Comparing DNA Isolation and Preparation Protocols for Dried Blood Spots in the Context of Genomic Newborn Screening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. DNA Isolation Protocols
2.3. Comparative Measurements
2.3.1. Practical Outcomes
2.3.2. Technical Outcomes
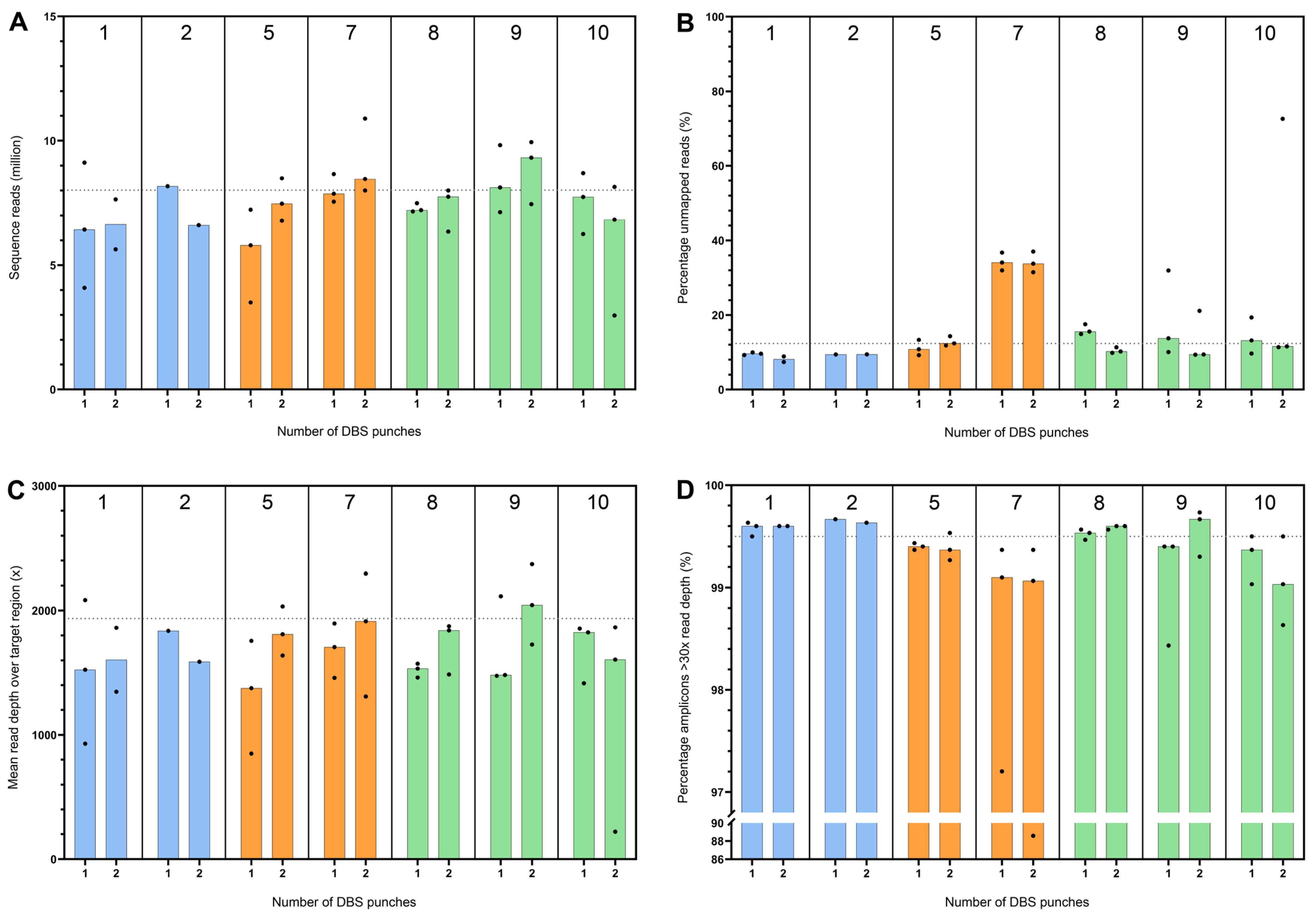
2.3.3. Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
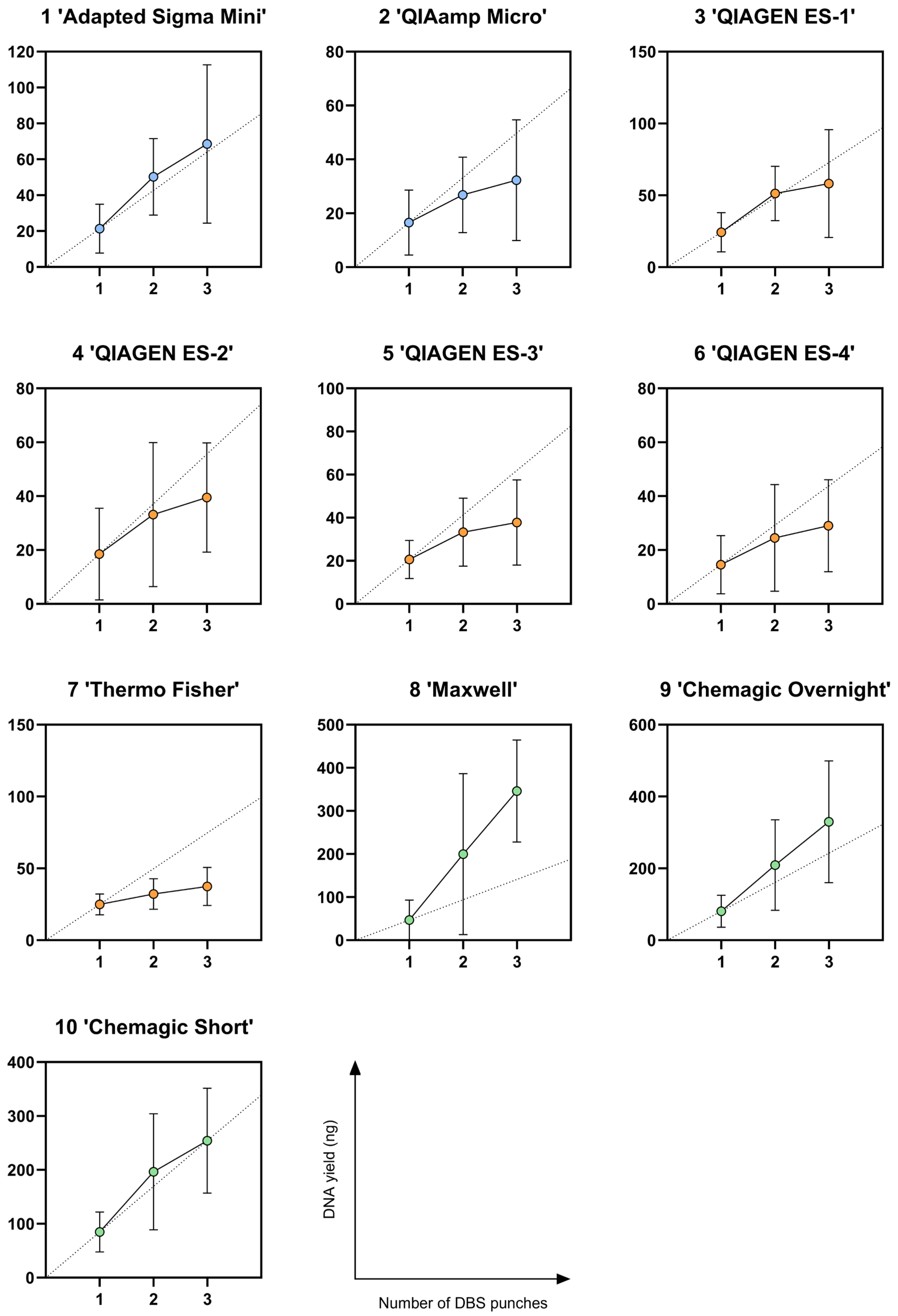
3.1. Operational Performance
| Number | DNA Isolation Protocols | Technique | Total Elution Volume (µL) | Costs (€) | Hands-on Time (Hours) | Turnaround Time (Hours) | Scalability | Plastic Footprint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adapted Sigma Mini | Column, manual | 20 | 2–4 | 1.5 | 2.75 | Poor | Fair |
| 2 | QIAamp Micro | Column, manual | 20 | 5–7 | 1.5 | 2.75 | Poor | Fair |
| 3 | QIAGEN ES-1 (30′–100 μL elution) | Lysis, manual | 100 | <1 | 0.25 | 1 | Excellent | Excellent |
| 4 | QIAGEN ES-2 (15′–100 μL elution) | Lysis, manual | 100 | <1 | 0.25 | 0.75 | Excellent | Excellent |
| 5 | QIAGEN ES-3 (30′–50 μL elution) | Lysis, manual | 50 | <1 | 0.25 | 1 | Excellent | Excellent |
| 6 | QIAGEN ES-4 (15′–50 μL elution) | Lysis, manual | 50 | <1 | 0.25 | 0.75 | Excellent | Excellent |
| 7 | Thermo Fisher | Lysis, manual | 40 | 1–2 | 0.5 | 1 | Average | Average |
| 8 | Maxwell | Magnetic beads, semi-automated | 50 | 8–10 | 0.5 | 1.5 | Fair | Fair |
| 9 | Chemagic Overnight | Magnetic beads, semi-automated | 55 | 1–2 | 1 | 18 | Good | Poor |
| 10 | Chemagic Short | Magnetic beads, semi-automated | 55 | 1–2 | 1 | 5 | Good | Poor |
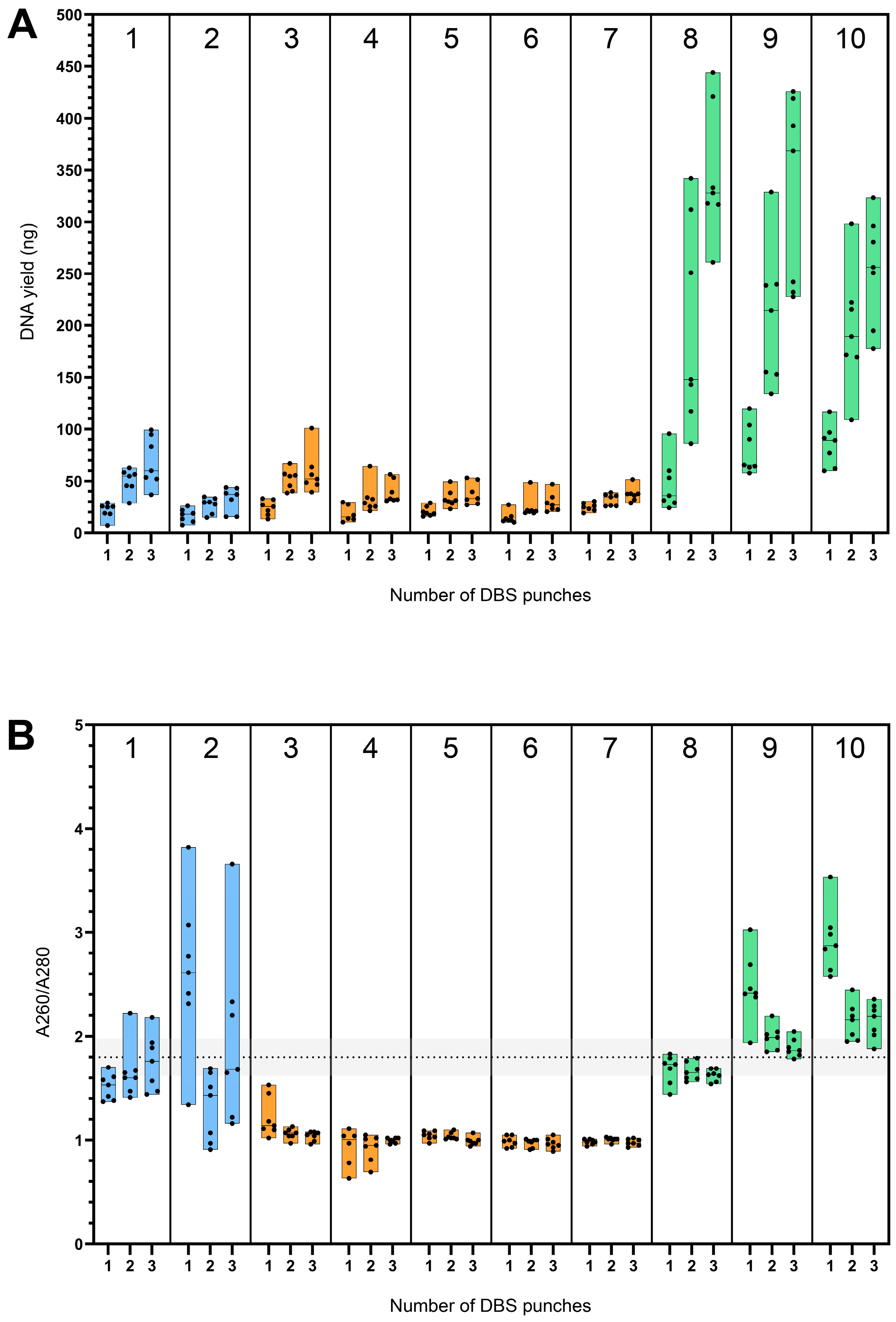
3.2. DNA Yield
3.3. DNA Purity
3.4. Molecular Weight
3.5. Sequencing Performance
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| DBS | Dried blood spot |
| GIAB | Genome in a bottle |
| LUMC | Leiden University Medical Center |
| LuVDS | LUMC Healthy Donor Service, in Dutch: LUMC Vrijwillige Donoren Service |
