The Mind-Body Problem—Three Equations and One Solution Represented by Immaterial-Material Data
Highlights
- Interaction between immaterial data and material brain is not possible, the mind body problem referring rather to procession of immaterial data by our material brain.
- Procession of abstract data by our brain is possible through association between immaterial data and material/nervous impulses of the brain, interface of this association being represented by time.
Highlights
- ✓
- Interaction between immaterial data and material brain is not possible, the mind body problem referring rather to procession of immaterial data by our material brain.
- ✓
- Procession of abstract data by our brain is possible through association between immaterial data and material/nervous impulses of the brain, interface of this association being represented by time
Abstract
Introduction
Discussion
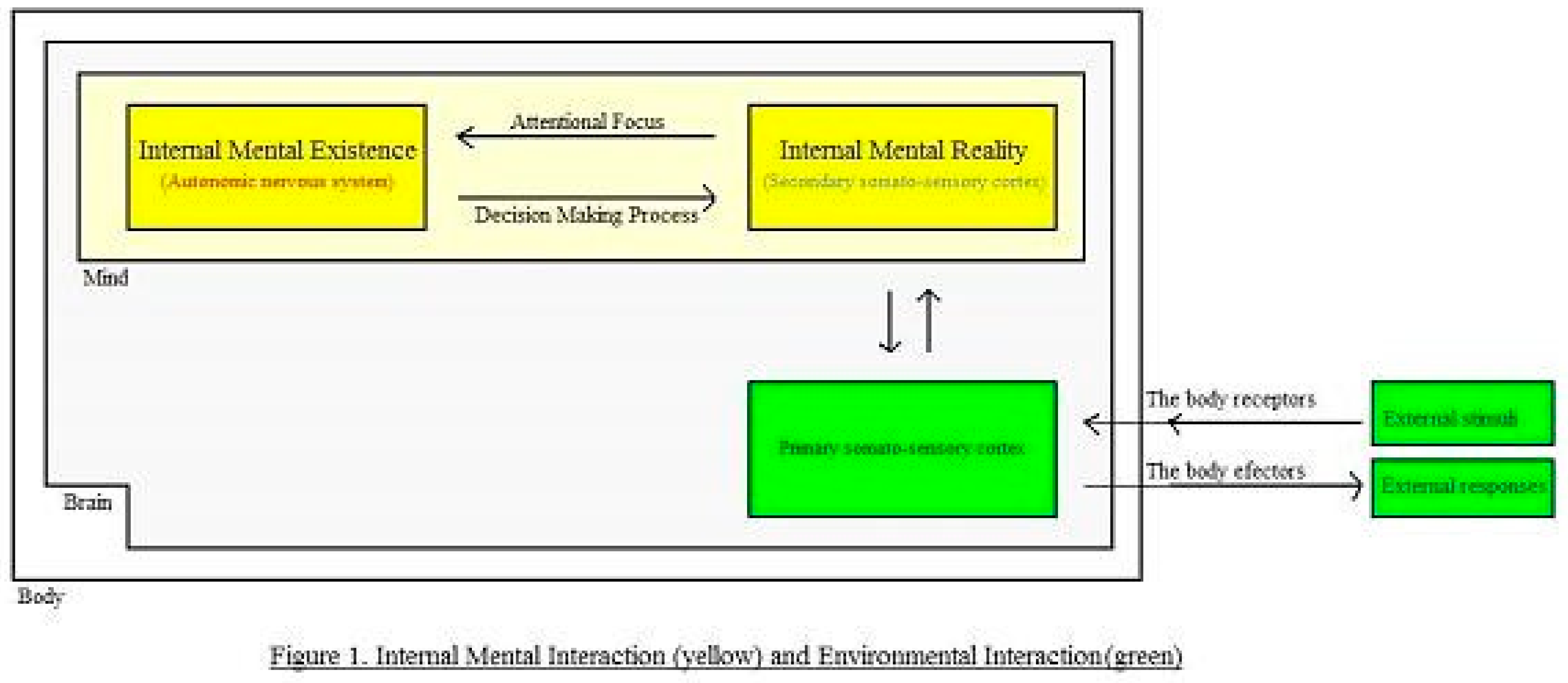
- Psychological existence and the corresponding cerebral support; internal mental existence
- 2.
- Conscious representation of social data in the form of mental reality

- 3.
- Bio-social transmission of abstract social data

- 4.
