Unhealthy Lifestyle and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome—The Romanian Experience
Highlights
- MetS is currently considered as a public health problem and identifying the risk factors is very important. The most important risk factors for MetS in this study are the rural environment and a low education level.
- This study suggests the importance of healthy dietary patterns for reducing the incidence of MetS.
Abstract
:Highlights
- ✓ MetS is currently considered as a public health problem and identifying the risk factors is very important. The most important risk factors for MetS in this study are the rural environment and a low education level.
- ✓ This study suggests the importance of healthy dietary patterns for reducing the incidence of MetS.
Introduction
Material and Methods
Questionnaires
Anthropometric measure
Blood pressure and cardiovascular diseases
Blood samples
Metabolic syndrome definition
Statistical analyses
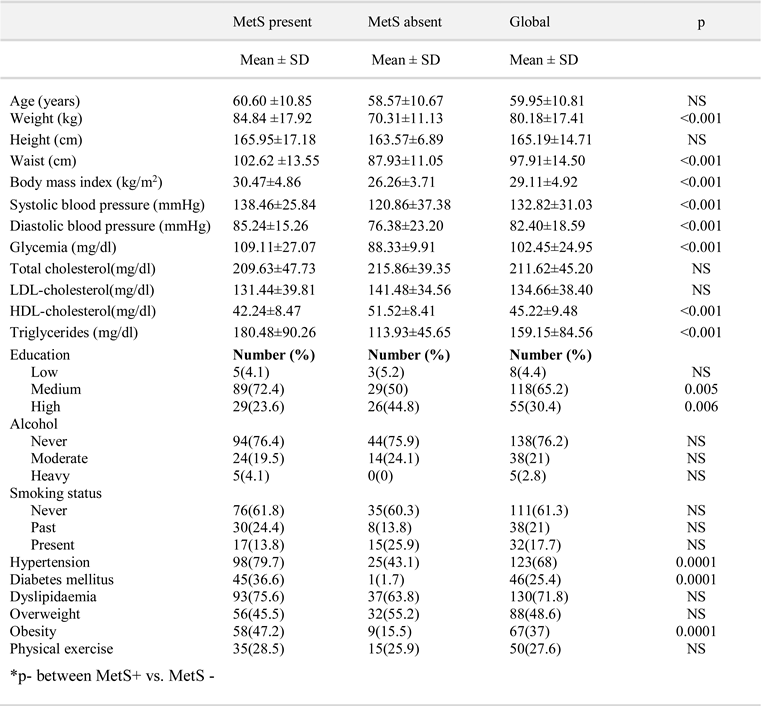
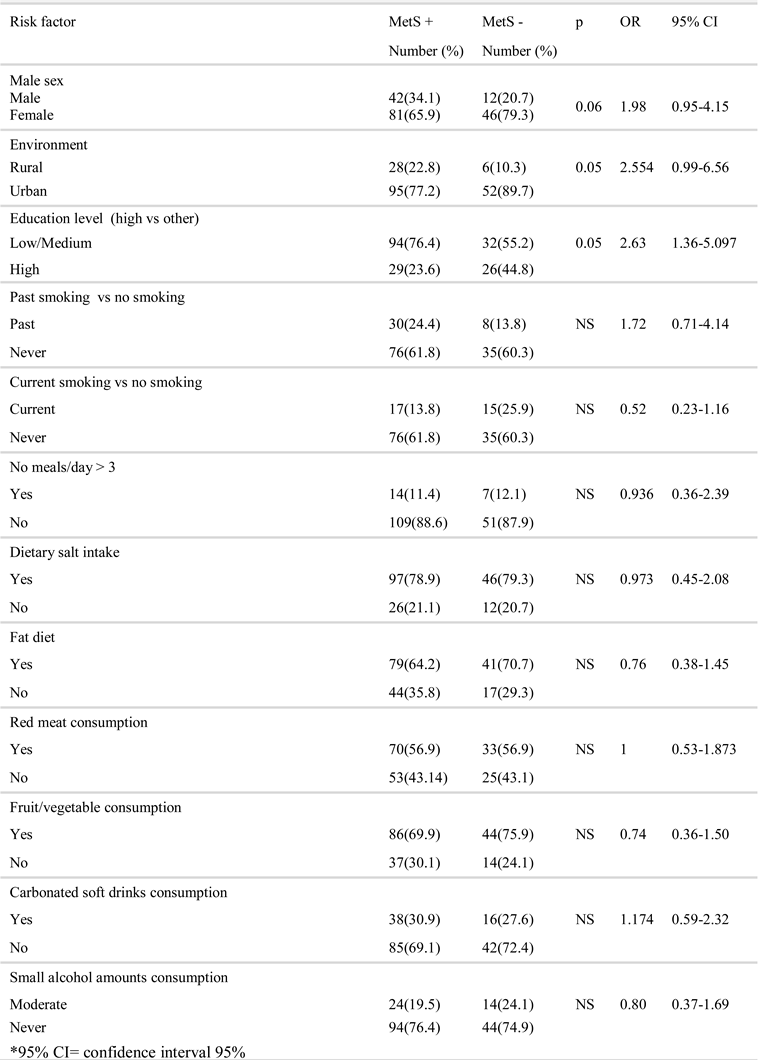
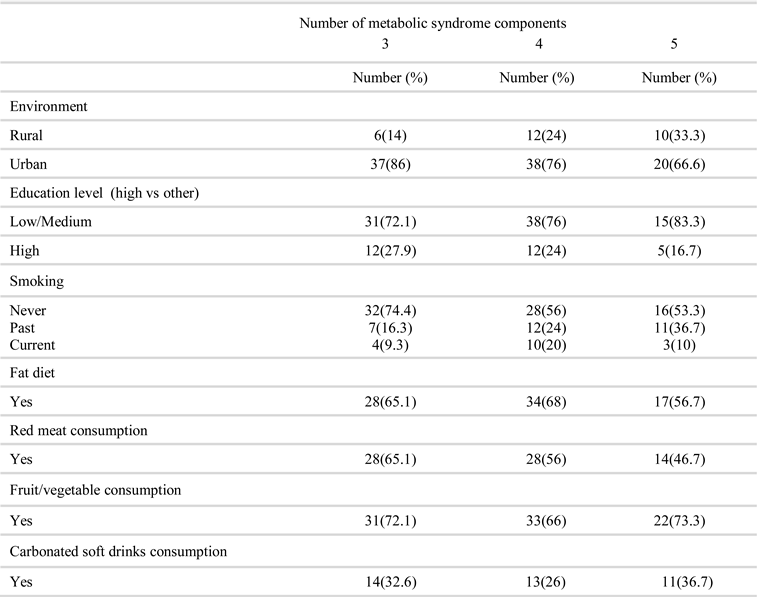
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
References
- Paek, K.W.; Chun, K.H.; Jin, K.N.; Lee, K.S. Do health behaviors moderate the effect of socioeconomic status on metabolic syndrome? Ann Epidemiol. 2006, 34, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Nordhorn, J.; Binting, S.; Roll, S.; Willich, S.N. An update on regional variation in cardiovascular mortality within Europe. Eur Heart J. 2008, 29, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.G.; Hyun, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Bang, S.Y.; Chu, S.H.; Jeon, J.Y.; Kang, M.S. A randomized controlled trial of therapeutic lifestyle modification in rural women with metabolic syndrome: a pilot study. Metabolism. 2008, 57, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, A.; Lim, S.Y.; Sung, J.; Shin, H.R.; Kim, J. Dietary intake, eating habits, and metabolic syndrome in Korean men. J Am Diet Assoc. 2009, 109, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Arora, S.; Goswami, B.; Mallika, V. Metabolic syndrome: a review of emerging markers and management. Diab Met Syndr: Clin Res & Rev. 2009, 3, 240–254. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.S.; Oh, S.W.; Cho, S.I.; Choi, W.H.; Kim, Y.S. The metabolic syndrome and associated lifestyle factors among South Korean adults. Int J Epidemiol. 2004, 33, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isomaa, B.; Almgren, P.; Tuomi, T.; Forsén, B.; Lahti, K.; Nissén, M.; Taskinen, M.R.; Groop, L. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2001, 24, 683–689 PMID: 11315831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khader, Y.; Bateiha, A.; El-Khateeb, M.; Al-Shaikh, A.; Ajlouni, K. High prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among Northern Jordanians. J Diabetes Complications. 2007, 21, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguz, A.; Temizhan, A.; Abaci, A.; Kozan, O.; Erol, C.; Ongen, Z.; Celik, S. The prevalance of metabolic syndrome in turkish adults according to IDF definition. Atherosclerosis Supplements. 2008, 9, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misraa, R.; Patelb, T.; Kothac, P.; Rajid, A.; Gandae, O.; Banerjif, M.A.; Shahf, V.; Vijayg, K.; Mudaliarc, S.; Iyerh, D.; Balasubramanyamh, A. Prevalence of diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular risk factors in US Asian Indians: results from a national study. Journal Diabetes Complications 2010, 24, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.N.; Ho, S.Y.; Janus, E.D.; Lam, K.S.; Hedley, A.J.; Lam, T.H. Hong Kong Cardiovascular Risk Factor Prevalence Study Steering Committee. The US National Cholesterol Education Programme Adult Treatment Panel III (NCEP ATP III) prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in a Chinese population. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005, 67, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibai, A.M.; Obeid, O.; Batal, M.; Adra, N.; Khoury, D.E.; Hwalla, N. Prevalence and correlates of metabolic syndrome in an adult Lebanese population. CVD Prevention and Control 2008, 3, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llisterri, J.L.; Cea-Calvo, L.; Martí-Canales, J.C.; Lozano, J.V.; Aznar, J.; Redón, J. En representación de los investigadores del estudio PREV-ICTUS. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Spanish population aged 60 years-old or more. PREV- ICTUS, a population-based study. Med Clin (Barc). 2009, 132, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Mokán, M.; Galajda, P.; Prídavková, D.; Tomásková, V.; Sutarík, L.; Krucinská, L.; Bukovská, A.; Rusnáková, G. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome in Slovakia. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008, 81, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Deedwania, P.C.; Gupta, A.; Rastogi, S.; Panwar, R.B.; Kothari, K. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in an Indian urban population. Int J Cardiol. 2004, 97, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, F.; Salehi, P.; Etemadi, A.; Zahedi-Asl, S. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in an urban population: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2003, 61, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ravikiran, M.; Bhansali, A.; Ravikumar, P.; Bhansali, S.; Dutta, P.; Thakur, J.S.; Sachdeva, N.; Bhadada, S.; Walia, R. Prevalence and risk factors of metabolic syndrome among Asian Indians: A community survey. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010, 89, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaya, F.T.; Gu, A.; Saunders, E. Metabolic syndrome prevalence in an urban African American population. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2007, 1, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, A.J.; Magliano, D.J.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Welborn, T.; Shaw, J.E. The Metabolic Syndrome in Australia: Prevalence using four definitions. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007, 77, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gündogan, K.; Bayram, F.; Capak, M.; Tanriverdi, F.; Karaman, A.; Ozturk, A.; Altunbas, H.; Gökce, C.; Kalkan, A.; Yazici, C. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in the Mediterranean region of Turkey: evaluation of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, and dyslipidemia. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2009, 7, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, H.E. Metabolic syndrome in American Indians. Diab Care. 2002, 25, 1246–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athyros, V.G.; Ganotakis, E.S.; Tziomalos, K.; Papageorgiou, A.A.; Anagnostis, P.; Griva, T.; Kargiotis, K.; Mitsiou, E.K.; Karagiannis, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Comparison of four definitions of the metabolic syndrome in a Greek (Mediterranean) population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010, 26, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magi, L.; Stramenga, C.; Morosini, P.; Gruppo di Studio SIMAP. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among Italian adults. Findings from the SIMAP study. Recenti Prog Med. 2005, 96, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pitsavos, C. The prevalence of the metabolic syndrome is high in Balkan countries. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2008, 49, 310–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Babio, N.; Bulló, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Mediterranean diet and metabolic syndrome: the evidence. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matei, C.; Pop, I.; Jurcut, R.; Suceveanu, M.; Predescu, D.; Nechita, E.; Ionescu, P.; Ciovica, D.; Ginghina, C. Romanian multicentric study of the prevalence of metabolic syndrome-ROMES. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2008, 49, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feldeisen, S.E.; Tucker, K.L. Nutritional strategies in the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2007, 32, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schooling, C.M. Risk factors for the metabolic syndrome in contemporary China. CVD Prevention and Control. 2009, 4, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saely, C.H.; Koch, L.; Schmid, F.; Marte, T.; Aczel, S.; Langer, P.; Hoefle, G.; Drexel, H. Adult Treatment Panel III 2001 but not International Diabetes Federation 2005 criteria of the metabolic syndrome predict clinical cardiovascular events in subjects who underwent coronary angiography. Diabetes Care. 2006, 29, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S. Does the metabolic syndrome exist? Diabetes Care. 2006, 29, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motofei, I.G.; Rowland, D.L.; Baconi, D.L.; Georgescu, S.R.; Paunica, S.; Constantin, V.D.; Balalau, D.; Paunica, I.; Balalau, C.; Baston, C.; Sinescu, I. Therapeutic considerations related to finasteride administration in male androgenic alopecia and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Farmacia 2017, 65, 660–666. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.M.; Sanderson, B.K.; Bittner, V. Drugs are not enough: the metabolic syndrome-a call for intensive therapeutic lifestyle change. J Cardiometab Syndr. 2009, 4, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, T.; Urashima, M.; Fukumoto, T.; Joki, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Oda, S. Effective prevention of metabolic syndrome: A motto for healthy habits - “none of one, less of two, more of three”. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2007, 1, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, L.F.; Brown, A.J.; Ard, J.D.; Loria, C.; Erlinger, T.P.; Feldstein, A.C.; Lin, P.H.; Champagne, C.M.; King, A.C.; McGuire, H.L.; Stevens, V.J.; Brantley, P.J.; Harsha, D.W.; McBurnie, M.A.; Appel, L.J.; Svetkey, L.P. Effects of PREMIER lifestyle modifications on participants with and without the metabolic syndrome. Hypertension. 2007, 50, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.Y.; Jung, C.H.; Park, J.S.; Rhee, E.J.; Kim, S.W. Effects of smoking, alcohol, exercise, education, and family history on the metabolic syndrome as defined by the ATP III. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005, 67, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djoussé, L.; Padilla, H.; Nelson, T.L.; Gaziano, J.M.; Mukamal, K.J. Diet and Metabolic Syndrome. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2010, 10, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M.T.; Hamilton, D.G.; Zderic, T.W. Role of low energy expenditure and sitting in obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes. 2007, 56, 2655–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paunica, M.; Manole, A.; Motofei, C.; Tanase, G.L. The Globalization in the actual Context of the European Union Economy. Proceedings of the international conference on business excellence. 2018, 12, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.C.; Carroll, D.; Thomas, G.N.; Gale, C.R.; Deary, I.; Batty, G.D. The influence of multiple indices of socioeconomic disadvantage across the adult life course on the metabolic syndrome: the Vietnam Experience Study. Metabolism. 