Highlights
- The diabetic patient represents one of the challenges of current medicine, by the complexity of multiple organ disorders associated with this pathology, its evolution and treatment particularities.
- Vasculopathies and neuropathies are frequent complications in the course of the illness and sudden hearing loss comes with significant damage to the quality of life.
Highlights
- ✔
- The diabetic patient represents one of the challenges of current medicine, by the complexity of multiple organ disorders associated with this pathology, its evolution and treatment particularities.
- ✔
- Vasculopathies and neuropathies are frequent complications in the course of the illness and sudden hearing loss comes with significant damage to the quality of life.
Abstract
The aim of our paper is to highlight the main therapeutic principles and the management options in the case of a diabetic patient who has had a sudden hearing loss. Mainly, the aim is to underline the sudden hearing loss treatment adjustment of the diabetic patient compared to the non-diabetic patient. By understanding the mechanism of sudden hearing loss in a diabetic patient, namely the impact of glycemic variations and their implication on the microvascular structures of the inner ear, we try to underline the treatment principles and management options of the previously mentioned combined pathologies. Thus, it is necessary to adapt the classes of drugs used in the case of sudden sensorineural hearing loss of the diabetic patient in comparison with the non-diabetic patient, in order not to aggravate or complicate the patient’s functional status. Therefore, the treatment will need to be adapted both by classes of medication and by the type of administration used. Adequate control of the progression, treatment and complications of diabetes mellitus ensures optimal treatment management in case of a sudden hearing loss and therefore interferes with the favorable functional hearing outcomes. The role of this paper is not only to state the therapeutic principles in the case of sudden hearing loss in a diabetic patient, but also to analyze the impact on the management of potential local and systemic risk factors.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, one of the comorbidities that, if not adequately treated, have an increased potential for developing complex and extensive complications is known to be diabetes mellitus (DM). This condition is one of the fastest developing chronic pathologies of the moment.
Diabetes is a disease that involves a series of metabolic afflictions determined by modified insulin secretion and following the altered and adjusted actions of the previously mentioned hormone that defines a higher level of blood sugar. This metabolic damage may determine misuse of proteins, fats and carbohydrates that make the body readapt and create compensatory mechanisms to work by the new dictated parameters.
Hyperglycemia, emerged as compensation for the new metabolic changes, determines the poor functioning of various systems and organs.
Because the diabetic patient has either a severely deficient insulin production or the body is not capable of using the insulin produced by the pancreas, there are two main types of diabetes mellitus described in the literature. Type I Diabetes Mellitus is defined as the autoimmune destruction of the beta-cells within the pancreas, while the patients suffering from this condition are insulin- dependent and need to pay attention to their glycemic values, to accurately control blood glucose levels during the day. This type of diabetes is found in children and adolescents.
Type II Diabetes Mellitus is defined by an inadequate response of fat and muscle cells of the body to insulin and a compensatory production of insulin by the liver to try and dispute that improper response. This type of diabetes is typical in adults, frequently associated with obesity and may or may not be insulin-dependent, depending on the moment when diabetes is discovered.
Thus, as diabetes progresses, it can lead to different complications such as nephropathy, neuropathy, oculopathy, microangiopathy and even heart conditions [].
A possible, but not so much discussed complication of this condition is hearing impairment and, usually, in the case of a diabetic patient, the hearing loss is bilateral, sensorineural, symmetrical and with a tendency of mainly affecting the low and mid frequencies.
Specialty literature studies show that when discussing diabetic patients, they are more susceptible to developing sudden sensorineural hearing loss than non-diabetic patients, especially as a result of microvascular complications [].
This paper mainly aims to underline the sudden hearing loss treatment adjustments of the diabetic patient compared to the non-diabetic one.
2. Discussions
The sudden idiopathic hearing loss represents a form of acute hearing loss audiometrically expressed as a sensorineural hearing loss higher than 30dB, on three consecutive frequencies, with an onset of symptomatology of maximum 72 hours before the presentation of the patient to the ENT physician’s office. In most cases, it is unilateral, the prognosis of hearing recovery being often favorable.
