Assessment of Long-Read Sequencing-Based Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Genotyping Assay for Newborns in Fujian, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
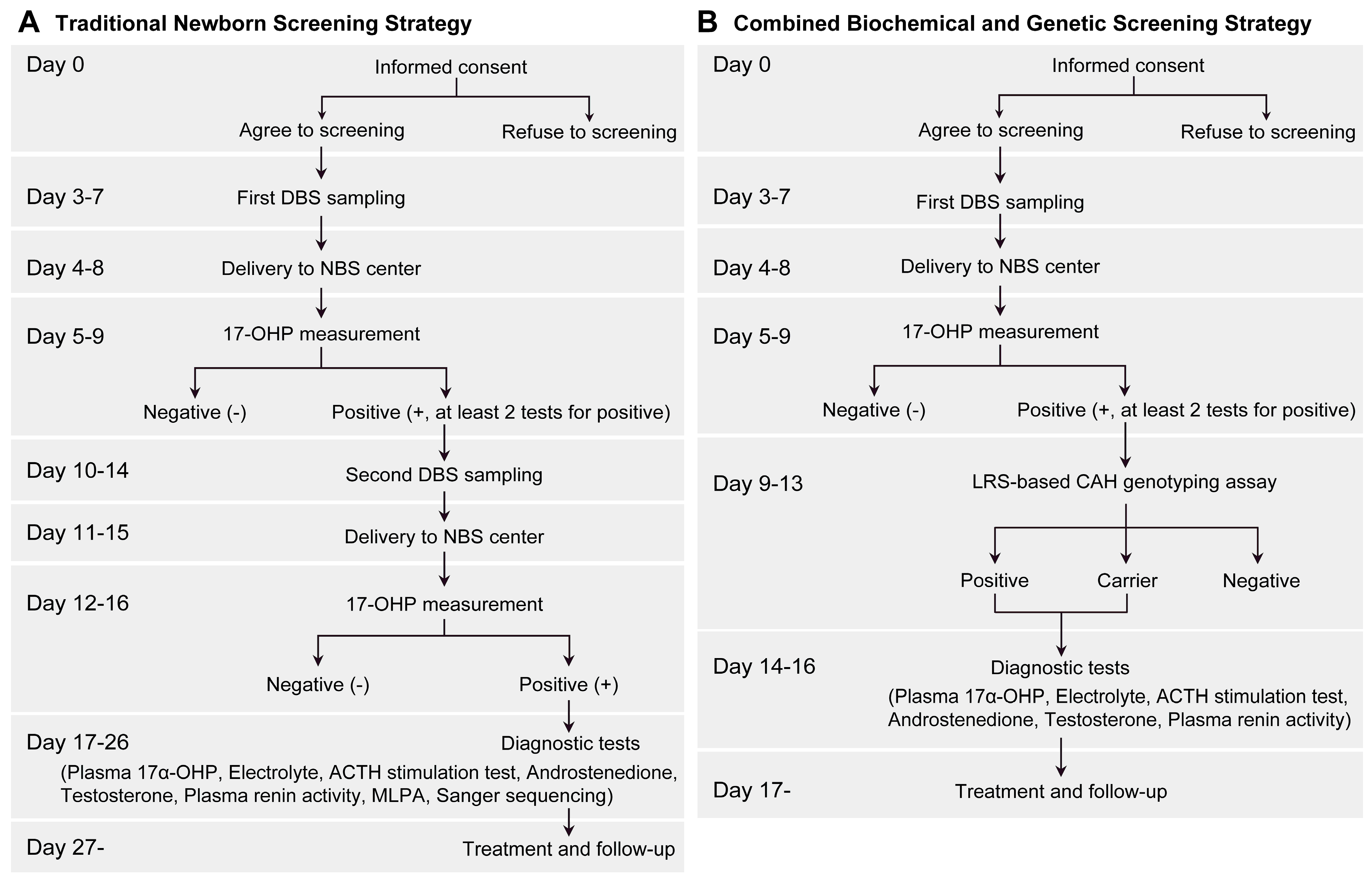
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Newborn Screening for 17α-OHP Level
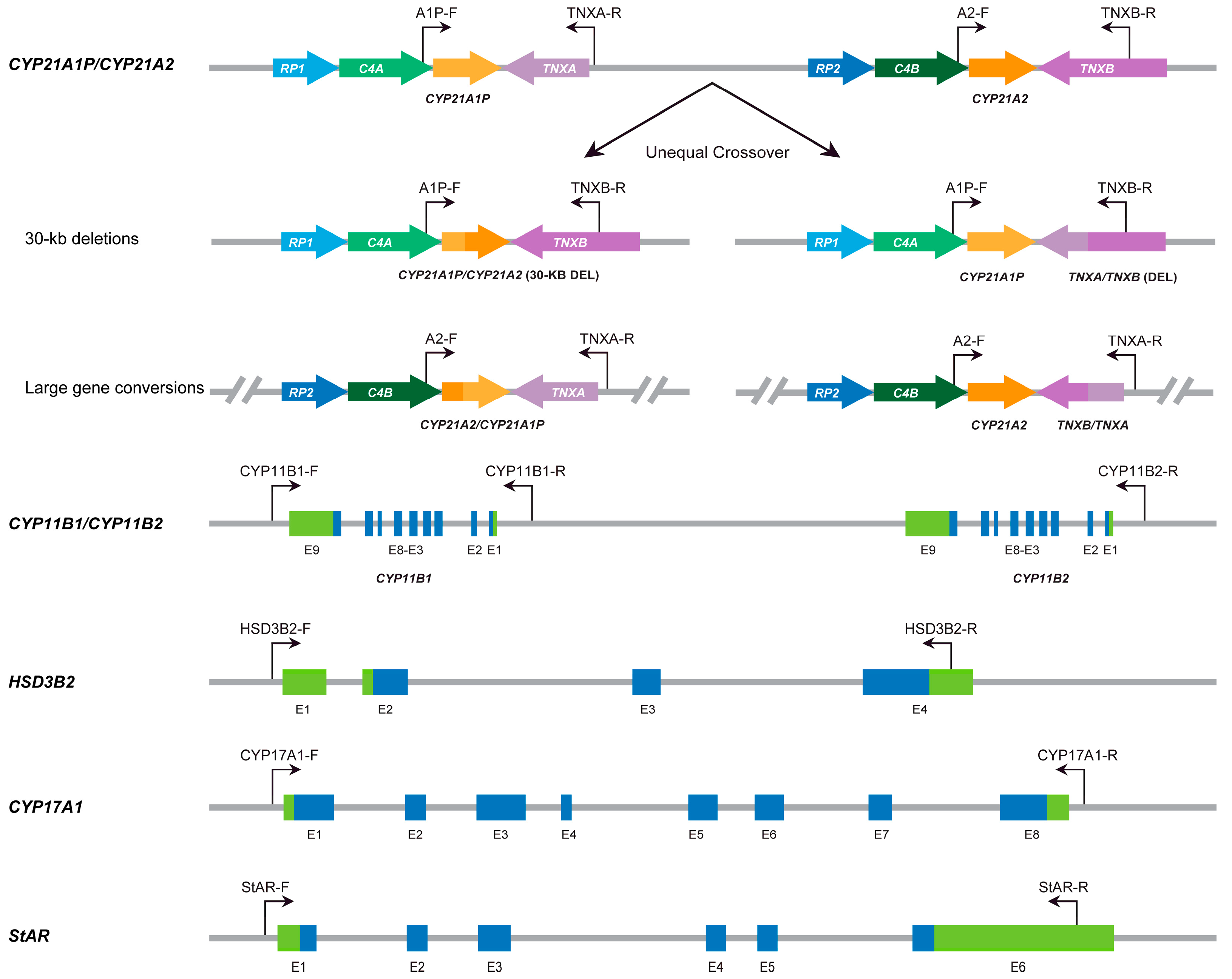
2.3. LRS-Based CAH Genotyping Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
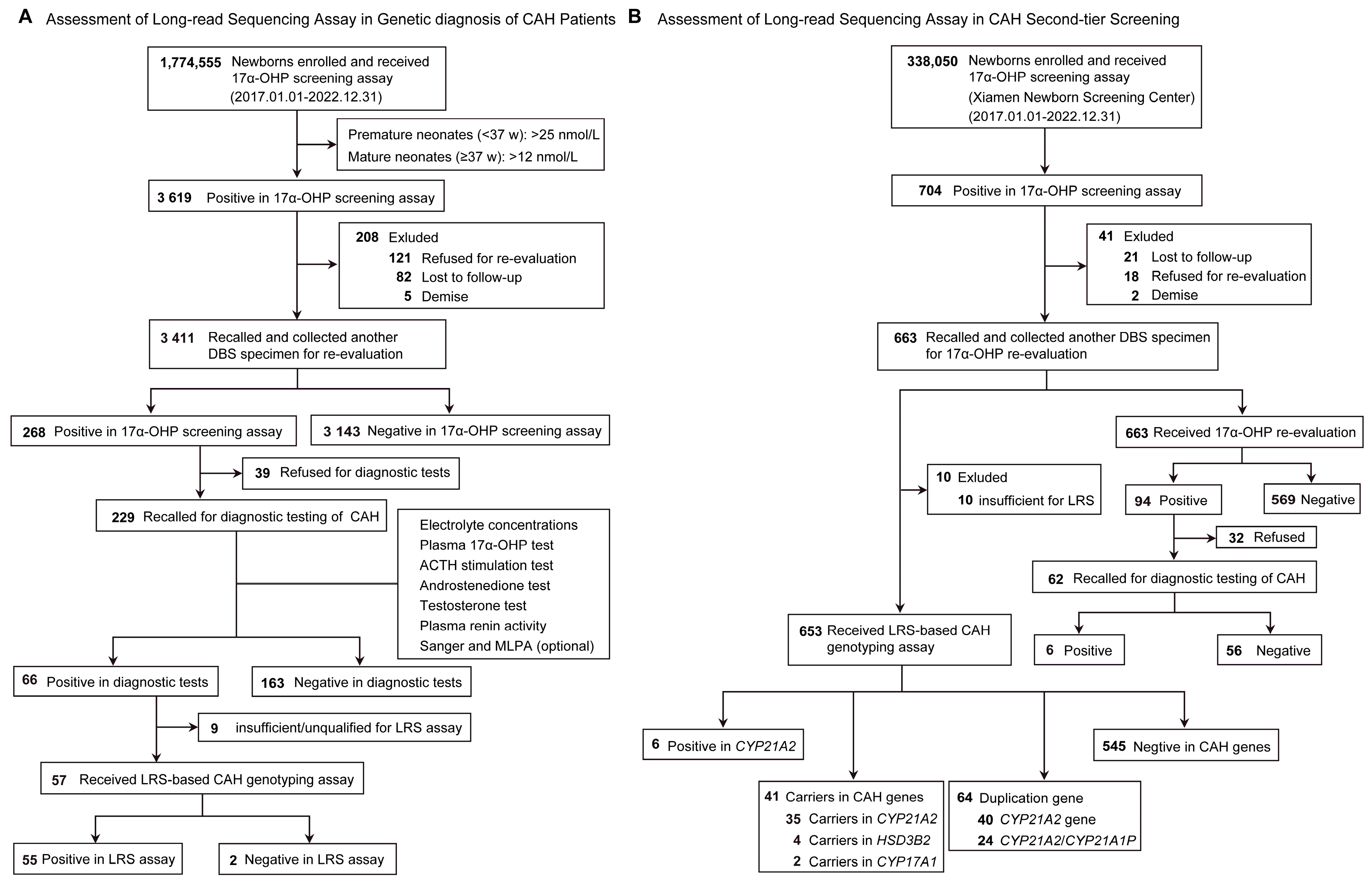
3.1. Study Population
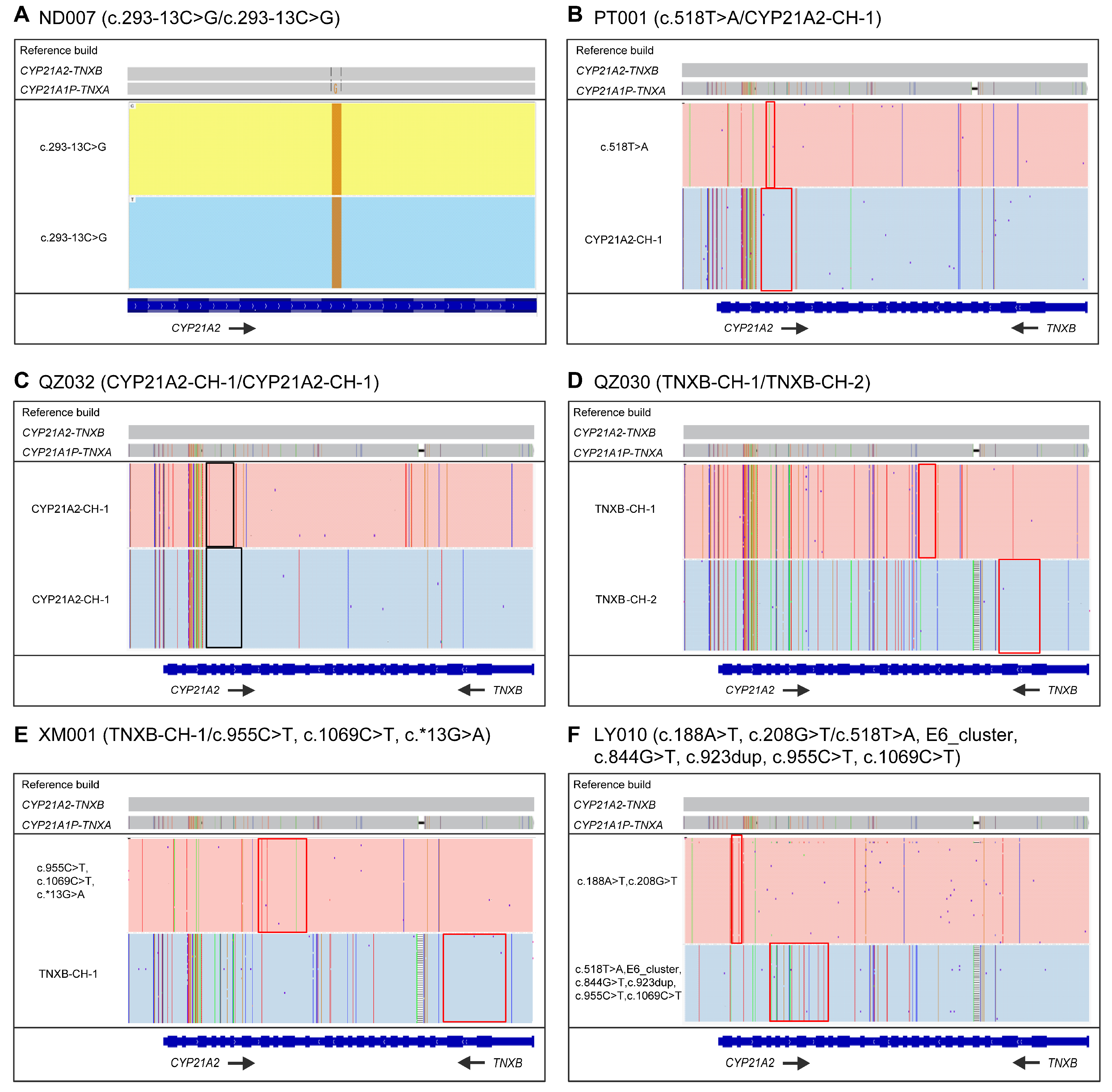
3.2. LRS-Based CAH Genotyping Assay in CAH Genetic Diagnosis
3.3. LRS-Based CAH Genotyping Assay in CAH Second-Tier Screening
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Auer, M.K.; Nordenström, A.; Lajic, S.; Reisch, N. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet 2023, 401, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmougy, F.; Sharaf, S.; Hafez, M.; Khattab, A.; Abou-Yousef, H.; Elsharkawy, M.; Baz, H.; Ekladious, S.; Sherif, B.; Musa, N.; et al. CYP21A2 genetic profile in 14 Egyptian children with suspected congenital adrenal hyperplasia: A diagnostic challenge. Ann. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1415, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falhammar, H.; Nordenström, A. Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: Clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. Endocrine 2015, 50, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.Y.; Wallace, M.A.; Hofman, L.; Thuline, H.C.; Dorche, C.; Lyon, I.C.; Dobbins, R.H.; Kling, S.; Fujieda, K.; Suwa, S. Worldwide experience in newborn