- A bio-psycho-social integration
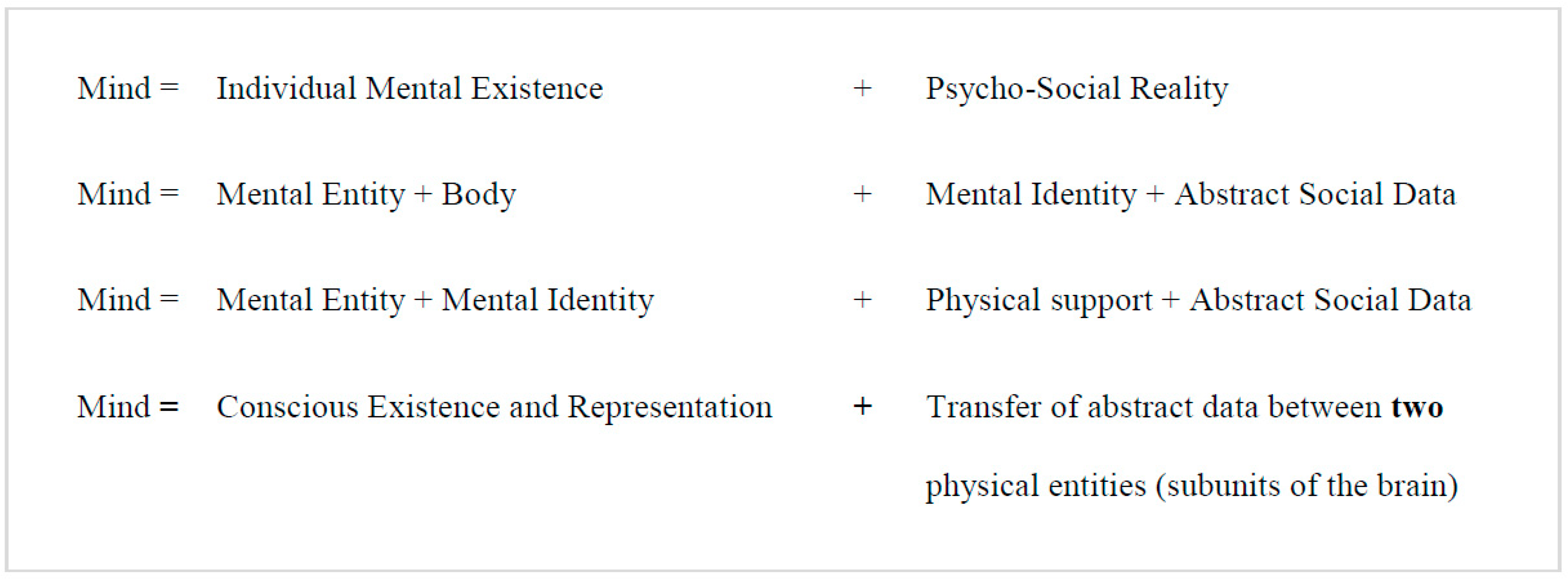
- 5.
- Consciousness within a supra-physiologic interpretation
Conclusions
References
- Francken, J.C.; Slors, M. From commonsense to science, and back: the use of cognitive concepts in neuroscience. Conscious Cogn. 2014, 29, 248–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, A. Organic unity theory: the mind-body problem revisited. Am J Psychiatry. 1991, 148, 553–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, L.; Keane, M.T. A model of plausibility. Cogn Sci. 2006, 30, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingelkurts, A.A.; Fingelkurts, A.A.; Bagnato, S.; Boccagni, C.; Galardi, G. The Chief Role of Frontal Operational Module of the Brain Default Mode Network in the Potential Recovery of Consciousness from the Vegetative State: A Preliminary Comparison of Three Case Reports. Open Neuroimag J 2016, 10, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobos-Aguilar, H.; Viniegra-Velázquez, L.; Pérez- Cortés, P. Role of creative discussion in the learning of critical reading of scientific articles. Rev Invest Clin. 2011, 63, 268–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merenda, P.F. Similarities between Prescott Lecky’s theory of self-consistency and Carl Rogers’ self- theory. Psychol Rep. 2010, 107, 647–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, D.; Xu, S.; Zhu, S.; Fang, Z.; Spaeth, A.M.; Xin, Y.; Feng, T.; Rao, H. Resting spontaneous activity in the default mode network predicts performance decline during prolonged attention workload. Neuroimage. 2015, 120, 323–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Chen, H.; He, C.; Long, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Uddin, L.Q.; Chen, H. Resting-state functional under- connectivity within and between large-scale cortical networks across three low-frequency bands in adolescents with autism. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017, 79, 434–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Qian, A.; Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Ye, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, M. Disrupted Control-Related Functional Brain Networks in Drug-Naive Children with Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2017, 8, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, S.B.; Katz, S. Can Indirect Realism be Demonstrated in the Psychological Laboratory? Philosophy of the Social Sciences 1984, 14, 149–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, D.L.; Motofei, I.G. Psycho-physiologic emergentism; four minds in a body. J Mind Med Sci. 2017, 4, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motofei, I.G.; Rowland, D.L. Solving the mind-body problem through two distinct concepts: internal- mental existence and internal mental reality. J Mind Med Sci. 2015, 2, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Cruijsen, R.; Peters, S.; Crone, E.A. Neural correlates of evaluating self and close-other in physical, academic and prosocial domains. Brain Cogn 2017, 118, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Learning, attentional control, and action video games. Curr Biol. 2012, 22, R197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guss-West, C.; Wulf, G. Attentional focus in classical ballet: a survey of professional dancers. J Dance Med Sci. 2016, 20, 23–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igamberdiev, A.U. Evolutionary transition from biological to social systems via generation of reflexive models of externality. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2017, 131, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendler, K.S. A psychiatric dialogue on the mind- body problem. Am J Psychiatry. 2001, 158, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; James, T.W. Enhanced effectiveness in visuo-haptic object-selective brain regions with increasing stimulus salience. Hum Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 678–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiman-Weiner, M.; Saxe, R.; Tenenbaum, J.B. Learning a commonsense moral theory. Cognition. 2017, 167, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee Masson, H.; Bulthé, J.; Op de Beeck, H.P.; Wallraven, C. Visual and Haptic Shape Processing in the Human Brain: Unisensory Processing, Multisensory Convergence, and Top-Down Influences. Cereb Cortex. 