The pathogenic mechanism is not readily identifiable, since there are very few cases in which it is possible to tell with precision what hearing loss was caused by [].
Specialty literature mentions the involvement of infectious factors (viral or bacterial), vascular (hemorrhagic or ischemic), autoimmune (Cogan’s disease, autoimmune thyroiditis, sarcoidosis, Wegener’s granulomatosis), tumors (acoustic neurilemmoma which often causes slow progressive hearing loss without excluding a possible clinical onset in the form of sudden hearing loss), traumatic, chemical or toxic causes (ototoxic medication), etc. []. Suddenly installed hearing loss is a medical emergency, although some literature studies have shown that, in some cases, hearing may improve even if no treatment is administered.
Nevertheless, it is worth mentioning that the presence of other conditions such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemias, and even the age of the patient, can lead to a bad response compared to patients who do not suffer from the previously mentioned conditions []. These comorbidities directly or indirectly influence the appearance, evolution, responsiveness to treatment and prognosis of the sudden hearing loss [].
However, literature has not shown yet if the associated comorbidities and age influence, together or separately, the prognosis of patients who have sudden sensorineural hearing loss.
An essential element to be mentioned is that diabetes, as well as other comorbidities, influence the therapeutic strategy that the patient needs to undertake, due to the certain possible complications that might occur and may or may not contraindicate specific therapies [,,].
Researchers investigated the prevalence of diabetes in patients with sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss compared to a diabetic patient with normal hearing and revealed that it was almost double. It seems that through cerebral microangiopathy and due to diabetic changes in blood viscosity, sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss is mediated in a diabetic patient, although the proper mechanism which determines hearing loss has not been discovered yet [].
Several studies conducted on humans have shown the thickening of the capillary walls of the stria vascularis, the basilar membrane and the endolymphatic sac, atherosclerotic narrowing of the internal auditory artery, atrophy of the stria vascularis, loss of outer hair cells (OHCs) mainly in the lower basal cochlear turn, spiral ganglion neural atrophy, and VIII cranial nerve demyelination [,].
A rigorous anamnesis, as well as a detailed history of the disease, can provide important elements that will lead to a possible cause or triggering factor of the suddenly installed hearing loss.
Practice guidelines strongly recommend the correct differentiation between sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) and conductive hearing loss in patients who undergo an episode of sudden hearing loss (Figure 1).
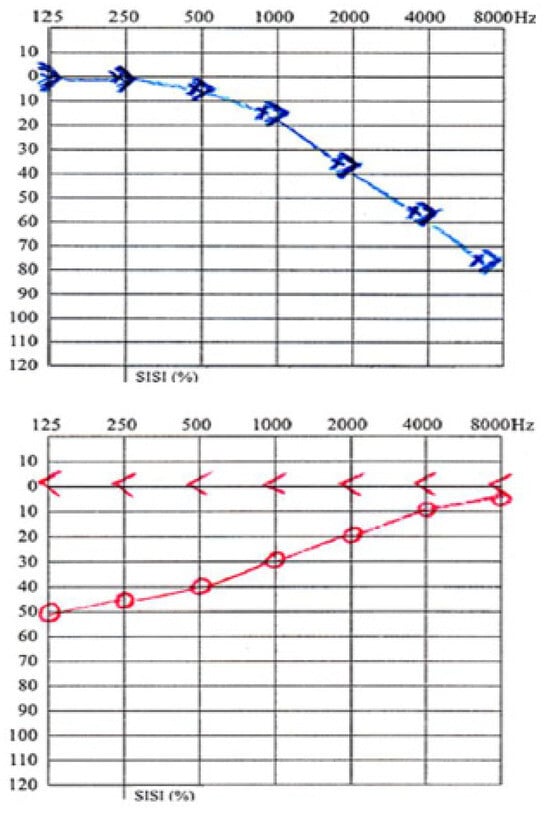
Figure 1.
