Age-Related Blood Levels of Creatine Kinase-MM in Newborns and Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Considerations for the Development of Newborn Screening Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimens
2.2. Testing Instrument and Assay Kit
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
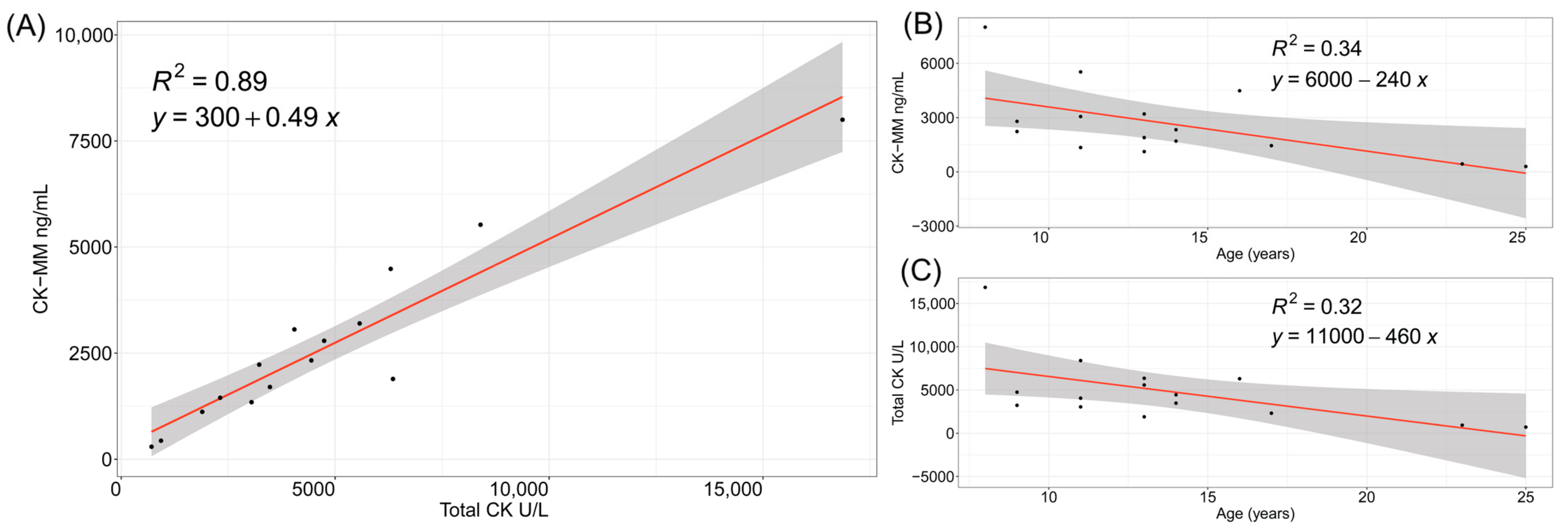
3.1. CK and CK-MM Levels in Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
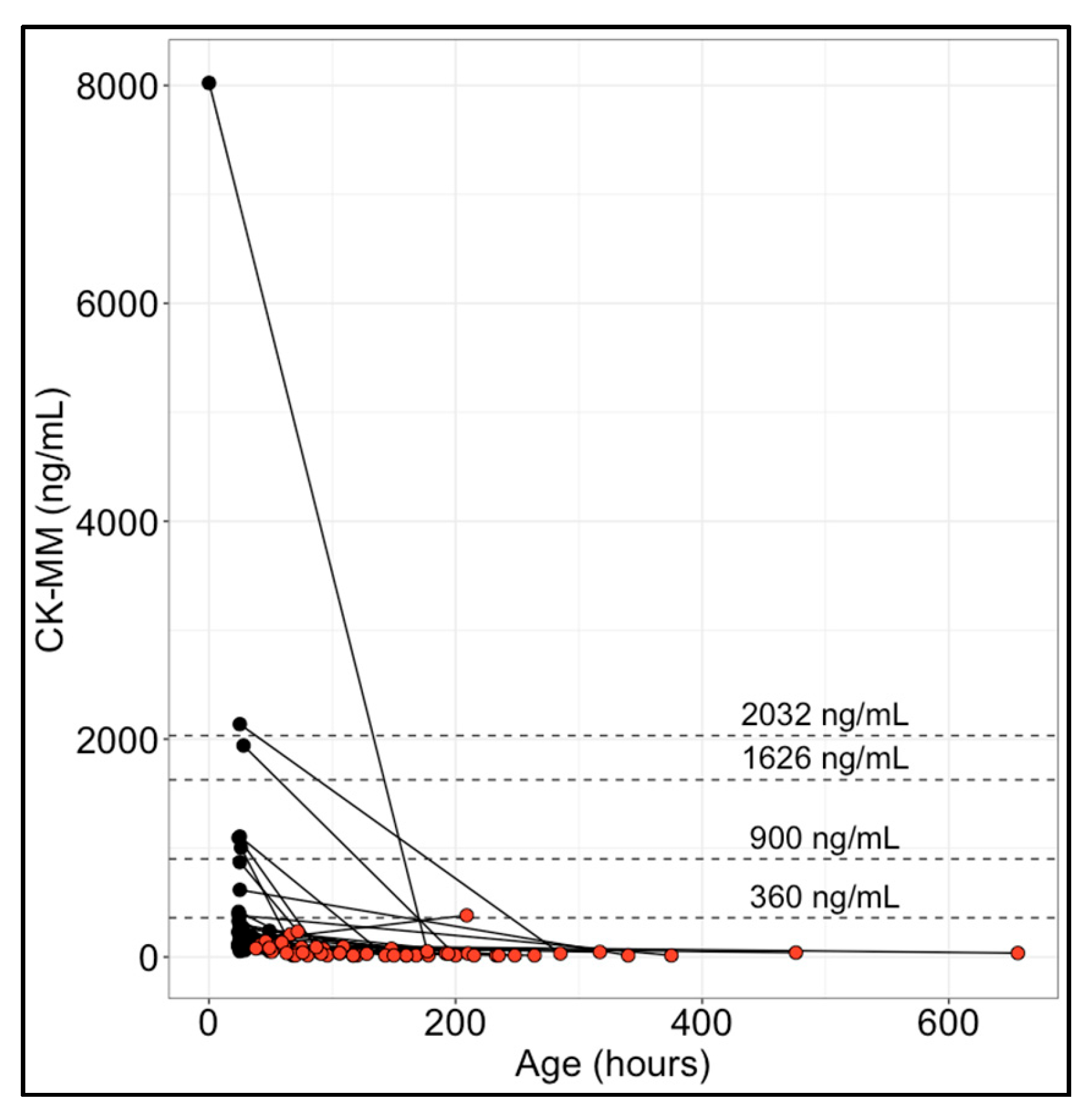
3.2. CK-MM Levels in Paired Initial and Repeat Newborn Specimens
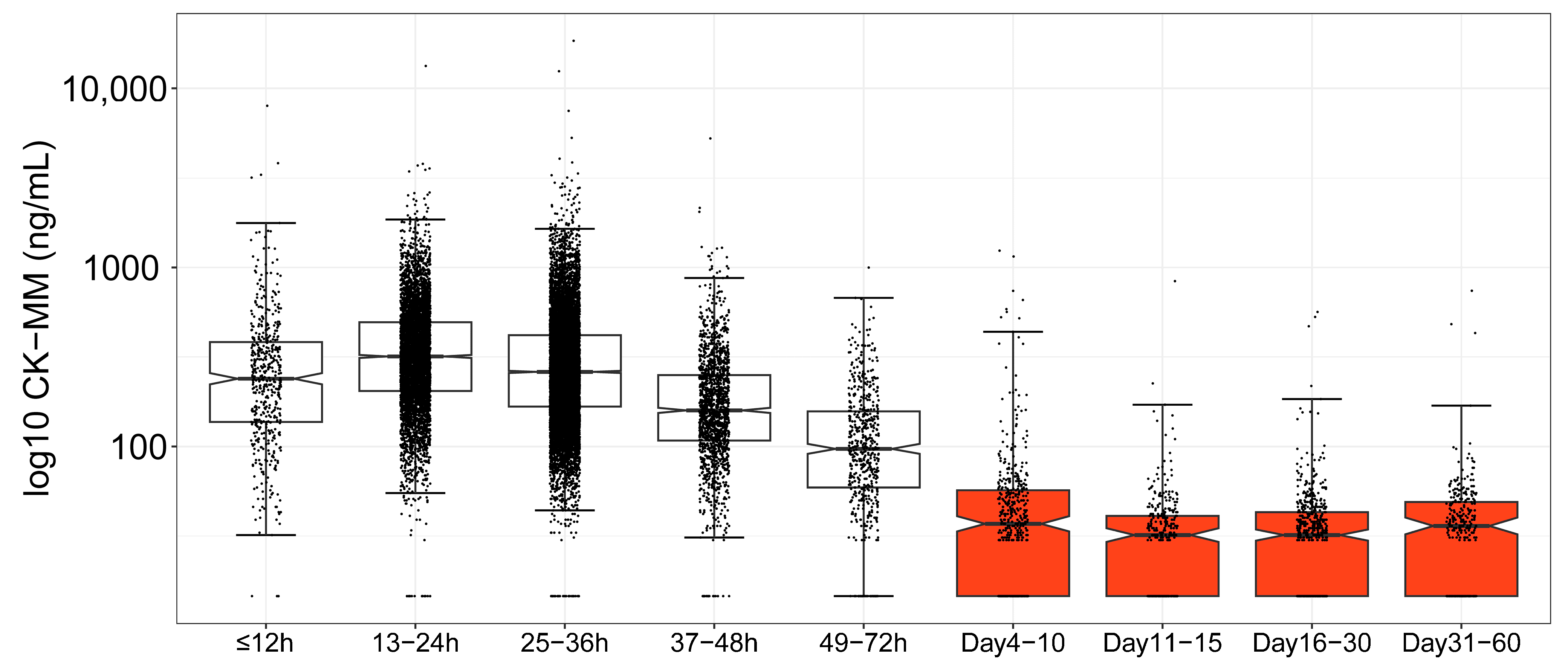
3.3. Age-Based CK-MM Ranges in the Newborn Period
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baird, M.F.; Graham, S.M.; Baker, J.S.; Bickerstaff, G.F. Creatine-kinase- and exercise-related muscle damage implications for muscle performance and recovery. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 960363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatheridge, M.A.; Kwon, J.M.; Mendell, J.M.; Scheuerbrandt, G.; Moat, S.J.; Eyskens, F.; Rockman-Greenberg, C.; Drousiotou, A.; Griggs, R.C. Identifying Non-Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy-Positive and False Negative Results in Prior Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Newborn Screening Programs: A Review. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovering, R.M.; Porter, N.C.; Bloch, R.J. The muscular dystrophies: From genes to therapies. Phys. Ther. 2005, 85, 1372–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, E.P.; Brown, R.H., Jr.; Kunkel, L.M. Dystrophin: The protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell 1987, 51, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciafaloni, E.; Fox, D.J.; Pandya, S.; Westfield, C.P.; Puzhankara, S.; Romitti, P.A.; Mathews, K.D.; Miller, T.M.; Matthews, D.J.; Miller, L.A.; et al. Delayed diagnosis in duchenne muscular dystrophy: Data from the Muscular Dystrophy Surveillance, Tracking, and Research Network (MD