| NBS | Newborn screening |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| nWMO | Non-Medical Research Involving Human Subjects act |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SCID | Severe combined immunodeficiency |
| SMA | Spinal muscular atrophy |
| TREC | T-cell receptor excision circle |
| WES | Whole exome sequencing |
| WGS | Whole genome sequencing |
| XLA | X-linked agammaglobulinemia |
References
- Therrell, B.L.; Padilla, C.D.; Borrajo, G.J.C.; Khneisser, I.; Schielen, P.; Knight-Madden, J.; Malherbe, H.L.; Kase, M. Current Status of Newborn Bloodspot Screening Worldwide 2024: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Activities (2020–2023). Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2024, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Puck, J.M. Development of population-based newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Spek, J.; Groenwold, R.H.; van der Burg, M.; van Montfrans, J.M. TREC Based Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borte, S.; von Dobeln, U.; Fasth, A.; Wang, N.; Janzi, M.; Winiarski, J.; Sack, U.; Pan-Hammarstrom, Q.; Borte, M.; Hammarstrom, L. Neonatal screening for severe primary immunodeficiency diseases using high-throughput triplex real-time PCR. Blood 2012, 119, 2552–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.L.; Lee, F.K.; Yazdanpanah, G.K.; Staropoli, J.F.; Liu, M.; Carulli, J.P.; Sun, C.; Dobrowolski, S.F.; Hannon, W.H.; Vogt, R.F. Newborn blood spot screening test using multiplexed real-time PCR to simultaneously screen for spinal muscular atrophy and severe combined immunodeficiency. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Mateo, C.; Timonen, A.; Vaahtera, K.; Jaakkola, M.; Hougaard, D.M.; Bybjerg-Grauholm, J.; Baekvad-Hansen, M.; Adamsen, D.; Filippov, G.; Dallaire, S.; et al. Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Newborn Screening of SCID, SMA, and XLA. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2019, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetterstrand, K.A. DNA Sequencing Costs: Data from the NHGRI Genome Sequencing Program (GSP). Available online: www.genome.gov/sequencingcostsdata (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Polonis, K.; Blommel, J.H.; Hughes, A.E.O.; Spencer, D.; Thompson, J.A.; Schroeder, M.C. Innovations in Short-Read Sequencing Technologies and Their Applications to Clinical Genomics. Clin. Chem. 2025, 71, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Jungner, G. The Principles and Practice of Screening for Disease; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- King, J.R.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Hammarstrom, L. An appraisal of the Wilson & Jungner criteria in the context of genomic-based newborn screening for inborn errors of immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mousa, H.; Al-Dakheel, G.; Jabr, A.; Elbadaoui, F.; Abouelhoda, M.; Baig, M.; Monies, D.; Meyer, B.; Hawwari, A.; Dasouki, M. High Incidence of Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease in Saudi Arabia Detected Through Combined T Cell Receptor Excision Circle and Next Generation Sequencing of Newborn Dried Blood Spots. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, J.; Gul, K.A.; Erichsen, H.C.; Lundman, E.; Berge, M.C.; Tromborg, A.K.; Sorgjerd, L.K.; Ytre-Arne, M.; Hogner, S.; Halsne, R.; et al. Second-Tier Next Generation Sequencing Integrated in Nationwide Newborn Screening Provides Rapid Molecular Diagnostics of Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Fan, C.; Huang, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Jin, W.; et al. Genomic Sequencing as a First-Tier Screening Test and Outcomes of Newborn Screening. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2331162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunke, S.; Bouffler, S.E.; Downie, L.; Caruana, J.; Amor, D.J.; Archibald, A.; Bombard, Y.; Christodoulou, J.; Clausen, M.; De Fazio, P.; et al. Prospective cohort study of genomic newborn screening: BabyScreen+ pilot study protocol. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e081426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.S.; Zettler, B.; Genetti, C.A.; Hickingbotham, M.R.; Coleman, T.F.; Lebo, M.; Nagy, A.; Zouk, H.; Mahanta, L.; Christensen, K.D.; et al. The BabySeq Project: A clinical trial of genome sequencing in a diverse cohort of infants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 111, 2094–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsmore, S.F.; Wright, M.; Smith, L.D.; Liang, Y.; Mowrey, W.R.; Protopsaltis, L.; Bainbridge, M.; Baker, M.; Batalov, S.; Blincow, E.; et al. Prequalification of genome-based newborn screening for severe childhood genetic diseases through federated training based on purifying hyperselection. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 111, 2618–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.C.H.; Mak, C.M.; Yeung, M.C.W.; Law, E.C.; Cheung, J.; Wong, T.K.; Cheng, V.W.; Lee, J.K.H.; Wong, J.C.L.; Fung, C.W.; et al. Harnessing Next-Generation Sequencing as a Timely and Accurate Second-Tier Screening Test for Newborn Screening of Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2024, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boemer, F.; Hovhannesyan, K.; Piazzon, F.; Minner, F.; Mni, M.; Jacquemin, V.; Mashhadizadeh, D.; Benmhammed, N.; Bours, V.; Jacquinet, A.; et al. Population-based, first-tier genomic newborn screening in the maternity ward. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, A.; Chung, W.K. Newborn Screening Using Genome Sequencing for Early Actionable Conditions-Reply. JAMA 2025, 333, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, M.M.; Cuthbert, C.D.; Cordovado, S.K. Assessing the Performance of Dried-Blood-Spot DNA Extraction Methods in Next Generation Sequencing. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, Z.; Scott, R.H. Genomic newborn screening for rare diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanne, M.; Chung, W.K. DNA Sequencing in Newborn Screening: Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Directions. Clin. Chem. 2025, 71, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, J.B.; Lescai, F.; Grove, J.; Baekvad-Hansen, M.; Christiansen, M.; Hagen, C.M.; Maller, J.; Stevens, C.