2009, 59, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.W.; Zhu, S.; Palaniappan, L.; Heshka, S.; Carnethon, M.R.; Heymsfield, S.B. The metabolic syndrome: prevalence and associated risk factor findings in the US population from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Arch Intern Med. 2003, 163, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wamala, S.P.; Lynch, J.; Horsten, M.; Mittleman, M.A.; Schenck-Gustafsson, K.; Orth-Gomér, K. Education and the metabolic syndrome in women. Diabetes Care. 1999, 22, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.C.; Severo, M.; Barros, H. Incidence and risk factors for the metabolic syndrome in an urban South European population. Prev Med. 2010, 50, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet. 2005, 365, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tincu, R.C.; Cobilinschi, C.; Tomescu, D.; Coman, L.; Tincu, I.; Diaconu, C.; Macovei, R.A. Favourable results for L-carnitine use in valproic acid acute poisoning. Farmacia. 2017, 65, 396–400. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, W.Y.; Palomaki, G.E.; Haddow, J.E. Cigarette smoking and serum lipid and lipoprotein concentrations: an analysis of published data. BMJ. 1989, 298, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Attvall, S.; Fowelin, J.; Lager, I.; Von Schenck, H.; Smith, U. Smoking induces insulin resistance-a potential link with the insulin resistance syndrome. J Intern Med. 1993, 233, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliasson, B.; Attvall, S.; Taskinen, M.R.; Smith, U. Insulin resistance in smokers is a function of smoking habits. Atherosclerosis. 1994, 109, 28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.; Nimmo, L.; Elatrozy, T.; Anyaoku, V.; Hughes, C.; Robinson, S.; Richmond, W.; Elkeles, R.S. Smoking is associated with increased hepatic lipase activity, insulin resistance, dyslipidaemia and early atherosclerosis in Type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. 2001, 156, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Li, T.C.; Chang, P.C.; Liu, C.S.; Lin, W.Y.; Wu, M.T.; Li, C.I.; Lai, M.M.; Lin, C.C. Association among cigarette smoking, metabolic syndrome, and its individual components: the metabolic syndrome study in Taiwan. Metabolism. 2008, 57, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Li, T.C.; Chang, P.C.; Liu, C.S.; Lin, W.Y.; Wu, M.T.; Li, C.I.; Lai, M.M.; Lin, C.C. Association among cigarette smoking, metabolic syndrome, and its individual components: the metabolic syndrome study in Taiwan. Metabolism. 2008, 57, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishizaka, N.; Ishizaka, Y.; Toda, E.; Hashimoto, H.; Nagai, R.; Yamakado, M. Association between cigarette smoking, metabolic syndrome, and carotid arteriosclerosis in Japanese individuals. Atherosclerosis. 2005, 181, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hishida, A.; Koyama, A.; Tomota, A.; Katase, S.; Asai, Y.; Hamajima, N. Smoking cessation, alcohol intake and transient increase in the risk of metabolic syndrome among Japanese smokers at one health checkup institution. BMC 2009, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; St-Onge, M.P.; Heshka, S.; Heymsfield, S.B. Lifestyle behaviors associated with lower risk of having the metabolic syndrome. Metabolism. 2004, 53, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Nakao, M.; Nomura, K.; Yano, E. Association of metabolic syndrome with smoking and alcohol intake in Japanese men. Nicotine Tob Res. 2009, 11, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onat, A.; Ozhan, H.; Esen, A.M.; Albayrak, S.; Karabulut, A.; Can, G.; Hergenç, G. Prospective epidemiologic evidence of a "protective" effect of smoking on metabolic syndrome and diabetes among Turkish women-without associated overall health benefit. Atherosclerosis. 