2016, 26, 3402–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissek, S.; Glaubitz, B.; Güntürkün, O.; Tegenthoff, M. Noradrenergic stimulation modulates activation of extinction-related brain regions and enhances contextual extinction learning without affecting renewal. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchaiah, V.; Zhao, F.; Widen, S.; Auzenne, J.; Beukes, E.W.; Ahmadi, T.; Tomé, D.; Mahadeva, D.; Krishna, R.; Germundsson, P. Social Representation of “Loud Music” in Young Adults: A Cross-Cultural Study. J Am Acad Audiol. 2017, 28, 522–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melloni, M.; Lopez, V.; Ibanez, A. Empathy and contextual social cognition. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2014, 14, 407–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzak, P.D.; Lavigne, K.M.; Woodward, T.S. Functional brain networks involved in reality monitoring. Neuropsychologia. 2015, 75, 50–60.PMID. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minert, A.; Devor, M. Brainstem node for loss of consciousness due to GABA(A) receptor-active anesthetics. Exp Neurol. 2016, 275 Pt 1, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffett, M.W. Human identity and the evolution of societies. Hum Nat. 2013, 24, 219–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, N. Styles of remembering and types of experience: an experimental investigation of reconstructive memory. Integr Psychol Behav Sci. 2008, 42, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motofei, I.G. A dual physiological character for cerebral mechanisms of sexuality and cognition: common somatic peripheral afferents. BJU Int. 2011, 108, 1634–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motofei, I.G.; Rowland, D.L. The ventral- hypothalamic input route: a common neural network for abstract cognition and sexuality. BJU Int. 2014, 113, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motofei, I.G.; Rowland, D.L. The mind body problem, part three: ascension of sexual function to cerebral level. J Mind Med Sci. 2016, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motofei, I.G.; Rowland, D.L. Structural dichotomy of the mind; the role of sexual neuromodulators. J Mind Med Sci. 2016, 3, 131–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motofei, I.G.; Rowland, D.L. Informational dichotomy of the mind; the role of sexual neuromodulators. J Mind Med Sci. 2017, 4, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Niimi, S. Changes in speaking fundamental frequency characteristics with aging. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2008, 60, 120–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, I.R.; McCoy, D.; Klobusicky, E.; Ross, L.A. Social cognition and the anterior temporal lobes: a review and theoretical framework. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2013, 8, 123–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggi, I.; D’Errico, F.; Vinciarelli, A. Social signals: from theory to applications. Cogn Process. 2012, 13, 389–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posner, M.I. Cognitive neuropsychology and the problem of selective attention. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl. 1987, 39, 313–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.J. The anatomy of language: a review of 100 fMRI studies published in 2009. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010, 1191, 62–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Wilcke, T.; Rosengarth, K.; Luerding, R.; Bogdahn, U.; Greenlee, M.W. Distinct patterns of functional and structural neuroplasticity associated with learning Morse code. Neuroimage. 2010, 51, 1234–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skuse, D.; Morris, J.; Lawrence, K. The amygdala and development of the social brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003, 1008, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motofei, I.G. A dual physiological character for sexual function: libido and sexual pheromones. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 1702–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motofei, I.G. The etiology of premature ejaculation starting from a bihormonal model of normal sexual stimulation. Int J Impot Res. 2001, 13, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motofei, I.G.; Rowland, D.L.; Păunică, I.; Tănăsescu, O.C.; Banu, P.; Păunică, S. Finasteride as a model for personalized medicine. J Mind Med Sci. 2017, 4, 125–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvieli, A.; Zaig, T.; Ayal, I.; Thieberger, G.; Rothschild, S; Barak, Y. The Impact of Self-directed Voice of Love Messages on Anger: A Pilot Study. Adv Mind Body Med. 2017, 31, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hogea, L.M.; Nussbaum, L.A.; Chiriac, D.V.; Ageu, L.Ş.; Andreescu, N.I.; Grigoraş, M.L.; Folescu, R.; Bredicean, A.C.; Puiu, M.; Roşca, E.C.; Simu, M.A.; Levai, C.M. Integrative clinico-biological, pharmacogenetic, neuroimagistic, neuroendocrinological and psychological correlations in depressive and anxiety disorders. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2017, 58, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Overwalle, F. Social cognition and the brain: a meta-analysis. Hum Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 829–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolever, R.Q.; Bobinet, K.J.; McCabe, K.; Mackenzie, E.R.; Fekete, E.; Kusnick, C.A.; Baime, M. Effective and viable mind-body stress reduction in the workplace: a randomized controlled trial. J Occup Health Psychol. 2012, 17, 246–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.F.; Smith, A.C.; Pierce, E.T.; Harrell, P.G.; Walsh, J.L.; Salazar-Gómez, A.F.; Tavares, C.L.; Purdon, P.L.; Brown, E.N. Statistical modeling of behavioral dynamics during propofol-induced loss of consciousness. J Neurosci Methods. 2014, 227, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachariae, R. Psychoneuroimmunology: a bio- psycho-social approach to health and disease. Scand J Psychol. 2009, 50, 645–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Weidner, R.; Fink, G.R.; Chen, Q. Neural correlates underlying the attentional spotlight in human parietal cortex independent of task difficulty. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 4996–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuriff, G.E. Science and Human Behavior, dualism, and conceptual modification. J Exp Anal Behav. 2003, 80, 345–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, D.L.; Motofei, I.G.; Popa, F.; Constantin, V.D.; Vasilache, A.; Păunică, I.; Bălălău, C.; Păunică, G.P.; Banu, P.; Păunică, S. The postfinasteride syndrome; an overview. J Mind Med Sci. 2016, 3, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motofei, I.G.; Rowland, D.L.; Popa, F.; Bratucu, E.; Straja, D.; Manea, M.; Georgescu, S.R.; Paunica, S.; Bratucu, M.; Balalau, C.; Constantin, V.D. A Pilot Study on Tamoxifen Sexual Side Effects and Hand Preference in Male Breast Cancer. Arch Sex Behav. 2015, 44, 1589–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu, S.R.; Tampa, M.; Paunica, S.; Balalau, C.; Constantin, V.; Paunica, G.; Motofei, I.G. Distribution of post-finasteride syndrome in men with androgenic alopecia. J Invest Dermatol. 2015, 135, S40–S40. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the author. 2018 Ion G. Motofei, David L. Rowland
Share and Cite
Motofei, I.G.; Rowland, D.L. The Mind-Body Problem—Three Equations and One Solution Represented by Immaterial-Material Data. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2018, 5, 59-69. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.51.P5969
Motofei IG, Rowland DL. The Mind-Body Problem—Three Equations and One Solution Represented by Immaterial-Material Data. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2018; 5(1):59-69. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.51.P5969
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotofei, Ion G., and David L. Rowland. 2018. "The Mind-Body Problem—Three Equations and One Solution Represented by Immaterial-Material Data" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 5, no. 1: 59-69. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.51.P5969
APA StyleMotofei, I. G., & Rowland, D. L. (2018). The Mind-Body Problem—Three Equations and One Solution Represented by Immaterial-Material Data. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 5(1), 59-69. https://doi.org/10.22543/7674.51.P5969