Left—Sensorineural hearing loss; Right—Conductive Hearing loss.
Several elements help establish a definite diagnosis in case of suddenly installed hearing loss:
- ○
- Pure tone audiometry, vocal audiometry and acoustic immittance, which are routine audiometric tests;
- ○
- Otoscopy to appreciate the local appearance of the external auditory meatus and the tympanic membrane and thus eliminate possible local causes that could determine sudden hearing loss;
- ○
- Instrumental measuring of hearing acuity using a 512Hz tuning fork that helps differentiate between sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss in an emergency room (bilateral positive Rinne, Weber lateralized in the healthy ear) (Figure 2);
 Figure 2. 512Hz tuning Fork.
Figure 2. 512Hz tuning Fork.
- ○
- Brainstem auditory evoked potential that helps identify the possible lesional headquarters by studying the distinctions between ears in terms of the differences between the I-III and I-V intervals;
- ○
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging using contrast medium is considered to be “the gold standard” method in identifying an acoustic neuroma, a labyrinthine hemorrhage, an inflammatory process or an endolymphatic hydrops;
- ○
- Vestibular evaluation to complement the patient’s clinical examination if there is vestibular symptomatology (vertigo, imbalance) in addition to hearing loss. In patients experiencing a vertiginous crisis, this examination should be performed at the head of the bed and involves the evaluation of nystagmus, oculomotricity, and the development of evidence to help differentiate between central and peripheral vertigo [].
The treatment administered in case of sudden hearing loss is non-specific and attempts to cover the possible pathogenic mechanisms involved. There are some treatment principles and options which are worth mentioning, but in the case of a diabetic patient, the essential element that always has to be taken into account when choosing and controlling the treatment and prognosis of a sudden idiopathic hearing loss is the blood glucose level. The treatment strategy is also influenced by the age of the patient, gender, body mass index, presence of tinnitus, dizziness, ear fullness sensation and presence of cerebral microangiopathy besides associated diseases [,].
Thus, here are the main therapeutic options used in the treatment of sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss:
Anti-inflammatory agents such as corticosteroids, whose role is to reduce perineural auditory and cochlear inflammation, influencing any anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive reaction and vascular permeability []. This is the most common treatment used in sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss, but it should never be used in high dosage therapy in case of diabetic patients, since it determines the increase of blood glucose levels and may lead to poor prognosis. A more extended treatment regarding the period of drug administration with lower dosage is preferable in diabetic patients compared to non-diabetic patients, in whose case higher dosage therapy is used. Literature highlights the use of intra- tympanic cortisone, but with low good outcomes compared to oral cortisone therapy [].
The use of Vasodilators such as Lipo-Prostaglandin E1 is justified by their ability to improve the blood flow to the cochlea and thus prevent local hypoxia. The duration of diabetes and the pre-existence of microvascular diabetic complications may compromise the use of these agents [].
Rheological agents are also used, since they improve oxygen flow by modifying blood viscosity through the use of low-molecular-weight dextrans, pentoxifylline or anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin). The use of these medications may cause hypoglycemia, so special care should be taken not to decompensate the patient’s diabetes and to properly adjust the treatment of the associated conditions before initiating the treatment for the sudden hearing loss [].
Antiviral agents are used only if a viral cause is suspected. Literature describes a limited use of acyclovir and amantadine in the treatment of sudden idiopathic hearing loss. Taking into account that the diabetic patient has a compromised and irregular reactive immune system, the probability of contacting a viral infection increases, thus the idea of associating antiviral agents in the treatment of sudden idiopathic hearing loss in a diabetic patient is strongly recommended [,].
Diuretics or diuretic-like medication are used when there is a suspicion of endolymphatic hydrops, since these drugs can help reduce the fluid pressure load that can occur in the inner ear. They are helpful while trying to prevent an attack, but lack effectiveness in case of an already triggered attack. Diuretics or diuretic-like medication may decrease the effectiveness of the oral antidiabetic treatment [].