screening for classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Pediatrics 1988, 81, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, L.; Du, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Liang, Y.; Luo, X. Analysis of the Screening Results for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Involving 7.85 Million Newborns in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 624507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speiser, P.W.; Arlt, W.; Auchus, R.J.; Baskin, L.S.; Conway, G.S.; Merke, D.P.; Meyer-Bahlburg, H.F.L.; Miller, W.L.; Murad, M.H.; Oberfield, S.E.; et al. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 4043–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witchel, S.F. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2017, 30, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, B.; Marques, C.J.; Santos-Silva, R.; Fontoura, M.; Carvalho, D.; Carvalho, F. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: An Update on Genetic Analysis of CYP21A2 Gene. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2021, 129, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maouche, D.; Arlt, W.; Merke, D.P. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet 2017, 390, 2194–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusié-Luna, M.T.; White, P.C. Gene conversions and unequal crossovers between CYP21 (steroid 21-hydroxylase gene) and CYP21P involve different mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10796–10800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xu, Z.; Sullivan, A.; Finkielstain, G.P.; Van Ryzin, C.; Merke, D.P.; McDonnell, N.B. Junction site analysis of chimeric CYP21A1P/CYP21A2 genes in 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Mao, A.; Li, J.; Bao, S.; Li, J. Long-read sequencing: An effective method for genetic analysis of CYP21A2 variation in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 547, 117419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, S.; Srivastava, P.; Panigrahi, I.; Seenappa, V.; Kumar, R.; Yadav, J.; Daniel, R.; Dayal, D. Characterization of the CYP21A2 Gene Mutations in Children with Classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Indian J. Pediatr. 2022, 91, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, G.Y.; Carvalho, D.F.; de Miranda, M.C.; Faure, C.; Vallejos, C.; Brito, V.N.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Madureira, G.; Mendonca, B.B.; Bachega, T.A. Neonatal 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels adjusted according to age at sample collection and birthweight improve the efficacy of congenital adrenal hyperplasia newborn screening. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 86, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner-Parzer, S.; Witsch-Baumgartner, M.; Hoeppner, W. EMQN best practice guidelines for molecular genetic testing and reporting of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 1341–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaoğlan, M.; Nacarkahya, G.; Aytaç, E.H.; Keskin, M. Challenges of CYP21A2 genotyping in children with 21-hydroxylase deficiency: Determination of genotype-phenotype correlation using next generation sequencing in Southeastern Anatolia. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Mao, A.; Teng, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z.; Liang, D.; Wu, L. Comprehensive Analysis of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Using Long-Read Sequencing. Clin. Chem. 2022, 68, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Han, R.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Li, H.; Wan, Z.; Qi, Y.; Sun, S.; Ye, L.; Ning, G. Targeted gene panel sequencing for molecular diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 211, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, L.; Bruque, C.D.; Fernández, C.S.; Benavides-Mori, B.; Delea, M.; Kolomenski, J.E.; Espeche, L.D.; Buzzalino, N.D.; Nadra, A.D.; Dain, L. CYP21A2 mutation update: Comprehensive analysis of databases and published genetic variants. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Gene. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah-Shmouni, F.; Chen, W.; Merke, D.P. Genetics of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. A. 2017, 46, 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Liang, L.; Lin, S.; Ou, H.; Liu, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Z. Analysis of phenotypes and genotypes in 84 patients with 21-Hydroxylase deficiency in southern China. Steroids 2019, 151, 108474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Wang, W.; Zheng, S.; Han, R.; Xie, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, S.; Ye, L. Nonclassic Adrenal Hyperplasia (NCAH) due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: A cohort of 78 patients. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 225, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chitnis, N.; Monos, D.; Dinh, A. Next-generation sequencing technologies: An overview. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeau, M.L.; O′Neill, K.; Dixon, K.; Reisle, C.; Mungall, K.L.; Krzywinski, M.; Shen, Y.; Lim, H.J.; Cheng, D.; Tse, K.; et al. Improved structural variant interpretation for hereditary cancer susceptibility using long-read sequencing. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimosa, M.L.; Al-Ameri, W.; Simpson, J.T.; Nakhla, M.; Boissinot, K.; Munoz, D.G.; Das, S.; Feilotter, H.; Fattouh, R.; Saleeb, R.M. A Novel Approach to Detect IDH Point Mutations in Gliomas Using Nanopore Sequencing: Test Validation for the Clinical Laboratory. J. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 25, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Harting, J.; Farrow, E.; Thiffault, I.; Kasperaviciute, D.; Hoischen, A.; Gilissen, C.; Pastinen, T.; Eberle, M.A. Comprehensive SMN1 and SMN2 profiling for spinal muscular atrophy analysis using long-read PacBio HiFi sequencing. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 110, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Qin, T.; Tian, M. Detection of hemoglobin H disease by long molecule sequencing. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhang, H.; Ren, J.; Chen, H.; Du, Z.; Zhao, T.; Mao, A.; Xu, R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Analysis of rare thalassemia genetic variants based on third-generation sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Mao, A.; Liu, H.; Gui, B.; Choy, K.W.; Huang, H.