiah A., Michele Lloyd-Puryear, Annie Kennedy, Veronica Lopez, and Jerry R. Mendell. 2017. "A Roadmap to Newborn Screening for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 3, no. 2: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns3020008
APA StyleAl-Zaidy, S. A., Lloyd-Puryear, M., Kennedy, A., Lopez, V., & Mendell, J. R. (2017). A Roadmap to Newborn Screening for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 3(2), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns3020008