Supplementation with vitamin D can bring a modest benefit to the diabetic patient with hearing loss. The role of vitamin D is well known in chronic pathology and is now considered to be a vitamin-hormone with multiple beneficial actions. In most cases, the benefit is maximum if associated with magnesium. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to a degree of osteoporosis of the temporal bone, which will affect the transmission of sounds. Some studies even suggest supplementation with vitamin D intrapartum to prevent congenital deafness [,].
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, if used since the early stages, can significantly improve hearing loss. Salvage therapy with hyperbaric oxygen results are compared in the literature with the results obtained by using corticosteroids, thus being considered an effective treatment option [,,].
Carbogen inhalation. This gas is composed of 95% Oxygen and 5% Carbon dioxide. It is believed that the administration of this combination of gases, will result in the vasodilation of the inner ear and increased blood flow and oxygen to the damaged hair cells that may encourage hearing loss recovery if a vascular disorder was the cause of it. The benefits of this therapy have been debated over the years, but ENT specialists have not reached a final decision yet. According to Kallinen et al., this inhalation therapy was proven to be more useful in patients with a low response on flat and high-pitched tones [,]. In a clinical analysis in 2004, Ni y. et al. concluded that drug therapy combined with Carbogen administration has better results in treating sudden hearing loss []. Some authors suggest a five day-course of inhaler administration for an hour a day and others elect a shorter course of 3 days, but with a more intensive frequency: 10 minutes every hour while the patient is awake. As Ni y. and others concluded that Carbogen use is an excellent adjuvant in the systemic drug treatment.
Studies have shown that treatments for sudden idiopathic hearing loss based on the use of corticosteroids, i.e., lipo-Prostaglandin E1 and carbogen gas inhalation, are more effective than other treatment strategies studied and have great results even in patients with diabetes mellitus [].
Regarding the prognosis of suddenly installed hearing loss, its spontaneous recovery rate is generally good (approximately 47-63%, according to specialty studies), but depending on associated comorbidities, such as diabetes and its complications, as well as the onset of the treatment administered depending on the duration of diabetes, glycemic control and the onset of the sudden idiopathic hearing loss, it is associated with a lower recovery rate.
It has been shown that the more severe the hearing loss, associated with a lack of proper diabetes control and/ or diabetic complications, the more unfavorable the prognosis.
Patients who do not fully recover hearing may be advised on the possibilities of hearing impairment depending on age, degree of hearing loss and associated comorbidities.
Although in most cases, hearing loss associated with diabetes is bilateral, sensorineural, symmetrical and with a tendency of mainly affecting the low and mid frequencies, there are cases in which a sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss can occur.
A sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss in a diabetic patient can have a bad onset with deep hearing loss compared to the case of a non-diabetic person, depending on blood glucose levels, pre-existent management and complications of diabetes and can also associate poor prognosis and recovery as well as lack of treatment compliance.
Periodic and constant blood glucose level control helps adapt the treatment for hearing loss properly.
The most effective medications for the treatment of sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss in a diabetic patient are equally considered to be the corticosteroids, i.e., lipo-prostaglandin E1 and Carbogen gas inhalation.
The availability of certain treatment options as well as the time passed between the patient’s presentation to the physician and the onset of hearing loss or the initiation of the treatment are important elements that dictate the prognosis of hearing recovery as well as the efficiency of the treatments of choice. Although, as previously described, there is a wide range of therapeutic options that can be used in the case of sudden idiopathic hearing loss, most of them ranked as non-specific, their availability and degree of applicability to each individual that must be treated are some of the major challenges of an ENT physician.