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Lin, N.; et al. Long-Molecule Sequencing: A New Approach for Identification of Clinically Significant DNA Variants in α-Thalassemia and β-Thalassemia Carriers. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, E.; Nakagawa, R.; Tsuji-Hosokawa, A. A MinION-based Long-Read Sequencing Application With One-Step PCR for the Genetic Diagnosis of 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
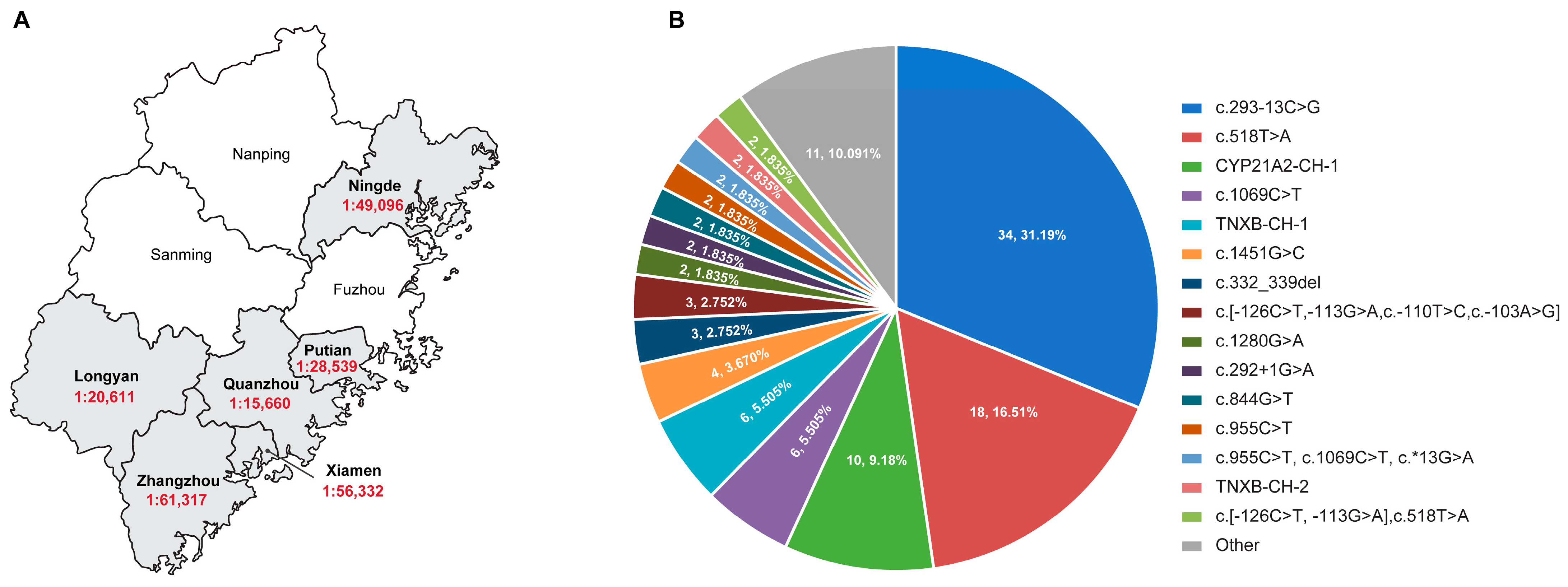
| Variant Type | Nucleotide Change | Protein Change | Allele Number (n = 109) | Frequency (n = 109) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNV/indels | c.293-13C>G | - | 34 | 31.19% |
| c.518T>A | p.Ile173Asn | 18 | 16.51% | |
| c.1069C>T | p.Arg357Trp | 6 | 5.50% | |
| c.1451G>C | p.Arg484Pro | 4 | 3.67% | |
| c.332_339del | p.Gly111Valfs | 3 | 2.75% | |
| c.1280G>A | p.Arg427His | 2 | 1.83% | |
| c.292+1G>A | - | 2 | 1.83% | |
| c.844G>T | p.Val282Leu | 2 | 1.83% | |
| c.955C>T | p.Gln319Ter | 2 | 1.83% | |
| c.1451_1452delinsC | p.Arg484fs | 1 | 0.92% | |
| c.949C>T | p.Arg317Ter | 1 | 0.92% | |
| c.725C>T | p.Leu242Pro | 1 | 0.92% | |
| Deletion | CYP21A2-CH-1 | - | 10 | 9.17% |
| TNXB-CH-1 | - | 6 | 5.50% | |
| TNXB-CH-2 | - | 2 | 1.83% | |
| CYP21A2-CH-3 | - | 1 | 0.92% | |
| TNXB-CH-3 | - | 1 | 0.92% | |
| CYP21A2-CH4 | - | 1 | 0.92% | |
| Complex mutations | c.[-126C>T, -113G>A, c.-110T>C, c.-103A>G] | - | 3 | 2.75% |
| c.955C>T, c.1069C>T, c.*13G>A | p.Gln319Ter, p.Arg357Trp, | 2 | 1.83% | |
| c.[-126C>T, -113G>A], c.518T>A | p.Ile173Asn | 2 | 1.83% | |