STARnet). J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Conway, K.M.; Fapo, O.; Street, N.; Mathews, K.D.; Mann, J.R.; Romitti, P.A.; Soim, A.; Westfield, C.; Fox, D.J.; et al. Time to diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy remains unchanged: Findings from the Muscular Dystrophy Surveillance, Tracking, and Research Network, 2000–2015. Muscle Nerve 2022, 66, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyawasam, D.; D’Silva, A.; Mowat, D.; Russell, J.; Sampaio, H.; Jones, K.; Taylor, P.; Farrar, M. Incidence of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in the modern era; an Australian study. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 30, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Goemans, N.; Takeda, S.; Mercuri, E.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Adachi, K.; Matsumura, T.; Kimura, E. Female dystrophinopathy: Review of current literature. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2018, 28, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.H.; Lee, N.C.; Weng, W.C.; Chen, L.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Wu, C.S.; Hwu, W.L. Duchenne muscular dystrophy newborn screening: The first 50,000 newborns screened in Taiwan. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 4563–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantonio, P.; Tavakoli, N.P.; Migliore, B.; McCown, E.; Lim, T.; Park, S.; Caggana, M.; Kucera, K.S.; Phan, H.; Street, N.; et al. Multi-Laboratory Evaluation of Prototype Dried Blood Spot Quality Control Materials for Creatine Kinase-MM Newborn Screening Assays. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2023, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartnett, M.J.; Lloyd-Puryear, M.A.; Tavakoli, N.P.; Wynn, J.; Koval-Burt, C.L.; Gruber, D.; Trotter, T.; Caggana, M.; Chung, W.K.; Armstrong, N.; et al. Newborn Screening for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: First Year Results of a Population-Based Pilot. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2022, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Jiang, X.; Huang, Y. A pilot study of newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy in Guangzhou. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhao, D.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Lv, S.; Li, R.; Zhu, X.; Liu, S. Newborn screening and genomic analysis of duchenne muscular dystrophy in Henan, China. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 539, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Griggs, R.; Wiley, V.; Connolly, A.; Kwon, J.; Qi, M.; Sheehan, D.; Ciafaloni, E.; Howell, R.R.; et al. Newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy in China: Follow-up diagnosis and subsequent treatment. World J. Pediatr. 2017, 13, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, K.S.; Boyea, B.L.; Migliore, B.; Potter, S.N.; Robles, V.R.; Kutsa, O.; Cope, H.; Okoniewski, K.C.; Wheeler, A.; Rehder, C.W.; et al. Two years of newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy as a part of the statewide Early Check research program in North Carolina. Genet. Med. 2024, 26, 101009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, B.; Park, S.; Sowizral, M.; Brackett, I.; Moslehi, R.; Chung, W.K.; Gruber, D.; Brower, A.; Lloyd-Puryear, M.; Caggana, M.; et al. Factors influencing creatine kinase-MM concentrations in newborns and implications for newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin. Biochem. 2023, 118, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, B.A.; Zhou, L.; Duparc, M.; Robles, V.R.; Rehder, C.W.; Peay, H.L.; Kucera, K.S. Evaluation of the GSP Creatine Kinase-MM Assay and Assessment of CK-MM Stability in Newborn, Patient, and Contrived Dried Blood Spots for Newborn Screening for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2022, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parad, R.B.; Sheldon, Y.; Bhattacharjee, A. Implementation of Hospital-Based Supplemental Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Newborn Screening (sDMDNBS): A Pathway to Broadening Adoption. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2021, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Maloney, B.; Caggana, M.; Tavakoli, N.P. Creatine kinase-MM concentration in dried blood spots from newborns and implications for newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2022, 65, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, N.P.; Gruber, D.; Armstrong, N.; Chung, W.K.; Maloney, B.; Park, S.; Wynn, J.; Koval-Burt, C.; Verdade, L.; Tegay, D.H.; et al. Newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: A two-year pilot study. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2023, 10, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, A.; Lloyd-Puryear, M.; Hougaard, D.M.; Meriö, L.; Mäkinen, P.; Laitala, V.; Pölönen, T.; Skogstrand, K.; Kennedy, A.; Airenne, S.; et al. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Newborn Screening: Evaluation of a New GSP(®) Neonatal Creatine Kinase-MM Kit in a US and Danish Population. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2019, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; Nagel, R.; Hüppi, P. [Creatine-kinase MM in the perinatal period]. Klin. Padiatr. 1991, 203, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moat, S.J.; Korpimäki, T.; Furu, P.; Hakala, H.; Polari, H.; Meriö, L.; Mäkinen, P.; Weeks, I. Characterization of a Blood Spot Creatine Kinase Skeletal Muscle Isoform Immunoassay for High-Throughput Newborn Screening of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Resources & Services Administration. Newborn Screening Process. Available online: https://newbornscreening.hrsa.gov/newborn-screening-process (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Farrar, M.A.; Kariyawasam, D.; Grattan, S.; Bayley, K.; Davis, M.; Holland, S.; Waddel, L.B.; Jones, K.; Lorentzos, M.; Ravine, A.; et al. Newborn Screening for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2023, 10, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.C.; Ferdinand, K.C.; Ycas, J.; Miller, E. Relationship of ethnic origin, gender, and age to blood creatine kinase levels. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, D.; Lloyd-Puryear, M.; Armstrong, N.; Scavina, M.; Tavakoli, N.P.; Brower, A.M.; Caggana, M.; Chung, W.K. Newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy-early detection and diagnostic algorithm for female carriers of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.H.; Hwu, W.L. The modern face of newborn screening. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2023, 64 (Suppl. S1), S22–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Taylor, J.L.; Redmond, C.; Hadd, A.G.; Kemppainen, J.A.; Haynes, B.C.; Shone, S.; Bailey, D.B., Jr.; Latham, G.J. Validation of Fragile X Screening in the Newborn Population Using a Fit-for-Purpose FMR1 PCR Assay System. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, N.M.; Koeks, Z.; Signorelli, M.; Verwey, N.; Overzier, M.; Bakker, J.A.; Sajeev, G.; Signorovitch, J.; Ricotti, V.; Verschuuren, J.; et al. Longitudinal Assessment of Creatine Kinase, Creatine/Creatinine(ratio), and Myostatin as Monitoring Biomarkers in Becker Muscular Dystrophy. Neurology 2023, 100, e975–e984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatz, M.; Rapaport, D.; Vainzof, M.; Passos-Bueno, M.R.; Bortolini, E.R.; Pavanello Rde, C.; Peres, C.A. Serum creatine-kinase (CK) and pyruvate-kinase (PK) activities in Duchenne (DMD) as compared with Becker (BMD) muscular dystrophy. J. Neurol. Sci. 1991, 102, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palma, F.D.E.; Nunziato, M.; D’Argenio, V.; Savarese, M.; Esposito, G.; Salvatore, F. Comprehensive Molecular Analysis of DMD Gene Increases the Diagnostic Value of Dystrophinopathies: A Pilot Study in a Southern Italy Cohort of Patients. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratter, C.; Dalgleish, R.; Allen, S.K.; Santos, R.; Abbs, S.; Tuffery-Giraud, S.; Ferlini, A. EMQN best practice guidelines for genetic testing in dystrophinopathies. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 1141–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Dai, Y.; Yu, P.; Qu, N.; Lan, Z.; Hong, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, G.; Xie, S.; Shi, Q.; et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing as a comprehensive test for patients with and female carriers of DMD/BMD: A multi-population diagnostic study. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