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; et al. High-Quality Exome Sequencing of Whole-Genome Amplified Neonatal Dried Blood Spot DNA. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoholm, M.I.; Dillner, J.; Carlson, J. Assessing quality and functionality of DNA from fresh and archival dried blood spots and recommendations for quality control guidelines. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Owen, M.; Le, J.; Batalov, S.; Chau, K.; Kwon, Y.H.; Van Der Kraan, L.; Bezares-Orin, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Veeraraghavan, N.; et al. Scalable, high quality, whole genome sequencing from archived, newborn, dried blood spots. NPJ Genom. Med. 2023, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelker, D.; Schmidt, R.J.; Ankala, A.; McDonald Gibson, K.; Bowser, M.; Sharma, H.; Duffy, E.; Hegde, M.; Santani, A.; Lebo, M.; et al. Navigating highly homologous genes in a molecular diagnostic setting: A resource for clinical next-generation sequencing. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantere, T.; Kersten, S.; Hoischen, A. Long-Read Sequencing Emerging in Medical Genetics. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logsdon, G.A.; Vollger, M.R.; Eichler, E.E. Long-read human genome sequencing and its applications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trier, C.; Fournous, G.; Strand, J.M.; Stray-Pedersen, A.; Pettersen, R.D.; Rowe, A.D. Next-generation sequencing of newborn screening genes: The accuracy of short-read mapping. NPJ Genom. Med. 2020, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivucci, G.; Iovino, E.; Innella, G.; Turchetti, D.; Pippucci, T.; Magini, P. Long read sequencing on its way to the routine diagnostics of genetic diseases. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1374860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrorosa, F.K.; Miller, D.E.; Eichler, E.E. Applications of long-read sequencing to Mendelian genetics. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandotra, N.; Tyagi, A.; Tikhonova, I.; Storer, C.; Scharfe, C. CFTR haplotype phasing using long-read genome sequencing from ultralow input DNA. Genet. Med. Open 2025, 3, 101962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Neonatal Screening. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duintjer, A.J.; Imholz, S.; Pico-Knijnenburg, I.; Heuperman, A.; Hodemaekers, H.; Deutekom, E.S.; Voorhoeve, E.; Dollé, M.E.T.; van der Burg, M. Comparing DNA Isolation and Preparation Protocols for Dried Blood Spots in the Context of Genomic Newborn Screening. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2025, 11, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11030075
Duintjer AJ, Imholz S, Pico-Knijnenburg I, Heuperman A, Hodemaekers H, Deutekom ES, Voorhoeve E, Dollé MET, van der Burg M. Comparing DNA Isolation and Preparation Protocols for Dried Blood Spots in the Context of Genomic Newborn Screening. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2025; 11(3):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11030075
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuintjer, Annelotte J., Sandra Imholz, Ingrid Pico-Knijnenburg, Adinda Heuperman, Hennie Hodemaekers, Eva S. Deutekom, Els Voorhoeve, Martijn E. T. Dollé, and Mirjam van der Burg. 2025. "Comparing DNA Isolation and Preparation Protocols for Dried Blood Spots in the Context of Genomic Newborn Screening" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 11, no. 3: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11030075
APA StyleDuintjer, A. J., Imholz, S., Pico-Knijnenburg, I., Heuperman, A., Hodemaekers, H., Deutekom, E. S., Voorhoeve, E., Dollé, M. E. T., & van der Burg, M. (2025). Comparing DNA Isolation and Preparation Protocols for Dried Blood Spots in the Context of Genomic Newborn Screening. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 11(3), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11030075