| c.[-126C>T, -113G>A] | - | 1 | 0.92% | |
| c.[-126C>T, -113G>A, -110T>C, -103A>G], c.92C>T | p.Pro31Leu | 1 | 0.92% | |
| c.[-113G>A, -110T>C] | - | 1 | 0.92% | |
| c.188A>T, c.208G>T | p.His63Leu, p.Val70Leu | 1 | 0.92% | |
| c.518T>A, E6_cluster (c.710T>A, c.713T>A, c.719T>A), c.844G>T, c.923dup, c.955C>T, c.1069C>T | p.Ile173Asn, p.Val282Leu, p.Leu308Phefs p.Gln319Ter, p.Arg357Trp | 1 | 0.92% |
| Gene | Variant Type | Genotype | Protein Change | Phenotype | Case Number | Carrier RATE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP21A2 | SNV | c.955C>T/+ | p.Gln319Ter | SW/+ | 5/647 (0.77%) | 1:65 |
| SNV | c.293-13C>G/+ | - | SW/+ | 2/647 (0.31%) | ||
| SNV | c.518T>A/+ | p.Ile173Asn | SV/+ | 2/647 (0.31%) | ||
| Deletion | CYP21A2-CH-8/+ | - | Classic CAH | 1/647 (0.15%) | ||
| SNV | c.371C>T/+ | p.Thr124Ile | NC/+ | 14/647 (2.16%) | 1:26 | |
| SNV | c.844G>T/+ | p.Val282Leu | NC/+ | 3/647 (0.46%) | ||
| SNV | c.[-126C>T, -113G>A]/+ | - | NC/+ | 3/647 (0.46%) | ||
| SNV | c.913G>A/+ | p.Val305Met | NC/+ | 2/647 (0.31%) | ||
| SNV | c.1099C>T/+ | p.Arg367Cys | NC/+ | 1/647 (0.15%) | ||
| SNV | c.-126C>T/+ | - | NC/+ | 1/647 (0.15%) | ||
| SNV | c.143A>G/+ | p.Tyr48Cys | NC/+ | 1/647 (0.15%) | ||
| Dup | CYP21A2 | - | 40/647 (6.18%) | 1:10 | ||
| Dup | CYP21A2/CYP21A1P | - | 24/647 (3.71%) | |||
| HSD3B2 | SNV | c.1003C>T/+ | p.Arg335Ter | 2/647 (0.31%) | 1:162 | |
| SNV | c.674T>A/+ | p.Val225Ala | 1/647 (0.15%) | |||
| SNV | c.244G>A/+ | p.Ala82Thr | 1/647 (0.15%) | |||
| CYP17A1 | SNV | c.715C>T/+ | p.Arg239Ter | 1/647 (0.15%) | 1:324 | |