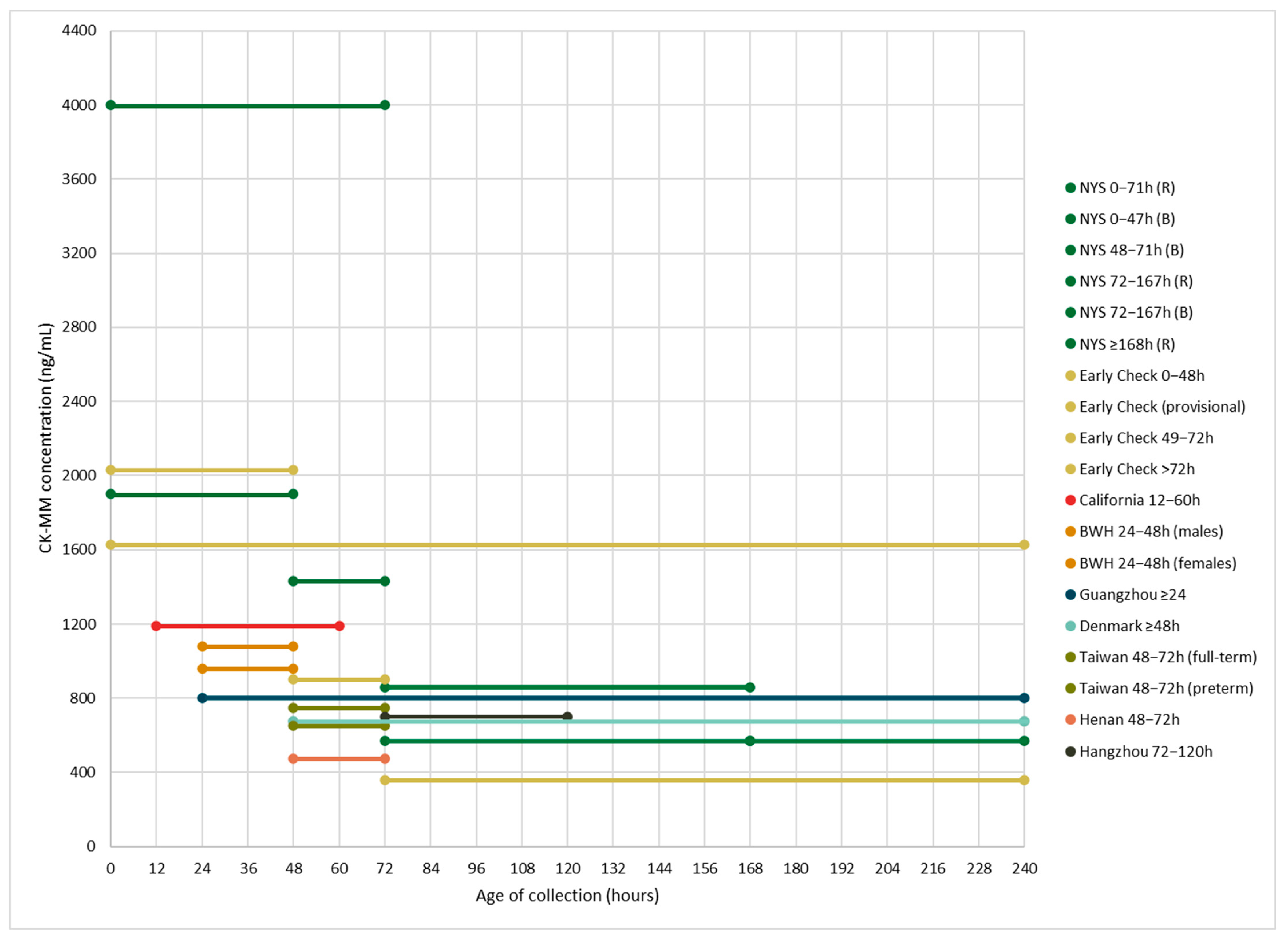
| Population and Publication(s) | N | Age at Collection Range (Hours) and CK-MM Cutoffs (ng/mL) | Percentile Cutoff |
|---|---|---|---|
| New York State NBS program 1 Hartnett et al. (2022)—[12] Maloney et al. (2023)—[17] Park et al. (2022)—[20] Tavakoli et al. (2023)—[21] | 36,781 | 0–47 h: 1990 (B), 4000 (R) 48–71 h: 1430 (B), 4000 (R) 72–167 h: 571 (B), 860 (R) ≥168 h: 571 (R) | 99.5th |
| Early Check NBS voluntary research study (RTI International) 2 Kucera et al. (2024)—[16] Migliore et al. (2022)—[18] | 13,354 | Provisional cutoff: 1626 0–48 h (BW: >1500 g): 2032 49–72 h: 900 >72 h (BW: ≤1500 g): 360 | 99.5th |
| California Biobank Program and Danish Neonatal Screening Biobank Timonen et al. (2019)—[22] | California (CA): 719 Denmark (DK): 1422 | 12–60 h (CA): 1190 ≥48 h (DK): 675 | CA: 99th DK: 99.5th |
| Guangzhou NBS Center (Guangzhou City, China) Jia et al. (2022)—[13] | 62,553 | ≥24: 800 | 99.7th |
| Supplemental DMD NBS Program (Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts) 3 Parad et al. (2021)—[19] | 1379 | 24–48 h: 1080 (males), 958 (females) | N/A |
| NBS Center at National Taiwan University Hospital Chien et al. (2022)—[10] | 50,572 | 48–72 h: 750 (full-term), 650 (preterm) | 99th |
| NBS Center of Henan (Henan Province, China) 4 Jia et al. (2023)—[14] | 13,110 | 48–72 h: 472 | 99.8th |
| Hangzhou NBS program (Zhejiang Province, China) 4 Ke et al. (2017)—[15] | 18,424 | 72–120 h: 700 | 99.985th |
| Percentiles | % Below 360 ng/mL | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | N | Mean | Median | Max | SD | 99.0th | 99.5th | 99.75th | |
| ≤12 h | 499 | 327 | 238 | 3830 | 360 | 619 | 3241 | 3698 | 73.1 |
| 13–24 h | 5167 | 394 | 318 | 3799 | 298 | 721 | 1857 | 2253 | 57.6 |
| 25–36 h | 10,776 | 338 | 261 | 7513 | 290 | 638 | 1699 | 2232 | 67.8 |
| 37–48 h | 1595 | 208 | 159 | 5268 | 212 | 371 | 1159 | 1309 | 89.0 |