Another important factor that dictates the prognosis and the good course of treatment is the patient’s reluctance towards some non-infusible or drug-staging treatments and, in the absence of appropriate medical knowledge or a good understanding of the effectiveness of these therapeutic options, they are categorized as unconventional by the patient and do not make him choose this specific treatment despite its availability, namely Carbogen gas inhalation or hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Diabetes belongs to a pathological field in which constant advances are made regarding the available therapies. As in other specialties, such as neurology, cardiology or oncology, on-going studies and research give us more and more options regarding the treatment of choice [,]. Especially in cases where diabetes is associated with other comorbidities, the therapy options are limited by the patient’s general condition and tolerance to aggressive treatments.
Unfortunately, there is no international consensus regarding the treatment of sudden hearing loss. There are some American authors who recommend cortisone therapy for one month from the onset of hearing loss and there are some French authors who recommend cortisone therapy for 10 days from the onset of hearing loss. Moreover, there are differences of opinion regarding the proper moment for therapy initiation, given the moment of hearing loss occurrence. Some authors maintain the hypothesis of its important initiation in the first 24 to 72 hours, while others allow initiation even up to 5-7 days after the onset of sudden hearing loss. We are talking about the existence of a high risk of malpractice and a questionable therapeutic attitude that depends on the clinical experience and constantly improved medical knowledge of the ENT physician.
This lack of pre-established therapeutic protocols compared to other pathologies, such as cancer or any other well-known and classified disease in terms of staging and treatment options, creates a tendency of treatment adaptation at a national level, in relation with geographic, cultural and socio-economic factors.
3. Conclusions
Diabetes mellitus, as one of the fastest developing chronic pathologies of the moment, is defined by a group of metabolic disorders which could determine a complex series of complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nervous system and peripheral blood vessels.
Sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss that occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus has been associated with more severe hearing loss and also with poor prognosis that could become irrecoverable in case no treatment is administered and it also regards the duration of diabetes, the onset of the hearing loss, as well as the presence or absence of diabetic comorbidities, the age of the patient and other associated conditions.
Similarly, the post-prandial glucose level and the proper control of blood glucose levels are more likely to affect the evolution of the disease.
Sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss occurring in a patient with arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus or dyslipidemia or in elderly patients, is associated with an increased prevalence of cerebral microangiopathy, highlighted by magnetic resonance imaging, and it determines a slower hearing recovery, as shown if following the improvements in speech discrimination tests.
Conflicts of Interest disclosure
There are no known conflicts of interest in the publication of this article. The manuscript was read and approved by all authors.
Compliance with ethical standards
Any aspect of the work covered in this manuscript has been conducted with the ethical approval of all relevant bodies and that such approvals are acknowledged within the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
All authors had an equal scientific contribution and shared the first authorship.
References
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014, 37, S81–S90. [Google Scholar]
- Ziani de David, L.; Machado Finamor, M.; Buss, C. Possible hearing implications of diabetes mellitus: A literature review. Rev. CEFAC. 2015, 17, 2018–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Anandhalakshmi Mythili, B.; Viswanatha, R. Evaluation of the Incidence of Sensorineural hearing loss in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Biol Med Res. 2011, 2, 982–987. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Kadono, M.; Mogami, S.; Ohnishi, M.; Hirata, C.; Ichio, N.; Wada, K.; Kishimoto, C.; Okada, H.; Miyata, H.; Yoshikawa, T. Idiopathic sudden hearing loss in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004, 63, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaoka, J.; Anjos, M.F.; Takata, T.T.; Chaim, R.M.; Barros, F.; Penido, N.O. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Evolution in the presence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemias. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 76, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aimoni, C.; Bianchini, C.; Borin, M.; Ciorba, A.; Fellin, R.; Martini, A.; Scanelli, G.; Volpato, S. Diabetes, Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Case-Control Study. Audiol Neurotol. 2010, 15, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, S.; Chen, Y.; Hsu, C.; Tseng, F. Clinical Features of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Diabetic Patients. The Laryngoscope. 2005, 115, 1676–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Sugiura, S.; Ando, F.; et al. Diabetes reduces auditory sensitivity in middle-aged listeners more than in elderly listeners: A population-based study of age- related hearing loss. Med Sci Monit. 2010, 16, PH63–8. [Google Scholar]