2007, 193, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moagar-Poladian Folea, V.; Paunica, M. Competitiveness of EU member states in attracting EU funding for research and innovation. Romanian journal of economic forecasting. 2017, 20, 150–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, I.S.; Cubeddu, L.X. Salt and the metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009, 19, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Steffen, L.M.; Stevens, J. Dietary intake and the development of the metabolic syndrome: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Circulation. 2008, 117, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaillzadeh, A.; Kimiagar, M.; Mehrabi, Y.; Azadbakht, L.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C. Fruit and vegetable intakes, C-reactive protein, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006, 84, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, E.S.; Mokdad, A.H.; Giles, W.H.; Brown, D.W. The metabolic syndrome and antioxidant concentrations: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes. 2003, 52, 2346–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.; Nicklas, T.; Baranowski, T.; Zakeri, I.F.; Yang, S.J.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Berenson, G.S. Comparison of dietary intakes associated with metabolic syndrome risk factors in young adults: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004, 80, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, R.; Sullivan, L.; Jacques, P.F.; Wang, T.J.; Fox, C.S.; Meigs, J.B.; D'Agostino, R.B.; Gaziano, J.M.; Vasan, R.S. Soft drink consumption and risk of developing cardiometabolic risk factors and the metabolic syndrome in middle-aged adults in the community. Circulation. 2007, 116, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaconu, C.C.; Dediu, G.N.; Iancu, M.A. Drug-induced arterial hypertension, a frequently ignored cause of secondary hypertension: a review. Acta Cardiologica. 2018. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereecken, C.A.; Inchley, J.; Subramanian, S.V.; Hublet, A.; Maes, L. The relative influence of individual and contextual socio-economic status on consumption of fruit and soft drinks among adolescents in Europe. Eur J Public Health. 2005, 15, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, T.L.; Swithers, S.E. A Pavlovian approach to the problem of obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004, 28, 933–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.B.; Malik, V.S. Sugar-sweetened beverages and risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes: epidemiologic evidence. Physiol Behav. 2010, 100, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.A.; Kartashov, A.I.; Ebbeling, C.B.; Van Horn, L.; Slattery, M.L.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Ludwig, D.S. Fast-food habits, weight gain, and insulin resistance (the CARDIA study): 15-year prospective analysis. Lancet. 2005, 365, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampersaud, G.C.; Bailey, L.B.; Kauwell, G.P. National survey beverage consumption data for children and adolescents indicate the need to encourage a shift toward more nutritive beverages. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003, 103, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkerwi, A.; Boutsen, M.; Vaillant, M.; Barre, J.; Lair, M.L.; Albert, A.; Guillaume, M.; Dramaix, M. Alcohol consumption and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Atherosclerosis. 2009, 204, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, A.Z.; Russell, M.; Dorn, J.; Freudenheim, J.L.; Nochajski, T.; Hovey, K.; Trevisan, M. Lifetime alcohol drinking pattern is related to the prevalence of metabolic syndrome. The Western New York Health Study (WNYHS). Eur J Epidemiol. 