| 49–72 h | 577 | 126 | 97 | 999 | 104 | 245 | 668 | 855 | 96.0 |
| Days 4–10 | 477 | 58 | 37 | 1242 | 108 | 86 | 991 | 1224 | 97.5 |
| Days 11–15 | 341 | 35 | 32 | 839 | 50 | 55 | 403 | 839 | 99.7 |
| Days 16–30 | 563 | 36 | 32 | 564 | 43 | 57 | 480 | 550 | 99.5 |
| Days 31–60 | 311 | 42 | 36 | 741 | 56 | 61 | 596 | 741 | 99.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potter, S.N.; Migliore, B.; Carter, J.; Copeland, V.R.; Smith, E.C.; Peay, H.L.; Kucera, K.S. Age-Related Blood Levels of Creatine Kinase-MM in Newborns and Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Considerations for the Development of Newborn Screening Algorithms. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2024, 10, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns10020041
Potter SN, Migliore B, Carter J, Copeland VR, Smith EC, Peay HL, Kucera KS. Age-Related Blood Levels of Creatine Kinase-MM in Newborns and Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Considerations for the Development of Newborn Screening Algorithms. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2024; 10(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns10020041
Chicago/Turabian StylePotter, Sarah Nelson, Brooke Migliore, Javan Carter, Veronica R. Copeland, Edward C. Smith, Holly L. Peay, and Katerina S. Kucera. 2024. "Age-Related Blood Levels of Creatine Kinase-MM in Newborns and Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Considerations for the Development of Newborn Screening Algorithms" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 10, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns10020041
APA StylePotter, S. N., Migliore, B., Carter, J., Copeland, V. R., Smith, E. C., Peay, H. L., & Kucera, K. S. (2024). Age-Related Blood Levels of Creatine Kinase-MM in Newborns and Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Considerations for the Development of Newborn Screening Algorithms. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 10(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns10020041