- Thurman, M.; Amedee, R.G. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Etiologies and treatments. J La State Med Soc. 1998, 150, 200–203. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, T.H.; Guida, H.L. Hearing loss in patients with diabetes mellitus. Braz J Otorhinolaryngology. 2009, 75, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaz, A.A.; Kishore, C.S.; Vadish, B. Clinical Evaluation of Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Diabetes Mellitus. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR- JDMS). 2016, 15, Ver. IX: 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, R.; Sonkhya, D.; Sonkhya, N. Evaluation of hearing loss in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016, 4, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.K.; Shin, J.H.; Chang, M.Y.; Min, H.J.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Yang, S.H.; Hong, Y.H.; Mun, S.K. Impact of control of blood glucose level during treatment of sudden deafness in diabetics: Relationship with prognosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Jung, Y.G.; Eun, Y.G. Effect of steroid, carbogen inhalation, and lipoprostaglandin E1 combination therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otolaryngol. 2011, 32, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinnamon, U.; Bendet, E.; Kronenberg, J. Steroids, carbogen or placebo for sudden hearing loss: A prospective double-blind study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2001, 258, 477–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, C.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Yang, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Ban, M.J.; Moon, I.S. Therapeutic Effects of Carbogen Inhalation and Lipo-Prostaglandin E1 in Sudden Hearing Loss. Yonsei Med J. 2012, 53, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settineri, S.; Frisone, F.; Alibrandi, A.; Pino, G.; Lupo, N.J.; Merlo, E.M. Psychological Types and Learning Styles in Medical Education. Mediterranean Journal of Clinical Psychology 2018, 6, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantea Stoian, A.; Bala, C.; Rusu, A.; et al. Gender Differences in the Association of Ferritin and 25- hydroxyvitamin D. Rev Chim. 2018, 69, 864–869. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, C.S.; Lee, T.Y.; Wu, M.F. Adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen treatment for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2017, 44, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almosnino, G.; Holm, J.R.; Schwartz, S.R.; Zeitler, D.M. The Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen as Salvage Therapy for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2018, 127, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanescu, D.C.; Hainarosie, R.; Zainea, V.; Corneci, D.; Jecan, R.C. The Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in the Management of Patients with Sudden Hearing Loss. Rev Chim. 2018, 69, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hender, K. Is carbogen gas effective in the treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss? Evidence Centre Evidence Report; Clayton, VIC: Centre for Clinical Effectiveness (CCE), 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Edamatsu, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Oku, T.; et al. Treatment of sudden deafness: Carbon dioxide and oxygen inhalation and steroids. Clin Otolaryngol. 1985, 10, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallinen, J.; Laurikainen, E.; Laippala, P.; Grénman, R. Sudden deafness: A comparison of anticoagulant therapy and carbogen inhalation therapy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1997, 106, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nuovo, S.F.; Angelica, A.; Santoro, G.; Platania, S. Intelligence and Mental Imagery in Intellectual Disability. Mediterranean Journal of Clinical Psychology 2018, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, L.; Petrescu, S.; Panea, C.A. Treatment principles in the management of early coagulopathy following rtPA therapy—Discussion based on a particular case report. Cerebrovascular Diseases. 2018, 45, 182–182. [Google Scholar]
- Mandruta, I.R.; Bajenaru, O.A.; Panea, C.A.; et al. Experience with Lacosamide in treating focal epilepsy patients in Romania: Efficacy, safety and time to reach response. Epilepsia. 2014, 55, 110–110. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the author. 2019 Andreea Rusescu, Viorel Zainea, Oana Ruxandra Iana, Irina Ioniță, George Traian Alexandru Burcea-Dragomiroiu, Dragos Cristian Ștefănescu, Dumitru Cristinel Badiu, Florentina Gherghiceanu, Cătălina Pietroșanu, Corina Silvia Pop, Razvan Hainarosie, Mura Hainarosie