| Indels | c.1459_1467del/+ | p.Asp487_Phe489del | 1/647 (0.15%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Neonatal Screening. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Zheng, F.; Lin, K.; Liao, M.; Dong, Y.; Chen, T.; He, Y.; Lu, M.; Chen, J.; et al. Assessment of Long-Read Sequencing-Based Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Genotyping Assay for Newborns in Fujian, China. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2025, 11, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11010022
Wang X, Lu X, Zheng F, Lin K, Liao M, Dong Y, Chen T, He Y, Lu M, Chen J, et al. Assessment of Long-Read Sequencing-Based Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Genotyping Assay for Newborns in Fujian, China. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2025; 11(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xudong, Xingxiu Lu, Faming Zheng, Kun Lin, Minjuan Liao, Yi Dong, Tiantian Chen, Ying He, Mei Lu, Jing Chen, and et al. 2025. "Assessment of Long-Read Sequencing-Based Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Genotyping Assay for Newborns in Fujian, China" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 11, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11010022
APA StyleWang, X., Lu, X., Zheng, F., Lin, K., Liao, M., Dong, Y., Chen, T., He, Y., Lu, M., Chen, J., Li, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Assessment of Long-Read Sequencing-Based Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Genotyping Assay for Newborns in Fujian, China. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 11(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns11010022