2006, 21, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, D.L.; Motofei, I.G.; Popa, F.; Constantin, V.D.; Vasilache, A.; Păunică, I.; Bălălău, C.; Păunică, G.P.; Banu, P.; Păunică, S. The postfinasteride syndrome; an overview. J Mind Med Sci. 2016, 3, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillman, M.W.; Cook, N.R.; Evans, D.A.; Rosner, B.; Hennekens, C.H. Relationship of alcohol intake with blood pressure in young adults. Hypertension. 1995, 25, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaziano, J.M.; Buring, J.E.; Breslow, J.L.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Rosner, B.; VanDenburgh, M.; Willett, W.; Hennekens, C.H. Moderate alcohol intake, increased levels of high-density lipoprotein and its subfractions, and decreased risk of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1993, 329, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Monforte, M.; Sánchez, E.; Barrio, F.; Costa, B.; Flores-Mateo, G. Metabolic syndrome and dietary patterns: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Nutr. 2017, 56, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangiry, L.; Montazeri, A.; Najafi, M.; Yaseri Farhangi, M.A. An interactive web-based intervention on nutritional status, physical activity and health-related quality of life in patient with metabolic syndrome: a randomized-controlled trial (The Red Ruby Study). Nutr Diabetes. 2017, 7, e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennberg, M.; Gustafsson, P.E.; Wennberg, P.; Hammarström, A. Irregular eating of meals in adolescence and the metabolic syndrome in adulthood: results from a 27-year prospective cohort. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narain, A.; Kwok, C.S.; Mamas, M.A. Soft drink intake and the risk of metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2017, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2008 by the author. 2008 Angela Cozma, Adela Sitar-Taut, Laura Urian, Adriana Fodor, Ramona Suharoschi, Crina Muresan, Vasile Negrean, Dorel Sampelean, Dumitru Zdrenghea, Dana Pop, Leucuta Daniel and Olga Hilda Orasan
Share and Cite
Cozma, A.; Sitar-Taut, A.; Urian, L.; Fodor, A.; Suharoschi, R.; Muresan, C.; Negrean, V.; Sampelean, D.; Zdrenghea, D.; Pop, D.; et al. Unhealthy Lifestyle and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome—The Romanian Experience. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2018, 5, 218-229. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.52.P218229
Cozma A, Sitar-Taut A, Urian L, Fodor A, Suharoschi R, Muresan C, Negrean V, Sampelean D, Zdrenghea D, Pop D, et al. Unhealthy Lifestyle and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome—The Romanian Experience. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2018; 5(2):218-229. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.52.P218229
Chicago/Turabian StyleCozma, Angela, Adela Sitar-Taut, Laura Urian, Adriana Fodor, Ramona Suharoschi, Crina Muresan, Vasile Negrean, Dorel Sampelean, Dumitru Zdrenghea, Dana Pop, and et al. 2018. "Unhealthy Lifestyle and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome—The Romanian Experience" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 5, no. 2: 218-229. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.52.P218229
APA StyleCozma, A., Sitar-Taut, A., Urian, L., Fodor, A., Suharoschi, R., Muresan, C., Negrean, V., Sampelean, D., Zdrenghea, D., Pop, D., Daniel, L., & Orasan, O. H. (2018). Unhealthy Lifestyle and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome—The Romanian Experience. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 5(2), 218-229. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.52.P218229



